Northern Michigan, also known as Northern Lower Michigan (known colloquially to residents of more southerly parts of the state and summer residents from cities such as
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
as "
Up North"), is a region of the
U.S. state
In the United States, a state is a constituent political entity, of which there are 50. Bound together in a political union, each state holds governmental jurisdiction over a separate and defined geographic territory where it shares its sove ...
of
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
. A popular tourist destination, it is home to several small- to medium-sized cities, extensive state and national forests, lakes and rivers, and a large portion of
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
shoreline. The region has a significant seasonal population much like other regions that depend on tourism as their main industry. Northern Lower Michigan is distinct from the more northerly
Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
and
Isle Royale
Isle Royale National Park is an American national park consisting of Isle Royale – known as Minong to the native Ojibwe – along with more than 400 small adjacent islands and the surrounding waters of Lake Superior, in the state of Michigan. ...
, which are also located in "northern" Michigan. In the northernmost 21 counties in the
Lower Peninsula of Michigan
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
, the total population of the region is 506,658 people.
[The largest city is ]Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
. The 4 counties surrounding it make up Traverse City Micropolitan Area
The Traverse City Micropolitan Statistical Area, as defined by the United States Census Bureau, is an area consisting of four counties in Northern Michigan, anchored by the city of Traverse City.
As of the 2020 census, the Traverse City micropol ...
and have a population of 143,372, 7th in nation.
Geography
Boundary description
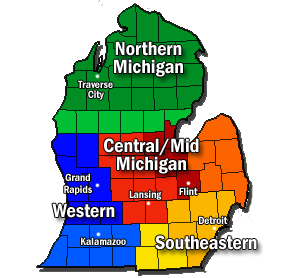
The southern boundary of the region is not precisely defined. Some residents in the southern part of the state consider its southern limit to be just north of
Flint
Flint, occasionally flintstone, is a sedimentary cryptocrystalline form of the mineral quartz, categorized as the variety of chert that occurs in chalk or marly limestone. Flint was widely used historically to make stone tools and sta ...
,
Port Huron
Port Huron is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of St. Clair County. The population was 30,184 at the 2010 census. The city is adjacent to Port Huron Township but is administered separately.
Located along the St. Clair ...
, and
Grand Rapids, but more northern residents restrict it to the area north of
Mount Pleasant: the "fingers" of the mitten-like shape of the
Lower Peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
. The
45th parallel runs across Northern Michigan. Signs in the Lower Peninsula that mark that line are at
Mission Point Light
Mission Point Light is a lighthouse located in the U.S. state of Michigan at the end of Old Mission Point, a peninsula jutting into Grand Traverse Bay north of Traverse City. When it was built in 1870, it was an exact copy of the Mama Juda Ligh ...
(just north of
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
);
Suttons Bay; Cairn Highway in
Kewadin; Alba, Michigan, on U.S. 131 Highway (approximately two miles north of County Road 42, with signs on both sides of the highway);
Gaylord;
Atlanta
Atlanta ( ) is the capital and most populous city of the U.S. state of Georgia. It is the seat of Fulton County, the most populous county in Georgia, but its territory falls in both Fulton and DeKalb counties. With a population of 498,715 ...
; and
Alpena. These are six of 29 places in the U.S.A. where such signs or monuments are known to exist. One other such sign is in
Menominee, Michigan
Menominee ( ) is a city in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 8,599 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Menominee County. Menominee is the fourth-largest city in the Upper Peninsula, behind Marquett ...
, in the
Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
.
Definition excludes the Upper Peninsula
Across the
Straits of Mackinac, to the north, west, and northeast, lies the
Upper Peninsula of Michigan
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
(the "U.P."). Despite its geographic location as the most northerly part of Michigan, the Upper Peninsula is not usually included in the definition of Northern Michigan (although
Northern Michigan University
Northern Michigan University (Northern Michigan, Northern or NMU) is a public university in Marquette, Michigan. It was established in 1899 by the Michigan Legislature as Northern State Normal School. In 1963, the state designated Northern a uni ...
is located in the U.P. city of
Marquette), and is instead regarded by Michigan residents as a distinct region of the state, although residents of the Upper Peninsula often say that "Northern Michigan" is not in the Lower Peninsula. They insist the region must only be referred to as "Northern Lower Michigan", and this can sometimes become a topic of contention between people who are from different Peninsulas. The two regions are connected by the 5-mile-long
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge spanning the Straits of Mackinac, connecting the Upper and Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. Opened in 1957, the bridge (familiarly known as "Big Mac" and "Mighty Mac") is the worl ...
.
Other definitions of Northern Michigan
All of the northern
Lower Peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
– north of a line from
Manistee County
Manistee County is a county located in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 25,032. The county seat is Manistee. The name "Manistee" is from an Ojibwe word first applied to the principal river of the county. Th ...
on the west to
Iosco County on the east (the second orange tier up on the map) – is considered to be part of the
Roman Catholic Diocese of Gaylord.
Topography, climate and soil
The geographical theme of this region is shaped by rolling hills, Great Lakes shorelines including
coastal dunes on the west coast, large inland lakes, numerous rivers and large forests. A
tension zone is identified running from Muskegon to Saginaw Bay marked by a change in soil type and common tree species. North of the line the historic presettlement forests were beech and sugar maple, mixed with hemlock, white pine, and
yellow birch
''Betula alleghaniensis'', the yellow birch, golden birch, or swamp birch, is a large tree and an important lumber species of birch native to northeastern North America. Its vernacular names refer to the golden color of the tree's bark. In the pa ...
which only grew on moist soils further south. Southern Michigan forests were primarily deciduous with oaks, red maple,
shagbark hickory, basswood and cottonwood which are uncommon further north. Northern Michigan soils tend to be coarser, and the growing season is shorter with a cooler climate.
Lake effect weather brings significant snowfalls to snow belt areas of Northern Michigan.
Glaciers shaped the area, creating a unique regional ecosystem. A large portion of the area is the so-called Grayling outwash plain, which consists of broad outwash plain including sandy ice-disintegration ridges; jack pine barrens, some white pine-red pine forest, and northern hardwood forest. Large lakes were created by glacial action.
Weather
The region has the four seasons in their extremes, with sometimes hot and humid summer days (although, mild in comparison to some parts of the
south) to
subzero days in winter. With the expansive
hardwood forest
Temperate broadleaf and mixed forest is a temperate climate terrestrial habitat type defined by the World Wide Fund for Nature, with broadleaf tree ecoregions, and with conifer and broadleaf tree mixed coniferous forest ecoregions.
These fo ...
in Northern Michigan,
"fall color" tourists are found throughout the area in early to mid-autumn. When the spring rains come, many roads and bridges become impassable due to flooding or muddy to the point a
four-wheel drive
Four-wheel drive, also called 4×4 ("four by four") or 4WD, refers to a two-axled vehicle drivetrain capable of providing torque to all of its wheels simultaneously. It may be full-time or on-demand, and is typically linked via a transfer cas ...
cannot pass. Snow fall totals can vary throughout the region due to
lake-effect snow from the
prevailing westerly winds off of
Lake Michigan, with average yearly snow fall of 141.4" (359.2 cm) in
Gaylord to 52.4" (133.1 cm) in
Harrisville. Both the high and low temperature records for all of Michigan are held by communities in Northern Lower Michigan. The high is 112 °F (44 °C) set in
Mio on July 13, 1936 and the low is −51 °F (−46 °C) set in
Vanderbilt on February 9, 1934.
Population






In the northernmost 21 counties in the
Lower Peninsula of Michigan
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
, the total population of the region is 506,658 people.
The most populated city in Northern Michigan is
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
, with over 15 thousand inhabitants. The most populated municipality as a whole in the region is
Garfield Township, with over 19 thousand.
Grand Traverse County, the location of both Traverse City and Garfield Township, is by far the most populated county in Northern Michigan, with a population of over 95,000. The smallest county by population in Northern Michigan is Oscoda County with 8,219 residents in 2020.
The area was populated by many different ethnicities, including groups from
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
(Maine, Vermont, New York),
Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster Scots dialect, Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the Atlantic Ocean, North Atlantic Ocean, in Northwestern Europe, north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel (Grea ...
,
Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, and
Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. The Odawa nation is located in Emmet County (Little Traverse Band of Odawa Indians). Other
Native American reservation
An Indian reservation is an area of land land tenure, held and governed by a federally recognized Tribe (Native American), Native American tribal nation whose government is accountable to the United States Bureau of Indian Affairs and not ...
s exist at Mount Pleasant and on the
Leelanau Peninsula
The Leelanau Peninsula ( ) is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan that extends about from the western side of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan into Lake Michigan. Leelanau County encompasses the entire peninsula. It is often referred to ...
.
Counties
There are 21 counties traditionally associated with Northern Michigan:
In addition to these 21, six more counties to the south are also occasionally referred to as Northern Michigan, but are generally considered to be part of other regions. This counties are:
Cities, villages, and unincorporated communities
Below is a list of cities, villages, and unincorporated communities in northern Michigan:
Tourism
Summer destinations
Boating, golf, and camping are leading activities. Sailing, kayaking, canoeing, birding, bicycling, horse back riding, motorcycling, and 'off roading' are important avocations. The forest activities are available everywhere. There are a great many
Michigan state parks and other protected areas which make these truly a 'pleasant peninsula.' These would include the
Huron National Forest and the
Manistee National Forest
The Manistee National Forest is a national forest located in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It has a total area of . It was established in 1938, and combined with the Huron National Forest in 1945 for administrative purposes, creating the Hur ...
, plus the
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore is a United States National Lakeshore located along the northwest coast of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan in Leelanau and Benzie counties near Empire, Michigan. The park covers a stretch of Lake Michiga ...
(a 35-mile stretch of eastern Lake Michigan dunes) and the
Nordhouse Dunes Wilderness
The Nordhouse Dunes Wilderness is a listed wilderness area within the Manistee National Forest. It is located north of Ludington, Michigan, and is best known for its 4 miles (6.4 km) of undeveloped Lake Michigan shoreline.
Geology
The la ...
.
*Many city dwellers from "downstate" and nearby areas (notably
Chicago
(''City in a Garden''); I Will
, image_map =
, map_caption = Interactive Map of Chicago
, coordinates =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type = Country
, subdivision_name ...
) have summer vacation homes in Northern Michigan. The largest resort cities in Northern Michigan are in the west on
Lake Michigan, with its sandy beaches and warm bays. Popular tourist towns in Northern Michigan include
Northport,
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
,
Elk Rapids,
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
,
Boyne City,
Petoskey,
Manistee,
Ludington,
Bear Lake,
Empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
,
Frankfort,
Harbor Springs, and
Leland. It should also be noted that there is a large wine district in the area along the
Lake Michigan Shore.
*At the top of the
lower peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
are
Mackinaw City, and
Mackinac Island (which lies between the Lower and Upper Peninsulas in the
Straits of Mackinac).
*Less well known and less developed is the northeastern
lower peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
along the
Lake Huron shore. It offers many great vacation spots, particularly along the coast. These are, in order from south-to-north,
Standish,
Omer,
Au Gres,
Tawas City,
East Tawas,
Oscoda,
Greenbush,
Harrisville,
Alpena,
Presque Isle,
Rogers City,
Cheboygan, and points in between. Some consider these to be more 'up north' than the relatively congested west coast. Indeed, the Detroit Free Press noted that the area between Oscoda and Ossineke included beaches that are "overlooked" and among the "top ten in Michigan." This would include the area around Harrisville (and two state parks). It was noted that: "Old-fashioned lake vacations abound on this pretty stretch of Lake Huron."
*In between the two (or three, depending on how you count) coasts, there are a large number of inland cities and lakes (Michigan has 11,037 lakes), and a varied landscape that has many rivers. Such places as
Cadillac,
Kalkaska,
Grayling,
West Branch West Branch may refer to:
Communities
* West Branch, Iowa, city in Cedar and Johnson counties
* West Branch, Michigan, city in Ogemaw County
* West Branch, New Brunswick, in the Local Service District of Weldford Parish
* West Branch River John, i ...
and
Gaylord are also prized summer destinations for Michiganders and visitors from other states. Among many others,
Houghton Lake,
Higgins Lake,
Torch Lake, called Grand Lake (there are at least two in Northern Michigan) and
Hubbard Lake
Hubbard Lake is a lake in Alcona County in Northern Michigan. The lake covers 8,850 acres (36 km²) and is seven miles (11 km) long (north-south) and two miles (3 km) wide. It has a maximum depth of 85 feet (26 m) with an average ...
are large inland lakes within the region.
*The Michigan
Shore to Shore Riding & Hiking Trail runs from
Empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
to
Oscoda, and points north and south. It is a interconnected system of trails.
*The
Great Lakes Circle Tour is a designated scenic road system connecting all of the Great Lakes and the St. Lawrence River.
Non-summer destinations
Some of the
downhill
Downhill may refer to:
Arts and entertainment
* ''Downhill'' (1927 film), a British film by Alfred Hitchcock
* ''Downhill'' (2014 film), a British comedy directed by James Rouse
* ''Downhill'' (2016 film), a Chilean thriller directed by Patrici ...
and
Nordic skiing (cross-country) resorts located in the Northern Lower include
Boyne Mountain
Boyne Mountain Resort is a ski resort with a collection of accommodations in Northern Michigan located near Boyne City operated by Boyne Resorts. The center piece is an upscale resort called The Mountain Grand Lodge and Spa.
Boyne Mountain has c ...
,
Boyne Highlands,
Otsego Club & Resort (since 1939),
Crystal Mountain Resort,
Snow Snake Ski and Golf,
Nub's Nob,
Caberfae Peaks and
Schuss Mountain. Some of these also serve as summer golf resorts.
Frederic, Michigan is a particularly noteworthy center for
cross country skiing
Cross-country skiing is a form of skiing where skiers rely on their own locomotion to move across snow-covered terrain, rather than using ski lifts or other forms of assistance. Cross-country skiing is widely practiced as a sport and recreatio ...
.
Fall activities include
harvest festival
A harvest festival is an annual celebration that occurs around the time of the main harvest of a given region. Given the differences in climate and crops around the world, harvest festivals can be found at various times at different places. ...
s, seasonal beer and wine events, and fall color tours.
Hunting
Hunting is the human practice of seeking, pursuing, capturing, or killing wildlife or feral animals. The most common reasons for humans to hunt are to harvest food (i.e. meat) and useful animal products ( fur/ hide, bone/tusks, horn/antler, ...
in Northern Michigan is a popular fall pastime. There are seasons for bow hunting and a muzzle-loader season as well as for using modern rifle season. The opening day of
deer season (November 15) is a major day for some residents. Some schools close November 15, due to low attendance as a result of the opening day of deer season.
In winter, a variety of sports are enjoyed by the locals which also draw visitors to Northern Michigan.
Snowmobiling
A snowmobile, also known as a Ski-Doo, snowmachine, sled, motor sled, motor sledge, skimobile, or snow scooter, is a motorized vehicle designed for winter travel and recreation on snow. It is designed to be operated on snow and ice and does not ...
, also called sledding, is popular, and with hundreds of miles of interconnected groomed trails cross the region.
Ice fishing
Ice fishing is the practice of catching fish with lines and fish hooks or spears through an opening in the ice on a frozen body of water. Ice fishers may fish in the open or in heated enclosures, some with bunks and amenities.
Shelters
Longe ...
is also popular. Tip-up Town on
Houghton Lake is a major ice-fishing, snowmobiling and winter sports festival, and is unique in that it is a village that assembles out on the frozen lake surface.
Higgins Lake also offers good ice fishing and has many snowmobiling, cross country skiing, and snowshoeing trails at the
North Higgins Lake State Park.
Grayling and
Gaylord and their environs are recognized for Nordic skiing.
Cadillac is reputed to be even more popular during the winter than it is in the summer.
Other tourist attractions
*
Pierce Stocking Scenic Drive
The Pierce Stocking Scenic Drive is a scenic route within Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore, in western Northern Michigan in the United States. The roadway, with its "scenic vistas and gentle curves", is located off state highway M-109 bet ...
*
Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary
Thunder Bay National Marine Sanctuary and Underwater Preserve is a United States National Marine Sanctuary on Lake Huron's Thunder Bay (Michigan), Thunder Bay, within the Northern Michigan, northeastern region of the U.S. state of Michigan. It pr ...
*
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore is a United States National Lakeshore located along the northwest coast of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan in Leelanau and Benzie counties near Empire, Michigan. The park covers a stretch of Lake Michiga ...
*
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge spanning the Straits of Mackinac, connecting the Upper and Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. Opened in 1957, the bridge (familiarly known as "Big Mac" and "Mighty Mac") is the worl ...
*
Boyne Mountain
Boyne Mountain Resort is a ski resort with a collection of accommodations in Northern Michigan located near Boyne City operated by Boyne Resorts. The center piece is an upscale resort called The Mountain Grand Lodge and Spa.
Boyne Mountain has c ...
*
Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac was an 18th-century French, and later British, fort and trading post at the Straits of Mackinac; it was built on the northern tip of the lower peninsula of the present-day state of Michigan in the United States. Built aroun ...
* Many
State Parks
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the sub-national level within those nations which use "state" as a political subdivision. State parks are typically established by a state to preserve a location on account of its natural ...
The
Lumberman's Monument honors lumberjacks that shaped the area, exploiting the natural resource. It is located on the
River Road National Scenic Byway, which runs parallel with the
Au Sable River, and is a designated
National Scenic Byway for the that go into Oscoda. The State of Michigan has designated
Oscoda as the official home of
Paul Bunyan
Paul Bunyan is a giant lumberjack and folk hero in American and Canadian folklore. His exploits revolve around the tall tales of his superhuman labors, and he is customarily accompanied by Babe the Blue Ox. The character originated in the o ...
due to the earliest documented publications in the ''Oscoda Press'', August 10, 1906, by James MacGillivray (later revised and published in ''The Detroit News'' in 1910).
Hartwick Pines State Park is a state park and logging museum located in
Crawford County Crawford County is the name of eleven counties in the United States:
* Crawford County, Arkansas
* Crawford County, Georgia
* Crawford County, Illinois
* Crawford County, Indiana
* Crawford County, Iowa
* Crawford County, Kansas
* Crawford Count ...
near
Grayling and I-75. It is the third largest state park on Michigan's Lower Peninsula and the state's fifth-biggest park overall. The park contains an old growth forest of white pines and red pines that resembles the appearance of all of Northern Michigan prior to the logging era. Also to be noted is
Interlochen State Park
Interlochen State Park is a public recreation area covering between Green Lake and Duck Lake in Grand Traverse County, Michigan. It was the State of Michigan's first officially recognized state park. It was established by the Michigan Legi ...
, which is the oldest state park and the other remaining stand of virgin
Eastern White Pine in the
Lower Peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
.
The
Besser Museum for Northeast Michigan is a community museum serving
Alpena County and surrounding counties in the U.S. state of
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
.
Alpena is a port city on
Lake Huron. The museum defines its role broadly to preserve, protect and present history and culture closely connected with the heritage of Northern Michigan and the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
. The museum includes a small publicly-owned
planetarium.
The institution says "Our mission is to collect, preserve, interpret, and exhibit authentic articles and artifacts of art, history, and science to inspire curiosity, foster community pride, and cultivate personal legacy."
There were more than 150 past and present
lighthouses
A lighthouse is a tower, building, or other type of physical structure designed to emit light from a system of lamps and lenses and to serve as a beacon for navigational aid, for maritime pilots at sea or on inland waterways.
Lighthouses mar ...
around Michigan's
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
coasts, including several in Northern Michigan. They serve as functioning warnings to mariners, but are also integral to the region's culture and history. See
the list of Michigan lighthouses for more information on individual lighthouses.
Festivals
A number of annual festivals occur in Northern Michigan, including:
History
Pre-colonial era: itinerant Native American tribes
For thousands of years before the French and English set up colonies in the region, Northern Michigan was seasonally inhabited by itinerant
Native American cultures and succeeding tribes. Northern Michigan was the southern extent of the area scholars believed occupied by prehistoric inhabitants known as the
Laurel complex. They were part of the Hopewell Indian exchange system, which is named after a prehistoric
tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confli ...
that existed in the
Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canadian–American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadian p ...
.
According to
Menominee
The Menominee (; mez, omǣqnomenēwak meaning ''"Menominee People"'', also spelled Menomini, derived from the Ojibwe language word for "Wild Rice People"; known as ''Mamaceqtaw'', "the people", in the Menominee language) are a federally recog ...
tradition, this tribe's original homeland was farther north, near present-day Sault Ste. Marie and Michilimackinac. At some period before European contact (probably around 1400), they were forced southwest to the
Menominee River
The Menominee River is a river in northwestern Michigan and northeastern Wisconsin in the United States. It is approximately long,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed Dece ...
by arrival of the Ojibwe and Potawatomi from the east.
Odawa history written by
Andrew Blackbird records that
Emmet County was thickly populated by a race of Indians that they called the
Mush-co-desh, which means "the prairie tribe". The Mush-co-desh had an agrarian society and were said to have "shaped the land by making the woodland into prairie as they abandoned their old worn out gardens which formed grassy plains". Ottawa tradition claims that they slaughtered from forty to fifty thousand Mush-co-desh and drove the rest from the land after the Mush-co-desh insulted an Ottawa war party.
In the historic period, the
Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawat ...
/
Algonquian-speaking peoples known as the
Ojibwa,
Potawatomi and
Odawa, formed a loose confederation which they called the
Council of Three Fires
The Council of Three Fires (in oj, label=Anishinaabe, Niswi-mishkodewinan, also known as the People of the Three Fires; the Three Fires Confederacy; or the United Nations of Chippewa, Ottawa, and Potawatomi Indians) is a long-standing Anishina ...
. They inhabited areas surrounding the straits in the upper and lower peninsulas of Michigan as well as in Canada along Lake Huron.
French and English colonial eras: fur trade and exploration based at the Straits
Initial colonial influence on Natives: French exploration and Beaver Wars
In 1608,
Samuel de Champlain established
Quebec
Quebec ( ; )According to the Canadian government, ''Québec'' (with the acute accent) is the official name in Canadian French and ''Quebec'' (without the accent) is the province's official name in Canadian English is one of the thirtee ...
as part of
New France
New France (french: Nouvelle-France) was the area colonized by France in North America, beginning with the exploration of the Gulf of Saint Lawrence by Jacques Cartier in 1534 and ending with the cession of New France to Great Britain and Spa ...
. He sent
coureur des bois such as
Étienne Brûlé
Étienne Brûlé (; – c. June 1633) was the first European explorer to journey beyond the St. Lawrence River into what is now known as Canada. He spent much of his early adult life among the Hurons, and mastered their language and learne ...
into the woods to establish relations with the Indians. Around 1615 or 1616, Champlain traveled to
Georgian Bay
Georgian Bay (french: Baie Georgienne) is a large bay of Lake Huron, in the Laurentia bioregion. It is located entirely within the borders of Ontario, Canada. The main body of the bay lies east of the Bruce Peninsula and Manitoulin Island. To ...
via the
French River and met Ottawa and Huron Indians near
Manitoulin Island
Manitoulin Island is an island in Lake Huron, located within the borders of the Canadian province of Ontario, in the bioregion known as Laurentia. With an area of , it is the largest lake island in the world, large enough that it has over 100 ...
.
The French established the
North American fur trade with Indian tribes. In the decades that followed, French explorers and missionaries continued to explore the
"Upper Country" of New France that included the Upper
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
. In 1634,
Jean Nicolet passed through the straits of Mackinac on the way to Wisconsin. While France colonized the interior lands along the
St. Lawrence River
The St. Lawrence River (french: Fleuve Saint-Laurent, ) is a large river in the middle latitudes of North America. Its headwaters begin flowing from Lake Ontario in a (roughly) northeasterly direction, into the Gulf of St. Lawrence, connecting ...
, the Dutch and English began colonizing the East Coast of North America, setting up fur trade and arming the
Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian-speaking confederacy of First Nations peoples in northeast North America/ Turtle Island. They were known during the colonial years to ...
along the east and southeast of the Great Lakes. Competition for trade and pelts resulted in the brutal
Beaver Wars, as the Iroquois pushed west into the Great Lakes territory, displacing the tribes who had settled there before.
As a result of an Iroquois attack and dispersal of the
Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
from
Southern Ontario
Southern Ontario is a primary region of the province of Ontario, Canada, the other primary region being Northern Ontario. It is the most densely populated and southernmost region in Canada. The exact northern boundary of Southern Ontario is disp ...
in 1649, the Huron settled in
Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
in 1651.
[Fenton, William N.]
KONDIARONK, Le Rat.
''Dictionary of Canadian Biography''. ©2000 University of Toronto/Universite Laval. Web. 21 Feb. 2012. In 1668 the French established a mission at
Sault Ste. Marie. By the conclusion of the Beaver Wars in the 1660s and 1670s, the Potawatami had fled from northern Michigan and
Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawat ...
/
Algonquian(
Ojibwa,
Potawatomi and
Odawa), calling themselves the
Council of Three Fires
The Council of Three Fires (in oj, label=Anishinaabe, Niswi-mishkodewinan, also known as the People of the Three Fires; the Three Fires Confederacy; or the United Nations of Chippewa, Ottawa, and Potawatomi Indians) is a long-standing Anishina ...
, were the main tribal authority in the area.
Jesuit Mission at St. Ignace (1671–1696)

Jesuit
Father Marquette
Jacques Marquette S.J. (June 1, 1637 – May 18, 1675), sometimes known as Père Marquette or James Marquette, was a French Jesuit missionary who founded Michigan's first European settlement, Sault Sainte Marie, and later founded Saint Ign ...
set up a
mission in St. Ignace in 1671. While the Beaver Wars raged on, Marquette evangelized the Indians, planted a large cross in
Cross Village
Cross Village Township is a civil township of Emmet County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the township population was 281.
Communities
* Cross Village is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in the town ...
and established a mission in
L'Arbre Croche
L'Arbre Croche, known by the Odawa people as Waganagisi, was a large Odawa settlement in Northern Michigan. The French called it L'Arbre Croche for the large crocked tree that marked the center of the settlement and was visible for many miles. It c ...
("Crooked Tree"). From May 17, 1673 until Marquette's death near
Ludington on May 18, 1675, Father Marquette and
Louis Jolliet
Louis Jolliet (September 21, 1645after May 1700) was a French-Canadian explorer known for his discoveries in North America. In 1673, Jolliet and Jacques Marquette, a Jesuit Catholic priest and missionary, were the first non-Natives to explore and ...
explored and mapped Lake Michigan and the northern portion of the Mississippi River. In 1679,
René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle and
Father Louis Hennepin
Father Louis Hennepin, O.F.M. baptized Antoine, (; 12 May 1626 – 5 December 1704) was a Belgian Roman Catholic priest and missionary of the Franciscan Recollet order (French: ''Récollets'') and an explorer of the interior of North Amer ...
set out on ''
Le Griffon
''Le Griffon'' (, ''The Griffin'') was a sailing vessel built by René-Robert Cavelier, Sieur de La Salle in 1679.
''Le Griffon'' was constructed and launched at or near Cayuga Island on the Niagara River and was armed with seven cannons. The ...
'' to find the
Northwest Passage
The Northwest Passage (NWP) is the sea route between the Atlantic and Pacific oceans through the Arctic Ocean, along the northern coast of North America via waterways through the Canadian Arctic Archipelago. The eastern route along the Arc ...
; it was the first known sailing ship to sail in Northern Michigan. They sailed across
Lake Erie
Lake Erie ( "eerie") is the fourth largest lake by surface area of the five Great Lakes in North America and the eleventh-largest globally. It is the southernmost, shallowest, and smallest by volume of the Great Lakes and therefore also h ...
,
Lake Huron, and
Lake Michigan through uncharted waters, which previously only men in
canoes
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
had explored. After Marquette's death, the mission was taken over by Father Phillip Pierson, and then
Father Nouvel.
Father Henri Nouvel was "superior of the Ottowa mission", Nouvel served in this position from 1672 to 1680 (with a two-year break in 1678–1679), and again from 1688 to 1695. Under Nouvel, a new chapel was built in approximately 1674. By 1683 the mission was so successful and prosperous that three priests, Fathers Nicholas Potier, Enjalran, and
Pierre Bailloquet, were assigned there.
The establishment of a French garrison at St. Ignace in 1679 disrupted relations between the French and the local population, as the soldiers were less educated and amiable than the missionaries.
1680s: Fortification (Fort de Buade) at St. Ignace
In 1683, Governor
Joseph-Antoine de La Barre ordered
Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut
Daniel Greysolon, Sieur du Lhut ( 1639 – 25 February 1710) was a French soldier and explorer who is the first European known to have visited the area where the city of Duluth, Minnesota, United States, is now located and the head of Lake Superi ...
and
Olivier Morel de La Durantaye to establish a strategic presence on the north shore of the
Straits of Mackinac, which connected
Lake Michigan and
Lake Huron of the Great Lakes. They fortified the Jesuit mission at St. Ignace and
La Durantaye settled in as overall commander of the French forts in the northwest:
Fort Saint Louis des Illinois (
Utica, Illinois);
Fort Kaministigoya (
Thunder Bay, Ontario
Thunder Bay is a city in and the seat of Thunder Bay District, Ontario, Canada. It is the most populous municipality in Northwestern Ontario and the second most populous (after Greater Sudbury) municipality in Northern Ontario; its population ...
); and
Fort la Tourette (
Lake Nipigon, Ontario
Animbiigoo Zaagi'igan Anishinaabek First Nation is an Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According t ...
). He was also responsible for the region around Green Bay in present-day Wisconsin. In the spring of 1684, La Durantaye led a relief expedition from Saint Ignace to Fort Saint Louis des Illinois, which had been besieged by the
Seneca
Seneca may refer to:
People and language
* Seneca (name), a list of people with either the given name or surname
* Seneca people, one of the six Iroquois tribes of North America
** Seneca language, the language of the Seneca people
Places Extrat ...
(part of the Iroquois Confederacy) as part of the
Beaver Wars; they sought to gain more hunting grounds in order to control the lucrative fur trade. That summer and again in 1687, La Durantaye led
coureurs de bois
A coureur des bois (; ) or coureur de bois (; plural: coureurs de(s) bois) was an independent entrepreneurial French-Canadian trader who travelled in New France and the interior of North America, usually to trade with First Nations peoples by e ...
and Indians from the Straits against the Seneca homeland in the territory of western upper New York state. During these years, English traders from New York penetrated the Great Lakes and also traded at
Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
. This, and the
outbreak of war between England and France in 1689, led to the new commandant
Louis de La Porte de Louvigny directing construction of Fort de Buade in 1690.
1690s: Cadillac at Fort de Buade; St. Ignace Fort and Mission later abandoned
In the 1690s, commander
Antoine de la Mothe Cadillac used
Fort de Buade as a base of operations to explore and map the Great Lakes. Cadillac left St. Ignace in 1697 and the Jesuits vacated their residence and church by 1705.
The Beaver Wars ended when the
Great Peace of Montreal
The Great Peace of Montreal (french: La Grande paix de Montréal) was a peace treaty between New France and 39 First Nations of North America that ended the Beaver Wars. It was signed on August 4, 1701, by Louis-Hector de Callière, governor of ...
was signed in 1701 in Montreal by the French and 39 Indian chiefs including
Kondiaronk
Kondiaronk (c. 1649–1701) (Gaspar Soiaga, Souojas, Sastaretsi), known as ''Le Rat'' (The Rat), was Chief of the Native American Wendat people at Michilimackinac in New France. As a result of an Iroquois attack and dispersal of the Hurons in 16 ...
(the chief of the Mackinaw-area
Huron
Huron may refer to:
People
* Wyandot people (or Wendat), indigenous to North America
* Wyandot language, spoken by them
* Huron-Wendat Nation, a Huron-Wendat First Nation with a community in Wendake, Quebec
* Nottawaseppi Huron Band of Potawatomi ...
). When
Antoine Laumet de La Mothe, sieur de Cadillac left the area in 1701 to found
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, taking many of the St. Ignace residents with him, the importance of the mission declined dramatically.
Early 1700s: Fort Michilimackinac established as a New France outpost
The St. Ignace mission remained open until 1705, when it was abandoned and burned by Father
Étienne de Carheil.
[ and ] It was reopened in 1712, and operated on the north shore of the Straits until 1741, when it was relocated to the south shore.
With the relocation of the mission, the exact location of Marquette's chapel was lost.
In 1712, at the beginning of
a 25-year war between the French and the
Fox tribe, Canadian Governor
Philippe de Rigaud de Vaudreuil
Philippe de Rigaud, Marquis de Vaudreuil (; c. 1643 – 10 October 1725) was a French military officer who served as Governor General of New France (now Canada and U.S. states of the Mississippi Valley) from 1703 to 1725, throughout Queen A ...
sent
Constant le Marchand de Lignery
Constant le Marchand de Lignery, generally known as ''Lignery'' (baptized March 27, 1662 in Charentilly, near Tours, France – February 19, 1732 in Trois-Rivières, New France) was a French military officer in New France (Canada). He was twice ...
to reoccupy the former post of Michilimackinac, which had been abandoned in 1696 by royal orders.
Around 1715 (during the
First Fox War), the French re-established a Northern Michigan military outpost at a new site on the northern tip of the lower peninsula and called it
Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac was an 18th-century French, and later British, fort and trading post at the Straits of Mackinac; it was built on the northern tip of the lower peninsula of the present-day state of Michigan in the United States. Built aroun ...
. This location became the new locus for fur and other trade, and mission work with the natives.
Lignery returned to the command of Michilimackinac in 1722 after an absence of about three years fighting the Fox in Illinois. He carried out the orders of acting Governor
Charles Le Moyne de Longueuil and (starting in 1726) New France governor
Charles de la Boische, Marquis de Beauharnois
Charles de la Boische, Marquis de Beauharnois ( 12 October 1671 – 12 July 1749) was a French Naval officer who served as Governor of New France from 1726 to 1746.
Biography
Son of François IV de Beauharnais, Charles had two brothers wh ...
.
From 1720 to 1722,
Pierre François Xavier de Charlevoix stopped at
Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
and other points in Northern Michigan while seeking a Pacific Ocean passage. In 1728, fur trader
Augustin Langlade obtained a fur trading license at
Michilimackinac
Michilimackinac ( ) is derived from an Ottawa Ojibwe name for present-day Mackinac Island and the region around the Straits of Mackinac between Lake Huron and Lake Michigan.. Early settlers of North America applied the term to the entire region ...
. He and his half-Ottawa son
Charles Michel de Langlade
Charles Michel Mouet de Langlade (9 May 1729 – after 26 July 1801)''Dictionnaire Généalogique Tanguay'' was a Great Lakes fur trader and war chief who was important in protecting French territory in North America. His mother was Ottawa and hi ...
(born at the fort in 1729) would later strongly influence the Northern Michigan fur trade as well as French relations with Great Lakes tribes during the 1712 to 1733
Fox Wars
The Fox Wars were two conflicts between the French and the Fox (Meskwaki or Red Earth People; Renards; Outagamis) Indians that lived in the Great Lakes region (particularly near the Fort of Detroit) from 1712 to 1733.In their book ''The Fox Wars' ...
and the 1754–1763
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
.
By 1745, the Odawa had created settlements down the coast of Lake Michigan into the
Grand Traverse Bay
Grand Traverse Bay is a deep bay of Lake Michigan formed by the Leelanau Peninsula in the northwestern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The bay is long, wide, and up to deep in spots. It is further divided into two east and west arms by the Ol ...
area, with an approximate population between 1,550 and 3,000. This population varied with the seasons, as the tradition was to migrate inland to different camps (sometimes as far as to Illinois) depending upon the season.
Some Ojibwe bands also shared the Grand Traverse Bay region with the Odawa.
In 1751, a Jesuit Mission to the Odawa was established in Manistee.
1760s: Beginning of the British era
In the 1760s after defeating the French in the
French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the ...
(and in the
Seven Years' War
The Seven Years' War (1756–1763) was a global conflict that involved most of the European Great Powers, and was fought primarily in Europe, the Americas, and Asia-Pacific. Other concurrent conflicts include the French and Indian War (175 ...
in Europe), the British took control of the Straits of Mackinac and other French territory east of the Mississippi River. They encountered resistance from the Natives, who rose up in what was called
Pontiac's War
Pontiac's War (also known as Pontiac's Conspiracy or Pontiac's Rebellion) was launched in 1763 by a loose confederation of Native Americans dissatisfied with British rule in the Great Lakes region following the French and Indian War (1754–176 ...
(1763–1766). On June 2, 1763
Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
and
Sauk warriors killed the majority of white residents at
Fort Michilimackinac
Fort Michilimackinac was an 18th-century French, and later British, fort and trading post at the Straits of Mackinac; it was built on the northern tip of the lower peninsula of the present-day state of Michigan in the United States. Built aroun ...
.
Alexander Henry the elder
Alexander is a male given name. The most prominent bearer of the name is Alexander the Great, the king of the Ancient Greek kingdom of Macedonia who created one of the largest empires in ancient history.
Variants listed here are Aleksandar, Al ...
, one of the survivors, was taken captive and transported to Beaver Island but was rescued by the
Odawa ''
Wawatam
Wawatam (''little goose'') ( ''fl.'' 1762 – 1764) was an 18th-century Odawa chief who lived in the northern region of present-day Michigan's Lower Peninsula in an area along the Lake Michigan shoreline known by the Odawa as Waganawkezee (''i ...
''. The British built the more substantial
Fort Mackinac
Fort Mackinac ( ) is a former British and American military outpost garrisoned from the late 18th century to the late 19th century in the city of Mackinac Island, Michigan, on Mackinac Island. The British built the fort during the American Re ...
at the site in 1780.
The success of rebels in the American Revolutionary War led to another change in parties in the region. Great Britain formally ceded
Fort Mackinac
Fort Mackinac ( ) is a former British and American military outpost garrisoned from the late 18th century to the late 19th century in the city of Mackinac Island, Michigan, on Mackinac Island. The British built the fort during the American Re ...
at
Mackinac Island to the newly independent
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
in the
Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
in 1783, but the
British Army
The British Army is the principal land warfare force of the United Kingdom, a part of the British Armed Forces along with the Royal Navy and the Royal Air Force. , the British Army comprises 79,380 regular full-time personnel, 4,090 Gurk ...
refused to evacuate the posts on the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
until 1796. At that time, they transferred the forts at
Detroit
Detroit ( , ; , ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is also the largest U.S. city on the United States–Canada border, and the seat of government of Wayne County. The City of Detroit had a population of 639,111 at t ...
, Mackinac, and
Niagara to the Americans. British and American forces contested the area again throughout the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
. The boundary was not settled until 1828, when Fort Drummond, a British post on nearby
Drummond Island
Drummond may refer to:
Places Antarctica
* Drummond Peak, King Edward VII Land
* Drummond Glacier, Graham Land
Canada
* Drummond (electoral district), a Quebec federal riding
* Drummond (provincial electoral district), Quebec
* Drummon ...
, was evacuated.
1780s to 1830s: United States territorial acquisition, continued fur trade, and territorial disputes
The entire Straits area was officially acquired by the United States from the British through the
Treaty of Paris Treaty of Paris may refer to one of many treaties signed in Paris, France:
Treaties
1200s and 1300s
* Treaty of Paris (1229), which ended the Albigensian Crusade
* Treaty of Paris (1259), between Henry III of England and Louis IX of France
* Trea ...
in 1783 and settlement permitted by the
Northwest Ordinance of 1787. However, much of the British forces did not leave the Great Lakes area until after 1794, when
Jay's Treaty
The Treaty of Amity, Commerce, and Navigation, Between His Britannic Majesty and the United States of America, commonly known as the Jay Treaty, and also as Jay's Treaty, was a 1794 treaty between the United States and Great Britain that averted ...
established U.S. sovereignty over the
Northwest Territory with Northern Michigan part of
"Knox County". Between 1795 and 1815 a system of
Métis (descendants of indigenous women who married French (and later Scottish) fur trappers and traders) settlements and trading posts was established throughout Michigan, Wisconsin, and to a lesser extent in Illinois and Indiana. As late as 1829 the Métis were dominant in the economy of Wisconsin and influential in Northern Michigan in part because they were able to work as intermediaries between natives and white fur traders. US settlement of the
Michigan Territory (established in 1805) was punctuated by misunderstandings with Native Americans over land ownership. Meanwhile, in 1804, Mackinac Island was the center of the American fur trade.
Gurdon Saltonstall Hubbard was one of many of
John Jacob Astor
John Jacob Astor (born Johann Jakob Astor; July 17, 1763 – March 29, 1848) was a German-American businessman, merchant, real estate mogul, and investor who made his fortune mainly in a fur trade monopoly, by History of opium in China, smuggl ...
's trappers and
voyageurs
The voyageurs (; ) were 18th and 19th century French Canadians who engaged in the transporting of furs via canoe during the peak of the North American fur trade. The emblematic meaning of the term applies to places (New France, including th ...
who plied the waters of the Great Lakes in
Mackinaw boats and collected pelts to be sold in Europe. As US Congress passed
trade and intercourse acts to regulate trade with the natives, the
Office of Indian Trade established a
US Trading Post "factory" at Mackinaw that was in place until the War of 1812. One of the first engagements of the
War of 1812
The War of 1812 (18 June 1812 – 17 February 1815) was fought by the United States, United States of America and its Indigenous peoples of the Americas, indigenous allies against the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland, United Kingdom ...
, the
Siege of Fort Mackinac was conducted by
British
British may refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* British people, nationals or natives of the United Kingdom, British Overseas Territories, and Crown Dependencies.
** Britishness, the British identity and common culture
* British English, ...
and
Native American. They captured the island soon after the outbreak of war between Britain and the
United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
. Encouraged by the easy British victory, more Native Americans subsequently rallied to their support. Native American cooperation was an important factor in several British victories during the remainder of the war. For the rest of 1812 and 1813, the British hold on Mackinac was secure since they also held
Detroit, the territorial capital, which the Americans would have to recapture before attacking Mackinac. After the September 1813
Battle of Lake Erie
The Battle of Lake Erie, sometimes called the Battle of Put-in-Bay, was fought on 10 September 1813, on Lake Erie off the shore of Ohio during the War of 1812. Nine vessels of the United States Navy defeated and captured six vessels of the Briti ...
, the
British abandoned Detroit leaving an opportunity for the Americans try to retake the waters of Northern Michigan. In July 1814, as Commander of Fort Mackinaw
Robert McDouall
Major-General Robert McDouall, CB (March 1774 – 15 November 1848) was a Scottish-born officer in the British Army, who saw much action during the Napoleonic Wars and the Anglo-American War of 1812. He is best known for serving as the command ...
was struggling to supply war efforts
Siege of Prairie du Chien
The siege of Prairie du Chien was a British victory in the far western theater of the War of 1812. During the war, Prairie du Chien was a small frontier settlement with residents loyal to both American and British causes. By 1814, both nations w ...
, Americans attacked Mackinaw in July 1814 during the
Battle of Mackinac Island
The Battle of Mackinac Island (pronounced ''Mackinaw'') was a British victory in the War of 1812. Before the war, Fort Mackinac had been an important American trading post in the straits between Lake Michigan and Lake Huron. It was important for ...
. The Americans failed to take over the post, and the British held Mackinac Island until the peace in 1815, after which it was re-occupied by the US.
Mackinac Island continued to be a locus of trade for the
American Fur Company and was the site where Army doctor
William Beaumont
William Beaumont (November 21, 1785 – April 25, 1853) was a surgeon in the U.S. Army who became known as the "Father of Gastric Physiology" following his research on human digestion. became Post surgeon in 1820 and began conducting his famous digestion experiments on 19-year-old
Alexis St. Martin between 1822 and 1833. Mackinac Island was also the site where
Henry Schoolcraft
Henry Rowe Schoolcraft (March 28, 1793 – December 10, 1864) was an American geographer, geologist, and ethnologist, noted for his early studies of Native American cultures, as well as for his 1832 expedition to the source of the Mississippi R ...
located his
US Indian Agent headquarters starting in 1833. Following the 1830
Indian Removal Act
The Indian Removal Act was signed into law on May 28, 1830, by United States President Andrew Jackson. The law, as described by Congress, provided "for an exchange of lands with the Indians residing in any of the states or territories, and for ...
, Schoolcraft negotiated the 1836
Treaty of Washington which opened up the land north of Grand Rapids for unequivocal legal ownership and settlement of lands in Northern Michigan, with provision that land sales would provide some monetary means to fund skills training for the Natives to assimilate to "civilized" life.
Despite the presence of fur trade, US military and Indian offices, and various tradesmen, the settled population of Michilimackinac (defined as all the settlements from Saginaw to Green Bay) was between 800 and 1000 for the time period between 1820 and 1840.
Early coastal settlements in the 1830s through 1850s
Decline of Mackinaw and fur trade
By the 1840s, the
American Fur Company was in steep decline as
silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
hats replaced
beaver hats in European fashion. The straits of Mackinac declined in influence as government offices moved towards the capital at Detroit. While fishing slightly increased, the loss of the fur industry dealt a blow to Michilimackinac's economic significance.
Increased ship traffic along Northern Michigan coasts
The
Erie Canal
The Erie Canal is a historic canal in upstate New York that runs east-west between the Hudson River and Lake Erie. Completed in 1825, the canal was the first navigable waterway connecting the Atlantic Ocean to the Great Lakes, vastly reducing t ...
opened in 1825, allowing settlers from
New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York (state), New York to the west and by the Can ...
and New York to reach Michigan by water through
Albany and
Buffalo. This route opening and the incorporation of Chicago in 1837, increased
Great Lakes steamboat traffic from Detroit through the straits of Mackinac to Chicago. While the coastal areas were travelled, practically nothing was known about the interior parts of Northern Michigan. When Michigan became a state in 1837, one of its first acts was to name
Douglass Houghton
Douglass Houghton (September 21, 1809 – October 13, 1845) was an American geologist and physician, primarily known for his exploration of the Keweenaw Peninsula of Michigan. It was the site of a copper boom and extensive copper mining beginnin ...
as the lead of the
Michigan Geological Survey
The Michigan Geological Survey is a scientific agency of the U.S. state of Michigan. The survey is headed by the State Geologist of Michigan.
The survey has been composed of three individual surveys: the first from 1837 through 1845, the second fr ...
, an effort to understand the geological and mineralogical, zoological, botanical, and topographical aspects of the lesser known parts of Michigan. Early settlers came to the coasts along Northern Michigan, including fishermen, missionaries to the Native Americans, and participants in early Great Lakes maritime industries such as fishing, lighthouses, and cutting cordwood for passing ships. In 1835, Lieutenant Benjamin Poole of the
3rd U.S. Artillery.
surveyed a former Indian path between
Saginaw
Saginaw () is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the seat of Saginaw County. The city of Saginaw and Saginaw County are both in the area known as Mid-Michigan. Saginaw is adjacent to Saginaw Charter Township and considered part of Greater ...
and Mackinac that would become known as the
Mackinac Trail.
Indian missions
Missions to Native Americans included Rev. Peter Dougherty and Rev. John Fleming's 1839 Presbyterian mission on the
Old Mission Peninsula
Peninsula Township is a civil township of Grand Traverse County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the township population was 6,068, up from 5,433 at the 2010 census. The township is coterminous with the Old Mission Peninsul ...
,
William Montague Ferry
William Montague Ferry Sr. (September 8, 1796 – December 30, 1867) was a Presbyterian minister, missionary, and community leader who founded several settlements in Ottawa County, Michigan. He became known as the father of Grand Haven and fathe ...
's Presbyterian-affiliated 1825
Mission House
The Mission House at Kerikeri in New Zealand was completed in 1822 as part of the Kerikeri Mission Station by the Church Missionary Society, and is New Zealand's oldest surviving building. It is sometimes known as Kemp House.
Samuel Marsden est ...
/
Mission Church on Mackinac Island,
Magdelaine Laframboise
Magdelaine La Framboise (1780–1846), born Marguerite-Magdelaine Marcot,David A. Armour, "MARCOT, MARGUERITE-MAGDELAINE," in ''Dictionary of Canadian Biography,'' vol. 7, University of Toronto/Université Laval, 2003–, accessed September 11, 2 ...
and
Samuel Charles Mazzuchelli
Samuel Charles Mazzuchelli, O.P. (November 4, 1806 – February 23, 1864) was a pioneer Italian Dominican friar and Catholic missionary priest who helped bring the church to the Iowa-Illinois-Wisconsin tri-state area. He founded several parishes ...
's Catholic
Sainte Anne Church on Mackinac Island in 1830,
Frederic Baraga
Irenaeus Frederic Baraga (June 29, 1797 – January 19, 1868; sl, Irenej Friderik Baraga) was a Slovenian Roman Catholic missionary to the United States and a grammarian by and author of Christian poetry and hymns in Native American langua ...
Francis Xavier Pierz
Francis Xavier Pierz ( sl, Franc Pirc or ''Franc Pirec''; german: link=no, Franz Pierz) (November 20, 1785 – January 22, 1880) was a Roman Catholic priest and missionary to the Ottawa and Ojibwe Indians in present-day Michigan, Wisconsin, Ontar ...
and
Ignatius Mrak
Ignatius Mrak (October 16, 1810 – January 2, 1901) was a Slovenian-born American prelate of the Catholic Church who served as Bishop of Saulte Saint Marie and Marquette from 1869 to 1879.
Biography Early life
Ignatius Mrak was born on Octob ...
's Catholic mission to the people of the Chippewa and Ottawa at
L'Arbre Croche
L'Arbre Croche, known by the Odawa people as Waganagisi, was a large Odawa settlement in Northern Michigan. The French called it L'Arbre Croche for the large crocked tree that marked the center of the settlement and was visible for many miles. It c ...
and
Peshawbestown (on the
Leelanau Peninsula
The Leelanau Peninsula ( ) is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan that extends about from the western side of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan into Lake Michigan. Leelanau County encompasses the entire peninsula. It is often referred to ...
), Peter Greensky's Methodist
Greensky Hill church founded near the
Little Traverse Bay in 1844, and an 1848 congregationalist mission founded by Chief Peter Waukazoo and Reverend George Smith in
Northport (on the
Leelanau Peninsula
The Leelanau Peninsula ( ) is a peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan that extends about from the western side of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan into Lake Michigan. Leelanau County encompasses the entire peninsula. It is often referred to ...
). The
Strangite Mormon community move to Beaver Island in 1848 brought additional conflicts as the Mormon leaders sought to enforce laws and restrict use of alcohol on the Beaver Archipelago.
Fishing settlements
Key fishing settlements included "Fishtown" in
Leland, Michigan and the
Beaver Island Archipelago.
Lighthouses
Early
Northern Michigan lighthouses included
Thunder Bay Island Light (1831),
Old Presque Isle Light (1840),
South Manitou Island Lighthouse
South Manitou Island Lighthouse is located on South Manitou Island in Lake Michigan, west of Leland, Michigan. It is in Leelanau County in western Northern Michigan.
History
This is the third lighthouse built on the island. Construction of th ...
(1840),
DeTour Reef Light
The DeTour Reef Light is a non-profit-operated lighthouse marking the southern entrance of the DeTour Passage between the eastern end of Michigan's Upper Peninsula and Drummond Island. The light is an automated active aid to navigation. It mark ...
(1847),
Waugoshance Light
The ruined lighthouse at Waugoshance protects boats from a shoal area at the northern end of Lake Michigan. The lighthouse is located in Emmet County, Michigan, United States, and in U.S. Coast Guard District No. 9. It is about west of Mackina ...
(1851),
Grand Traverse Light
Grand Traverse Light is a lighthouse in the U.S. state of Michigan, located at the tip of the Leelanau Peninsula, which separates Lake Michigan and Grand Traverse Bay. It marks the Manitou passage, where Lake Michigan elides into Grand Traverse ...
(1852),
Tawas Point Light (1853),
Beaver Island Harbor Light (1856),
Beaver Island Head Light (1858), and
Point Betsie Light (1858).
While the
United States Lifesaving Service
The United States Life-Saving ServiceDespite the lack of hyphen in its insignia, the agency itself is hyphenated in government documents including: and was a United States government agency that grew out of private and local humanitarian effort ...
did not establish a system of Great Lakes
Lifeboat stations on the Great Lakes until the 1870s,
[ ] some volunteer stations, such as the
North Manitou Island Lifesaving Station were created as early as 1854.
Tension between White settlement and Native American land claims
In the 1836
Treaty of Washington, Michigan tribes ceded claims to land in Northern Michigan—and opened it to settlement. In the 1840s, Odawa villages lined the Lake Michigan shore, especially from present-day
Harbor Springs to
Cross Village
Cross Village Township is a civil township of Emmet County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the township population was 281.
Communities
* Cross Village is an unincorporated community and census-designated place in the town ...
. The area on the tip of the peninsula was mostly reserved for native tribes by treaty provisions with the U.S. federal government until 1875. Early government had been centered around Mackinac Island and St. Ignace, but between 1840 and 1853, the state broke up this single large
Michilimackinac County and established names and boundaries of about 21 counties across Northern Michigan. This naming and
surveying allowed specific
plat
In the United States, a plat ( or ) (plan) is a cadastral map, drawn to scale, showing the divisions of a piece of land. United States General Land Office surveyors drafted township plats of Public Lands Surveys to show the distance and bea ...
ted lands to be sold at the
Land Office. Increased white immigration and homesteading in Northern Michigan brought difficulties in dispatching of Native American land claims stemming from the treaty of 1836. Bands of Chippewa and Odawa Indians sought redress through the
Treaty of 1855; by this 1855 treaty agreement, lands and payments would be set aside for individual Native American families related to the 1836 treaty, but after this treaty, the US would cease to owe anything ("land, money or other thing guaranteed to them") to Indians or their tribes.
1860s to 1890s: Homestead Act settlements and industrial developments
Increased settlement and establishment of port cities
Now that the land was surveyed and outstanding native land claims eliminated, Northern Michigan settlement increased even further. The
Homestead Act of 1862
The Homestead Acts were several laws in the United States by which an applicant could acquire ownership of government land or the public domain, typically called a homestead. In all, more than of public land, or nearly 10 percent of th ...
brought many Civil War veterans and speculators to Northern Michigan, by making 160 acre tracts of land available for $1.25 an acre. The cutting of wood for passing ships morphed into a full-fledged lumber industry, contributing to the rise of port cities like
Manistee,
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
,
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
, and
Ludington.

1870s: Arrival of rail infrastructure, rampant lumbering and fishing, and economic slowdown
Starting in the 1870s, railroads were built connecting Northern Michigan to larger industrial areas to the south. The
Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad
The Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad at its height provided passenger and freight railroad services between Cincinnati, Ohio, and the Straits of Mackinac in Michigan, USA. The company was formed on January 18, 1854.
Beginnings
After grappl ...
reached Traverse City in December 1872 (via
Walton Junction and
Traverse City Rail Road Company) and reached Petoskey (known up to that point as "
Bear River") in 1873. The
Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad The Flint and Pere Marquette Railroad (F&PM) is a defunct railroad which operated in the U.S. state of Michigan between 1857 and 1899. It was one of the three companies which merged to become the Pere Marquette Railway.
Early history
The F&PM was c ...
completed its terminal at Ludington in 1874. While the
Michigan Central Railroad reached
Otsego County in the fall of 1872, rail investments slowed for several years due to the
financial panic of 1873 and the ensuing
five year economic slowdown.
Cheboygan and Mackinaw City did not have rail service until the early 1880s.
Despite setbacks from the
Great Michigan Fire in 1871 in
Manistee and other lumbering ports, lumbering in Northern Michigan greatly increased. New mechanical tools such as
steam-powered
A steam engine is a heat engine that performs mechanical work using steam as its working fluid. The steam engine uses the force produced by steam pressure to push a piston back and forth inside a cylinder. This pushing force can be tr ...
(versus water-powered) sawmills and
circular saws expanded the ability to process high volumes of lumber quickly.
Narrow-gauge moveable rails made it possible to harvest timber year round, in previously inaccessible places away from rivers. The Michigan lumber market experienced a crash in July 1877 that coincided with the
Great Railroad Strike of 1877
The Great Railroad Strike of 1877, sometimes referred to as the Great Upheaval, began on July 14 in Martinsburg, West Virginia, after the Baltimore and Ohio Railroad (B&O) cut wages for the third time in a year. This strike finally ended 52 day ...
. By 1880 the
Great Lakes region
The Great Lakes region of North America is a binational Canadian–American region that includes portions of the eight U.S. states of Illinois, Indiana, Michigan, Minnesota, New York, Ohio, Pennsylvania and Wisconsin along with the Canadian p ...
would dominate
logging, with
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
producing more lumber than any other state.
The
commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often ...
industry also flourished in the 1880s. By 1881, the rich fishing areas around the Beaver Archipelago led to Beaver Island becoming the largest supplier of fresh-water fish in the United States. By 1886, there was a drastic reduction in the amount of fishing produced, due to overfishing. In 1893, the
Michigan Fish Commission commissioned the University of Nebraska Zoologist
Henry Ward to study the sources of food for Traverse Bay area fish.

The
passenger pigeon
The passenger pigeon or wild pigeon (''Ectopistes migratorius'') is an extinct species of pigeon that was endemic to North America. Its common name is derived from the French word ''passager'', meaning "passing by", due to the migratory habits ...
was hunted in Northern Michigan as a source of food, but by the 1870s, a combination of increased population and economic scarcity led to over-hunting and eventual extinction. The massive flocks of passenger pigeons stopped darkening the skies of Northern Michigan, especially after the last large scale nestings and subsequent slaughters of millions of birds in 1874 and 1878. By this time, large nestings only took place in the north, around the Great Lakes. The last large nesting was in
Petoskey, Michigan, in 1878 (following one in Pennsylvania a few days earlier), where 50,000 birds were killed each day for nearly five months. The surviving adults attempted a second nesting at new sites, but were killed by professional hunters before they had a chance to raise any young. Scattered nestings were reported into the 1880s, but the birds were now weary, and commonly abandoned their nests if persecuted.
1880s: Emergence of resort and vacation industry
Rail connections to the large midwestern cities through rail centers like
Kalamazoo
Kalamazoo ( ) is a city in the southwest region of the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Kalamazoo County. At the 2010 census, Kalamazoo had a population of 74,262. Kalamazoo is the major city of the Kalamazoo-Portage Metropoli ...
led to settlers immigrating and wealthy
resorters establishing summer home associations in
Bay View Association near Petoskey, the
Belvedere Club in Charlevoix, and other lakeside getaways. Starting in 1875 (until 1895) the
Mackinac National Park
Mackinac National Park was a United States national park that existed from 1875 to 1895 on Mackinac Island in northern Michigan, making it the second U.S. national park after Yellowstone National Park. The park was created in response to the gr ...
became the second
National Park in the United States after
Yellowstone National Park
Yellowstone National Park is an American national park located in the western United States, largely in the northwest corner of Wyoming and extending into Montana and Idaho. It was established by the 42nd U.S. Congress with the Yellowst ...
in the
Rocky Mountains
The Rocky Mountains, also known as the Rockies, are a major mountain range and the largest mountain system in North America. The Rocky Mountains stretch in straight-line distance from the northernmost part of western Canada, to New Mexico ...
.
Sport fishing

Sport fishing along the
Au Sable River became a tourist attraction for wealthy sportsmen from Detroit, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Buffalo, Toledo, Indianapolis, and Chicago.
After the
Jackson, Lansing and Saginaw Railroad reached Grayling in the late 1870s, it began to advertise hunting and fishing trips in Crawford County, home of the
arctic grayling
The Arctic grayling (''Thymallus arcticus'') is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family Salmonidae. ''T. arcticus'' is widespread throughout the Arctic and Pacific drainages in Canada, Alaska, and Siberia, as well as the upper Mis ...
.
In the same way, the Grand Rapids and Indiana Railway published a "Guide to the Health, Pleasure, Game and Fishing Resorts of Northern Michigan reached by the Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad" in 1882. In 1880, Ansel Judd Northrup, a lawyer from New York, published a detailed account of his train trip to fish Northern Michigan, and he assessed the Au Sable,
Manistee River
The Manistee River ( '), seldom referred to as the Big Manistee River, runs U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed November 21, 2011 through the northwestern Lower Peninsula o ...
,
Cheboygan River
The Cheboygan River ( ) is a short but significant river in the Lake Huron drainage basin of the U.S. state of Michigan.
in length,U.S. Geological Survey. National Hydrography Dataset high-resolution flowline dataThe National Map, accessed Novemb ...
,
Pigeon River, and
Jordan River for trout and grayling fishing. The state of Michigan, having created a
Board of Fish Commissioners in 1873, stocked rivers with
whitefish,
black bass
Black is a color which results from the absence or complete absorption of visible light. It is an achromatic color, without hue, like white and grey. It is often used symbolically or figuratively to represent darkness. Black and white have o ...
, and non-native species such as
California salmon,
California trout
California Trout is a San Francisco-based 501(c)(3) conservation group with a mission to ensure resilient wild fish in California waters.
California Trout have three conservation initiatives focused on:
* Strongholds
* Source Water Areas
* Wil ...
,
German carp, and
brook trout. The Board of Fish Commissioners created its first fish hatchery at Crystal Springs Creek in
Pokagon, Cass County, Michigan and shipped rail cars full of small fish to streams across Michigan. As the grayling vanished from the Au Sable, Manistee and other rivers, the state propped up the Northern Michigan fishing industry with non-native
brook trout,
brown trout, and
rainbow trout (
steelhead
Steelhead, or occasionally steelhead trout, is the common name of the anadromous form of the coastal rainbow trout or redband trout (O. m. gairdneri). Steelhead are native to cold-water tributaries of the Pacific basin in Northeast Asia and ...
). Ultimately, the
Arctic grayling
The Arctic grayling (''Thymallus arcticus'') is a species of freshwater fish in the salmon family Salmonidae. ''T. arcticus'' is widespread throughout the Arctic and Pacific drainages in Canada, Alaska, and Siberia, as well as the upper Mis ...
that had inhabited much of Northern Michigan was eventually wiped out. The logging practice of using river beds to move logs in the springtime destroyed the breeding grounds for these fish. Before they could recover, non-native sport fish such as
brook trout took over the grayling's habitat and made them disappear from northern Michigan.
Industrial growth and diversification

The effect of rail connections was ultimately transformative; timber and other goods could be produced in the north and shipped to urban markets to the south. Diverse industries developed, such as iron works, tanneries, mills, cement plants, and agricultural enterprises. By 1885, the intense harvesting and export of pine trees led to visible decline in the lumber industry's ability to produce white pine. Logging in Michigan peaked in 1889. Where available, hardwoods and hemlock were harvested, temporarily extending the life of lumbering in the area, especially around East Jordan, the Traverse Bay, and near
Crawford County Crawford County is the name of eleven counties in the United States:
* Crawford County, Arkansas
* Crawford County, Georgia
* Crawford County, Illinois
* Crawford County, Indiana
* Crawford County, Iowa
* Crawford County, Kansas
* Crawford Count ...
.
William Howard White's lumber railroad (
Boyne City, Gaylord & Alpena Railroad Company), David Ward's
Detroit and Charlevoix Railroad, and the
East Jordan and Southern Railroad enabled access to remote timber areas. As lumbering declined, rail lines began to promote Northern Michigan as a "fresh air" resort destination, and the logging companies promoted their cut-over, stump-filled tracts for their agricultural potential.
20th century: resort era
Early resorts
The resort era flourished in lakeside areas of Northern Michigan even as the fishing and lumbering industries experienced slow decline. Historian
Bruce Catton
Charles Bruce Catton (October 9, 1899 – August 28, 1978) was an American historian and journalist, known best for his books concerning the American Civil War. Known as a narrative historian, Catton specialized in popular history, featuring in ...
's memoir ''Waiting for the Morning Train'' (1972) documents his personal experiences of early 20th-century life in a small Northern Michigan town as Michigan's logging era was ending.
Ernest Hemingway
Ernest Miller Hemingway (July 21, 1899 – July 2, 1961) was an American novelist, short-story writer, and journalist. His economical and understated style—which he termed the iceberg theory—had a strong influence on 20th-century f ...
also documented turn-of-the-century life in Northern Michigan through his "
Nick Adams" stories; Hemingway's own parents were resorters, wintering in
Oak Park, Illinois
Oak Park is a village in Cook County, Illinois, adjacent to Chicago. It is the 29th-most populous municipality in Illinois with a population of 54,583 as of the 2020 U.S. Census estimate. Oak Park was first settled in 1835 and later incorporated ...
but summering in the
Windemere cottage on
Walloon Lake
Walloon Lake is a glacier-formed lake located in Charlevoix and Emmet counties, just southwestward from the northern tip of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It is now home to many vacation homes and cottages. Though the end of the west arm of t ...
starting in 1899.
State parks
As lumbering died down, many parts of Northern Michigan returned to their forested state through conservation efforts. The
Huron National Forest was set aside in 1909. and the
Manistee National Forest
The Manistee National Forest is a national forest located in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It has a total area of . It was established in 1938, and combined with the Huron National Forest in 1945 for administrative purposes, creating the Hur ...
was set aside in 1938. State parks were established as well, to include:
*
Interlochen State Park
Interlochen State Park is a public recreation area covering between Green Lake and Duck Lake in Grand Traverse County, Michigan. It was the State of Michigan's first officially recognized state park. It was established by the Michigan Legi ...
(1917)
*
Mitchell State Park (1919)
*
Traverse City State Park (1920)
*
Orchard Beach State Park (1921)
*
Harrisville State Park (1921)
*
Hoeft State Park (1922)
*
Aloha State Park (1923)
*
Straits State Park (1924)
*
South Higgins Lake State Park (1927)
*
Hartwick Pines State Park (1927)
*
Wilderness State Park
Wilderness State Park is a public recreation area bordering Lake Michigan, five miles southwest of Mackinaw City in Emmet County in Northern Michigan. The state park's include of shoreline, diverse forested dune and swale complexes, wetla ...
(1928)
*
Cheboygan State Park
Cheboygan State Park is a public recreation area covering on the shores of Lake Huron in Cheboygan County, Michigan, United States. The state park
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the sub-national level within those ...
(1962)
*
Clear Lake State Park (Michigan) (1966)
*
Petoskey State Park (1970)
*
Rockport State Park (Michigan)
Rockport State Recreation Area is a state park located along the shore of Lake Huron in Alpena and Presque Isle counties in the state of Michigan. It is operated by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources and was established in 2012. The ...
(2012)
*
Leelanau State Park
Leelanau State Park is a public recreation area covering on the Leelanau Peninsula in Leelanau County, Michigan. The state park
State parks are parks or other protected areas managed at the sub-national level within those nations which use ...
(???)
*
Fisherman's Island State Park (???)
*
Burt Lake State Park (???)
*
Tawas Point State Park (???)
*
North Higgins Lake State Park (???)
*
Negwegon State Park (???)
*
Thompson's Harbor State Park (???)
Ski resorts
Hanson Hills in
Grayling was the first
downhill ski
A ski is a narrow strip of semi-rigid material worn underfoot to glide over snow. Substantially longer than wide and characteristically employed in pairs, skis are attached to ski boots with ski bindings, with either a free, lockable, or partial ...
area in Michigan. It opened in 1929 and was served by rail service.
Caberfae Peaks Ski & Golf Resort
Caberfae Peaks ( ) is a downhill ski area located in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan near Cadillac, Michigan. It gets its name from the Gaelic word for "stag's head".
History
Caberfae Peaks' official opening was in January, 1938, making it on ...
near Cadillac opened in 1938 and was served by rail service.
Boyne Mountain Resort
Boyne Mountain Resort is a ski resort with a collection of accommodations in Northern Michigan located near Boyne City operated by Boyne Resorts. The center piece is an upscale resort called The Mountain Grand Lodge and Spa.
Boyne Mountain has c ...
opened in 1948.
Crystal Mountain in
Benzie County
Benzie County ( ) is a county in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 17,970. The county seat is Beulah. The county was initially set off in 1863 and organized in 1869. opened in 1956.
Nub's Nob opened in 1958 near Harbor Springs.
Decline of rail
As passenger railroad usage ended in the 1960s (due in part to increased automobile travel), aggressive promotion of Northern Michigan by local chambers of commerce led to many of the festivals and attractions that bring visitors north even today.
Education
Interlochen Center for the Arts is a notable arts center that offers a high-school-level academy and summer camp near Traverse City. There are also several institutions of
higher education
Higher education is tertiary education leading to award of an academic degree. Higher education, also called post-secondary education, third-level or tertiary education, is an optional final stage of formal learning that occurs after comple ...
in Northern Michigan. Community colleges include
North Central Michigan College
North Central Michigan College (NCMC) is a public community college in Petoskey, Michigan. It was established in 1959 and is Michigan's 12th community college. NCMC has two additional learning centers, one in Gaylord, Michigan and one in Cheboy ...
(NCMC, pronounced "nuck-muck" by locals),
Alpena Community College, Huron Shores Campus-Alpena Community College,
Kirtland Community College
Kirtland Community College is a public community college in Grayling, Michigan.
History
Kirtland was founded in 1966 under the provisions of Michigan's Public Act 188 of 1955, it is the state's largest community college district geographically ...
,
West Shore Community College
West Shore Community College is a public community college in Scottville, Michigan.
History
In 1967 West Shore was established on 365 acres between Ludington and Manistee in Mason County, Michigan. Along with this main campus, West Shore also ...
, and
Northwestern Michigan College
Northwestern Michigan College (NMC) is a public community college in Traverse City, Michigan. Founded in 1951, it enrolls nearly 4,000 students. NMC offers associate degrees and professional certificates, bachelor's degrees through the Great La ...
(NMC) including the
Great Lakes Maritime Academy
The Great Lakes Maritime Academy at Northwestern Michigan College is located on West Grand Traverse Bay in Traverse City, Michigan. The academy was established in 1969 as a Maritime college to train men and women to be licensed mariners on ships ...
, the only U.S. maritime academy on freshwater. Northern Michigan has arguably only one four-year university (depending on the definition of the southern boundary of the region),
Ferris State University
Ferris State University (FSU or Ferris) is a public university with its main campus in Big Rapids, Michigan. It was founded in 1884 and became a public institution in 1950. Ferris is the ninth-largest institutions of higher education by enrol ...
in
Big Rapids. Other nearby universities are in the
Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
(
Northern Michigan University
Northern Michigan University (Northern Michigan, Northern or NMU) is a public university in Marquette, Michigan. It was established in 1899 by the Michigan Legislature as Northern State Normal School. In 1963, the state designated Northern a uni ...
and
Lake Superior State University
Lake Superior State University (colloquially Lake State, Lake Superior State, Soo Tech, and LSSU) is a public college in Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. It is enrolls approximately 2,000 students. Due to its proximity to the Canadian border, and th ...
), as well as
Central Michigan University and
Ferris State University
Ferris State University (FSU or Ferris) is a public university with its main campus in Big Rapids, Michigan. It was founded in 1884 and became a public institution in 1950. Ferris is the ninth-largest institutions of higher education by enrol ...
in the more southern reaches of the state. The University of Michigan runs the
University of Michigan Biological Station
The University of Michigan Biological Station (UMBS) is a research and teaching facility operated by the University of Michigan. It is located on the south shore of Douglas Lake in Cheboygan County, Michigan. The station consists of 10,000 acres ...
out of
Pellston, MI.
Central Michigan University runs the CMU Biological Station on
Beaver Island.
Hillsdale College runs the biological station in
Lake County.
Many four-year universities located downstate offer bachelor's and master's degree programs through Northwestern Michigan College's unique University Center program, located in Traverse City. The University Center, located in Traverse City, is a joint program with Northwestern Michigan College and various universities around the state that allows local students to "attend" universities that offer bachelor's and master's degrees programs not available through NMC, a two-year college, locally without leaving Northern Michigan. NMC supplies the facilities while the senior universities provide the education and endorsement. Universities offering programs here include Michigan State University, Western Michigan University, Central Michigan University, Grand Valley State University, Ferris State University, Spring Arbor University, and others.
Economy
The economy of Northern Michigan is limited by its lower population, few industries and reduced agriculture compared to lower Michigan. Seasonal and tourism related employment is significant. Unemployment rates are generally high. (In June 2007, seven of the ten highest unemployment rates occurred in counties in the Northern Michigan area.
Historically,
Fur trade, lumbering and
commercial fishing
Commercial fishing is the activity of catching fish and other seafood for commercial profit, mostly from wild fisheries. It provides a large quantity of food to many countries around the world, but those who practice it as an industry must often ...
were among the most important industries. The fur trade essentially died out in the 1840s.
Logging is still important but at a mere fraction of its heyday (1860–1910) output. Commercial fishing is a minor activity.
Vacation and tourism
A major draw to Northern Michigan is
tourism
Tourism is travel for pleasure or business; also the theory and practice of touring, the business of attracting, accommodating, and entertaining tourists, and the business of operating tours. The World Tourism Organization defines tourism mor ...
.
Real estate
Real estate is property consisting of land and the buildings on it, along with its natural resources such as crops, minerals or water; immovable property of this nature; an interest vested in this (also) an item of real property, (more general ...
, especially condominiums and summer homes, is another significant source of income. Because money spent in the real estate and tourism market in Northern Michigan is dependent upon visitors from southern Michigan and the Chicago area, the Northern Michigan economy is sensitive to downswings in the
automobile
A car or automobile is a motor vehicle with wheels. Most definitions of ''cars'' say that they run primarily on roads, seat one to eight people, have four wheels, and mainly transport people instead of goods.
The year 1886 is regarde ...
and other industries.
Agriculture

Agriculture is limited by the climate and soil conditions compared to southern regions of the state. However, there are significant
potato
The potato is a starchy food, a tuber of the plant ''Solanum tuberosum'' and is a root vegetable native to the Americas. The plant is a perennial in the nightshade family Solanaceae.
Wild potato species can be found from the southern Unit ...
and
dry bean farms in the east.
Wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from fermented grapes. Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different varieties of grapes and strains of yeasts are m ...
grapes, vegetables and
cherries are produced in the west in the protected
microclimate
A microclimate (or micro-climate) is a local set of atmospheric conditions that differ from those in the surrounding areas, often with a slight difference but sometimes with a substantial one. The term may refer to areas as small as a few squ ...
s around
Grand Traverse Bay
Grand Traverse Bay is a deep bay of Lake Michigan formed by the Leelanau Peninsula in the northwestern Lower Peninsula of Michigan. The bay is long, wide, and up to deep in spots. It is further divided into two east and west arms by the Ol ...
. The Grand Traverse region has two of Michigan's four federally-recognized
wine growing areas. The Grand Traverse Bay area is listed as one of the most endangered agricultural regions in the U.S. as its scenic land is highly sought after for vacation homes.
Heavy industry
Heavy industrial developments are sparse. The northeast corner has an industrial base.
Quarrying and mining
Cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
-making and the mining of
limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
and
gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
for
Portland Cement
Portland cement is the most common type of cement in general use around the world as a basic ingredient of concrete, mortar, stucco, and non-specialty grout. It was developed from other types of hydraulic lime in England in the early 19th ...
are major exports of the area. Charlevoix's Medusa Cement Plant was bought by
Cemex
CEMEX S.A.B. de C.V., known as Cemex, is a Mexican multinational building materials company headquartered in San Pedro, near Monterrey, Mexico. It manufactures and distributes cement, ready-mix concrete and aggregates in more than 50 countries ...
in the 1990s. Alpena is home to the
Lafarge Company's holdings in the world's largest cement plant and is home to Besser Block Co. (
Jesse M. Besser invented concrete block in 1904 and founded the
Besser Block Co. in
Alpena after making the concrete block making machine).
USG Corporation
USG Corporation, also known as United States Gypsum Corporation, is an American company which manufactures construction materials, most notably drywall and joint compound. The company is the largest distributor of wallboard in the United States ...
, also known as United States
Gypsum
Gypsum is a soft sulfate mineral composed of calcium sulfate dihydrate, with the chemical formula . It is widely mined and is used as a fertilizer and as the main constituent in many forms of plaster, blackboard or sidewalk chalk, and drywal ...
Corporation, operates several quarries, including one at
Alabaster
Alabaster is a mineral or rock that is soft, often used for carving, and is processed for plaster powder. Archaeologists and the stone processing industry use the word differently from geologists. The former use it in a wider sense that include ...
, and one in
Rogers City. Rogers City is the locale of the world's largest limestone quarry, which is also used in steel making all along the Great Lakes.
Energy (oil and natural gas)

Northern Michigan has significant
natural gas
Natural gas (also called fossil gas or simply gas) is a naturally occurring mixture of gaseous hydrocarbons consisting primarily of methane in addition to various smaller amounts of other higher alkanes. Low levels of trace gases like carbo ...
reserves along the
Antrim shale formation in northern Michigan. By some estimates it is the 15th largest gas field in the nation. Drilling activity peaked in the late 1980s and early 1990s, In 2014,
Encana
Ovintiv Inc. is a hydrocarbon exploration and production company organized in Delaware and headquartered in Denver, United States. It was founded and headquartered in Calgary, Alberta, under its previous name Encana. It was the largest energy c ...
, the Canadian company who had been drilling in Northern Michigan, sold their mineral rights to
Marathon Oil order to focus on more profitable operations elsewhere. For oil interest, Encana amassed rights for the
Collingwood-Utica Shale (Michigan) between 2008 and 2010, mostly in
Cheboygan,
Kalkaska, Michigan
Kalkaska ( ) is a village in the U.S. state of Michigan. Kalkaska is the county seat and only incorporated community of Kalkaska County, and is considered part of Northern Michigan. The population was 2,132 at the 2020 census, an increase from 2, ...
and
Missaukee counties. The Collingwood layer is two miles below the surface and would require horizontal drilling.
Manufacturing
Alpena has a hardboard manufacturing facility owned by Decorative Panels, International. Nearer to the Lake Michigan shore, Cadillac and Manistee have manufacturing and chemical industries.
Morton Salt
Morton Salt is an American food company producing salt for food, water conditioning, industrial, agricultural, and road/highway use. Based in Chicago, the business is North America's leading producer and marketer of salt. It is a subsidiary of h ...
operates one of the largest salt plants in the world in
Manistee. Also, the
East Jordan Iron Works corporate offices, as well as the original foundry, are located in
East Jordan.
Maritime
A small number of people work on the
Great Lakes freighter
Lake freighters, or lakers, are bulk carrier vessels that operate on the Great Lakes of North America. These vessels are traditionally called boats, although classified as ships.
Since the late 19th century, lakers have carried bulk cargoes of ma ...
s. Adjacent to the
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
Cherry Capital Airport
Cherry Capital Airport is a public use airport located southeast of the central business district of Traverse City in Grand Traverse County, Michigan, United States. It is owned by Grand Traverse and Leelanau counties.. Federal Aviation Adm ...
is a
United States Coast Guard
The United States Coast Guard (USCG) is the maritime security, search and rescue, and law enforcement service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the country's eight uniformed services. The service is a maritime, military, mu ...
air station (CGAS), which is responsible for both maritime and land-based
search and rescue operations in the northern
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
region.
Military
Military presence in Northern Michigan is as follows:
*
Alpena Combat Readiness Training Center in
Alpena, Michigan
Alpena ( ') is the only city in and county seat of Alpena County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 10,483 at the 2010 census. After Traverse City, it is the second most populated city in the Northern Michigan region. The city ...
is run by the
Air National Guard and is co-located with the
Alpena County Regional Airport
Alpena County Regional Airport is a county-owned, public-use, joint civil-military airport in Alpena County, Michigan, United States. The airport is located six nautical miles (7 mi, 11 km) west of the central business distri ...
.
*
Camp Grayling
Camp Grayling is a military training facility located near Grayling, Michigan, primarily in Crawford County, and spread over three counties. Camp Grayling is the main training facility for the Michigan National Guard and is the largest US Nationa ...
near
Grayling, Michigan
Grayling ( ') is a city and the county seat of Crawford County in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the only incorporated community in Crawford County. The population was 1,884 at the 2010 census. The city is surrounded by Grayling Charter Town ...
. Camp Grayling is the largest military installation east of the
Mississippi River
The Mississippi River is the second-longest river and chief river of the second-largest drainage system in North America, second only to the Hudson Bay drainage system. From its traditional source of Lake Itasca in northern Minnesota, it fl ...
, and the nation's largest National Guard training site. It is used by the
U.S. National Guard, as well as active and reserve components of the Army, Navy, Air Force and Marine Corps. Year-round training is conducted on its in
Crawford,
Kalkaska and
Otsego counties. Much of the land (including
Lake Margrethe) is accessible to the public for hunting, fishing, snowmobiling and other recreational uses (when military training is not happening).
*
Wurtsmith Air Force Base
Wurtsmith Air Force Base is a decommissioned United States Air Force base in Iosco County, Michigan. It operated from 1923 until decommissioned in 1993. On January 18, 1994 it was listed as a Superfund due to extensive groundwater contaminatio ...
near
Oscoda closed in 1993 and has been converted to civilian use as
Oscoda-Wurtsmith Airport.
* The Coast Guard has a presence in
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
and
Traverse City
Traverse City ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the county seat of Grand Traverse County, although a small portion extends into Leelanau County. It is the largest city in the 21-county Northern Michigan region. The population was ...
.
Transportation
Transportation by air
Airports serving Northern Michigan include
MBS International Airport
MBS International Airport , located in Freeland, Michigan, is a commercial and general aviation airport serving the nearby cities of Midland, Bay City, and Saginaw. It is included in the Federal Aviation Administration (FAA) National Plan of ...
near
Freeland
Freeland may refer to:
Places Canada
*Freeland, Prince Edward Island
United Kingdom
*Freeland, Oxfordshire
United States
*Freeland, Maryland
*Freeland, Michigan
*Freeland, Ohio
*Freeland, Pennsylvania
*Freeland, Washington
Other uses
*Freel ...
,
Pellston Regional Airport,
Traverse City Cherry Capital Airport and
Alpena County Regional Airport
Alpena County Regional Airport is a county-owned, public-use, joint civil-military airport in Alpena County, Michigan, United States. The airport is located six nautical miles (7 mi, 11 km) west of the central business distri ...
in the
Lower peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
. Depending on one's destination,
Chippewa County International Airport
Chippewa County International Airport is a public use airport in Chippewa County, Michigan, United States. It is located 15 nautical miles (17 mi, 28 km) south of the central business district of Sault Ste. Marie, Michigan. The ...
in
Sault Ste. Marie, in the eastern
Upper peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
might be a viable alternative. Grand Rapids and Bishop airport at Flint (although neither is within the area) also have scheduled service proximate to parts of the region.
The
Oscoda-Wurtsmith Airport is now a public airport which gives 24-hour near-all-weather service for general aviation.
Transportation by water
Several ferries still operate in the region.
*The
SS ''Badger'' carferry
A train ferry is a ship (ferry) designed to carry railway vehicles. Typically, one level of the ship is fitted with railway tracks, and the vessel has a door at the front and/or rear to give access to the wharves. In the United States, train f ...
departs from
Ludington and arrives in
Wisconsin
Wisconsin () is a state in the upper Midwestern United States. Wisconsin is the 25th-largest state by total area and the 20th-most populous. It is bordered by Minnesota to the west, Iowa to the southwest, Illinois to the south, Lake M ...
.
*Ferry service between
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
and
Beaver Island is provided by M/V Emerald Isle, and occasionally, the older M/V Beaver Islander.
*The
Straits of Mackinac is home to lake ferries that take passengers to
Mackinac Island from either
Mackinaw City in the Lower Peninsula or
St. Ignace
St. Ignace is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Mackinac County. The city had a population of 2,452 at the 2010 census. St. Ignace Township is located just to the north of the city, but the two are administered auto ...
in the Upper Peninsula.
*A ferry for tours of
Charity Island in the middle of
Saginaw Bay and the
Charity Island Light (and even dinner cruises) are available. It leaves from
Au Gres on the mainland, south of
Tawas
Tawas City is a city in and county seat of Iosco County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 1,834 at the 2020 census. The city is mostly surrounded by Tawas Township, but the two area administered automously.
History
Tawas City ...
.
*The ''Kristen D'' is a ferry which operates between
Cheboygan and
Bois Blanc Island.
The largest bridge in Northern Michigan is the
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge spanning the Straits of Mackinac, connecting the Upper and Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. Opened in 1957, the bridge (familiarly known as "Big Mac" and "Mighty Mac") is the worl ...
connecting Northern Michigan to the Upper Peninsula. The second largest is the
Zilwaukee Bridge.
Transportation by land
On land, Michigan is a unique travel environment. Consequently, drivers should be forewarned: travel distances should not be underestimated. Michigan's overall length is only and width – but because of the lakes those distances cannot be traveled directly. The distance from northwest to the southeast corner is "as the crow flies". However, travelers must go around the
Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lak ...
. For example, when traveling to the Upper Peninsula, it is well to realize that it is roughly from Detroit to the
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge spanning the Straits of Mackinac, connecting the Upper and Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. Opened in 1957, the bridge (familiarly known as "Big Mac" and "Mighty Mac") is the worl ...
, but it is another from
St. Ignace
St. Ignace is a city in the U.S. state of Michigan and the county seat of Mackinac County. The city had a population of 2,452 at the 2010 census. St. Ignace Township is located just to the north of the city, but the two are administered auto ...
to
Ironwood
Ironwood is a common name for many woods or plants that have a reputation for hardness, or specifically a wood density that is heavier than water (approximately 1000 kg/m3, or 62 pounds per cubic foot), although usage of the name ironwood in E ...
.
Likewise direct routes are few and far between
Interstate 75
Interstate 75 (I-75) is a major north–south Interstate Highway in the Great Lakes and Southeastern regions of the United States. As with most Interstates that end in 5, it is a major cross-country, north–south route, traveling from St ...
(I-75) and
M-115 do angle from the southeast to the northwest), but most roads are oriented either east–west or north–south (oriented with township lines set up under the
Land Ordinance of 1785).
Automobile roads


The primary means of transportation in Northern Michigan is by automobile. Northern Michigan is served by one
Interstate
The Dwight D. Eisenhower National System of Interstate and Defense Highways, commonly known as the Interstate Highway System, is a network of controlled-access highways that forms part of the National Highway System in the United States. Th ...
, and a number of
U.S. Highways and
Michigan state trunklines.
* runs northwest–southeast through the region between the
Flint/Tri-Cities
Central Michigan, also called Mid Michigan, is a region in the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. As its name implies, it is the middle area of the Lower Peninsula. Lower Michigan is said to resemble a mitten, and Mid Michigan corr ...
area and
Mackinac Bridge
The Mackinac Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge spanning the Straits of Mackinac, connecting the Upper and Lower peninsulas of the U.S. state of Michigan. Opened in 1957, the bridge (familiarly known as "Big Mac" and "Mighty Mac") is the worl ...
at
Mackinaw City, which leads on to the
Upper Peninsula
The Upper Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Upper Michigan or colloquially the U.P. – is the northern and more elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; it is separated from the Lower Peninsula by ...
.
* enters
Michigan
Michigan () is a U.S. state, state in the Great Lakes region, Great Lakes region of the Upper Midwest, upper Midwestern United States. With a population of nearly 10.12 million and an area of nearly , Michigan is the List of U.S. states and ...
after it crosses
Lake Michigan from Manitowoc to Ludington. US 10 runs from Ludington through Baldwin and Reed City before it becomes a
freeway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms ...
west of US 127 near the junction with M-115. US 10 bypasses Midland and terminates at I-75 in Bay City.
* runs northward for about along (or parallel with) the
Lake Huron shoreline as the Sunrise Side Coastal Highway from the Flint/Tri-Cities area.
* mainly parallels the Lake Michigan shore from the Ludington area north to Mackinaw City; near Traverse City, the highway cuts the base of the Leelanau Peninsula.
* ends at Grayling, connecting Northern Michigan with points south
* is a primary north–south highway that is a freeway from Manton southwards; north of the freeway terminus, the highway is mostly two lanes, connecting Kalkaska, Mancelona, and ending at US 31 in
Petoskey.
* runs between Midland County, through Prudenville and Roscommon to M-72 in Crawford County.
* follows the Lake Michigan shoreline from Traverse City to Manistee and is a scenic drive along the Leelanau Peninsula and the
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore
Sleeping Bear Dunes National Lakeshore is a United States National Lakeshore located along the northwest coast of the Lower Peninsula of Michigan in Leelanau and Benzie counties near Empire, Michigan. The park covers a stretch of Lake Michiga ...
.
* runs along the old route of
US 27 between Indian River and Cheboygan.
* runs between East Jordan and Alpena.
* runs between Alger (northwest of Standish) and Cheboygan.
* runs from Battle Creek via Grand Rapids to Traverse City and the Old Mission Peninsula.
* is a short route between Manton and M-66 north of Lake City.
* is a transpeninsular highway at the southern edge of the region from Manistee to Tawas City.
* runs northward from Au Gres (just north of Standish) to Rogers City,.
* traverses almost the entire north–south distance of the Lower Peninsula ending at Charlevoix.
* is an east–west state highway that runs from Alanson to Rogers City; it passes through Indian River, Afton, Tower, and Onaway.
* crosses the Lower Peninsula from Empire via Traverse City to Harrisville.
* is a connector between US-131 and Boyne City, and, despite its proximity to the highway, is not related to I-75.
* traverses Antrim County from Eastport to Mancelona via a handful of small towns.
* is a short highway connecting Camp Grayling, Hartwick Pines, and the city of Grayling in Crawford County.
* serves as a scenic loop off M-22 in the Sleeping Bear Dunes.
* runs across southern Grand Traverse County connecting M-37, US-131, and the village of Kingsley.
* is a "diagonal highway", taking a generally northwest–southeast direction from Clare to Frankfort.
* spurs off US-31 near Petoskey through Harbor Springs and along the Lake Michigan Coast as the
Tunnel of Trees.
* is a short highway running from US-31 to Interlochen Center for the Arts. The highway has become famous among students.
* cuts across Leelanau County from Leland to Suttons Bay.
* is the shortest signed highway in the state, connecting Aloha State Park to M-33 south of Cheboygan.
Past railroads
The Northern Lower Peninsula was home to many different railroads during the late 19th and early 20th centuries. One of these lines was the Detroit, Bay City & Alpena Railroad, later known as the
Detroit and Mackinac Railway
The Detroit and Mackinac Railway , informally known as the "Turtle Line", was a railroad in the northeastern part of the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The railroad had its main offices and shops in Tawas City with its main line ...
. The railroad had a main line along the Lake Huron shore and branch lines connecting to logging camps and gravel quarries. The railroad was a part owner of the
SS Chief Wawatam, a rail
car ferry that crossed the
Straits of Mackinac. Running down the center of the Northern Lower Peninsula was the
Michigan Central Railroad, which connected Mackinaw City with Bay City, Detroit, Lansing, and beyond. This line later became the
New York Central and was sold to the
Detroit and Mackinac Railway
The Detroit and Mackinac Railway , informally known as the "Turtle Line", was a railroad in the northeastern part of the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The railroad had its main offices and shops in Tawas City with its main line ...
in 1976. Several other railroads have existed in Alpena's history.
On the west side of the peninsula, the
Chicago and West Michigan Railway The Chicago and West Michigan Railway (C&WM) is a defunct railroad which operated in the state of Michigan between 1881 and 1899.Pere Marquette Railway
The Pere Marquette Railway operated in the Great Lakes region of the United States and southern parts of Ontario in Canada. It had trackage in the states of Michigan, Ohio, Indiana and the Canadian province of Ontario. Its primary connections in ...
) and several commercial cruise lines were early in generating traffic to Northern Michigan destinations. The Pere Marquette Railway operated rail car ferries across Lake Michigan out of
Ludington. The most known ferry is the
SS Badger which is still in use today for automobiles and passengers.
The
Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad
The Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad at its height provided passenger and freight railroad services between Cincinnati, Ohio, and the Straits of Mackinac in Michigan, USA. The company was formed on January 18, 1854.
Beginnings
After grappl ...
provided rail service between
Cincinnati, Ohio
Cincinnati ( ) is a city in the U.S. state of Ohio and the county seat of Hamilton County. Settled in 1788, the city is located at the northern side of the confluence of the Licking and Ohio rivers, the latter of which marks the state line wi ...
and Mackinaw City. It was later bought out by the
Pennsylvania Railroad. It served resort towns such as Traverse City, Petoskey, and Cadillac. In 1975 the line was bought by the
Michigan Department of Transportation
The Michigan Department of Transportation (MDOT) is a constitutional government principal department of the US state of Michigan. The primary purpose of MDOT is to maintain the Michigan State Trunkline Highway System which includes all Interstat ...
and the
Michigan Northern Railway was contracted to operate. By 1984 much of the railroad was abandoned and operations were handed over to the
Tuscola and Saginaw Bay Railway.
The
Ann Arbor was a railroad stretching from
Toledo, Ohio
Toledo ( ) is a city in and the county seat of Lucas County, Ohio, United States. A major Midwestern United States port city, Toledo is the fourth-most populous city in the state of Ohio, after Columbus, Cleveland, and Cincinnati, and according ...
to
Elberta, Michigan
Elberta is a village in Benzie County in the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 372 at the 2010 census. The village located in the east of Gilmore Township, on the south side of Lake Betsie, which is formed by the Betsie River before flow ...
where it operated a rail car ferry until 1982. The ferry serviced the cities of
Manitowoc, Wisconsin
Manitowoc () is a city in and the county seat of Manitowoc County, Wisconsin, United States. The city is located on Lake Michigan at the mouth of the Manitowoc River. According to the 2020 census, Manitowoc had a population of 34,626, with ove ...
,
Menominee, Michigan
Menominee ( ) is a city in the Upper Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The population was 8,599 at the 2010 census. It is the county seat of Menominee County. Menominee is the fourth-largest city in the Upper Peninsula, behind Marquett ...
, and
Manistique, Michigan
Manistique, formerly Monistique, is the only city and county seat of Schoolcraft County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2020 census, the city population was 2,828.
The city borders the adjacent Manistique Township, but the two are ...
. The Ann Arbor became a part of
Conrail and then was later divided up between the
Michigan Northern Railway and the
Michigan Interstate Railway Company. The remaining portions of the line were absorbed into the state owned lines operated by the
Tuscola and Saginaw Bay Railway.
Present railroads
Currently, Northern Michigan's railroad system is a skeleton of its former self. After the Chief Wawatam stopped running in 1984, rail lines serving the Straits of Mackinac were soon abandoned. In years past, four different railroads served Mackinaw City and St. Igance, and now none are left.
The remainder of the former
Detroit and Mackinac Railway
The Detroit and Mackinac Railway , informally known as the "Turtle Line", was a railroad in the northeastern part of the Lower Peninsula of the U.S. state of Michigan. The railroad had its main offices and shops in Tawas City with its main line ...
is now the
Lake State Railway. It operates a line from Bay City to Pinconning where it then branches northeast to Alpena and northwest to Gaylord.
Portions of the former Pere Marquette Railway, Grand Rapids and Indiana Railroad, and the Ann Arbor Railroad became the Tuscola and Saginaw Bay Railway. The main line of this railway runs from Ann Arbor north to Petoskey, with branch lines to Yuma and Traverse City. The railroad was renamed the
Great Lakes Central Railroad
The Great Lakes Central Railroad is an American Class II regional railroad, operating in the state of Michigan. It was originally called the Tuscola and Saginaw Bay Railway , which was formed on August 26, 1977, to operate over former Penn Cen ...
. There have been discussions of reviving passenger service along this line.
Flora and fauna
Common plants

Northern Michigan has many tree types including
maple
''Acer'' () is a genus of trees and shrubs commonly known as maples. The genus is placed in the family Sapindaceae.Stevens, P. F. (2001 onwards). Angiosperm Phylogeny Website. Version 9, June 2008 nd more or less continuously updated since http ...
,
birch
A birch is a thin-leaved deciduous hardwood tree of the genus ''Betula'' (), in the family Betulaceae, which also includes alders, hazels, and hornbeams. It is closely related to the beech- oak family Fagaceae. The genus ''Betula'' contains ...
,
oak
An oak is a tree or shrub in the genus ''Quercus'' (; Latin "oak tree") of the beech family, Fagaceae. There are approximately 500 extant species of oaks. The common name "oak" also appears in the names of species in related genera, notably ''L ...
,
ash,
white cedar,
aspen
Aspen is a common name for certain tree species; some, but not all, are classified by botanists in the section ''Populus'', of the '' Populus'' genus.
Species
These species are called aspens:
*'' Populus adenopoda'' – Chinese aspen (Chin ...
,
pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanical Garden accepts ...
, and
beech.
Fern
A fern (Polypodiopsida or Polypodiophyta ) is a member of a group of vascular plants (plants with xylem and phloem) that reproduce via spores and have neither seeds nor flowers. The polypodiophytes include all living pteridophytes exce ...
s,
milkweed
''Asclepias'' is a genus of herbaceous, perennial, flowering plants known as milkweeds, named for their latex, a milky substance containing cardiac glycosides termed cardenolides, exuded where cells are damaged. Most species are toxic to humans ...
,
Queen Anne's lace, and
chicory
Common chicory (''Cichorium intybus'') is a somewhat woody, perennial herbaceous plant of the family Asteraceae, usually with bright blue flowers, rarely white or pink. Native to the Old World, it has been introduced to North America and Austra ...
grow in the open fields and along roadsides. Forest plants include
wild leeks,
morel mushrooms, and
trillium
''Trillium'' (trillium, wakerobin, toadshade, tri flower, birthroot, birthwort, and sometimes "wood lily") is a genus of about fifty flowering plant species in the family Melanthiaceae. ''Trillium'' species are native to temperate regions of No ...
s.
Marram grass
''Ammophila'' (synonymous with ''Psamma'' P. Beauv.) is a genus of flowering plants consisting of two or three very similar species of grasses. The common names for these grasses include marram grass, bent grass, and beachgrass. These grasses ar ...
grows on beaches. Several
mosses cover the land.
Common mammals
Common mammals in Northern Michigan include
white-tailed deer
The white-tailed deer (''Odocoileus virginianus''), also known as the whitetail or Virginia deer, is a medium-sized deer native to North America, Central America, and South America as far south as Peru and Bolivia. It has also been introduced t ...
,
fox,
raccoon
The raccoon ( or , ''Procyon lotor''), sometimes called the common raccoon to distinguish it from other species, is a mammal native to North America. It is the largest of the procyonid family, having a body length of , and a body weight of ...
s,
porcupines, and
rabbits.
black bear
Black bear or Blackbear may refer to:
Animals
* American black bear (''Ursus americanus''), a North American bear species
* Asian black bear (''Ursus thibetanus''), an Asian bear species
Music
* Black Bear (band), a Canadian First Nations group ...
,
elk,
coyote,
bobcat,
wolves
The wolf (''Canis lupus''; : wolves), also known as the gray wolf or grey wolf, is a large canine native to Eurasia and North America. More than thirty subspecies of ''Canis lupus'' have been recognized, and gray wolves, as popularly un ...
, and
mountain lions
The cougar (''Puma concolor'') is a large cat native to the Americas. Its range spans from the Canadian Yukon to the southern Andes in South America and is the most widespread of any large wild terrestrial mammal in the Western Hemisphere. ...
are also present. Although not common, the presence of
cougars has been persistently reported over many years. Fish include
whitefish,
yellow perch
The yellow perch (''Perca flavescens''), commonly referred to as perch, striped perch, American perch, American river perch or preacher is a freshwater perciform fish native to much of North America. The yellow perch was described in 1814 by Sam ...
,
trout
Trout are species of freshwater fish belonging to the genera '' Oncorhynchus'', '' Salmo'' and '' Salvelinus'', all of the subfamily Salmoninae of the family Salmonidae. The word ''trout'' is also used as part of the name of some non-salm ...
,
bass,
northern pike
The northern pike (''Esox lucius'') is a species of carnivorous fish of the genus ''Esox'' (the pikes). They are typical of brackish and fresh waters of the Northern Hemisphere (''i.e.'' holarctic in distribution). They are known simply as a p ...
,
walleye
The walleye (''Sander vitreus'', synonym ''Stizostedion vitreum''), also called the yellow pike or yellow pickerel, is a freshwater perciform fish native to most of Canada and to the Northern United States. It is a North American close relat ...
,
muskie, and
sunfish.
Common birds
Common birds are
ducks,
seagulls
Gulls, or colloquially seagulls, are seabirds of the family Laridae in the suborder Lari. They are most closely related to the terns and skimmers and only distantly related to auks, and even more distantly to waders. Until the 21st century, ...
,
wild turkey
The wild turkey (''Meleagris gallopavo'') is an upland ground bird native to North America, one of two extant species of turkey and the heaviest member of the order Galliformes. It is the ancestor to the domestic turkey, which was originally d ...
,
great blue herons,
northern cardinals,
blue jays,
black-capped chickadee
The black-capped chickadee (''Poecile atricapillus'') is a small, non-migratory, North American songbird that lives in deciduous and mixed forests. It is a passerine bird in the tit family, the Paridae. It is the state bird of Massachusetts and ...
s,
hummingbirds,
Baltimore oriole, and
ruffed grouse
The ruffed grouse (''Bonasa umbellus'') is a medium-sized grouse occurring in forests from the Appalachian Mountains across Canada to Alaska. It is the most widely distributed game bird in North America. It is non-migratory. It is the only specie ...
.
Canada geese
The Canada goose (''Branta canadensis''), or Canadian goose, is a large wild goose with a black head and neck, white cheeks, white under its chin, and a brown body. It is native to the arctic and temperate regions of North America, and it is o ...
may be seen flying over head in spring and fall. Less well known birds that are unique in Michigan to the Northern Lower Peninsula are
spruce grouse
The spruce grouse (''Canachites canadensis''), also known as Canada grouse, spruce hen or fool hen, is a medium-sized grouse closely associated with the coniferous boreal forests or taiga of North America. It is the only member of the genus ''C ...
,
sharp-tailed grouse
The sharp-tailed grouse (''Tympanuchus phasianellus''), also known as the sharptail or fire grouse, is a medium-sized prairie grouse. One of three species in the genus '' Tympanuchus'', the sharp-tailed grouse is found throughout Alaska, much of ...
,
red-throated loon
The red-throated loon (North America) or red-throated diver (Britain and Ireland) (''Gavia stellata'') is a migratory aquatic bird found in the northern hemisphere. The most widely distributed member of the loon or diver family, it breeds prim ...
,
Swainson's hawk
Swainson's hawk (''Buteo swainsoni'') is a large bird species in the Accipitriformes order. This species was named after William Swainson, a British naturalist. It is colloquially known as the grasshopper hawk or locust hawk, as it is very fond ...
, and the
boreal owl
The boreal owl or Tengmalm's owl (''Aegolius funereus'') is a small owl in the "true owl" family Strigidae. It is known as the boreal owl in North America and as Tengmalm's owl in Europe after Swedish naturalist Peter Gustaf Tengmalm or, more ...
.
The
Au Sable State Forest
The Au Sable State Forest is a state forest in the north-central Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It is operated by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources.
The Au Sable State Forest is a byproduct of the lumbering boom in Michigan during the ...
is a state forest in the north-central Lower Peninsula of Michigan. Much of the forest is used for wildlife game management and the fostering of endangered and rare species, such as the
Kirtland's warbler
Kirtland's warbler (''Setophaga kirtlandii''), also known in Michigan by the common name jack pine bird, or the jack pine warbler, is a small songbird of the New World warbler family (Parulidae), named after Jared Potter Kirtland, an Ohio doct ...
– there are regular controlled burns to maintain its habitat. The Kirtland's warbler has its habitat in an increasing part of the area. There is a Kirtland's Warbler Festival, which is sponsored in part by Kirtland Community College.
The
American Bird Conservancy
American Bird Conservancy (ABC) is a non-profit membership organization with the mission of conserving wild birds and their habitats throughout the Americas. Its focus is on threats to birds in the Western Hemisphere – threats which include ov ...
and the
National Audubon Society have designated several locations as internationally
Important Bird Areas.
Common insects
Insect populations are similar to those found elsewhere in the
midwestern United States
The Midwestern United States, also referred to as the Midwest or the American Midwest, is one of four census regions of the United States Census Bureau (also known as "Region 2"). It occupies the northern central part of the United States. I ...
.
ladybug
Coccinellidae () is a widespread family of small beetles ranging in size from . They are commonly known as ladybugs in North America and ladybirds in Great Britain. Some entomologists prefer the names ladybird beetles or lady beetles as they ...
s,
crickets
Crickets are orthopteran insects which are related to bush crickets, and, more distantly, to grasshoppers. In older literature, such as Imms,Imms AD, rev. Richards OW & Davies RG (1970) ''A General Textbook of Entomology'' 9th Ed. Methuen 8 ...
,
dragonflies
A dragonfly is a flying insect belonging to the infraorder Anisoptera below the order Odonata. About 3,000 extant species of true dragonfly are known. Most are tropical, with fewer species in temperate regions. Loss of wetland habitat threa ...
,
mosquito
Mosquitoes (or mosquitos) are members of a group of almost 3,600 species of small flies within the family Culicidae (from the Latin ''culex'' meaning " gnat"). The word "mosquito" (formed by ''mosca'' and diminutive ''-ito'') is Spanish for "li ...
es,
ant
Ants are eusocial insects of the family Formicidae and, along with the related wasps and bees, belong to the order Hymenoptera. Ants evolved from vespoid wasp ancestors in the Cretaceous period. More than 13,800 of an estimated total of ...
s,
house flies, and
grasshoppers are common, as is the
Western conifer seed bug, and several kinds of
butterflies and
moth
Moths are a paraphyletic group of insects that includes all members of the order Lepidoptera that are not butterflies, with moths making up the vast majority of the order. There are thought to be approximately 160,000 species of moth, many of w ...
s (for example,
monarch butterflies
The monarch butterfly or simply monarch (''Danaus plexippus'') is a milkweed butterfly (subfamily Danainae) in the family Nymphalidae. Other common names, depending on region, include milkweed, common tiger, wanderer, and black-veined brown. ...
and
tomato worm moths). Notable deviations in insect populations are a high population of
June bugs during June as well as a scarcity of
lightning bugs because of the lower average temperatures year round and especially in the summer.
Northern Michigan is home to Michigan's most endangered species and one of the most endangered species in the world: the
Hungerford's crawling water beetle
Hungerford's crawling water beetle (''Brychius hungerfordi'') is a critically endangered member of the family Haliplidae of water beetles. The US Fish and Wildlife Service Draft Recovery Plan for the species published in August 2004 estimates ro ...
. The species lives in only five locations in the world, four of which are in Northern Michigan (one is in
Bruce County, Ontario. Indeed, the only stable population of the rare beetle occurs along a two and a half mile stretch of the East Branch of the Maple River in
Emmet County, Michigan
Emmet County is a county located in the U.S. state of Michigan. It is the northernmost county in the Lower Peninsula. As of the 2020 Census, the population was 34,112. The county seat is Petoskey.
Emmet County is located at the top of the L ...
.
Common reptiles
There are no fatally poisonous snakes native to Northern Michigan. The poisonous
Eastern Massasauga Rattlesnake lives in Michigan, but it is not common, particularly in Northern Michigan. In any event, its non-fatal bite may make an adult sick, but it should be medically treated without delay.
Snakes present include the
eastern hog-nosed snake,
brown snake,
common garter snake
The common garter snake (''Thamnophis sirtalis'') is a species of thamnophis snake, in the natricine subfamily, which is indigenous to North America and found widely across the continent. Most common garter snakes have a pattern of yellow strip ...
,
eastern milk snake
''Lampropeltis triangulum triangulum'', commonly known as the eastern milk snake or eastern milksnake, is a subspecies of the milk snake (''Lampropeltis triangulum''). The nonvenomous, colubrid snake is indigenous to eastern and central North Am ...
and the
northern ribbon snake. The only common reptiles and amphibians are various pond
frog
A frog is any member of a diverse and largely carnivorous group of short-bodied, tailless amphibians composing the order Anura (ανοὐρά, literally ''without tail'' in Ancient Greek). The oldest fossil "proto-frog" ''Triadobatrachus'' is ...
s,
toad
Toad is a common name for certain frogs, especially of the family Bufonidae, that are characterized by dry, leathery skin, short legs, and large bumps covering the parotoid glands.
A distinction between frogs and toads is not made in scient ...
s,
salamander
Salamanders are a group of amphibians typically characterized by their lizard-like appearance, with slender bodies, blunt snouts, short limbs projecting at right angles to the body, and the presence of a tail in both larvae and adults. All t ...
s, and small
turtle
Turtles are an order of reptiles known as Testudines, characterized by a special shell developed mainly from their ribs. Modern turtles are divided into two major groups, the Pleurodira (side necked turtles) and Cryptodira (hidden necked t ...
s.
State Forests and conservation areas
The state forests in the U.S. state of Michigan are managed by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources, Forest, Mineral and Fire Management unit. It is the largest state forest system in the nation at . ''See
List of Michigan state forests''. The Northern
lower peninsula
The Lower Peninsula of Michigan – also known as Lower Michigan – is the larger, southern and less elevated of the two major landmasses that make up the U.S. state of Michigan; the other being the Upper Peninsula, which is separated by the S ...
includes three forests:
*
Mackinaw State Forest
The Mackinaw State Forest is a forested area owned by the U.S. state of Michigan and operated by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources. It is located in the northern area of the Lower Peninsula within the eight counties of Alpena, Antri ...
** Atlanta FMU (Alpena, northeast Cheboygan, most of Montmorency, and most of Presque Isle counties)
** Gaylord FMU (Antrim, Charlevoix, most of Cheboygan, Emmet, and most of Otsego counties)
** Pigeon River Country FMU (southeast Cheboygan, northwest Montmorency, northeast Otsego, and southwest Presque Isle counties)
*
Pere Marquette State Forest
** Cadillac FMU (Lake, Mason, Mecosta, Missaukee, Newaygo, Oceana, Osceola, and Wexford counties)
** Traverse City FMU (Benzie, Grand Traverse, Leelanau, Kalkaska, Manistee counties)
*
Au Sable State Forest
The Au Sable State Forest is a state forest in the north-central Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It is operated by the Michigan Department of Natural Resources.
The Au Sable State Forest is a byproduct of the lumbering boom in Michigan during the ...
** Gladwin FMU (Arenac, Bay, Clare, Gladwin, southern Iosco, Isabella, and Midland counties)
** Grayling FMU (Alcona, Crawford, Oscoda, and northern Iosco counties)
** Roscommon FMU (Ogemaw and Roscommon counties)
In addition, large portions of this area are covered by the
Manistee National Forest
The Manistee National Forest is a national forest located in the Lower Peninsula of Michigan. It has a total area of . It was established in 1938, and combined with the Huron National Forest in 1945 for administrative purposes, creating the Hur ...
and the
Huron National Forest. In the former, a unique environment is present at the
Nordhouse Dunes Wilderness
The Nordhouse Dunes Wilderness is a listed wilderness area within the Manistee National Forest. It is located north of Ludington, Michigan, and is best known for its 4 miles (6.4 km) of undeveloped Lake Michigan shoreline.
Geology
The la ...
. This relatively small area of , on
Lake Michigan's east shore, is one of few
wilderness area
Wilderness or wildlands (usually in the plural), are natural environments on Earth that have not been significantly modified by human activity or any nonurbanized land not under extensive agricultural cultivation. The term has traditionally re ...
s in the U.S. with an extensive lake shore
dunes ecosystem. The dunes are 3500 to 4000 years old, and rise to nearly higher than the lake. The Nordhouse Dunes are interspersed with woody vegetation such as
jack pine
Jack pine (''Pinus banksiana'') is an eastern North American pine. Its native range in Canada is east of the Rocky Mountains from the Mackenzie River in the Northwest Territories to Cape Breton Island in Nova Scotia, and the north-central and ...
,
juniper and
hemlock. Many small water holes and marshes dot the landscape, and dune grass covers some of the dunes. The wide and sandy beach is ideal for walks and sunset viewing.
Eight islands off the Lakes Michigan and Huron coasts –
Charlevoix
Charlevoix ( , ) is a cultural and natural region in Quebec, on the north shore of the Saint Lawrence River as well as in the Laurentian Mountains area of the Canadian Shield. This dramatic landscape includes rolling terrain, fjords, headlands ...
and
Alpena counties, respectively – are part of the
Michigan Islands National Wildlife Refuge
The Michigan Islands National Wildlife Refuge is a designation for nine Michigan islands in the North American Great Lakes. Owned by the United States federal government, they were set aside for ecosystem protection purposes by President Frankli ...
.
Notable people
See the "Notable people" sections in the various settlement articles.
Media
Northern Michigan is in the
Designated Market Area
A media market, broadcast market, media region, designated market area (DMA), television market area, or simply market is a region where the population can receive the same (or similar) television and radio station offerings, and may also incl ...
s of "
Traverse City-Cadillac" (116), "
Alpena" (208), and some portions of "
Flint-Saginaw-Bay City" (66).
Newspapers
* ''
Alcona County Review'', Harrisville
* ''
The Alpena News''
* ''
Boyne City Gazette''
* ''
Cadillac Evening News''
* ''
Charlevoix Courier''
* ''
Cheboygan Daily Tribune
The ''Cheboygan Daily Tribune'' is a daily newspaper published Tuesdays through Saturdays in Cheboygan, Michigan, United States. It is owned by Gannett.
In addition to the daily newspaper, Gannett also publishes the ''Shopper's Fair'' pennysave ...
''
* ''
Citizen-Journal'', Boyne City, East Jordan
* ''
Crawford County Avalanche'', Grayling
* ''
Gaylord Herald Times
The ''Gaylord Herald Times'' is a twice-weekly newspaper in Gaylord, Michigan, United States.
History
The ''Gaylord Herald Times'' was founded in 1875. The paper started publishing twice weekly in May 1999. In 2006, it was purchased by Schurz C ...
''
* ''Grand Traverse Herald'', weekly in Traverse City
* ''
Iosco County News-Herald'', Tawas City
* ''The Leader and the Kalkaskian'', Kalkaska
* ''
Leelanau Enterprise'', Leland
* ''
Ludington Daily News
The ''Ludington Daily News'' is the daily newspaper of Ludington, Michigan
Ludington ( ) is the largest city and county seat of Mason County in the U.S. state of Michigan. As of the 2010 census, the city population was 8,076.
Ludington is a h ...
''
* ''
Manistee Daily News Advocate''
* ''
Mears News'', historical/defunct
* ''
Midland Daily News
The ''Midland Daily News'' is a daily newspaper which serves Midland County, Michigan. The offices for the paper are located at 219 East Main Street in downtown Midland; the paper is widely circulated around Midland County.
The newspaper also p ...
''
* ''
Missaukee Sentinel'' (Lake City)
* ''Northern Express Weekly'', weekly in Traverse City
* ''Onaway Outlook''
* ''Oscoda Press''
* ''
Petoskey News-Review
The ''Petoskey News-Review'' is the daily newspaper of Petoskey, Michigan.
History
Started in 1878 as the ''Petoskey City Record'', after subsequent mergers it became ''The Petoskey Evening News''. In 1953, this paper merged with ''The Northern ...
''
* ''
Presque Isle County Advance'', Rogers City
* ''
St. Ignace News'', serving the Straits area
* ''The Town Meeting'', Elk Rapids
* ''
Traverse City Record-Eagle
The ''Traverse City Record-Eagle'' is a daily morning newspaper based in Traverse City, Michigan. It calls itself "Northern Michigan's Newspaper". and is the newspaper of record for Grand Traverse County.
History
The newspaper was owned by Dow ...
''
* ''White Pine Press'',
Northwestern Michigan College
Northwestern Michigan College (NMC) is a public community college in Traverse City, Michigan. Founded in 1951, it enrolls nearly 4,000 students. NMC offers associate degrees and professional certificates, bachelor's degrees through the Great La ...
Daily editions of the ''
Detroit Free Press
The ''Detroit Free Press'' is the largest daily newspaper in Detroit, Michigan, US. The Sunday edition is titled the ''Sunday Free Press''. It is sometimes referred to as the Freep (reflected in the paper's web address, www.freep.com). It primari ...
'' and ''
The Detroit News
''The Detroit News'' is one of the two major newspapers in the U.S. city of Detroit, Michigan. The paper began in 1873, when it rented space in the rival ''Detroit Free Press'' building. ''The News'' absorbed the ''Detroit Tribune'' on Februar ...
'' are also available throughout the area with the ''
Bay City Times'' and ''
Saginaw News'' available in the east and ''
The Grand Rapids Press
''The Grand Rapids Press'' is a daily newspaper published in Grand Rapids, Michigan. It is the largest of the eight Booth newspapers. It is sold for $1.50 daily and $7.99 on Sunday.
AccuWeather provides weather content to the ''Grand Rapids ...
'' available in the west.
Magazines
*''
Traverse'' is published monthly with a focus on regional interests.
Radio
FM
// designates a simulcast.
AM
Broadcast television
The following stations serve parts of Northern Michigan as their viewing area, and also some areas outside of the region.
See also
*
List of counties in Michigan
*
Upstate New York
Upstate New York is a geographic region consisting of the area of New York State that lies north and northwest of the New York City metropolitan area. Although the precise boundary is debated, Upstate New York excludes New York City and Long Is ...
*
Downstate Illinois
Downstate Illinois refers to the part of the U.S. state of Illinois south of the Chicago metropolitan area, which is in the northeast corner of the state and has been dominant in American history, politics, and culture. It is defined as the part ...
Notes
References
Further reading
*
*
*
*
*
*
*
External links
Clarke Historical Library, Central Michigan University– bibliographies organized by county and region
Great Lakes Coast WatchInfo Michigan – detailed information on 630 citiesPure Michigan: Michigan's Official Travel and Tourism Site
Northern Michigan culture and community websiteHarbors, hunting, resources and more
from the Michigan Department of Natural Resources
{{Michigan
Regions of Michigan
 The southern boundary of the region is not precisely defined. Some residents in the southern part of the state consider its southern limit to be just north of
The southern boundary of the region is not precisely defined. Some residents in the southern part of the state consider its southern limit to be just north of 




 In the northernmost 21 counties in the
In the northernmost 21 counties in the 
 The
The  Sport fishing along the Au Sable River became a tourist attraction for wealthy sportsmen from Detroit, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Buffalo, Toledo, Indianapolis, and Chicago. After the Jackson, Lansing and Saginaw Railroad reached Grayling in the late 1870s, it began to advertise hunting and fishing trips in Crawford County, home of the
Sport fishing along the Au Sable River became a tourist attraction for wealthy sportsmen from Detroit, Cleveland, Cincinnati, Buffalo, Toledo, Indianapolis, and Chicago. After the Jackson, Lansing and Saginaw Railroad reached Grayling in the late 1870s, it began to advertise hunting and fishing trips in Crawford County, home of the  The effect of rail connections was ultimately transformative; timber and other goods could be produced in the north and shipped to urban markets to the south. Diverse industries developed, such as iron works, tanneries, mills, cement plants, and agricultural enterprises. By 1885, the intense harvesting and export of pine trees led to visible decline in the lumber industry's ability to produce white pine. Logging in Michigan peaked in 1889. Where available, hardwoods and hemlock were harvested, temporarily extending the life of lumbering in the area, especially around East Jordan, the Traverse Bay, and near
The effect of rail connections was ultimately transformative; timber and other goods could be produced in the north and shipped to urban markets to the south. Diverse industries developed, such as iron works, tanneries, mills, cement plants, and agricultural enterprises. By 1885, the intense harvesting and export of pine trees led to visible decline in the lumber industry's ability to produce white pine. Logging in Michigan peaked in 1889. Where available, hardwoods and hemlock were harvested, temporarily extending the life of lumbering in the area, especially around East Jordan, the Traverse Bay, and near 
 The primary means of transportation in Northern Michigan is by automobile. Northern Michigan is served by one
The primary means of transportation in Northern Michigan is by automobile. Northern Michigan is served by one  Northern Michigan has many tree types including
Northern Michigan has many tree types including