Nebulae on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in
 Around 150 AD,
Around 150 AD,
 There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the
There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the
File:Hubble Sees a Stellar "Sneezing Fit" (11467249715).jpg, Herbig–Haro HH 161 and
 Planetary nebulae are the remnants of the final stages of stellar evolution for mid-mass stars (varying in size between 0.5-~8 solar masses). Evolved
Planetary nebulae are the remnants of the final stages of stellar evolution for mid-mass stars (varying in size between 0.5-~8 solar masses). Evolved
 * Ant Nebula
* Barnard's Loop
*
* Ant Nebula
* Barnard's Loop
*
Nebulae
SEDS Messier Pages
Fusedweb.pppl.govHistorical pictures of nebulae
digital library of Paris Observatory {{Authority control Concepts in astronomy
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
and also cosmic dust
Cosmic dust, also called extraterrestrial dust, star dust or space dust, is dust which exists in outer space, or has fallen on Earth. Most cosmic dust particles measure between a few molecules and 0.1 mm (100 micrometers). Larger particles are c ...
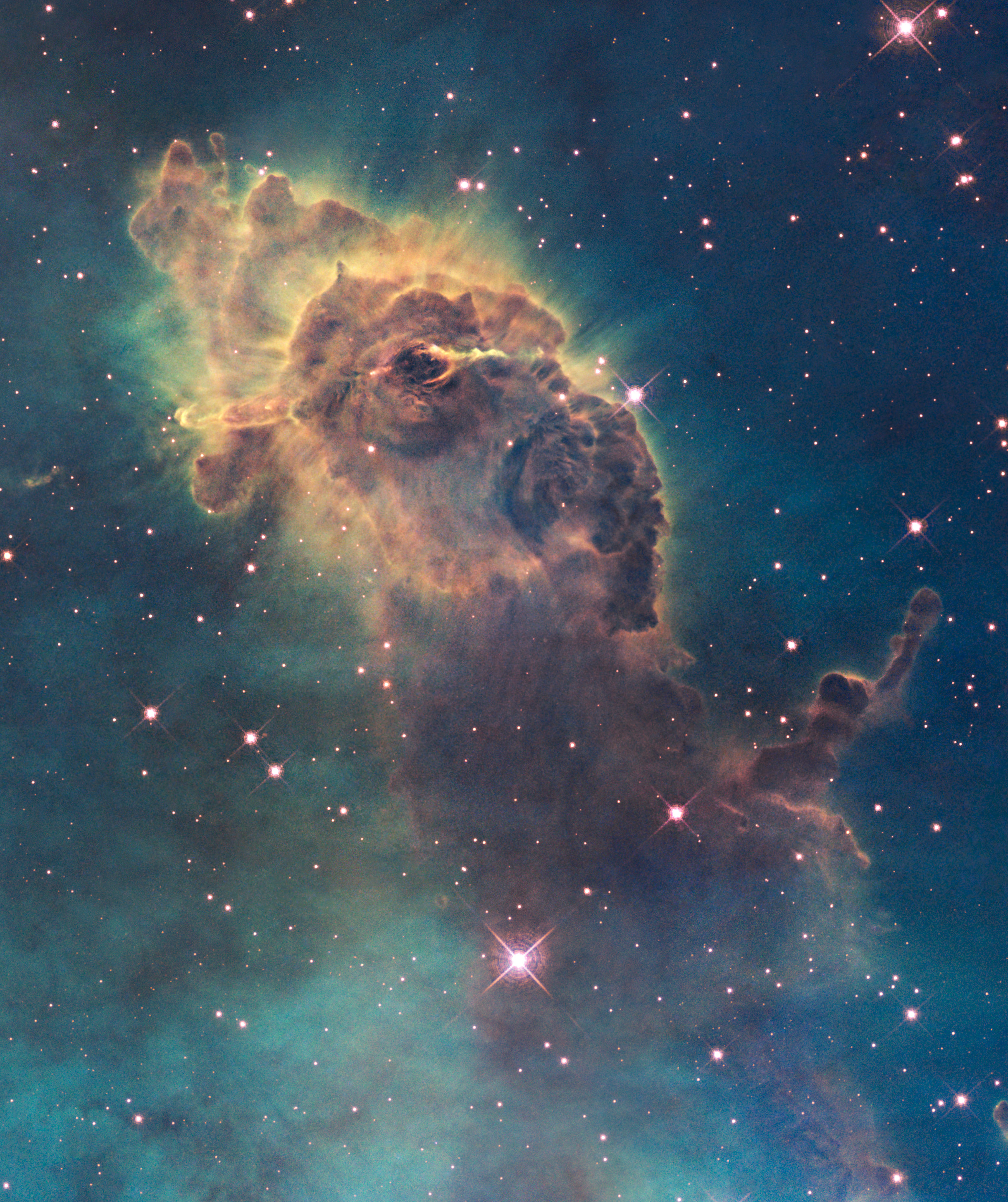
. Nebulae are often star-forming regions, such as in the " Pillars of Creation" in the Eagle Nebula. In these regions, the formations of gas, dust, and other materials "clump" together to form denser regions, which attract further matter, and eventually will become dense enough to form star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
s. The remaining material is then thought to form planet
A planet is a large, rounded astronomical body that is neither a star nor its remnant. The best available theory of planet formation is the nebular hypothesis, which posits that an interstellar cloud collapses out of a nebula to create a you ...
s and other planetary system
A planetary system is a set of gravitationally bound non- stellar objects in or out of orbit around a star or star system. Generally speaking, systems with one or more planets constitute a planetary system, although such systems may also consi ...
objects.
Most nebulae are of vast size; some are hundreds of light-year
A light-year, alternatively spelled light year, is a large unit of length used to express astronomical distance, astronomical distances and is equivalent to about 9.46 Orders of magnitude (numbers)#1012, trillion kilometers (), or 5.88 ...
s in diameter. A nebula that is visible to the human eye from Earth would appear larger, but no brighter, from close by. The Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the ni ...
, the brightest nebula in the sky and occupying an area twice the angular diameter of the full Moon, can be viewed with the naked eye but was missed by early astronomers. Although denser than the space surrounding them, most nebulae are far less dense than any vacuum
A vacuum is a space devoid of matter. The word is derived from the Latin adjective ''vacuus'' for "vacant" or " void". An approximation to such vacuum is a region with a gaseous pressure much less than atmospheric pressure. Physicists often ...
created on Earth – a nebular cloud the size of the Earth
Earth is the third planet from the Sun and the only astronomical object known to harbor life. While large volumes of water can be found throughout the Solar System, only Earth sustains liquid surface water. About 71% of Earth's sur ...
would have a total mass of only a few kilogram
The kilogram (also kilogramme) is the unit of mass in the International System of Units (SI), having the unit symbol kg. It is a widely used measure in science, engineering and commerce worldwide, and is often simply called a kilo colloquially. ...
s. Earth's air has a density of approximately 10 molecules per cubic centimeter; by contrast the densest nebulae can have densities of 10,000 molecules per cubic centimeter. Many nebulae are visible due to fluorescence caused by embedded hot stars, while others are so diffused that they can be detected only with long exposures and special filters. Some nebulae are variably illuminated by T Tauri
T Tauri is a variable star in the constellation Taurus, the prototype of the T Tauri stars. It was discovered in October 1852 by John Russell Hind. T Tauri appears from Earth amongst the Hyades cluster, not far from ε Tauri, but i ...
variable stars.
Originally, the term "nebula" was used to describe any diffused astronomical object
An astronomical object, celestial object, stellar object or heavenly body is a naturally occurring physical entity, association, or structure that exists in the observable universe. In astronomy, the terms ''object'' and ''body'' are often u ...
, including galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System ...
beyond the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
. The Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
, for instance, was once referred to as the ''Andromeda Nebula'' (and spiral galaxies in general as "spiral nebulae") before the true nature of galaxies was confirmed in the early 20th century by Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher (; November 11, 1875 – November 8, 1969) was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing ...
, Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.
Hubble proved that many objects previousl ...
and others. Edwin Hubble discovered that most nebulae are associated with stars and illuminated by starlight. He also helped categorize nebulae based on the type of light spectra they produced.
Observational history
 Around 150 AD,
Around 150 AD, Ptolemy
Claudius Ptolemy (; grc-gre, Πτολεμαῖος, ; la, Claudius Ptolemaeus; AD) was a mathematician, astronomer, astrologer, geographer, and music theorist, who wrote about a dozen scientific treatises, three of which were of importanc ...
recorded, in books VII–VIII of his ''Almagest
The ''Almagest'' is a 2nd-century Greek-language mathematical and astronomical treatise on the apparent motions of the stars and planetary paths, written by Claudius Ptolemy ( ). One of the most influential scientific texts in history, it can ...
'', five stars that appeared nebulous. He also noted a region of nebulosity between the constellation
A constellation is an area on the celestial sphere in which a group of visible stars forms a perceived pattern or outline, typically representing an animal, mythological subject, or inanimate object.
The origins of the earliest constellation ...
s Ursa Major
Ursa Major (; also known as the Great Bear) is a constellation in the northern sky, whose associated mythology likely dates back into prehistory. Its Latin name means "greater (or larger) bear," referring to and contrasting it with nearby Ursa ...
and Leo that was not associated with any star
A star is an astronomical object comprising a luminous spheroid of plasma (physics), plasma held together by its gravity. The List of nearest stars and brown dwarfs, nearest star to Earth is the Sun. Many other stars are visible to the naked ...
. The first true nebula, as distinct from a star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely cl ...
, was mentioned by the Muslim Persian astronomer Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi
ʿAbd al-Rahman al-Sufi ( fa, عبدالرحمن صوفی; December 7, 903 – May 25, 986) was an iranianRobert Harry van Gent. Biography of al-Sūfī'. "The Persian astronomer Abū al-Husayn ‘Abd al-Rahmān ibn ‘Umar al-Sūfī was born in ...
, in his ''Book of Fixed Stars
The ''Book of Fixed Stars'' ( ar, كتاب صور الكواكب ', literally ''The Book of the Shapes of Stars'') is an astronomical text written by Abd al-Rahman al-Sufi (Azophi) around 964. Following the translation movement in the 9th centu ...
'' (964). He noted "a little cloud" where the Andromeda Galaxy
The Andromeda Galaxy (IPA: ), also known as Messier 31, M31, or NGC 224 and originally the Andromeda Nebula, is a barred spiral galaxy with the diameter of about approximately from Earth and the nearest large galaxy to the Milky Way. The gal ...
is located. He also cataloged the Omicron Velorum star cluster as a "nebulous star" and other nebulous objects, such as Brocchi's Cluster
Brocchi's Cluster (also known as Collinder 399, Cr 399 or Al Sufi's Cluster) is a asterism of six stars in an apparent row, across 1.3° of the night sky and four others, in the south of the constellation Vulpecula, thus near Sagitta. Its nic ...
. The supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
that created the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. The common name comes from William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1842 u ...
, the SN 1054
SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 1054, and remained visible until 1056.
The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a docu ...
, was observed by Arabic and Chinese astronomers in 1054.
In 1610, Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc
Nicolas-Claude Fabri de Peiresc (1 December 1580 – 24 June 1637), often known simply as Peiresc, or by the Latin form of his name, Peirescius, was a French astronomer, antiquary and savant, who maintained a wide correspondence with scientis ...
discovered the Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the ni ...
using a telescope. This nebula was also observed by Johann Baptist Cysat
Johann Baptist Cysat (Latinized as Cysatus; in French, Jean-Baptiste Cysat) (c. 1587 – March 17, 1657) was a Swiss Jesuit mathematician and astronomer, after whom the lunar crater Cysatus is named. He was born in Lucerne, as the eighth of 14 ...
in 1618. However, the first detailed study of the Orion Nebula was not performed until 1659, by Christiaan Huygens
Christiaan Huygens, Lord of Zeelhem, ( , , ; also spelled Huyghens; la, Hugenius; 14 April 1629 – 8 July 1695) was a Dutch mathematician, physicist, engineer, astronomer, and inventor, who is regarded as one of the greatest scientists o ...
, who also believed he was the first person to discover this nebulosity.
In 1715, Edmond Halley
Edmond (or Edmund) Halley (; – ) was an English astronomer, mathematician and physicist. He was the second Astronomer Royal in Britain, succeeding John Flamsteed in 1720.
From an observatory he constructed on Saint Helena in 1676–77, H ...
published a list of six nebulae. This number steadily increased during the century, with Jean-Philippe de Cheseaux
Jean-Philippe Loys de Cheseaux (; 4 May 1718 – 30 November 1751) was a Swiss astronomer.
Biography
Loys de Cheseaux was born on 4 May 1718 in Lausanne, Vaud, to Paul-Etienne Loys de Cheseaux, a banneret, and Estienne-Judith de Crousaz. His ...
compiling a list of 20 (including eight not previously known) in 1746. From 1751 to 1753, Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille
Abbé Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille (; 15 March 171321 March 1762), formerly sometimes spelled de la Caille, was a French astronomer and geodesist who named 14 out of the 88 constellations. From 1750 to 1754, he studied the sky at the Cape of Good ...
cataloged 42 nebulae from the Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
, most of which were previously unknown. Charles Messier
Charles Messier (; 26 June 1730 – 12 April 1817) was a French astronomer. He published an astronomical catalogue consisting of 110 nebulae and star clusters, which came to be known as the ''Messier objects''. Messier's purpose ...
then compiled a catalog of 103 "nebulae" (now called Messier object
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only in ...
s, which included what are now known to be galaxies) by 1781; his interest was detecting comet
A comet is an icy, small Solar System body that, when passing close to the Sun, warms and begins to release gases, a process that is called outgassing. This produces a visible atmosphere or coma, and sometimes also a tail. These phenomena ...
s, and these were objects that might be mistaken for them.
The number of nebulae was then greatly increased by the efforts of William Herschel
Frederick William Herschel (; german: Friedrich Wilhelm Herschel; 15 November 1738 – 25 August 1822) was a German-born British astronomer and composer. He frequently collaborated with his younger sister and fellow astronomer Caroline ...
and his sister Caroline Herschel
Caroline Lucretia Herschel (; 16 March 1750 – 9 January 1848) was a German born British astronomer, whose most significant contributions to astronomy were the discoveries of several comets, including the periodic comet 35P/Herschel–Rigolle ...
. Their ''Catalogue of One Thousand New Nebulae and Clusters of Stars'' was published in 1786. A second catalog of a thousand was published in 1789 and the third and final catalog of 510 appeared in 1802. During much of their work, William Herschel believed that these nebulae were merely unresolved clusters of stars. In 1790, however, he discovered a star surrounded by nebulosity and concluded that this was a true nebulosity, rather than a more distant cluster.
Beginning in 1864, William Huggins
Sir William Huggins (7 February 1824 – 12 May 1910) was an English astronomer best known for his pioneering work in astronomical spectroscopy together with his wife, Margaret.
Biography
William Huggins was born at Cornhill, Middlesex, in ...
examined the spectra of about 70 nebulae. He found that roughly a third of them had the emission spectrum
The emission spectrum of a chemical element or chemical compound is the spectrum of frequencies of electromagnetic radiation emitted due to an electron making a transition from a high energy state to a lower energy state. The photon energy of ...
of a gas. The rest showed a continuous spectrum and thus were thought to consist of a mass of stars. A third category was added in 1912 when Vesto Slipher
Vesto Melvin Slipher (; November 11, 1875 – November 8, 1969) was an American astronomer who performed the first measurements of radial velocities for galaxies. He was the first to discover that distant galaxies are redshifted, thus providing ...
showed that the spectrum of the nebula that surrounded the star Merope matched the spectra of the Pleiades
The Pleiades (), also known as The Seven Sisters, Messier 45 and other names by different cultures, is an asterism and an open star cluster containing middle-aged, hot B-type stars in the north-west of the constellation Taurus. At a distance ...
open cluster
An open cluster is a type of star cluster made of up to a few thousand stars that were formed from the same giant molecular cloud and have roughly the same age. More than 1,100 open clusters have been discovered within the Milky Way galaxy, an ...
. Thus the nebula radiates by reflected star light.
About 1923, following the Great Debate, it had become clear that many "nebulae" were in fact galaxies far from the Milky Way
The Milky Way is the galaxy that includes our Solar System, with the name describing the galaxy's appearance from Earth: a hazy band of light seen in the night sky formed from stars that cannot be individually distinguished by the naked eye. ...
.
Slipher and Edwin Hubble
Edwin Powell Hubble (November 20, 1889 – September 28, 1953) was an American astronomer. He played a crucial role in establishing the fields of extragalactic astronomy and observational cosmology.
Hubble proved that many objects previousl ...
continued to collect the spectra from many different nebulae, finding 29 that showed emission spectra and 33 that had the continuous spectra of star light. In 1922, Hubble announced that nearly all nebulae are associated with stars, and their illumination comes from star light. He also discovered that the emission spectrum nebulae are nearly always associated with stars having spectral classifications of B or hotter (including all O-type main sequence stars), while nebulae with continuous spectra appear with cooler stars. Both Hubble and Henry Norris Russell concluded that the nebulae surrounding the hotter stars are transformed in some manner.
Formation
 There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the
There are a variety of formation mechanisms for the different types of nebulae. Some nebulae form from gas that is already in the interstellar medium
In astronomy, the interstellar medium is the matter and radiation that exist in the space between the star systems in a galaxy. This matter includes gas in ionic, atomic, and molecular form, as well as dust and cosmic rays. It fills interstella ...
while others are produced by stars. Examples of the former case are giant molecular clouds, the coldest, densest phase of interstellar gas, which can form by the cooling and condensation of more diffuse gas. Examples of the latter case are planetary nebulae formed from material shed by a star in late stages of its stellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is cons ...
.
Star-forming region
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in The "medium" is present further soon.-->interstellar space
s are a class of emission nebula associated with giant molecular clouds. These form as a molecular cloud collapses under its own weight, producing stars. Massive stars may form in the center, and their ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
ionizes the surrounding gas, making it visible at optical wavelength
In physics, the wavelength is the spatial period of a periodic wave—the distance over which the wave's shape repeats.
It is the distance between consecutive corresponding points of the same phase on the wave, such as two adjacent crests, tr ...
s. The region of ionized hydrogen surrounding the massive stars is known as an H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
while the shells of neutral hydrogen surrounding the H II region are known as photodissociation region
In astrophysics, photodissociation regions (or photon-dominated regions, PDRs) are predominantly neutral regions of the interstellar medium in which far ultraviolet photons strongly influence the gas chemistry and act as the most important source ...
. Examples of star-forming regions are the Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the ni ...
, the Rosette Nebula
The Rosette Nebula (also known as Caldwell 49) is an H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244 (Caldwell 50) is closely associated with the nebulosity, t ...
and the Omega Nebula
The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula (catalogued as Messier 17 or M17 or NGC 6618) is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys d ...
. Feedback from star-formation, in the form of supernova explosions of massive stars, stellar winds or ultraviolet radiation from massive stars, or outflows from low-mass stars may disrupt the cloud, destroying the nebula after several million years.
Other nebulae form as the result of supernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
explosions; the death throes of massive, short-lived stars. The materials thrown off from the supernova explosion are then ionized by the energy and the compact object that its core produces. One of the best examples of this is the Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. The common name comes from William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1842 u ...
, in Taurus. The supernova event was recorded in the year 1054 and is labeled SN 1054
SN 1054 is a supernova that was first observed on 1054, and remained visible until 1056.
The event was recorded in contemporary Chinese astronomy, and references to it are also found in a later (13th-century) Japanese document, and in a docu ...
. The compact object that was created after the explosion lies in the center of the Crab Nebula and its core is now a neutron star
A neutron star is the collapsed core of a massive supergiant star, which had a total mass of between 10 and 25 solar masses, possibly more if the star was especially metal-rich. Except for black holes and some hypothetical objects (e.g. w ...
.
Still other nebulae form as planetary nebulae
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelated t ...
. This is the final stage of a low-mass star's life, like Earth's Sun. Stars with a mass up to 8–10 solar masses evolve into red giant
A red giant is a luminous giant star of low or intermediate mass (roughly 0.3–8 solar masses ()) in a late phase of stellar evolution. The outer atmosphere is inflated and tenuous, making the radius large and the surface temperature around o ...
s and slowly lose their outer layers during pulsations in their atmospheres. When a star has lost enough material, its temperature increases and the ultraviolet radiation
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation i ...
it emits can ionize the surrounding nebula that it has thrown off. The Sun will produce a planetary nebula and its core will remain behind in the form of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
.
Types
HH 164
HH may refer to:
Organizations
* Happy Hippie Foundation, a non-profit organization founded by Miley Cyrus
* Hartmann House Preparatory School, an independent preparatory school in Harare, Zimbabwe
* Heirs Holdings, a Nigerian conglomerate with ...
.
File:Omega Nebula.jpg, The Omega Nebula
The Omega Nebula, also known as the Swan Nebula, Checkmark Nebula, Lobster Nebula, and the Horseshoe Nebula (catalogued as Messier 17 or M17 or NGC 6618) is an H II region in the constellation Sagittarius. It was discovered by Philippe Loys d ...
, an example of an emission nebula
An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emissio ...
File:Horsehead-Hubble.jpg, The Horsehead Nebula
The Horsehead Nebula (also known as Barnard 33) is a small dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of Alnitak, the easternmost star of Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion molecular cloud co ...
, an example of a dark nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection neb ...
.
File:NGC6543.jpg, The Cat's Eye Nebula
The Cat's Eye Nebula (also known as NGC 6543 and Caldwell 6) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by t ...
, an example of a planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
.
File:PIA04533.jpg, The Red Rectangle Nebula
The Red Rectangle Nebula, so called because of its red color and unique rectangular shape, is a protoplanetary nebula in the Monoceros constellation. Also known as HD 44179, the nebula was discovered in 1973 during a rocket flight associated w ...
, an example of a protoplanetary nebula.
File:SNR 0509.jpg, The delicate shell of SNR B0509-67.5
File:Tycho xrayonly.jpg, Tycho Supernova remnant in X-ray light
File:Southern Ring Nebula by Webb Telescope (2022).jpg, Southern Ring Nebula, Planetary Nebula
Classical types
Objects named nebulae belong to 4 major groups. Before their nature was understood,galaxies
A galaxy is a system of stars, stellar remnants, interstellar gas, dust, dark matter, bound together by gravity. The word is derived from the Greek ' (), literally 'milky', a reference to the Milky Way galaxy that contains the Solar System ...
("spiral nebulae") and star cluster
Star clusters are large groups of stars. Two main types of star clusters can be distinguished: globular clusters are tight groups of ten thousand to millions of old stars which are gravitationally bound, while open clusters are more loosely cl ...
s too distant to be resolved as stars were also classified as nebulae, but no longer are.
* H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
s, large diffuse nebulae containing ionized hydrogen
* Planetary nebula
A planetary nebula (PN, plural PNe) is a type of emission nebula consisting of an expanding, glowing shell of ionized gas ejected from red giant stars late in their lives.
The term "planetary nebula" is a misnomer because they are unrelate ...
e
* Supernova remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar mat ...
(e.g., Crab Nebula)
* Dark nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection neb ...
Not all cloud-like structures are named nebulae; Herbig–Haro object
Herbig–Haro (HH) objects are bright patches of nebulosity associated with newborn stars. They are formed when narrow jets of partially ionised gas ejected by stars collide with nearby clouds of gas and dust at several hundred kilometres per s ...
s are an example.
Flux Nebula
Diffuse nebulae
Most nebulae can be described as diffuse nebulae, which means that they are extended and contain no well-defined boundaries. Diffuse nebulae can be divided intoemission nebula
An emission nebula is a nebula formed of ionized gases that emit light of various wavelengths. The most common source of ionization is high-energy ultraviolet photons emitted from a nearby hot star. Among the several different types of emissio ...
e, reflection nebula Reflection or reflexion may refer to:
Science and technology
* Reflection (physics), a common wave phenomenon
** Specular reflection, reflection from a smooth surface
*** Mirror image, a reflection in a mirror or in water
** Signal reflection, in ...
e and dark nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection neb ...
e.
Visible light nebulae may be divided into emission nebulae, which emit spectral line
A spectral line is a dark or bright line in an otherwise uniform and continuous spectrum, resulting from emission or absorption of light in a narrow frequency range, compared with the nearby frequencies. Spectral lines are often used to ident ...
radiation from excited or ionized gas (mostly ionized hydrogen
Hydrogen is the chemical element with the symbol H and atomic number 1. Hydrogen is the lightest element. At standard conditions hydrogen is a gas of diatomic molecules having the formula . It is colorless, odorless, tasteless, non-to ...
); they are often called H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
s, H II referring to ionized hydrogen), and reflection nebulae which are visible primarily due to the light they reflect.
Reflection nebulae themselves do not emit significant amounts of visible light, but are near stars and reflect light from them. Similar nebulae not illuminated by stars do not exhibit visible radiation, but may be detected as opaque clouds blocking light from luminous objects behind them; they are called dark nebula
A dark nebula or absorption nebula is a type of interstellar cloud, particularly molecular clouds, that is so dense that it obscures the visible wavelengths of light from objects behind it, such as background stars and emission or reflection neb ...
e.
Although these nebulae have different visibility at optical wavelengths, they are all bright sources of infrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of Light, visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from ...
emission, chiefly from dust
Dust is made of fine particles of solid matter. On Earth, it generally consists of particles in the atmosphere that come from various sources such as soil lifted by wind (an aeolian process), volcanic eruptions, and pollution. Dust in ...
within the nebulae.
Planetary nebulae
 Planetary nebulae are the remnants of the final stages of stellar evolution for mid-mass stars (varying in size between 0.5-~8 solar masses). Evolved
Planetary nebulae are the remnants of the final stages of stellar evolution for mid-mass stars (varying in size between 0.5-~8 solar masses). Evolved asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
stars expel their outer layers outwards due to strong stellar winds, thus forming gaseous shells while leaving behind the star's core in the form of a white dwarf
A white dwarf is a stellar core remnant composed mostly of electron-degenerate matter. A white dwarf is very dense: its mass is comparable to the Sun's, while its volume is comparable to the Earth's. A white dwarf's faint luminosity comes ...
. Radiation from the hot white dwarf excites the expelled gases, producing emission nebulae with spectra similar to those of emission nebulae found in star formation
Star formation is the process by which dense regions within molecular clouds in The "medium" is present further soon.-->interstellar space
regions. They are H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
s, because mostly hydrogen is ionized, but planetary are denser and more compact than nebulae found in star formation regions.
Planetary nebulae were given their name by the first astronomical observers who were initially unable to distinguish them from planets, and who tended to confuse them with planets, which were of more interest to them. Our Sun is expected to spawn a planetary nebula about 12 billion years after its formation.
Protoplanetary nebula
A protoplanetary nebula (PPN) is an astronomical object at the short-lived episode during a star's rapidstellar evolution
Stellar evolution is the process by which a star changes over the course of time. Depending on the mass of the star, its lifetime can range from a few million years for the most massive to trillions of years for the least massive, which is cons ...
between the late asymptotic giant branch
The asymptotic giant branch (AGB) is a region of the Hertzsprung–Russell diagram populated by evolved cool luminous stars. This is a period of stellar evolution undertaken by all low- to intermediate-mass stars (about 0.5 to 8 solar masses) lat ...
(LAGB) phase and the following planetary nebula (PN) phase. During the AGB phase, the star undergoes mass loss, emitting a circumstellar shell of hydrogen gas. When this phase comes to an end, the star enters the PPN phase.
The PPN is energized by the central star, causing it to emit strong infrared radiation and become a reflection nebula. Collimated stellar winds from the central star shape and shock the shell into an axially symmetric form, while producing a fast moving molecular wind. The exact point when a PPN becomes a planetary nebula (PN) is defined by the temperature of the central star. The PPN phase continues until the central star reaches a temperature of 30,000 K, after which it is hot enough to ionize the surrounding gas.
Supernova remnants
Asupernova
A supernova is a powerful and luminous explosion of a star. It has the plural form supernovae or supernovas, and is abbreviated SN or SNe. This transient astronomical event occurs during the last evolutionary stages of a massive star or whe ...
occurs when a high-mass star reaches the end of its life. When nuclear fusion
Nuclear fusion is a reaction in which two or more atomic nuclei are combined to form one or more different atomic nuclei and subatomic particles ( neutrons or protons). The difference in mass between the reactants and products is manife ...
in the core of the star stops, the star collapses. The gas falling inward either rebounds or gets so strongly heated that it expands outwards from the core, thus causing the star to explode. The expanding shell of gas forms a supernova remnant
A supernova remnant (SNR) is the structure resulting from the explosion of a star in a supernova. The supernova remnant is bounded by an expanding shock wave, and consists of ejected material expanding from the explosion, and the interstellar mat ...
, a special diffuse nebula
A nebula ('cloud' or 'fog' in Latin; pl. nebulae, nebulæ or nebulas) is a distinct luminescent part of interstellar medium, which can consist of ionized, neutral or molecular hydrogen and also cosmic dust. Nebulae are often star-forming region ...
. Although much of the optical and X-ray
An X-ray, or, much less commonly, X-radiation, is a penetrating form of high-energy electromagnetic radiation. Most X-rays have a wavelength ranging from 10 picometers to 10 nanometers, corresponding to frequencies in the range 30&nb ...
emission from supernova remnants originates from ionized gas, a great amount of the radio
Radio is the technology of signaling and communicating using radio waves. Radio waves are electromagnetic waves of frequency between 30 hertz (Hz) and 300 gigahertz (GHz). They are generated by an electronic device called a tr ...
emission is a form of non-thermal emission called synchrotron emission. This emission originates from high-velocity electron
The electron ( or ) is a subatomic particle with a negative one elementary electric charge. Electrons belong to the first generation of the lepton particle family,
and are generally thought to be elementary particles because they have n ...
s oscillating within magnetic field
A magnetic field is a vector field that describes the magnetic influence on moving electric charges, electric currents, and magnetic materials. A moving charge in a magnetic field experiences a force perpendicular to its own velocity and to ...
s.
Examples
 * Ant Nebula
* Barnard's Loop
*
* Ant Nebula
* Barnard's Loop
*Boomerang Nebula
The Boomerang Nebula is a protoplanetary nebula located 5,000 light-years away from Earth in the constellation Centaurus. It is also known as the Bow Tie Nebula and catalogued as LEDA 3074547. The nebula's temperature is measured at making i ...
*Cat's Eye Nebula
The Cat's Eye Nebula (also known as NGC 6543 and Caldwell 6) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Draco, discovered by William Herschel on February 15, 1786. It was the first planetary nebula whose spectrum was investigated by t ...
*Crab Nebula
The Crab Nebula (catalogue designations M1, NGC 1952, Taurus A) is a supernova remnant and pulsar wind nebula in the constellation of Taurus. The common name comes from William Parsons, 3rd Earl of Rosse, who observed the object in 1842 u ...
* Eagle Nebula
*Eskimo Nebula
The Eskimo Nebula (NGC 2392), also known as the Clown-faced Nebula, Lion Nebula, or Caldwell 39, is a bipolar double-shell planetary nebula (PN). It was discovered by astronomer William Herschel in 1787. The formation resembles a person's head ...
*Carina Nebula
The Carina Nebula or Eta Carinae Nebula (catalogued as NGC 3372; also known as the Great Carina Nebula) is a large, complex area of bright and dark nebulosity in the constellation Carina, located in the Carina–Sagittarius Arm of the Milky ...
* Fox Fur Nebula
*Helix Nebula
The Helix Nebula (also known as NGC 7293 or Caldwell 63) is a planetary nebula (PN) located in the constellation Aquarius. Discovered by Karl Ludwig Harding, probably before 1824, this object is one of the closest of all the bright planetary ...
*Horsehead Nebula
The Horsehead Nebula (also known as Barnard 33) is a small dark nebula in the constellation Orion. The nebula is located just to the south of Alnitak, the easternmost star of Orion's Belt, and is part of the much larger Orion molecular cloud co ...
*Engraved Hourglass Nebula
The Engraved Hourglass Nebula (also known as MyCn 18) is a young planetary nebula in the southern constellation Musca. It was discovered by Annie Jump Cannon and Margaret W. Mayall during their work on an extended Henry Draper Catalogue (the ...
*Lagoon Nebula
The Lagoon Nebula (catalogued as Messier 8 or M8, NGC 6523, Sharpless 25, RCW 146, and Gum 72) is a giant interstellar cloud in the constellation Sagittarius. It is classified as an emission nebula and as an H II region.
The Lagoon Nebula was ...
*Orion Nebula
The Orion Nebula (also known as Messier 42, M42, or NGC 1976) is a diffuse nebula situated in the Milky Way, being south of Orion's Belt in the constellation of Orion. It is one of the brightest nebulae and is visible to the naked eye in the ni ...
*Pelican Nebula
The Pelican Nebula (also known as IC 5070 and IC 5067) is an H II region associated with the North America Nebula in the constellation Cygnus. The gaseous contortions of this emission nebula bear a resemblance to a pelican, giving rise to its ...
*Red Square Nebula
The Red Square Nebula is a celestial object located in the area of the sky occupied by star MWC 922 in the constellation Serpens. The first images of this bipolar nebula, taken using the Mt. Palomar Hale telescope in California, were released ...
*Ring Nebula
The Ring Nebula (also catalogued as Messier 57, M57 and NGC 6720) is a planetary nebula in the northern constellation of Lyra. Such a nebula is formed when a star, during the last stages of its evolution before becoming a white dwarf, expels a ...
*Rosette Nebula
The Rosette Nebula (also known as Caldwell 49) is an H II region located near one end of a giant molecular cloud in the Monoceros region of the Milky Way Galaxy. The open cluster NGC 2244 (Caldwell 50) is closely associated with the nebulosity, t ...
*Tarantula Nebula
The Tarantula Nebula (also known as 30 Doradus) is a large H II region in the Large Magellanic Cloud (LMC), forming its south-east corner (from Earth's perspective).
Discovery
The Tarantula Nebula was observed by Nicolas-Louis de Lacaille durin ...
Catalogs
* Gum catalog * RCW Catalogue *Sharpless catalog
The Sharpless catalog is a list of 313 H II regions (emission nebulae) intended to be comprehensive north of declination −27°. (It does include some nebulae south of that declination as well.) The first edition was published in 1953 with 1 ...
*Messier Catalogue
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only in ...
*Caldwell Catalogue
The Caldwell catalogue is an astronomical catalogue of 109 star clusters, nebulae, and galaxies for observation by amateur astronomers. The list was compiled by Patrick Moore as a complement to the Messier catalogue.
While the Messier catal ...
*Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae
The Abell Catalog of Planetary Nebulae was created in 1966 by George O. Abell and was composed of 86 entries thought to be planetary nebulae that were collected from discoveries, about half by Albert George Wilson and the rest by Abell, Robe ...
See also
*H I region
An HI region or H I region (read ''H one'') is a cloud in the interstellar medium composed of neutral atomic hydrogen (HI), in addition to the local abundance of helium and other elements. (H is the chemical symbol for hydrogen, and "I" is the R ...
* H II region
An H II region or HII region is a region of interstellar atomic hydrogen that is ionized. It is typically in a molecular cloud of partially ionized gas in which star formation has recently taken place, with a size ranging from one to hundreds ...
*List of largest nebulae
Below is a list of the largest nebulae so far discovered, ordered by actual size (not angular diameter). This list is prone to change because of inconsistencies between studies, the great distances of nebulae from our stellar neighbourhood, and t ...
* List of diffuse nebulae
This is a list of diffuse nebulae. Most nebulae are diffuse, meaning they do not have well-defined boundaries. Types of diffuse nebulae include emission nebulae and reflection nebula Reflection or reflexion may refer to:
Science and technology
...
* Lists of nebulae
* Molecular cloud
A molecular cloud, sometimes called a stellar nursery (if star formation is occurring within), is a type of interstellar cloud, the density and size of which permit absorption nebulae, the formation of molecules (most commonly molecular hydroge ...
* Magellanic Clouds
The Magellanic Clouds (''Magellanic system'' or ''Nubeculae Magellani'') are two irregular dwarf galaxies in the southern celestial hemisphere. Orbiting the Milky Way galaxy, these satellite galaxies are members of the Local Group. Because bo ...
* Messier object
The Messier objects are a set of 110 astronomical objects catalogued by the French astronomer Charles Messier in his ''Catalogue des Nébuleuses et des Amas d'Étoiles'' (''Catalogue of Nebulae and Star Clusters'').
Because Messier was only in ...
* Nebular hypothesis
The nebular hypothesis is the most widely accepted model in the field of cosmogony to explain the formation and evolution of the Solar System (as well as other planetary systems). It suggests the Solar System is formed from gas and dust orbiting t ...
* Orion molecular cloud complex
* Timeline of knowledge about the interstellar and intergalactic medium
Timeline of knowledge about the interstellar medium and intergalactic medium
* 1848 — Lord Rosse studies M1 and names it the Crab Nebula. The telescope is much larger than the small refactors typical of this period and it also reveals ...
References
External links
Nebulae
SEDS Messier Pages
Fusedweb.pppl.gov
digital library of Paris Observatory {{Authority control Concepts in astronomy