North March on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast ''
The Northern March or North March (german: Nordmark) was created out of the division of the vast ''
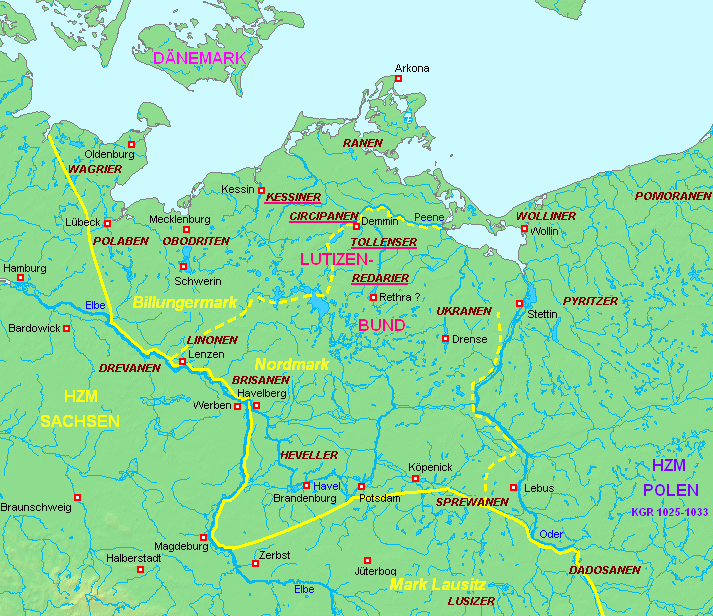 During the
During the
Medieval Lands Project, Grafen von Stade (family of Lothar)
{{coord missing, Brandenburg Marches of the Holy Roman Empire Former states and territories of Brandenburg States and territories established in the 960s 960s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 965 establishments States and territories disestablished in the 980s 980s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire 983 disestablishments
Marca Geronis
The ''Marca Geronis'' (march of Gero) was a vast super-march in the middle of the tenth century. It was created probably for Thietmar (in the 920s) and passed to his two sons consecutively: Siegfried and Gero. On Gero's death in 965 it was divi ...
'' in 965. It initially comprised the northern third of the ''Marca'' (roughly corresponding to the modern state of Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
) and was part of the territorial organisation of areas conquered from the Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
. A Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
an rebellion in 983 reversed German control over the region until the establishment of the March of Brandenburg by Albert the Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142.
Life
Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Bal ...
in the 12th century.
Slavic background
Migration Period
The Migration Period was a period in European history marked by large-scale migrations that saw the fall of the Western Roman Empire and subsequent settlement of its former territories by various tribes, and the establishment of the post-Roma ...
, many Germanic peoples
The Germanic peoples were historical groups of people that once occupied Central Europe and Scandinavia during antiquity and into the early Middle Ages. Since the 19th century, they have traditionally been defined by the use of ancient and ear ...
began migrating towards the Roman frontier. In the northeast they were replaced primarily by Slavic peoples
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic language, Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout ...
(Veleti
The Veleti, also known as Wilzi, Wielzians, and Wiltzes, were a group of medieval Lechitic tribes within the territory of Hither Pomerania, related to Polabian Slavs. They had formed together the Confederation of the Veleti, a loose monarchic c ...
, later Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
). The first Slavs were certainly in the Brandenburg area by 720, after the arrival of the Avars in Europe. These Slavs had come via Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The ...
, where they had arrived in the mid-seventh century. The remnants of the Germanic Semnoni
The Semnones were a Germanic and specifically a Suevian people, who were settled between the Elbe and the Oder in the 1st century when they were described by Tacitus in ''Germania'':
"The Semnones give themselves out to be the most ancient and r ...
were absorbed into these Slavic groups.
The group of people who settled at the Spree
Spree may refer to:
Geography
* Spree (river), river in Germany
Film and television
* '' The Spree'', a 1998 American television film directed by Tommy Lee Wallace
* ''Spree'' (film), a 2020 American film starring Joe Keery
* "Spree" (''Numbers ...
river became known as Sprevani. They settled east of the line formed by the Havel and Nuthe
The Nuthe is a river in Brandenburg, Germany, left tributary of the Havel. Its total length is . The Nuthe originates in the Fläming region, near Niedergörsdorf. It flows north through Jüterbog, Luckenwalde, Trebbin and Saarmund. The Nuth ...
rivers, in the current Barnim and Teltow regions. They built their main fortification at the confluence of the Spree and the Dahme rivers at Köpenick
Köpenick () is a historic town and locality (''Ortsteil'') in Berlin, situated at the confluence of the rivers Dahme and Spree in the south-east of the German capital. It was formerly known as Copanic and then Cöpenick, only officially adopt ...
. The Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
lived west of that line, in the current Havelland
Geographically, the Havelland is the region around which the River Havel flows in a U-shape between Oranienburg to the northeast and Rhinow to the northwest. The northern boundary of the Havelland is formed by the River Rhin and the Rhin Canal. ...
and Zauche
Utrata (german: Zauche) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Izbicko, within Strzelce County, Opole Voivodeship, in south-western Poland. It lies approximately north-east of Izbicko
Izbicko (German: Stubendorf) is a village i ...
regions. They were named ''Habelli'' for the ancient Germanic name of the river "Habula" (Havel
The Havel () is a river in northeastern Germany, flowing through the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Brandenburg, Berlin and Saxony-Anhalt. It is a right tributary of the Elbe and long. However, the direct distance from its source to its mo ...
). The name for themselves was the ''Stodoranie''. They built their main fortification at "Brenna" (modern Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
). The Hevelli also built a large outpost at the current site of Spandau Citadel
The Spandau Citadel (german: Zitadelle Spandau) is a fortress in Berlin, Germany, one of the best-preserved Renaissance military structures of Europe. Built from 1559–94 atop a medieval fort on an island near the meeting of the Havel and ...
in Berlin
Berlin ( , ) is the capital and largest city of Germany by both area and population. Its 3.7 million inhabitants make it the European Union's most populous city, according to population within city limits. One of Germany's sixteen constitu ...
. The Sprevani and Hevelli waged war against not only their German neighbors, but also their Slavic neighbours.
History of the Northern March
Establishment and loss, 965–983
After the Saxon War of 808, the victoriousCharlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
bestowed on the Slavic tribes allied with him (such as the Obotrites
The Obotrites ( la, Obotriti, Abodritorum, Abodritos…) or Obodrites, also spelled Abodrites (german: Abodriten), were a confederation of medieval West Slavic tribes within the territory of modern Mecklenburg and Holstein in northern Germany ...
) part of the Saxon lands between the Elbe
The Elbe (; cs, Labe ; nds, Ilv or ''Elv''; Upper and dsb, Łobjo) is one of the major rivers of Central Europe. It rises in the Giant Mountains of the northern Czech Republic before traversing much of Bohemia (western half of the Czech Re ...
and the Baltic Sea
The Baltic Sea is an arm of the Atlantic Ocean that is enclosed by Denmark, Estonia, Finland, Germany, Latvia, Lithuania, Poland, Russia, Sweden and the North and Central European Plain.
The sea stretches from 53°N to 66°N latitude and from ...
. A period of quiet followed in the region. The Bishoprics of Brandenburg and Havelberg
Havelberg () is a town in the district of Stendal, in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is situated on the Havel, and part of the town is built on an island in the centre of the river. The two parts were incorporated as a town in 1875. It has a populati ...
were established around 940 and the Christianisation
Christianization ( or Christianisation) is to make Christian; to imbue with Christian principles; to become Christian. It can apply to the conversion of an individual, a practice, a place or a whole society. It began in the Roman Empire, conti ...
of the pagan Slavs began.
Henry I of Germany conquered Brandenburg in 928–929 and imposed tribute upon the tribes up to the Oder
The Oder ( , ; Czech, Lower Sorbian and ; ) is a river in Central Europe. It is Poland's second-longest river in total length and third-longest within its borders after the Vistula and Warta. The Oder rises in the Czech Republic and flows ...
. By 948 his son Otto I
Otto I (23 November 912 – 7 May 973), traditionally known as Otto the Great (german: Otto der Große, it, Ottone il Grande), was East Frankish king from 936 and Holy Roman Emperor from 962 until his death in 973. He was the oldest son of He ...
had established German control over the many remaining pagans, who were collectively referred to as Slavs or Wends
Wends ( ang, Winedas ; non, Vindar; german: Wenden , ; da, vendere; sv, vender; pl, Wendowie, cz, Wendové) is a historical name for Slavs living near Germanic settlement areas. It refers not to a homogeneous people, but to various people ...
by contemporaries. Slavic settlements such as Brenna, Budišin (Bautzen
Bautzen () or Budyšin () is a hill-top town in eastern Saxony, Germany, and the administrative centre of the district of Bautzen. It is located on the Spree river. In 2018 the town's population was 39,087. Until 1868, its German name was ''Budi ...
), and Chotebuž (Cottbus
Cottbus (; Lower Sorbian: ''Chóśebuz'' ; Polish: Chociebuż) is a university city and the second-largest city in Brandenburg, Germany. Situated around southeast of Berlin, on the River Spree, Cottbus is also a major railway junction with exte ...
) came under German control through the installation of margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the ...
s. The main function of the margravial office was to defend and protect the marches
In medieval Europe, a march or mark was, in broad terms, any kind of borderland, as opposed to a national "heartland". More specifically, a march was a border between realms or a neutral buffer zone under joint control of two states in which diff ...
(frontier districts) of the Kingdom of Germany
The Kingdom of Germany or German Kingdom ( la, regnum Teutonicorum "kingdom of the Germans", "German kingdom", "kingdom of Germany") was the mostly Germanic-speaking East Frankish kingdom, which was formed by the Treaty of Verdun in 843, espec ...
. After the death of the margrave Gero the Great in 965, the vast collection of marches (a "super-march") was divided by Otto into five smaller commands. The Northern March was one of these. The others were the Eastern March, the March of Merseburg {{Unreferenced, date=June 2019, bot=noref (GreenC bot)
The March of Merseburg (german: Mark Merseburg) was a short-lived march of the Holy Roman Empire. It comprised the lands of the Polabian Slavs beyond the margravial residence at Merseburg on th ...
, the March of Meissen
The Margravate of Meissen (german: Markgrafschaft Meißen) was a medieval principality in the area of the modern German state of Saxony. It originally was a frontier march of the Holy Roman Empire, created out of the vast ''Marca Geronis'' (Saxon ...
, and the March of Zeitz
The March of Zeitz (german: Mark Zeitz) was a march of the Holy Roman Empire. It was created by Emperor Otto I in the division of the ''marca Geronis'' in 965, following the death of Gero the Great. Its capital was Zeitz. Its first and only margr ...
.
The rebellion of 983, initiated by the Lutici
The Lutici or Liutizi (known by various spelling variants) were a federation of West Slavic Polabian tribes, who between the 10th and 12th centuries lived in what is now northeastern Germany. Four tribes made up the core of the federation: th ...
, led to a factual disestablishment of the Northern and Billung marches as well as the corresponding bishoprics, though titular margraves and bishops were still appointed. Until the collapse of the Liutizi alliance in the middle of the 11th century, the German expansion in the direction of the Northern March remained at a standstill and the Wends east of the Elbe remained independent for approximately 150 years.
March of Brandenburg
In the beginning of the 12th century, the German kings re-established control over the mixed Slav-inhabited lands on the eastern borders of theHoly Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
. In 1134, in the wake of the Wendish Crusade of 1147, the German magnate Albert the Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142.
Life
Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Bal ...
was granted the Northern March by Emperor Lothair III. The Slavs were subsequently assimilated by German settlers during the Ostsiedlung
(, literally "East-settling") is the term for the Early Medieval and High Medieval migration-period when ethnic Germans moved into the territories in the eastern part of Francia, East Francia, and the Holy Roman Empire (that Germans had a ...
. The church under Albert established dioceses, which with their walled towns protected the townspeople from attack. With the arrival of monks and bishops begins anew the recorded history of the town of Brandenburg, from which would develop the eponymous margraviate.
Albert's control of the region was nominal for several decades, but he engaged in a variety of military and diplomatic actions against the Wends, and saw his control become more real by the middle of the century. In 1150, Albert formally inherited Brandenburg from its last Hevelli
The Hevelli or Hevellians/ Navellasîni (sometimes ''Havolane''; german: Heveller or ''Stodoranen''; pl, Hawelanie or ''Stodoranie''; cs, Havolané or ''Stodorané'') were a tribe of the Polabian Slavs, who settled around the middle Havel river ...
ruler, the Christian Pribislav. Albert and his Ascanian
The House of Ascania (german: Askanier) was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schlos ...
descendants made considerable progress in Christianising the captured lands.
List of margraves
The Margraves of the Nordmark were closely related to both theCounts of Stade
The Counts of Stade were members of the Saxony nobility beginning in the 10th century. Stade had developed since the 8th century as a principal center of trade and communications. The Counts of Stade created their domain between the lower Elbe and ...
, many holding dual titles, and the Counts of Walbeck. The early counts and margraves were discussed by Thietmar of Merseburg, a descendant of the original rulers.
Counts of Haldensleben
*Dietrich
Dietrich () is an ancient German name meaning "Ruler of the People.” Also "keeper of the keys" or a "lockpick" either the tool or the profession.
Given name
* Dietrich, Count of Oldenburg (c. 1398 – 1440)
* Thierry of Alsace (german: Dietri ...
, 965–983, possibly the son of Wichman the Elder, an early Count of Stade
The Counts of Stade were members of the Saxony nobility beginning in the 10th century. Stade had developed since the 8th century as a principal center of trade and communications. The Counts of Stade created their domain between the lower Elbe an ...
Counts of Walbeck
*Lothair I
Lothair I or Lothar I ( Dutch and Medieval Latin: ''Lotharius''; German: ''Lothar''; French: ''Lothaire''; Italian: ''Lotario'') (795 – 29 September 855) was emperor (817–855, co-ruling with his father until 840), and the governor of Bava ...
, 983–1003, the first margrave of the House of Walbeck, and son of Lothar II the Old, Count of Walbeck
* Werner, 1003–1009, son of the previous and cousin of Thietmar of MerseburgCounts of Haldensleben
*Bernard I, 1009–1018, son of Dietrich * Bernard II, 1018–1051, son of the previous *William
William is a male given name of Germanic origin.Hanks, Hardcastle and Hodges, ''Oxford Dictionary of First Names'', Oxford University Press, 2nd edition, , p. 276. It became very popular in the English language after the Norman conquest of Engl ...
, 1051–1056, son of the previous
* Otto, 1056–1057, illegitimate son of Bernard Counts of Stade
* Lothair Udo I, 1056–1057, also Count of Stade (as Lothair Udo II), first of theHouse of Udonids The Udonids (Udonen) were a German noble family, ruling as both the Counts of Stade and Margraves of the Nordmark, or Northern March, from the 9th to the 12th century. The first formal member of this family was Henry I the Bald, who took his seat i ...
, and son of Siegfried II, Count of Stade
* Lothair Udo II, 1057–1082, also Count of Stade (as Lothair Udo III), son of the previous
* Henry I the Long, 1082–1087, also Count of Stade (as Henry III the Long), son of the previous
* Lothair Udo III, 1087–1106, also Count of Stade (as Lothair Udo IV), brother of the previous
* Rudolf I, 1106–1112, also Count of Stade, brother of the previousCounts of Plötzkau
* Helperich von Plötzkau, 1112–1114, nondynastic, but part of the House of Walbeck as grandson ofConrad, Count of Walbeck Conrad (1018–1073), Count of Walbeck and Viscount (Burggraf) of Magdeburg, son of Friedrick, Count of Walbeck Friedrick (''Friedrich von Walbeck''; 974–1018), Count of Walbeck and Viscount (Burggraf) of Magdeburg, son of Siegfried I the Olde ...
Counts of Stade
* Henry II, 1114–1128, son of Lothair Udo III * Udo IV, 1128–1130, son of Rudolf ICounts of Plötzkau
* Conrad, 1130–1133, son of HelperichCounts of Stade
*Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
, 1133–1134, son of Rudolf I and the last of the House of Udonids The Udonids (Udonen) were a German noble family, ruling as both the Counts of Stade and Margraves of the Nordmark, or Northern March, from the 9th to the 12th century. The first formal member of this family was Henry I the Bald, who took his seat i ...
Counts of Ballenstedt (Ascanians)
*Albert the Bear
Albert the Bear (german: Albrecht der Bär; 1100 – 18 November 1170) was the first margrave of Brandenburg from 1157 to his death and was briefly duke of Saxony between 1138 and 1142.
Life
Albert was the only son of Otto, Count of Bal ...
, 1134–1170
Under Albert, the march was expanded with the acquisition of Slavic lands around Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
in 1157. The expanded march became a hereditary possession of Albert's house, the Ascanian
The House of Ascania (german: Askanier) was a dynasty of German rulers. It is also known as the House of Anhalt, which refers to its longest-held possession, Anhalt.
The Ascanians are named after Ascania (or Ascaria) Castle, known as ''Schlos ...
s, and was called the March of Brandenburg.
For a lists of margravines (margrave's wives), see List of consorts of Brandenburg.
Notes
Sources
* Reuter, Timothy. ''Germany in the Early Middle Ages 800–1056''. New York: Longman, 1991. * Thompson, James Westfall. ''Feudal Germany, Volume II''. New York: Frederick Ungar Publishing Co., 1928. *Warner, David A., ''Ottonian Germany: The Chronicon of Thietmar of Merseburg'', Manchester University Press, Manchester, 2001Medieval Lands Project, Grafen von Stade (family of Lothar)
{{coord missing, Brandenburg Marches of the Holy Roman Empire Former states and territories of Brandenburg States and territories established in the 960s 960s establishments in the Holy Roman Empire 965 establishments States and territories disestablished in the 980s 980s disestablishments in the Holy Roman Empire 983 disestablishments