Numbers in Norse mythology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The numbers
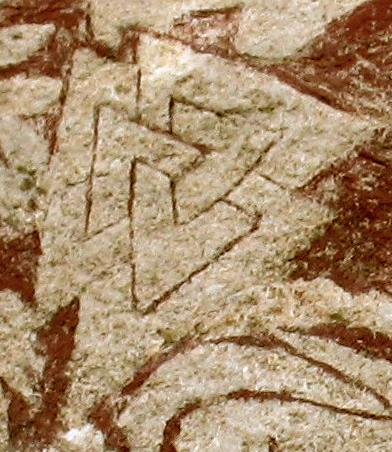 The number nine is also a significant number:
* The
The number nine is also a significant number:
* The
three
3 is a number, numeral, and glyph.
3, three, or III may also refer to:
* AD 3, the third year of the AD era
* 3 BC, the third year before the AD era
* March, the third month
Books
* '' Three of Them'' (Russian: ', literally, "three"), a 1901 ...
and nine are significant numbers in Norse mythology
Norse, Nordic, or Scandinavian mythology is the body of myths belonging to the North Germanic peoples, stemming from Old Norse religion and continuing after the Christianization of Scandinavia, and into the Nordic folklore of the modern per ...
and Germanic paganism. Both numbers (and multiples thereof) appear throughout surviving attestations of Norse mythology, in both mythology and Germanic paganism
Germanic paganism or Germanic religion refers to the traditional, culturally significant religion of the Germanic peoples. With a chronological range of at least one thousand years in an area covering Scandinavia, the British Isles, modern Germ ...
..
While the number three appears significant in many cultures, Norse mythology appears to put special emphasis on the number nine. Along with the number 27, both numbers also figure into the lunar
Lunar most commonly means "of or relating to the Moon".
Lunar may also refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Lunar'' (series), a series of video games
* "Lunar" (song), by David Guetta
* "Lunar", a song by Priestess from the 2009 album ''Prior t ...
Germanic calendar
The early Germanic calendars were the regional calendars used among the early Germanic peoples before they adopted the Julian calendar in the Early Middle Ages. The calendars were an element of early Germanic culture.
The Germanic peoples had nam ...
.
Attestations
Three
The number three occurs with great frequency in grouping individuals and artefacts: *There were three original beings: the primordial cow Audhumla,Ymir
In Norse mythology, Ymir (, ), also called Aurgelmir, Brimir, or Bláinn, is the ancestor of all jötnar. Ymir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional material, in the ''Prose Edda'', writ ...
the first giant, and Búri
In Norse mythology, Búri ( Old Norse: ), is a divinity god 'producer, father' of all other gods,Simek (Simek 2007:47). and an early ancestor of the Æsir gods of the principal pantheon in Norse religion. Búri was licked free from salty rime sto ...
the first god and grandfather of Odin
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victory, ...
.
*For three days Audhumla licked the ice of Ginnungagap
In Norse mythology, Ginnungagap ( old Norse: ; "gaping abyss", "yawning void") is the primordial void mentioned in the Gylfaginning, the Eddaic text recording Norse cosmogony.
Etymology
''Ginnunga-'' is usually interpreted as deriving from a ver ...
until Búri was freed.
*Ymir had three direct offspring: a boy and girl who grew from beneath his arms and a six-headed son who sprang from the coupling of his feet.
*There were three generations of giants before the race as a whole was destroyed by the deluge
A deluge is a large downpour of rain, often a flood.
The Deluge refers to the flood narrative in the Biblical book of Genesis.
Deluge may also refer to:
History
*Deluge (history), the Swedish and Russian invasion of the Polish-Lithuanian Com ...
of Ymir's blood, after which time his grandson Bergelmir
Bergelmir ( ; Old Norse: ) is a jötunn in Norse mythology.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Bergelmir'' has been variously translated as 'bear-yeller', 'mountain-yeller', or 'bare-yeller'. According to linguist Jan de Vries, the name should be read ...
became the progenitor of a new line.
*The heart of the giant Hrungnir
Hrungnir (Old Norse: , 'brawler') is a jötunn in Norse mythology. He is described as made of stone and is ultimately killed in a duel with the thunder god Thor.
Prior to his demise, Hrungnir engaged in a wager with Odin in which Odin stakes his ...
was triangular
A triangle is a polygon with three edges and three vertices. It is one of the basic shapes in geometry. A triangle with vertices ''A'', ''B'', and ''C'' is denoted \triangle ABC.
In Euclidean geometry, any three points, when non- collinea ...
and made of stone.
*There are three named Norns
The Norns ( non, norn , plural: ) are deities in Norse mythology responsible for shaping the course of human destinies.'' Nordisk familjebok'' (1907)
In the '' Völuspá'', the three primary Norns Urðr (Wyrd), Verðandi, and Skuld draw w ...
.
*Odin had two brothers, Vili and Vé
In Norse mythology, Vili ( ; Old Norse: ) and Vé ( ; O.N.: ) are the brothers of the god Odin (from Old Norse ''Óðinn''), sons of Bestla, daughter of Bölþorn; and Borr, son of Búri
Name
The Old Norse theonym ''Vé'' (or ''Véi'') is cogn ...
(or Lodur and Hoenir according to ''Völuspá''), numbering three sons of Borr
In Norse mythology, Borr or BurrThe ''Konungsbók'' or ''Codex Regius'' MS of the ''Völuspá'' reads ''Búrr''; the Hauksbók MS reads ''Borr''. Cf. Nordal (1980:31). The latter form alone was used by 13th-century historian and poet Snorri Sturlu ...
who created the world and gave life to the first human beings.
*Odin is the ruler of the third generation of gods as the son of Borr and grandson of Búri.
* Yggdrasil the World Tree
The world tree is a motif present in several religions and mythologies, particularly Indo-European religions, Siberian religions, and Native American religions. The world tree is represented as a colossal tree which supports the heavens, thereb ...
has three roots. Under the three roots are three sacred wells, one for each, including the Well of Urd in Asgard
In Nordic mythology, Asgard (Old Norse: ''Ásgarðr'' ; "enclosure of the Æsir") is a location associated with the gods. It appears in a multitude of Old Norse sagas and mythological texts. It is described as the fortified home of the Æsir ...
, the Well of Mimir located "among the frost giants", and Hvergelmir
In Norse mythology, Hvergelmir (Old Norse: ; "bubbling boiling spring"Orchard (1997:93)) is a major spring. Hvergelmir is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', writte ...
in Niflheim.
*Odin endured three hardships upon the World Tree in his quest for the runes
Runes are the letters in a set of related alphabets known as runic alphabets native to the Germanic peoples. Runes were used to write various Germanic languages (with some exceptions) before they adopted the Latin alphabet, and for specialised ...
: he hanged himself, wounded himself with a spear, and suffered from hunger and thirst.
*In the ''Gylfaginning
''Gylfaginning'' (Old Norse: 'The Beguiling of Gylfi' or 'The Deluding of Gylfi'; c. 20,000 words; 13th century Old Norse pronunciation ) is the first part of the 13th century ''Prose Edda'' after the Prologue. The ''Gylfaginning'' deals with t ...
'' section of the ''Prose Edda
The ''Prose Edda'', also known as the ''Younger Edda'', ''Snorri's Edda'' ( is, Snorra Edda) or, historically, simply as ''Edda'', is an Old Norse textbook written in Iceland during the early 13th century. The work is often assumed to have been ...
'', King Gylfi
In Norse mythology, Gylfi (Old Norse: ), ''Gylfe'', ''Gylvi'', or ''Gylve'' was the earliest recorded king in Scandinavia. He often uses the name Gangleri when appearing in disguise. The traditions on Gylfi deal with how he was tricked by the god ...
is confronted by a triple throne at the home of the gods, one being seated and occupied atop another.
*Loki
Loki is a god in Norse mythology. According to some sources, Loki is the son of Fárbauti (a jötunn) and Laufey (mentioned as a goddess), and the brother of Helblindi and Býleistr. Loki is married to Sigyn and they have two sons, Narfi ...
has three malign progeny by the giantess Angrboda: the wolf Fenrir
Fenrir (Old Norse: ; "fen-dweller")Orchard (1997:42). or Fenrisúlfr (O.N.: ; "Fenrir's wolf", often translated "Fenris-wolf"),Simek (2007:81). also referred to as Hróðvitnir (O.N.: ; "fame-wolf")Simek (2007:160). and Vánagandr (O.N.: ; " ...
, Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr ( non, Jǫrmungandr, lit=the Vast gand, see Etymology), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent ( non, Miðgarðsormr), is an unfathomably large sea serpent or worm who dwells in the world sea, encir ...
the World Serpent, and Hel.
*Prior to Ragnarök
In Norse mythology, (; non, wikt:ragnarǫk, Ragnarǫk) is a series of events, including a great battle, foretelling the death of numerous great figures (including the Æsir, gods Odin, Thor, Týr, Freyr, Heimdallr, and Loki), natural disast ...
, there will be three hard winters without an intervening summer, the Fimbulwinter
In Norse mythology, (commonly rendered in English as Fimbulwinter), is the immediate prelude to the events of Ragnarök. It means 'great winter'.
Summary
is the harsh winter that precedes the end of the world and puts an end to all life o ...
.
*There are three main events leading up to Ragnarök itself: the birth of Loki's three monstrous children, the death of Baldr
Baldr (also Balder, Baldur) is a god in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, Baldr (Old Norse: ) is a son of the god Odin and the goddess Frigg, and has numerous brothers, such as Thor and Váli. In wider Germanic mythology, the god was ...
and subsequent punishment of Loki, and the onset of Fimbulwinter.
*The wolf Fenrir was bound by three fetters: Loeding, Drómi, and Gleipnir
In Norse mythology, Gleipnir (Old Norse "open one")Orchard (1997:58). is the binding that holds the mighty wolf Fenrir (as attested in chapter 34 of the ''Prose Edda'' book ''Gylfaginning''). The Gods had attempted to bind Fenrir twice before wit ...
, of which only the last held him.
*Loki is bound with three bonds made from the entrails of his son through holes in three upright slabs of rock, the first under his shoulders, the second under his loins and the third under the backs of his knees.
*In the poem ''Völuspá
''Vǫluspá'' (also ''Völuspá'', ''Vǫlospá'' or ''Vǫluspǫ́''; Old Norse: 'Prophecy of the völva, a seeress'; reconstructed Old Norse: ) is the best known poem of the ''Poetic Edda''. It tells the story of the creation of the world and ...
'' from the ''Poetic Edda
The ''Poetic Edda'' is the modern name for an untitled collection of Old Norse anonymous narrative poems, which is distinct from the ''Prose Edda'' written by Snorri Sturluson. Several versions exist, all primarily of text from the Icelandic med ...
'', the monstrous hound Garmr
In Norse mythology, Garmr or Garm (Old Norse: ; "rag") is a wolf or dog associated with both Hel and Ragnarök, and described as a blood-stained guardian of Hel's gate.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Garmr'' has been interpreted as meaning "rag." ...
howls three times at the Gnipa-cave (or at least, the description of his howling is repeated three times).
*In ''Völuspá'', the gods burn Gullveig three times and three times she is reborn.
*During the onset of Ragnarök three cockerel
The chicken (''Gallus gallus domesticus'') is a domesticated junglefowl species, with attributes of wild species such as the grey and the Ceylon junglefowl that are originally from Southeastern Asia. Rooster or cock is a term for an adult m ...
s will begin to crow, heralding the final conflict: Gullinkambi for the gods, Fjalar for the giants and an unnamed third for the dead.
*Bifröst
In Norse mythology, Bifröst (), also called Bilröst, is a burning rainbow bridge that reaches between Midgard (Earth) and Asgard, the realm of the gods. The bridge is attested as ''Bilröst'' in the '' Poetic Edda''; compiled in the 13th cen ...
the rainbow bridge has three colours. It also has two other names, Ásbrú and Bilröst, thus having three names.
* Heimdall has three special powers in his role as guardian of the rainbow bridge. He needs less sleep than a bird, can see at night for a hundred leagues and is able to hear grass growing on the earth.
*Odin has three special possessions: His spear Gungnir
In Norse mythology, Gungnir (, "the rocking") is the spear of the god Odin.
Attestations ''Poetic Edda''
In the Poetic Edda poem ''Völuspá'', the Æsir-Vanir War is described as officially starting when Odin throws a spear over the heads of ...
, his golden ring Draupnir and his eight-legged horse Sleipnir
In Norse mythology, Sleipnir (Old Norse: ; "slippy"Orchard (1997:151). or "the slipper"Kermode (1904:6).) is an eight-legged horse ridden by Odin. Sleipnir is attested in the '' Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier tradition ...
.
*Thor
Thor (; from non, Þórr ) is a prominent god in Germanic paganism. In Norse mythology, he is a hammer-wielding god associated with lightning, thunder, storms, sacred groves and trees, strength, the protection of humankind, hallowing, ...
has three main weapons for use against the giants: his hammer Mjolnir, a magical belt that doubles his strength and a pair of iron gauntlets that allow him to wield the hammer.
*Freyr
Freyr (Old Norse: 'Lord'), sometimes anglicized as Frey, is a widely attested god in Norse mythology, associated with kingship, fertility, peace, and weather. Freyr, sometimes referred to as Yngvi-Freyr, was especially associated with Sweden an ...
has three magical items, including the ship Skidbladnir, his boar Gullinbursti and a sword with the ability to fight on its own which he gave to Skirnir in return for his role in the courtship of Gerd.
*Freyja
In Norse paganism, Freyja (Old Norse "(the) Lady") is a goddess associated with love, beauty, fertility, sex, war, gold, and seiðr (magic for seeing and influencing the future). Freyja is the owner of the necklace Brísingamen, rides a chario ...
also has three special artefacts, including the priceless necklace Brisingamen, a cloak that allows her to assume the form of a falcon and a chariot drawn by a pair of great cats.
*In the stronghold of the giant Útgarda-Loki, Thor drank three mighty draughts from a horn during a drinking contest but gave up when he was unable to empty the horn of its contents; this was also one of three tasks he did -and failed- during his stay, the other two being to lift a cat (he made it lift a paw, leaving three on ground) and to defeat an old woman; it is later revealed that the horn was connected to the sea (which he leveled down by three fingers), the cat was the World Serpent and the old woman, the Old Age itself. Previous to this, Thor and his companions had met the giant, who was under the assumed name Skrýmir, in the forest outside the castle. When Skrymir had gone to sleep during their journey together, Thor became annoyed by his loud snoring and struck at him three times with his hammer, but in each case the blow was misdirected through magic and illusion.
*The builder of the walls of Asgard offered to build them in three seasons in return for three prizes: the sun and moon and the hand of Freyja in marriage.
*Odin spent three nights with the giantess Gunnlod in order to obtain the mead of poetry. She then allowed him to take three drinks of the mead, one from each of three vessels.
*The group of dwarves known only as the sons of Ivaldi fashioned three wondrous artefacts, including the ship of Freyr, the spear of Odin and the golden hair of Sif
In Norse mythology, Sif (Old Norse: ) is a golden-haired goddess associated with earth. Sif is attested in the ''Poetic Edda'', compiled in the 13th century from earlier traditional sources, and the ''Prose Edda'', written in the 13th century ...
. The dwarf brothers Eitri and Brokk also created three items, including the boar of Freyr, the golden ring of Odin and the hammer of Thor.
*There were three statues of Odin, Thor and Freyr in the Temple at Uppsala
The Temple at Uppsala was a religious center in the ancient Norse religion once located at what is now Gamla Uppsala (Swedish "Old Uppsala"), Sweden attested in Adam of Bremen's 11th-century work '' Gesta Hammaburgensis ecclesiae pontificum'' and ...
.
*Three of Odin's sons remain after Ragarök: Vidar, Baldr and Hǫðr.
Nine
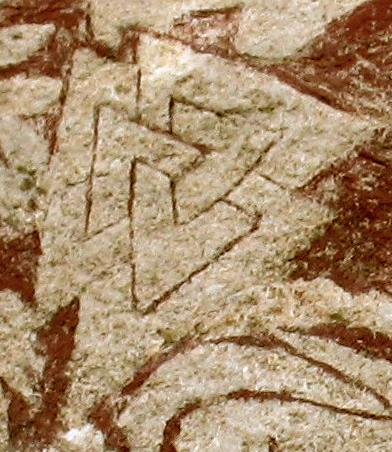 The number nine is also a significant number:
* The
The number nine is also a significant number:
* The Norse cosmology
Norse cosmology is the study of the cosmos (cosmology) as perceived by the ancient North Germanic peoples. The topic encompasses concepts from Norse mythology, such as notions of time and space, cosmogony, personifications, anthropogeny, and es ...
knows nine worlds that are supported by Yggdrasil.
* The Anglo-Saxon paganism
Anglo-Saxon paganism, sometimes termed Anglo-Saxon heathenism, Anglo-Saxon pre-Christian religion, or Anglo-Saxon traditional religion, refers to the religious beliefs and practices followed by the Anglo-Saxons between the 5th and 8th centurie ...
nine-herbs charm, as the name implies, invokes nine herbs, and also contains a rare mention of Woden
Odin (; from non, Óðinn, ) is a widely revered god in Germanic paganism. Norse mythology, the source of most surviving information about him, associates him with wisdom, healing, death, royalty, the gallows, knowledge, war, battle, victor ...
.
* At the end of ''Skáldskaparmál
''Skáldskaparmál'' (Old Norse: 'The Language of Poetry'; c. 50,000 words; ; ) is the second part of the ''Prose Edda''.
The section consists of a dialogue between Ægir, the divine personification of the sea, and Bragi, the god of poetry, ...
'' is a list of nine heavenly realms provided by Snorri, including, from the nethermost to the highest, Vindblain (also Heidthornir or Hregg-Mimir), Andlang, Vidblain, Vidfedmir, Hrjod, Hlyrnir, Gimir, Vet-Mimir and Skatyrnir which "stands higher than the clouds, beyond all worlds."
* Every ninth year, people from all over Sweden
Sweden, formally the Kingdom of Sweden,The United Nations Group of Experts on Geographical Names states that the country's formal name is the Kingdom of SwedenUNGEGN World Geographical Names, Sweden./ref> is a Nordic countries, Nordic c ...
assembled at the Temple at Uppsala. There was feasting for nine days and sacrifices of both men and male animals according to Adam of Bremen
Adam of Bremen ( la, Adamus Bremensis; german: Adam von Bremen) (before 1050 – 12 October 1081/1085) was a German medieval chronicler. He lived and worked in the second half of the eleventh century. Adam is most famous for his chronicle ''Gest ...
.
* The 600s Stentoften Runestone mentions a sacrifice of nine he-goats and nine stallions
A stallion is a male horse that has not been gelded (castrated).
Stallions follow the conformation and phenotype of their breed, but within that standard, the presence of hormones such as testosterone may give stallions a thicker, "cresty" neck ...
, very similar to Adam's account.
* In ''Skírnismál
''Skírnismál'' (Old Norse: 'The Lay of Skírnir') is one of the poems of the '' Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the 13th-century manuscripts Codex Regius and AM 748 I 4to but may have been originally composed in the early 10th century. Many ...
'', Freyr is obliged to wait nine nights to consummate his union with Gerd.
* In '' Svipdagsmál'', the witch Gróa grants nine charms to her son Svipdag. In the same poem there are nine maidens who sit at the knees of Menglod.
* In '' Fjölsvinnsmál'', Laegjarn's chest is fastened with nine locks.
* During Ragnarök, Thor kills Jörmungandr but staggers back nine steps before falling dead himself, poisoned by the venom that the Serpent
Serpent or The Serpent may refer to:
* Snake, a carnivorous reptile of the suborder Serpentes
Mythology and religion
* Sea serpent, a monstrous ocean creature
* Serpent (symbolism), the snake in religious rites and mythological contexts
* Serp ...
spewed over him and after that, he resurrected himself.
* According to the very late Trollkyrka poem, the fire for the blót
( Old Norse) and or ( Old English) are terms for "blood sacrifice" in Norse paganism and Anglo-Saxon paganism respectively. A comparanda can also be reconstructed for wider Germanic paganism.
A ' could be dedicated to any of the Germanic ...
was lit with nine kinds of wood.
* Odin's ring Draupnir releases eight golden drops every ninth night, forming rings of equal worth for a total of nine rings.
* In the guise of ''Grímnir'' in the poem ''Grímnismál
''Grímnismál'' (Old Norse: ; 'The Lay of Grímnir') is one of the mythological poems of the ''Poetic Edda''. It is preserved in the Codex Regius manuscript and the AM 748 I 4to fragment. It is spoken through the voice of ''Grímnir'', one of ...
'', Odin allows himself to be held by King Geirröd for eight days and nights and kills him on the ninth after revealing his true identity.
* There are nine daughters of Ægir
A daughter is a female offspring; a girl or a woman in relation to her parents. Daughterhood is the state of being someone's daughter. The male counterpart is a son. Analogously the name is used in several areas to show relations between gro ...
.
* There are nine mothers of Heimdall.
* There are nine great lindworm
The lindworm (''worm'' meaning snake), also spelled lindwyrm or lindwurm, is a mythical creature in Northern and Central European folklore living deep in the forest that traditionally has the shape of a giant serpent monster. It can be seen as a ...
s: Jörmungandr
In Norse mythology, Jörmungandr ( non, Jǫrmungandr, lit=the Vast gand, see Etymology), also known as the Midgard Serpent or World Serpent ( non, Miðgarðsormr), is an unfathomably large sea serpent or worm who dwells in the world sea, encir ...
, Níðhöggr
In Norse mythology, Níðhöggr (''Malice Striker'', in Old Norse traditionally also spelled Níðhǫggr , often anglicized NidhoggWhile the suffix of the name, ''-höggr'', clearly means "striker" the prefix is not as clear. In particular, the ...
, Grábakr, Grafvölluðr, Ofnir, Svafnir, Grafvitni and his sons Góinn and Móinn.
* The god Hermod rode Sleipnir for nine nights on his quest to free Baldr
Baldr (also Balder, Baldur) is a god in Germanic mythology. In Norse mythology, Baldr (Old Norse: ) is a son of the god Odin and the goddess Frigg, and has numerous brothers, such as Thor and Váli. In wider Germanic mythology, the god was ...
from the underworld
The underworld, also known as the netherworld or hell, is the supernatural world of the dead in various religious traditions and myths, located below the world of the living. Chthonic is the technical adjective for things of the underwo ...
.
* The giant Baugi
Baugi (Old Norse: ; "ring-shaped") is a jötunn in Norse mythology. He is brother of Suttungr, the giant from whom Odin obtained the mead of poetry.
Name
The Old Norse name ''Baugi'' has been translated as 'ring-shaped'.
Attestations
The name ...
had nine thralls who killed each other in their desire to possess Odin's magical sharpening stone
Sharpening stones, or whetstones, are used to sharpen the edges of steel tools such as knives through grinding and honing.
Such stones come in a wide range of shapes, sizes, and material compositions. They may be flat, for working flat edg ...
.
* The god Njord and his wife Skadi decided to settle their argument over where to live by agreeing to spend nine nights in Thrymheim and nine nights at Nóatún.
* The giant Thrivaldi has nine heads.
* The clay giant Mokkurkalfi measured nine leagues high and three broad beneath the arms.
* When Odin sacrificed himself to himself, he hung upon the gallows
A gallows (or scaffold) is a frame or elevated beam, typically wooden, from which objects can be suspended (i.e., hung) or "weighed". Gallows were thus widely used to suspend public weighing scales for large and heavy objects such as sacks ...
of Yggdrasill for nine days and nights. In return, he secured rúnar 'runes, secret knowledge'.
* The valknut symbol is three interlocking triangles forming nine points.
* There are nine surviving deities of Ragnarök, including Baldr and Hödr, Magni and Modi, Vidar and Váli
In Norse mythology, Váli (Old Norse: ) is a God and the son of the god Odin and the giantess Rindr. Váli has numerous brothers including Thor, Baldr, and Víðarr. He was born for the sole purpose of avenging Baldr, and does this by killing ...
, Hoenir, the daughter of Sól and a ninth "powerful, mighty one, he who rules over everything".This last being from ''Völuspá'', who will "come from on high", is found only in the '' Hauksbók'' manuscript. Some scholars, including , consider this to be a later Christian interpolation and a reference to the Last Judgment
The Last Judgment, Final Judgment, Day of Reckoning, Day of Judgment, Judgment Day, Doomsday, Day of Resurrection or The Day of the Lord (; ar, یوم القيامة, translit=Yawm al-Qiyāmah or ar, یوم الدین, translit=Yawm ad-Dīn, ...
.
See also
*Numerology
Numerology (also known as arithmancy) is the belief in an occult, divine or mystical relationship between a number and one or more coinciding events. It is also the study of the numerical value, via an alphanumeric system, of the letters in ...
* Rök Stone
Notes
References
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Numbers In Germanic Paganism Germanic paganism Germanic paganism and mythology lists Language and mysticism Norse mythology Numerology