Naval Air Station Keflavik on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Naval Air Station Keflavik (NASKEF) was a
 After being granted self-governance by
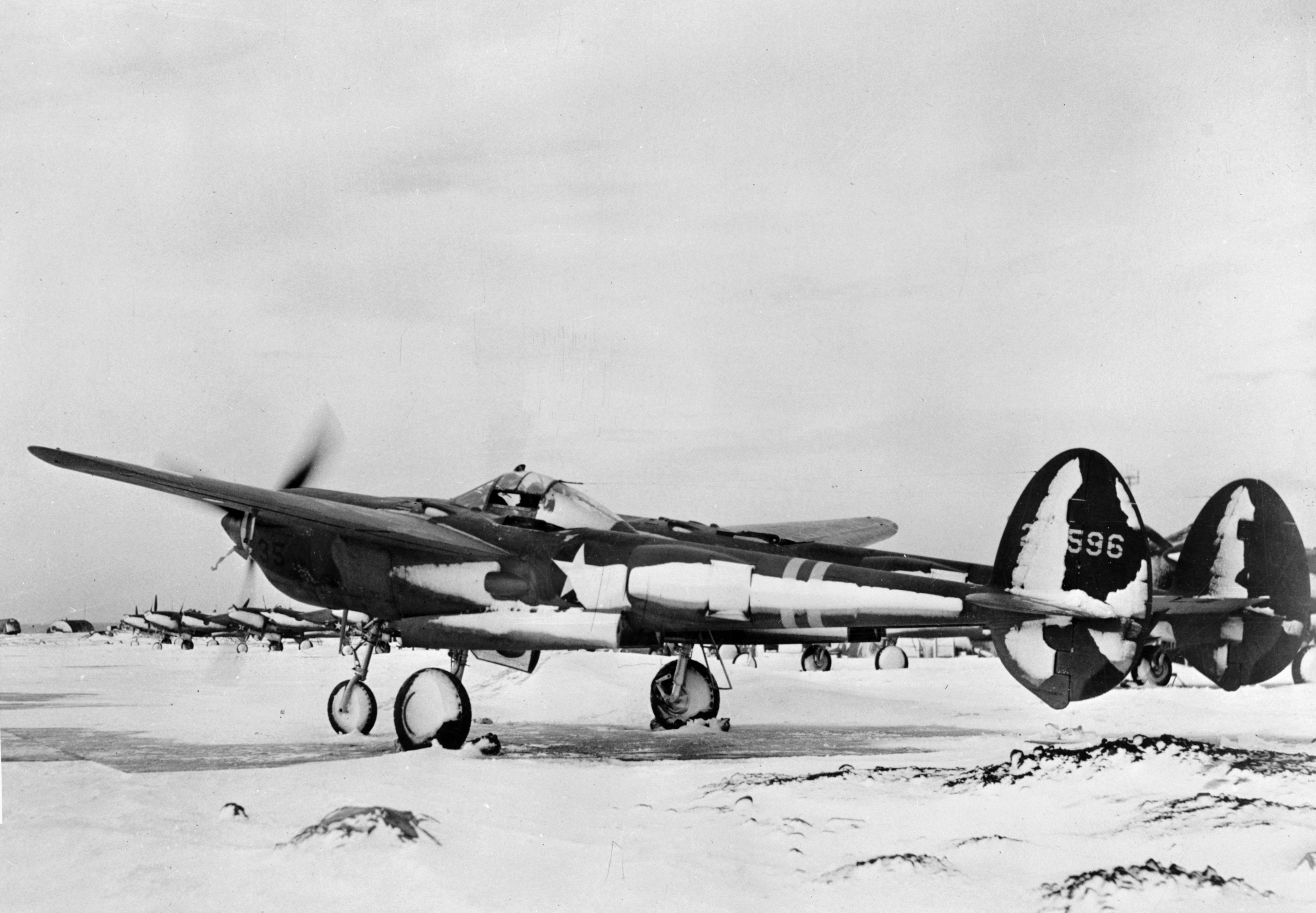
After being granted self-governance by


 Another agreement signed between the United States and Iceland in 1946 permitted continued use of the base by the United States. The United States provided all the maintenance and operation of the airport through an American civilian contractor.
Another agreement signed between the United States and Iceland in 1946 permitted continued use of the base by the United States. The United States provided all the maintenance and operation of the airport through an American civilian contractor.
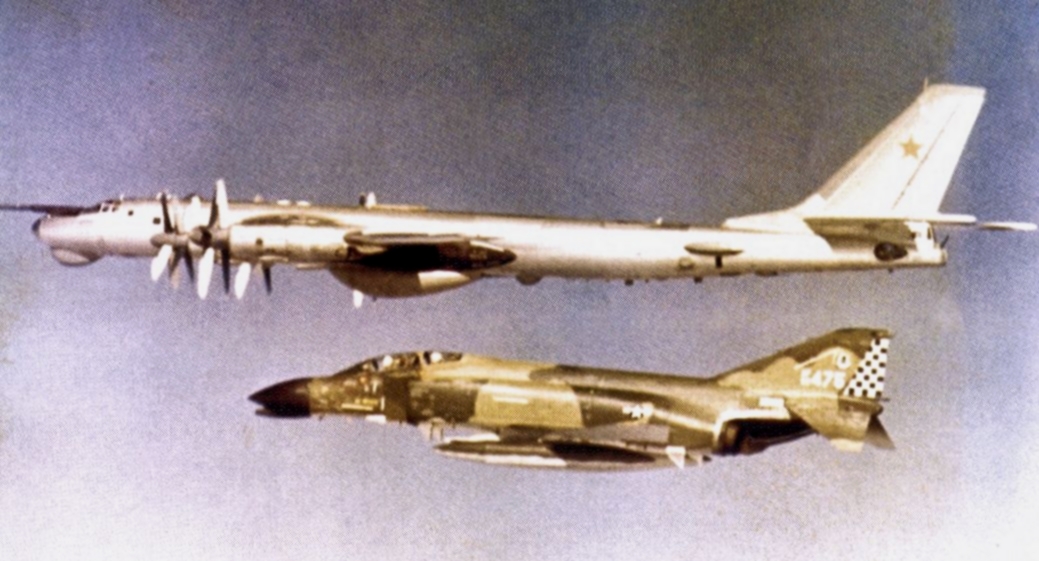
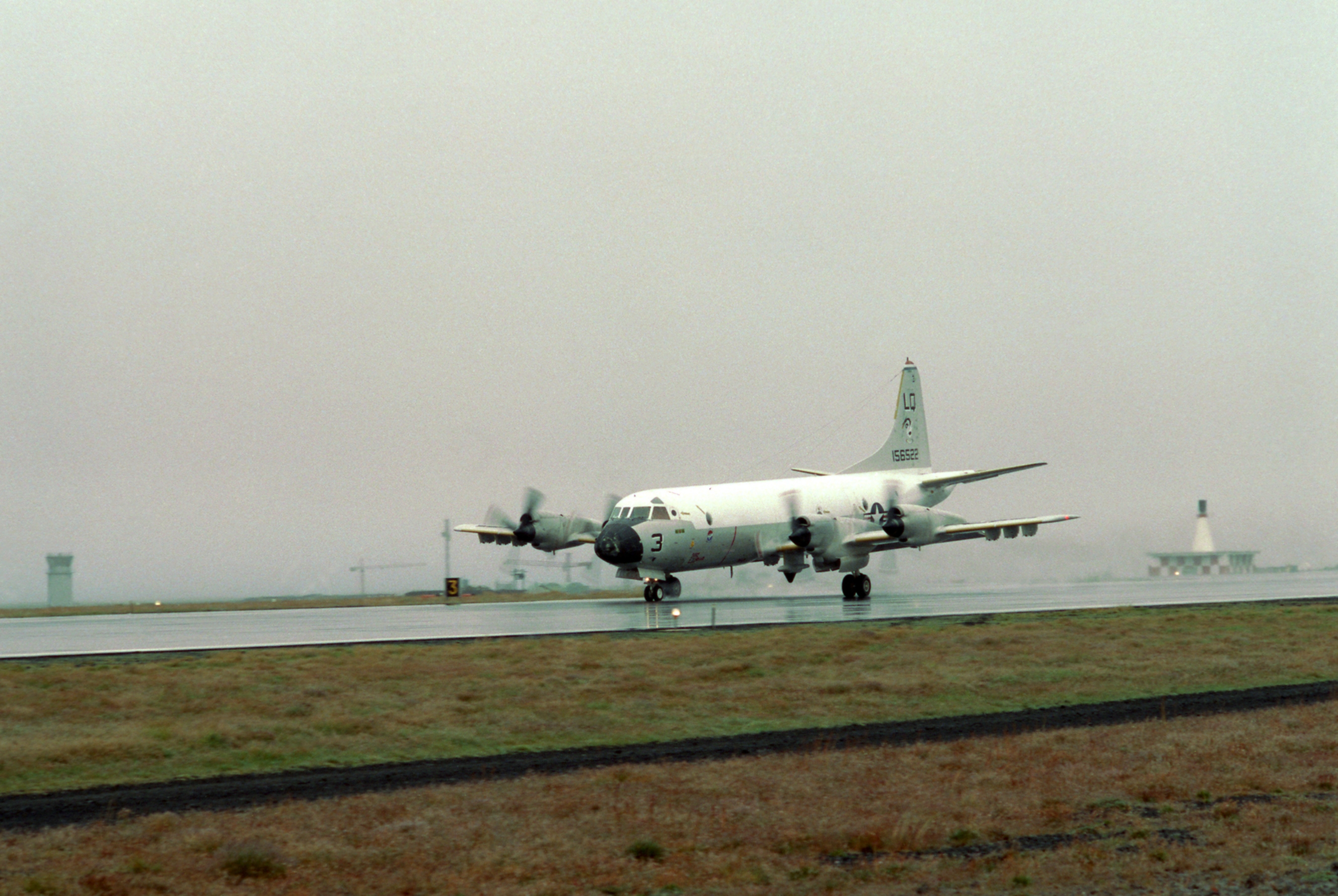 U.S. Navy use of the facility allowed the housing of rotational P-3 Orion squadrons, aircraft, flight crews, maintenance and administrative support personnel from their CONUS home bases for six-month deployments in support of antisubmarine warfare and maritime patrol missions until 2004. As a NATO mission, the U.S. Navy P-3s were frequently augmented by U.S. United States Navy Reserve, Navy Reserve P-3 squadrons and detachments of Canadian Forces CP-140 Aurora, Royal Netherlands Navy P-3, German Navy Breguet Atlantique and Royal Air Force Hawker Siddeley Nimrod MR2 maritime patrol aircraft.
Army National Guard units and Interim Marine Corps Security Force Battalion, Marine Security Forces stormed the lava fields surrounding the base during training exercises such as Northern Viking.
NAS Keflavik employed approximately 900 Icelandic civilians who worked with military personnel, providing the services necessary to operate the base. Twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, the airfield was available for maritime patrol activities, air defense and for transiting aircraft between North America and Europe, in addition to supporting Iceland's international civilian aviation.
U.S. Navy use of the facility allowed the housing of rotational P-3 Orion squadrons, aircraft, flight crews, maintenance and administrative support personnel from their CONUS home bases for six-month deployments in support of antisubmarine warfare and maritime patrol missions until 2004. As a NATO mission, the U.S. Navy P-3s were frequently augmented by U.S. United States Navy Reserve, Navy Reserve P-3 squadrons and detachments of Canadian Forces CP-140 Aurora, Royal Netherlands Navy P-3, German Navy Breguet Atlantique and Royal Air Force Hawker Siddeley Nimrod MR2 maritime patrol aircraft.
Army National Guard units and Interim Marine Corps Security Force Battalion, Marine Security Forces stormed the lava fields surrounding the base during training exercises such as Northern Viking.
NAS Keflavik employed approximately 900 Icelandic civilians who worked with military personnel, providing the services necessary to operate the base. Twenty-four hours a day, seven days a week, the airfield was available for maritime patrol activities, air defense and for transiting aircraft between North America and Europe, in addition to supporting Iceland's international civilian aviation.
 The NATO base did not have a Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA) with the Icelandic Government and the base lacked the roadway entrance security gates characteristic of most military installations, having only Icelandic Customs officials instead. Icelandic nationals had unrestricted access to most of the base, especially since the civilian international airport terminal was also located on the base at the time. Icelandic nationals were only barred from actual security-restricted military facilities such as aircraft parking areas, squadron and hangar facilities and classified operations centers. During the height of the Cold War, this access situation created definitive operational security (OPSEC) concerns by U.S. and NATO officials due to potential espionage activities by Soviet operatives masquerading as Icelandic nationals. In addition, during this same time period, the former Soviet Union constructed one of their largest embassy facilities in the nearby capital, Reykjavik, which doubled as a diplomatic cover for intelligence collection activities against U.S. and NATO military forces. Access to the base was restricted to authorized military and civilian personnel after the construction of a new civilian passenger terminal on the opposite side of the airfield in the mid-1980s.
The base offered a wide variety of recreational services which included bowling, swimming, gymnasium, theater, social clubs, a Wendy's restaurant, and hobby centers. Other services included a Navy Exchange, commissary, bank, credit union, hospital, beauty shop, tour office and morale flights to the rest of Europe and the United States. Golfing was available in a nearby community.
The American base staff had their own names for various places in Iceland, e.g., "Kef" for Keflavík and "Hurdygurdy" for Hveragerði.
The NATO base did not have a Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA) with the Icelandic Government and the base lacked the roadway entrance security gates characteristic of most military installations, having only Icelandic Customs officials instead. Icelandic nationals had unrestricted access to most of the base, especially since the civilian international airport terminal was also located on the base at the time. Icelandic nationals were only barred from actual security-restricted military facilities such as aircraft parking areas, squadron and hangar facilities and classified operations centers. During the height of the Cold War, this access situation created definitive operational security (OPSEC) concerns by U.S. and NATO officials due to potential espionage activities by Soviet operatives masquerading as Icelandic nationals. In addition, during this same time period, the former Soviet Union constructed one of their largest embassy facilities in the nearby capital, Reykjavik, which doubled as a diplomatic cover for intelligence collection activities against U.S. and NATO military forces. Access to the base was restricted to authorized military and civilian personnel after the construction of a new civilian passenger terminal on the opposite side of the airfield in the mid-1980s.
The base offered a wide variety of recreational services which included bowling, swimming, gymnasium, theater, social clubs, a Wendy's restaurant, and hobby centers. Other services included a Navy Exchange, commissary, bank, credit union, hospital, beauty shop, tour office and morale flights to the rest of Europe and the United States. Golfing was available in a nearby community.
The American base staff had their own names for various places in Iceland, e.g., "Kef" for Keflavík and "Hurdygurdy" for Hveragerði.
The Defence Relationship of Iceland and the United States and the Closure of Keflavík base
PhD thesis, University of Lapland.
* Donald, David, "Century Jets – USAF Frontline Fighters of the Cold War". * Endicott, Judy G., USAF Active Flying, Space, and Missile Squadrons as of 1 October 1995. Office of Air Force History * Fletcher, Harry R., Air Force Bases Volume II, Active Air Force Bases outside the United States of America on 17 September 1982, Office of Air Force History, 1989 * Hill, Mike and Campbell, John, Tactical Air Command – An Illustrated History 1946–1992, 2001 * Martin, Patrick, Tail Code: The Complete History Of USAF Tactical Aircraft Tail Code Markings, 1994 * Maurer Maurer, Air Force Combat Units Of World War II, Office of Air Force History, 1983 * Rogers, Brian, ''United States Air Force Unit Designations Since 1978'', 2005 * Ravenstein, Charles A., Air Force Combat Wings Lineage and Honors Histories 1947–1977, Office of Air Force History, 1984
Official Navy disestablishment press release
Archived NAS Keflavik website
provided by the Internet Archive * Reports on the withdrawal of U.S. forces in 2006
348934862999
(in Icelandic language, Icelandic)
Establishing the Iceland Base Command
a chapter in
' a publication of the United States Army Center of Military History
Map of the former site of the base
on OpenStreetMap {{Authority control United States Naval Air Stations, Keflavik Airfields of the United States Army Air Forces Air Transport Command on the North Atlantic Route Military installations established in 1942 Iceland–United States relations Airports established in 1942 Buildings and structures in Keflavík 1942 establishments in Iceland World War II sites in Iceland Closed installations of the United States Navy
United States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
station at Keflavík International Airport
Keflavík Airport ( is, Keflavíkurflugvöllur ) , also known as Reykjavík–Keflavík Airport, is the largest airport in Iceland and the country's main hub for international transportation. The airport is west of Keflavík and southwest of ...
, Iceland
Iceland ( is, Ísland; ) is a Nordic island country in the North Atlantic Ocean and in the Arctic Ocean. Iceland is the most sparsely populated country in Europe. Iceland's capital and largest city is Reykjavík, which (along with its ...
, located on the Reykjanes
Reykjanes () is a small headland on the southwestern tip of the Reykjanes Peninsula in Iceland, giving the main peninsula its name. The region is about from Iceland's international airport.
As the name means "smoking peninsula" connected to vol ...
peninsula on the south-west portion of the island. NASKEF was closed on 8 September 2006, and its facilities were taken over by the Icelandic Defence Agency
Iceland's defence forces consist of the Icelandic Coast Guard, which patrols Icelandic waters and monitors its airspace, and other services such as the National Commissioner's National Security and Special Forces Units. Iceland maintains no sta ...
as their primary base until 1 January 2011, when the Agency was abolished and the base handed over to the Icelandic Coast Guard
The Icelandic Coast Guard (, or simply ) is the Icelandic defence service responsible for search and rescue, maritime safety and security surveillance, and law enforcement in the seas surrounding Iceland. The Coast Guard maintains the Iceland ...
, which has since then operated the base.
The base was built during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
by the United States Army
The United States Army (USA) is the land service branch of the United States Armed Forces. It is one of the eight U.S. uniformed services, and is designated as the Army of the United States in the U.S. Constitution.Article II, section 2, ...
as part of its mission to maintain the defense of Iceland and secure northern Atlantic air routes. It served to ferry personnel, equipment, and supplies to Europe. Intended as a temporary wartime base under an agreement with Iceland and the British, U.S. forces withdrew by 1947 but returned in 1951 as the Iceland Defense Force
The Iceland Defense Force ( is, Varnarlið Íslands; IDF) was a military command of the United States Armed Forces from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to p ...
resident on a North Atlantic Treaty Organization
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two No ...
(NATO) base. The base was regularly visited by the American military and other NATO allies for military exercises, NATO Air Policing
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states – 28 European and two Nor ...
, and other tasks.
In 2017, the United States announced its intention to modify the largest hangar on the Icelandic base in order to house the new Boeing P-8 Poseidon
The Boeing P-8 Poseidon is an American maritime patrol and reconnaissance aircraft developed and produced by Boeing Defense, Space & Security, and derived from the civilian Boeing 737-800. It was developed for the United States Navy (USN).
T ...
ASW aircraft being introduced.
History
Background

 After being granted self-governance by
After being granted self-governance by Denmark
)
, song = ( en, "King Christian stood by the lofty mast")
, song_type = National and royal anthem
, image_map = EU-Denmark.svg
, map_caption =
, subdivision_type = Sovereign state
, subdivision_name = Kingdom of Denmark
, establish ...
in 1918 with the signing of the 25-year Danish-Icelandic Act of Union, Iceland followed a policy of strict neutrality in international affairs. In 1939, with war imminent in Europe, the German Reich
German ''Reich'' (lit. German Realm, German Empire, from german: Deutsches Reich, ) was the constitutional name for the German nation state that existed from 1871 to 1945. The ''Reich'' became understood as deriving its authority and sovereignty ...
pressed for landing rights for Deutsche Luft Hansa
''Deutsche Luft Hansa A.G.'' (from 1933 styled as ''Deutsche Lufthansa'' and also known as ''Luft Hansa'', ''Lufthansa'', or DLH) was a German airline, serving as flag carrier of the country during the later years of the Weimar Republic and t ...
's aircraft for alleged trans-Atlantic flights. The Icelandic government turned them down.
A British request to establish bases in Iceland for the protection of the vital North Atlantic supply lines after German forces occupied Denmark and Norway in April 1940 was also turned down in accordance with the neutrality policy. In response, on 10 May 1940 the people of Reykjavík
Reykjavík ( ; ) is the capital and largest city of Iceland. It is located in southwestern Iceland, on the southern shore of Faxaflói bay. Its latitude is 64°08' N, making it the world's northernmost capital of a sovereign state. With a po ...
awoke to the sight of a British invasion force. The government of Iceland protested the invasion but asked the populace to treat the occupying force as guests.
Following talks between British Prime Minister Winston Churchill
Sir Winston Leonard Spencer Churchill (30 November 187424 January 1965) was a British statesman, soldier, and writer who served as Prime Minister of the United Kingdom twice, from 1940 to 1945 during the Second World War, and again from ...
and President Franklin D. Roosevelt of the United States, Iceland agreed to a tripartite treaty under which United States Marines
The United States Marine Corps (USMC), also referred to as the United States Marines, is the maritime land force service branch of the United States Armed Forces responsible for conducting expeditionary and amphibious operations through com ...
were to relieve the British garrison in Iceland on the condition that all military forces be withdrawn from Iceland immediately upon the conclusion of the war in Europe. In addition to their defense role, U.S. forces constructed the Keflavik Airport as a refueling point for aircraft deliveries and cargo flights to Europe.
Second World War era (1940s)
The airport was built by theUnited States military
The United States Armed Forces are the military forces of the United States. The armed forces consists of six service branches: the Army, Marine Corps, Navy, Air Force, Space Force, and Coast Guard. The president of the United States is ...
during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, as a replacement for a small British landing strip at Garður to the north. It consisted of two separate two-runway airfields, built simultaneously just 4 km apart. ''Patterson Field'' in the south-east opened in 1942 despite being partly incomplete. It was named after a young pilot who died in Iceland. ''Meeks Field'' to the north-west opened on 23 March 1943. It was named after another young pilot, George Meeks, who died on the Reykjavík airfield. Patterson Field was closed after the war, but Meeks Field and the adjoining structures were returned to Iceland's control and renamed Naval Air Station Keflavik after the nearby town of Keflavík. In 1951, the U.S. military returned to the airport under a defense agreement between Iceland and the U.S. signed on 5 May 1951.
With the end of the war in Europe, Keflavik Airport became a transit point for aircraft returning from the European Theater of Operations
The European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA) was a Theater of Operations responsible for directing United States Army operations throughout the European theatre of World War II, from 1942 to 1945. It commanded Army Ground For ...
to the United States. With American air activities greatly reduced in Europe in the immediate postwar months, U.S. flying operations were similarly reduced in preparation for transfer of the base to the Icelandic government at the end of 1946. With all noncritical surplus equipment and supplies disposed of, all U.S. air activity ended at the airfield on 11 March 1947.
Military Air Transport Service era (1951–1961)



 Another agreement signed between the United States and Iceland in 1946 permitted continued use of the base by the United States. The United States provided all the maintenance and operation of the airport through an American civilian contractor.
Another agreement signed between the United States and Iceland in 1946 permitted continued use of the base by the United States. The United States provided all the maintenance and operation of the airport through an American civilian contractor. American Overseas Airlines
American Overseas Airlines (AOA) was an airline that operated between the United States and Europe between 1945 and 1950. It was headquartered in Midtown Manhattan, New York City.
History
American Export Airlines (AEA), commonly known as Am E ...
, followed by Airport Overseas Corporation personnel, operated the military portion of Keflavik Airport after its reversion to Icelandic control at the end of March 1947.
In 1949, Iceland voted to join the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO) among protests about the US militarizing the country, and the base assumed the status of significant strategic importance in the Cold War
The Cold War is a term commonly used to refer to a period of geopolitical tension between the United States and the Soviet Union and their respective allies, the Western Bloc and the Eastern Bloc. The term '' cold war'' is used because t ...
. Though reluctant to sanction the stationing of foreign troops in significant numbers on their soil, Icelandic officials decided in light of the fact they had no standing army to speak of, that membership in NATO alone was not a sufficient defense; and at the request of NATO, Iceland entered into a defense agreement with the United States directly. This was the beginning of the Iceland Defense Force. Over the next four decades, the Defense Force was "at the front" of the Cold War and was credited with playing a significant role in deterrence.
On 25 May 1951 the United States Air Force
The United States Air Force (USAF) is the air service branch of the United States Armed Forces, and is one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. Originally created on 1 August 1907, as a part of the United States Army Si ...
(USAF) reestablished its presence at Keflavik Airport with the stationing of the 1400th Air Base Group. Jurisdiction of the airport was assumed by Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NA ...
(MATS). MATS re-established a military air terminal and refueling point for trans-Atlantic air service between the United States and Europe at Keflavik. MATS (later Military Airlift Command
The Military Airlift Command (MAC) is an inactive United States Air Force List of Major Commands of the United States Air Force, major command (MAJCOM) that was headquartered at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois. Established on 1 January 1966, M ...
and Air Mobility Command
Air Mobility Command (AMC) is a major command (MAJCOM) of the U.S. Air Force. It is headquartered at Scott Air Force Base, Illinois, east of St. Louis, Missouri.
Air Mobility Command was established on 1 June 1992, and was formed from elemen ...
) units remained at the airport until the withdrawal of United States military units from Iceland in 2006.
During 1947–51, while the base was operated by a U.S. civilian contractor company most of the World War II temporary structures were left empty and became badly deteriorated. The airfield complex, one of the largest in the world during the war, also required upgrading to accommodate modern aircraft. The contractor had extended one runway, constructed a new passenger terminal and hotel building, one aircraft hangar, a hospital, housing units and other facilities for the staff. But this was insufficient for the new Defense Force, so additional facilities had to be provided quickly. A crash reconstruction program was initiated and temporary housing was erected during the construction of permanent housing. The airfield was extended by the Nello L. Teer Company and two new aircraft hangars were constructed. Most of this work was completed by 1957.
Soon after the return of U.S. forces to Keflavik. Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inac ...
(ADC) established a temporary radar station at the airport, equipped with World War II-era AN/TPS-1
The AN/TPS-1 Radar was an early warning and tactical control radar developed by Bell Labs and the MIT Radiation Laboratory during World War II. Initially used by the US Army, it was later used by the United States Air Force Air Defense Command, a ...
and AN/TPS-3A radars that operated until a permanent radar station could be constructed at nearby Rockville AS.
Between 1952 and 2006, Air Forces Iceland
The 85th Group is an inactive United States Air Force organization. Its last assignment was with United States Air Forces in Europe at Naval Air Station Keflavik, Iceland, assigned as a unit of the 48th Fighter Wing whose home station is at RAF ...
provided air defense for Iceland, operated Keflavik Airport, and furnished base support for all U.S. military forces in Iceland participating in its defense under NATO. Also Air Force component of NATO Iceland Defense Force
The Iceland Defense Force ( is, Varnarlið Íslands; IDF) was a military command of the United States Armed Forces from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to p ...
.
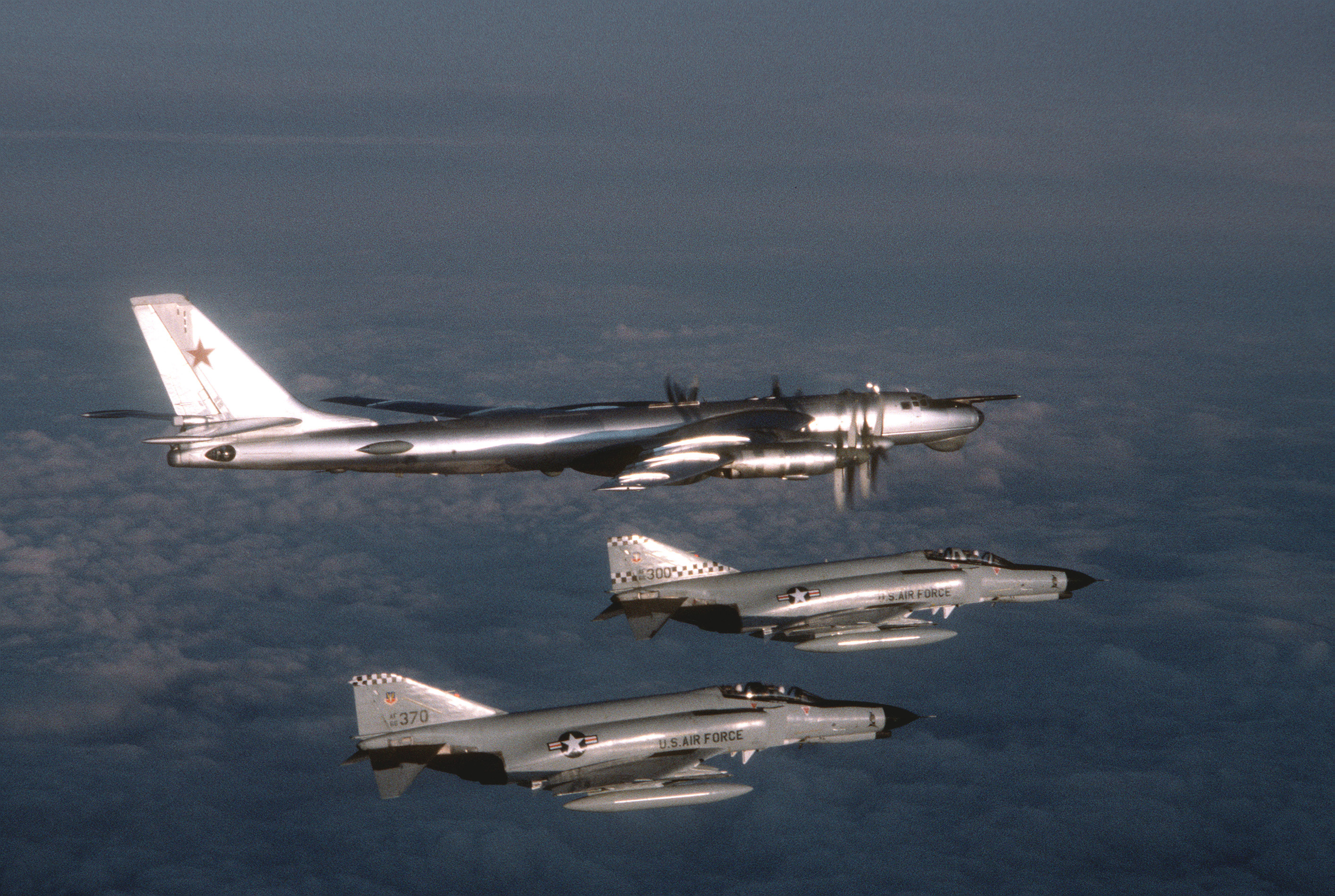
ADC, later renamed Aerospace Defense Command used the facility for air surveillance of Iceland and the North Atlantic, employing F-102 Delta Dagger
The Convair F-102 Delta Dagger was an American interceptor aircraft designed and manufactured by Convair.
Built as part of the backbone of the United States Air Force's air defenses in the late 1950s, it entered service in 1956. Its main purpo ...
and then F-4C Phantom II
The McDonnell Douglas F-4 Phantom II is an American Tandem#Aviation, tandem two-seat, twinjet, twin-engine, all-weather, long-range supersonic aircraft, supersonic jet interceptor aircraft, interceptor and fighter-bomber originally developed ...
fighters as interceptors. Over 1,000 intercepts of Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
aircraft took place inside Iceland's Military Air Defense Identification Zone (ADIZ).
US Navy era (1960s–2000s)
TheUnited States Navy
The United States Navy (USN) is the maritime service branch of the United States Armed Forces and one of the eight uniformed services of the United States. It is the largest and most powerful navy in the world, with the estimated tonnage ...
assumed the responsibility of running the air station from MATS in 1961.
In 1974, the left-wing Government of Iceland's new proposal to close the base triggered a petition that garnered 55,000 signatures, about a quarter of the population of the entire nation. This led to the ruling coalition collapsing and the 1974 Icelandic parliamentary election
Parliamentary elections were held in Iceland on 30 June 1974. Dieter Nohlen & Philip Stöver (2010) ''Elections in Europe: A data handbook'', p962 The Independence Party remained the largest party in the Lower House of the Althing, winning 17 o ...
being held.
On 1 October 1979 Tactical Air Command
Tactical Air Command (TAC) is an inactive United States Air Force organization. It was a Major Command of the United States Air Force, established on 21 March 1946 and headquartered at Langley Air Force Base, Virginia. It was inactivated on 1 Ju ...
(TAC) absorbed ADC's assets, and the F-4E Phantom II aircraft of the 57th Fighter Interceptor Squadron (57 FIS). In July 1985, F-15Cs and F-15Ds replaced the aging F-4s, and the tail code "IS" was assigned to Air Forces Iceland (AFI).
During the height of the Cold War in the 1980s, Keflavik also hosted rotational E-3 Sentry
The Boeing E-3 Sentry is an American airborne early warning and control (AEW&C) aircraft developed by Boeing. E-3s are commonly known as AWACS (Airborne Warning and Control System). Derived from the Boeing 707 airliner, it provides all-wea ...
AWACS aircraft and KC-135 Stratotanker
The Boeing KC-135 Stratotanker is an American military aerial refueling aircraft that was developed from the Boeing 367-80 prototype, alongside the Boeing 707 airliner. It is the predominant variant of the C-135 Stratolifter family of trans ...
aircraft from CONUS
''Conus'' is a genus of predatory sea snails, or cone snails, marine gastropod mollusks in the family Conidae.Bouchet, P.; Gofas, S. (2015). Conus Linnaeus, 1758. In: MolluscaBase (2015). Accessed through: World Register of Marine Species a ...
to support the air defense mission and rotational HC-130
The Lockheed HC-130 is an extended-range, search and rescue (SAR)/combat search and rescue (CSAR) version of the C-130 Hercules military transport aircraft, with two different versions operated by two separate services in the U.S. armed forc ...
Hercules aircraft from RAF Woodbridge
Royal Air Force Woodbridge or RAF Woodbridge, is a former Royal Air Force station located east of Woodbridge in the county of Suffolk, England.
Constructed in 1943 as a Royal Air Force (RAF) military airfield during the Second World War to a ...
from the 67th Aerospace Rescue and Recovery Squadron to support their detachment of Keflavik-based HH-3 Jolly Green Giant and later HH-60G Pave Hawk
The Sikorsky MH-60G/HH-60G Pave Hawk is a four-blade, twin-engine, medium-lift utility military helicopter manufactured by Sikorsky Aircraft. It is a derivative of the UH-60 Black Hawk and incorporates the US Air Force PAVE electronic systems ...
helicopters in their search and rescue mission.
Beginning in 1984, the 932d Air Control Squadron
The 932d Air Control Squadron is an inactive United States Air Force unit. It was last assigned to the 85th Group, Third Air Force, stationed at Keflavik Air Station, Iceland. It was inactivated on 27 June 2006.Hq, USAFE Special Order GD-29, 22 J ...
established a Radar Operations Control Center at Keflavik which coordinated the 57th FIS interceptors to contacts passing through the GIUK gap
The GIUK gap (sometimes written G-I-UK) is an area in the northern Atlantic Ocean that forms a naval choke point. Its name is an acronym for ''Greenland, Iceland'', and the ''United Kingdom'', the gap being the two stretches of open ocean betwe ...
. It received long-range radar inputs from five radar sites: the four sites in Iceland plus a data-tie from the Tórshavn
Tórshavn (; lit. " Thor's harbour"), usually locally referred to as simply ''Havn'', is the capital and largest city of the Faroe Islands. It is located in the southern part on the east coast of Streymoy. To the northwest of the city lies the ...
AS radar in the Faroe Islands
The Faroe Islands ( ), or simply the Faroes ( fo, Føroyar ; da, Færøerne ), are a North Atlantic island group and an autonomous territory of the Kingdom of Denmark.
They are located north-northwest of Scotland, and about halfway bet ...
. Tórshavn was located atop mount Sornfelli
Sornfelli is a mountain plateau on the island of Streymoy in the Faroe Islands about 12 km from the capital Tórshavn (20 km by road). It is the site of a military station at 725m above sea level (asl). The Sornfelli Meteorological Stat ...
. The ROCC remained active until the turnover of the facility in 2006.
Air Forces Iceland continued the air defense mission of Iceland as a tenant organization at Keflavik. Under ADC until 1979 and under TAC until 1992. On 1 June 1992, Air Combat Command (ACC) assumed command and control of AFI and the 57 FIS. Less than a year later, the 57 FIS was redesignated as the 57 Fighter Squadron (57 FS) and reassigned to the 35th Fighter Wing that was transferred from the closing George AFB, California.
On 1 October 1994, the 35th Wing was inactivated at Keflavik and reactivated that same day at Misawa Air Base in Misawa, Aomori, Misawa, Japan. The 35th Wing was replaced by the newly activated 85th Wing. On 1 March 1995, the 57th FS was inactivated and the interceptor force was replaced by Regular Air Force and Air National Guard F-15 Eagle fighter aircraft rotating every 90 days to Iceland until the USAF inactivated the 85th Group in 2002. United States Air Forces in Europe (USAFE) took over ACC responsibilities at Keflavik on 1 October 2002 as part of a larger restructuring of the unified commands.
The 85th was reduced to a Group level and supported rotational deployments. The 85th Group continued to support rotational deployments until it was inactivated during a ceremony on 28 June 2006, as a result of the USAF reduction in forces in Iceland. All rotational fighters left and the 56th Rescue Squadron ceased operation at the end of the fiscal year.
Deactivation and post-military use (2006–2015)
On 15 March 2006, the List of ambassadors of the United States to Iceland, U.S. Ambassador to Iceland announced that the United States had decided to substantially reduce the size of the Iceland Defense Force. During a six-month transition to reduce the military presence in Iceland, most facilities closed and most of the service members departed, leaving behind a core team of active duty and Reserve personnel to finish the job. By mid-July 2006, many of the military spouses and military active duty staff had transferred. On 8 September 2006, NASKEF's last commanding officer, Capt. Mark S. Laughton, presided over a ceremony effecting the disestablishment of the air station. On 26 October the government of Iceland established the Keflavik Airport Development Corporation or Kadeco which was given the task of converting those portions of the base no longer needed into civilian use.Since May 2008 Keflavik has periodically hosted NATO fighter, AWACS and support aircraft participating in Icelandic Air Policing deployments. In January 2010, Verne Holdings announced that it had received equity funding from the Wellcome Trust to build a data center at Keflavik. The data center will take advantage of the available geothermal power and free cooling to minimize its carbon footprint.Reactivation (2015 – present)
In September 2015, news media reported U.S. government officials expressed a desire to reopen aspects of the NATO base of Keflavik Naval Air Station, to cope with increasing Russian military activity around Iceland. In 2016 the United States began preparations to establish regular patrol rotations at the base, and in 2017 announced its intention to build new hangars to house Navy P-8 Poseidon aircraft.Station names
* Reykjavik Administrative Area, 6 August 1941 * Meeks Field, 1 July 1942 * Keflavik Airport*, 25 October 1946 – 28 June 2006 : Under United States Navy Jurisdiction, 1 July 1961 – 28 June 2006Major USAF Commands
* Iceland Base Command, United States Army, February 1942 * European Theater of Operations, United States Army (ETOUSA), 10 June 1942 * Eastern Defense Command, United States Army, 30 July 1944 * Air Transport Command (United States Air Force), Air Transport Command, 1 January 1946 – 7 April 1947 Returned to control of Icelandic Government on 7 April 1947; returned to joint Icelandic-USAF control, 23 May 1951. * Joint Task Force No. 109, 7 May 1951 *Iceland Defense Force
The Iceland Defense Force ( is, Varnarlið Íslands; IDF) was a military command of the United States Armed Forces from 1951 to 2006. The IDF, created at the request of NATO, came into existence when the United States signed an agreement to p ...
, 6 July 1951
* Military Air Transport Service
The Military Air Transport Service (MATS) is an inactive United States Department of Defense, Department of Defense Unified Command. Activated on 1 June 1948, MATS was a consolidation of the United States Navy's Naval Air Transport Service (NA ...
*, 1 September 1951
* Air Defense Command
Aerospace Defense Command was a major command of the United States Air Force, responsible for continental air defense. It was activated in 1968 and disbanded in 1980. Its predecessor, Air Defense Command, was established in 1946, briefly inac ...
, 1 July 1962
: Re-designated Aerospace Defense Command, 15 January 1968
* Tactical Air Command, 1 October 1979
* Air Combat Command, 1 June 1992
* United States Air Forces in Europe, 1 October 1992 – 28 June 2006
Major USAF units assigned
* 14th Detachment, North Atlantic Wing, Air Transport Command (United States Air Force), Air Transport Command (ATC Station #14), 28 August 1943 – 1 August 1944 * Iceland Base Command, 16 June 1942 – 24 March 1947 * 342d Composite Group, 11 September 1942 – 18 March 1944 * 386th Army Air Force Base Unit, 1 August 1944 – 18 February 1946 * 1400th Air Base Group, 23 May 1951 – 1 July 1960 * 932d Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron (ADC), 1 October 1952 – 1 August 1957 * 192d Fighter-Bomber Squadron, 1 September 1952 – 1 December 1952 (F-51D/H) * 435th Fighter-Bomber Squadron, 1 December 1952 – 27 March 1953 (F-51D/H) * 436th Fighter-Bomber Squadron, 1 December 1952 – 2 December 1953 (F-51D/H) * 53d Air Rescue Squadron, 14 November 1952 – 24 March 1960 * 82d Fighter-Interceptor Squadron, 1 April 1953 – 22 October 1954 (F-94B) * 57th Fighter-Interceptor Squadron*, 12 November 1954 – 1 March 1995 * Iceland Air Defense Force, 1 April 1952 : Re-designated Air Forces Iceland, 1 January 1960 : Re-designated 85th Tactical Fighter Wing, 31 July 1985 – 31 May 1993 : Re-designated 85th Wing, 29 September 1994 : Re-designated 85th Group, 1 July 1995 – 28 June 2006. * 667th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron, 8 August 1956 – 16 April 1957 * 934th Aircraft Control and Warning Squadron, 8 September 1956 – 30 May 1957 * 960th Airborne Air Control Squadron, 960th Airborne Warning and Control Squadron, 1 Jan 1979 - 1 Jul 1992 * 35th Fighter Wing, 35th Wing, 1 June 1992 – 1 October 2002, F-15C/D Eagle * 56th Rescue Squadron: 1 July 1995 – 28 June 2006 * 86th Airlift Wing*, 1 October 2002 – 8 October 2004, F-15C/D Eagle * 48th Fighter Wing**, 8 October 2004 – 28 June 2006, F-15C/D EagleOperations
Naval Air Station Keflavik was the host command for all U.S. defense activities in Iceland. The major commands stationed on the base were the USAF's 85th Group, Fleet Air Keflavik, the headquarters of the U.S.-provided Iceland Defense Force, Naval Computer and Telecommunications Station (NCTS) Keflavik, U.S. Naval Hospital Keflavik and the SOSUS, Sound Surveillance System (SOSUS) shore terminal at Naval Facility (NAVFAC) Keflavik. The positions of Commander, Fleet Air Keflavik and Commander, Iceland Defence Force were held by the same U.S. Navy rear admiral. There were more than 25 different commands of various sizes and personnel from the U.S. Army, U.S. Navy, U.S. Air Force, U.S. Marine Corps, and U.S. Coast Guard in Iceland. Also present were representatives from Canada, the Netherlands, Norway, and Denmark. NASKEF was responsible for providing all support facilities, including the runways, housing, supply and recreational facilities. The primary mission of Naval Air Station Keflavik was to maintain and operate facilities and provide services and material to support operations of aviation activities and units of the operating forces of the Navy and other activities and units, as designated by the Chief of Naval Operations. The NATO base did not have a Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA) with the Icelandic Government and the base lacked the roadway entrance security gates characteristic of most military installations, having only Icelandic Customs officials instead. Icelandic nationals had unrestricted access to most of the base, especially since the civilian international airport terminal was also located on the base at the time. Icelandic nationals were only barred from actual security-restricted military facilities such as aircraft parking areas, squadron and hangar facilities and classified operations centers. During the height of the Cold War, this access situation created definitive operational security (OPSEC) concerns by U.S. and NATO officials due to potential espionage activities by Soviet operatives masquerading as Icelandic nationals. In addition, during this same time period, the former Soviet Union constructed one of their largest embassy facilities in the nearby capital, Reykjavik, which doubled as a diplomatic cover for intelligence collection activities against U.S. and NATO military forces. Access to the base was restricted to authorized military and civilian personnel after the construction of a new civilian passenger terminal on the opposite side of the airfield in the mid-1980s.
The base offered a wide variety of recreational services which included bowling, swimming, gymnasium, theater, social clubs, a Wendy's restaurant, and hobby centers. Other services included a Navy Exchange, commissary, bank, credit union, hospital, beauty shop, tour office and morale flights to the rest of Europe and the United States. Golfing was available in a nearby community.
The American base staff had their own names for various places in Iceland, e.g., "Kef" for Keflavík and "Hurdygurdy" for Hveragerði.
The NATO base did not have a Status of Forces Agreement (SOFA) with the Icelandic Government and the base lacked the roadway entrance security gates characteristic of most military installations, having only Icelandic Customs officials instead. Icelandic nationals had unrestricted access to most of the base, especially since the civilian international airport terminal was also located on the base at the time. Icelandic nationals were only barred from actual security-restricted military facilities such as aircraft parking areas, squadron and hangar facilities and classified operations centers. During the height of the Cold War, this access situation created definitive operational security (OPSEC) concerns by U.S. and NATO officials due to potential espionage activities by Soviet operatives masquerading as Icelandic nationals. In addition, during this same time period, the former Soviet Union constructed one of their largest embassy facilities in the nearby capital, Reykjavik, which doubled as a diplomatic cover for intelligence collection activities against U.S. and NATO military forces. Access to the base was restricted to authorized military and civilian personnel after the construction of a new civilian passenger terminal on the opposite side of the airfield in the mid-1980s.
The base offered a wide variety of recreational services which included bowling, swimming, gymnasium, theater, social clubs, a Wendy's restaurant, and hobby centers. Other services included a Navy Exchange, commissary, bank, credit union, hospital, beauty shop, tour office and morale flights to the rest of Europe and the United States. Golfing was available in a nearby community.
The American base staff had their own names for various places in Iceland, e.g., "Kef" for Keflavík and "Hurdygurdy" for Hveragerði.
Naval Facility (NAVFAC) Keflavik
The 1965 decision to deploy the Sound Surveillance System to the Norwegian Sea was followed by establishment of Naval Facility Keflavik in which output of the array at sea was processed and displayed by means of the Low Frequency Analyzer and Recorder (LOFAR). In 1966 the first deployment of a 3 X 16 element array system was terminated at the facility. NAVFAC Keflavik was commissioned 1 March 1966 with nine officers and sixty-nine enlisted personnel, eventually reaching 15 officers and 163 enlisted. The first detection of Soviet Victor-class submarine, ''Victor''- and Charlie-class submarine, ''Charlie''-class submarines was in 1968 with systems terminating at the facility followed by the first detection of a Soviet Delta-class submarine, Delta Class Nuclear submarine in 1974. The first detection of a Soviet nuclear submarine had been by United States Naval Facility, Barbados on 6 July 1962 of a submarine off the coast of Norway as it entered the GIUK gap, Greenland-Iceland-United Kingdom (GIUK) gap. Naval Facility Keflavik was decommissioned on 13 December 1996.In popular culture
NAS Keflavik features prominently in Tom Clancy's 1986 techno-thriller novel ''Red Storm Rising''. NAS Keflavik also features prominently in Icelandic author Arnaldur Indriðason's 1999 mystery thriller ''Napóleonsskjölin'', published in English in 2011 as ''Operation Napoleon.''See also
* Naval Radio Transmitter Facility Grindavik * Iceland Defense Force, Iceland Defence Force * Iceland in the Cold War * Military of Iceland * 1949 anti-NATO riot in IcelandFurther reading
* Pétursson, Gustav (2020)The Defence Relationship of Iceland and the United States and the Closure of Keflavík base
PhD thesis, University of Lapland.
References
* Baugher, Joe. ''USAAS-USAAC-USAAF-USAF Aircraft Serial Numbers—1908 to present''* Donald, David, "Century Jets – USAF Frontline Fighters of the Cold War". * Endicott, Judy G., USAF Active Flying, Space, and Missile Squadrons as of 1 October 1995. Office of Air Force History * Fletcher, Harry R., Air Force Bases Volume II, Active Air Force Bases outside the United States of America on 17 September 1982, Office of Air Force History, 1989 * Hill, Mike and Campbell, John, Tactical Air Command – An Illustrated History 1946–1992, 2001 * Martin, Patrick, Tail Code: The Complete History Of USAF Tactical Aircraft Tail Code Markings, 1994 * Maurer Maurer, Air Force Combat Units Of World War II, Office of Air Force History, 1983 * Rogers, Brian, ''United States Air Force Unit Designations Since 1978'', 2005 * Ravenstein, Charles A., Air Force Combat Wings Lineage and Honors Histories 1947–1977, Office of Air Force History, 1984
Official Navy disestablishment press release
External links
Archived NAS Keflavik website
provided by the Internet Archive * Reports on the withdrawal of U.S. forces in 2006
3489
(in Icelandic language, Icelandic)
Establishing the Iceland Base Command
a chapter in
' a publication of the United States Army Center of Military History
Map of the former site of the base
on OpenStreetMap {{Authority control United States Naval Air Stations, Keflavik Airfields of the United States Army Air Forces Air Transport Command on the North Atlantic Route Military installations established in 1942 Iceland–United States relations Airports established in 1942 Buildings and structures in Keflavík 1942 establishments in Iceland World War II sites in Iceland Closed installations of the United States Navy