Olympic Dam, South Australia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Olympic Dam mine is a large poly-metallic underground mine located in
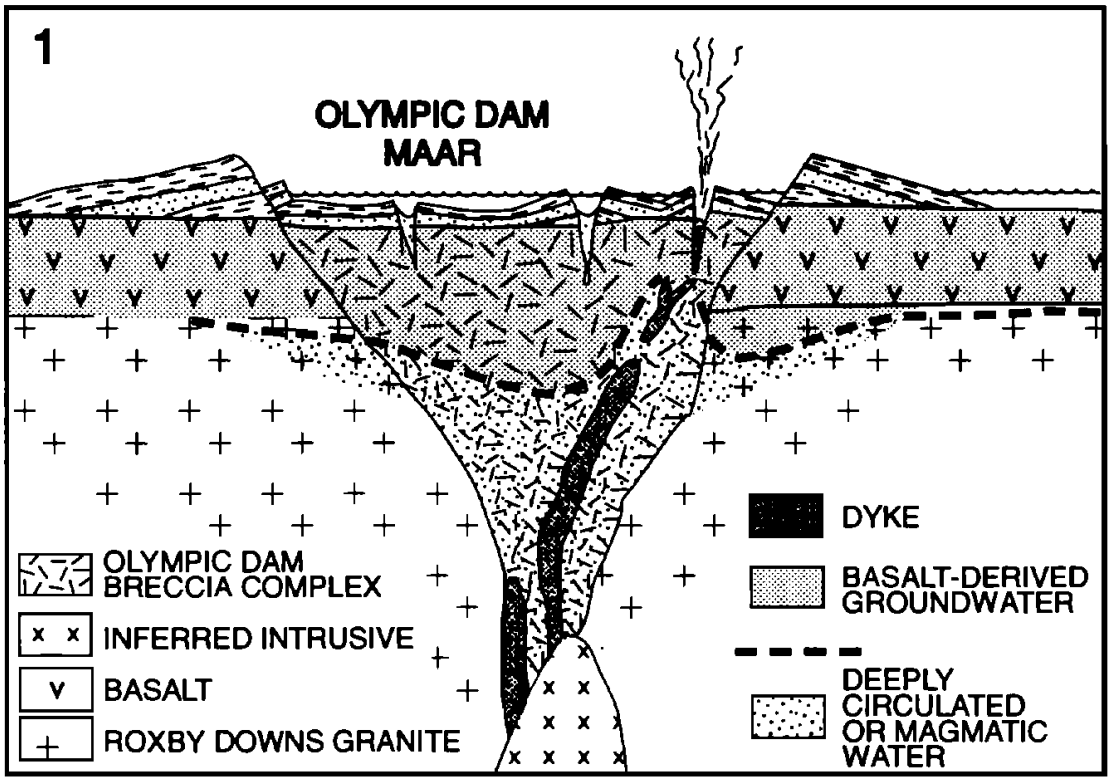 In 1979 a joint venture partnership was established between
In 1979 a joint venture partnership was established between
/ref> In May 2009, the company released an extensive environmental impact statement for public comment. It revealed the detailed plans for the proposed construction and its future operation. Among the project's new infrastructure requirements were: a desalination plant at Point Lowly (
 Seawater desalination had been considered by Western Mining Corporation as early as 1997, but at that time it was considered to be neither economically nor environmentally viable. By 2005, Western Mining Corporation had revisited the possibility of seawater desalination from upper Spencer Gulf. A pre-feasibility study was underway at the time of the BHP Billiton takeover, and was completed by the project's new owners.
In order to meet the project's increasing demand for water, the BHP Billiton expansion plan proposed to construct a large-scale reverse osmosis seawater
Seawater desalination had been considered by Western Mining Corporation as early as 1997, but at that time it was considered to be neither economically nor environmentally viable. By 2005, Western Mining Corporation had revisited the possibility of seawater desalination from upper Spencer Gulf. A pre-feasibility study was underway at the time of the BHP Billiton takeover, and was completed by the project's new owners.
In order to meet the project's increasing demand for water, the BHP Billiton expansion plan proposed to construct a large-scale reverse osmosis seawater  In February 2012,
In February 2012,



 In 2006, the Government of South Australia established the Olympic Dam Task Force to assist BHP Billiton with their mine expansion plans.
In 2006, the Government of South Australia established the Olympic Dam Task Force to assist BHP Billiton with their mine expansion plans.
South Australian HistoryInfomine MinesitesBHP BillitonSocial and Ecological Impact of Water Extraction for a Copper-Uranium MineOlympic Dam Project on mining-technology.com
{{Australian anti-nuclear Copper mines in South Australia Gold mines in South Australia Silver mines in Australia Underground mines in Australia Far North (South Australia) Mining in South Australia 1988 establishments in Australia Uranium mines in South Australia
South Australia
South Australia (commonly abbreviated as SA) is a state in the southern central part of Australia. It covers some of the most arid parts of the country. With a total land area of , it is the fourth-largest of Australia's states and territories ...
, NNW of Adelaide
Adelaide ( ) is the capital city of South Australia, the state's largest city and the fifth-most populous city in Australia. "Adelaide" may refer to either Greater Adelaide (including the Adelaide Hills) or the Adelaide city centre. The dem ...
. It is the fourth largest copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
deposit and the largest known single deposit of uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
in the world. Copper is the largest contributor to total revenue, accounting for approximately 70% of the mine's revenue, with the remaining 25% from uranium, and around 5% from silver and gold.http://www.aph.gov.au/parliamentary_business/committees/house_of_representatives_committees?url=jsct/8august2006/subs2/sub34_1.pdf BHP
BHP Group Limited (formerly known as BHP Billiton) is an Australian multinational mining, metals, natural gas petroleum public company that is headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
The Broken Hill Proprietary Company was founded ...
has owned and operated the mine since 2005. The mine was previously owned by Western Mining Corporation
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
* Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that ...
.
Since it opened in 1988, an extensive underground mine, an integrated metallurgical processing plant and expansive open-air tailings storage facilities have been constructed. The adjacent Olympic Dam mining centre and the nearby township of Roxby Downs Roxby Downs may refer to.
* Roxby Downs, South Australia, a town and a locality
* Roxby Council, formerly Municipal Council of Roxby Downs, a local government area
See also
*Roxby Downs Station
Roxby Downs Station was a pastoral lease in centra ...
service the mine and accommodate its workforce. Daily flights to and from Adelaide are provided via the Olympic Dam Airport.
BHP
BHP Group Limited (formerly known as BHP Billiton) is an Australian multinational mining, metals, natural gas petroleum public company that is headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
The Broken Hill Proprietary Company was founded ...
planned to expand the mine by establishing a new open cut pit and building extensive supporting infrastructure. In 2012 the expansion was postponed indefinitely pending investigation of a "new and cheaper design".
Scale of production
As of 2013, Olympic Dam is the second largest uranium-producing mine in the world, having produced of uranium metal in the financial year ending June 2013. The only larger producer is theMcArthur River uranium mine
The McArthur River Uranium Mine, in northern Saskatchewan, Canada, is the world's largest high-grade uranium deposit.
The McArthur River deposit was discovered in 1988. The property is located as the crow flies north of Saskatoon, Saskatchewan ...
in Canada. Given the energy density of uranium, this quantity is equal to a heating value
The heating value (or energy value or calorific value) of a substance, usually a fuel or food (see food energy), is the amount of heat released during the combustion of a specified amount of it.
The ''calorific value'' is the total energy relea ...
of 820 TWh (equivalent to ) at a CANDU-typical burnup
In nuclear power technology, burnup (also known as fuel utilization) is a measure of how much energy is extracted from a primary nuclear fuel source. It is measured as the fraction of fuel atoms that underwent fission in %FIMA (fissions per ini ...
of 200 MWhthermal/kg. Other reactor types which require uranium enrichment
Enriched uranium is a type of uranium in which the percent composition of uranium-235 (written 235U) has been increased through the process of isotope separation. Naturally occurring uranium is composed of three major isotopes: uranium-238 (238 ...
will recover slightly different amounts of heat from this amount of uranium. For comparison to get the same amount of heat energy by burning coal (energy density ranging from 24 to 35 MJ/kg) one would need between and of coal depending on grade
Grade most commonly refers to:
* Grade (education), a measurement of a student's performance
* Grade, the number of the year a student has reached in a given educational stage
* Grade (slope), the steepness of a slope
Grade or grading may also ref ...
. The largest coal mine in the world, North Antelope Rochelle Mine in Wyoming, produced of coal in 2019 at a grade of equivalent to roughly of heat energy.
History
 In 1979 a joint venture partnership was established between
In 1979 a joint venture partnership was established between Western Mining Corporation
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
* Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that ...
and BP Minerals with the intention of establishing the mine. Three years later, the ''Roxby Downs (Indenture Ratification) Act 1982'' was signed, creating a legal framework for the development to proceed. The first shaft was constructed that year, and named the Whenan Shaft after Ted Whenan, one of the exploration drillers who discovered the ore body. The new municipality of Roxby Downs Roxby Downs may refer to.
* Roxby Downs, South Australia, a town and a locality
* Roxby Council, formerly Municipal Council of Roxby Downs, a local government area
See also
*Roxby Downs Station
Roxby Downs Station was a pastoral lease in centra ...
was also established in 1982, as an intended service centre and community hub for the mine workers and their families. In 1983, the mine's first Environmental Impact Statement was approved, authorising copper production of up to 150,000 tonnes per annum. Over a decade would pass before this production target was achieved.
In 1987, a decline entrance to the mine was created, and the Olympic Dam Special Mining Lease was connected to the South Australian electricity grid. The mine was officially opened the following year, and the first shipments of copper cathodes and uranium oxide were made. Roxby Downs township was officially opened, and the town's newspaper, the ''Roxby Downs Sun'' commenced publication. In 1989, the Olympic Dam refinery produced its first gold and silver bars.
In 1993, Western Mining Corporation bought BP's 49% shareholding and assumed total control of the project. Several stages of expansion occurred around this time and production increased. In 1986, the mine's target production had been set at 45,000 tonnes of copper per annum. In 1992, output reached 66,000 tonnes, then 84,000 in 1995.
The mine's first major expansion was announced in 1996 with the objective of producing 200,000 tonnes per annum once complete. A second Environmental Impact Statement was approved, allowing the mine to expand production up to 350,000 tonnes of copper per annum.
In 1998 the mine poured its 500th bar of gold. Two years later the mine produced 200,000 tonnes of copper in a year for the first time. Optimisation efforts increased output to 235,000 tonnes per annum in 2002.
BHP made a successful bid for Western Mining Corporation in March 2005 and the offer was accepted by the Australian Competition & Consumer Commission
The Australian Competition and Consumer Commission (ACCC) is the chief competition regulator of the Government of Australia, located within the Department of the Treasury. It was established in 1995 with the amalgamation of the Australian Trad ...
in April. BHP Billiton was not the only resources company to express interest in the project. Xstrata
Xstrata plc was an Anglo-Swiss multinational mining company headquartered in Zug, Switzerland and with its registered office in London, United Kingdom. It was a major producer of coal (and the world's largest exporter of thermal coal), copper, ...
had made prior takeover bids in late 2004, and French state-run nuclear industrial company Areva had entered into what were rumoured to be partnership discussions with WMC Resources in February.
After the acquisition, BHP began to plan what would become a proposed $30 billion expansion project, involving the excavation of a new open cut mine within the existing Special Mining Lease. The expansion plan was expected to be a boon to the South Australian economy- forecast to generate an estimated 23,000 direct and indirect jobs. Major new infrastructure would need to be constructed to facilitate the expansion, including a new airport at Olympic Dam, a rail link, a seawater desalination plant at Point Lowly, a barge-landing facility near Port Augusta and a worker village near Andamooka.
The company's access to the Government of South Australia was enhanced by the formation of the Olympic Dam Task Force in 2006, which has since served as a single entry-point for the company's interactions with the state. BHP also began to develop relationships with scientific and academic institutions with the objective of facilitating relevant technical, environmental and policy research.
Research sponsorship and partnerships
Academic research related to the Olympic Dam mine and funded by BHP Billiton has been undertaken by at least four major South Australian institutions since the take-over. Works have included producing a projection of future skill requirements for Olympic Dam by Flinders University, research into novel "liquid mining" techniques conducted by a team at theSouth Australian Museum
The South Australian Museum is a natural history museum and research institution in Adelaide, South Australia, founded in 1856 and owned by the Government of South Australia. It occupies a complex of buildings on North Terrace in the cultu ...
, numerous studies at the Environment Institute and Institute for Mineral and Energy Resources (IMER) at the University of Adelaide
The University of Adelaide (informally Adelaide University) is a public research university located in Adelaide, South Australia. Established in 1874, it is the third-oldest university in Australia. The university's main campus is located on N ...
and numerous more at the Ian Wark Research Institute at the University of South Australia
The University of South Australia (UniSA) is a public research university in the Australian state of South Australia. It is a founding member of the Australian Technology Network of universities, and is the largest university in South Australi ...
.
In 2008, the Ian Wark Research Institute entered a research partnership with BHP. The company committed to provide $500,000 per annum for five consecutive years for research programs. The institute's annual report that year referred to BHP Billiton as having had a representative on their advisory board for "many years". In 2012, the Institute for Mineral and Energy Resources at the University of Adelaide was awarded over $2.5 million as part of the Australian Research Council's Industrial Transformation Program. Funds were to be spent over six years during the establishment of a research hub for advancing copper-uranium production. BHP Billiton partnered with IMER on the project and is providing $2.5 million in cash plus additional in-kind contributions.
BHP executives have also held numerous board memberships within academic institutions since the Olympic Dam take-over. Andrew Shook, general manager of BHP Billiton's Uranium Customer Sector Group, held a position on the advisory board of the Ian Wark Research Institute from 2009 to 2011, and Robert Sumner held a position as an adjunct senior research fellow there for the same period. John England, the vice president of technology, Uranium Customer Sector Group at BHP Billiton, was appointed to the advisory board of IMER from its establishment in 2009 until 2014. President of Uranium Dean Dalla Valle also held a position on the IMER advisory board in 2009 to 2010 and another on the board of the South Australian Museum from 2011 to 2012. Vice President Sustainability at BHP Billiton, Carl Binning, has held a position on the Board of the Environment Institute since at least 2011. He ceased working for BHP Billiton in 2012 but continues to hold his board position.
Industry associations
BHP Olympic Dam is a member of theWorld Nuclear Association
World Nuclear Association is the international organization that promotes nuclear power and supports the companies that comprise the global nuclear industry. Its members come from all parts of the nuclear fuel cycle, including uranium mining, ur ...
, whose mission is "to promote a wider understanding of nuclear energy among key international influencers by producing authoritative information, developing common industry positions, and contributing to the energy debate." BHP Billiton is also a full member of the Minerals Council of Australia's Uranium Forum, where the interests of the Olympic Dam project are represented.
Sponsorships
BHP sponsors a variety of events and organisations. Some are directly linked to the company's uranium portfolio, which is exclusively represented by the Olympic Dam mine. In 2016, BHP Billiton was the major sponsor of the Australian Radiation Protection Society's (ARPS) 2016 Conference, held in Adelaide. Tours of the Olympic Dam mine have also been offered to delegates of uranium and mining industry conferences held in South Australia.Proposed expansion
At the time of the BHP takeover, WMC Resources was investigating ways to expand the mine, including considering constructing a prospective seawater desalination plant atPort Bonython
Port Bonython is the location of a deepwater port, gas fractionation plant and diesel storage facility west of Point Lowly in the Upper Spencer Gulf region of South Australia. It lies 16 km east-northeast of Whyalla, South Australia and app ...
( Point Lowly).
In 2008, BHP completed a pre-feasibility study into the expansion of the mine's operations, with the first step of expansion scheduled for completion by late 2013. In December 2008, South Australia's Premier Mike Rann
Michael David Rann, , (born 5 January 1953) is an Australian former politician who was the 44th premier of South Australia from 2002 to 2011. He was later Australian High Commissioner to the United Kingdom from 2013 to 2014, and Australian am ...
revealed advice from BHP that the project would proceed as an open-cut operation.
While being welcomed at the time by state and federal governments as a major boost to the economy, the proposed expansion of mining operations also attracted considerable criticism. In 2007, BHP Billiton attracted public attention for delaying the release of its environmental impact statement for the Olympic Dam expansion, and for the company's response to inconsistencies in the scope and configuration of the proposed expansion.Uranium mining and the question of corporate social responsibility/ref> In May 2009, the company released an extensive environmental impact statement for public comment. It revealed the detailed plans for the proposed construction and its future operation. Among the project's new infrastructure requirements were: a desalination plant at Point Lowly (
Port Bonython
Port Bonython is the location of a deepwater port, gas fractionation plant and diesel storage facility west of Point Lowly in the Upper Spencer Gulf region of South Australia. It lies 16 km east-northeast of Whyalla, South Australia and app ...
), a rail link to Pimba, a worker accommodation village between Olympic Dam and Andamooka and a barge landing facility near Port Augusta.
In May 2011, the company released a Supplementary Environmental Impact Statement in response to the 4,197 submissions received during a 14-week public comment period.
On 10 October 2011, state and federal government approvals for the mine expansion were granted.
Seawater desalination at Point Lowly
 Seawater desalination had been considered by Western Mining Corporation as early as 1997, but at that time it was considered to be neither economically nor environmentally viable. By 2005, Western Mining Corporation had revisited the possibility of seawater desalination from upper Spencer Gulf. A pre-feasibility study was underway at the time of the BHP Billiton takeover, and was completed by the project's new owners.
In order to meet the project's increasing demand for water, the BHP Billiton expansion plan proposed to construct a large-scale reverse osmosis seawater
Seawater desalination had been considered by Western Mining Corporation as early as 1997, but at that time it was considered to be neither economically nor environmentally viable. By 2005, Western Mining Corporation had revisited the possibility of seawater desalination from upper Spencer Gulf. A pre-feasibility study was underway at the time of the BHP Billiton takeover, and was completed by the project's new owners.
In order to meet the project's increasing demand for water, the BHP Billiton expansion plan proposed to construct a large-scale reverse osmosis seawater desalination plant
Desalination is a process that takes away mineral components from saline water. More generally, desalination refers to the removal of salts and minerals from a target substance, as in soil desalination, which is an issue for agriculture. Saltw ...
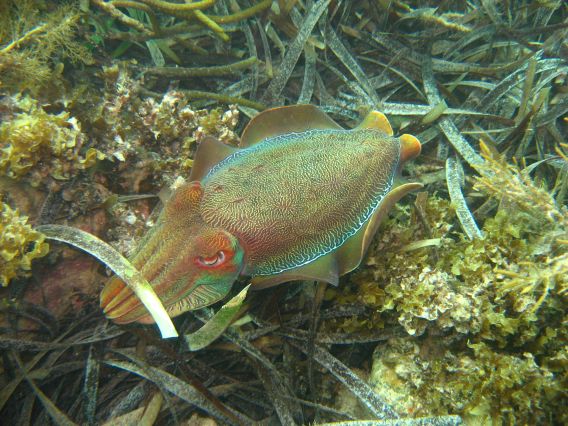
at Point Lowly in upper Spencer Gulf. The water would then be pumped over 300 km north to the Olympic Dam mine site and Roxby Downs township. The proposed plant's location remains controversial due to the proximity of the proposed brine discharge to critical breeding habitat for the Giant Australian Cuttlefish, which are sensitive to increases in ocean salinity.
In August 2009, a South Australian parliamentary committee recommended that BHP Billiton investigate alternative locations for the proposed plant after concluding that brine could harm the marine ecology of upper Spencer Gulf.
In 2010 and 2011, three petitions (signed by a total of 910 South Australians) were tabled in the Parliament of South Australia calling for the relocation of the proposed desalination plant, so that it would discharge brine into an oceanic environment rather than into Spencer Gulf.
Arabana
The Arabana, also known as the Ngarabana, are an Aboriginal Australian people of South Australia.
Name
The older tribal Exonym and endonym, autonym was Ngarabana, which may have been misheard by white settlers as Arabana, the term now generall ...
elder Kevin Buzzacott
Kevin Buzzacott (born 1947), often referred to as Uncle Kev as an Aboriginal elder, is an Indigenous Australian from the Arabunna nation in northern South Australia. He has campaigned widely for cultural recognition, justice and land rights fo ...
legally challenged the Commonwealth Environment Minister Tony Burke's environmental approval of the Olympic Dam mine expansion. Buzzacott was represented by the Environmental Defenders' Office and appeared in the Federal Court in Adelaide on 3 and 4 April 2012. His case was dismissed on 20 April 2012. An appeal of the judge's decision in 2013 was also unsuccessful.
In July 2012, more than 400 people joined the "Lizard's Revenge" protest at the Olympic Dam site. The anti-nuclear
The anti-nuclear movement is a social movement that opposes various nuclear technologies. Some direct action groups, environmental movements, and professional organisations have identified themselves with the movement at the local, nationa ...
activists, including Buzzacott, protested against the mine expansion and the uranium industry. They say the company and the government have put short-term economic gain ahead of environmental and health concerns. Organiser Nectaria Calan said police harassed protesters, demanding identification and controlling access to and from their campsite.
The original development of the mine also attracted public opposition from Australia's anti-nuclear movement. Hundreds of arrests occurred at and around the mine site during a variety of actions and demonstrations in 1983 and 1984. The protesters alleged that they had been provoked by police and that they had been unfairly represented as the antagonists in various media reports.
In August 2012, BHP Billiton announced that the expansion was being postponed indefinitely pending investigation of a "new and cheaper design". The South Australian Mineral Resources and Energy Minister, Tom Koutsantonis in response to this announcement stated "they will be developed (and) it will bring a great deal of prosperity." However the Premier, Jay Weatherill
Jay Wilson Weatherill (born 3 April 1964) is an Australian politician who was the 45th Premier of South Australia, serving from 21 October 2011 until 19 March 2018. Weatherill represented the House of Assembly seat of Cheltenham as a member of ...
, warned BHP "given that this is the second time they have disappointed South Australians, there can be no doubt that this community permission will come at a (greater) cost" next time. Eight months later, the service town of Roxby Downs was reportedly "in a slump".
In December 2013, the federal government expressed its support for the revival of the Olympic Dam expansion project. The announcements were made in the wake of news that General Motors Holden
Holden, formerly known as General Motors-Holden, was an Australian subsidiary company of General Motors. It was an Australian automobile manufacturer, importer, and exporter which sold cars under its own marque in Australia. In its last three ...
would be ceasing its car production operations in South Australia in 2017. Members of South Australia's business community believe that the state's future prosperity should not be dependent on the Olympic Dam expansion proceeding and have expressed the need for Government to support a diversified economy.
In September 2014, environmental approval was received for heap-leaching trials to commence at the mine in an effort to reduce processing costs.
In 2015, the Olympic Dam mine's workforce began a staged contraction in company-wide efforts to reduce operating costs. A review of the workforce was announced in January. Since the review commenced, 50 contractor positions were shed in March and 140 jobs were lost in June. A spokesperson from BHP Billiton told ''Australian Mining:''''"''All areas of our business, including labour productivity, are being examined. A review is currently progressing in our operational areas and we expect there will be further workforce reductions".
Operations

Underground mine
The Olympic Dam mine works an extremely large iron oxide copper gold deposit with estimated reserves of 2.95 billion tonnes of ore grading 1.2%copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pinkis ...
, 0.04% uranium
Uranium is a chemical element with the symbol U and atomic number 92. It is a silvery-grey metal in the actinide series of the periodic table. A uranium atom has 92 protons and 92 electrons, of which 6 are valence electrons. Uranium is weak ...
, .5 g/t of gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile me ...
and 6 g/t of silver
Silver is a chemical element with the symbol Ag (from the Latin ', derived from the Proto-Indo-European ''h₂erǵ'': "shiny" or "white") and atomic number 47. A soft, white, lustrous transition metal, it exhibits the highest electrical ...
.
The deposit was originally discovered by Western Mining Corporation
Western may refer to:
Places
*Western, Nebraska, a village in the US
* Western, New York, a town in the US
* Western Creek, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
* Western Junction, Tasmania, a locality in Australia
*Western world, countries that ...
in 1975 near Roxby Downs Sheep Station and production officially commenced in 1988. It now belongs to BHP
BHP Group Limited (formerly known as BHP Billiton) is an Australian multinational mining, metals, natural gas petroleum public company that is headquartered in Melbourne, Victoria, Australia.
The Broken Hill Proprietary Company was founded ...
, which acquired WMC Resources in 2005. The mine currently operates by an underground mining method called sublevel open stoping, using modern and highly productive mining equipment. The March 2005 mine production rate is an annualised 9.1 million tonnes making it one of Australia's larger mines. 2005 metal production is thought to be in excess of 220,000 tonnes of copper, 4500 tonnes of uranium oxide
Uranium oxide is an oxide of the element uranium.
The metal uranium forms several oxides:
* Uranium dioxide or uranium(IV) oxide (UO2, the mineral uraninite or pitchblende)
* Diuranium pentoxide or uranium(V) oxide (U2O5)
* Uranium trioxide o ...
, plus gold and silver. The copper and uranium oxide are exported through Port Adelaide. Most of the mine workers live in the nearby towns of Roxby Downs Roxby Downs may refer to.
* Roxby Downs, South Australia, a town and a locality
* Roxby Council, formerly Municipal Council of Roxby Downs, a local government area
See also
*Roxby Downs Station
Roxby Downs Station was a pastoral lease in centra ...
and Andamooka. Regular flights between Adelaide and the Olympic Dam Airport serve the mine project.

Uranium production
The production of uranium at Olympic dam accounts for approximately 25% of the mine's revenue. Since 2013, Olympic Dam has been Australia's largest producer of uranium oxide or 'yellowcake'.Electricity supply
The Olympic Dam mine is South Australia's single largest consumer of electricity, and is connected (at 275kV) at end of the grid via Port Augusta. In 2009, BHP Billiton defined its typical annual electricity consumption as 870,000 MWh (or 125 MW). In 2015, BHP requested a more reliable grid connection. The 2016 storm and heatwaves disrupted production and caused financial losses, and the state started initiatives to increase grid reliability. The mine has ordered 210MW wind power and 110MW solar for 2022.Water supply
The Olympic Dam mine uses 35 megalitres ofGreat Artesian Basin
The Great Artesian Basin (GAB), located in Australia, is the largest and deepest artesian basin in the world, stretching over , with measured water temperatures ranging from . The basin provides the only source of fresh water through much ...
water each day, making it the largest industrial user of underground water in the southern hemisphere. Water is pumped along an underground pipeline from two bore fields which are located 110 km and 200 km to the north of the mine. The salty bore water requires desalination before it is used. Contaminated water from mining operations is passed through a series of sealed ponds where it evaporates. 3 megalitres of the 35 megalitres extracted daily is supplied to the township of Roxby Downs. Water usage has increased significantly since the 1990s. In 1995, the Olympic Dam project, including the Roxby Downs township, consumed an average of 14.3 megalitres of water daily.
The high use of artesian water as a result of mine operations threatens areas of high ecological significance. In particular, the pumping of water from the bore fields has been linked to observations of reductions in flow or drying out in nearby mound springs. As mound springs are the only permanent source of water in the arid interior of South Australia a delicate yet intricate ecological balance has been established with prolonged isolation causing the existence of many rare and endemic species.
Air pollution
Airborne pollution emissions from the Olympic Dam processing facility are reported annually to the National Pollution Inventory. Emissions exceeding 500 tonnes per annum as of 2013 are (from largest to smallest): particulate matter (10 um),oxides of nitrogen Nitrogen oxide may refer to a binary compound of oxygen and nitrogen, or a mixture of such compounds:
Charge-neutral
*Nitric oxide (NO), nitrogen(II) oxide, or nitrogen monoxide
*Nitrogen dioxide (), nitrogen(IV) oxide
* Nitrogen trioxide (), or n ...
, sulfur dioxide and carbon monoxide
Carbon monoxide (chemical formula CO) is a colorless, poisonous, odorless, tasteless, flammable gas that is slightly less dense than air. Carbon monoxide consists of one carbon atom and one oxygen atom connected by a triple bond. It is the simple ...
.
Public sector support
 In 2006, the Government of South Australia established the Olympic Dam Task Force to assist BHP Billiton with their mine expansion plans.
In 2006, the Government of South Australia established the Olympic Dam Task Force to assist BHP Billiton with their mine expansion plans. Paul Heithersay
Paul Sinclair Heithersay is a public servant employed by the Government of South Australia. He is the chief executive of the Department for Energy and Mining. He was appointed to this role by the then recently elected Liberal government in Jun ...
is the task force's Chief Executive and as of 2015 also serves as Deputy Chief Executive for the Department of State Development. Current and former senior public servants who have also worked on the Olympic Dam project as employees of BHP Billiton or Western Mining Corporation include Richard Yeeles and Kym Winter-Dewhirst.
See also
* Ian Duncan *Arvi Parbo
Sir Arvi Hillar Parbo (10 February 1926 – 1 May 2019) was a business executive who was concurrently chairman of three of Australia's largest companies, Alcoa World Alumina & Chemicals, Munich Re, and Zurich Australian Insurance.
Early lif ...
* Hugh Morgan
* List of Australian inquiries into uranium mining
* Uranium mining in Australia
Radioactive ores were first extracted in South Australia at Radium Hill in 1906 and Mount Painter in 1911. 2,000 tons of ore were treated to recover radium for medical use. Several hundred kilograms of uranium were also produced for use in ce ...
* Uranium ore deposits
Uranium ore deposits are economically recoverable concentrations of uranium within the Earth's crust. Uranium is one of the more common elements in the Earth's crust, being 40 times more common than silver and 500 times more common than gold. It ...
References
External links
South Australian History
{{Australian anti-nuclear Copper mines in South Australia Gold mines in South Australia Silver mines in Australia Underground mines in Australia Far North (South Australia) Mining in South Australia 1988 establishments in Australia Uranium mines in South Australia