Early life and career
Obama was born on August 4, 1961, at, ''
Education
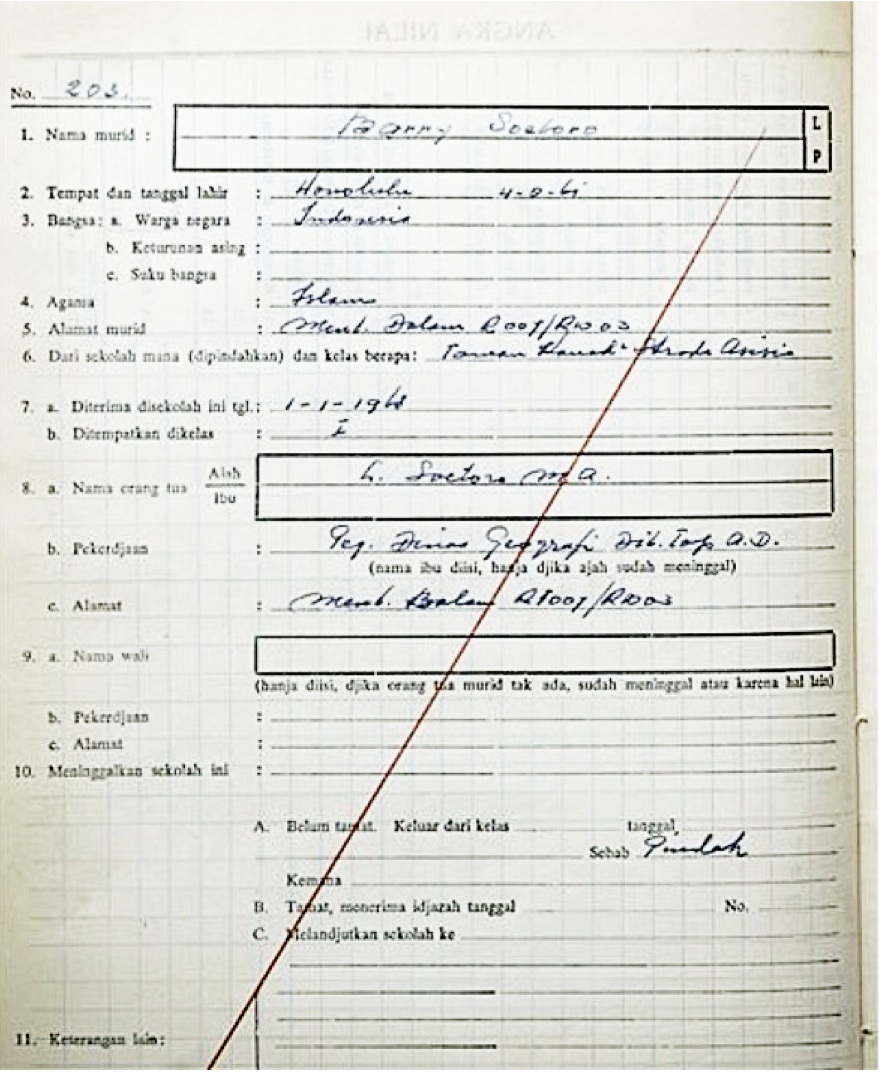 At the age of six, Obama and his mother had moved to Indonesia to join his stepfather. From age six to ten, he attended local Indonesian-language schools: ''Sekolah Dasar Katolik Santo Fransiskus Asisi'' (St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Elementary School) for two years and ''Sekolah Dasar Negeri Menteng 01'' (State Elementary School Menteng 01) for one and a half years, supplemented by English-language
At the age of six, Obama and his mother had moved to Indonesia to join his stepfather. From age six to ten, he attended local Indonesian-language schools: ''Sekolah Dasar Katolik Santo Fransiskus Asisi'' (St. Francis of Assisi Catholic Elementary School) for two years and ''Sekolah Dasar Negeri Menteng 01'' (State Elementary School Menteng 01) for one and a half years, supplemented by English-language College and research jobs
After graduating from high school in 1979, Obama moved toCommunity organizer and Harvard Law School
Two years after graduating from Columbia, Obama moved from New York to Chicago when he was hired as director of the Developing Communities Project, a church-based community organization originally comprising eight Catholic parishes in Roseland, West Pullman, and Riverdale on Chicago's South Side. He worked there as a community organizer from June 1985 to May 1988. He helped set up a job training program, a college preparatory tutoring program, and a tenants' rights organization inUniversity of Chicago Law School
In 1991, Obama accepted a two-year position as Visiting Law and Government Fellow at theFamily and personal life
In a 2006 interview, Obama highlighted the diversity of family of Barack Obama, his extended family: "It's like a little mini-United Nations," he said. "I've got relatives who look like Bernie Mac, and I've got relatives who look like Margaret Thatcher." Obama has a half-sister with whom he was raised (Maya Soetoro-Ng) and seven other half-siblings from his Kenyan father's family—six of them living. Obama's mother was survived by her Kansas-born mother, Madelyn Dunham, until her death on November 2, 2008, two days before his election to the presidency. Obama also has roots in Ireland; he met with his Irish cousins in Moneygall in May 2011. In ''Dreams from My Father'', Obama ties his mother's family history to possible Native American ancestors and distant relatives of Jefferson Davis, President of the Confederate States of America during the American Civil War. He also shares distant ancestors in common with In June 1989, Obama met Michelle Obama, Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of Sidley Austin. Robinson was assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, and she joined him at several group social functions but declined his initial requests to date. They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992. After suffering a miscarriage, Michelle underwent in vitro fertilization to conceive their children. The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born in 1998, followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), in 2001. The Obama daughters attended the University of Chicago Laboratory Schools. When they moved to Washington, D.C., in January 2009, the girls started at the Sidwell Friends School. The Obamas had two Portuguese Water Dogs; the first, a male named Bo (dog), Bo, was a gift from Senator Ted Kennedy. In 2013, Bo was joined by Sunny (dog), Sunny, a female. Bo died of cancer on May 8, 2021.
In June 1989, Obama met Michelle Obama, Michelle Robinson when he was employed as a summer associate at the Chicago law firm of Sidley Austin. Robinson was assigned for three months as Obama's adviser at the firm, and she joined him at several group social functions but declined his initial requests to date. They began dating later that summer, became engaged in 1991, and were married on October 3, 1992. After suffering a miscarriage, Michelle underwent in vitro fertilization to conceive their children. The couple's first daughter, Malia Ann, was born in 1998, followed by a second daughter, Natasha ("Sasha"), in 2001. The Obama daughters attended the University of Chicago Laboratory Schools. When they moved to Washington, D.C., in January 2009, the girls started at the Sidwell Friends School. The Obamas had two Portuguese Water Dogs; the first, a male named Bo (dog), Bo, was a gift from Senator Ted Kennedy. In 2013, Bo was joined by Sunny (dog), Sunny, a female. Bo died of cancer on May 8, 2021.
 Obama is a supporter of the Chicago White Sox, and he threw out the first pitch at the 2005 American League Championship Series, 2005 ALCS when he was still a senator. In 2009, he threw out the ceremonial first pitch at the 2009 Major League Baseball All-Star Game, All-Star Game while wearing a White Sox jacket. He is also primarily a Chicago Bears football fan in the National Football League, NFL, but in his childhood and adolescence was a Steeler Nation, fan of the Pittsburgh Steelers, and rooted for them ahead of their victory in Super Bowl XLIII 12 days after he took office as president. In 2011, Obama invited the 1985 Chicago Bears season, 1985 Chicago Bears to the White House; the team had not visited the White House after their Super Bowl XX, Super Bowl win in 1986 due to the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster. He plays basketball, a sport he participated in as a member of his high school's varsity team, and he is left-handed.
In 2005, the Obama family applied the proceeds of a book deal and moved from a Hyde Park, Chicago condominium to a $1.6million house (equivalent to $million in ) in neighboring Kenwood, Chicago. The purchase of an adjacent lot—and sale of part of it to Obama by the wife of developer, campaign donor and friend Tony Rezko—attracted media attention because of Rezko's subsequent indictment and conviction on political corruption charges that were unrelated to Obama.
In December 2007, ''Money (magazine), Money Magazine'' estimated Obama's net worth at $1.3million (equivalent to $million in ). Their 2009 tax return showed a household income of $5.5million—up from about $4.2million in 2007 and $1.6million in 2005—mostly from sales of his books. On his 2010 income of $1.7million, he gave 14 percent to non-profit organizations, including $131,000 to Fisher House Foundation, a charity assisting wounded veterans' families, allowing them to reside near where the veteran is receiving medical treatments. Per his 2012 financial disclosure, Obama may be worth as much as $10million.
Obama is a supporter of the Chicago White Sox, and he threw out the first pitch at the 2005 American League Championship Series, 2005 ALCS when he was still a senator. In 2009, he threw out the ceremonial first pitch at the 2009 Major League Baseball All-Star Game, All-Star Game while wearing a White Sox jacket. He is also primarily a Chicago Bears football fan in the National Football League, NFL, but in his childhood and adolescence was a Steeler Nation, fan of the Pittsburgh Steelers, and rooted for them ahead of their victory in Super Bowl XLIII 12 days after he took office as president. In 2011, Obama invited the 1985 Chicago Bears season, 1985 Chicago Bears to the White House; the team had not visited the White House after their Super Bowl XX, Super Bowl win in 1986 due to the Space Shuttle Challenger disaster. He plays basketball, a sport he participated in as a member of his high school's varsity team, and he is left-handed.
In 2005, the Obama family applied the proceeds of a book deal and moved from a Hyde Park, Chicago condominium to a $1.6million house (equivalent to $million in ) in neighboring Kenwood, Chicago. The purchase of an adjacent lot—and sale of part of it to Obama by the wife of developer, campaign donor and friend Tony Rezko—attracted media attention because of Rezko's subsequent indictment and conviction on political corruption charges that were unrelated to Obama.
In December 2007, ''Money (magazine), Money Magazine'' estimated Obama's net worth at $1.3million (equivalent to $million in ). Their 2009 tax return showed a household income of $5.5million—up from about $4.2million in 2007 and $1.6million in 2005—mostly from sales of his books. On his 2010 income of $1.7million, he gave 14 percent to non-profit organizations, including $131,000 to Fisher House Foundation, a charity assisting wounded veterans' families, allowing them to reside near where the veteran is receiving medical treatments. Per his 2012 financial disclosure, Obama may be worth as much as $10million.
Last name
Obama (surname), Obama's last name originates from Luo people. In Luo language, it means "bent over" or "limping".Religious views
Obama is a Protestant Christian whose religious views developed in his adult life. He wrote in '' The Audacity of Hope'' that he "was not raised in a religious household." He described his mother, raised by non-religious parents, as being detached from religion, yet "in many ways the most spiritually awakened person... I have ever known", and "a lonely witness for secular humanism." He described his father as a "confirmed Atheism, atheist" by the time his parents met, and his stepfather as "a man who saw religion as not particularly useful." Obama explained how, through working with black churches as a In January 2008, Obama told ''Christianity Today'': "I am a Christian, and I am a devout Christian. I believe in the Redeemer (Christianity), redemptive death and resurrection of Jesus Christ. I believe that faith gives me a path to be cleansed of sin and have eternal life." On September 27, 2010, Obama released a statement commenting on his religious views, saying:
Obama met Trinity United Church of Christ pastor Jeremiah Wright in October 1987 and became a member of Trinity in 1992. During Obama's first presidential campaign in May 2008, he resigned from Trinity after Jeremiah Wright controversy, some of Wright's statements were criticized. Since moving to Washington, D.C., in 2009, the Obama family has attended several Protestant churches, including Shiloh Baptist Church (Washington, D.C.), Shiloh Baptist Church and St. John's Episcopal Church, Lafayette Square, St. John's Episcopal Church, as well as Evergreen Chapel at Camp David, but the members of the family do not attend church on a regular basis.
In 2016, he said that he gets inspiration from a few items that remind him "of all the different people I've met along the way", adding: "I carry these around all the time. I'm not that superstitious, so it's not like I think I necessarily have to have them on me at all times." The items, "a whole bowl full", include rosary beads given to him by Pope Francis, a figurine of the Hindu deity Hanuman, a Coptic cross from Ethiopia, a small Buddha statue given by a monk, and a metal poker chip that used to be the lucky charm of a motorcyclist in Iowa.
In January 2008, Obama told ''Christianity Today'': "I am a Christian, and I am a devout Christian. I believe in the Redeemer (Christianity), redemptive death and resurrection of Jesus Christ. I believe that faith gives me a path to be cleansed of sin and have eternal life." On September 27, 2010, Obama released a statement commenting on his religious views, saying:
Obama met Trinity United Church of Christ pastor Jeremiah Wright in October 1987 and became a member of Trinity in 1992. During Obama's first presidential campaign in May 2008, he resigned from Trinity after Jeremiah Wright controversy, some of Wright's statements were criticized. Since moving to Washington, D.C., in 2009, the Obama family has attended several Protestant churches, including Shiloh Baptist Church (Washington, D.C.), Shiloh Baptist Church and St. John's Episcopal Church, Lafayette Square, St. John's Episcopal Church, as well as Evergreen Chapel at Camp David, but the members of the family do not attend church on a regular basis.
In 2016, he said that he gets inspiration from a few items that remind him "of all the different people I've met along the way", adding: "I carry these around all the time. I'm not that superstitious, so it's not like I think I necessarily have to have them on me at all times." The items, "a whole bowl full", include rosary beads given to him by Pope Francis, a figurine of the Hindu deity Hanuman, a Coptic cross from Ethiopia, a small Buddha statue given by a monk, and a metal poker chip that used to be the lucky charm of a motorcyclist in Iowa.
Legal career
Civil Rights attorney
He joined Davis, Miner, Barnhill & Galland, a 13-attorney law firm specializing in civil rights litigation and neighborhood economic development, where he was an associate attorney, associate for three years from 1993 to 1996, then of counsel from 1996 to 2004. In 1994, he was listed as one of the lawyers in ''Buycks-Roberson v. Citibank Fed. Sav. Bank'', 94 C 4094 (N.D. Ill.). This Class-action lawsuit, class action lawsuit was filed in 1994 with Selma Buycks-Roberson as lead plaintiff and alleged that Citibank Federal Savings Bank had engaged in practices forbidden under the Equal Credit Opportunity Act and the Fair Housing Act. The case was settled out of court. Final judgment was issued on May 13, 1998, with Citibank Federal Savings Bank agreeing to pay attorney fees. From 1994 to 2002, Obama served on the boards of directors of the Woods Fund of Chicago—which in 1985 had been the first foundation to fund the Developing Communities Project—and of the Joyce Foundation. He served on the board of directors of the Chicago Annenberg Challenge from 1995 to 2002, as founding president and chairman of the board of directors from 1995 to 1999. Obama's law license became inactive in 2007.Legislative career
Illinois Senate (1997–2004)
 Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding Democratic State Senator Alice Palmer (politician), Alice Palmer from Illinois's 13th District, which, at that time, spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park–Kenwood, Chicago, Kenwood south to South Shore, Chicago, South Shore and west to Chicago Lawn, Chicago, Chicago Lawn. Once elected, Obama gained bipartisan support for legislation that reformed ethics and health care laws. He sponsored a law that increased tax credits for low-income workers, negotiated welfare reform, and promoted increased subsidies for childcare. In 2001, as co-chairman of the bipartisan Joint Committee on Administrative Rules, Obama supported Republican Governor Ryan's payday loan regulations and Predatory lending, predatory mortgage lending regulations aimed at averting home foreclosures.
He was reelected to the Illinois Senate in 1998, defeating Republican Yesse Yehudah in the general election, and was re-elected again in 2002. In 2000, he lost a 2000 Illinois's 1st congressional district election, Democratic primary race for Illinois's 1st congressional district in the United States House of Representatives to four-term incumbent Bobby Rush by a margin of two to one.
In January 2003, Obama became chairman of the Illinois Senate's Health and Human Services Committee when Democrats, after a decade in the minority, regained a majority. He sponsored and led unanimous, bipartisan passage of legislation to monitor racial profiling by requiring police to record the race of drivers they detained, and legislation making Illinois the first state to mandate videotaping of homicide interrogations. During his 2004 general election campaign for the U.S. Senate, police representatives credited Obama for his active engagement with police organizations in enacting Capital punishment in the United States, death penalty reforms. Obama resigned from the Illinois Senate in November 2004 following his election to the U.S. Senate.
Obama was elected to the Illinois Senate in 1996, succeeding Democratic State Senator Alice Palmer (politician), Alice Palmer from Illinois's 13th District, which, at that time, spanned Chicago South Side neighborhoods from Hyde Park, Chicago, Hyde Park–Kenwood, Chicago, Kenwood south to South Shore, Chicago, South Shore and west to Chicago Lawn, Chicago, Chicago Lawn. Once elected, Obama gained bipartisan support for legislation that reformed ethics and health care laws. He sponsored a law that increased tax credits for low-income workers, negotiated welfare reform, and promoted increased subsidies for childcare. In 2001, as co-chairman of the bipartisan Joint Committee on Administrative Rules, Obama supported Republican Governor Ryan's payday loan regulations and Predatory lending, predatory mortgage lending regulations aimed at averting home foreclosures.
He was reelected to the Illinois Senate in 1998, defeating Republican Yesse Yehudah in the general election, and was re-elected again in 2002. In 2000, he lost a 2000 Illinois's 1st congressional district election, Democratic primary race for Illinois's 1st congressional district in the United States House of Representatives to four-term incumbent Bobby Rush by a margin of two to one.
In January 2003, Obama became chairman of the Illinois Senate's Health and Human Services Committee when Democrats, after a decade in the minority, regained a majority. He sponsored and led unanimous, bipartisan passage of legislation to monitor racial profiling by requiring police to record the race of drivers they detained, and legislation making Illinois the first state to mandate videotaping of homicide interrogations. During his 2004 general election campaign for the U.S. Senate, police representatives credited Obama for his active engagement with police organizations in enacting Capital punishment in the United States, death penalty reforms. Obama resigned from the Illinois Senate in November 2004 following his election to the U.S. Senate.
2004 U.S. Senate campaign
U.S. Senate (2005–2008)
 Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005, becoming the only Senate member of the Congressional Black Caucus. He introduced two initiatives that bore his name: Lugar–Obama, which expanded the Nunn–Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction concept to conventional weapons; and the Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006, which authorized the establishment of USAspending.gov, a web search engine on federal spending. On June 3, 2008, Senator Obama—along with Senators Tom Carper, Tom Coburn, and John McCain—introduced follow-up legislation: Strengthening Transparency and Accountability in Federal Spending Act of 2008. He also Sponsor (legislative), cosponsored the Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act.
In December 2006, President Bush signed into law the Democratic Republic of the Congo Relief, Security, and Democracy Promotion Act, marking the first federal legislation to be enacted with Obama as its primary sponsor. In January 2007, Obama and Senator Feingold introduced a corporate jet provision to the Honest Leadership and Open Government Act, which was signed into law in September 2007.
Obama was sworn in as a senator on January 3, 2005, becoming the only Senate member of the Congressional Black Caucus. He introduced two initiatives that bore his name: Lugar–Obama, which expanded the Nunn–Lugar Cooperative Threat Reduction concept to conventional weapons; and the Federal Funding Accountability and Transparency Act of 2006, which authorized the establishment of USAspending.gov, a web search engine on federal spending. On June 3, 2008, Senator Obama—along with Senators Tom Carper, Tom Coburn, and John McCain—introduced follow-up legislation: Strengthening Transparency and Accountability in Federal Spending Act of 2008. He also Sponsor (legislative), cosponsored the Secure America and Orderly Immigration Act.
In December 2006, President Bush signed into law the Democratic Republic of the Congo Relief, Security, and Democracy Promotion Act, marking the first federal legislation to be enacted with Obama as its primary sponsor. In January 2007, Obama and Senator Feingold introduced a corporate jet provision to the Honest Leadership and Open Government Act, which was signed into law in September 2007.
 Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act to add safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges. This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008. He sponsored the Disinvestment from Iran, Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which was never enacted but later incorporated in the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism. Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the State Children's Health Insurance Program, providing one year of job protection for family members caring for soldiers with combat-related injuries.
Obama held assignments on the Senate Committees for United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations, Foreign Relations, United States Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works, Environment and Public Works and United States Senate Committee on Veterans' Affairs, Veterans' Affairs through December 2006. In January 2007, he left the Environment and Public Works committee and took additional assignments with United States Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and United States Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs. He also became Chairman of the Senate's subcommittee on United States Senate Foreign Relations Subcommittee on Europe and Regional Security Cooperation, European Affairs. As a member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, Obama made official trips to Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and Africa. He met with Mahmoud Abbas before Abbas became President of the Palestinian National Authority, and gave a speech at the University of Nairobi in which he condemned corruption within the Kenyan government.
Obama resignation from the United States Senate, resigned his Senate seat on November 16, 2008, to focus on his transition period for the presidency.
Later in 2007, Obama sponsored an amendment to the Defense Authorization Act to add safeguards for personality-disorder military discharges. This amendment passed the full Senate in the spring of 2008. He sponsored the Disinvestment from Iran, Iran Sanctions Enabling Act supporting divestment of state pension funds from Iran's oil and gas industry, which was never enacted but later incorporated in the Comprehensive Iran Sanctions, Accountability, and Divestment Act of 2010; and co-sponsored legislation to reduce risks of nuclear terrorism. Obama also sponsored a Senate amendment to the State Children's Health Insurance Program, providing one year of job protection for family members caring for soldiers with combat-related injuries.
Obama held assignments on the Senate Committees for United States Senate Committee on Foreign Relations, Foreign Relations, United States Senate Committee on Environment and Public Works, Environment and Public Works and United States Senate Committee on Veterans' Affairs, Veterans' Affairs through December 2006. In January 2007, he left the Environment and Public Works committee and took additional assignments with United States Senate Committee on Health, Education, Labor and Pensions, Health, Education, Labor and Pensions and United States Senate Committee on Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs, Homeland Security and Governmental Affairs. He also became Chairman of the Senate's subcommittee on United States Senate Foreign Relations Subcommittee on Europe and Regional Security Cooperation, European Affairs. As a member of the Senate Foreign Relations Committee, Obama made official trips to Eastern Europe, the Middle East, Central Asia and Africa. He met with Mahmoud Abbas before Abbas became President of the Palestinian National Authority, and gave a speech at the University of Nairobi in which he condemned corruption within the Kenyan government.
Obama resignation from the United States Senate, resigned his Senate seat on November 16, 2008, to focus on his transition period for the presidency.
Presidential campaigns
2008
 On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the United States in front of the Old State Capitol State Historic Site (Illinois), Old State Capitol building in Springfield, Illinois. The choice of the announcement site was viewed as symbolic, as it was also where Abraham Lincoln delivered his Lincoln's House Divided Speech, "House Divided" speech in 1858. Obama emphasized issues of rapidly ending the Iraq War, increasing Energy policy of the United States, energy independence, and Health care reform in the United States, reforming the health care system.
Numerous candidates entered the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries, Democratic Party presidential primaries. The field narrowed to Obama and Senator
On February 10, 2007, Obama announced his candidacy for President of the United States in front of the Old State Capitol State Historic Site (Illinois), Old State Capitol building in Springfield, Illinois. The choice of the announcement site was viewed as symbolic, as it was also where Abraham Lincoln delivered his Lincoln's House Divided Speech, "House Divided" speech in 1858. Obama emphasized issues of rapidly ending the Iraq War, increasing Energy policy of the United States, energy independence, and Health care reform in the United States, reforming the health care system.
Numerous candidates entered the 2008 Democratic Party presidential primaries, Democratic Party presidential primaries. The field narrowed to Obama and Senator 2012
Presidency (2009–2017)

First 100 days
 The First inauguration of Barack Obama, inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th president took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office, Obama issued
The First inauguration of Barack Obama, inauguration of Barack Obama as the 44th president took place on January 20, 2009. In his first few days in office, Obama issued Domestic policy
The first bill signed into law by Obama was the Lilly Ledbetter Fair Pay Act of 2009, relaxing the statute of limitations for equal-pay lawsuits. Five days later, he signed the reauthorization of the State Children's Health Insurance Program to cover an additional four million uninsured children. In March 2009, Obama reversed a Bush-era policy that had limited funding of embryonic stem cell research and pledged to develop "strict guidelines" on the research. Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his presidency. He nominated
Obama appointed two women to serve on the Supreme Court in the first two years of his presidency. He nominated  On January 16, 2013, one month after the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting, Obama signed 23 executive orders and outlined a series of sweeping proposals regarding Gun politics in the United States, gun control. He urged Congress to reintroduce an Federal Assault Weapons Ban, expired ban on military-style assault weapons, such as those used in several recent mass shootings, impose limits on ammunition magazines to 10 rounds, introduce background checks on all gun sales, pass a ban on possession and sale of armor-piercing bullets, introduce harsher penalties for gun-traffickers, especially unlicensed dealers who buy arms for criminals and approving the appointment of the head of the federal Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives for the first time since 2006. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers. In a 2016 editorial in ''The New York Times'', Obama compared the struggle for what he termed "common-sense gun reform" to women's suffrage and other civil rights movements in American history. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers.
In 2011, Obama signed a four-year renewal of the Patriot Act. Following the Global surveillance disclosures (2013–present), 2013 global surveillance disclosures by whistleblower Edward Snowden, Obama condemned the leak as unpatriotic, but called for increased restrictions on the National Security Agency (NSA) to address violations of privacy. Obama continued and expanded surveillance programs set up by George W. Bush, while implementing some reforms. He supported legislation that would have limited the NSA's ability to collect phone records in bulk under a single program and supported bringing more transparency to the United States Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court, Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC).
On January 16, 2013, one month after the Sandy Hook Elementary School shooting, Obama signed 23 executive orders and outlined a series of sweeping proposals regarding Gun politics in the United States, gun control. He urged Congress to reintroduce an Federal Assault Weapons Ban, expired ban on military-style assault weapons, such as those used in several recent mass shootings, impose limits on ammunition magazines to 10 rounds, introduce background checks on all gun sales, pass a ban on possession and sale of armor-piercing bullets, introduce harsher penalties for gun-traffickers, especially unlicensed dealers who buy arms for criminals and approving the appointment of the head of the federal Bureau of Alcohol, Tobacco, Firearms and Explosives for the first time since 2006. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers. In a 2016 editorial in ''The New York Times'', Obama compared the struggle for what he termed "common-sense gun reform" to women's suffrage and other civil rights movements in American history. On January 5, 2016, Obama announced new executive actions extending background check requirements to more gun sellers.
In 2011, Obama signed a four-year renewal of the Patriot Act. Following the Global surveillance disclosures (2013–present), 2013 global surveillance disclosures by whistleblower Edward Snowden, Obama condemned the leak as unpatriotic, but called for increased restrictions on the National Security Agency (NSA) to address violations of privacy. Obama continued and expanded surveillance programs set up by George W. Bush, while implementing some reforms. He supported legislation that would have limited the NSA's ability to collect phone records in bulk under a single program and supported bringing more transparency to the United States Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court, Foreign Intelligence Surveillance Court (FISC).
Racial issues
In his speeches as president, Obama did not make more overt references to race relations than his predecessors, but according to one study, he implemented stronger policy action on behalf of African-Americans than any president since the Nixon era. Following Obama's election, many pondered the existence of a "Post-racial America, postracial America." However, lingering racial tensions quickly became apparent, and many African-Americans expressed outrage over what they saw as an intense racial animosity directed at Obama. The Trial of George Zimmerman, acquittal of George Zimmerman following the killing of Trayvon Martin sparked national outrage, leading to Obama giving a speech in which he noted that "Trayvon Martin could have been me 35 years ago." The shooting of Shooting of Michael Brown, Michael Brown in Ferguson, Missouri Ferguson unrest, sparked a wave of protests. These and other events led to the birth of the Black Lives Matter movement, which campaigns against violence and Institutional racism, systemic racism toward black people. Though Obama entered office reluctant to talk about race, by 2014 he began openly discussing the disadvantages faced by many members of minority groups. Several incidents during Obama's presidency generated disapproval from the African-American community and/or with law enforcement, and Obama sought to build trust between law enforcement officials and civil rights activists, with mixed results. Some in law enforcement criticized Obama's condemnation of racial bias after incidents in which police action led to the death of African-American men, while some racial justice activists criticized Obama's expressions of empathy for the police. In a March 2016 Gallup poll, nearly one third of Americans said they worried "a great deal" about race relations, a higher figure than in any previous Gallup poll since 2001.LGBT rights and same-sex marriage
On October 8, 2009, Obama signed the Matthew Shepard and James Byrd Jr. Hate Crimes Prevention Act, a measure that expanded the Hate crime laws in the United States#Federal prosecution of hate crimes, 1969 United States federal hate-crime law to include crimes motivated by a victim's actual or perceived gender, sexual orientation, gender identity, or disability. On October 30, 2009, Obama lifted the ban on travel to the United States by those infected with HIV. The lifting of the ban was celebrated by Immigration Equality. On December 22, 2010, Obama signed the Don't Ask, Don't Tell Repeal Act of 2010, which fulfilled a promise made in the 2008 presidential campaign to end the don't ask, don't tell policy of 1993 that had prevented gay and lesbian people from serving openly in the United States Armed Forces. In 2016, the Pentagon ended the policy that barred Transgender personnel in the United States military, transgender people from serving openly in the military. As a candidate for the Illinois state senate in 1996, Obama stated he favored legalizing Same-sex marriage in the United States, same-sex marriage. During his Senate run in 2004, he said he supported civil unions and domestic partnerships for same-sex partners but opposed same-sex marriages. In 2008, he reaffirmed this position by stating "I believe marriage is between a man and a woman. I am not in favor of gay marriage." On May 9, 2012, shortly after the official launch of his campaign for re-election as president, Obama said his views had evolved, and he publicly affirmed his personal support for the legalization of same-sex marriage, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to do so. During his second Second inauguration of Barack Obama, inaugural address on January 21, 2013, Obama became the first U.S. president in office to call for full equality for gay Americans, and the first to mention LGBT rights in the United States, gay rights or the word "gay" in an inaugural address. In 2013, the Obama administration filed briefs that urged the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court to rule in favor of same-sex couples in the cases of ''Hollingsworth v. Perry'' (regarding Same-sex marriage in the United States, same-sex marriage) and ''United States v. Windsor'' (regarding the Defense of Marriage Act).
As a candidate for the Illinois state senate in 1996, Obama stated he favored legalizing Same-sex marriage in the United States, same-sex marriage. During his Senate run in 2004, he said he supported civil unions and domestic partnerships for same-sex partners but opposed same-sex marriages. In 2008, he reaffirmed this position by stating "I believe marriage is between a man and a woman. I am not in favor of gay marriage." On May 9, 2012, shortly after the official launch of his campaign for re-election as president, Obama said his views had evolved, and he publicly affirmed his personal support for the legalization of same-sex marriage, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to do so. During his second Second inauguration of Barack Obama, inaugural address on January 21, 2013, Obama became the first U.S. president in office to call for full equality for gay Americans, and the first to mention LGBT rights in the United States, gay rights or the word "gay" in an inaugural address. In 2013, the Obama administration filed briefs that urged the Supreme Court of the United States, Supreme Court to rule in favor of same-sex couples in the cases of ''Hollingsworth v. Perry'' (regarding Same-sex marriage in the United States, same-sex marriage) and ''United States v. Windsor'' (regarding the Defense of Marriage Act).
Economic policy
On February 17, 2009, Obama signed the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, a $787billion (equivalent to $ billion in ) stimulus (economics), economic stimulus package aimed at helping the economy recover from the Great Recession, deepening worldwide recession. The act includes increased federal spending for health care, infrastructure, education, various tax breaks and tax incentive, incentives, and direct assistance to individuals. In March 2009, Obama's Treasury Secretary, Timothy Geithner, took further steps to manage the financial crisis of 2007–08, financial crisis, including introducing the Public–Private Investment Program for Legacy Assets, which contains provisions for buying up to $2trillion in depreciated real estate assets. Obama intervened in the automotive industry crisis of 2008–10, troubled automotive industry in March 2009, renewing loans for General Motors (GM) and Chrysler to continue operations while reorganizing. Over the following months the White House set terms for both firms' bankruptcies, including the Chrysler Chapter 11 reorganization, sale of Chrysler to Italian automaker Fiat and a General Motors Chapter 11 reorganization, reorganization of GM giving the U.S. government a temporary 60 percent equity stake in the company. In June 2009, dissatisfied with the pace of economic stimulus, Obama called on his cabinet to accelerate the investment. He signed into law the Car Allowance Rebate System, known colloquially as "Cash for Clunkers", which temporarily boosted the economy.
The Bush and Obama administrations authorized spending and loan guarantees from the Federal Reserve System, Federal Reserve and the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury. These guarantees totaled about $11.5trillion, but only $3trillion had been spent by the end of November 2009. On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Obama signed the bipartisan Budget Control Act of 2011. The legislation enforced limits on discretionary spending until 2021, established a procedure to increase the debt limit, created a Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and established automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee did not achieve such savings. By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent a Federal government of the United States, U.S. government Default (finance), default on its obligations.
The unemployment rate rose in 2009, reaching a peak in October at 10.0 percent and averaging 10.0 percent in the fourth quarter. Following a decrease to 9.7 percent in the first quarter of 2010, the unemployment rate fell to 9.6 percent in the second quarter, where it remained for the rest of the year. Between February and December 2010, employment rose by 0.8 percent, which was less than the average of 1.9 percent experienced during comparable periods in the past four employment recoveries. By November 2012, the unemployment rate fell to 7.7 percent, decreasing to 6.7 percent in the last month of 2013. During 2014, the unemployment rate continued to decline, falling to 6.3 percent in the first quarter. GDP growth returned in the third quarter of 2009, expanding at a rate of 1.6 percent, followed by a 5.0 percent increase in the fourth quarter. Growth continued in 2010, posting an increase of 3.7 percent in the first quarter, with lesser gains throughout the rest of the year. In July 2010, the Federal Reserve System, Federal Reserve noted that economic activity continued to increase, but its pace had slowed, and chairman Ben Bernanke said the economic outlook was "unusually uncertain." Overall, the economy expanded at a rate of 2.9 percent in 2010.
Obama intervened in the automotive industry crisis of 2008–10, troubled automotive industry in March 2009, renewing loans for General Motors (GM) and Chrysler to continue operations while reorganizing. Over the following months the White House set terms for both firms' bankruptcies, including the Chrysler Chapter 11 reorganization, sale of Chrysler to Italian automaker Fiat and a General Motors Chapter 11 reorganization, reorganization of GM giving the U.S. government a temporary 60 percent equity stake in the company. In June 2009, dissatisfied with the pace of economic stimulus, Obama called on his cabinet to accelerate the investment. He signed into law the Car Allowance Rebate System, known colloquially as "Cash for Clunkers", which temporarily boosted the economy.
The Bush and Obama administrations authorized spending and loan guarantees from the Federal Reserve System, Federal Reserve and the United States Department of the Treasury, Department of the Treasury. These guarantees totaled about $11.5trillion, but only $3trillion had been spent by the end of November 2009. On August 2, 2011, after a lengthy congressional debate over whether to raise the nation's debt limit, Obama signed the bipartisan Budget Control Act of 2011. The legislation enforced limits on discretionary spending until 2021, established a procedure to increase the debt limit, created a Congressional Joint Select Committee on Deficit Reduction to propose further deficit reduction with a stated goal of achieving at least $1.5trillion in budgetary savings over 10 years, and established automatic procedures for reducing spending by as much as $1.2trillion if legislation originating with the new joint select committee did not achieve such savings. By passing the legislation, Congress was able to prevent a Federal government of the United States, U.S. government Default (finance), default on its obligations.
The unemployment rate rose in 2009, reaching a peak in October at 10.0 percent and averaging 10.0 percent in the fourth quarter. Following a decrease to 9.7 percent in the first quarter of 2010, the unemployment rate fell to 9.6 percent in the second quarter, where it remained for the rest of the year. Between February and December 2010, employment rose by 0.8 percent, which was less than the average of 1.9 percent experienced during comparable periods in the past four employment recoveries. By November 2012, the unemployment rate fell to 7.7 percent, decreasing to 6.7 percent in the last month of 2013. During 2014, the unemployment rate continued to decline, falling to 6.3 percent in the first quarter. GDP growth returned in the third quarter of 2009, expanding at a rate of 1.6 percent, followed by a 5.0 percent increase in the fourth quarter. Growth continued in 2010, posting an increase of 3.7 percent in the first quarter, with lesser gains throughout the rest of the year. In July 2010, the Federal Reserve System, Federal Reserve noted that economic activity continued to increase, but its pace had slowed, and chairman Ben Bernanke said the economic outlook was "unusually uncertain." Overall, the economy expanded at a rate of 2.9 percent in 2010.
Environmental policy
 On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore drilling rig at the Macondo Prospect in the Gulf of Mexico, causing a Deepwater Horizon oil spill, major sustained oil leak. Obama visited the Gulf, announced a federal investigation, and formed a bipartisan commission to recommend new safety standards, after a review by United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar and concurrent Congressional hearings. He then announced a six-month moratorium on new deepwater drilling permits and leases, pending regulatory review. As multiple efforts by BP failed, some in the media and public expressed confusion and criticism over various aspects of the incident, and stated a desire for more involvement by Obama and the federal government. Prior to the oil spill, on March 31, 2010, Obama ended a ban on oil and gas drilling along the majority of the East Coast of the United States and along the coast of Arctic Alaska, northern Alaska in an effort to win support for an energy and climate bill and to reduce foreign imports of oil and gas.
In July 2013, Obama expressed reservations and said he "would reject the Keystone XL pipeline if it increased carbon pollution [or] greenhouse emissions." On February 24, 2015, Obama vetoed a bill that would have authorized the pipeline. It was the third veto of Obama's presidency and his first major veto.
In December 2016, Obama permanently banned new offshore oil and gas drilling in most United States-owned waters in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Arctic Oceans using the 1953 Outer Continental Shelf Act.
Obama emphasized the Conservation movement, conservation of federal lands during his term in office. He used his power under the Antiquities Act to create 25 new National monument (United States), national monuments during his presidency and expand four others, protecting a total of of federal lands and waters, more than any other U.S. president.
On April 20, 2010, an explosion destroyed an offshore drilling rig at the Macondo Prospect in the Gulf of Mexico, causing a Deepwater Horizon oil spill, major sustained oil leak. Obama visited the Gulf, announced a federal investigation, and formed a bipartisan commission to recommend new safety standards, after a review by United States Secretary of the Interior, Secretary of the Interior Ken Salazar and concurrent Congressional hearings. He then announced a six-month moratorium on new deepwater drilling permits and leases, pending regulatory review. As multiple efforts by BP failed, some in the media and public expressed confusion and criticism over various aspects of the incident, and stated a desire for more involvement by Obama and the federal government. Prior to the oil spill, on March 31, 2010, Obama ended a ban on oil and gas drilling along the majority of the East Coast of the United States and along the coast of Arctic Alaska, northern Alaska in an effort to win support for an energy and climate bill and to reduce foreign imports of oil and gas.
In July 2013, Obama expressed reservations and said he "would reject the Keystone XL pipeline if it increased carbon pollution [or] greenhouse emissions." On February 24, 2015, Obama vetoed a bill that would have authorized the pipeline. It was the third veto of Obama's presidency and his first major veto.
In December 2016, Obama permanently banned new offshore oil and gas drilling in most United States-owned waters in the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic and Arctic Oceans using the 1953 Outer Continental Shelf Act.
Obama emphasized the Conservation movement, conservation of federal lands during his term in office. He used his power under the Antiquities Act to create 25 new National monument (United States), national monuments during his presidency and expand four others, protecting a total of of federal lands and waters, more than any other U.S. president.
Health care reform
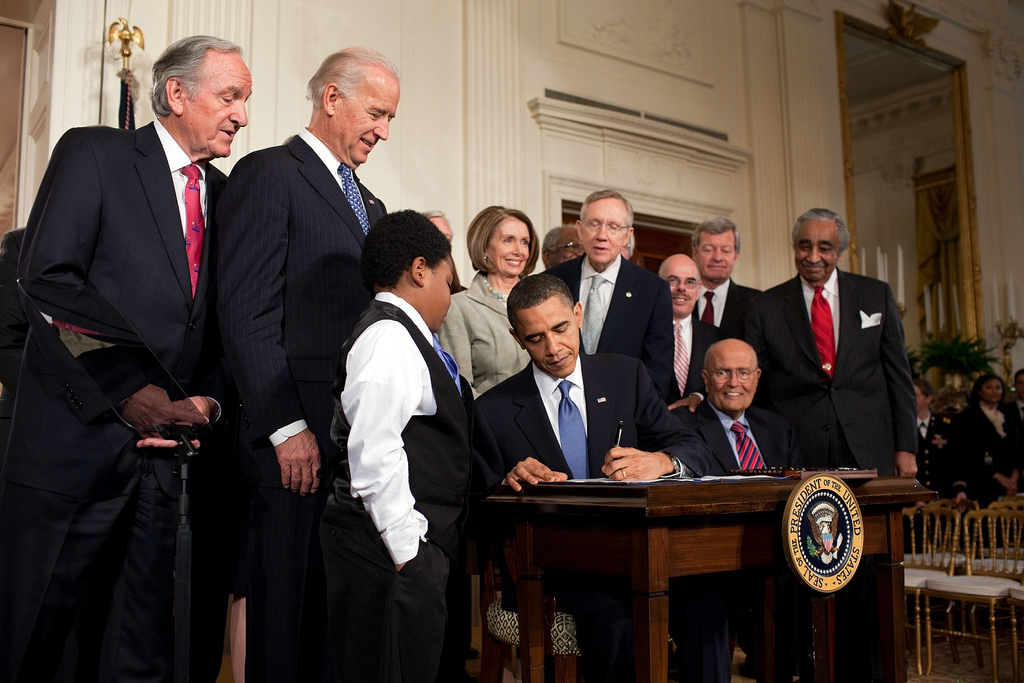 Obama called for United States Congress, Congress to pass legislation reforming health care in the United States, a key campaign promise and a top legislative goal. He proposed an expansion of health insurance coverage to cover the uninsured, cap premium increases, and allow people to retain their coverage when they leave or change jobs. His proposal was to spend $900billion over ten years and include a government insurance plan, also known as the public health insurance option, public option, to compete with the corporate insurance sector as a main component to lowering costs and improving quality of health care. It would also make it illegal for insurers to drop sick people or deny them coverage for pre-existing conditions, and require every American to carry health coverage. The plan also includes medical spending cuts and taxes on insurance companies that offer expensive plans.
Obama called for United States Congress, Congress to pass legislation reforming health care in the United States, a key campaign promise and a top legislative goal. He proposed an expansion of health insurance coverage to cover the uninsured, cap premium increases, and allow people to retain their coverage when they leave or change jobs. His proposal was to spend $900billion over ten years and include a government insurance plan, also known as the public health insurance option, public option, to compete with the corporate insurance sector as a main component to lowering costs and improving quality of health care. It would also make it illegal for insurers to drop sick people or deny them coverage for pre-existing conditions, and require every American to carry health coverage. The plan also includes medical spending cuts and taxes on insurance companies that offer expensive plans.
 On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009. After public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered Barack Obama speech to joint session of Congress, September 2009, a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals. In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on using federal funds for stem cell research.
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House. On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39. On March 21, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212. Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.
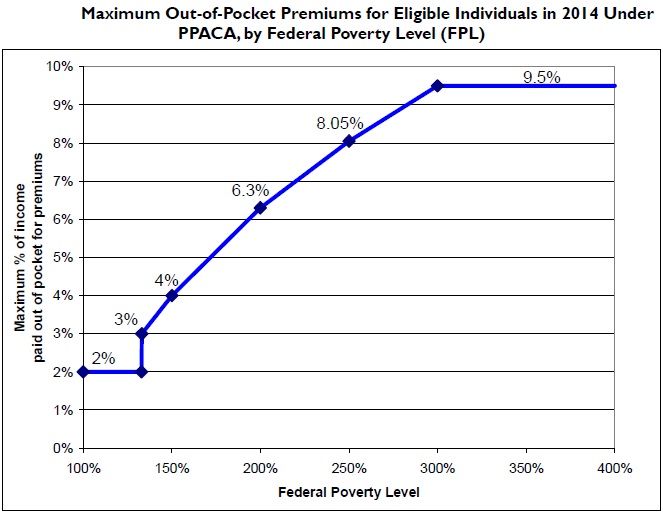
The ACA includes Provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percentof the federal poverty level (FPL) starting in 2014, subsidizing insurance premiums for people making up to 400 percentof the FPL ($88,000 for family of four in 2010) so their maximum "out-of-pocket" payment for annual premiums will be from 2 percent to 9.5 percent of income, providing incentives for businesses to provide health care benefits, prohibiting denial of coverage and denial of claims based on pre-existing conditions, establishing health insurance exchanges, prohibiting annual coverage caps, and support for medical research. According to White House and CBO figures, the maximum share of income that enrollees would have to pay would vary depending on their income relative to the federal poverty level.
On July 14, 2009, House Democratic leaders introduced a 1,017-page plan for overhauling the U.S. health care system, which Obama wanted Congress to approve by the end of 2009. After public debate during the Congressional summer recess of 2009, Obama delivered Barack Obama speech to joint session of Congress, September 2009, a speech to a joint session of Congress on September 9 where he addressed concerns over the proposals. In March 2009, Obama lifted a ban on using federal funds for stem cell research.
On November 7, 2009, a health care bill featuring the public option was passed in the House. On December 24, 2009, the Senate passed its own bill—without a public option—on a party-line vote of 60–39. On March 21, 2010, the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act (ACA) passed by the Senate in December was passed in the House by a vote of 219 to 212. Obama signed the bill into law on March 23, 2010.
The ACA includes Provisions of the Patient Protection and Affordable Care Act, health-related provisions, most of which took effect in 2014, including expanding Medicaid eligibility for people making up to 133 percentof the federal poverty level (FPL) starting in 2014, subsidizing insurance premiums for people making up to 400 percentof the FPL ($88,000 for family of four in 2010) so their maximum "out-of-pocket" payment for annual premiums will be from 2 percent to 9.5 percent of income, providing incentives for businesses to provide health care benefits, prohibiting denial of coverage and denial of claims based on pre-existing conditions, establishing health insurance exchanges, prohibiting annual coverage caps, and support for medical research. According to White House and CBO figures, the maximum share of income that enrollees would have to pay would vary depending on their income relative to the federal poverty level.
 The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income tax bracket, brackets, taxes on indoor tanning, cuts to the Medicare Advantage program in favor of traditional Medicare, and fees on medical devices and pharmaceutical companies; there is also a tax penalty for those who do not obtain health insurance, unless they are exempt due to low income or other reasons. In March 2010, the CBO estimated that the net effect of both laws will be a reduction in the federal deficit by $143billion over the first decade.
The law faced several legal challenges, primarily based on the argument that an individual mandate requiring Americans to buy health insurance was unconstitutional. On June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court ruled by a 5–4 vote in ''National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius'' that the mandate was constitutional under the U.S. Congress's taxing authority. In ''Burwell v. Hobby Lobby Stores, Inc., Burwell v. Hobby Lobby'' the Court ruled that "closely-held" for-profit corporations could be exempt on religious grounds under the Religious Freedom Restoration Act from regulations adopted under the ACA that would have required them to pay for insurance that covered certain contraceptives. In June 2015, the Court ruled 6–3 in ''King v. Burwell'' that subsidies to help individuals and families purchase health insurance were authorized for those doing so on both the federal exchange and state exchanges, not only those purchasing plans "established by the State", as the statute reads.
The costs of these provisions are offset by taxes, fees, and cost-saving measures, such as new Medicare taxes for those in high-income tax bracket, brackets, taxes on indoor tanning, cuts to the Medicare Advantage program in favor of traditional Medicare, and fees on medical devices and pharmaceutical companies; there is also a tax penalty for those who do not obtain health insurance, unless they are exempt due to low income or other reasons. In March 2010, the CBO estimated that the net effect of both laws will be a reduction in the federal deficit by $143billion over the first decade.
The law faced several legal challenges, primarily based on the argument that an individual mandate requiring Americans to buy health insurance was unconstitutional. On June 28, 2012, the Supreme Court ruled by a 5–4 vote in ''National Federation of Independent Business v. Sebelius'' that the mandate was constitutional under the U.S. Congress's taxing authority. In ''Burwell v. Hobby Lobby Stores, Inc., Burwell v. Hobby Lobby'' the Court ruled that "closely-held" for-profit corporations could be exempt on religious grounds under the Religious Freedom Restoration Act from regulations adopted under the ACA that would have required them to pay for insurance that covered certain contraceptives. In June 2015, the Court ruled 6–3 in ''King v. Burwell'' that subsidies to help individuals and families purchase health insurance were authorized for those doing so on both the federal exchange and state exchanges, not only those purchasing plans "established by the State", as the statute reads.
Foreign policy
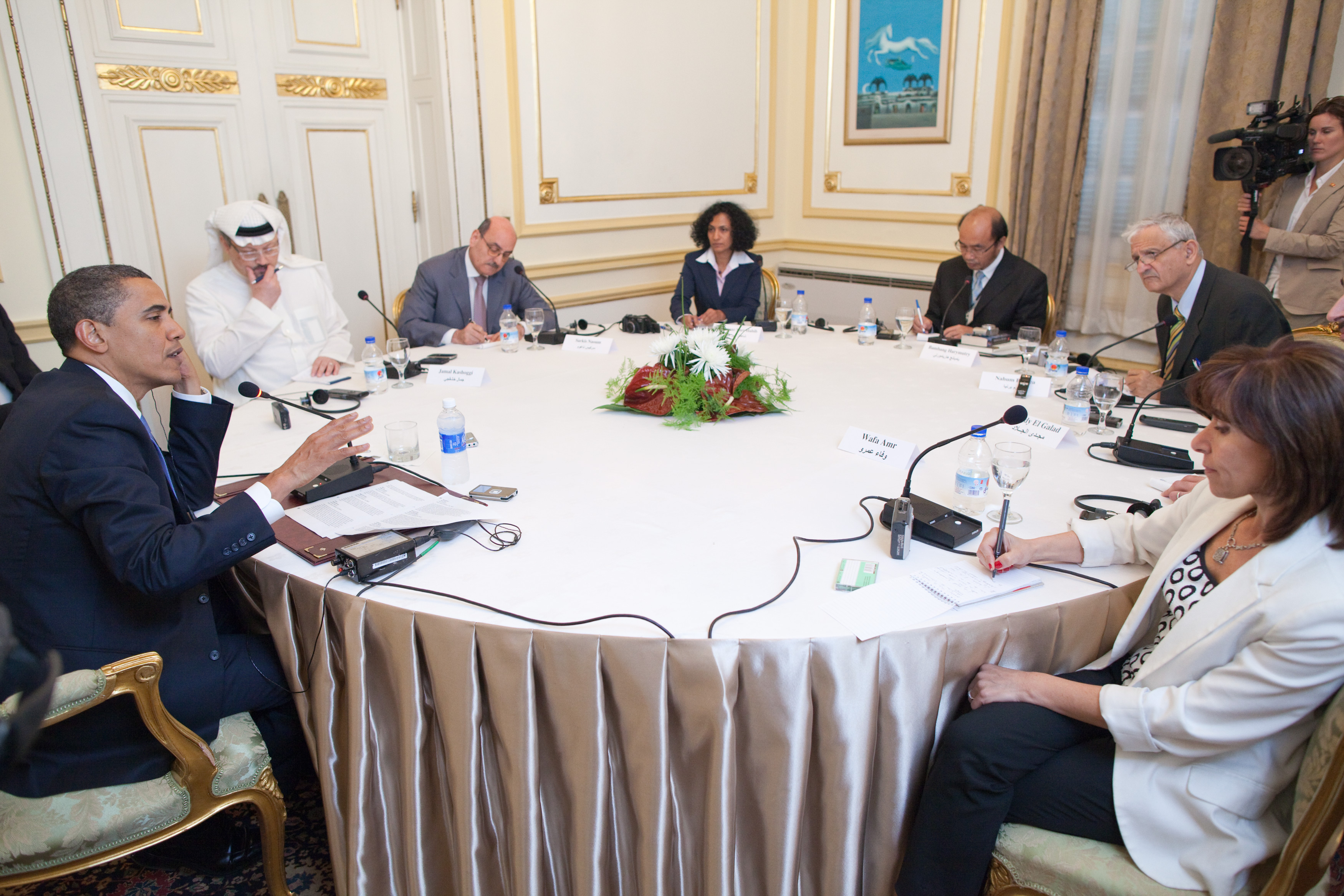 In February and March 2009, Vice President Joe Biden and United States Secretary of State, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and "Russian reset, reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration. Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab satellite TV network, Al Arabiya. On March 19, Obama continued his outreach to the Muslim world, releasing a New Year's video message to the people and government of Iran. On June 4, 2009, Obama delivered a speech at Cairo University in Egypt calling for "A New Beginning (speech), A New Beginning" in relations between the Islamic world and the United States and promoting Middle East peace. On June 26, 2009, Obama condemned the Iranian government's actions towards protesters following 2009 Iranian presidential election, Iran's 2009 presidential election.
In 2011, Obama ordered a drone strike in Yemen which targeted and killed Anwar al-Awlaki, an American imam suspected of being a leading Al-Qaeda organizer. al-Awlaki became the first Citizenship of the United States, U.S. citizen to be targeted and killed by a Drone strike, U.S. drone strike. The Department of Justice released a memo justifying al-Awlaki's death as a lawful act of war, while civil liberties advocates described it as a violation of al-Awlaki's constitutional right to due process. The killing led to significant controversy. His Abdulrahman al-Awlaki, teenage son and Death of Nawar al-Awlaki, young daughter, also Americans, were later killed in separate Raid on Yakla, US military actions, although they were not targeted specifically.
In February and March 2009, Vice President Joe Biden and United States Secretary of State, Secretary of State Hillary Clinton made separate overseas trips to announce a "new era" in U.S. foreign relations with Russia and Europe, using the terms "break" and "Russian reset, reset" to signal major changes from the policies of the preceding administration. Obama attempted to reach out to Arab leaders by granting his first interview to an Arab satellite TV network, Al Arabiya. On March 19, Obama continued his outreach to the Muslim world, releasing a New Year's video message to the people and government of Iran. On June 4, 2009, Obama delivered a speech at Cairo University in Egypt calling for "A New Beginning (speech), A New Beginning" in relations between the Islamic world and the United States and promoting Middle East peace. On June 26, 2009, Obama condemned the Iranian government's actions towards protesters following 2009 Iranian presidential election, Iran's 2009 presidential election.
In 2011, Obama ordered a drone strike in Yemen which targeted and killed Anwar al-Awlaki, an American imam suspected of being a leading Al-Qaeda organizer. al-Awlaki became the first Citizenship of the United States, U.S. citizen to be targeted and killed by a Drone strike, U.S. drone strike. The Department of Justice released a memo justifying al-Awlaki's death as a lawful act of war, while civil liberties advocates described it as a violation of al-Awlaki's constitutional right to due process. The killing led to significant controversy. His Abdulrahman al-Awlaki, teenage son and Death of Nawar al-Awlaki, young daughter, also Americans, were later killed in separate Raid on Yakla, US military actions, although they were not targeted specifically.
 In March 2015, Obama declared that he had authorized U.S. forces to provide logistical and intelligence support to the Saudis in their Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen, military intervention in Yemen, establishing a "Joint Planning Cell" with Saudi Arabia. In 2016, the Obama administration proposed a series of Saudi Arabia–United States relations, arms deals with Saudi Arabia worth $115billion. Obama halted the sale of guided munition technology to Saudi Arabia after Saudi warplanes 2016 Sana'a funeral airstrike, targeted a funeral in Yemen's capital Sanaa, killing more than 140 people.
In March 2015, Obama declared that he had authorized U.S. forces to provide logistical and intelligence support to the Saudis in their Saudi Arabian-led intervention in Yemen, military intervention in Yemen, establishing a "Joint Planning Cell" with Saudi Arabia. In 2016, the Obama administration proposed a series of Saudi Arabia–United States relations, arms deals with Saudi Arabia worth $115billion. Obama halted the sale of guided munition technology to Saudi Arabia after Saudi warplanes 2016 Sana'a funeral airstrike, targeted a funeral in Yemen's capital Sanaa, killing more than 140 people.
War in Iraq
On February 27, 2009, Obama announced that combat operations in Iraq would end within 18 months. The Obama administration scheduled the withdrawal of combat troops to be completed by August 2010, decreasing troop's levels from 142,000 while leaving a transitional force of about 50,000 in Iraq until the end of 2011. On August 19, 2010, the last U.S. combat brigade exited Iraq. Remaining troops transitioned from combat operations to counter-terrorism and the training, equipping, and advising of Iraqi security forces. On August 31, 2010, Obama announced that the United States combat mission in Iraq was over. On October 21, 2011, President Obama announced that all U.S. troops would leave Iraq in time to be "home for the holidays." In June 2014, following the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014)#Fall of Mosul and push into Kirkuk, capture of Mosul by Islamic State, ISIL, Obama sent 275 troops to provide support and security for U.S. personnel and the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad. ISIS continued to gain ground and to commit Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant#Human rights abuse and war crime findings, widespread massacres and ethnic cleansing. In August 2014, during the Sinjar massacre, Obama ordered a American-led intervention in Iraq (2014–present)#United States airstrikes, campaign of U.S. airstrikes against ISIL. By the end of 2014, 3,100 American ground troops were committed to the conflict and 16,000 sorties were flown over the battlefield, primarily by U.S. Air Force and Navy pilots. In early 2015, with the addition of the "Panther Brigade" of the 82nd Airborne Division the number of U.S. ground troops in Iraq increased to 4,400, and by July American-led coalition air forces counted 44,000 sorties over the battlefield.
In June 2014, following the Northern Iraq offensive (June 2014)#Fall of Mosul and push into Kirkuk, capture of Mosul by Islamic State, ISIL, Obama sent 275 troops to provide support and security for U.S. personnel and the U.S. Embassy in Baghdad. ISIS continued to gain ground and to commit Islamic State of Iraq and the Levant#Human rights abuse and war crime findings, widespread massacres and ethnic cleansing. In August 2014, during the Sinjar massacre, Obama ordered a American-led intervention in Iraq (2014–present)#United States airstrikes, campaign of U.S. airstrikes against ISIL. By the end of 2014, 3,100 American ground troops were committed to the conflict and 16,000 sorties were flown over the battlefield, primarily by U.S. Air Force and Navy pilots. In early 2015, with the addition of the "Panther Brigade" of the 82nd Airborne Division the number of U.S. ground troops in Iraq increased to 4,400, and by July American-led coalition air forces counted 44,000 sorties over the battlefield.
Afghanistan and Pakistan
 In his election campaign, Obama called the war in Iraq a "dangerous distraction" and that emphasis should instead be put on the war in Afghanistan, the region he cites as being most likely where an attack against the United States could be launched again. Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan. He announced an increase in U.S. troop levels to 17,000 military personnel in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires." He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General David D. McKiernan, with former Special Forces (United States Army), Special Forces commander Lt. Gen. Stanley A. McChrystal in May 2009, indicating that McChrystal's Special Forces experience would facilitate the use of counterinsurgency tactics in the war. On December 1, 2009, Obama announced the deployment of an additional 30,000 military personnel to Afghanistan and proposed to begin troop withdrawals 18 months from that date; this took place in July 2011. David Petraeus replaced McChrystal in June 2010, after McChrystal's staff criticized White House personnel in a magazine article. In February 2013, Obama said the U.S. military would reduce the troop level in Afghanistan from 68,000 to 34,000 U.S. troops by February 2014. In October 2015, the White House announced a plan to keep U.S. Forces in Afghanistan indefinitely in light of the deteriorating security situation.
Regarding neighboring
In his election campaign, Obama called the war in Iraq a "dangerous distraction" and that emphasis should instead be put on the war in Afghanistan, the region he cites as being most likely where an attack against the United States could be launched again. Early in his presidency, Obama moved to bolster U.S. troop strength in Afghanistan. He announced an increase in U.S. troop levels to 17,000 military personnel in February 2009 to "stabilize a deteriorating situation in Afghanistan", an area he said had not received the "strategic attention, direction and resources it urgently requires." He replaced the military commander in Afghanistan, General David D. McKiernan, with former Special Forces (United States Army), Special Forces commander Lt. Gen. Stanley A. McChrystal in May 2009, indicating that McChrystal's Special Forces experience would facilitate the use of counterinsurgency tactics in the war. On December 1, 2009, Obama announced the deployment of an additional 30,000 military personnel to Afghanistan and proposed to begin troop withdrawals 18 months from that date; this took place in July 2011. David Petraeus replaced McChrystal in June 2010, after McChrystal's staff criticized White House personnel in a magazine article. In February 2013, Obama said the U.S. military would reduce the troop level in Afghanistan from 68,000 to 34,000 U.S. troops by February 2014. In October 2015, the White House announced a plan to keep U.S. Forces in Afghanistan indefinitely in light of the deteriorating security situation.
Regarding neighboring =Death of Osama bin Laden
= Starting with information received from Central Intelligence Agency operatives in July 2010, the CIA developed intelligence over the next several months that determined what they believed to be the hideout of Osama bin Laden. He was living in seclusion in Osama bin Laden's compound in Abbottabad, a large compound in Abbottabad, Pakistan, a suburban area from Islamabad. CIA head Leon Panetta reported this intelligence to President Obama in March 2011. Meeting with his national security advisers over the course of the next six weeks, Obama rejected a plan to bomb the compound, and authorized a "surgical raid" to be conducted by United States Navy SEALs. The operation took place on May 1, 2011, and resulted in the shooting death of bin Laden and the seizure of papers, computer drives and disks from the compound. DNA testing was one of five methods used to positively identify bin Laden's corpse, which was buried at sea several hours later. Within minutes of the President's announcement from Washington, DC, late in the evening on May 1, there were spontaneous celebrations around the country as crowds gathered outside the White House, and at New York City's World Trade Center site, Ground Zero and Times Square. Reactions to the death of Osama bin Laden, Reaction to the announcement was positive across party lines, including from former presidents Bill Clinton and George W. Bush.Relations with Cuba
Since the spring of 2013, secret meetings were conducted between the United States and Cuba in the neutral locations of Canada and Vatican City. The Vatican first became involved in 2013 when Pope Francis advised the U.S. and Cuba to prisoner exchange, exchange prisoners as a gesture of goodwill. On December 10, 2013, Cuban President Raúl Castro, in a significant public moment, greeted and shook hands with Obama at the Death of Nelson Mandela, Nelson Mandela memorial service in Johannesburg. In December 2014, after the secret meetings, it was announced that Obama, with Pope Francis as an intermediary, had negotiated a restoration of relations with Cuba, after nearly sixty years of détente. Popularly dubbed the Cuban Thaw, ''The New Republic'' deemed the Cuban Thaw to be "Obama's finest foreign policy achievement." On July 1, 2015, President Obama announced that formal diplomatic relations between Cuba and the United States would resume, and embassies would be opened in Washington and Havana. The countries' respective "interests sections" in one another's capitals were upgraded to embassies on July 20 and August 13, 2015, respectively. Obama visited Havana, Cuba for two days in March 2016, becoming the first sitting U.S. president to arrive since Calvin Coolidge in 1928.Israel
 During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including increased military aid, re-establishment of the Joint Political Military Group, U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group, and an increase in visits among high-level military officials of both countries. The Obama administration asked Congress to allocate money toward funding the Iron Dome program in response to the waves of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel. In March 2010, Obama took a public stance against plans by the government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to continue building Jewish housing projects in predominantly Arab neighborhoods of East Jerusalem. In 2011, the United States vetoed a Security Council resolution condemning Israeli settlements, with the United States being the only nation to do so. Obama supports the two-state solution to the Arab–Israeli conflict based on the 1967 borders with land swaps.
In 2013, Jeffrey Goldberg reported that, in Obama's view, "with each new settlement announcement, Netanyahu is moving his country down a path toward near-total isolation." In 2014, Obama likened the Zionist movement to the civil rights movement in the United States. He said both movements seek to bring justice and equal rights to historically persecuted peoples, explaining: "To me, being pro-Israel and pro-Jewish is part and parcel with the values that I've been fighting for since I was politically conscious and started getting involved in politics." Obama expressed support for Israel's right to defend itself during the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict. In 2015, Obama was harshly criticized by Israel for advocating and signing the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, Iran Nuclear Deal; Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, who had advocated the U.S. congress to oppose it, said the deal was "dangerous" and "bad."
On December 23, 2016, under the Obama Administration, the United States abstained from United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, which condemned Israeli settlement building in the occupied Palestinian territories as a violation of international law, effectively allowing it to pass. Netanyahu strongly criticized the Obama administration's actions, and the Israeli government withdrew its annual dues from the organization, which totaled $6million, on January 6, 2017. On January 5, 2017, the United States House of Representatives voted 342–80 to condemn the UN Resolution.
During the initial years of the Obama administration, the U.S. increased military cooperation with Israel, including increased military aid, re-establishment of the Joint Political Military Group, U.S.-Israeli Joint Political Military Group and the Defense Policy Advisory Group, and an increase in visits among high-level military officials of both countries. The Obama administration asked Congress to allocate money toward funding the Iron Dome program in response to the waves of Palestinian rocket attacks on Israel. In March 2010, Obama took a public stance against plans by the government of Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu to continue building Jewish housing projects in predominantly Arab neighborhoods of East Jerusalem. In 2011, the United States vetoed a Security Council resolution condemning Israeli settlements, with the United States being the only nation to do so. Obama supports the two-state solution to the Arab–Israeli conflict based on the 1967 borders with land swaps.
In 2013, Jeffrey Goldberg reported that, in Obama's view, "with each new settlement announcement, Netanyahu is moving his country down a path toward near-total isolation." In 2014, Obama likened the Zionist movement to the civil rights movement in the United States. He said both movements seek to bring justice and equal rights to historically persecuted peoples, explaining: "To me, being pro-Israel and pro-Jewish is part and parcel with the values that I've been fighting for since I was politically conscious and started getting involved in politics." Obama expressed support for Israel's right to defend itself during the 2014 Israel–Gaza conflict. In 2015, Obama was harshly criticized by Israel for advocating and signing the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, Iran Nuclear Deal; Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu, who had advocated the U.S. congress to oppose it, said the deal was "dangerous" and "bad."
On December 23, 2016, under the Obama Administration, the United States abstained from United Nations Security Council Resolution 2334, which condemned Israeli settlement building in the occupied Palestinian territories as a violation of international law, effectively allowing it to pass. Netanyahu strongly criticized the Obama administration's actions, and the Israeli government withdrew its annual dues from the organization, which totaled $6million, on January 6, 2017. On January 5, 2017, the United States House of Representatives voted 342–80 to condemn the UN Resolution.
Libya
 In February 2011, protests in Libya began against long-time dictator Muammar Gaddafi as part of the Arab Spring. They soon turned violent. In March, as forces loyal to Gaddafi advanced on rebels across Libya, calls for a no-fly zone came from around the world, including Europe, the Arab League, and a resolution passed unanimously by the U.S. Senate. In response to the unanimous passage of United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 on March 17, Gaddafi—who had previously vowed to "show no mercy" to the rebels of Benghazi—announced an immediate cessation of military activities.
The next day, on Obama's orders, the U.S. military took part in air strikes to destroy the Libyan government's air defense capabilities to protect civilians and enforce a no-fly-zone, including the use of Tomahawk (missile), Tomahawk missiles, Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit, B-2 Spirits, and fighter jets. Six days later, on March 25, by unanimous vote of all its 28 members, NATO took over leadership of the effort, dubbed Operation Unified Protector. Some Representatives questioned whether Obama had the constitutional authority to order military action in addition to questioning its cost, structure and aftermath. Obama later expressed regret for playing a leading role in the destabilization of Libya, calling the certain situation there "a mess." He has stated that the lack of preparation surrounding the days following the government's overthrow was the "worst mistake" of his presidency.
In February 2011, protests in Libya began against long-time dictator Muammar Gaddafi as part of the Arab Spring. They soon turned violent. In March, as forces loyal to Gaddafi advanced on rebels across Libya, calls for a no-fly zone came from around the world, including Europe, the Arab League, and a resolution passed unanimously by the U.S. Senate. In response to the unanimous passage of United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973 on March 17, Gaddafi—who had previously vowed to "show no mercy" to the rebels of Benghazi—announced an immediate cessation of military activities.
The next day, on Obama's orders, the U.S. military took part in air strikes to destroy the Libyan government's air defense capabilities to protect civilians and enforce a no-fly-zone, including the use of Tomahawk (missile), Tomahawk missiles, Northrop Grumman B-2 Spirit, B-2 Spirits, and fighter jets. Six days later, on March 25, by unanimous vote of all its 28 members, NATO took over leadership of the effort, dubbed Operation Unified Protector. Some Representatives questioned whether Obama had the constitutional authority to order military action in addition to questioning its cost, structure and aftermath. Obama later expressed regret for playing a leading role in the destabilization of Libya, calling the certain situation there "a mess." He has stated that the lack of preparation surrounding the days following the government's overthrow was the "worst mistake" of his presidency.
Syrian civil war
On August 18, 2011, several months after the start of the Syrian civil war, Obama issued a written statement that said: "The time has come for Bashar al-Assad, President Assad to step aside." This stance was reaffirmed in November 2015. In 2012, Obama authorized multiple Timber Sycamore, programs run by the CIA and the Pentagon to train anti-Assad rebels. The Pentagon-run program was later found to have failed and was formally abandoned in October 2015. In the wake of a Ghouta chemical attack, chemical weapons attack in Syria, U.S. Government Assessment of the Syrian Government's Use of Chemical Weapons on August 21, 2013, formally blamed by the Obama administration on the Assad government, Obama chose not to enforce the "red line" he had pledged and, rather than authorize the promised military action against Assad, went along with the Russia-brokered deal that led to Assad Destruction of Syria's chemical weapons, giving up chemical weapons; however attacks with chlorine gas continued. In 2014, Obama authorized an Military intervention against ISIL, air campaign aimed primarily at ISIL.Iran nuclear talks
 On October 1, 2009, the Obama administration went ahead with a Bush administration program, increasing nuclear weapons production. The "Complex Modernization" initiative expanded two existing nuclear sites to produce new bomb parts. The administration built new plutonium pits at the Los Alamos lab in New Mexico and expanded enriched uranium processing at the Y-12 facility in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In November 2013, the Obama administration opened Negotiations leading to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, negotiations with Iran to prevent it from acquiring nuclear weapons, which included an Joint Plan of Action, interim agreement. Negotiations took two years with numerous delays, with a deal being announced on July 14, 2015. The deal titled the "Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action" saw sanctions removed in exchange for measures that would prevent Iran from producing nuclear weapons. While Obama hailed the agreement as being a step towards a more hopeful world, the deal drew strong criticism from Republican and conservative quarters, and from Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. In addition, the transfer of $1.7billion in cash to Iran shortly after the deal was announced was criticized by the Republican party. The Obama administration said that the payment in cash was because of the "effectiveness of U.S. and international sanctions." In order to advance the deal, the Obama administration shielded Hezbollah from the Drug Enforcement Administration's Project Cassandra investigation regarding drug smuggling and from the Central Intelligence Agency.
On a side note, the very same year, in December 2015, Obama started a $348billion worth program to back the biggest U.S. buildup of nuclear arms since Ronald Reagan left the White House.
On October 1, 2009, the Obama administration went ahead with a Bush administration program, increasing nuclear weapons production. The "Complex Modernization" initiative expanded two existing nuclear sites to produce new bomb parts. The administration built new plutonium pits at the Los Alamos lab in New Mexico and expanded enriched uranium processing at the Y-12 facility in Oak Ridge, Tennessee. In November 2013, the Obama administration opened Negotiations leading to the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action, negotiations with Iran to prevent it from acquiring nuclear weapons, which included an Joint Plan of Action, interim agreement. Negotiations took two years with numerous delays, with a deal being announced on July 14, 2015. The deal titled the "Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action" saw sanctions removed in exchange for measures that would prevent Iran from producing nuclear weapons. While Obama hailed the agreement as being a step towards a more hopeful world, the deal drew strong criticism from Republican and conservative quarters, and from Israeli Prime Minister Benjamin Netanyahu. In addition, the transfer of $1.7billion in cash to Iran shortly after the deal was announced was criticized by the Republican party. The Obama administration said that the payment in cash was because of the "effectiveness of U.S. and international sanctions." In order to advance the deal, the Obama administration shielded Hezbollah from the Drug Enforcement Administration's Project Cassandra investigation regarding drug smuggling and from the Central Intelligence Agency.
On a side note, the very same year, in December 2015, Obama started a $348billion worth program to back the biggest U.S. buildup of nuclear arms since Ronald Reagan left the White House.
Russia
 In March 2010, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President Dmitry Medvedev to replace the START I, 1991 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty with a new pact reducing the number of long-range nuclear weapons in the arsenals of both countries by about a third. Obama and Medvedev signed the New START treaty in April 2010, and the United States Senate, U.S. Senate ratified it in December 2010. In December 2011, Obama instructed agencies to consider LGBT rights by country or territory, LGBT rights when issuing financial aid to foreign countries. In August 2013, he criticized Russia's law that discriminates against gays, but he stopped short of advocating a boycott of the upcoming 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia.
After Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, Russia's invasion of Crimea in 2014, Russian military intervention in Syria, military intervention in Syria in 2015, and the 2016 United States election interference by Russia, interference in the 2016 United States presidential election, 2016 U.S. presidential election, George Robertson, Baron Robertson of Port Ellen, George Robertson, a former UK defense secretary and NATO secretary-general, said Obama had "allowed Putin to jump back on the world stage and test the resolve of the West", adding that the legacy of this disaster would last.
In March 2010, an agreement was reached with the administration of Russian President Dmitry Medvedev to replace the START I, 1991 Strategic Arms Reduction Treaty with a new pact reducing the number of long-range nuclear weapons in the arsenals of both countries by about a third. Obama and Medvedev signed the New START treaty in April 2010, and the United States Senate, U.S. Senate ratified it in December 2010. In December 2011, Obama instructed agencies to consider LGBT rights by country or territory, LGBT rights when issuing financial aid to foreign countries. In August 2013, he criticized Russia's law that discriminates against gays, but he stopped short of advocating a boycott of the upcoming 2014 Winter Olympics in Sochi, Russia.
After Annexation of Crimea by the Russian Federation, Russia's invasion of Crimea in 2014, Russian military intervention in Syria, military intervention in Syria in 2015, and the 2016 United States election interference by Russia, interference in the 2016 United States presidential election, 2016 U.S. presidential election, George Robertson, Baron Robertson of Port Ellen, George Robertson, a former UK defense secretary and NATO secretary-general, said Obama had "allowed Putin to jump back on the world stage and test the resolve of the West", adding that the legacy of this disaster would last.
Cultural and political image
Obama's family history, upbringing, and Ivy League education differ markedly from those of African-American politicians who launched their careers in the 1960s through participation in the civil rights movement. Expressing puzzlement over questions about whether he is "black enough", Obama told an August 2007 meeting of the National Association of Black Journalists that "we're still locked in this notion that if you appeal to white folks then there must be something wrong." Obama acknowledged his youthful image in an October 2007 campaign speech, saying: "I wouldn't be here if, time and again, the torch had not been passed to a new generation." Additionally, Obama has frequently been referred to as an exceptional orator. During his pre-inauguration transition period and continuing into his presidency, Obama delivered a series of weekly Internet video addresses. Polls showed strong support for Obama in other countries both before and during his presidency. In a February 2009 poll conducted in Western Europe and the U.S. by Harris Insights & Analytics, Harris Interactive for France 24 and the ''International Herald Tribune'', Obama was rated as the most respected world leader, as well as the most powerful. In a similar poll conducted by Harris in May 2009, Obama was rated as the most popular world leader, as well as the one figure most people would pin their hopes on for pulling the world out of the economic downturn.
On October 9, 2009, the Norwegian Nobel Committee announced that Obama had won the 2009 Nobel Peace Prize "for his extraordinary efforts to strengthen international diplomacy and cooperation between peoples," which drew a mixture of praise and criticism from world leaders and media figures. He became the fourth U.S. president to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, and the third to become a Nobel laureate while in office.
Polls showed strong support for Obama in other countries both before and during his presidency. In a February 2009 poll conducted in Western Europe and the U.S. by Harris Insights & Analytics, Harris Interactive for France 24 and the ''International Herald Tribune'', Obama was rated as the most respected world leader, as well as the most powerful. In a similar poll conducted by Harris in May 2009, Obama was rated as the most popular world leader, as well as the one figure most people would pin their hopes on for pulling the world out of the economic downturn.
On October 9, 2009, the Norwegian Nobel Committee announced that Obama had won the 2009 Nobel Peace Prize "for his extraordinary efforts to strengthen international diplomacy and cooperation between peoples," which drew a mixture of praise and criticism from world leaders and media figures. He became the fourth U.S. president to be awarded the Nobel Peace Prize, and the third to become a Nobel laureate while in office.
Racism towards Obama
Obama's election was also met with hostile reactions connected to his race, birthplace, and religion, and as president, he faced numerous taunts, racist remarks and generally racialized criticisms by some conservative pundits. Some also falsely Barack Obama religion conspiracy theories, claimed that Obama practiced Islam – at a time when Islamophobia, anti-Muslim sentiments were Islamophobia in the United States, prevalent in the United States – with a 2015 CNN poll finding that 29% of Americans believed Obama to be a Muslim. Starting in 2011, Donald Trump – who would later directly succeed Obama as president – would regularly promote conspiracy theories that Obama had Barack Obama citizenship conspiracy theories, been born in Kenya, and therefore, was not an American citizen. Trump winning the presidency right after Obama was described by some commentators as the culmination of decades of white backlash against Black Americans achieving social mobility in the face of racist policies against them. Carol Anderson, author of the book ''White Rage'' and a professor of Black studies, African-American studies, said that Obama was caught off guard by the backlash, and "was surprised by how racist this country is." In September 2009, former President Jimmy Carter stated that “I think an overwhelming portion of the intensely demonstrated animosity toward President Barack Obama is based on the fact that he is a black man.” Though Obama publicly disagreed with Carter's assessment at the time, in a 2015 interview with ''NPR'', he also said, when asked about critics who believed he was making their country worse: In the same interview, however, he also stated that, despite the existence of racially motivated criticism against him, others who criticize his policies may still have "perfectly good reasons" for doing so.Post-presidency (2017–present)
 Obama's presidency ended on January 20, 2017, upon the Inauguration of Donald Trump, inauguration of his successor, Donald Trump. The family moved to a house they rented in Kalorama, Washington, D.C. On March 2, 2017, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum awarded the Profile in Courage Award to Obama "for his enduring commitment to democratic ideals and elevating the standard of political courage." His first public appearance since leaving the office was a seminar at the University of Chicago on April 24, where he appealed for a new generation to participate in politics.
Obama's presidency ended on January 20, 2017, upon the Inauguration of Donald Trump, inauguration of his successor, Donald Trump. The family moved to a house they rented in Kalorama, Washington, D.C. On March 2, 2017, the John F. Kennedy Presidential Library and Museum awarded the Profile in Courage Award to Obama "for his enduring commitment to democratic ideals and elevating the standard of political courage." His first public appearance since leaving the office was a seminar at the University of Chicago on April 24, where he appealed for a new generation to participate in politics.
 On September 7, 2017, Obama partnered with former presidents Jimmy Carter, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush to work with One America Appeal to help the victims of Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Irma in the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast and Texas communities.
Obama hosted the inaugural summit of the Obama Foundation in Chicago from October 31 to November 1, 2017. He intends for the foundation to be the central focus of his post-presidency and part of his ambitions for his subsequent activities following his presidency to be more consequential than his time in office.
Barack and Michelle Obama signed a deal on May 22, 2018, to produce docu-series, documentaries and features for Netflix under the Obamas' newly formed production company, Higher Ground Productions. Higher Ground's first film, ''American Factory,'' won the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature in 2020.
On September 7, 2017, Obama partnered with former presidents Jimmy Carter, George H. W. Bush, Bill Clinton, and George W. Bush to work with One America Appeal to help the victims of Hurricane Harvey and Hurricane Irma in the Gulf Coast of the United States, Gulf Coast and Texas communities.
Obama hosted the inaugural summit of the Obama Foundation in Chicago from October 31 to November 1, 2017. He intends for the foundation to be the central focus of his post-presidency and part of his ambitions for his subsequent activities following his presidency to be more consequential than his time in office.
Barack and Michelle Obama signed a deal on May 22, 2018, to produce docu-series, documentaries and features for Netflix under the Obamas' newly formed production company, Higher Ground Productions. Higher Ground's first film, ''American Factory,'' won the Academy Award for Best Documentary Feature in 2020.
 He received a 63% approval rating in Gallup's 2018 job approval poll for the past 10 U.S. presidents.
A pipe bomb addressed to Obama was intercepted by the Secret Service on October 24, 2018. It was one of several pipe-bombs that had been October 2018 United States mail bombing attempts, mailed out to Democratic lawmakers and officials.
In 2019, Barack and Michelle Obama bought a home on Martha's Vineyard from Wyc Grousbeck. On October 29, 2019, Obama criticized "wokeness" and Cancel culture, call-out culture at the Obama Foundation's annual summit.
Obama was reluctant to make an endorsement in the 2020 Democratic presidential primaries because he wanted to position himself to unify the party, no matter who the nominee was. On April 14, 2020, Obama endorsed his former vice president Joe Biden, the presumptive Democratic nominee, for president in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, stating that he has "all the qualities we need in a president right now." In May 2020, Obama criticized President Trump for Trump administration communication during the COVID-19 pandemic, his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, COVID-19 pandemic, calling his response to the crisis "an absolute chaotic disaster", and stating that the consequences of Presidency of Donald Trump, the Trump presidency have been "our worst impulses unleashed, our proud reputation around the world badly diminished, and our democratic institutions threatened like never before." Trump retaliated by accusing Obama of having committed "the biggest political crime in American history", although he refused to say what he was talking about, telling reporters: "You know what the crime is, the crime is very obvious to everybody."
Obama wrote a presidential memoir, in a $65million deal with Penguin Random House. The book, ''
He received a 63% approval rating in Gallup's 2018 job approval poll for the past 10 U.S. presidents.
A pipe bomb addressed to Obama was intercepted by the Secret Service on October 24, 2018. It was one of several pipe-bombs that had been October 2018 United States mail bombing attempts, mailed out to Democratic lawmakers and officials.
In 2019, Barack and Michelle Obama bought a home on Martha's Vineyard from Wyc Grousbeck. On October 29, 2019, Obama criticized "wokeness" and Cancel culture, call-out culture at the Obama Foundation's annual summit.
Obama was reluctant to make an endorsement in the 2020 Democratic presidential primaries because he wanted to position himself to unify the party, no matter who the nominee was. On April 14, 2020, Obama endorsed his former vice president Joe Biden, the presumptive Democratic nominee, for president in the 2020 United States presidential election, 2020 election, stating that he has "all the qualities we need in a president right now." In May 2020, Obama criticized President Trump for Trump administration communication during the COVID-19 pandemic, his handling of the COVID-19 pandemic in the United States, COVID-19 pandemic, calling his response to the crisis "an absolute chaotic disaster", and stating that the consequences of Presidency of Donald Trump, the Trump presidency have been "our worst impulses unleashed, our proud reputation around the world badly diminished, and our democratic institutions threatened like never before." Trump retaliated by accusing Obama of having committed "the biggest political crime in American history", although he refused to say what he was talking about, telling reporters: "You know what the crime is, the crime is very obvious to everybody."
Obama wrote a presidential memoir, in a $65million deal with Penguin Random House. The book, '' On April 5, 2022, Obama visited the White House for the first time since leaving office, in an event celebrating the 12th annual anniversary of the signing of the Affordable Care Act.
In 2022, he narrated the Netflix documentary series ''Our Great National Parks'', which later won him a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Narrator.
In June 2022, it was announced that the Obamas and their podcast production company, Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground, signed a multi-year deal with Audible (service), Audible.
In September 2022, Obama visited the White House to unveil his and Michelle's official White House portraits.
On April 5, 2022, Obama visited the White House for the first time since leaving office, in an event celebrating the 12th annual anniversary of the signing of the Affordable Care Act.
In 2022, he narrated the Netflix documentary series ''Our Great National Parks'', which later won him a Primetime Emmy Award for Outstanding Narrator.
In June 2022, it was announced that the Obamas and their podcast production company, Higher Ground Productions, Higher Ground, signed a multi-year deal with Audible (service), Audible.
In September 2022, Obama visited the White House to unveil his and Michelle's official White House portraits.
Legacy
 Historian Julian E. Zelizer, Julian Zelizer credits Obama with "a keen sense of how the institutions of government work and the ways that his team could design policy proposals." Zelizer notes Obama's policy successes included the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, economic stimulus package which ended the Great Recession in the United States, Great Recession and the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Dodd-Frank financial and consumer protection reforms, as well as the
Historian Julian E. Zelizer, Julian Zelizer credits Obama with "a keen sense of how the institutions of government work and the ways that his team could design policy proposals." Zelizer notes Obama's policy successes included the American Recovery and Reinvestment Act of 2009, economic stimulus package which ended the Great Recession in the United States, Great Recession and the Dodd–Frank Wall Street Reform and Consumer Protection Act, Dodd-Frank financial and consumer protection reforms, as well as the Presidential library
The Barack Obama Presidential Center is Obama's planned Presidential library system, presidential library. It will be hosted by the University of Chicago and located in Jackson Park (Chicago), Jackson Park on the South Side, Chicago, South Side of Chicago.Bibliography
Books
* * * *Audiobooks
* 2006: ''The Audacity of Hope: Thoughts on Reclaiming the American Dream'' (read by the author), Random House Audio, * 2020: ''A Promised Land'' (read by the author)Articles
* * Uncredited case comment. * * * * * * * * * *See also
Politics
* DREAM Act * Fraud Enforcement and Recovery Act of 2009 * Immigration Reform and Control Act of 1986 * IRS targeting controversy * Middle Class Tax Relief and Job Creation Act of 2012 * National Broadband Plan (United States) * Office of Energy Efficiency and Renewable Energy * Social policy of the Barack Obama administration * SPEECH Act * Stay with It * White House Office of Energy and Climate Change PolicyOther
* Roberts Court * Speeches of Barack ObamaLists
* Assassination threats against Barack Obama * List of African-American United States senators * List of Barack Obama 2008 presidential campaign endorsements * List of Barack Obama 2012 presidential campaign endorsements * Political scandals during the Obama administration, List of federal political scandals, 2009–17 * List of people granted executive clemency by Barack Obama * List of things named after Barack ObamaReferences
/span>: It would take time for Obama to join and become fully engaged in Wright's church, a place where he would be baptized and married; that would not happen until later, during his second time around in Chicago, but the process started then, in October 1987... Jerry Kellman: "He wasn't a member of the church during those first three years, but he was drawn to Jeremiah." *
Bibliography
* * * * * *Further reading
* * * * * * * Parmar, Inderjeet, and Mark Ledwidge. "...'a foundation-hatched black': Obama, the US establishment, and foreign policy." ''International Politics'' 54.3 (2017): 373–38online
External links
Official
* of The Obama Foundation * of the Barack Obama Presidential Library * of Organizing for ActionWhite House biography
Other
Column archive
at ''HuffPost, The Huffington Post'' * * * * * * * * * *
Barack Obama
at Politifact * {{DEFAULTSORT:Obama, Barack Barack Obama, 1961 births 20th-century American male writers 20th-century American non-fiction writers 20th-century Protestants 20th-century African-American academics 20th-century American academics 21st-century American male writers 21st-century American non-fiction writers 21st-century American politicians 21st-century presidents of the United States 21st-century Protestants 21st-century scholars Activists from Hawaii Activists from Illinois African-American Christians African-American educators African-American feminists African-American lawyers African-American non-fiction writers African-American politicians African-American state legislators in Illinois African-American candidates for President of the United States African-American United States senators American civil rights lawyers American community activists American feminist writers American gun control activists American legal scholars American male non-fiction writers American memoirists American Nobel laureates American people of English descent American people of French descent American people of German descent American people of Irish descent American people of Kenyan descent American people of Luo descent American people of Scottish descent American people of Swiss descent American people of Welsh descent American political writers American Protestants Articles containing video clips Candidates in the 2008 United States presidential election Candidates in the 2012 United States presidential election Columbia College (New York) alumni Democratic Party presidents of the United States Democratic Party (United States) presidential nominees Democratic Party United States senators from Illinois Grammy Award winners Harvard Law School alumni Illinois lawyers Democratic Party Illinois state senators LGBT rights activists from the United States Living people Male feminists Members of the American Philosophical Society Netflix people Nobel Peace Prize laureates Obama family Outstanding Narrator Primetime Emmy Award winners Politicians from Chicago Politicians from Honolulu Presidents of the United States Proponents of Christian feminism Punahou School alumni Scholars of constitutional law Time Person of the Year University of Chicago Law School faculty Writers from Chicago Writers from Honolulu