Novempopulania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
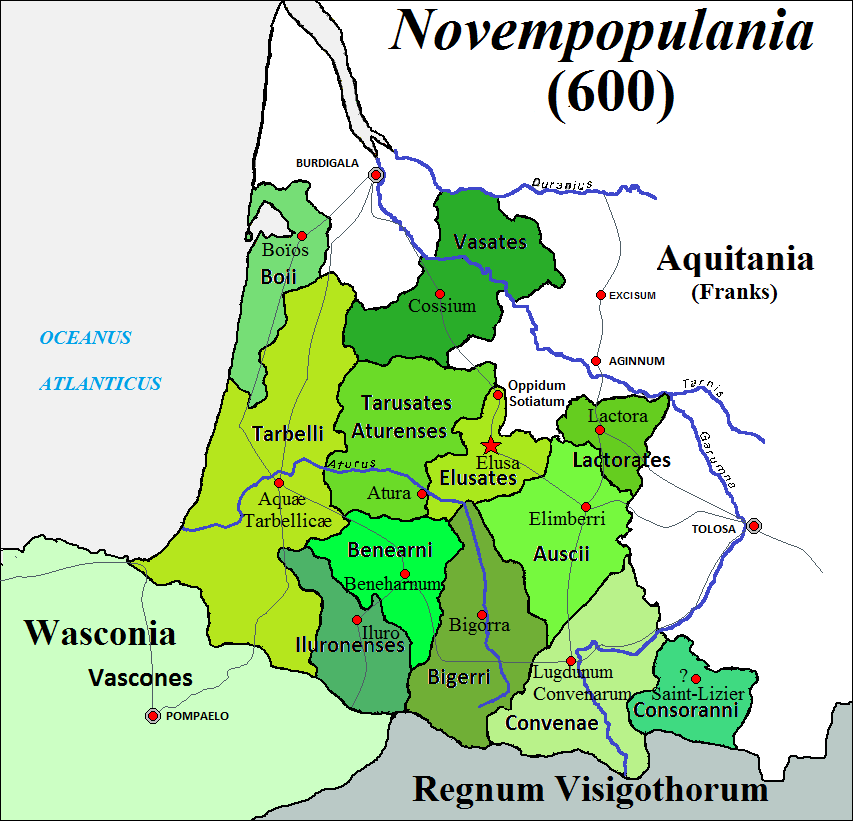 Novempopulania (
Novempopulania (
 Novempopulania (
Novempopulania (Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
for "country of the nine peoples") was one of the provinces created by Diocletian
Diocletian (; la, Gaius Aurelius Valerius Diocletianus, grc, Διοκλητιανός, Diokletianós; c. 242/245 – 311/312), nicknamed ''Iovius'', was Roman emperor from 284 until his abdication in 305. He was born Gaius Valerius Diocles ...
(Roman emperor from 284 to 305) out of Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gal ...
, which was also called ''Aquitania Tertia''.
Early Roman period
The area of Novempopulania was first named ''Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gal ...
'', as it was where the Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region '' Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such ...
dwelt. The territory extended within the triangular area outlined by the River Garonne
The Garonne (, also , ; Occitan, Catalan, Basque, and es, Garona, ; la, Garumna
or ) is a river of southwest France and northern Spain. It flows from the central Spanish Pyrenees to the Gironde estuary at the French port of Bordeaux – ...
, the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
and the Bay of Biscay
The Bay of Biscay (), known in Spain as the Gulf of Biscay ( es, Golfo de Vizcaya, eu, Bizkaiko Golkoa), and in France and some border regions as the Gulf of Gascony (french: Golfe de Gascogne, oc, Golf de Gasconha, br, Pleg-mor Gwaskogn), ...
, as described by Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC – 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, an ...
in his ''Commentarii de Bello Gallico
''Commentarii de Bello Gallico'' (; en, Commentaries on the Gallic War, italic=yes), also ''Bellum Gallicum'' ( en, Gallic War, italic=yes), is Julius Caesar's firsthand account of the Gallic Wars, written as a third-person narrative. In it C ...
'' for Gallia Aquitania
Gallia Aquitania ( , ), also known as Aquitaine or Aquitaine Gaul, was a province of the Roman Empire. It lies in present-day southwest France, where it gives its name to the modern region of Aquitaine. It was bordered by the provinces of Gal ...
. In his work, Caesar describes the Aquitania as being different in language and body make-up from their northerly neighbours and more similar to the Celtiberians
The Celtiberians were a group of Celts and Celticized peoples inhabiting an area in the central-northeastern Iberian Peninsula during the final centuries BCE. They were explicitly mentioned as being Celts by several classic authors (e.g. Strab ...
. The province of Aquitania was enlarged by Augustus
Caesar Augustus (born Gaius Octavius; 23 September 63 BC – 19 August AD 14), also known as Octavian, was the first Roman emperor; he reigned from 27 BC until his death in AD 14. He is known for being the founder of the Roman Pr ...
, and it began to signify a larger and more diverse territory.
Late antiquity
The name Novempopulania stands for the nine peoples making up the original territory (Aquitania Tertia). It seems clear that at the time of the lower empire (2nd to 4th century), the nine peoples were granted by the emperor the right to detach from theGauls
The Gauls ( la, Galli; grc, Γαλάται, ''Galátai'') were a group of Celtic peoples of mainland Europe in the Iron Age and the Roman period (roughly 5th century BC to 5th century AD). Their homeland was known as Gaul (''Gallia''). They sp ...
proper (Celts) by means of the ''magister pagi'' Verus Flamen Dumvir and, as a result, a celebrating altar was erected which was dedicated to the deity of the pagus
In ancient Rome, the Latin word (plural ) was an administrative term designating a rural subdivision of a tribal territory, which included individual farms, villages (), and strongholds () serving as refuges, as well as an early medieval geogra ...
. This fact is accounted for by the remains of the altar unearthed in the current Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
town of Hasparren
Hasparren (; eu, Hazparne) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department in south-western France. A resident of Hasparren is known as a 'Hazpandar'.
Geography Location
It's a ''commune fait partie'' of the Basque Province of Labou ...
.
The newly acquired status may have affected not only the tax system but the conscription and military order too, since two separate bodies were created within Aquitania, i.e. the "Cohortes Aquitanorum" for old Aquitanians and "Cohortes Aquitanorum Biturigum" for those of proper Gaulish
Gaulish was an ancient Celtic language spoken in parts of Continental Europe before and during the period of the Roman Empire. In the narrow sense, Gaulish was the language of the Celts of Gaul (now France, Luxembourg, Belgium, most of Switze ...
origin.
The number of peoples went on to be twelve later, the tribes being identified with a corresponding capital town or ''civitas'', namely Civitas Ausciorum, Civ. Aquensium, Civ. Lactoratium, Civ. Convenarum, Civ. Consorannorum, Civ. Boatium, Civ. Benarnensium, Civ. Aturensium, Civ. Vasatica, Civ. Turba, Civ. Illoronensium and Civ. Elusatium. These civitas are in turn identifiable with present-day towns and cities as follows: Auch
Auch (; oc, label= Gascon, Aush ) is a commune in southwestern France. Located in the region of Occitanie, it is the capital of the Gers department. Auch is the historical capital of Gascony.
Geography
Localization
Hydrography
The ...
, Dax, Lectoure
Lectoure (; Gascon: ''Leitora'' ) is a commune in the Gers department in the Occitanie region in southwestern France.
It is located north of Auch, the capital of the department, south of Agen and approximately northwest of Toulouse.
Geogr ...
, Comminges
The Comminges (; Occitan/ Gascon: ''Comenge'') is an ancient region of southern France in the foothills of the Pyrenees, corresponding closely to the arrondissement of Saint-Gaudens in the department of Haute-Garonne. This natural region is nor ...
, Couserans
125px, Coat of arms of CouseransCouserans (; Gascon: ''Coserans'' ) is a small former province of France located in the Pyrenees mountains. Today Couserans makes up the western half of the Ariège ''département'', around the towns of Saint-Gir ...
, Buch
Buch (the German word for book or a modification of the German word '' Buche'' for beech) may refer to:
People
* Buch (surname), a list of people with the surname Buch Geography
;Germany:
* Buch am Wald, a town in the district of Ansbach, Bavaria ...
and Born, Béarn
The Béarn (; ; oc, Bearn or ''Biarn''; eu, Bearno or ''Biarno''; or ''Bearnia'') is one of the traditional provinces of France, located in the Pyrenees mountains and in the plain at their feet, in southwest France. Along with the three B ...
or Lescar
Lescar (; oc, Lescar) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department and Nouvelle-Aquitaine region of south-western France.
Lescar is the site of the Roman city known variously as Benearnum, Beneharnum or Civitas Benarnensium, the lo ...
, Aire-sur-l'Adour
Aire-sur-l'Adour (; oc, Aira d'Ador or simply ) is a commune in the Landes department, Nouvelle-Aquitaine, southwestern France.
It lies on the river Adour in the wine area of southwest France. It is an episcopal see of the Diocese of Aire and ...
, Bazas, Tarbes
Tarbes (; Gascon: ''Tarba'') is a commune in the Hautes-Pyrénées department in the Occitanie region of southwestern France. It is the capital of Bigorre and of the Hautes-Pyrénées. It has been a commune since 1790. It was known as ''Turba'' ...
, Oloron
Oloron-Sainte-Marie (; oc, Auloron e Senta Maria; eu, Oloroe-Donamaria) is a commune in the Pyrénées-Atlantiques department, region of Nouvelle-Aquitaine (before 2015: Aquitaine), southwestern France.
History
The town was founded by the ...
, Eauze. Elusa ( Eauze) remained the capital city of Novempopulania throughout most of its existence.
Wide evidence of stone inscriptions have been found scattered all over the area which constitutes Novempopulania. These recordings feature names of deities, persons and places with easily identifiable similarities to present-day Basque, a fact that provides, along with current and ancient place-names north of the Pyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
(e.g. ''Illiberris'' mentioned by Ptolemy on the eastern fringes of Novempopulania) and traces of Basque in the Gascon language (especially in the Béarnese dialect
Béarnese ( endonym or ) designates the whole of the Occitano-Romance languages of Béarn.
Linguistics does not distinguish Béarnese from Gascon; these languages form a homogeneous whole within the Pyrenees- Atlantic-Garonne triangle. The o ...
), the basis for an Aquitanian proto-Basque
Proto-Basque ( eu, aitzineuskara; es, protoeuskera, protovasco; french: proto-basque), or Pre-Basque, is the reconstructed predecessor of the Basque language before the Roman conquests in the Western Pyrenees.
Background
The first linguist w ...
theory.
In 418, in the stir of the crumbling rule of the Roman Empire and its territories overrun by Germanic tribes, emperor Honorius allocated Aquitania to the Visigoths
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is k ...
as ''foederati'', with their tribes settling on the fringes of Novempopulania at both banks of the River Garonne
The Garonne (, also , ; Occitan, Catalan, Basque, and es, Garona, ; la, Garumna
or ) is a river of southwest France and northern Spain. It flows from the central Spanish Pyrenees to the Gironde estuary at the French port of Bordeaux – ...
as far south as Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
, where they established their seat. Other than this, their power tenure over Novempopulania may have been more nominal than real. Furthermore, after the 507 Battle of Vouille, they were expelled from the area by the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
.
Accounts of events taking place at that time on the territory of Novempopulania are confusing and blurred, and so are the names of the peoples and their geographical locations, who are as of now dubbed ''Vascones'', ''Wasconia'', ''Guasconia'' (as opposed to the ''Spanoguasconia'', according to the Ravenna Cosmography) with no clear boundaries. At that point, Vascones
The Vascones were a pre-Roman tribe who, on the arrival of the Romans in the 1st century, inhabited a territory that spanned between the upper course of the Ebro river and the southern basin of the western Pyrenees, a region that coincides wi ...
had taken on an extended meaning arguably encompassing all Basque-language tribes, different from the more restricted definition provided at the time of Augustus.
The crisis of Late antiquity brought about much unrest and turmoil in Novempopulania, where the bagaudae
Bagaudae (also spelled bacaudae) were groups of peasant insurgents in the later Roman Empire who arose during the Crisis of the Third Century, and persisted until the very end of the Western Empire, particularly in the less-Romanised areas of G ...
and Vascon raids that occurred later on are often mentioned in various documents. Novempopulania was to become the core region of the Duchy of Vasconia, which was established by the Franks at the beginning of the 7th century with a view to holding back the Basque
Basque may refer to:
* Basques, an ethnic group of Spain and France
* Basque language, their language
Places
* Basque Country (greater region), the homeland of the Basque people with parts in both Spain and France
* Basque Country (autonomous co ...
s, but which often conducted a semi-autonomous governance of Basque-Aquitanian background. It later split into the Duchy of Gascony
The Duchy of Gascony or Duchy of Vasconia ( eu, Baskoniako dukerria; oc, ducat de Gasconha; french: duché de Gascogne, duché de Vasconie) was a duchy located in present-day southwestern France and northeastern Spain, an area encompassing the m ...
and the County of Vasconia
The County of Vasconia Citerior (literally, the "nearer Vasconia") was a medieval domain attested as of 824. It may have comprised the lands between the western Pyrenees and the river Adour.
After Pepin the Short's war on Aquitaine, Charlemagne st ...
.
See also
*Aquitani
The Aquitani were a tribe that lived in the region between the Pyrenees, the Atlantic ocean, and the Garonne, in present-day southwestern France in the 1st century BCE. The Romans dubbed this region '' Gallia Aquitania''. Classical authors such ...
* Duchy of Vasconia
*Gascony
Gascony (; french: Gascogne ; oc, Gasconha ; eu, Gaskoinia) was a province of the southwestern Kingdom of France that succeeded the Duchy of Gascony (602–1453). From the 17th century until the French Revolution (1789–1799), it was part ...
*Northern Basque Country
The French Basque Country, or Northern Basque Country ( eu, Iparralde (), french: Pays basque, es, País Vasco francés) is a region lying on the west of the French department of the Pyrénées-Atlantiques. Since 1 January 2017, it constitu ...
* Basque language
References
{{Coord missing, France Basque history Late Roman provinces Provinces of Roman Gaul History of Aquitaine Gascony