Organic electronics on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Organic electronics is a field of materials science concerning the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of organic molecules or
Organic electronics is a field of materials science concerning the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of organic molecules or
 Organic conductive materials can be grouped into two main classes: polymers and conductive molecular solids and salts. Polycyclic aromatic compounds such as
Organic conductive materials can be grouped into two main classes: polymers and conductive molecular solids and salts. Polycyclic aromatic compounds such as
 OLED organic
OLED organic
 An
An

Niedertemperaturabscheidung von Dünnschicht-Silicium für Solarzellen auf Kunststofffolien
Doctoral Thesis, ipe.uni-stuttgart.de # The so-called '
orgworld
– ''Organic Semiconductor World'' homepage. {{Electronic systems Artificial materials
 Organic electronics is a field of materials science concerning the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of organic molecules or
Organic electronics is a field of materials science concerning the design, synthesis, characterization, and application of organic molecules or polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
s that show desirable electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
properties such as conductivity
Conductivity may refer to:
*Electrical conductivity, a measure of a material's ability to conduct an electric current
**Conductivity (electrolytic), the electrical conductivity of an electrolyte in solution
** Ionic conductivity (solid state), ele ...
. Unlike conventional inorganic conductors and semiconductor
A semiconductor is a material which has an electrical conductivity value falling between that of a conductor, such as copper, and an insulator, such as glass. Its resistivity falls as its temperature rises; metals behave in the opposite way. ...
s, organic electronic materials are constructed from organic (carbon-based) molecules or polymers using synthetic strategies developed in the context of organic chemistry
Organic chemistry is a subdiscipline within chemistry involving the scientific study of the structure, properties, and reactions of organic compounds and organic materials, i.e., matter in its various forms that contain carbon atoms.Clayden, ...
and polymer chemistry
Polymer chemistry is a sub-discipline of chemistry that focuses on the structures of chemicals, chemical synthesis, and chemical and physical properties of polymers and macromolecules. The principles and methods used within polymer chemistry are a ...
.
One of the promised benefits of organic electronics is their potential low cost compared to traditional electronics. Attractive properties of polymeric conductors include their electrical conductivity (which can be varied by the concentrations of dopant
A dopant, also called a doping agent, is a trace of impurity element that is introduced into a chemical material to alter its original electrical or optical properties. The amount of dopant necessary to cause changes is typically very low. When ...
s) and comparatively high mechanical flexibility
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a bo ...
. Challenges to the implementation of organic electronic materials are their inferior thermal stability
In thermodynamics, thermal stability describes the stability of a water body and its resistance to mixing.Schmidt, W. 1928. Über Temperatur und Stabilitätsverhältnisse von Seen. Geogr. Ann 10: 145 - 177. It is the amount of work needed to t ...
, high cost, and diverse fabrication issues.
History
;Electrically conductive polymers Traditional conductive materials areinorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemist ...
, especially metals
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typical ...
such as copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
and aluminum
Aluminium (aluminum in American and Canadian English) is a chemical element with the symbol Al and atomic number 13. Aluminium has a density lower than those of other common metals, at approximately one third that of steel. It ha ...
as well as many alloy
An alloy is a mixture of chemical elements of which at least one is a metal. Unlike chemical compounds with metallic bases, an alloy will retain all the properties of a metal in the resulting material, such as electrical conductivity, ductilit ...
s.
In 1862 Henry Letheby
Henry Letheby (1816 – 28 March 1876) was an English analytical chemist and public health officer.
Early life
Letheby was born at Plymouth, England, in 1816, and studied chemistry at the Royal Cornwall Polytechnic Society. In 1837 he commenc ...
described polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of ...
, which was subsequently shown to be electrically conductive. Work on other polymeric organic materials began in earnest in the 1960s. For example in 1963, a derivative of tetraiodopyrrole was shown to exhibit conductivity of 1 S/cm (S = Siemens). In 1977, it was discovered that oxidation enhanced the conductivity of polyacetylene
Polyacetylene (IUPAC name: polyethyne) usually refers to an organic polymer with the repeating unit . The name refers to its conceptual construction from polymerization of acetylene to give a chain with repeating olefin groups. This compound ...
. The 2000 Nobel Prize in Chemistry was awarded to Alan J. Heeger, Alan G. MacDiarmid, and Hideki Shirakawa
is a Japanese chemist, engineer, and Professor Emeritus at the University of Tsukuba and Zhejiang University. He is best known for his discovery of conductive polymers. He was co-recipient of the 2000 Nobel Prize in Chemistry jointly with Alan Ma ...
jointly for their work on polyacetylene and related conductive polymers. Many families of electrically conducting polymers have been identified including polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents at ...
, polyphenylene sulfide
Polyphenylene sulfide (PPS) is an organic polymer consisting of aromatic rings linked by sulfides. Synthetic fiber and textiles derived from this polymer resist chemical and thermal attack. PPS is used in filter fabric for coal boilers, paper ...
, and others.
J.E. Lilienfeld first proposed the field-effect transistor
The field-effect transistor (FET) is a type of transistor that uses an electric field to control the flow of current in a semiconductor. FETs ( JFETs or MOSFETs) are devices with three terminals: ''source'', ''gate'', and ''drain''. FETs cont ...
in 1930, but the first OFET was not reported until 1987, when Koezuka et al. constructed one using Polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents at ...
which shows extremely high conductivity. Other conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s have been shown to act as semiconductors, and newly synthesized and characterized compounds are reported weekly in prominent research journals. Many review articles exist documenting the development of these materials
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolog ...
.
In 1987, the first organic diode was produced at Eastman Kodak by Ching W. Tang
Ching Wan Tang (; born July 23, 1947) is a Hong Kong Americans, Hong Kong–American Physical chemistry, physical chemist. He was inducted into the National Inventors Hall of Fame in 2018 for inventing OLED (together with Steven Van Slyke), and ...
and Steven Van Slyke.
;Electrically conductive charge transfer salts
In the 1950s, organic molecules were shown to exhibit electrical conductivity. Specifically, the organic compound pyrene was shown to form semiconducting charge-transfer complex salts
In chemistry, a salt is a chemical compound consisting of an ionic assembly of positively charged cations and negatively charged anions, which results in a compound with no net electric charge. A common example is table salt, with positively c ...
with halogens
The halogens () are a group in the periodic table consisting of five or six chemically related elements: fluorine (F), chlorine (Cl), bromine (Br), iodine (I), astatine (At), and tennessine (Ts). In the modern IUPAC nomenclature, this group i ...
. In 1972, researchers found metallic conductivity (conductivity comparable to a metal) in the charge-transfer complex TTF-TCNQ.
;Light and electrical conductivity
André Bernanose was the first person to observe electroluminescence in organic materials
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolog ...
. Ching W. Tang and Steven Van Slyke, reported fabrication of the first practical OLED device in 1987. The OLED device incorporated a double-layer structure motif composed of copper phthalocyanine
Copper phthalocyanine (CuPc), also called phthalocyanine blue, phthalo blue and many other names, is a bright, crystalline, synthetic blue pigment from the group of phthalocyanine dyes. Its brilliant blue is frequently used in paints and dy ...
and a derivative of perylenetetracarboxylic dianhydride.
In 1990, a polymer
A polymer (; Greek '' poly-'', "many" + ''-mer'', "part")
is a substance or material consisting of very large molecules called macromolecules, composed of many repeating subunits. Due to their broad spectrum of properties, both synthetic a ...
light emitting diodes was demonstrated by Bradley
Bradley is an English surname derived from a place name meaning "broad wood" or "broad meadow" in Old English.
Like many English surnames Bradley can also be used as a given name and as such has become popular.
It is also an Anglicisation of t ...
, Burroughes, Friend
Friendship is a relationship of mutual affection between people. It is a stronger form of interpersonal bond than an "acquaintance" or an "association", such as a classmate, neighbor, coworker, or colleague.
In some cultures, the concept of ...
. Moving from molecular to macromolecular materials solved the problems previously encountered with the long-term stability of the organic films and enabled high-quality films to be easily made. In the late 1990's, highly efficient electroluminescent dopants were shown to dramatically increase the light-emitting efficiency of OLEDs These results suggested that electroluminescent materials could displace traditional hot-filament lighting. Subsequent research developed multilayer polymers and the new field of plastic electronics and organic light-emitting diode
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED or organic LED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light i ...
s (OLED) research and device production grew rapidly.
Conductive organic materials
 Organic conductive materials can be grouped into two main classes: polymers and conductive molecular solids and salts. Polycyclic aromatic compounds such as
Organic conductive materials can be grouped into two main classes: polymers and conductive molecular solids and salts. Polycyclic aromatic compounds such as pentacene
Pentacene () is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and t ...
and rubrene often form semiconducting materials when partially oxidized.
Conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s are often typically intrinsically conductive or at least semiconductors. They sometimes show mechanical properties comparable to those of conventional organic polymers. Both organic synthesis and advanced dispersion
Dispersion may refer to:
Economics and finance
* Dispersion (finance), a measure for the statistical distribution of portfolio returns
* Price dispersion, a variation in prices across sellers of the same item
*Wage dispersion, the amount of variat ...
techniques can be used to tune the electrical
Electricity is the set of physical phenomena associated with the presence and motion of matter that has a property of electric charge. Electricity is related to magnetism, both being part of the phenomenon of electromagnetism, as described ...
properties of conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s, unlike typical inorganic
In chemistry, an inorganic compound is typically a chemical compound that lacks carbon–hydrogen bonds, that is, a compound that is not an organic compound. The study of inorganic compounds is a subfield of chemistry known as ''inorganic chemist ...
conductors. Well-studied class of conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s include polyacetylene
Polyacetylene (IUPAC name: polyethyne) usually refers to an organic polymer with the repeating unit . The name refers to its conceptual construction from polymerization of acetylene to give a chain with repeating olefin groups. This compound ...
, polypyrrole, polythiophene
Polythiophenes (PTs) are polymerized thiophenes, a sulfur heterocycle. The parent PT is an insoluble colored solid with the formula (C4H2S)n. The rings are linked through the 2- and 5-positions. Poly(alkylthiophene)s have alkyl substituents at ...
s, and polyaniline
Polyaniline (PANI) is a conducting polymer and organic semiconductor of the semi-flexible rod polymer family. The compound has been of interest since the 1980s because of its electrical conductivity and mechanical properties. Polyaniline is one of ...
. Poly(p-phenylene vinylene) and its derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
s are electroluminescent
Electroluminescence (EL) is an optical and electrical phenomenon, in which a material emits light in response to the passage of an electric current or to a strong electric field. This is distinct from black body light emission resulting from ...
semiconducting polymers. Poly(3-alkythiophenes) have been incorporated into prototypes of solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s and transistor
upright=1.4, gate (G), body (B), source (S) and drain (D) terminals. The gate is separated from the body by an insulating layer (pink).
A transistor is a semiconductor device used to Electronic amplifier, amplify or electronic switch, switch ...
s.
Organic light-emitting diode
AnOLED
An organic light-emitting diode (OLED or organic LED), also known as organic electroluminescent (organic EL) diode, is a light-emitting diode (LED) in which the emissive electroluminescent layer is a film of organic compound that emits light i ...
(organic light-emitting diode) consists of a thin film of organic material that emits light under stimulation by an electric current. A typical OLED consists of an anode, a cathode, OLED organic material and a conductive layer.

 OLED organic
OLED organic materials
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolog ...
can be divided into two major families: small-molecule-based and polymer-based. Small molecule OLEDs (SM-OLEDs) include tris(8-hydroxyquinolinato)aluminium fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
and phosphorescent
Phosphorescence is a type of photoluminescence related to fluorescence. When exposed to light (radiation) of a shorter wavelength, a phosphorescent substance will glow, absorbing the light and reemitting it at a longer wavelength. Unlike fluor ...
dyes, and conjugated dendrimers. Fluorescent
Fluorescence is the emission of light by a substance that has absorbed light or other electromagnetic radiation. It is a form of luminescence. In most cases, the emitted light has a longer wavelength, and therefore a lower photon energy, ...
dyes can be selected according to the desired range of emission wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, t ...
s; compounds like perylene and rubrene are often used. Devices based on small molecules are usually fabricated by thermal
A thermal column (or thermal) is a rising mass of buoyant air, a convective current in the atmosphere, that transfers heat energy vertically. Thermals are created by the uneven heating of Earth's surface from solar radiation, and are an example ...
evaporation under vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often di ...
. While this method enables the formation of well-controlled homogeneous film; is hampered by high cost and limited scalability.
Polymer light-emitting diodes (PLEDs) are generally more efficient than SM-OLEDs. Common polymers used in PLEDs include derivative
In mathematics, the derivative of a function of a real variable measures the sensitivity to change of the function value (output value) with respect to a change in its argument (input value). Derivatives are a fundamental tool of calculus. ...
s of poly(p-phenylene vinylene) and polyfluorene
Polyfluorene is a polymer with chemical formula, formula , consisting of fluorene units linked in a linear chain — specifically, at carbon atoms 2 and 7 in the standard fluorene numbering. It can also be described as a chain of benzene rings lin ...
. The emitted color
Color (American English) or colour (British English) is the visual perceptual property deriving from the spectrum of light interacting with the photoreceptor cells of the eyes. Color categories and physical specifications of color are assoc ...
by the structure of the polymer. Compared to thermal evaporation, solution-based methods are more suited to creating films with large dimensions.
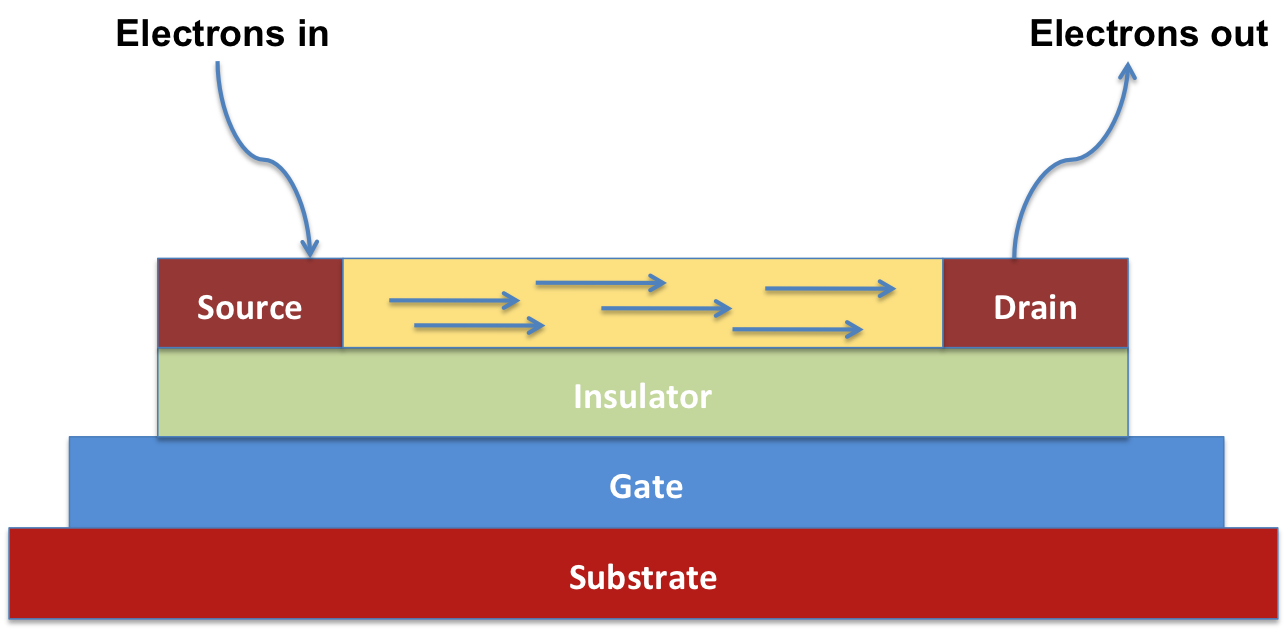
Organic field-effect transistor
Organic field-effect transistor
An organic field-effect transistor (OFET) is a field-effect transistor using an organic semiconductor in its channel. OFETs can be prepared either by vacuum evaporation of small molecules, by solution-casting of polymers or small molecules, or ...
is a field-effect transistor utilizing organic molecules or polymers as the active semiconducting layer. A field-effect transistor ( FET) is any semiconductor material that utilizes electric field to control the shape of a channel of one type of charge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
carrier, thereby changing its conductivity. Two major classes of FET are n-type and p-type semiconductor, classified according to the charge type carried. In the case of organic FETs (OFETs), p-type OFET compounds are generally more stable than n-type due to the susceptibility of the latter to oxidative damage.
As for OLEDs, some OFETs are molecular and some are polymer-based system. Rubrene-based OFETs show high carrier mobility of 20–40 cm2/(V·s). Another popular OFET material is Pentacene
Pentacene () is a polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon
A polycyclic aromatic hydrocarbon (PAH) is a class of organic compounds that is composed of multiple aromatic rings. The simplest representative is naphthalene, having two aromatic rings and t ...
. Due to its low solubility
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solub ...
in most organic solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
s, it's difficult to fabricate thin film transistors ( TFTs) from pentacene itself using conventional spin-cast or, dip coating
image:Dip coating.svg, A schematic of the continuous dip coating process.
Roll of coarse cloth
Cloth
Bath
Liquid material
Rollers
Oven
Scrapers
Excess liquid falls back
A coating remains on the fabric cloth.
Dip coating is an industrial ...
methods, but this obstacle can be overcome by using the derivative TIPS-pentacene.
Organic electronic devices

Organic solar cell
An organic solar cell (OSC) or plastic solar cell is a type of photovoltaic that uses organic electronics, a branch of electronics that deals with conductive organic polymers or small organic molecules, for light absorption and charge transport t ...
s could cut the cost of solar power compared with conventional solar-cell manufacturing. Silicon thin-film solar cell
A thin-film solar cell is a second generation solar cell that is made by depositing one or more thin layers, or thin film (TF) of photovoltaic material on a substrate, such as glass, plastic or metal. Thin-film solar cells are commercially use ...
s on flexible substrates allow a significant cost reduction of large-area photovoltaics for several reasons:Koch, Christian (2002Niedertemperaturabscheidung von Dünnschicht-Silicium für Solarzellen auf Kunststofffolien
Doctoral Thesis, ipe.uni-stuttgart.de # The so-called '
roll-to-roll
In the field of electronic devices, roll-to-roll processing, also known as web processing, reel-to-reel processing or R2R, is the process of creating electronic devices on a roll of flexible plastic, metal foil, or flexible glass. In other fields p ...
'-deposition on flexible sheets is much easier to realize in terms of technological effort than deposition on fragile and heavy glass sheet
Glass is a non-crystalline, often transparent, amorphous solid that has widespread practical, technological, and decorative use in, for example, window panes, tableware, and optics. Glass is most often formed by rapid cooling (quenching) of ...
s.
# Transport and installation of lightweight flexible solar cells also saves cost as compared to cells on glass.
Inexpensive polymeric substrates like polyethylene terephthalate (PET) or polycarbonate (PC) have the potential for further cost reduction in photovoltaics. Protomorphous solar cells prove to be a promising concept for efficient and low-cost photovoltaics on cheap and flexible substrates for large-area production as well as small and mobile applications.
One advantage of printed electronics is that different electrical and electronic components can be printed on top of each other, saving space and increasing reliability and sometimes they are all transparent. One ink must not damage another, and low temperature annealing is vital if low-cost flexible materials such as paper and plastic film
Plastic film is a thin continuous polymeric material. Thicker plastic material is often called a "sheet". These thin plastic membranes are used to separate areas or volumes, to hold items, to act as barriers, or as printable surfaces.
Plas ...
are to be used. There is much sophisticated engineering and chemistry involved here, with iTi, Pixdro, Asahi Kasei, Merck & Co., Merck, BASF, HC Starck, Hitachi Chemical and Frontier Carbon Corporation among the leaders.
Electronic device
The field of electronics is a branch of physics and electrical engineering that deals with the emission, behaviour and effects of electrons using electronic devices. Electronics uses active devices to control electron flow by amplification ...
s based on organic compound
In chemistry, organic compounds are generally any chemical compounds that contain carbon-hydrogen or carbon-carbon bonds. Due to carbon's ability to catenate (form chains with other carbon atoms), millions of organic compounds are known. T ...
s are now widely used, with many new products under development. Sony
, commonly stylized as SONY, is a Japanese multinational conglomerate corporation headquartered in Minato, Tokyo, Japan. As a major technology company, it operates as one of the world's largest manufacturers of consumer and professiona ...
reported the first full-color, video-rate, flexible, plastic display made purely of organic materials
Material is a substance or mixture of substances that constitutes an object. Materials can be pure or impure, living or non-living matter. Materials can be classified on the basis of their physical and chemical properties, or on their geolog ...
; television
Television, sometimes shortened to TV, is a telecommunication medium for transmitting moving images and sound. The term can refer to a television set, or the medium of television transmission. Television is a mass medium for advertisin ...
screen based on OLED materials; biodegradable electronics based on organic compound and low-cost organic solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
are also available.
Fabrication methods
Small molecule semiconductors are ofteninsoluble
In chemistry, solubility is the ability of a substance, the solute, to form a solution with another substance, the solvent. Insolubility is the opposite property, the inability of the solute to form such a solution.
The extent of the solubil ...
, necessitating deposition via vacuum sublimation. Devices based on conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s can be prepared by solution processing methods. Both solution processing and vacuum based methods produce amorphous and polycrystalline
A crystallite is a small or even microscopic crystal which forms, for example, during the cooling of many materials. Crystallites are also referred to as grains.
Bacillite is a type of crystallite. It is rodlike with parallel longulites.
Stru ...
films with variable degree of disorder. "Wet" coating
A coating is a covering that is applied to the surface of an object, usually referred to as the substrate. The purpose of applying the coating may be decorative, functional, or both. Coatings may be applied as liquids, gases or solids e.g. Pow ...
techniques require polymers to be dissolved in a volatile solvent
A solvent (s) (from the Latin '' solvō'', "loosen, untie, solve") is a substance that dissolves a solute, resulting in a solution. A solvent is usually a liquid but can also be a solid, a gas, or a supercritical fluid. Water is a solvent for ...
, filtered and deposited onto a substrate. Common examples of solvent-based coating techniques include drop casting, spin-coating
Spin coating is a procedure used to deposit uniform thin films onto flat substrates. Usually a small amount of coating material is applied on the center of the substrate, which is either spinning at low speed or not spinning at all. The substrate ...
, doctor-blading, inkjet printing
Inkjet printing is a type of computer printing that recreates a digital image by propelling droplets of ink onto paper and plastic substrates. Inkjet printers were the most commonly used type of printer in 2008, and range from small inexpen ...
and screen printing. Spin-coating is a widely used technique for small area thin film
A thin film is a layer of material ranging from fractions of a nanometer ( monolayer) to several micrometers in thickness. The controlled synthesis of materials as thin films (a process referred to as deposition) is a fundamental step in many ...
production. It may result in a high degree of material loss. The doctor-blade technique results in a minimal material loss and was primarily developed for large area thin film production. Vacuum based thermal deposition of small molecules requires evaporation of molecules from a hot source. The molecules are then transported through vacuum onto a substrate. The process of condensing these molecules on the substrate surface results in thin film formation. Wet coating techniques can in some cases be applied to small molecules depending on their solubility.
Organic solar cells
Organic semiconductor diodes convert light into electricity. Figure to the right shows five commonly used organic photovoltaic materials. Electrons in these organic molecules can be delocalized in a delocalized π orbital with a corresponding π* antibonding orbital. The difference in energy between the π orbital, or highest occupied molecular orbital (HOMO
''Homo'' () is the genus that emerged in the (otherwise extinct) genus '' Australopithecus'' that encompasses the extant species ''Homo sapiens'' ( modern humans), plus several extinct species classified as either ancestral to or closely relat ...
), and π* orbital, or lowest unoccupied molecular orbital (LUMO
In chemistry, HOMO and LUMO are types of molecular orbitals. The acronyms stand for ''highest occupied molecular orbital'' and ''lowest unoccupied molecular orbital'', respectively. HOMO and LUMO are sometimes collectively called the ''frontie ...
) is called the band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
of organic photovoltaic materials. Typically, the band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
lies in the range of 1-4eV.
The difference in the band gap
In solid-state physics, a band gap, also called an energy gap, is an energy range in a solid where no electronic states can exist. In graphs of the electronic band structure of solids, the band gap generally refers to the energy difference ( ...
of organic photovoltaic materials leads to different chemical structures and forms of organic solar cell
A solar cell, or photovoltaic cell, is an electronic device that converts the energy of light directly into electricity by the photovoltaic effect, which is a physical and chemical phenomenon.
s. Different forms of solar cells includes single-layer organic photovoltaic cells, bilayer organic photovoltaic cells and heterojunction photovoltaic cells. However, all three of these types of solar cells share the approach of sandwiching the organic electronic layer between two metallic conductors, typically indium tin oxide Indium tin oxide (ITO) is a ternary composition of indium, tin and oxygen in varying proportions. Depending on the oxygen content, it can be described as either a ceramic or an alloy. Indium tin oxide is typically encountered as an oxygen-saturated ...
.

Organic field-effect transistors
An organic field-effect transistor is a three terminal device (source, drain and gate). The charge carriers move between source and drain, and the gate serves to control the path's conductivity. There are mainly two types of organic field-effect transistor, based on the semiconducting layer's charge transport, namely p-type (such as dinaphtho ,3-''b'':2′,3′-''f''hieno ,2-''b''hiophene, DNTT), and n-type (such phenyl C61 butyric acid methyl ester, PCBM). Certain organic semiconductors can also present both p-type and n-type (i.e., ambipolar) characteristics. Such technology allows for the fabrication of large-area, flexible, low-cost electronics. One of the main advantages is that being mainly a low temperature process compared to CMOS, different type of materials can be utilized. This makes them in turn great candidates for sensing.Features
Conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s are lighter, more flexible
Flexible may refer to:
Science and technology
* Power cord, a flexible electrical cable.
** Flexible cable, an Electrical cable as used on electrical appliances
* Flexible electronics
* Flexible response
* Flexible-fuel vehicle
* Flexible rake re ...
, and less expensive than inorganic conductors. This makes them a desirable alternative in many applications. It also creates the possibility of new applications that would be impossible using copper or silicon.
Organic electronics not only includes organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or ...
s, but also organic dielectric
In electromagnetism, a dielectric (or dielectric medium) is an electrical insulator that can be polarised by an applied electric field. When a dielectric material is placed in an electric field, electric charges do not flow through the mate ...
s, conductors and light emitter
A light-emitting diode (LED) is a semiconductor Electronics, device that Light#Light sources, emits light when Electric current, current flows through it. Electrons in the semiconductor recombine with electron holes, releasing energy i ...
s.
New applications include smart windows and electronic paper
Electronic paper, also sometimes electronic ink, e-ink or electrophoretic display, are display devices that mimic the appearance of ordinary ink on paper. Unlike conventional flat panel displays that emit light, an electronic paper display ...
. Conductive polymer
Conductive polymers or, more precisely, intrinsically conducting polymers (ICPs) are organic polymers that conduct electricity. Such compounds may have metallic conductivity or can be semiconductors. The biggest advantage of conductive polymers ...
s are expected to play an important role in the emerging science of molecular computer
DNA computing is an emerging branch of unconventional computing which uses DNA, biochemistry, and molecular biology hardware, instead of the traditional electronic computing. Research and development in this area concerns theory, experiments, a ...
s.
See also
* Annealing *Bioplastic
Bioplastics are plastic materials produced from renewable biomass sources, such as vegetable fats and oils, corn starch, straw, woodchips, sawdust, recycled food waste, etc. Some bioplastics are obtained by processing directly from natural bi ...
* Carbon nanotube
* Circuit deposition
* Conductive ink
Conductive ink is an ink that results in a printed object which conducts electricity. It is typically created by infusing graphite or other conductive materials into ink. There has been a growing interest in replacing metallic materials with nano ...
* Flexible display
A flexible display or rollable display is an electronic visual display which is flexible in nature, as opposed to the traditional flat screen displays used in most electronic devices. In recent years there has been a growing interest from nume ...
* Laminar
* Melanin
Melanin (; from el, μέλας, melas, black, dark) is a broad term for a group of natural pigments found in most organisms. Eumelanin is produced through a multistage chemical process known as melanogenesis, where the oxidation of the amino ...
* Organic field-effect transistor (OFET)
* Organic semiconductor
Organic semiconductors are solids whose building blocks are pi-bonded molecules or polymers made up by carbon and hydrogen atoms and – at times – heteroatoms such as nitrogen, sulfur and oxygen. They exist in the form of molecular crystals or ...
* Organic light-emitting diode (OLED)
* Photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or ...
* Printed electronics
Printed electronics is a set of printing methods used to create electrical devices on various substrates. Printing typically uses common printing equipment suitable for defining patterns on material, such as screen printing, flexography, gravur ...
* Radio frequency identification
Radio-frequency identification (RFID) uses electromagnetic fields to automatically identify and track tags attached to objects. An RFID system consists of a tiny radio transponder, a radio receiver and transmitter. When triggered by an electrom ...
* Radio tag
* Schön scandal
* Spin coating
Spin coating is a procedure used to deposit uniform thin films onto flat substrates. Usually a small amount of coating material is applied on the center of the substrate, which is either spinning at low speed or not spinning at all. The substrate ...
References
Further reading
* Grasser, Tibor., Meller, Gregor. Baldo, Marc. (Eds.) (2010) ''Organic electronics'' Springer, Heidelberg. (Print) 978-3-642-04538-7 (Online) * * * * ''Electronic Processes in Organic Crystals and Polymers, 2 ed. '' by Martin Pope and Charles E. Swenberg, Oxford University Press (1999), * ''Handbook of Organic Electronics and Photonics'' (3-Volume Set) by Hari Singh Nalwa, American Scientific Publishers. (2008),External links
*orgworld
– ''Organic Semiconductor World'' homepage. {{Electronic systems Artificial materials