Nicotine poisoning on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Nicotine poisoning describes the symptoms of the toxic effects of
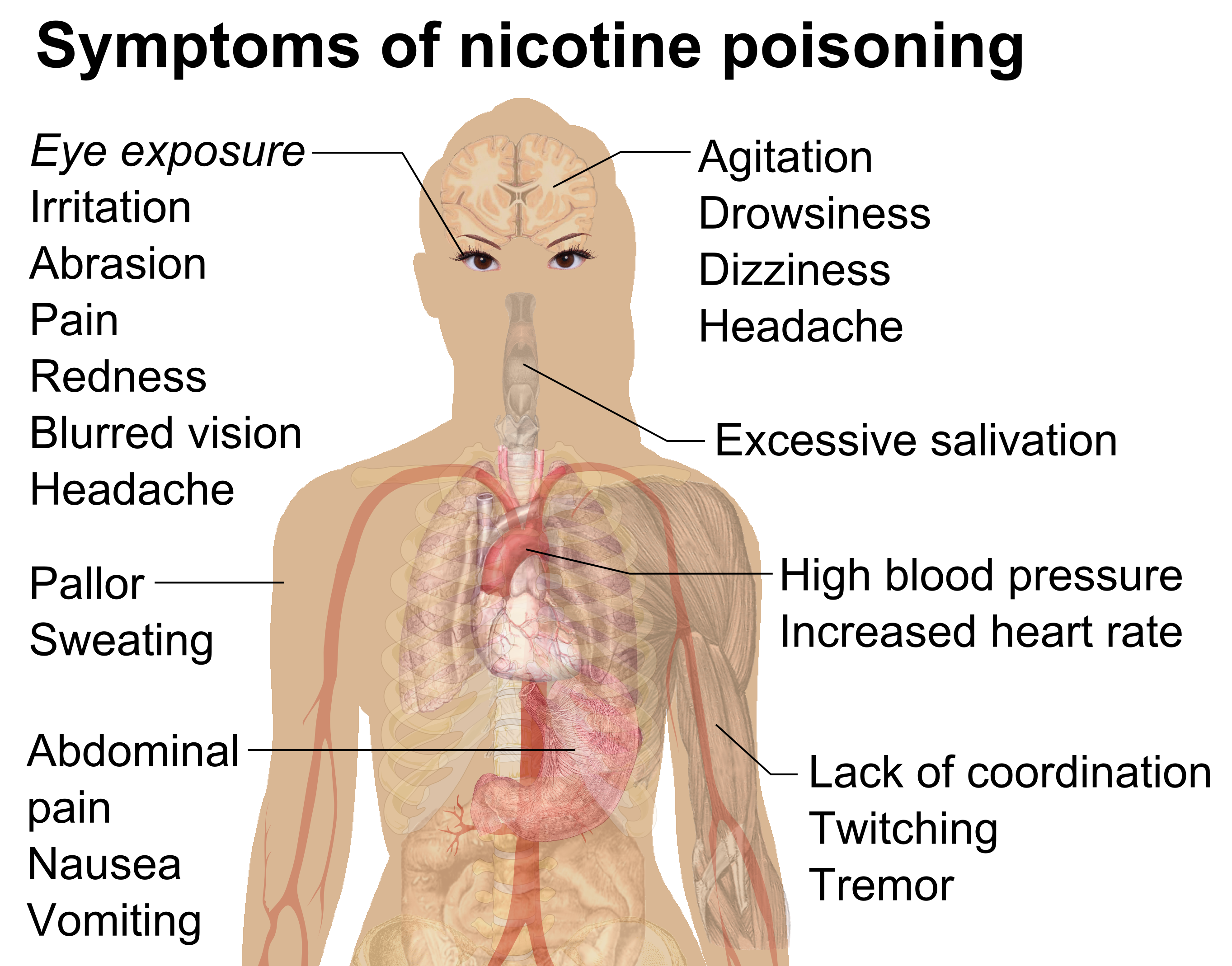 Nicotine poisoning tends to produce symptoms that follow a biphasic pattern. The initial symptoms are mainly due to stimulatory effects and include nausea and vomiting, excessive salivation, abdominal pain,
Nicotine poisoning tends to produce symptoms that follow a biphasic pattern. The initial symptoms are mainly due to stimulatory effects and include nausea and vomiting, excessive salivation, abdominal pain,
/ref> However the widely used human LD50 estimate of 0.5–1.0 mg/kg was questioned in a 2013 review, in light of several documented cases of humans surviving much higher doses; the 2013 review suggests that the lower limit causing fatal outcomes is 500–1000 mg of ingested nicotine, corresponding to 6.5–13 mg/kg orally. An accidental ingestion of only 6 mg may be lethal to children. It is unlikely that a person would overdose on nicotine through smoking alone. The US
nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
following ingestion, inhalation, or skin contact. Nicotine poisoning can potentially be deadly, though serious or fatal overdoses are rare. Historically, most cases of nicotine poisoning have been the result of use of nicotine as an insecticide
Insecticides are substances used to kill insects. They include ovicides and larvicides used against insect eggs and larvae, respectively. Insecticides are used in agriculture, medicine, industry and by consumers. Insecticides are claimed t ...
. More recent cases of poisoning typically appear to be in the form of Green Tobacco Sickness, or due to unintended ingestion of tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
or tobacco products or consumption of nicotine-containing plants.
Standard textbooks, databases, and safety sheets consistently state that the lethal dose of nicotine
Nicotine is a naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and '' Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As a pharmaceutical drug, it is use ...
for adults is 60 mg or less (30–60 mg), but there is overwhelming data indicating that more than 500 mg of oral nicotine is required to kill an adult.
Children may become ill following ingestion of one cigarette
A cigarette is a narrow cylinder containing a combustible material, typically tobacco, that is rolled into thin paper for smoking. The cigarette is ignited at one end, causing it to smolder; the resulting smoke is orally inhaled via the opp ...
; ingestion of more than this may cause a child to become severely ill. The nicotine in the e-liquid
An electronic cigarette is a handheld battery-powered vaporizer that simulates smoking, but without tobacco combustion. E-cigarette components include a mouthpiece (drip tip), a cartridge (liquid storage area), a heating element/ atomizer, a mic ...
of an electronic cigarette
An electronic cigarette is an electronic device that simulates tobacco smoking. It consists of an atomizer, a power source such as a battery, and a container such as a cartridge or tank. Instead of smoke, the user inhales vapor. As su ...
can be hazardous to infants and children, through accidental ingestion or skin contact. In some cases children have become poisoned by topical medicinal creams which contain nicotine.
People who harvest or cultivate tobacco may experience Green Tobacco Sickness (GTS), a type of nicotine poisoning caused by skin contact with wet tobacco leaves. This occurs most commonly in young, inexperienced tobacco harvesters who do not consume tobacco.
Signs and symptoms
 Nicotine poisoning tends to produce symptoms that follow a biphasic pattern. The initial symptoms are mainly due to stimulatory effects and include nausea and vomiting, excessive salivation, abdominal pain,
Nicotine poisoning tends to produce symptoms that follow a biphasic pattern. The initial symptoms are mainly due to stimulatory effects and include nausea and vomiting, excessive salivation, abdominal pain, pallor
Pallor is a pale color of the skin that can be caused by illness, emotional shock or stress, stimulant use, or anemia, and is the result of a reduced amount of oxyhaemoglobin and may also be visible as pallor of the conjunctivae of the eyes o ...
, sweating, hypertension
Hypertension (HTN or HT), also known as high blood pressure (HBP), is a long-term medical condition in which the blood pressure in the arteries is persistently elevated. High blood pressure usually does not cause symptoms. Long-term high b ...
, tachycardia
Tachycardia, also called tachyarrhythmia, is a heart rate that exceeds the normal resting rate. In general, a resting heart rate over 100 beats per minute is accepted as tachycardia in adults. Heart rates above the resting rate may be normal ( ...
, ataxia
Ataxia is a neurological sign consisting of lack of voluntary coordination of muscle movements that can include gait abnormality, speech changes, and abnormalities in eye movements. Ataxia is a clinical manifestation indicating dysfunction of ...
, tremor, headache, dizziness, muscle fasciculation
A fasciculation, or muscle twitch, is a spontaneous, involuntary muscle contraction and relaxation, involving fine muscle fibers. They are common, with as many as 70% of people experiencing them. They can be benign, or associated with more seri ...
s, and seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s. After the initial stimulatory phase, a later period of depressor effects can occur and may include symptoms of hypotension
Hypotension is low blood pressure. Blood pressure is the force of blood pushing against the walls of the arteries as the heart pumps out blood. Blood pressure is indicated by two numbers, the systolic blood pressure (the top number) and the di ...
and bradycardia
Bradycardia (also sinus bradycardia) is a slow resting heart rate, commonly under 60 beats per minute (BPM) as determined by an electrocardiogram. It is considered to be a normal heart rate during sleep, in young and healthy or elderly adults, ...
, central nervous system depression
Central nervous system (CNS) depression is a physiological state that can result in a decreased rate of breathing, decreased heart rate, and loss of consciousness possibly leading to coma or death.
It is the result of inhibited or suppressed brai ...
, coma
A coma is a deep state of prolonged unconsciousness in which a person cannot be awakened, fails to respond normally to painful stimuli, light, or sound, lacks a normal wake-sleep cycle and does not initiate voluntary actions. Coma patients exhi ...
, muscular weakness and/or paralysis, with difficulty breath
Breathing (or ventilation) is the process of moving air into and from the lungs to facilitate gas exchange with the internal environment, mostly to flush out carbon dioxide and bring in oxygen.
All aerobic creatures need oxygen for cellu ...
ing or respiratory failure
Respiratory failure results from inadequate gas exchange by the respiratory system, meaning that the arterial oxygen, carbon dioxide, or both cannot be kept at normal levels. A drop in the oxygen carried in the blood is known as hypoxemia; a rise ...
.
From September 1, 2010 to December 31, 2014, there were at least 21,106 traditional cigarette calls to US poison control centers. During the same period, the ten most frequent adverse effects to traditional cigarettes reported to US poison control centers were vomiting (80.0%), nausea (9.2%), drowsiness (7.8%), cough (7.2%), agitation (6.6%), pallor (3.0%), tachycardia (2.5%), diaphoresis (1.5%), dizziness (1.5%), and diarrhea (1.4%). 95% of traditional cigarette calls were related to children 5 years old or less. Most of the traditional cigarette calls were a minor effect.
Calls to US poison control centers related to e-cigarette exposures involved inhalations, eye exposures, skin exposures, and ingestion, in both adults and young children. Minor, moderate, and serious adverse effects involved adults and young children. Minor effects correlated with e-cigarette liquid poisoning were tachycardia, tremor, chest pain and hypertension. More serious effects were bradycardia, hypotension, nausea, respiratory paralysis, atrial fibrillation and dyspnea. The exact correlation
In statistics, correlation or dependence is any statistical relationship, whether causal or not, between two random variables or bivariate data. Although in the broadest sense, "correlation" may indicate any type of association, in statistic ...
is not fully known between these effects and e-cigarettes. 58% of e-cigarette calls to US poison control centers were related to children 5 years old or less. E-cigarette calls had a greater chance to report an adverse effect and a greater chance to report a moderate or major adverse effect than traditional cigarette calls. Most of the e-cigarette calls were a minor effect.
From September 1, 2010 to December 31, 2014, there were at least 5,970 e-cigarette calls to US poison control centers. During the same period, the ten most frequent adverse effects to e-cigarettes and e-liquid reported to US poison control centers were vomiting (40.4%), eye irritation or pain (20.3%), nausea (16.8%), red eye or conjunctivitis (10.5%), dizziness (7.5%), tachycardia (7.1%), drowsiness (7.1%), agitation (6.3%), headache (4.8%), and cough (4.5%).
E-cigarette exposure cases in the US National Poison Data System increased greatly between 2010 and 2014, peaking at 3,742 in 2014, fell in 2015 though 2017, and then between 2017 and 2018 e-cigarette exposure cases increased from 2,320 to 2,901. The majority of cases (65%) were in children under age five and 15% were in ages 5-24. Approximately 0.1% of cases developed life-threatening symptoms.
Toxicology
The of nicotine is 50 mg/kg for rats and 3 mg/kg formice
A mouse ( : mice) is a small rodent. Characteristically, mice are known to have a pointed snout, small rounded ears, a body-length scaly tail, and a high breeding rate. The best known mouse species is the common house mouse (''Mus musculus'' ...
. 0.5–1.0 mg/kg can be a lethal dosage for adult humans, and 0.1 mg/kg for children.IPCS INCHEM/ref> However the widely used human LD50 estimate of 0.5–1.0 mg/kg was questioned in a 2013 review, in light of several documented cases of humans surviving much higher doses; the 2013 review suggests that the lower limit causing fatal outcomes is 500–1000 mg of ingested nicotine, corresponding to 6.5–13 mg/kg orally. An accidental ingestion of only 6 mg may be lethal to children. It is unlikely that a person would overdose on nicotine through smoking alone. The US
Food and Drug Administration
The United States Food and Drug Administration (FDA or US FDA) is a federal agency of the Department of Health and Human Services. The FDA is responsible for protecting and promoting public health through the control and supervision of food ...
(FDA) stated in 2013: "There are no significant safety concerns associated with using more than one ver the counter OTC icotine replacement therapy NRT at the same time, or using an OTC NRT at the same time as another nicotine-containing product—including a cigarette." Ingestion of nicotine pharmaceuticals, tobacco products, or nicotine containing plants may also lead to poisoning. Smoking excessive amounts of tobacco has also led to poisoning; a case was reported where two brothers smoked 17 and 18 pipes of tobacco in succession and were both fatally poisoned. Spilling an extremely high concentration of nicotine onto the skin can result in intoxication or even death since nicotine readily passes into the bloodstream following skin contact.
The recent rise in the use of electronic cigarette
An electronic cigarette is an electronic device that simulates tobacco smoking. It consists of an atomizer, a power source such as a battery, and a container such as a cartridge or tank. Instead of smoke, the user inhales vapor. As su ...
s, many forms of which are designed to be refilled with nicotine-containing "e-liquid" supplied in small plastic bottles, has renewed interest in nicotine overdoses, especially the possibility of young children ingesting the liquids. A 2015 Public Health England
Public Health England (PHE) was an executive agency of the Department of Health and Social Care in England which began operating on 1 April 2013 to protect and improve health and wellbeing and reduce health inequalities. Its formation came as ...
report noted an "unconfirmed newspaper report of a fatal poisoning of a two-year old child" and two published case reports of children of similar age who had recovered after ingesting e-liquid and vomiting. They also noted case reports of suicides by nicotine, where adults drank liquid containing up to 1,500 mg of nicotine. They recovered (helped by vomiting), but an ingestion apparently of about 10,000 mg was fatal, as was an injection. They commented that "Serious nicotine poisoning seems normally prevented by the fact that relatively low doses of nicotine cause nausea and vomiting, which stops users from further intake." Four adults died in the US and Europe, after intentionally ingesting liquid. Two children, one in the US in 2014 and another in Israel in 2013, died after ingesting liquid nicotine.
The discrepancy between the historically stated 60-mg dose and published cases of nicotine intoxication has been noted previously (Matsushima et al. 1995; Metzler et al. 2005). Nonetheless, this value is still widely accepted over the 500mg figure as the basis for safety regulations of tobacco and other nicotine-containing products (such as the EU wide TPD, set at a maximum of 20mg/ml.
Pathophysiology
The symptoms of nicotine poisoning are caused by effects at nicotinic cholinergic receptors. Nicotine is anagonist
An agonist is a chemical that activates a receptor to produce a biological response. Receptors are cellular proteins whose activation causes the cell to modify what it is currently doing. In contrast, an antagonist blocks the action of the ag ...
at nicotinic acetylcholine receptor
Nicotinic acetylcholine receptors, or nAChRs, are receptor polypeptides that respond to the neurotransmitter acetylcholine. Nicotinic receptors also respond to drugs such as the agonist nicotine. They are found in the central and peripheral ner ...
which are present in the central
Central is an adjective usually referring to being in the center of some place or (mathematical) object.
Central may also refer to:
Directions and generalised locations
* Central Africa, a region in the centre of Africa continent, also known a ...
and autonomic nervous system
The autonomic nervous system (ANS), formerly referred to as the vegetative nervous system, is a division of the peripheral nervous system that supplies internal organs, smooth muscle and glands. The autonomic nervous system is a control system t ...
s, and the neuromuscular junction
A neuromuscular junction (or myoneural junction) is a chemical synapse between a motor neuron and a muscle fiber.
It allows the motor neuron to transmit a signal to the muscle fiber, causing muscle contraction.
Muscles require innervation ...
. At low doses nicotine causes stimulatory effects on these receptors, however, higher doses or more sustained exposures can cause inhibitory effects leading to neuromuscular blockade
Neuromuscular-blocking drugs block neuromuscular transmission at the neuromuscular junction, causing paralysis of the affected skeletal muscles. This is accomplished via their action on the post-synaptic acetylcholine (Nm) receptors.
In cli ...
.
It is sometimes reported that people poisoned by organophosphate
In organic chemistry, organophosphates (also known as phosphate esters, or OPEs) are a class of organophosphorus compounds with the general structure , a central phosphate molecule with alkyl or aromatic substituents. They can be considered ...
insecticides experience the same symptoms as nicotine poisoning. Organophosphates inhibit an enzyme called acetylcholinesterase, causing a buildup of acetylcholine, excessive stimulation of all types of cholinergic neuron
A cholinergic neuron is a nerve cell which mainly uses the neurotransmitter acetylcholine (ACh) to send its messages. Many neurological systems are cholinergic. Cholinergic neurons provide the primary source of acetylcholine to the cerebral corte ...
s, and a wide range of symptoms. Nicotine is specific for nicotinic cholinergic receptors only and has some, but not all of the symptoms of organophosphate poisoning.
Diagnosis
Increased nicotine orcotinine
Cotinine is an alkaloid found in tobacco and is also the predominant metabolite of nicotine. An anagram of the word "nicotine", it is used as a biomarker for exposure to tobacco smoke. Cotinine is currently being studied as a treatment for d ...
(the nicotine metabolite
In biochemistry, a metabolite is an intermediate or end product of metabolism.
The term is usually used for small molecules. Metabolites have various functions, including fuel, structure, signaling, stimulatory and inhibitory effects on enzymes, ...
) is detected in urine or blood, or serum nicotine concentrations increase.
Treatment
The initial treatment of nicotine poisoning may include the administration ofactivated charcoal
"Activated" is a song by English singer Cher Lloyd. It was released on 22 July 2016 through Vixen Records. The song was made available to stream exclusively on ''Rolling Stone'' a day before to release (on 21 July 2016).
Background
In an inter ...
to try to reduce gastrointestinal absorption. Treatment is mainly supportive and further care can include control of seizure
An epileptic seizure, informally known as a seizure, is a period of symptoms due to abnormally excessive or synchronous neuronal activity in the brain. Outward effects vary from uncontrolled shaking movements involving much of the body with lo ...
s with the administration of a benzodiazepine
Benzodiazepines (BZD, BDZ, BZs), sometimes called "benzos", are a class of depressant drugs whose core chemical structure is the fusion of a benzene ring and a diazepine ring. They are prescribed to treat conditions such as anxiety disorders, ...
, intravenous fluids for hypotension, and administration of atropine
Atropine is a tropane alkaloid and anticholinergic medication used to treat certain types of nerve agent and pesticide poisonings as well as some types of slow heart rate, and to decrease saliva production during surgery. It is typically given ...
for bradycardia. Respiratory failure may necessitate respiratory support with rapid sequence induction
In advanced airway management, rapid sequence induction (RSI) – also referred to as rapid sequence intubation or as rapid sequence induction and intubation (RSII) or as crash induction – is a special process for endotracheal intubation that is ...
and mechanical ventilation
Mechanical ventilation, assisted ventilation or intermittent mandatory ventilation (IMV), is the medical term for using a machine called a ventilator to fully or partially provide artificial ventilation. Mechanical ventilation helps move a ...
. Hemodialysis
Hemodialysis, also spelled haemodialysis, or simply dialysis, is a process of purifying the blood of a person whose kidneys are not working normally. This type of dialysis achieves the extracorporeal removal of waste products such as creatinin ...
, hemoperfusion
Hemoperfusion or hæmoperfusion (see spelling differences) is a method of filtering the blood extracorporeally (that is, outside the body) to remove a toxin. As with other extracorporeal methods, such as hemodialysis (HD), hemofiltration (HF), ...
or other extracorporeal
An extracorporeal is a medical procedure which is performed outside the body. Extracorporeal devices are the artificial organs that remain outside the body while treating a patient. Extracorporeal devices are useful in hemodialysis and cardiac su ...
techniques do not remove nicotine from the blood and are therefore not useful in enhancing elimination. Acidifying the urine could theoretically enhance nicotine excretion, although this is not recommended as it may cause complications of metabolic acidosis
Metabolic acidosis is a serious electrolyte disorder characterized by an imbalance in the body's acid-base balance. Metabolic acidosis has three main root causes: increased acid production, loss of bicarbonate, and a reduced ability of the kidneys ...
.
Prognosis
The prognosis is typically good when medical care is provided and patients adequately treated are unlikely to have any long-termsequela
A sequela (, ; usually used in the plural, sequelae ) is a pathological condition resulting from a disease, injury, therapy, or other trauma. Derived from the Latin word, meaning “sequel”, it is used in the medical field to mean a complication ...
e. However, severely affected patients with prolonged seizures or respiratory failure may have ongoing impairments secondary to the hypoxia. It has been stated that if a patient survives nicotine poisoning during the first 4 hours, they usually recover completely. At least at "normal" levels, as nicotine in the human body is broken down, it has an approximate biological half-life
Biological half-life (also known as elimination half-life, pharmacologic half-life) is the time taken for concentration of a biological substance (such as a medication) to decrease from its maximum concentration ( Cmax) to half of Cmax in the bl ...
of 1–2 hours. Cotinine
Cotinine is an alkaloid found in tobacco and is also the predominant metabolite of nicotine. An anagram of the word "nicotine", it is used as a biomarker for exposure to tobacco smoke. Cotinine is currently being studied as a treatment for d ...
is an active metabolite of nicotine that remains in the blood for 18–20 hours, making it easier to analyze due to its longer half-life.
See also
*Nicotine dependence
Nicotine dependence is a state of dependence upon nicotine. Nicotine dependence is a chronic, relapsing disease defined as a compulsive craving to use the drug, despite social consequences, loss of control over drug intake, and emergence of wit ...
* Nicotine withdrawal
References
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Nicotine Poisoning Toxic effects of substances chiefly nonmedicinal as to source Health effects of tobacco Cigarettes Electronic cigarettes