Ninawa on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nineveh (; akk, ; Biblical Hebrew: '; ar, نَيْنَوَىٰ '; syr, ܢܝܼܢܘܹܐ, Nīnwē) was an ancient
''A Dictionary of Archaeology''
John Wiley & Sons, 2002 p. 427 Also, for the Upper Mesopotamian region, the ''Early Jezirah'' chronology has been developed by archaeologists. According to this regional chronology, 'Ninevite 5' is equivalent to the Early Jezirah I–II period. Ninevite 5 was preceded by the Late
File:Painted Jar - Ninevite 5.jpg, Painted jar – Ninevite 5
File:Painted bowl - Uruk-Nineveh 5 transition.jpg, Painted bowl – Uruk-Nineveh 5 transition
File:Jamdat Nasr Period pottery - Oriental Institute Museum, University of Chicago - DSC06949.JPG, Jemdet Nasr ware
File:Vaso cerámico del periodo protoelamita - MARQ 01.jpg, Proto-Elamite ware 3100 BC
File:Saxsı küp, Təpəyatağı.JPG, Pottery jar, Tepeyatagi, Khudat district, Kura-Araxtes culture


 The greatness of Nineveh was short-lived. In around 627 BC, after the death of its last great king Ashurbanipal, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began to unravel through a series of bitter
The greatness of Nineveh was short-lived. In around 627 BC, after the death of its last great king Ashurbanipal, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began to unravel through a series of bitter
Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
n city of Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been ...
, located in the modern-day city of Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
in northern Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to the north, Iran to the east, the Persian Gulf and K ...
. It is located on the eastern bank of the Tigris
The Tigris () is the easternmost of the two great rivers that define Mesopotamia, the other being the Euphrates. The river flows south from the mountains of the Armenian Highlands through the Syrian and Arabian Deserts, and empties into the ...
River and was the capital and largest city of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
, as well as the largest city in the world for several decades. Today, it is a common name for the half of Mosul that lies on the eastern bank of the Tigris, and the country's Nineveh Governorate takes its name from it.
It was the largest city in the world for approximately fifty years until the year 612 BC when, after a bitter period of civil war in Assyria, it was sacked by a coalition of its former subject peoples including the Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
and Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
. The city was never again a political or administrative centre, but by Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
it was the seat of a Christian bishop. It declined relative to Mosul during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
and was mostly abandoned by the 13th century AD.
Its ruins lie across the river from the historical city center of Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
, in Iraq's Nineveh Governorate. The two main tells, or mound-ruins, within the walls are Tell Kuyunjiq and Tell Nabī Yūnus, site of a shrine to Jonah
Jonah or Jonas, ''Yōnā'', "dove"; gr, Ἰωνᾶς ''Iōnâs''; ar, يونس ' or '; Latin: ''Ionas'' Ben (Hebrew), son of Amittai, is a prophet in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran, from Gath-hepher of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria ...
, the prophet who preached to Nineveh. Large amounts of Assyrian sculpture
Assyrian sculpture is the sculpture of the ancient Assyrian states, especially the Neo-Assyrian Empire of 911 to 612 BC, which was centered around the city of Assur in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) which at its height, ruled over all of Mesopo ...
and other artifacts have been excavated there, and are now located in museums around the world.
Name
The English placename Nineveh comes fromLatin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
' and Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond ...
Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
''Nineuḗ'' () under influence of the Biblical Hebrew
Hebrew (; ; ) is a Northwest Semitic language of the Afroasiatic language family. Historically, it is one of the spoken languages of the Israelites and their longest-surviving descendants, the Jews and Samaritans. It was largely preserved ...
''Nīnəweh'' (),''Oxford English Dictionary'', 3rd ed. "Ninevite, ''n.'' and ''adj.''" Oxford University Press (Oxford), 2013. from the Akkadian ' ( ''Ninâ''). or Old Babylonian
Old Babylonian may refer to:
*the period of the First Babylonian dynasty (20th to 16th centuries BC)
*the historical stage of the Akkadian language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Camb ...
'. The original meaning of the name is unclear but may have referred to a patron goddess. The cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
for ''Ninâ'' () is a fish within a house (cf. Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
''nuna'', "fish"). This may have simply intended "Place of Fish" or may have indicated a goddess associated with fish or the Tigris, possibly originally of Hurrian
The Hurrians (; cuneiform: ; transliteration: ''Ḫu-ur-ri''; also called Hari, Khurrites, Hourri, Churri, Hurri or Hurriter) were a people of the Bronze Age Near East. They spoke a Hurrian language and lived in Anatolia, Syria and Northern ...
origin. The city was later said to be devoted to "the goddess Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
of Nineveh" and ''Nina'' was one of the Sumerian and Assyrian names of that goddess.
Additionally, the word נון/נונא in Old Babylonian
Old Babylonian may refer to:
*the period of the First Babylonian dynasty (20th to 16th centuries BC)
*the historical stage of the Akkadian language
Akkadian (, Akkadian: )John Huehnergard & Christopher Woods, "Akkadian and Eblaite", ''The Camb ...
refers to the Anthiinae genus of fish, further indicating the possibility of an association between the name Nineveh and fish.
The city was also known as ''Ninuwa'' in Mari; ''Ninawa'' in Aramaic
The Aramaic languages, short Aramaic ( syc, ܐܪܡܝܐ, Arāmāyā; oar, 𐤀𐤓𐤌𐤉𐤀; arc, 𐡀𐡓𐡌𐡉𐡀; tmr, אֲרָמִית), are a language family containing many varieties (languages and dialects) that originated in ...
; Ninwe (ܢܸܢܘܵܐ) in Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
; and ''Nainavā'' () in Persian
Persian may refer to:
* People and things from Iran, historically called ''Persia'' in the English language
** Persians, the majority ethnic group in Iran, not to be conflated with the Iranic peoples
** Persian language, an Iranian language of the ...
.
''Nabī Yūnus'' is the Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
for "Prophet Jonah
Jonah or Jonas, ''Yōnā'', "dove"; gr, Ἰωνᾶς ''Iōnâs''; ar, يونس ' or '; Latin: ''Ionas'' Ben (Hebrew), son of Amittai, is a prophet in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran, from Gath-hepher of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria ...
". ''Kuyunjiq'' was, according to Layard, a Turkish name (Layard used the form "kouyunjik", diminutive of "koyun", "sheep" in Turkish), and it was known as ''Armousheeah'' by the Arabs, and is thought to have some connection with the Kara Koyunlu
The Qara Qoyunlu or Kara Koyunlu ( az, Qaraqoyunlular , fa, قره قویونلو), also known as the Black Sheep Turkomans, were a culturally Persianate, Muslim Turkoman "Kara Koyunlu, also spelled Qara Qoyunlu, Turkish Karakoyunlular, En ...
dynasty. These toponyms refer to the areas to the North and South of the Khosr stream, respectively: Kuyunjiq is the name for the whole northern sector enclosed by the city walls and is dominated by the large (35 ha) mound of Tell Kuyunjiq, while Nabī (or more commonly Nebi) Yunus is the southern sector around of the mosque of Prophet Yunus/Jonah, which is located on Tell Nebi Yunus.
Geography
The remains of ancient Nineveh, the areas of Kuyunjiq and Nabī Yūnus with their mounds, are located on a level part of the plain at the junction of the Tigris and the Khosr Rivers within an area of circumscribed by a fortification wall. This whole extensive space is now one immense area of ruins overlaid by c. one third by the Nebi Yunus suburbs of the city of eastern Mosul. The site of ancient Nineveh is bisected by the Khosr river. North of the Khosr, the site is called Kuyunjiq, including the acropolis of Tell Kuyunjiq; the illegal village of Rahmaniye lay in eastern Kuyunjiq. South of the Khosr, the urbanized area is called Nebi Yunus (also Ghazliya, Jezayr, Jammasa), including Tell Nebi Yunus where the mosque of the Prophet Jonah and a palace ofEsarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
/ Ashurbanipal below it are located. South of the street Al-'Asady (made by Daesh
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic ter ...
destroying swaths of the city walls) the area is called Jounub Ninawah or Shara Pepsi.
Nineveh was an important junction for commercial routes crossing the Tigris on the great roadway between the Mediterranean Sea
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on the ...
and the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by t ...
, thus uniting the East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
and the West, it received wealth from many sources, so that it became one of the greatest of all the region's ancient cities, and the last capital of the Neo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
.
History
Early history
Nineveh was one of the oldest and greatest cities in antiquity. Texts from theHellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
period later offered an eponym
An eponym is a person, a place, or a thing after whom or which someone or something is, or is believed to be, named. The adjectives which are derived from the word eponym include ''eponymous'' and ''eponymic''.
Usage of the word
The term ''epon ...
ous Ninus Ninus ( el, Νίνος) was a mythology character who according to Greek historians writing in the Hellenistic period and later, was the founder of Nineveh (also called Νίνου πόλις "city of Ninus" in Greek), ancient capital of Assyria.
In ...
as the founder of Νίνου πόλις (Ninopolis), although there is no historical basis for this. Book of Genesis
The Book of Genesis (from Greek ; Hebrew: בְּרֵאשִׁית ''Bəreʾšīt'', "In hebeginning") is the first book of the Hebrew Bible and the Christian Old Testament. Its Hebrew name is the same as its first word, ( "In the beginning" ...
10:11 says "Nimrod", possibly meaning Sargon I, built Nineveh. The context of Nineveh was as one of many centers within the regional development of Upper Mesopotamia
Upper Mesopotamia is the name used for the uplands and great outwash plain of northwestern Iraq, northeastern Syria and southeastern Turkey, in the northern Middle East. Since the early Muslim conquests of the mid-7th century, the region has been ...
. This area is defined as the plains which can support rain-fed agriculture. It exists as a narrow band from the Syrian coast to the Zagros mountains
The Zagros Mountains ( ar, جبال زاغروس, translit=Jibal Zaghrus; fa, کوههای زاگرس, Kuh hā-ye Zāgros; ku, چیاکانی زاگرۆس, translit=Çiyakani Zagros; Turkish: ''Zagros Dağları''; Luri: ''Kuh hā-ye Zāgr ...
. It is bordered by deserts to the south and mountains to the north. The cultural practices, technology, and economy in this region were shared and they followed a similar trajectory out of the neolithic.
Neolithic
Caves in the Zagros Mountains adjacent to the north side of the Nineveh Plains were used asPPNA
Pre-Pottery Neolithic A (PPNA) denotes the first stage of the Pre-Pottery Neolithic, in early Levantine and Anatolian Neolithic culture, dating to years ago, that is, 10,000–8,800 BCE. Archaeological remains are located in the Levantine and U ...
settlements, most famously Shanidar Cave
Shanidar Cave ( ku, Zewî Çemî Şaneder ,ئەشکەوتی شانەدەر, ) is an archaeological site located on Bradost Mountain, within the Zagros Mountains, in the Erbil Governorate of Kurdistan Region in northern Iraq.
It is known for the ...
. Nineveh itself was founded as early as 6000 BC during the late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
period. Deep sounding at Nineveh uncovered soil layers that have been dated to early in the era of the Hassuna
Tell Hassuna is a tell, or settlement mound, in the Nineveh Province (Iraq), about 35km south-west of Nineveh. It is the type site for the Hassuna culture (early sixth millennium BCE).
History of archaeological research
Tell Hassuna was found ...
archaeological culture. The development and culture of Nineveh paralleled Tepe Gawra
Tepe Gawra (Kurdish for "Great Mound") is an ancient Mesopotamian settlement 15 miles NNE of Mosul in northwest Iraq that was occupied between 5000 and 1500 BC. It is roughly a mile from the site of Nineveh and 2 miles E of the site of Khors ...
and Tell Arpachiyah a few kilometers to the northeast. Nineveh was a typical farming village in the Halaf Period.
Chalcolithic
In 5000 BC, Nineveh transitioned from a Halaf village to an Ubaid village. During the Late Chalcolithic period Nineveh was part one of the few Ubaid villages in Upper Mesopotamia which became a proto-cityUgarit
)
, image =Ugarit Corbel.jpg
, image_size=300
, alt =
, caption = Entrance to the Royal Palace of Ugarit
, map_type = Near East#Syria
, map_alt =
, map_size = 300
, relief=yes
, location = Latakia Governorate, Syria
, region = ...
, Brak, Hamoukar, Arbela, Alep
)), is an adjective which means "white-colored mixed with black".
, motto =
, image_map =
, mapsize =
, map_caption =
, image_map1 =
...
, and regionally at Susa, Eridu, Nippur. During the period between 4500 and 4000 BC it grew to 40ha.
The greater Nineveh area is notable in the diffusion of metal technology across the near east as the first location outside of Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
to smelt copper. Tell Arpachiyah has the oldest copper smelting remains, and Tepe Gawa has the oldest metal work. The copper came from the mines at Ergani
Ergani ( ota, عثمانيه, translit=Osmaniye, ku, Erxenî), formerly known as Arghni or Arghana, is a district of Diyarbakır Province of Turkey. The district's area is 1489 km. Ergani District is located in the administrative as the Sou ...
.
Early Bronze Age
Nineveh became a trade colony ofUruk
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.Harm ...
during the Uruk Expansion
Uruk, also known as Warka or Warkah, was an ancient city of Sumer (and later of Babylonia) situated east of the present bed of the Euphrates River on the dried-up ancient channel of the Euphrates east of modern Samawah, Al-Muthannā, Iraq.H ...
because of its location as the highest navigable point on the Tigris. It was contemporary and had a similar function to Habuba Kabira on the Euphrates. By 3000 BC, Kish civilization had expanded into Nineveh. At this time, the main temple of Nineveh becomes known as Ishtar temple, re-dedicated to the Semite goddess Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
, in the form of Ishtar of Nineveh. Ishtar of Nineveh was conflated with Šauška
Šauška (also Shaushka, Šauša, Šawuška) was a Hurrian goddess who was also adopted into the Hittite pantheon. Her name has a Hurrian origin and means the great or magnificent one.
Character and iconography
Shaushka was a goddess of war and ...
from the Hurro-Urartian pantheon. This temple was called 'House of Exorcists' (Cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
: 𒂷𒈦𒈦 GA2.MAŠ.MAŠ; Sumerian: e2 mašmaš). The context of the etymology surrounding the name is the Exorcist called a Mashmash in Sumerian, was a freelance magician who operated independent of the official priesthood, and was in part a medical professional via the act of expelling demons.
Ninevite 5 period
The regional influence of Nineveh became particularly pronounced during the archaeological period known as ''Ninevite 5'', or ''Ninevite V'' (2900–2600 BC). This period is defined primarily by the characteristic pottery that is found widely throughout Upper Mesopotamia.Ian Shaw''A Dictionary of Archaeology''
John Wiley & Sons, 2002 p. 427 Also, for the Upper Mesopotamian region, the ''Early Jezirah'' chronology has been developed by archaeologists. According to this regional chronology, 'Ninevite 5' is equivalent to the Early Jezirah I–II period. Ninevite 5 was preceded by the Late
Uruk period
The Uruk period (ca. 4000 to 3100 BC; also known as Protoliterate period) existed from the protohistoric Chalcolithic to Early Bronze Age period in the history of Mesopotamia, after the Ubaid period and before the Jemdet Nasr period. Named after ...
. Ninevite 5 pottery is roughly contemporary to the Early Transcaucasian culture ware, and the Jemdet Nasr period
The Jemdet Nasr Period is an archaeological culture in southern Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq). It is generally dated from 3100 to 2900 BC. It is named after the type site Tell Jemdet Nasr, where the assemblage typical for this period was first r ...
ware. Iraqi ''Scarlet Ware'' culture also belongs to this period; this colourful painted pottery is somewhat similar to Jemdet Nasr ware. Scarlet Ware was first documented in the Diyala River basin in Iraq. Later, it was also found in the nearby Hamrin Basin, and in Luristan. It is also contemporary with the Proto-Elamite
The Proto-Elamite period, also known as Susa III, is a chronological era in the ancient history of the area of Elam, dating from . In archaeological terms this corresponds to the late Banesh period. Proto-Elamite sites are recognized as the olde ...
period in Susa.
Akkadian period
At this time Nineveh was still an autonomouscity-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
. It was incorporated into the Akkadian Empire
The Akkadian Empire () was the first ancient empire of Mesopotamia after the long-lived civilization of Sumer. It was centered in the city of Akkad () and its surrounding region. The empire united Akkadian and Sumerian speakers under one ...
. The early city (and subsequent buildings) was constructed on a fault line
In geology, a fault is a planar fracture or discontinuity in a volume of rock across which there has been significant displacement as a result of rock-mass movements. Large faults within Earth's crust result from the action of plate tectonic ...
and, consequently, suffered damage from a number of earthquakes. One such event destroyed the first temple of Ishtar, which was rebuilt in 2260 BC by the Akkadian king Manishtushu
Manishtushu (, ''Ma-an-ish-tu-su'') was the third king of the Akkadian Empire, reigning from c. 2270 BC until his assassination in 2255 BC (Middle Chronology). He was the son of Sargon the Great, the founder of the Akkadian Empire, and he was su ...
.
Ur III period
In the final phase of the Early Bronze, Mesopotamia was dominated by theUr III
The Third Dynasty of Ur, also called the Neo-Sumerian Empire, refers to a 22nd to 21st century BC ( middle chronology) Sumerian ruling dynasty based in the city of Ur and a short-lived territorial-political state which some historians consider t ...
empire.
Middle Bronze
After the fall of Ur in 2000 BC, with the transition into the Middle Bronze, Nineveh was absorbed into the rising power ofAssyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
.
Old Assyrian period
The historic Nineveh is mentioned in theOld Assyrian Empire
The Old Assyrian period was the second stage of Assyrian history, covering the history of the city of Assur from its rise as an independent city-state under Puzur-Ashur I 2025 BC to the foundation of a larger Assyrian territorial state after th ...
during the reign of Shamshi-Adad I
Shamshi-Adad ( akk, Šamši-Adad; Amorite: ''Shamshi-Addu''), ruled 1808–1776 BC, was an Amorite warlord and conqueror who had conquered lands across much of Syria, Anatolia, and Upper Mesopotamia.Some of the Mari letters addressed to Shamsi-Ad ...
(1809-1775) in about 1800 BC as a centre of worship
Worship is an act of religious devotion usually directed towards a deity. It may involve one or more of activities such as veneration, adoration, praise, and praying. For many, worship is not about an emotion, it is more about a recogniti ...
of Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
, whose cult was responsible for the city's early importance.
Late Bronze
Mitanni period
The goddess's statue was sent to Pharaoh Amenhotep III ofEgypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
in the 14th century BC, by orders of the king of Mitanni
Mitanni (; Hittite cuneiform ; ''Mittani'' '), c. 1550–1260 BC, earlier called Ḫabigalbat in old Babylonian texts, c. 1600 BC; Hanigalbat or Hani-Rabbat (''Hanikalbat'', ''Khanigalbat'', cuneiform ') in Assyrian records, or ''Naharin'' in ...
. The Assyria
Assyria ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , romanized: ''māt Aššur''; syc, ܐܬܘܪ, ʾāthor) was a major ancient Mesopotamian civilization which existed as a city-state at times controlling regional territories in the indigenous lands of the ...
n city of Nineveh became one of Mitanni's vassals for half a century until the early 14th century BC.
Middle Assyrian period
The Assyrian kingAshur-uballit I
Ashur-uballit I ''(Aššur-uballiṭ I)'', who reigned between 1363 and 1328 BC, was the first king of the Middle Assyrian Empire. After his father Eriba-Adad I had broken Mitanni influence over Assyria, Ashur-uballit I's defeat of the Mitanni ...
reclaimed it in 1365 BC while overthrowing the Mitanni Empire and creating the Middle Assyrian Empire (1365–1050 BC).
There is a large body of evidence to show that Assyrian monarchs built extensively in Nineveh during the late 3rd and 2nd millenniums BC; it appears to have been originally an "Assyrian provincial town". Later monarchs whose inscriptions have appeared on the high city include the Middle Assyrian Empire kings Shalmaneser I
Shalmaneser I (𒁹𒀭𒁲𒈠𒉡𒊕 md''sál-ma-nu-SAG'' ''Salmanu-ašared''; 1273–1244 BC or 1265–1235 BC) was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian Empire. Son of Adad-nirari I, he succeeded his father as king in 1265 BC.
Accord ...
(1274–1245 BC) and Tiglath-Pileser I
Tiglath-Pileser I (; from the Hebraic form of akk, , Tukultī-apil-Ešarra, "my trust is in the son of Ešarra") was a king of Assyria during the Middle Assyrian period (1114–1076 BC). According to Georges Roux, Tiglath-Pileser was "one of ...
(1114–1076 BC), both of whom were active builders in Assur
Aššur (; Sumerian: AN.ŠAR2KI, Assyrian cuneiform: ''Aš-šurKI'', "City of God Aššur"; syr, ܐܫܘܪ ''Āšūr''; Old Persian ''Aθur'', fa, آشور: ''Āšūr''; he, אַשּׁוּר, ', ar, اشور), also known as Ashur and Qal ...
(Ashur).
Iron Age
Neo-Assyrians
During theNeo-Assyrian Empire
The Neo-Assyrian Empire was the fourth and penultimate stage of ancient Assyrian history and the final and greatest phase of Assyria as an independent state. Beginning with the accession of Adad-nirari II in 911 BC, the Neo-Assyrian Empire grew t ...
, particularly from the time of Ashurnasirpal II (ruled 883–859 BC) onward, there was considerable architectural expansion. Successive monarchs such as Tiglath-pileser III
Tiglath-Pileser III ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "my trust belongs to the son of Ešarra"), was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 745 BC to his death in 727. One of the most prominent and historically significant Assyrian kings, T ...
, Sargon II, Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
, Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
, and Ashurbanipal maintained and founded new palaces, as well as temples to Sîn, Ashur, Nergal, Shamash, Ninurta, Ishtar
Inanna, also sux, 𒀭𒊩𒌆𒀭𒈾, nin-an-na, label=none is an ancient Mesopotamian goddess of love, war, and fertility. She is also associated with beauty, sex, divine justice, and political power. She was originally worshiped in Su ...
, Tammuz, Nisroch
Nisroch ( ''Nīsrōḵ''; arc, ܢܝܼܫܪܵܟ݂; el, Νεσεραχ; la, Nesroch) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Assyrian god in whose temple King Sennacherib was worshiping when he was assassinated by his sons Adrammelech and Sharezer ...
and Nabu
Nabu ( akk, cuneiform: 𒀭𒀝 Nabû syr, ܢܵܒܼܘܼ\ܢܒܼܘܿ\ܢܵܒܼܘܿ Nāvū or Nvō or Nāvō) is the ancient Mesopotamian patron god of literacy, the rational arts, scribes, and wisdom.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian "nab ...
.

Sennacherib's development of Nineveh
It wasSennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
who made Nineveh a truly magnificent city (c. 700 BC). He laid out new streets and squares and built within it the South West Palace, or "palace without a rival", the plan of which has been mostly recovered and has overall dimensions of about . It comprised at least 80 rooms, many of which were lined with sculpture. A large number of cuneiform
Cuneiform is a logo-syllabic script that was used to write several languages of the Ancient Middle East. The script was in active use from the early Bronze Age until the beginning of the Common Era. It is named for the characteristic wedge-sh ...
tablets were found in the palace. The solid foundation was made out of limestone blocks and mud bricks; it was tall. In total, the foundation is made of roughly of brick (approximately 160 million bricks). The walls on top, made out of mud brick, were an additional tall.
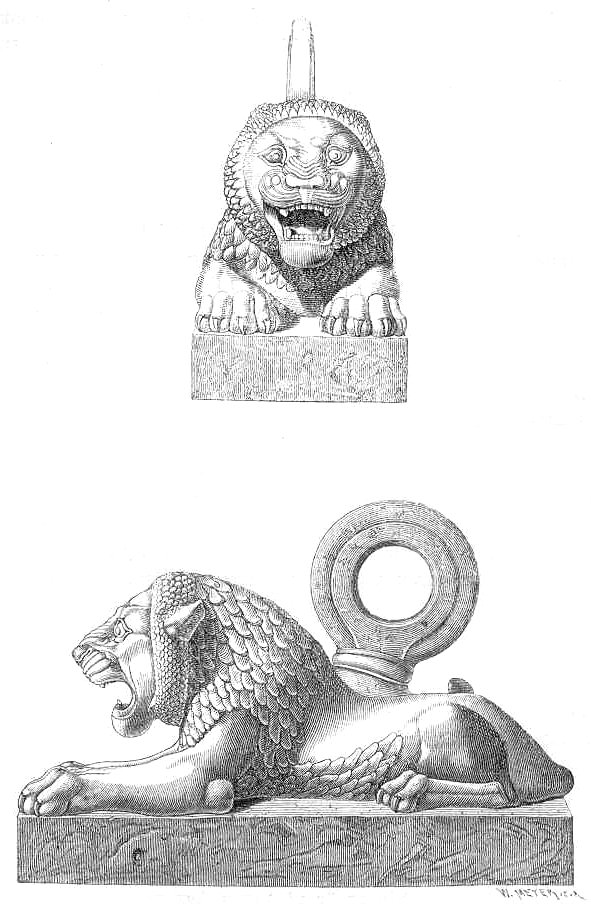
Some of the principal doorways were flanked by colossal stone ''lamassu
''Lama'', ''Lamma'', or ''Lamassu'' (Cuneiform: , ; Sumerian: lammař; later in Akkadian: ''lamassu''; sometimes called a ''lamassus'') is an Assyrian protective deity.
Initially depicted as a goddess in Sumerian times, when it was called ''La ...
'' door figures weighing up to ; these were winged Mesopotamian lions or bull
A bull is an intact (i.e., not castrated) adult male of the species ''Bos taurus'' (cattle). More muscular and aggressive than the females of the same species (i.e., cows), bulls have long been an important symbol in many religions,
includin ...
s, with human heads. These were transported from quarries at Balatai, and they had to be lifted up once they arrived at the site, presumably by a ramp
An inclined plane, also known as a ramp, is a flat supporting surface tilted at an angle from the vertical direction, with one end higher than the other, used as an aid for raising or lowering a load. The inclined plane is one of the six clas ...
. There are also of stone Assyrian palace reliefs
Assyrian sculpture is the sculpture of the ancient Assyrian states, especially the Neo-Assyrian Empire of 911 to 612 BC, which was centered around the city of Assur in Mesopotamia (modern-day Iraq) which at its height, ruled over all of Mesopotam ...
, that include pictorial records documenting every construction step including carving the statues and transporting them on a barge. One picture shows 44 men towing a colossal statue. The carving shows three men directing the operation while standing on the Colossus. Once the statues arrived at their destination, the final carving was done. Most of the statues weigh between .
The stone carvings in the walls include many battle scenes, impalings and scenes showing Sennacherib's men parading the spoils of war before him. The inscriptions boasted of his conquests: he wrote of Babylon: "Its inhabitants, young and old, I did not spare, and with their corpses I filled the streets of the city." A full and characteristic set shows the campaign leading up to the siege of Lachish in 701; it is the "finest" from the reign of Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
, and now in the British Museum. He later wrote about a battle in Lachish
Lachish ( he, לכיש; grc, Λαχίς; la, Lachis) was an ancient Canaanite and Israelite city in the Shephelah ("lowlands of Judea") region of Israel, on the South bank of the Lakhish River, mentioned several times in the Hebrew Bible. Th ...
: "And Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
of Judah who had not submitted to my yoke...him I shut up in Jerusalem his royal city like a caged bird. Earthworks I threw up against him, and anyone coming out of his city gate I made pay for his crime. His cities which I had plundered I had cut off from his land."
At this time, the total area of Nineveh comprised about , and fifteen great gates penetrated its walls. An elaborate system of eighteen canals brought water from the hills to Nineveh, and several sections of a magnificently constructed aqueduct erected by Sennacherib were discovered at Jerwan
Jerwan is a locality north of Mosul in the Nineveh Province of Iraq. The site is clear of vegetation and is sparsely settled.
The site is famous for the ruins of an enormous aqueduct crossing the Khenis River, constructed of more than two mill ...
, about distant. The enclosed area had more than 100,000 inhabitants (maybe closer to 150,000), about twice as many as Babylon at the time, placing it among the largest settlements worldwide.
Some scholars such as Stephanie Dalley at Oxford
Oxford () is a city in England. It is the county town and only city of Oxfordshire. In 2020, its population was estimated at 151,584. It is north-west of London, south-east of Birmingham and north-east of Bristol. The city is home to the ...
believe that the garden which Sennacherib built next to his palace, with its associated irrigation works, were the original Hanging Gardens of Babylon; Dalley's argument is based on a disputation of the traditional placement of the Hanging Gardens attributed to Berossus
Berossus () or Berosus (; grc, Βηρωσσος, Bērōssos; possibly derived from akk, , romanized: , "Bel is his shepherd") was a Hellenistic-era Babylonian writer, a priest of Bel Marduk and astronomer who wrote in the Koine Greek language ...
together with a combination of literary and archaeological evidence.
After Ashurbanipal
 The greatness of Nineveh was short-lived. In around 627 BC, after the death of its last great king Ashurbanipal, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began to unravel through a series of bitter
The greatness of Nineveh was short-lived. In around 627 BC, after the death of its last great king Ashurbanipal, the Neo-Assyrian Empire began to unravel through a series of bitter civil wars
A civil war or intrastate war is a war between organized groups within the same state (or country).
The aim of one side may be to take control of the country or a region, to achieve independence for a region, or to change government polici ...
between rival claimants for the throne, and in 616 BC Assyria was attacked by its own former vassals, the Babylonians
Babylonia (; Akkadian: , ''māt Akkadī'') was an ancient Akkadian-speaking state and cultural area based in the city of Babylon in central-southern Mesopotamia (present-day Iraq and parts of Syria). It emerged as an Amorite-ruled state c. 1 ...
, Chaldeans, Medes
The Medes ( Old Persian: ; Akkadian: , ; Ancient Greek: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Iranian people who spoke the Median language and who inhabited an area known as Media between western and northern Iran. Around the 11th century BC, ...
, Persians
The Persians are an Iranian ethnic group who comprise over half of the population of Iran. They share a common cultural system and are native speakers of the Persian language as well as of the languages that are closely related to Persian.
...
, Scythians
The Scythians or Scyths, and sometimes also referred to as the Classical Scythians and the Pontic Scythians, were an ancient Eastern
* : "In modern scholarship the name 'Sakas' is reserved for the ancient tribes of northern and eastern Centra ...
and Cimmerians
The Cimmerians (Akkadian: , romanized: ; Hebrew: , romanized: ; Ancient Greek: , romanized: ; Latin: ) were an ancient Eastern Iranian equestrian nomadic people originating in the Caspian steppe, part of whom subsequently migrated into Wes ...
. In about 616 BC Kalhu
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a majo ...
was sacked, the allied forces eventually reached Nineveh, besieging and sacking the city in 612 BC, following bitter house-to-house fighting, after which it was razed. Most of the people in the city who could not escape to the last Assyrian strongholds in the north and west were either massacred or deported out of the city and into the countryside where they founded new settlements. Many unburied skeletons were found by the archaeologists at the site. The Assyrian Empire then came to an end by 605 BC, the Medes and Babylonians dividing its colonies between themselves.
It is not clear whether Nineveh came under the rule of the Medes or the Neo-Babylonian Empire
The Neo-Babylonian Empire or Second Babylonian Empire, historically known as the Chaldean Empire, was the last polity ruled by monarchs native to Mesopotamia. Beginning with the coronation of Nabopolassar as the King of Babylon in 626 BC and bei ...
in 612. The Babylonian ''Chronicle Concerning the Fall of Nineveh
A chronicle ( la, chronica, from Greek language, Greek ''chroniká'', from , ''chrónos'' – "time") is a historical account of events arranged in chronology, chronological order, as in a timeline. Typically, equal weight is given for historic ...
'' records that Nineveh was "turned into mounds and heaps", but this is literary hyperbole. The complete destruction of Nineveh has traditionally been seen as confirmed by the Hebrew ''Book of Ezekiel
The Book of Ezekiel is the third of the Latter Prophets in the Tanakh and one of the major prophetic books, following Isaiah and Jeremiah. According to the book itself, it records six visions of the prophet Ezekiel, exiled in Babylon, during ...
'' and the Greek '' Retreat of the Ten Thousand'' of Xenophon
Xenophon of Athens (; grc, Ξενοφῶν ; – probably 355 or 354 BC) was a Greek military leader, philosopher, and historian, born in Athens. At the age of 30, Xenophon was elected commander of one of the biggest Greek mercenary armies o ...
(d. 354 BC).Stephanie Dalley (1993), "Nineveh after 612 BC", ''Altorientalische Forschungen'' 20(1): 134–147. There are no later cuneiform tablets in Akkadian from Nineveh. Although devastated in 612, the city was not completely abandoned. Yet, to the Greek historians Ctesias
Ctesias (; grc-gre, Κτησίας; fl. fifth century BC), also known as Ctesias of Cnidus, was a Greek physician and historian from the town of Cnidus in Caria, then part of the Achaemenid Empire.
Historical events
Ctesias, who lived in the fi ...
and Herodotus
Herodotus ( ; grc, , }; BC) was an ancient Greek historian and geographer
A geographer is a physical scientist, social scientist or humanist whose area of study is geography, the study of Earth's natural environment and human society ...
(c. 400 BC), Nineveh was a thing of the past; and when Xenophon passed the place in the 4th century BC he described it as abandoned.
Later history
The earliest piece of written evidence for the persistence of Nineveh as a settlement is possibly theCyrus Cylinder
The Cyrus Cylinder is an ancient clay cylinder, now broken into several pieces, on which is written a declaration in Akkadian cuneiform script in the name of Persia's Achaemenid king Cyrus the Great. Kuhrt (2007), p. 70, 72 It dates from the 6th c ...
of 539/538 BC, but the reading of this is disputed. If correctly read as Nineveh, it indicates that Cyrus the Great restored the temple of Ishtar at Nineveh and probably encouraged resettlement. A number of cuneiform Elamite
Elamite, also known as Hatamtite and formerly as Susian, is an extinct language that was spoken by the ancient Elamites. It was used in what is now southwestern Iran from 2600 BC to 330 BC. Elamite works disappear from the archeological record ...
tablets have been found at Nineveh. They probably date from the time of the revival of Elam in the century following the collapse of Assyria. The Hebrew ''Book of Jonah
The Book of Jonah is collected as one of the twelve minor prophets of the Nevi'im ("Prophets") in the Hebrew Bible, and as a book in its own right in the Christian Old Testament. The book tells of a Hebrew prophet named Jonah, son of Amittai, wh ...
'', which Stephanie Dalley asserts was written in the 4th century BC, is an account of the city's repentance and God's mercy which prevented destruction.
Archaeologically, there is evidence of repairs at the temple of Nabu after 612 and for the continued use of Sennacherib's palace. There is evidence of syncretic Hellenistic
In Classical antiquity, the Hellenistic period covers the time in Mediterranean history after Classical Greece, between the death of Alexander the Great in 323 BC and the emergence of the Roman Empire, as signified by the Battle of Actium in ...
cults. A statue of Hermes
Hermes (; grc-gre, wikt:Ἑρμῆς, Ἑρμῆς) is an Olympian deity in ancient Greek religion and Greek mythology, mythology. Hermes is considered the herald of the gods. He is also considered the protector of human heralds, travelle ...
has been found and a Greek inscription attached to a shrine of the Sebitti
The Sebitti or Sebittu are a group of seven minor war gods in Neo-Sumerian, Akkadian, Babylonian and especially Assyrian tradition. They also appear in sources from Emar. Multiple different interpretations of the term occur in Mesopotamian lite ...
. A statue of Herakles Epitrapezios dated to the 2nd century AD has also been found. The library of Ashurbanipal may still have been in use until around the time of Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, Ἀλέξανδρος, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC – 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
.
The city was actively resettled under the Seleucid Empire.Peter Webb, "Nineveh and Mosul", in O. Nicholason (ed.), '' The Oxford Dictionary of Late Antiquity'' (Oxford University Press, 2018), vol. 2, p. 1078. There is evidence of more changes in Sennacherib's palace under the Parthian Empire
The Parthian Empire (), also known as the Arsacid Empire (), was a major Iranian political and cultural power in ancient Iran from 247 BC to 224 AD. Its latter name comes from its founder, Arsaces I, who led the Parni tribe in conque ...
. The Parthians also established a municipal mint at Nineveh coining in bronze. According to Tacitus
Publius Cornelius Tacitus, known simply as Tacitus ( , ; – ), was a Roman historian and politician. Tacitus is widely regarded as one of the greatest Roman historians by modern scholars.
The surviving portions of his two major works—the ...
, in AD 50 Meherdates, a claimant to the Parthian throne with Roman support, took Nineveh.J. E. Reade (1998), "Greco-Parthian Nineveh", ''Iraq'' 60: 65–83.
By Late Antiquity
Late antiquity is the time of transition from classical antiquity to the Middle Ages, generally spanning the 3rd–7th century in Europe and adjacent areas bordering the Mediterranean Basin. The popularization of this periodization in English ha ...
, Nineveh was restricted to the east bank of the Tigris and the west bank was uninhabited. Under the Sasanian Empire, Nineveh was not an administrative centre. By the 2nd century AD there were Christians
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words '' Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρ ...
present and by 554 it was a bishopric
In church governance, a diocese or bishopric is the ecclesiastical district under the jurisdiction of a bishop.
History
In the later organization of the Roman Empire, the increasingly subdivided provinces were administratively associate ...
of the Church of the East. King Khosrow II (591–628) built a fortress on the west bank, and two Christian monasteries were constructed around 570 and 595. This growing settlement was not called Mosul
Mosul ( ar, الموصل, al-Mawṣil, ku, مووسڵ, translit=Mûsil, Turkish: ''Musul'', syr, ܡܘܨܠ, Māwṣil) is a major city in northern Iraq, serving as the capital of Nineveh Governorate. The city is considered the second larg ...
until after the Arab conquests. It may have been called Hesnā ʿEbrāyē (Jews' Fort).
In 627, the city was the site of the Battle of Nineveh between the Eastern Roman Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantin ...
and the Sasanians. In 641, it was conquered by the Arabs, who built a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
on the west bank and turned it into an administrative centre. Under the Umayyad dynasty
Umayyad dynasty ( ar, بَنُو أُمَيَّةَ, Banū Umayya, Sons of Umayya) or Umayyads ( ar, الأمويون, al-Umawiyyūn) were the ruling family of the Caliphate between 661 and 750 and later of Al-Andalus between 756 and 1031. In t ...
, it eclipsed Nineveh, which was reduced to a Christian suburb with limited new construction. By the 13th century, Nineveh was mostly ruins. A church was converted into a Muslim shrine to the prophet Jonah
Jonah or Jonas, ''Yōnā'', "dove"; gr, Ἰωνᾶς ''Iōnâs''; ar, يونس ' or '; Latin: ''Ionas'' Ben (Hebrew), son of Amittai, is a prophet in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran, from Gath-hepher of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria ...
, which continued to attract pilgrims until its destruction by ISIL in 2014.
Biblical Nineveh
In theHebrew Bible
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Ashur left that land, and built Nineveh". Some modern English translations interpret "Ashur" in the Hebrew of this verse as the country "Assyria" rather than a person, thus making
'' Ashur left that land, and built Nineveh". Some modern English translations interpret "Ashur" in the Hebrew of this verse as the country "Assyria" rather than a person, thus making
Nimrod
Nimrod (; ; arc, ܢܡܪܘܕ; ar, نُمْرُود, Numrūd) is a biblical figure mentioned in the Book of Genesis and Books of Chronicles. The son of Cush and therefore a great-grandson of Noah, Nimrod was described as a king in the land of ...
, rather than Ashur, the founder of Nineveh. Sir Walter Raleigh's notion that Nimrod built Nineveh, and the cities in Genesis 10:11–12, has also been refuted by scholars. The discovery of the fifteen Jubilees
The Book of Jubilees, sometimes called Lesser Genesis (Leptogenesis), is an ancient Jewish religious work of 50 chapters (1,341 verses), considered canonical by the Ethiopian Orthodox Church as well as Beta Israel (Ethiopian Jews), where it is ...
texts found amongst the Dead Sea Scrolls
The Dead Sea Scrolls (also the Qumran Caves Scrolls) are ancient Jewish and Hebrew religious manuscripts discovered between 1946 and 1956 at the Qumran Caves in what was then Mandatory Palestine, near Ein Feshkha in the West Bank, on the ...
has since shown that, according to the Jewish
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
sects of Qumran, Genesis 10:11 affirms the apportionment of Nineveh to Ashur. The attribution of Nineveh to Ashur is also supported by the Greek Septuagint
The Greek Old Testament, or Septuagint (, ; from the la, septuaginta, lit=seventy; often abbreviated ''70''; in Roman numerals, LXX), is the earliest extant Greek translation of books from the Hebrew Bible. It includes several books beyond th ...
, King James Bible, Geneva Bible, and by Roman historian Flavius Josephus
Flavius Josephus (; grc-gre, Ἰώσηπος, ; 37 – 100) was a first-century Romano-Jewish historian and military leader, best known for '' The Jewish War'', who was born in Jerusalem—then part of Roman Judea—to a father of priestly ...
in his '' Antiquities of the Jews'' (Antiquities, i, vi, 4).
Nineveh was the flourishing capital of the Assyrian Empire and was the home of King Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
, King of Assyria, during the Biblical reign of King Hezekiah
Hezekiah (; hbo, , Ḥīzqīyyahū), or Ezekias); grc, Ἐζεκίας 'Ezekías; la, Ezechias; also transliterated as or ; meaning "Yahweh, Yah shall strengthen" (born , sole ruler ), was the son of Ahaz and the 13th king of Kingdom of Jud ...
() and the lifetime of Judean prophet Isaiah
Isaiah ( or ; he, , ''Yəšaʿyāhū'', "God is Salvation"), also known as Isaias, was the 8th-century BC Israelite prophet after whom the Book of Isaiah is named.
Within the text of the Book of Isaiah, Isaiah himself is referred to as "the ...
(). As recorded in Hebrew scripture, Nineveh was also the place where Sennacherib died at the hands of his two sons, who then fled to the vassal land of ''`rrt'' (Urartu
Urartu (; Assyrian: ',Eberhard Schrader, ''The Cuneiform inscriptions and the Old Testament'' (1885), p. 65. Babylonian: ''Urashtu'', he, אֲרָרָט ''Ararat'') is a geographical region and Iron Age kingdom also known as the Kingdom of V ...
). The book of the prophet Nahum
Nahum ( or ; he, נַחוּם ''Naḥūm'') was a minor prophet whose prophecy is recorded in the ''Tanakh'', also called the Hebrew Bible and The Old Testament. His book comes in chronological order between Micah and Habakkuk in the Bible. ...
is almost exclusively taken up with prophetic denunciations against Nineveh. Its ruin and utter desolation are foretold. Its end was strange, sudden, and tragic. According to the Bible, it was God's doing, his judgment on Assyria's pride. In fulfillment of prophecy, God made "an utter end of the place". It became a "desolation". The prophet Zephaniah
Zephaniah (, ) is the name of several people in the Hebrew Bible and Jewish Tanakh, the most prominent one being the prophet who prophesied in the days of Josiah, king of Judah (640–609 BCE) and is attributed a book bearing his name among the ...
also predicts its destruction along with the fall of the empire of which it was the capital. Nineveh is also the setting of the Book of Tobit.
The Book of Jonah
The Book of Jonah is collected as one of the twelve minor prophets of the Nevi'im ("Prophets") in the Hebrew Bible, and as a book in its own right in the Christian Old Testament. The book tells of a Hebrew prophet named Jonah, son of Amittai, wh ...
, set in the days of the Assyrian Empire, describes it as an "exceedingly great city of three days' journey in breadth", whose population at that time is given as "more than 120,000". Genesis 10:11–12 lists four cities "Nineveh, Rehoboth, Calah, and Resen", ambiguously stating that either Resen or Calah is "the great city". The ruins of Kuyunjiq, Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a m ...
, Karamlesh
Karamlesh ( syr, ܟܪܡܠܫ, ar, كرمليس; also spelled ''Karemlash'', ''Karemles'', ''Karemlish'', etc.) is an Assyrian town in northern Iraq located less than south east of Mosul.
It is surrounded by many hills that along with it made up ...
and Khorsabad
Dur-Sharrukin ("Fortress of Sargon"; ar, دور شروكين, Syriac: ܕܘܪ ܫܪܘ ܘܟܢ), present day Khorsabad, was the Assyrian capital in the time of Sargon II of Assyria. Khorsabad is a village in northern Iraq, 15 km northeast of Mo ...
form the four corners of an irregular quadrilateral. The ruins of the "great city" Nineveh, with the whole area included within the parallelogram they form by lines drawn from the one to the other, are generally regarded as consisting of these four sites. The description of Nineveh in Jonah likely was a reference to greater Nineveh, including the surrounding cities of Rehoboth, Calah and Resen The Book of Jonah depicts Nineveh as a wicked city worthy of destruction. God sent Jonah to preach to the Ninevites of their coming destruction, and they fasted and repented because of this. As a result, God spared the city; when Jonah protests against this, God states he is showing mercy for the population who are ignorant of the difference between right and wrong ("who cannot discern between their right hand and their left hand") and mercy for the animals in the city.
Nineveh's repentance and salvation from evil can be found in the Hebrew Tanakh
The Hebrew Bible or Tanakh (;"Tanach"
'' Old Testament), and referred to in the Christian
 In 1847 the young British diplomat Austen Henry Layard explored the ruins. Layard did not use modern archaeological methods; his stated goal was "to obtain the largest possible number of well preserved objects of art at the least possible outlay of time and money". In the Kuyunjiq mound, Layard rediscovered in 1849 the lost palace of Sennacherib with its 71 rooms and colossal
In 1847 the young British diplomat Austen Henry Layard explored the ruins. Layard did not use modern archaeological methods; his stated goal was "to obtain the largest possible number of well preserved objects of art at the least possible outlay of time and money". In the Kuyunjiq mound, Layard rediscovered in 1849 the lost palace of Sennacherib with its 71 rooms and colossal
SBAH
led by Nicolò Marchetti, began (with four campaigns having taken place thus far between 2019 and 2022) a long-term project aiming at the excavation, conservation and public presentation of the lower town of Nineveh. Work was carried out in eighteen excavation areas, from the Adad Gate – now completely repaired (after removing hundreds of tons of debris from ISIL's destructions), explored and protected with a new roof – deep into the Nebi Yunus town. In a few areas a thick later stratigraphy was encountered, but the late 7th century BC stratum was reached everywhere (actually in two areas in the pre-Sennacherib lower town the excavations already exposed older strata, up to the 11th century BC until now, aiming in the future at exploring the first settlement therein). The site is greatly endangered with dumping of debris, illegal settlements and quarrying as the main threats.
 Today, Nineveh's location is marked by two large mounds, Tell Kuyunjiq and Tell ''Nabī Yūnus'' "Prophet
Today, Nineveh's location is marked by two large mounds, Tell Kuyunjiq and Tell ''Nabī Yūnus'' "Prophet  Tell Nebi Yunus is located about south of Kuyunjiq and is the secondary ruin mound at Nineveh. On the basis of texts of Sennacherib, the site has traditionally been identified as the "armory" of Nineveh, and a gate and pavements excavated by Iraqis in 1954 have been considered to be part of the "armory" complex. Excavations in 1990 revealed a monumental entryway consisting of a number of large inscribed
Tell Nebi Yunus is located about south of Kuyunjiq and is the secondary ruin mound at Nineveh. On the basis of texts of Sennacherib, the site has traditionally been identified as the "armory" of Nineveh, and a gate and pavements excavated by Iraqis in 1954 have been considered to be part of the "armory" complex. Excavations in 1990 revealed a monumental entryway consisting of a number of large inscribed
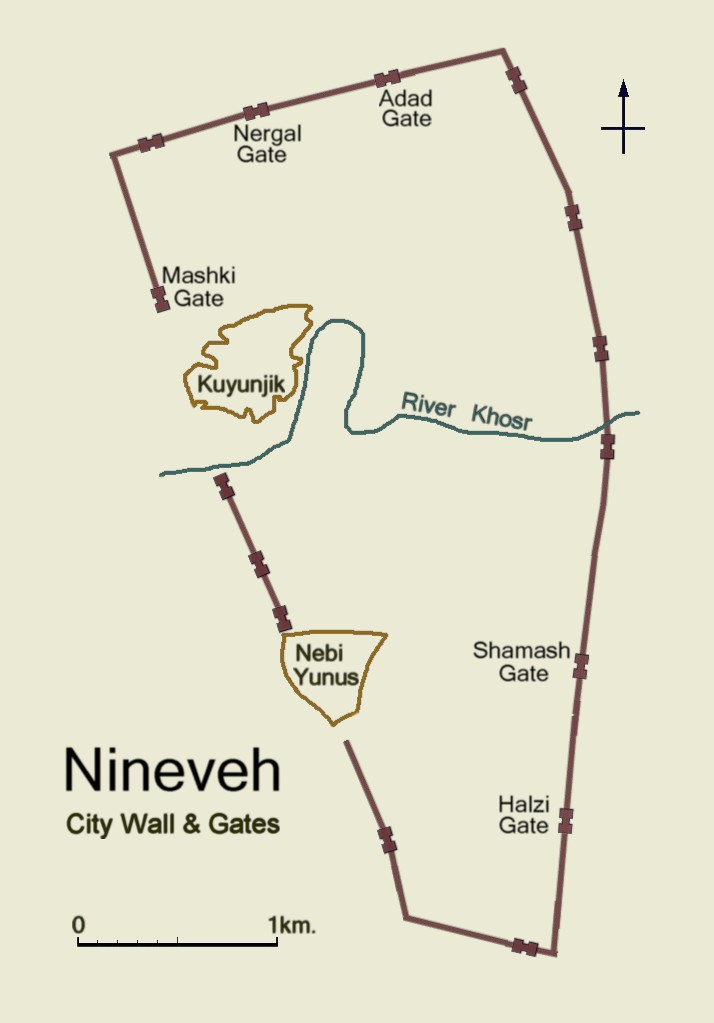

 The ruins of Nineveh are surrounded by the remains of a massive stone and mudbrick wall dating from about 700 BC. About 12 km in length, the wall system consisted of an ashlar stone retaining wall about high surmounted by a mudbrick wall about high and thick. The stone retaining wall had projecting stone towers spaced about every . The stone wall and towers were topped by three-step
The ruins of Nineveh are surrounded by the remains of a massive stone and mudbrick wall dating from about 700 BC. About 12 km in length, the wall system consisted of an ashlar stone retaining wall about high surmounted by a mudbrick wall about high and thick. The stone retaining wall had projecting stone towers spaced about every . The stone wall and towers were topped by three-step
 Atherstone's friend, the artist John Martin, created a painting of the same name inspired by the poem. The English poet
Atherstone's friend, the artist John Martin, created a painting of the same name inspired by the poem. The English poet
Joanne Farchakh-Bajjaly photos
of Nineveh taken in May 2003 showing damage from looters
John Malcolm Russell, "Stolen stones: the modern sack of Nineveh"
in ''Archaeology''; looting of sculptures in the 1990s
Nineveh page
at the British Museum's website. Includes photographs of items from their collection.
A teaching and research tool presenting a comprehensive picture of Nineveh within the history of archaeology in the Near East, including a searchable data repository for meaningful analysis of currently unlinked sets of data from different areas of the site and different episodes in the 160-year history of excavations
CyArk Digital Nineveh Archives
publicly accessible, free depository of the data from the previously linked UC Berkeley Nineveh Archives project, fully linked and georeferenced in a
Photos of Nineveh, 1989–1990
: Babylonian Chronicle Concerning the Fall of Nineveh
Layard's Nineveh and its Remains- full text
{{Authority control Populated places established in the 6th millennium BC Populated places disestablished in the 13th century Ancient Assyrian cities Destroyed cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Assyria Assyrian geography Hebrew Bible cities Nineveh Governorate Former populated places in Iraq Ancient Mesopotamia Jonah Tells (archaeology) Hassuna culture Nimrod Book of Jubilees Old Assyrian Empire City-states
'' Old Testament), and referred to in the Christian
New Testament
The New Testament grc, Ἡ Καινὴ Διαθήκη, transl. ; la, Novum Testamentum. (NT) is the second division of the Christian biblical canon. It discusses the teachings and person of Jesus, as well as events in first-century Chri ...
and Muslim Quran
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , s ...
. To this day, Syriac Syriac may refer to:
*Syriac language, an ancient dialect of Middle Aramaic
*Sureth, one of the modern dialects of Syriac spoken in the Nineveh Plains region
* Syriac alphabet
** Syriac (Unicode block)
** Syriac Supplement
* Neo-Aramaic languages a ...
and Oriental Orthodox churches commemorate the three days Jonah spent inside the fish during the Fast of Nineveh
In Syriac Christianity, the Fast of Nineveh ( syc, ܒܥܘܬܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܝ̈ܐ ', literally "Petition of the Ninevites") is a three-day fast starting the third Monday before Clean Monday from Sunday Midnight to Wednesday noon during participants ...
. Some Christians observe this holiday fast by refraining from food and drink, with churches encouraging followers to refrain from meat, fish and dairy products.
Archaeology
The location of Nineveh was known, to some, continuously through the Middle Ages. Benjamin of Tudela visited it in 1170; Petachiah of Regensburg soon after.Carsten Niebuhr
Carsten Niebuhr, or Karsten Niebuhr (17 March 1733 Lüdingworth – 26 April 1815 Meldorf, Dithmarschen), was a German mathematician, cartographer, and explorer in the service of Denmark. He is renowned for his participation in the Royal Danish ...
recorded its location during the 1761–1767 Danish expedition. Niebuhr wrote afterwards that "I did not learn that I was at so remarkable a spot, till near the river. Then they showed me a village on a great hill, which they call Nunia, and a mosque, in which the prophet Jonah was buried. Another hill in this district is called Kalla Nunia, or the Castle of Nineveh. On that lies a village Koindsjug."
Excavation history
In 1842, the French Consul General at Mosul, Paul-Émile Botta, began to search the vast mounds that lay along the opposite bank of the river. While at Tell Kuyunjiq he had little success, the locals whom he employed in these excavations, to their great surprise, came upon the ruins of a building at the 20 km far-away mound ofKhorsabad
Dur-Sharrukin ("Fortress of Sargon"; ar, دور شروكين, Syriac: ܕܘܪ ܫܪܘ ܘܟܢ), present day Khorsabad, was the Assyrian capital in the time of Sargon II of Assyria. Khorsabad is a village in northern Iraq, 15 km northeast of Mo ...
, which, on further exploration, turned out to be the royal palace of Sargon II, in which large numbers of reliefs were found and recorded, though they had been damaged by fire and were mostly too fragile to remove.
 In 1847 the young British diplomat Austen Henry Layard explored the ruins. Layard did not use modern archaeological methods; his stated goal was "to obtain the largest possible number of well preserved objects of art at the least possible outlay of time and money". In the Kuyunjiq mound, Layard rediscovered in 1849 the lost palace of Sennacherib with its 71 rooms and colossal
In 1847 the young British diplomat Austen Henry Layard explored the ruins. Layard did not use modern archaeological methods; his stated goal was "to obtain the largest possible number of well preserved objects of art at the least possible outlay of time and money". In the Kuyunjiq mound, Layard rediscovered in 1849 the lost palace of Sennacherib with its 71 rooms and colossal bas-relief
Relief is a sculptural method in which the sculpted pieces are bonded to a solid background of the same material. The term '' relief'' is from the Latin verb ''relevo'', to raise. To create a sculpture in relief is to give the impression that th ...
s. He also unearthed the palace and famous library of Ashurbanipal with 22,000 cuneiform clay tablets. Most of Layard's material was sent to the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
, but others were dispersed elsewhere as two large pieces which were given to Lady Charlotte Guest
Lady Charlotte Elizabeth Guest (née Bertie; 19 May 1812 – 15 January 1895), later Lady Charlotte Schreiber, was an English aristocrat who is best known as the first publisher in modern print format of the '' Mabinogion'', the earliest prose l ...
and eventually found their way to the Metropolitan Museum
The Metropolitan Museum of Art of New York City, colloquially "the Met", is the largest art museum in the Americas. Its permanent collection contains over two million works, divided among 17 curatorial departments. The main building at 1000 ...
. The study of the archaeology of Nineveh reveals the wealth and glory of ancient Assyria under kings such as Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
(681–669 BC) and Ashurbanipal (669–626 BC).
The work of exploration was carried on by Hormuzd Rassam
Hormuzd Rassam ( ar, هرمز رسام; syr, ܗܪܡܙܕ ܪܣܐܡ; 182616 September 1910), was an Assyriologist and author.
He is known for making a number of important archaeological discoveries from 1877 to 1882, including the clay tablets tha ...
(an Assyrian), George Smith and others, and a vast treasury of specimens of Assyria was incrementally exhumed for European museums. Palace after palace was discovered, with their decorations and their sculptured slabs, revealing the life and manners of this ancient people, their arts of war and peace, the forms of their religion, the style of their architecture, and the magnificence of their monarchs.
The mound of Kuyunjiq was excavated again by the archaeologists of the British Museum
The British Museum is a public museum dedicated to human history, art and culture located in the Bloomsbury area of London. Its permanent collection of eight million works is among the largest and most comprehensive in existence. It docum ...
, led by Leonard William King, at the beginning of the 20th century. Their efforts concentrated on the site of the Temple of Nabu
Nabu ( akk, cuneiform: 𒀭𒀝 Nabû syr, ܢܵܒܼܘܼ\ܢܒܼܘܿ\ܢܵܒܼܘܿ Nāvū or Nvō or Nāvō) is the ancient Mesopotamian patron god of literacy, the rational arts, scribes, and wisdom.
Etymology and meaning
The Akkadian "nab ...
, the god of writing, where another cuneiform library was supposed to exist. However, no such library was ever found: most likely, it had been destroyed by the activities of later residents.
The excavations started again in 1927, under the direction of Campbell Thompson Campbell may refer to:
People Surname
* Campbell (surname), includes a list of people with surname Campbell
Given name
* Campbell Brown (footballer), an Australian rules footballer
* Campbell Brown (journalist) (born 1968), American television ne ...
, who had taken part in King's expeditions. Some works were carried out outside Kuyunjiq, for instance on the mound of Tell Nebi Yunus, which was the ancient arsenal of Nineveh, or along the outside walls. Here, near the northwestern corner of the walls, beyond the pavement of a later building, the archaeologists found almost 300 fragments of prisms recording the royal annals of Sennacherib, Esarhaddon, and Ashurbanipal, beside a prism of Esarhaddon which was almost perfect.
After the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
, several excavations were carried out by Iraqi archaeologists. From 1951 to 1958, Mohammed Ali Mustafa worked the site. The work was continued from 1967 through 1971 by Tariq Madhloom. Some additional excavation occurred by Manhal Jabur from the early 1970s to 1987. For the most part, these digs focused on Tell Nebi Yunus.
The British archaeologist and Assyriologist Professor David Stronach
David Brian Stronach (10 June 1931 – 27 June 2020) was a British archaeologist of ancient Iran and Iraq. He was an emeritus professor at the University of California, Berkeley.
Stronach was an expert on the city of Pasargadae. He was edu ...
of the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
conducted a series of surveys and digs at the site from 1987 to 1990, focusing his attentions on the several gates and the existent mudbrick walls, as well as the system that supplied water to the city in times of siege. The excavation reports are in progress.
Most recently, an Iraqi–Italian Archaeological Expedition by the Alma Mater Studiorum – University of Bologna and the IraqSBAH
led by Nicolò Marchetti, began (with four campaigns having taken place thus far between 2019 and 2022) a long-term project aiming at the excavation, conservation and public presentation of the lower town of Nineveh. Work was carried out in eighteen excavation areas, from the Adad Gate – now completely repaired (after removing hundreds of tons of debris from ISIL's destructions), explored and protected with a new roof – deep into the Nebi Yunus town. In a few areas a thick later stratigraphy was encountered, but the late 7th century BC stratum was reached everywhere (actually in two areas in the pre-Sennacherib lower town the excavations already exposed older strata, up to the 11th century BC until now, aiming in the future at exploring the first settlement therein). The site is greatly endangered with dumping of debris, illegal settlements and quarrying as the main threats.
Archaeological remains
 Today, Nineveh's location is marked by two large mounds, Tell Kuyunjiq and Tell ''Nabī Yūnus'' "Prophet
Today, Nineveh's location is marked by two large mounds, Tell Kuyunjiq and Tell ''Nabī Yūnus'' "Prophet Jonah
Jonah or Jonas, ''Yōnā'', "dove"; gr, Ἰωνᾶς ''Iōnâs''; ar, يونس ' or '; Latin: ''Ionas'' Ben (Hebrew), son of Amittai, is a prophet in the Hebrew Bible and the Quran, from Gath-hepher of the northern Kingdom of Israel (Samaria ...
", and the remains of the city walls (about in circumference). The Neo-Assyrian levels of Kuyunjiq have been extensively explored. The other mound, ''Nabī Yūnus'', has not been as extensively explored because there was an Arab Muslim shrine dedicated to that prophet on the site. On July 24, 2014, the Islamic State
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
destroyed the shrine as part of a campaign to destroy religious sanctuaries it deemed "un-Islamic", but also to loot that site through tunneling.
The ruin mound of Kuyunjiq rises about above the surrounding plain of the ancient city. It is quite broad, measuring about . Its upper layers have been extensively excavated, and several Neo-Assyrian palaces and temples have been found there. A deep sounding by Max Mallowan revealed evidence of habitation as early as the 6th millennium BC. Today, there is little evidence of these old excavations other than weathered pits and earth piles. In 1990, the only Assyrian remains visible were those of the entry court and the first few chambers of the Palace of Sennacherib. Since that time, the palace chambers have received significant damage by looters. Portions of relief sculptures that were in the palace chambers in 1990 were seen on the antiquities market by 1996. Photographs of the chambers made in 2003 show that many of the fine relief sculptures there have been reduced to piles of rubble.
orthostats
This article describes several characteristic architectural elements typical of European megalithic ( Stone Age) structures.
Forecourt
In archaeology, a forecourt is the name given to the area in front of certain types of chamber tomb. Forecourts ...
and "bull-man" sculptures, some apparently unfinished.
Following the liberation of Mosul, the tunnels under Tell Nebi Yunus were explored in 2018, in which a 3000-year-old palace was discovered, including a pair of reliefs, each showing a row of women, along with reliefs of ''lamassu
''Lama'', ''Lamma'', or ''Lamassu'' (Cuneiform: , ; Sumerian: lammař; later in Akkadian: ''lamassu''; sometimes called a ''lamassus'') is an Assyrian protective deity.
Initially depicted as a goddess in Sumerian times, when it was called ''La ...
''.
City wall and gates
merlon
A merlon is the solid upright section of a battlement (a crenellated parapet) in medieval architecture or fortifications.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 202. Merlons are sometimes ...
s.
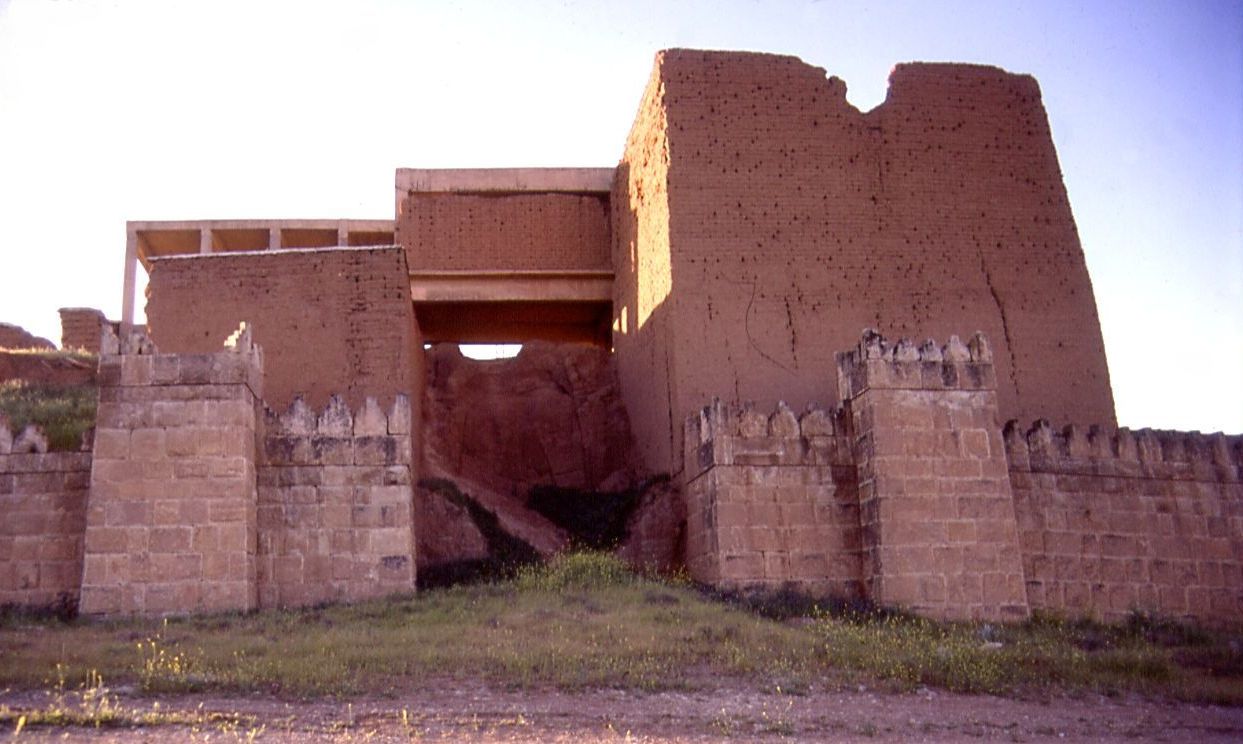
Five of the gateways have been explored to some extent by archaeologists:
* Mashki Gate (ماشکی دروازه): Translated "Gate of the Water Carriers" (''Mashki'' from Persian root word ''Mashk'', meaning waterskin), also ''Masqi Gate'' (Arabic: بوابة مسقي), it was perhaps used to take livestock to water from the Tigris which currently flows about to the west. It has been reconstructed in fortified mudbrick to the height of the top of the vaulted passageway. The Assyrian original may have been plastered and ornamented. It was bulldozed along with the Adad Gate during ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
occupation. During the restoration project, seven alabaster carvings depicting Sennacherib reliefs were found at the gate in 2022.
* Nergal Gate: Named for the god Nergal, it may have been used for some ceremonial purpose, as it is the only known gate flanked by stone sculptures of winged bull-men (''lamassu
''Lama'', ''Lamma'', or ''Lamassu'' (Cuneiform: , ; Sumerian: lammař; later in Akkadian: ''lamassu''; sometimes called a ''lamassus'') is an Assyrian protective deity.
Initially depicted as a goddess in Sumerian times, when it was called ''La ...
''). The reconstruction is conjectural, as the gate was excavated by Layard in the mid-19th century and reconstructed in the mid-20th century. The lamassu on this gate were defaced with a jackhammer by ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
forces.
* Adad Gate: Adad Gate was named for the god Adad
Hadad ( uga, ), Haddad, Adad ( Akkadian: 𒀭𒅎 '' DIM'', pronounced as ''Adād''), or Iškur ( Sumerian) was the storm and rain god in the Canaanite and ancient Mesopotamian religions.
He was attested in Ebla as "Hadda" in c. 2500 BCE. ...
. A reconstruction was begun in the 1960s by Iraqis but was not completed. The result was a mixture of concrete and eroding mudbrick, which nonetheless does give some idea of the original structure. The excavator left some features unexcavated, allowing a view of the original Assyrian construction. The original brickwork of the outer vaulted passageway was well exposed, as was the entrance of the vaulted stairway to the upper levels. The actions of Nineveh's last defenders could be seen in the hastily built mudbrick construction which narrowed the passageway from . Around April 13, 2016, ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
demolished both the gate and the adjacent wall by flattening them with a bulldozer.
* Shamash Gate: Named for the sun god Shamash, it opens to the road to Erbil. It was excavated by Layard in the 19th century. The stone retaining wall and part of the mudbrick structure were reconstructed in the 1960s. The mudbrick reconstruction has deteriorated significantly. The stone wall projects outward about from the line of main wall for a width of about . It is the only gate with such a significant projection. The mound of its remains towers above the surrounding terrain. Its size and design suggest it was the most important gate in Neo-Assyrian times.
* Hali Gate: Near the south end of the eastern city wall. Exploratory excavations were undertaken here by the University of California, Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant u ...
expedition of 1989–1990. There is an outward projection of the city wall, though not as pronounced as at the Shamash Gate. The entry passage had been narrowed with mudbrick to about as at the Adad Gate. Human remains from the final battle of Nineveh were found in the passageway. Located in the eastern wall, it is the southernmost and largest of all the remaining gates of ancient Nineveh.
Threats to the site
By 2003, the site of Nineveh was exposed to decay of its reliefs by a lack of proper protective roofing, vandalism and looting holes dug into chamber floors. Future preservation is further compromised by the site's proximity to expanding suburbs. The ailingMosul Dam
Mosul Dam ( ar, سد الموصل), formerly known as Saddam Dam (), is the largest dam in Iraq. It is located on the Tigris river in the western governorate of Nineveh, upstream of the city of Mosul. The dam serves to generate hydroelectricity ...
is a persistent threat to Nineveh as well as the city of Mosul. This is in no small part due to years of disrepair (in 2006, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers
, colors =
, anniversaries = 16 June (Organization Day)
, battles =
, battles_label = Wars
, website =
, commander1 = ...
cited it as the most dangerous dam in the world), the cancellation of a second dam project in the 1980s to act as flood relief in case of failure, and occupation by ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
in 2014 resulting in fleeing workers and stolen equipment. If the dam fails, the entire site could be under as much as 45 feet (14 m) of water.
In an October 2010 report titled ''Saving Our Vanishing Heritage ''Saving Our Vanishing Heritage: Safeguarding Endangered Cultural Heritage Sites in the Developing World'' was a report released by Global Heritage Fund on October 17, 2010. It illuminated five accelerating man-made threats facing global heritage si ...
'', Global Heritage Fund
Global Heritage Fund is a non-profit organization that operates internationally.
Founded in California, United States, California in 2002, its mission is to "transform local communities by investing in global heritage."
To date, it has partnere ...
named Nineveh one of 12 sites most "on the verge" of irreparable destruction and loss, citing insufficient management, development pressures and looting as primary causes.
By far, the greatest threat to Nineveh has been purposeful human actions by ISIL
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
, which first occupied the area in the mid-2010s. In early 2015, they announced their intention to destroy the walls of Nineveh if the Iraqis tried to liberate the city. They also threatened to destroy artifacts. On February 26 they destroyed several items and statues in the Mosul Museum
The Mosul Museum ( ar, متحف الموصل) is the second largest museum in Iraq after the National Museum of Iraq in Baghdad. It was heavily looted during the 2003 Iraq War. Founded in 1952, the museum consisted of a small hall until a new bu ...
and are believed to have plundered others to sell overseas. The items were mostly from the Assyrian exhibit, which ISIL declared blasphemous
Blasphemy is a speech crime and religious crime usually defined as an utterance that shows contempt, disrespects or insults a deity, an object considered sacred or something considered inviolable. Some religions regard blasphemy as a religio ...
and idolatrous
Idolatry is the worship of a cult image or "idol" as though it were God. In Abrahamic religions (namely Judaism, Samaritanism, Christianity, the Baháʼí Faith, and Islam) idolatry connotes the worship of something or someone other than the A ...
. There were 300 items remaining in the museum out of a total of 1,900, with the other 1,600 being taken to the National Museum of Iraq
The Iraq Museum ( ar, المتحف العراقي) is the national museum of Iraq, located in Baghdad. It is sometimes informally called the National Museum of Iraq, a recent phenomenon influenced by other nations' naming of their national museum ...
in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon. I ...
for security reasons prior to the 2014 Fall of Mosul
The Fall of Mosul occurred between 410 June 2014, when Islamic State insurgents, initially led by Abu Abdulrahman al-Bilawi, captured Mosul from the Iraqi Army, led by Lieutenant General Mahdi Al-Gharrawi.
On 4 June, the insurgents began their ...
. Some of the artifacts sold and/or destroyed were from Nineveh. Just a few days after the destruction of the museum pieces, they demolished remains at major UNESCO world heritage sites Khorsabad
Dur-Sharrukin ("Fortress of Sargon"; ar, دور شروكين, Syriac: ܕܘܪ ܫܪܘ ܘܟܢ), present day Khorsabad, was the Assyrian capital in the time of Sargon II of Assyria. Khorsabad is a village in northern Iraq, 15 km northeast of Mo ...
, Nimrud
Nimrud (; syr, ܢܢܡܪܕ ar, النمرود) is an ancient Assyrian city located in Iraq, south of the city of Mosul, and south of the village of Selamiyah ( ar, السلامية), in the Nineveh Plains in Upper Mesopotamia. It was a m ...
, and Hatra
Hatra ( ar, الحضر; syr, ܚܛܪܐ) was an ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The city lies northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul.
Hatra was a strongly fortified ...
.
Rogation of the Ninevites (Nineveh's Wish)
Assyrians of theAncient Church of the East
The Ancient Church of the East is an Eastern Christian denomination. It branched from the Assyrian Church of the East in 1964, under the leadership of Mar Thoma Darmo (d. 1969). It is one of three Assyrian Churches that claim continuity with t ...
, Chaldean Catholic Church, Syriac Catholic Church, Syriac Orthodox Church, Assyrian Church of the East and Saint Thomas Christians
The Saint Thomas Christians, also called Syrian Christians of India, ''Marthoma Suriyani Nasrani'', ''Malankara Nasrani'', or ''Nasrani Mappila'', are an ethno-religious community of Indian Christians in the state of Kerala ( Malabar region ...
of the Syro-Malabar Church
lat, Ecclesia Syrorum-Malabarensium mal, മലബാറിലെ സുറിയാനി സഭ
, native_name_lang=, image = St. Thomas' Cross (Chennai, St. Thomas Mount).jpg
, caption = The Mar Thoma Nasrani Sl ...
observe a fast called ''Ba'uta d-Ninwe'' (ܒܥܘܬܐ ܕܢܝܢܘܐ) which means ''Nineveh's Prayer''. Copts and Ethiopian Orthodox
The Ethiopian Orthodox Tewahedo Church ( am, የኢትዮጵያ ኦርቶዶክስ ተዋሕዶ ቤተ ክርስቲያን, ''Yäityop'ya ortodoks täwahedo bétäkrestyan'') is the largest of the Oriental Orthodox Churches. One of the few Chris ...
also maintain this fast.
Popular culture
The English Romantic poet Edwin Atherstone wrote an epic ''The Fall of Nineveh
''The Fall of Nineveh'' is a long poem in blank verse by Edwin Atherstone. It consists of thirty books preceded by a Prelude. The poem was written over many years and published 1828–1868. It tells of the battles and events during the war betwee ...
''. The work tells of an uprising against its king Sardanapalus of all the nations that were dominated by the Assyrian Empire. He is a great criminal. He has had one hundred prisoners of war executed. After a long struggle the town is conquered by Median and Babylonian troops led by prince Arbaces and priest Belesis. The king sets his own palace on fire and dies inside together with all his concubines.
 Atherstone's friend, the artist John Martin, created a painting of the same name inspired by the poem. The English poet
Atherstone's friend, the artist John Martin, created a painting of the same name inspired by the poem. The English poet John Masefield
John Edward Masefield (; 1 June 1878 – 12 May 1967) was an English poet and writer, and Poet Laureate of the United Kingdom, Poet Laureate from 1930 until 1967. Among his best known works are the children's novels ''The Midnight Folk'' and ...
's well-known, fanciful 1903 poem ''Cargoes
''Salt-Water Poems and Ballads'' is a book of poetry on themes of seafaring and maritime history by John Masefield. It was first published in 1916 by Macmillan Publishers, Macmillan, with illustrations by Charles Pears.
Many of the poems had b ...
'' mentions Nineveh in its first line. Nineveh is also mentioned in Rudyard Kipling
Joseph Rudyard Kipling ( ; 30 December 1865 – 18 January 1936)''The Times'', (London) 18 January 1936, p. 12. was an English novelist, short-story writer, poet, and journalist. He was born in British India, which inspired much of his work.
...
's 1897 poem '' Recessional'' and in Arthur O'Shaughnessy
Arthur William Edgar O'Shaughnessy (14 March 184430 January 1881) was a British poet and herpetologist. Of Irish descent, he was born in London. He is most remembered for his poem " Ode", from his 1874 collection ''Music and Moonlight'', which ...
's 1873 poem ''Ode
An ode (from grc, ᾠδή, ōdḗ) is a type of lyric poetry. Odes are elaborately structured poems praising or glorifying an event or individual, describing nature intellectually as well as emotionally. A classic ode is structured in three majo ...
''.
The 1962 Italian peplum film '' War Gods of Babylon'', is based on the sacking and fall of Nineveh by the combined rebel armies led by the Babylonians.
In '' Jonah: A VeggieTales Movie'', Jonah, much like his biblical counterpart, must travel to Nineveh due to God’s demands.
In the 1973 film ''The Exorcist
''The Exorcist'' is a 1973 American supernatural horror film directed by William Friedkin and written for the screen by William Peter Blatty, based on his 1971 novel of the same name. It stars Ellen Burstyn, Max von Sydow, Lee J. Cobb, Kitty ...
'', Father Lankester Merrin
Father Lankester Merrin is a fictional character in the novel ''The Exorcist'' (1971), one of the two main protagonists in the 1973 film adaptation, who also figures prominently in several of its prequel and sequel films.
In the novel
Merrin, ...
was on an archeological dig near Nineveh prior to returning to the United States and leading the exorcism of Reagan MacNiel.
See also
*Cities of the ancient Near East
The earliest cities in history were in the ancient Near East, an area covering roughly that of the modern Middle East: its history began in the 4th millennium BC and ended, depending on the interpretation of the term, either with the conquest by ...
* Destruction of cultural heritage by the Islamic State
Deliberate destruction and theft of cultural heritage has been conducted by the Islamic State since 2014 in Iraq, Syria, and to a lesser extent in Libya. The destruction targets various places of worship under ISIL control and ancient historical ...
* Historical urban community sizes
* Isaac of Nineveh
Isaac of Nineveh (; Arabic: إسحاق النينوي ''Ishaq an-Naynuwī''; grc-gre, Ἰσαὰκ Σῦρος; c. 613 – c. 700), also remembered as Saint Isaac the Syrian, Abba Isaac, Isaac Syrus and Isaac of Qatar, was a 7th-century Church o ...
* List of megalithic sites
* Nanshe
* Short chronology timeline
The chronology of the ancient Near East is a framework of dates for various events, rulers and dynasties. Historical inscriptions and texts customarily record events in terms of a succession of officials or rulers: "in the year X of king Y". Com ...
* Tel Keppe
Tel Keppe ( syr, ܬܸܠ ܟܹܐܦܹܐ ', ar, تل كيف ', alternatively spelled Tel Kaif or Telkef) is an Assyrian town in northern Iraq. It is located in the Nineveh Governorate, less than 8 mi (13 km) northeast of Mosul.Welcome to Te ...
Notes
References
:: * * * * ** ** ** ** ** * ** ** ** * * * - Nineveh 5, Vessel Pottery 2900 BC * - Early worship of Ishtar, Early / Prehistoric Nineveh * – Early / Prehistoric NinevehExternal links
Joanne Farchakh-Bajjaly photos
of Nineveh taken in May 2003 showing damage from looters
John Malcolm Russell, "Stolen stones: the modern sack of Nineveh"
in ''Archaeology''; looting of sculptures in the 1990s
Nineveh page
at the British Museum's website. Includes photographs of items from their collection.
A teaching and research tool presenting a comprehensive picture of Nineveh within the history of archaeology in the Near East, including a searchable data repository for meaningful analysis of currently unlinked sets of data from different areas of the site and different episodes in the 160-year history of excavations
CyArk Digital Nineveh Archives
publicly accessible, free depository of the data from the previously linked UC Berkeley Nineveh Archives project, fully linked and georeferenced in a
UC Berkeley
The University of California, Berkeley (UC Berkeley, Berkeley, Cal, or California) is a public land-grant research university in Berkeley, California. Established in 1868 as the University of California, it is the state's first land-grant uni ...
/CyArk
CyArk (from "cyber archive") is a 501(c)(3) nonprofit organization located in Oakland, California, United States founded in 2003. CyArk's mission is to "digitally record, archive and share the world's most significant cultural heritage and ensure ...
research partnership to develop the archive for open web use. Includes creative commons-licensed media items.
Photos of Nineveh, 1989–1990
: Babylonian Chronicle Concerning the Fall of Nineveh
Layard's Nineveh and its Remains- full text
{{Authority control Populated places established in the 6th millennium BC Populated places disestablished in the 13th century Ancient Assyrian cities Destroyed cities Archaeological sites in Iraq Assyria Assyrian geography Hebrew Bible cities Nineveh Governorate Former populated places in Iraq Ancient Mesopotamia Jonah Tells (archaeology) Hassuna culture Nimrod Book of Jubilees Old Assyrian Empire City-states