Native American culture on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Native American cultures across the
Native American cultures across the
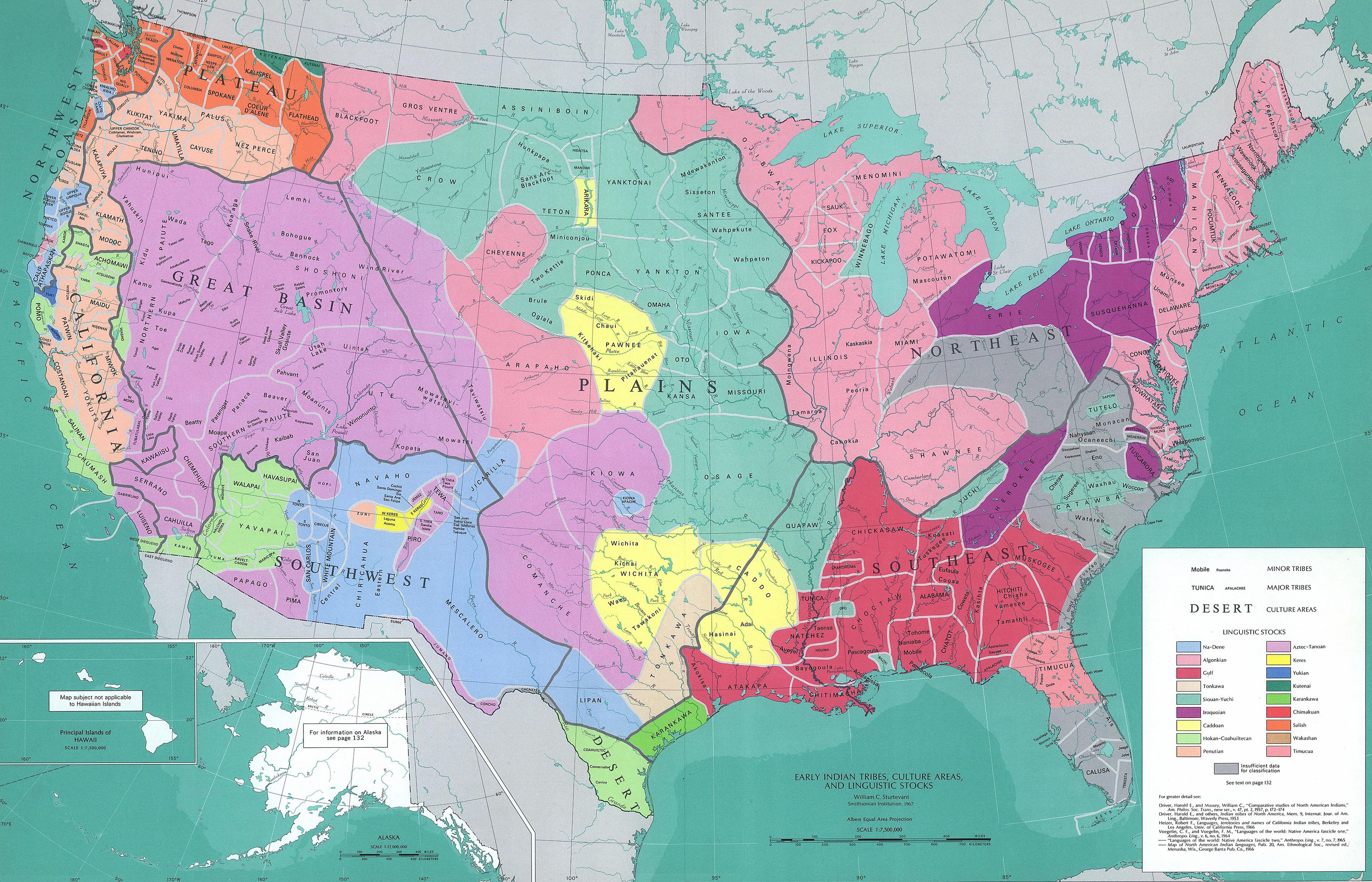 There are approximately 296 spoken (or formerly spoken) indigenous languages north of Mexico, 269 of which are grouped into 29 families.
The major ethno-linguistic phyla are:
*
There are approximately 296 spoken (or formerly spoken) indigenous languages north of Mexico, 269 of which are grouped into 29 families.
The major ethno-linguistic phyla are:
*
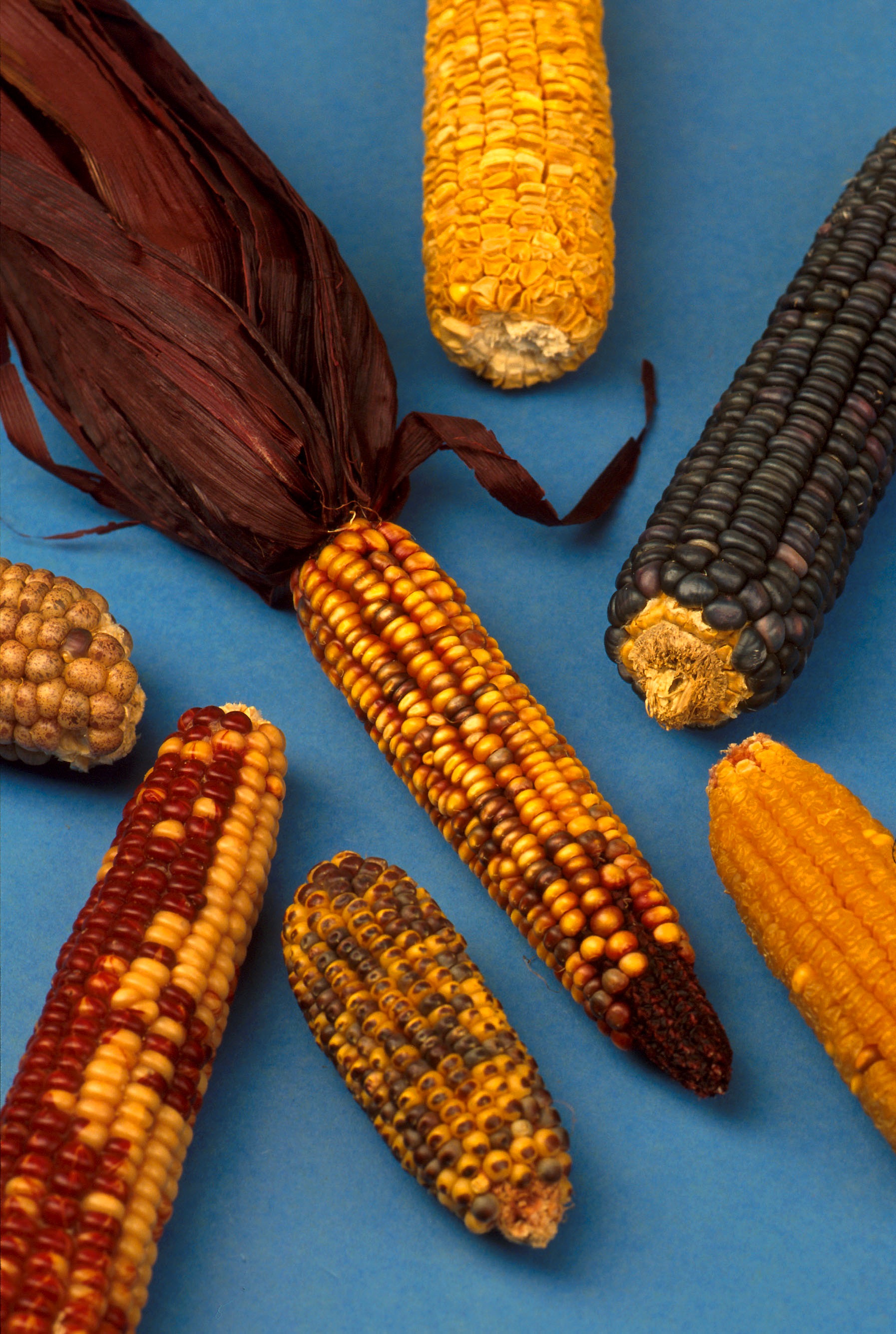


 The traditional diet of Native Americans has historically consisted of a combination of agriculture, hunting, and the gathering of wild foods, variable by bioregion.
Post-contact, European settlers in the northeastern region of the Americas observed that some of the Indigenous peoples cleared large areas for cropland. These fields in New England sometimes covered hundreds of acres. Colonists in Virginia noted thousands of acres under cultivation by Native Americans.
Native Americans commonly used tools such as the
The traditional diet of Native Americans has historically consisted of a combination of agriculture, hunting, and the gathering of wild foods, variable by bioregion.
Post-contact, European settlers in the northeastern region of the Americas observed that some of the Indigenous peoples cleared large areas for cropland. These fields in New England sometimes covered hundreds of acres. Colonists in Virginia noted thousands of acres under cultivation by Native Americans.
Native Americans commonly used tools such as the

 Traditional Native American ceremonies are still practiced by many tribes and bands, and the older theological belief systems are still held by many of the traditional people. Many Plains tribes have
Traditional Native American ceremonies are still practiced by many tribes and bands, and the older theological belief systems are still held by many of the traditional people. Many Plains tribes have
 Gender roles can vary significantly between tribal nations, with
Gender roles can vary significantly between tribal nations, with
''Publications of the Nebraska State Historical Society,'' Vol. 19, edited by Albert Watkins, Nebraska State Historical Society, 1919, p. 64, at GenNet, accessed 2011-08-25 In most of the Plains Nations, men traditionally hunt, trade and go to war. The women have traditionally held primary responsibility for the survival and welfare of the families (and future of the tribe). Traditionally, Plains women own the home, and tend to jobs such as gathering and cultivating plants for food and healing, along with caring for the young and the elderly, making clothing and processing and curing meat and skins. Plains women have historically tanned hides to make clothing as well as bags, saddle cloths, and tipi covers, and have used
 Native American leisure time led to competitive individual and team sports.
Native American leisure time led to competitive individual and team sports.
 Native American musicians have occasionally found broader fame in more mainstream American music. Artists such as
Native American musicians have occasionally found broader fame in more mainstream American music. Artists such as
 Native Americans in the United States have developed several original systems of communication, both in Pre-Columbian times, and later as a response to European influences. For example, the
Native Americans in the United States have developed several original systems of communication, both in Pre-Columbian times, and later as a response to European influences. For example, the
 There was fear on both sides, as the different peoples realized how different their societies were. The whites regarded the Indians as "savage" because they were not Christian. They were suspicious of cultures which they did not understand. The Native American author, Andrew J. Blackbird, wrote in his ''History of the
There was fear on both sides, as the different peoples realized how different their societies were. The whites regarded the Indians as "savage" because they were not Christian. They were suspicious of cultures which they did not understand. The Native American author, Andrew J. Blackbird, wrote in his ''History of the

 Native Americans were rewarded if they returned escaped slaves, and African Americans were rewarded for fighting in the late 19th-century
Native Americans were rewarded if they returned escaped slaves, and African Americans were rewarded for fighting in the late 19th-century
 Native American cultures across the
Native American cultures across the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
are notable for their wide variety and diversity of lifestyles, regalia, art forms and beliefs. The culture of indigenous North America
North America is a continent in the Northern Hemisphere and almost entirely within the Western Hemisphere. It is bordered to the north by the Arctic Ocean, to the east by the Atlantic Ocean, to the southeast by South America and th ...
is usually defined by the concept of the Pre-Columbian
In the history of the Americas, the pre-Columbian era spans from the original settlement of North and South America in the Upper Paleolithic period through European colonization, which began with Christopher Columbus's voyage of 1492. Usually, ...
culture area, namely a geographical region where shared cultural traits occur. The northwest culture area, for example shared common traits such as salmon fishing, woodworking, large villages or towns and a hierarchical social structure.
Though cultural features, language, clothing, and customs vary enormously from one tribe to another, there are certain elements which are encountered frequently and shared by many tribes. Early European American scholars described the Native Americans as having a society dominated by clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
s.
European colonization of the Americas had a major impact on Native American culture through what is known as the Columbian exchange
The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, precious metals, commodities, culture, human populations, technology, diseases, and ideas between the New World (the Americas) in ...
. The Columbian exchange, also known as the Columbian interchange, was the widespread transfer of plants, animals, culture, human populations, technology, and ideas between the Americas
The Americas, which are sometimes collectively called America, are a landmass comprising the totality of North America, North and South America. The Americas make up most of the land in Earth's Western Hemisphere and comprise the New World. ...
and the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by thei ...
in the 15th and 16th centuries, following Christopher Columbus
Christopher Columbus
* lij, Cristoffa C(or)ombo
* es, link=no, Cristóbal Colón
* pt, Cristóvão Colombo
* ca, Cristòfor (or )
* la, Christophorus Columbus. (; born between 25 August and 31 October 1451, died 20 May 1506) was a ...
's 1492 voyage. The Columbian exchange generally had a destructive impact on Native American culture through disease, and a 'clash of cultures', whereby European values of private property, the family, and labor led to conflict, appropriation of traditional communal lands and slavery.
In the early years, as these native peoples encountered European explorers and settlers and engaged in trade, they exchanged food, crafts, and furs for blankets, iron and steel implements, horses, trinkets, firearms, and alcoholic beverages.
Today, while remaining faithful to their traditions, Native American cultures continue to evolve and adapt to changing circumstances.
Cultural areas
Native Americans in the United States
Native Americans, also known as American Indians, First Americans, Indigenous Americans, and other terms, are the Indigenous peoples of the mainland United States ( Indigenous peoples of Hawaii, Alaska and territories of the United States ...
fall into a number of distinct ethno-linguistic and territorial phyla, whose only uniting characteristic is that they were in a stage of either Mesolithic
The Mesolithic ( Greek: μέσος, ''mesos'' 'middle' + λίθος, ''lithos'' 'stone') or Middle Stone Age is the Old World archaeological period between the Upper Paleolithic and the Neolithic. The term Epipaleolithic is often used synonymo ...
(hunter-gatherer
A traditional hunter-gatherer or forager is a human living an ancestrally derived lifestyle in which most or all food is obtained by foraging, that is, by gathering food from local sources, especially edible wild plants but also insects, fung ...
) or Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several pa ...
(subsistence farming) culture at the time of European contact.
They can be classified as belonging to a number of large cultural areas:
*Continental U.S.
**Californian tribes
The indigenous peoples of California (known as Native Californians) are the indigenous inhabitants who have lived or currently live in the geographic area within the current boundaries of California before and after the arrival of Europeans. ...
(Northern): Yok-Utian, Pacific Coast Athabaskan
Pacific Coast Athabaskan is a geographical and possibly genealogical grouping of the Athabaskan language family.
California Athabaskan
: 1. Hupa (dining'-xine:wh, a.k.a. Hoopa-Chilula)
:: dialects:
::* Hupa
::* Tsnungwe
::: - tse:ning-xwe
::: ...
, Coast Miwok
Coast Miwok are an indigenous people that was the second-largest group of Miwok people. Coast Miwok inhabited the general area of modern Marin County and southern Sonoma County in Northern California, from the Golden Gate north to Duncans Poi ...
, Yurok, Palaihnihan
Palaihnihan (also Palaihnih) is a language family of northeastern California. It consists of two closely related languages, both now extinct:
# Atsugewi ''(†)''
# Achumawi ''(†)'' (ís siwa wó disi, also known as Achomawi, Pit River India ...
, Chumashan
Chumashan was a family of languages that were spoken on the southern California coast by Native American Chumash people, from the Coastal plains and valleys of San Luis Obispo to Malibu, neighboring inland and Transverse Ranges valleys and ca ...
, Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
**Plateau tribes
Indigenous peoples of the Northwest Plateau, also referred to by the phrase Indigenous peoples of the Plateau, and historically called the Plateau Indians (though comprising many groups) are indigenous peoples of the Interior of British Columbi ...
: Interior Salish
The Interior Salish languages are one of the two main branches of the Salishan language family, the other being Coast Salish. It can be further divided into Northern and Southern subbranches. The first Salishan people encountered by American exp ...
, Plateau Penutian
**Great Basin tribes
The Indigenous peoples of the Great Basin are Native Americans of the northern Great Basin, Snake River Plain, and upper Colorado River basin. The "Great Basin" is a cultural classification of indigenous peoples of the Americas and a cultural re ...
: Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
** Pacific Northwest Coast: Pacific Coast Athabaskan
Pacific Coast Athabaskan is a geographical and possibly genealogical grouping of the Athabaskan language family.
California Athabaskan
: 1. Hupa (dining'-xine:wh, a.k.a. Hoopa-Chilula)
:: dialects:
::* Hupa
::* Tsnungwe
::: - tse:ning-xwe
::: ...
, Coast Salish
The Coast Salish is a group of ethnically and linguistically related Indigenous peoples of the Pacific Northwest Coast, living in the Canadian province of British Columbia and the U.S. states of Washington and Oregon. They speak one of the Coa ...
, Wakashan
Wakashan is a family of languages spoken in British Columbia around and on Vancouver Island, and in the northwestern corner of the Olympic Peninsula of Washington state, on the south side of the Strait of Juan de Fuca.
As is typical of the Nor ...
** Southwestern tribes: Uto-Aztecan
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
, Yuman, Southern Athabaskan
Southern Athabaskan (also Apachean) is a subfamily of Athabaskan languages spoken primarily in the Southwestern United States (including Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Utah) with two outliers in Oklahoma and Texas. The language is spoken to ...
**Plains Indians
Plains Indians or Indigenous peoples of the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies are the Native American tribes and First Nation band governments who have historically lived on the Interior Plains (the Great Plains and Canadian Prairies) of ...
: Siouan
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the ent ...
, Plains Algonquian, Southern Athabaskan
Southern Athabaskan (also Apachean) is a subfamily of Athabaskan languages spoken primarily in the Southwestern United States (including Arizona, New Mexico, Colorado, and Utah) with two outliers in Oklahoma and Texas. The language is spoken to ...
** Northeastern Woodlands tribes: Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
, Pequot, Mohican, Mohawk, Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoia ...
, Central Algonquian
The Central Algonquian languages are commonly grouped together as a subgroup of the larger Algonquian family, itself a member of the Algic family. Though the grouping is often encountered in the literature, it is an areal grouping, not a geneti ...
, Eastern Algonquian
The Eastern Algonquian languages constitute a subgroup of the Algonquian languages. Prior to European contact, Eastern Algonquian consisted of at least 17 languages, whose speakers collectively occupied the Atlantic coast of North America and adj ...
** Southeastern Woodlands tribes: Muskogean, Caddoan
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number ...
, Catawban
The Catawban, or Eastern Siouan, languages form a small language family in east North America. The Catawban family is a branch of the larger Siouan a.k.a. Siouan–Catawban family.
Family division
The Catawban family consists of two languages: ...
, Iroquoian
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoia ...
*Alaska Natives
Alaska Natives (also known as Alaskan Natives, Native Alaskans, Indigenous Alaskans, Aboriginal Alaskans or First Alaskans) are the indigenous peoples of Alaska and include Iñupiat, Yupik, Aleut, Eyak, Tlingit, Haida, Tsimshian, and a num ...
**Arctic: Eskimo–Aleut
**Subarctic: Northern Athabaskan
* Hawaiians
Language
 There are approximately 296 spoken (or formerly spoken) indigenous languages north of Mexico, 269 of which are grouped into 29 families.
The major ethno-linguistic phyla are:
*
There are approximately 296 spoken (or formerly spoken) indigenous languages north of Mexico, 269 of which are grouped into 29 families.
The major ethno-linguistic phyla are:
*Na-Dene languages
Na-Dene (; also Nadene, Na-Dené, Athabaskan–Eyak–Tlingit, Tlina–Dene) is a family of Native American languages that includes at least the Athabaskan languages, Eyak, and Tlingit languages. Haida was formerly included, but is now consider ...
,
*Iroquoian languages
The Iroquoian languages are a language family of indigenous peoples of North America. They are known for their general lack of labial consonants. The Iroquoian languages are polysynthetic and head-marking.
As of 2020, all surviving Iroquoian ...
,
*Caddoan languages
The Caddoan languages are a family of languages native to the Great Plains spoken by tribal groups of the central United States, from present-day North Dakota south to Oklahoma. All Caddoan languages are critically endangered, as the number of s ...
*Algonquian languages
The Algonquian languages ( or ; also Algonkian) are a subfamily of indigenous American languages that include most languages in the Algic language family. The name of the Algonquian language family is distinguished from the orthographically simi ...
*Algic languages
The Algic languages (also Algonquian–Wiyot–Yurok or Algonquian–Ritwan) are an indigenous language family of North America. Most Algic languages belong to the Algonquian subfamily, dispersed over a broad area from the Rocky Mountains to ...
,
*Siouan–Catawban languages
Siouan or Siouan–Catawban is a language family of North America that is located primarily in the Great Plains, Ohio and Mississippi valleys and southeastern North America with a few other languages in the east.
Name
Authors who call the entire ...
,
*Uto-Aztecan languages
Uto-Aztecan, Uto-Aztekan or (rarely in English) Uto-Nahuatl is a family of indigenous languages of the Americas, consisting of over thirty languages. Uto-Aztecan languages are found almost entirely in the Western United States and Mexico. The na ...
,
*Salishan languages
The Salishan (also Salish) languages are a family of languages of the Pacific Northwest in North America (the Canadian province of British Columbia and the American states of Washington, Oregon, Idaho and Montana). They are characterised by a ...
,
*Tanoan languages
Tanoan , also Kiowa–Tanoan or Tanoan–Kiowa, is a family of languages spoken by indigenous peoples in present-day New Mexico, Kansas, Oklahoma, and Texas.
Most of the languages – Tiwa (Taos, Picuris, Southern Tiwa), Tewa, and Towa – ...
* Eskimo–Aleut (Alaska)
The Na-Dené, Algic, and Uto-Aztecan families are the largest in terms of number of languages. Uto-Aztecan has the most speakers (1.95 million) if the languages in Mexico are considered (mostly due to 1.5 million speakers of Nahuatl
Nahuatl (; ), Aztec, or Mexicano is a language or, by some definitions, a group of languages of the Uto-Aztecan language family. Varieties of Nahuatl are spoken by about Nahua peoples, most of whom live mainly in Central Mexico and have small ...
); Na-Dené comes in second with approximately 200,000 speakers (nearly 180,000 of these are speakers of Navajo
The Navajo (; British English: Navaho; nv, Diné or ') are a Native Americans in the United States, Native American people of the Southwestern United States.
With more than 399,494 enrolled tribal members , the Navajo Nation is the largest fe ...
), and Algic in third with about 180,000 speakers (mainly Cree
The Cree ( cr, néhinaw, script=Latn, , etc.; french: link=no, Cri) are a North American Indigenous people. They live primarily in Canada, where they form one of the country's largest First Nations.
In Canada, over 350,000 people are Cree o ...
and Ojibwe
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
). Na-Dené and Algic have the widest geographic distributions: Algic currently spans from northeastern Canada across much of the continent down to northeastern Mexico (due to later migrations of the Kickapoo) with two outliers in California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
( Yurok and Wiyot
The Wiyot (Wiyot: Wíyot, Chetco-Tolowa: Wee-’at xee-she or Wee-yan’ Xee-she’, Euchre Creek Tututni: Wii-yat-dv-ne - "Mad River People“, Yurok: Weyet) are an indigenous people of California living near Humboldt Bay, California and a sma ...
). The remaining 27 languages are either isolates or unclassified), such as Penutian languages
Penutian is a proposed grouping of language families that includes many Native American languages of western North America, predominantly spoken at one time in British Columbia, Washington, Oregon, and California. The existence of a Penutian s ...
, Hokan, Gulf languages
The Gulf languages are a proposed family of native North American languages composed of the Muskogean languages, along with four language isolates: Natchez, Tunica, Atakapa, and (possibly) Chitimacha.
History of proposal
Gulf was proposed a ...
and others.
Organization

Gens structure
Early European American scholar described the Native Americans (as well as any othertribal
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to conflic ...
society) as having a society dominated by clans
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
or gentes (in the Roman model) before tribes were formed. There were some common characteristics:
*The right to elect its sachem
Sachems and sagamores are paramount chiefs among the Algonquians or other Native American tribes of northeastern North America, including the Iroquois. The two words are anglicizations of cognate terms (c. 1622) from different Eastern Al ...
and chiefs.
*The right to depose its sachem and chiefs.
*The obligation not to marry in the gens.
*Mutual rights of inheritance of the property of deceased members.
*Reciprocal obligations of help, defense, and redress of injuries.
*The right to bestow names on its members.
*The right to adopt strangers into the gens.
*Common religious rights, query.
*A common burial place.
*A council of the gens.
Tribal structure
Subdivision and differentiation took place between various groups. Some functions and attributes of tribes are: *The possession of the gentes. *The right to depose these sachems and chiefs. *The possession of religious faith and worship. *A supreme government consisting of a council of chiefs. *A head-chief of the tribe in some instances.Traditional diet

 The traditional diet of Native Americans has historically consisted of a combination of agriculture, hunting, and the gathering of wild foods, variable by bioregion.
Post-contact, European settlers in the northeastern region of the Americas observed that some of the Indigenous peoples cleared large areas for cropland. These fields in New England sometimes covered hundreds of acres. Colonists in Virginia noted thousands of acres under cultivation by Native Americans.
Native Americans commonly used tools such as the
The traditional diet of Native Americans has historically consisted of a combination of agriculture, hunting, and the gathering of wild foods, variable by bioregion.
Post-contact, European settlers in the northeastern region of the Americas observed that some of the Indigenous peoples cleared large areas for cropland. These fields in New England sometimes covered hundreds of acres. Colonists in Virginia noted thousands of acres under cultivation by Native Americans.
Native Americans commonly used tools such as the hoe
Hoe or HOE may refer to:
* Hoe (food), a Korean dish of raw fish
* Hoe (letter), a Georgian letter
* Hoe (tool), a hand tool used in gardening and farming
** Hoe-farming, a term for primitive forms of agriculture
* Backhoe, a piece of excavating ...
, maul, and dibber
A dibber or dibble or dibbler is a pointed wooden stick for making holes in the ground so that seeds, seedlings or small bulbs can be planted. Dibbers come in a variety of designs including the straight dibber, T-handled dibber, trowel dibber, a ...
. The hoe was the main tool used to till the land and prepare it for planting; then it was used for weeding. The first versions were made out of wood and stone. When the settlers brought iron, Native Americans switched to iron hoes and hatchets. The dibber was a digging stick, used to plant the seed. Once the plants were harvested, women prepared the produce for eating. They used the maul to grind the corn into mash. It was cooked and eaten that way or baked as corn bread.
Religion

 Traditional Native American ceremonies are still practiced by many tribes and bands, and the older theological belief systems are still held by many of the traditional people. Many Plains tribes have
Traditional Native American ceremonies are still practiced by many tribes and bands, and the older theological belief systems are still held by many of the traditional people. Many Plains tribes have sweatlodge
A sweat lodge is a low profile hut, typically dome-shaped or oblong, and made with natural materials. The structure is the ''lodge'', and the ceremony performed within the structure may be called by some cultures a purification ceremony or simply ...
ceremonies, though the specifics of the ceremony vary among tribes. Fasting, singing and prayer in the ancient languages of their people, and sometimes drumming, and dancing are also common.
The Midewiwin Lodge is a traditional medicine society inspired by the oral traditions and prophesies of the Ojibwa
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
(Chippewa) and related tribes.
Another significant religious body among some Native Americans is the Native American Church
The Native American Church (NAC), also known as Peyotism and Peyote Religion, is a Native American religion that teaches a combination of traditional Native American beliefs and Christianity, with sacramental use of the entheogen peyote. Th ...
. It is a syncretistic church incorporating elements of Native spiritual practice from a number of different tribes. Some varieties also include elements from Christianity
Christianity is an Abrahamic monotheistic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus of Nazareth. It is the world's largest and most widespread religion with roughly 2.38 billion followers representing one-third of the global popula ...
. Its main rite is the peyote
The peyote (; ''Lophophora williamsii'' ) is a small, spineless cactus which contains Psychoactive cactus, psychoactive alkaloids, particularly mescaline. ''Peyote'' is a Spanish word derived from the Nahuatl (), meaning "caterpillar Pupa#Cocoo ...
ceremony. Prior to 1890, traditional religious beliefs included Wakan Tanka. In the American Southwest, especially New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
, a syncretism between the Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
brought by Spanish missionaries and the Indigenous religions is common; the religious drums, chants, and dances of the Pueblo people
The Puebloans or Pueblo peoples, are Native Americans in the Southwestern United States who share common agricultural, material, and religious practices. Currently 100 pueblos are actively inhabited, among which Taos, San Ildefonso, Acoma, Z ...
are regularly part of Masses at Santa Fe's Saint Francis Cathedral
The Cathedral Basilica of Saint Francis of Assisi ( es, Catedral basílica de San Francisco de Asís), commonly known as Saint Francis Cathedral, is a Roman Catholic cathedral in downtown Santa Fe, New Mexico. It is the mother church of the Arc ...
. Native American-Catholic syncretism is also found elsewhere in the United States. (e.g., the National Kateri Tekakwitha
Kateri Tekakwitha ( in Mohawk), given the name Tekakwitha, baptized as Catherine and informally known as Lily of the Mohawks (1656 – April 17, 1680), is a Catholic saint and virgin who was an Algonquin– Mohawk. Born in the Mohawk village ...
Shrine in Fonda, New York and the National Shrine of the North American Martyrs in Auriesville, New York
Auriesville is a hamlet in the northeastern part of the Town of Glen in Montgomery County, New York, United States, along the south bank of the Mohawk River and west of Fort Hunter. It lies about forty miles west of Albany, the state capital. ...
).
The eagle feather law (Title 50 Part 22 of the Code of Federal Regulations) stipulates that only individuals of certifiable Native American ancestry enrolled in a federally recognized tribe are legally authorized to obtain eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
feathers for religious
Religion is usually defined as a social- cultural system of designated behaviors and practices, morals, beliefs, worldviews, texts, sanctified places, prophecies, ethics, or organizations, that generally relates humanity to supernatur ...
or spiritual use. The law does not allow Native Americans to give eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
feathers to non-Native Americans.
Gender roles
 Gender roles can vary significantly between tribal nations, with
Gender roles can vary significantly between tribal nations, with patriarchal
Patriarchy is a social system in which positions of dominance and privilege are primarily held by men. It is used, both as a technical anthropological term for families or clans controlled by the father or eldest male or group of males ...
, matriarchal
Matriarchy is a social system in which women hold the primary power positions in roles of authority. In a broader sense it can also extend to moral authority, social privilege and control of property.
While those definitions apply in general En ...
, and egalitarian traditions historically present among the over 500 federally-recognized tribes
This is a list of federally recognized tribes in the contiguous United States. There are also federally recognized Alaska Native tribes. , 574 Indian tribes were legally recognized by the Bureau of Indian Affairs (BIA) of the United States.
. Many tribes, such as the Haudenosaunee
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
Five Nations and the Southeast Muskogean tribes, had matrilineal
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's lineage – and which can involve the inheritance ...
systems, in which property and hereditary leadership were controlled by and passed through the maternal lines.
Others were patrilineal
Patrilineality, also known as the male line, the spear side or agnatic kinship, is a common kinship system in which an individual's family membership derives from and is recorded through their father's lineage. It generally involves the inheritan ...
tribes, such as the Omaha
Omaha ( ) is the largest city in the U.S. state of Nebraska and the county seat of Douglas County. Omaha is in the Midwestern United States on the Missouri River, about north of the mouth of the Platte River. The nation's 39th-largest c ...
, Osage and Ponca
The Ponca ( Páⁿka iyé: Páⁿka or Ppáⁿkka pronounced ) are a Midwestern Native American tribe of the Dhegihan branch of the Siouan language group. There are two federally recognized Ponca tribes: the Ponca Tribe of Nebraska and the ...
, where hereditary leadership passed through the male line, and children were considered to belong to the father and his clan
A clan is a group of people united by actual or perceived kinship
and descent. Even if lineage details are unknown, clans may claim descent from founding member or apical ancestor. Clans, in indigenous societies, tend to be endogamous, mea ...
. For this reason, when Europeans or American men took wives from such tribes, their children were considered "white" like their fathers, or " half-breeds". Generally such children could have no official place in the tribe because their fathers did not belong to it, unless they were adopted by a male and made part of his family. Melvin Randolph Gilmore, "The True Logan Fontenelle"''Publications of the Nebraska State Historical Society,'' Vol. 19, edited by Albert Watkins, Nebraska State Historical Society, 1919, p. 64, at GenNet, accessed 2011-08-25 In most of the Plains Nations, men traditionally hunt, trade and go to war. The women have traditionally held primary responsibility for the survival and welfare of the families (and future of the tribe). Traditionally, Plains women own the home, and tend to jobs such as gathering and cultivating plants for food and healing, along with caring for the young and the elderly, making clothing and processing and curing meat and skins. Plains women have historically tanned hides to make clothing as well as bags, saddle cloths, and tipi covers, and have used
cradleboard
Cradleboards (, se, gietkka, sms, ǩiõtkâm, smn, kietkâm, sje, gietkam) are traditional protective baby-carriers used by many indigenous cultures in North America and throughout northern Scandinavia amongst the Sámi. There are a variety ...
s to carry an infant while working or traveling.
Several dozen tribes have been documented to practiced polygyny
Polygyny (; from Neoclassical Greek πολυγυνία (); ) is the most common and accepted form of polygamy around the world, entailing the marriage of a man with several women.
Incidence
Polygyny is more widespread in Africa than in any ...
to sisters, with procedural and economic limits.
Apart from making homes, women have traditionally held many additional responsibilities essential for the survival of the tribes, including the manufacture of weapons and tools, maintenance of the roofs of their homes, as well as participating in the bison
Bison are large bovines in the genus ''Bison'' (Greek: "wild ox" (bison)) within the tribe Bovini. Two extant and numerous extinct species are recognised.
Of the two surviving species, the American bison, ''B. bison'', found only in North A ...
hunts.
In some of the Plains Indian tribes, medicine women gathered herbs and cured the ill.
The Lakota, Dakota, and Nakota girls have traditionally been encouraged to learn to ride, hunt and fight. Though fighting was predominantly the duty of men and boys, occasionally women fought as well, especially if the tribe was severely threatened.
Sports

 Native American leisure time led to competitive individual and team sports.
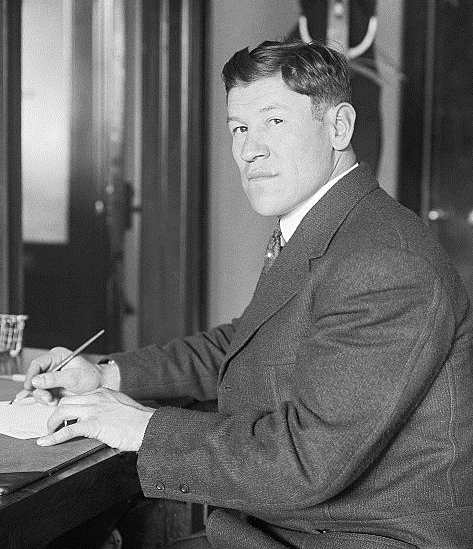
Native American leisure time led to competitive individual and team sports. Jim Thorpe
James Francis Thorpe ( Sac and Fox (Sauk): ''Wa-Tho-Huk'', translated as "Bright Path"; May 22 or 28, 1887March 28, 1953) was an American athlete and Olympic gold medalist. A member of the Sac and Fox Nation, Thorpe was the first Native ...
, Joe Hipp, Notah Begay III
Notah Ryan Begay III (born September 14, 1972) is a Native American professional golfer. He is one of the only Native American golfers to have played in the PGA Tour. Since 2013, Begay has served as an analyst with the Golf Channel and NBC Sport ...
, Jacoby Ellsbury, and Billy Mills are well known professional athletes.
Team based
Native American ball sports, sometimes referred to aslacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
, stickball, or baggataway, was often used to settle disputes, rather than going to war, as a civil way to settle potential conflict. The Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
called it ''isitoboli'' ("Little Brother of War");
the Onondaga name was ''dehuntshigwa'es'' ("men hit a rounded object"). There are three basic versions, classified as Great Lakes, Iroquoian, and Southern.
The game is played with one or two rackets/sticks and one ball. The object of the game is to land the ball on the opposing team's goal (either a single post or net) to score and to prevent the opposing team from scoring on your goal. The game involves as few as 20 or as many as 300 players with no height or weight restrictions and no protective gear. The goals could be from around apart to about ; in Lacrosse the field is .
Individual
Chunkey was a game that consisted of a disk shaped stone that was about 1–2 inches in diameter. The disk was thrown down a corridor so that it could roll past the players at great speed. The disk would roll down the corridor, and players would throw wooden shafts at the moving disk. The object of the game was to strike the disk or prevent your opponents from hitting it.Music
 Native American musicians have occasionally found broader fame in more mainstream American music. Artists such as
Native American musicians have occasionally found broader fame in more mainstream American music. Artists such as Robbie Robertson
Jaime Royal "Robbie" Robertson, OC (born July 5, 1943), is a Canadian musician. He is best known for his work as lead guitarist and songwriter for the Band, and for his career as a solo recording artist. With the deaths of Richard Manuel i ...
( The Band), Buffy Sainte-Marie
Buffy Sainte-Marie, (born Beverly Sainte-Marie, February 20, 1941) is an Indigenous Canadian-American (Piapot Cree Nation) singer-songwriter, musician, composer, visual artist, educator, pacifist, and social activist. While working in these ar ...
, and Redbone have had success on the rock and pop charts. Some, such as Sainte-Marie, John Trudell
John Trudell (February 15, 1946December 8, 2015) was a Native American author, poet, actor, musician, and political activist. He was the spokesperson for the Indians of All Tribes' takeover of Alcatraz beginning in 1969, broadcasting as ''Radi ...
, and Blackfoot
The Blackfoot Confederacy, ''Niitsitapi'' or ''Siksikaitsitapi'' (ᖹᐟᒧᐧᒣᑯ, meaning "the people" or "Blackfoot language, Blackfoot-speaking real people"), is a historic collective name for linguistically related groups that make up t ...
have used music as political commentary and part of their work as activists for Native American and First Nations causes. Others, such as flautists
This is a list of flute players, organized alphabetically by the musical genre in which they are best known, and whose notability is established by reliable sources in other Wikipedia articles.
In the final section below, any appropriate E ...
Charles Littleleaf
Charles Littleleaf, a Native American flute player and flute maker, is a tribal member of the Warm Springs Indian Reservation, Oregon. Charles is also an honorary member of the Piikani Nation, Alberta, Canada, and is the son of the late Chief ...
record traditional instruments with an aim of preserving the sounds of nature, or in the case of R. Carlos Nakai
Raymond Carlos Nakai (born April 16, 1946) is a Native American flutist of Navajo and Ute heritage. Nakai played brass instruments in high school and college, and auditioned for the Armed Forces School of Music after a two-year period in the ...
, integrate traditional instruments with more modern instrumentation. A variety of small and medium-sized recording companies offer an abundance of contemporary music by Native Americans and descendants, ranging from pow-wow drum music to rock-and-roll and rap.
A popular Native American musical form is pow wow
A powwow (also pow wow or pow-wow) is a gathering with dances held by many Native American and First Nations communities. Powwows today allow Indigenous people to socialize, dance, sing, and honor their cultures. Powwows may be private or p ...
drumming and singing, which happens at events like the annual Gathering of Nations
The Gathering of Nations is the largest pow-wow in the United States and North America. It is held annually on the fourth weekend in April, on the Powwow Grounds at Expo NM, in Albuquerque, New Mexico. Over 565 tribes from around the United State ...
in Albuquerque
Albuquerque ( ; ), ; kee, Arawageeki; tow, Vakêêke; zun, Alo:ke:k'ya; apj, Gołgéeki'yé. abbreviated ABQ, is the most populous city in the U.S. state of New Mexico. Its nicknames, The Duke City and Burque, both reference its founding i ...
, New Mexico
)
, population_demonym = New Mexican ( es, Neomexicano, Neomejicano, Nuevo Mexicano)
, seat = Santa Fe, New Mexico, Santa Fe
, LargestCity = Albuquerque, New Mexico, Albuquerque
, LargestMetro = Albuquerque metropolitan area, Tiguex
, Offi ...
. One form involves members of drum groups sitting in a circle around a large drum, playing in unison while they sing together in their Indigenous language. Often they are accompanied by dancers in colorful regalia. Most Indigenous communities in the United States also maintain private, traditional songs and ceremonies, which are only shared within the community.
Art
Writing and communication
 Native Americans in the United States have developed several original systems of communication, both in Pre-Columbian times, and later as a response to European influences. For example, the
Native Americans in the United States have developed several original systems of communication, both in Pre-Columbian times, and later as a response to European influences. For example, the Iroquois
The Iroquois ( or ), officially the Haudenosaunee ( meaning "people of the longhouse"), are an Iroquoian Peoples, Iroquoian-speaking Confederation#Indigenous confederations in North America, confederacy of First Nations in Canada, First Natio ...
, living around the Great Lakes
The Great Lakes, also called the Great Lakes of North America, are a series of large interconnected freshwater lakes in the mid-east region of North America that connect to the Atlantic Ocean via the Saint Lawrence River. There are five lakes ...
and extending east and north, used strings or belts called '' wampum'' that served a dual function: the knots and beaded designs mnemonically chronicled tribal stories and legends, and further served as a medium of exchange and a unit of measure. The keepers of the articles were seen as tribal dignitaries. Another form of communication was the Wiigwaasabak
''Wiigwaasabak'' (in Anishinaabe syllabics: , plural: ''wiigwaasabakoon'' ) are birch bark scrolls, on which the Ojibwa (Anishinaabe) people of North America wrote complex geometrical patterns and shapes, also known as a "written language." ...
, birch bark
Birch bark or birchbark is the bark of several Eurasian and North American birch trees of the genus ''Betula''.
The strong and water-resistant cardboard-like bark can be easily cut, bent, and sewn, which has made it a valuable building, craftin ...
scrolls on which the Ojibwa
The Ojibwe, Ojibwa, Chippewa, or Saulteaux are an Anishinaabe people in what is currently southern Canada, the northern Midwestern United States, and Northern Plains.
According to the U.S. census, in the United States Ojibwe people are one of ...
(Anishinaabe
The Anishinaabeg (adjectival: Anishinaabe) are a group of culturally related Indigenous peoples present in the Great Lakes region of Canada and the United States. They include the Ojibwe (including Saulteaux and Oji-Cree), Odawa, Potawa ...
) people wrote complex geometrical patterns and shapes, can also be considered a form of writing.
A widely used form of communication was Plains Indian Sign Language
Plains Indian Sign Language (PISL), also known as Hand Talk, Plains Sign Talk, and First Nation Sign Language, is a trade language, formerly trade pidgin, that was once the lingua franca across what is now central Canada, the central and weste ...
(PISL), also known as Plains Sign Talk, Plains Sign Language and First Nation Sign Language. PISL is a trade language (or international auxiliary language
An international auxiliary language (sometimes acronymized as IAL or contracted as auxlang) is a language meant for communication between people from all different nations, who do not share a common first language. An auxiliary language is primaril ...
), formerly a trade pidgin
A pidgin , or pidgin language, is a grammatically simplified means of communication that develops between two or more groups of people that do not have a language in common: typically, its vocabulary and grammar are limited and often drawn from s ...
, that was once the lingua franca
A lingua franca (; ; for plurals see ), also known as a bridge language, common language, trade language, auxiliary language, vehicular language, or link language, is a language systematically used to make communication possible between groups ...
across central Canada, central and western United States and northern Mexico, used among the various Plains Nations. It was also used for story-telling, oratory, various ceremonies, and by deaf people for ordinary daily use.
In the late 1810s and early 1820s, the Cherokee syllabary was invented by the silversmith Sequoyah
Sequoyah (Cherokee language, Cherokee: ᏍᏏᏉᏯ, ''Ssiquoya'', or ᏎᏉᏯ, ''Se-quo-ya''; 1770 – August 1843), also known as George Gist or George Guess, was a Native Americans in the United States, Native American polymath of the Ch ...
to write the Cherokee language
200px, Number of speakers
Cherokee or Tsalagi ( chr, ᏣᎳᎩ ᎦᏬᏂᎯᏍᏗ, ) is an endangered-to- moribund Iroquoian language and the native language of the Cherokee people. ''Ethnologue'' states that there were 1,520 Cherokee speak ...
. His creation of the syllabary
In the linguistic study of written languages, a syllabary is a set of written symbols that represent the syllables or (more frequently) moras which make up words.
A symbol in a syllabary, called a syllabogram, typically represents an (option ...
is particularly noteworthy as he could not previously read any script. He first experimented with logogram
In a written language, a logogram, logograph, or lexigraph is a written character that represents a word or morpheme. Chinese characters (pronounced '' hanzi'' in Mandarin, ''kanji'' in Japanese, ''hanja'' in Korean) are generally logograms, ...
s, before developing his system into a syllabary. In his system, each symbol represents a syllable
A syllable is a unit of organization for a sequence of speech sounds typically made up of a syllable nucleus (most often a vowel) with optional initial and final margins (typically, consonants). Syllables are often considered the phonological ...
rather than a single phoneme
In phonology and linguistics, a phoneme () is a unit of sound that can distinguish one word from another in a particular language.
For example, in most dialects of English, with the notable exception of the West Midlands and the north-wes ...
; the 85 (originally 86) characters provide a suitable method to write Cherokee. Although some symbols resemble Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
, Greek
Greek may refer to:
Greece
Anything of, from, or related to Greece, a country in Southern Europe:
*Greeks, an ethnic group.
*Greek language, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
**Proto-Greek language, the assumed last common ancestor ...
, and Cyrillic
The Cyrillic script ( ), Slavonic script or the Slavic script, is a writing system used for various languages across Eurasia. It is the designated national script in various Slavic, Turkic, Mongolic, Uralic, Caucasian and Iranic-speaking co ...
letters, the relationship between symbols and sounds is different.
The success of the Cherokee syllabary inspired James Evans, a missionary in what is now Manitoba
Manitoba ( ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province of Canada at the Centre of Canada, longitudinal centre of the country. It is Canada's Population of Canada by province and territory, fifth-most populous province, with a population o ...
, during the 1840s to develop Cree syllabics
Cree syllabics are the versions of Canadian Aboriginal syllabics used to write Cree dialects, including the original syllabics system created for Cree and Ojibwe. There are two main varieties of syllabics for Cree: Western Cree syllabics and ...
. Evans had originally adapted the Latin script
The Latin script, also known as Roman script, is an alphabetic writing system based on the letters of the classical Latin alphabet, derived from a form of the Greek alphabet which was in use in the ancient Greek city of Cumae, in southern ...
to Ojibwe (see Evans system), but after learning of the Cherokee syllabary, he experimented with invented scripts based on his familiarity with shorthand
Shorthand is an abbreviated symbolic writing method that increases speed and brevity of writing as compared to longhand, a more common method of writing a language. The process of writing in shorthand is called stenography, from the Greek ''s ...
and Devanagari
Devanagari ( ; , , Sanskrit pronunciation: ), also called Nagari (),Kathleen Kuiper (2010), The Culture of India, New York: The Rosen Publishing Group, , page 83 is a left-to-right abugida (a type of segmental writing system), based on the ...
. When Evans later worked with the closely related Cree, and ran into trouble with the Latin alphabet, he turned to his Ojibwe project and in 1840 adapted it to the Cree language
Cree (also known as Cree– Montagnais– Naskapi) is a dialect continuum of Algonquian languages spoken by approximately 117,000 people across Canada, from the Northwest Territories to Alberta to Labrador. If considered one language, it is th ...
. The result contained just nine glyph shapes, each of which stood for a syllable with the vowels determined by the orientations of these shapes. Cree syllabics are primarily a Canadian phenomenon, but are used occasionally in the United States by communities that straddle the border.
Interracial relations
Interracial relations between Native Americans, Europeans, and Africans is a complex issue that has been mostly neglected with "few in-depth studies on interracial relationships". Some of the first documented cases of European/Native American intermarriage and contact were recorded in Post-ColumbianMexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
. One case is that of Gonzalo Guerrero
Gonzalo Guerrero (also known as Gonzalo Marinero, Gonzalo de Aroca and Gonzalo de Aroza) was a sailor from Palos, in Spain who was shipwrecked along the Yucatán Peninsula and was taken as a slave by the local Maya. Earning his freedom, Gue ...
, a European from Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
, who was shipwrecked along the Yucatan Peninsula, and fathered three Mestizo
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
children with a Mayan
Mayan most commonly refers to:
* Maya peoples, various indigenous peoples of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Maya civilization, pre-Columbian culture of Mesoamerica and northern Central America
* Mayan languages, language family spoken ...
noblewoman. Another is the case of Hernán Cortés
Hernán Cortés de Monroy y Pizarro Altamirano, 1st Marquess of the Valley of Oaxaca (; ; 1485 – December 2, 1547) was a Spanish ''conquistador'' who led an expedition that caused the fall of the Aztec Empire and brought large portions of w ...
and his mistress La Malinche
Marina or Malintzin ( 1500 – 1529), more popularly known as La Malinche , a Nahua woman from the Mexican Gulf Coast, became known for contributing to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521), by acting as an interpreter, ad ...
, who gave birth to another of the first multi-racial people in the Americas.
Assimilation
European impact was immediate, widespread, and profound—more than any other race that had contact with Native Americans during the early years of colonization and nationhood. Europeans living among Native Americans were often called "White Indians". They "lived in native communities for years, learned native languages fluently, attended native councils, and often fought alongside their native companions." Early contact was often charged with tension and emotion, but also had moments of friendship, cooperation, and intimacy. Marriages took place in English, Spanish, and French colonies between Native Americans and Europeans. Given the preponderance of men among the colonists in the early years, generally European men married American Indian women. There was fear on both sides, as the different peoples realized how different their societies were. The whites regarded the Indians as "savage" because they were not Christian. They were suspicious of cultures which they did not understand. The Native American author, Andrew J. Blackbird, wrote in his ''History of the
There was fear on both sides, as the different peoples realized how different their societies were. The whites regarded the Indians as "savage" because they were not Christian. They were suspicious of cultures which they did not understand. The Native American author, Andrew J. Blackbird, wrote in his ''History of the Ottawa
Ottawa (, ; Canadian French: ) is the capital city of Canada. It is located at the confluence of the Ottawa River and the Rideau River in the southern portion of the province of Ontario. Ottawa borders Gatineau, Quebec, and forms the c ...
and Chippewa Indians of Michigan,'' (1897), that white settlers introduced some immoralities into Native American tribes. Many Indians suffered because the Europeans introduced alcohol and the whiskey trade resulted in alcoholism among the people, who were alcohol-intolerant.
As European-American women started working independently at missions and Indian schools in the western states, there were more opportunities for their meeting and developing relationships with Native American men. For instance, Charles Eastman, a man of European and Lakota descent whose father sent both his sons to Dartmouth College
Dartmouth College (; ) is a private research university in Hanover, New Hampshire. Established in 1769 by Eleazar Wheelock, it is one of the nine colonial colleges chartered before the American Revolution. Although founded to educate Native ...
, got his medical degree at Boston University
Boston University (BU) is a private research university in Boston, Massachusetts. The university is nonsectarian, but has a historical affiliation with the United Methodist Church. It was founded in 1839 by Methodists with its original cam ...
and returned to the West to practice. He married Elaine Goodale, whom he met in South Dakota. He was the grandson of Seth Eastman, a military officer from Maine, and a chief's daughter. Goodale was a young European-American teacher from Massachusetts and a reformer, who was appointed as the US superintendent of Native American education for the reservations in the Dakota Territory. They had six children together.
Slavery
The majority of Native American tribes did practice some form of slavery before the European introduction of African slavery into North America, but none exploited slave labor on a large scale. In addition, Native Americans did not buy and sell captives in the pre-colonial era, although they sometimes exchanged enslaved individuals with other tribes in peace gestures or in exchange for their own members. The conditions of enslaved Native Americans varied among the tribes. In many cases, young enslaved captives were adopted into the tribes to replace warriors killed during warfare or by disease. Other tribes practiced debt slavery or imposed slavery on tribal members who had committed crimes; but, this status was only temporary as the enslaved worked off their obligations to the tribal society. Among somePacific Northwest
The Pacific Northwest (sometimes Cascadia, or simply abbreviated as PNW) is a geographic region in western North America bounded by its coastal waters of the Pacific Ocean to the west and, loosely, by the Rocky Mountains to the east. Thou ...
tribes, about a quarter of the population were slaves. Other slave-owning tribes of North America were, for example, Comanche
The Comanche or Nʉmʉnʉʉ ( com, Nʉmʉnʉʉ, "the people") are a Native American tribe from the Southern Plains of the present-day United States. Comanche people today belong to the federally recognized Comanche Nation, headquartered in ...
of Texas, Creek of Georgia, the Pawnee, and Klamath. There was heavily incentive by Europeans as a way of driving deeper wedges between Africans and Europeans as the Seminole Confederation had proved formidable. Slaveholding societies, like the Choctaw, were given highest privilege and respect amongst the Europeans and trade preference.
European enslavement
During the European colonization of North America, Native Americans changed their practice ofslavery
Slavery and enslavement are both the state and the condition of being a slave—someone forbidden to quit one's service for an enslaver, and who is treated by the enslaver as property. Slavery typically involves slaves being made to perf ...
dramatically. Native Americans began selling war captives to white settlers rather than integrating them into their own societies as they had done before. As the demand for labor in the West Indies
The West Indies is a subregion of North America, surrounded by the North Atlantic Ocean and the Caribbean Sea that includes 13 independent island countries and 18 dependencies and other territories in three major archipelagos: the Greate ...
grew with the cultivation of sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
, European settlers frequently transported enslaved Native Americans to the Caribbean to work on plantation
A plantation is an agricultural estate, generally centered on a plantation house, meant for farming that specializes in cash crops, usually mainly planted with a single crop, with perhaps ancillary areas for vegetables for eating and so on. Th ...
s. White settlers in European colonies established in the American South
The Southern United States (sometimes Dixie, also referred to as the Southern States, the American South, the Southland, or simply the South) is a geographic and cultural region of the United States of America. It is between the Atlantic Ocean ...
purchased or captured Native Americans to use as forced labor in cultivating tobacco, rice, and indigo on plantations as well. Accurate records of the numbers enslaved do not exist. Scholars estimate tens of thousands of Native Americans may have been enslaved by the Europeans, sometimes being sold by Native Americans themselves but often war prizes with Europeans, similar to what occurred in the aftermath of the Pequot War
The Pequot War was an armed conflict that took place between 1636 and 1638 in New England between the Pequot tribe and an alliance of the colonists from the Massachusetts Bay, Plymouth, and Saybrook colonies and their allies from the Narraga ...
.
Slavery in Colonial America soon became racialized, including Native Americans and Africans but excluding Europeans. The Virginia General Assembly defined some terms of slavery in 1705:
The slave trade of Native Americans lasted only until around 1730. It gave rise to a series of devastating wars among the tribes, including the Yamasee War
The Yamasee War (also spelled Yamassee or Yemassee) was a conflict fought in South Carolina from 1715 to 1717 between British settlers from the Province of Carolina and the Yamasee and a number of other allied Native American peoples, incl ...
. The Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
of the early 18th century, combined with the increasing importation of African slaves, effectively ended the Native American slave trade by 1750. Colonists found that Native American slaves could easily escape, as they knew the country. The wars cost the lives of numerous colonial slave traders and disrupted their early societies. The remaining Native American groups banded together to face the Europeans from a position of strength. Many surviving Native American peoples of the southeast strengthened their loose coalitions of language groups and joined confederacies such as the Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
, the Creek, and the Catawba for protection.
Native American women were at risk for rape whether they were enslaved or not; during the early colonial years, settlers were disproportionately male. They turned to Native women for sexual relationships. Both Native American and African enslaved women suffered rape and sexual harassment by male slaveholders and other white men.

Relation with Africans in the United States
African and Native Americans have interacted for centuries. The earliest record of Native American and African contact occurred in April 1502, when Spanish colonists transported the first Africans toHispaniola
Hispaniola (, also ; es, La Española; Latin and french: Hispaniola; ht, Ispayola; tnq, Ayiti or Quisqueya) is an island in the Caribbean that is part of the Greater Antilles. Hispaniola is the most populous island in the West Indies, and th ...
to serve as slaves.
 Native Americans were rewarded if they returned escaped slaves, and African Americans were rewarded for fighting in the late 19th-century
Native Americans were rewarded if they returned escaped slaves, and African Americans were rewarded for fighting in the late 19th-century Indian Wars
The American Indian Wars, also known as the American Frontier Wars, and the Indian Wars, were fought by European governments and colonists in North America, and later by the United States and Canadian governments and American and Canadian settle ...
.
While numerous tribes used captive enemies as servants and slaves, they also often adopted younger captives into their tribes to replace members who had died. In the Southeast, a few Native American tribes began to adopt a slavery system similar to that of the American colonists, buying African American slaves, especially the Cherokee
The Cherokee (; chr, ᎠᏂᏴᏫᏯᎢ, translit=Aniyvwiyaʔi or Anigiduwagi, or chr, ᏣᎳᎩ, links=no, translit=Tsalagi) are one of the indigenous peoples of the Southeastern Woodlands of the United States. Prior to the 18th century, th ...
, Choctaw
The Choctaw (in the Choctaw language, Chahta) are a Native American people originally based in the Southeastern Woodlands, in what is now Alabama and Mississippi. Their Choctaw language is a Western Muskogean language. Today, Choctaw people are ...
, and Creek. Though less than 3% of Native Americans owned slaves, divisions grew among the Native Americans over slavery. Among the Cherokee, records show that slave holders in the tribe were largely the children of European men that had shown their children the economics of slavery. As European colonists took slaves into frontier areas, there were more opportunities for relationships between African and Native American peoples.
Among the Five Civilized Tribes, mixed-race slaveholders were generally part of an elite hierarchy, often based on their mothers' clan status, as the societies had matrilineal
Matrilineality is the tracing of kinship through the female line. It may also correlate with a social system in which each person is identified with their matriline – their mother's lineage – and which can involve the inheritance ...
systems. As did Benjamin Hawkins, European fur traders and colonial officials tended to marry high-status women, in strategic alliances seen to benefit both sides. The Choctaw, Creek and Cherokee believed they benefited from stronger alliances with the traders and their societies. The women's sons gained their status from their mother's families; they were part of hereditary leadership lines who exercised power and accumulated personal wealth in their changing Native American societies. The chiefs of the tribes believed that some of the new generation of mixed-race, bilingual chiefs would lead their people into the future and be better able to adapt to new conditions influenced by European Americans.
Philosophy
Native American authors have written about aspects of "tribal philosophy" as opposed to the modern or Western worldview. Thus,Yankton Dakota
The Dakota (pronounced , Dakota language: ''Dakȟóta/Dakhóta'') are a Native American tribe and First Nations band government in North America. They compose two of the three main subcultures of the Sioux people, and are typically divided int ...
author Vine Deloria Jr. in an essay "Philosophy and the Tribal Peoples" argued that whereas a "traditional Westerner" might reason, "Man is mortal; Socrates is a man; therefore, Socrates is mortal," aboriginal thinking might read, 'Socrates is mortal, because I once met Socrates and he is a man like me, and I am mortal.'
Deloria explains that both of the statements assume that all men are mortal, and that these statements are not verifiable on these grounds. The line of Indian thinking, however uses empirical evidence through memory to verify that Socrates was in fact a man like the person originally making the statement, and enhances the validity of the thinking. Deloria made the distinction, "whereas the Western syllogism simply introduces a doctrine using general concepts and depends on faith in the chain of reasoning for its verification, the Indian statement would stand by itself without faith and belief." Deloria also comments that Native American thinking is very specific (in the way described above) compared to the broadness of traditional Western thinking, which leads to different interpretations of basic principles. American thinkers have previously denounced Native ideas because of this narrower approach, as it leads to 'blurry' distinctions between the 'real' and the 'internal.'
According to Carlin Romano, the best resource on a characteristically "Native American Philosophy" is Scott L. Pratt
Scott L. Pratt (born 1959) is a professor of philosophy at the University of Oregon. His research and teaching is focused primarily upon American philosophy, especially in the areas of Indigenous American philosophy, Native American philosophy, pr ...
's, ''Native Pragmatism: Rethinking the Roots of American Philosophy'', which relates the ideas of many 'American' philosophers like Pierce, James, and Dewey to important concepts in early Native thought.
Pratt's publication takes his readers on a journey through American philosophical history from the colonial time period, and via detailed analysis, connects the experimental nature of early American pragmatism to the empirical habit of indigenous Americans. Though Pratt makes these alliances very comprehensible, he also makes clear that the lines between the ideas of Native Americans and American philosophers are complex and historically difficult to trace. Pratt, Scott L. Native Pragmatism: Rethinking the Roots of American Philosophy. Bloomington: Indiana University Press, 2002. 6-10. Print.
References
{{Indigenous peoples of the Americas Native American culture Native American art Native American topics Indigenous culture in the United States