National Waterway 4 (India) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 National Waterway 4 (NW-4) is a long
National Waterway 4 (NW-4) is a long

 The concept of National Waterways was introduced in 1982 to promote the development of inland water transport in the country. At present, out of six declared National Waterways, developmental works are being carried out on NW-1, 2, and 3 only by Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI). The first three National Waterways (NW-1, 2 & 3) are being developed for shipping and navigation by providing basic inland transport infrastructural facilities, including navigational channel with required depth and width, aids for day and night navigation, and terminals at selected locations for berthing and loading/unloading of vessels.
In NW-1 & 2, IWAI undertakes river conservatory works to provide navigational channel of , , and depth in different stretches during the low water period. In NW–3, IWAI is carrying out dredging to provide a navigational depth and width of and , respectively. Development works are being carried out with the objective of making all three National waterways fully operational with cargo and other inland vessels by March 2012.
For National Waterways 4 and 5, IWAI initiated the proposals for development in July 2010. Techno-economic studies for establishment of National Waterways NW-4 was done by Water And Power Consultancy Services (WAPCOS), a subsidiary of Ministry of Water Resources
The completion period for NW-4 was estimated at seven years by
The concept of National Waterways was introduced in 1982 to promote the development of inland water transport in the country. At present, out of six declared National Waterways, developmental works are being carried out on NW-1, 2, and 3 only by Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI). The first three National Waterways (NW-1, 2 & 3) are being developed for shipping and navigation by providing basic inland transport infrastructural facilities, including navigational channel with required depth and width, aids for day and night navigation, and terminals at selected locations for berthing and loading/unloading of vessels.
In NW-1 & 2, IWAI undertakes river conservatory works to provide navigational channel of , , and depth in different stretches during the low water period. In NW–3, IWAI is carrying out dredging to provide a navigational depth and width of and , respectively. Development works are being carried out with the objective of making all three National waterways fully operational with cargo and other inland vessels by March 2012.
For National Waterways 4 and 5, IWAI initiated the proposals for development in July 2010. Techno-economic studies for establishment of National Waterways NW-4 was done by Water And Power Consultancy Services (WAPCOS), a subsidiary of Ministry of Water Resources
The completion period for NW-4 was estimated at seven years by
ITC Bhadrachalam
and Andhra Pradesh paper mill
(APPML)
are located. Apart from this, many small paper mills are located in the
(MFL)
plant located at
waterway
A waterway is any navigable body of water. Broad distinctions are useful to avoid ambiguity, and disambiguation will be of varying importance depending on the nuance of the equivalent word in other languages. A first distinction is necessary b ...
in India
India, officially the Republic of India (Hindi: ), is a country in South Asia. It is the seventh-largest country by area, the second-most populous country, and the most populous democracy in the world. Bounded by the Indian Ocean on the so ...
. It has been declared as an Indian National Waterway and is currently under development. It connects the Indian states of Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, and the union territory of Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
. The NW-4 runs along the Coromandal Coast through Kakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
, Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The cit ...
, Commanur, Buckingham Canals and also through part of Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
and Godavari
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
rivers in South India
South India, also known as Dakshina Bharata or Peninsular India, consists of the peninsular southern part of India. It encompasses the Indian states of Andhra Pradesh, Karnataka, Kerala, Tamil Nadu, and Telangana, as well as the union territ ...
. It was declared a National Waterway on 24 November 2008 under the Provisions of National Waterways Bill, 2006. It is being developed by the Inland Waterways Authority of India
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is the statutory authority in charge of the waterways in India. It was constituted under IWAI Act-1985 by the Parliament of India.http://iwai.nic.in/showfile.php?lid=882 See section 3 of the act Its hea ...
(IWAI), and was scheduled for completion by 2013. The National Waterways Act, 2016 has extended the length of NW-4 from to by connecting the Krishna and Godavari Rivers. The Project would be undertaken in 3 phases with first phase beginning in October, 2017 and to be completed by June, 2019
History
National waterways in India
In India, the national waterways are developed by thecentral government
A central government is the government that is a controlling power over a unitary state. Another distinct but sovereign political entity is a federal government, which may have distinct powers at various levels of government, authorized or dele ...
through the Inland Waterways Authority of India
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is the statutory authority in charge of the waterways in India. It was constituted under IWAI Act-1985 by the Parliament of India.http://iwai.nic.in/showfile.php?lid=882 See section 3 of the act Its hea ...
(IWAI) – the regulatory body for the Inland Waterways Transport (IWT) sector. IWAI was set up by the Inland Waterways Authority of India Act in 1985 and given responsibility of development, maintenance, and regulation of national waterways in the country. It is a statutory autonomous body for regulating and developing navigation and shipping in the inland waterways. Along with IWAI, Central Inland Water Transport Corporation (CIWTC) also supports the IWT sector through transportation of cargo via inland waterways and the operation and maintenance of the vessels and waterway terminals. The first national waterways established in India were the NW-1,2 & 3 (est. in mid 1980s & 1993). They have a combined length of .
Development of NW-4, 5 & 6
As early as 1993–95, IWAI commenced studies for developing an integrated canal linking Kakinada and Chennai. The Indian government initiated the process for developing three more national waterways in 2005. In July 2006, T. R. Baalu, the Minister of Shipping, Road Transport and Highways announced the proposal for development of NW-4 in theLok Sabha
The Lok Sabha, constitutionally the House of the People, is the lower house of India's bicameral Parliament, with the upper house being the Rajya Sabha. Members of the Lok Sabha are elected by an adult universal suffrage and a first-p ...
. In addition to the three existing national waterways, the government also declared the following inland waterways as national waterways:
* NW-4: Kakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
-Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
canals along with Godavari
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
and Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
rivers ()
* NW-5: East Coast Canal along with Brahmani river
The Brahmani is a major seasonal river in the Odisha state of eastern India. The Brahmani is formed by the confluence of the Sankh and South Koel rivers, and flows through the districts of Sundargarh, Deogarh, Angul, Dhenkanal, Cuttack ...
and Mahanadi delta ()
* NW-6: River Barak ()
The proposals were made into law with the passage of The Inland Vessels (Amendment) Bill, 2005 in 2007. In October 2008, another bill – the National waterways Bill, 2006 – was passed in Parliament. It declared the Kakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
-Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
stretch of canals comprising the Kakinada canal, Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The cit ...
canal, Commamur canal, Buckingham canal
The Buckingham Canal is a -long fresh water navigation canal, that parallels the Coromandel Coast of South India from Kakinada City in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh to Viluppuram District in Tamil Nadu. The canal connects most ...
, the Kaluvelly tank, Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
- Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
stretch of rivers Godavari
The Godavari (IAST: ''Godāvarī'' �od̪aːʋəɾiː is India's second longest river after the Ganga river and drains into the third largest basin in India, covering about 10% of India's total geographical area. Its source is in Trimbakeshwa ...
, Wazirabad-Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
stretch of river Krishna in Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, and Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
as national waterways. It will take seven years and for the completion of the proposed new national waterways. The national waterway will be owned by Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) and will be operated by Central Inland Water Transport Corporation (CIWTC)
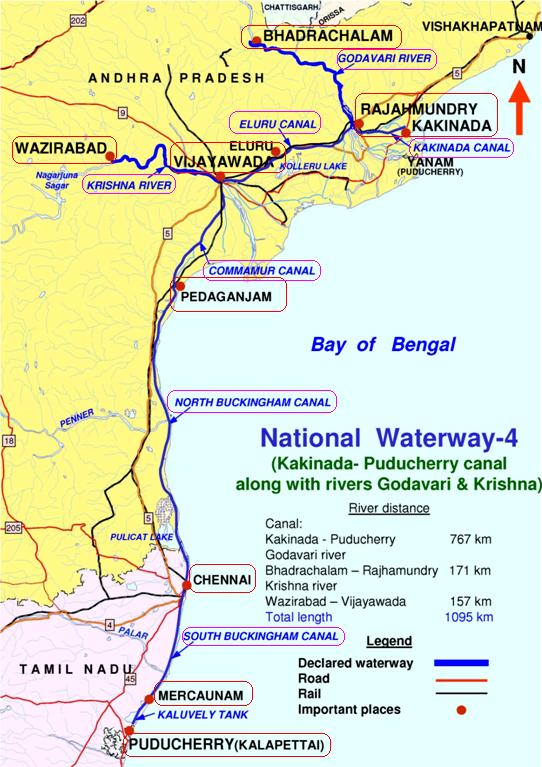
Course
The National Waterway NW-4 comprises nearly ofcanal
Canals or artificial waterways are waterways or engineered channels built for drainage management (e.g. flood control and irrigation) or for conveyancing water transport vehicles (e.g. water taxi). They carry free, calm surface flo ...
and of river sections. In turn, the river section of the NW-4 comprises two major sections:
* Godavari river section
* Krishna river section.
The Godavari River section stretches from Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
, Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on the high Deccan Plateau. It is the eleventh-largest state and the twelfth-most populated state in India with a geographical area of and 3 ...
to Dowleiswaram, Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
, Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
. The Krishna River section stretches from Wazirabad Nalgonda district
Nalgonda district is a district in the Telangana state of India. Nalgonda district has the highest number of mandals in the state with 31 mandals. The district shares boundaries with Suryapet, Rangareddy, Yadadri and Nagarkurnool districts an ...
, Telangana to Prakasam Barrage
The Prakasam Barrage stretches 1223.5 m across the Krishna River connecting Vijayawada, NTR and Mangalagiri Tadepalle Municipal Corporation, Guntur districts in Andhra Pradesh, India. The barrage serves also as a road bridge and spans over a l ...
, Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
, Andhra Pradesh.
The canal section of NW-4 is formed by a combination of the Kakinada canal, the Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The cit ...
canal, Commamur canal, and the Buckingham canal
The Buckingham Canal is a -long fresh water navigation canal, that parallels the Coromandel Coast of South India from Kakinada City in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh to Viluppuram District in Tamil Nadu. The canal connects most ...
. The Kakinada canal runs between Kakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
and Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
for a length of . Starting from Dowleiswaram on the left bank of the river Godavari through a head sluice and lock to Kakinada (approx. downstream from Kakinada Port). The canal gets its water from the Godavari river through the Dowleiswaram barrage and thereafter connects Kakinada anchorage port. It connects the Godavari river section from Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
to Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
. The Eluru canal comprises two distinct irrigation-cum – navigation canals, namely the Krishna Eluru canal of the eastern Krishna delta and the Godavari Eluru canal of western Godavari delta. It runs between Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
to Vijjeswaram lock at Sir Arthur Thomas Cotton Barrage for a total distance of . The Krishna Eluru canal takes off from the river section on the left bank of Krishna river on the upstream of Prakasam barrage through a head sluice at Vijayawada and meets Godavari Eluru canal at east Tammileru
Tammileru is a medium river which forms the boundary between Krishna district and Eluru district of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by ar ...
lock at Eluru
Eluru is a city and the district headquarters of Eluru district in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is one of the 14 municipal corporations in the state and the mandal headquarters of Eluru mandal in the Eluru revenue division. The cit ...
. The Godavari Eluru canal takes off from the River section of river Godavari at Vijjeswaram () in Rajahmundry on the upstream of Dowleiswaram anicut through a head sluice and joins Krishna Eluru canal at East Tammileru
Tammileru is a medium river which forms the boundary between Krishna district and Eluru district of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by ar ...
lock. The Commamur canal runs between Vijayawada Seethanagaram lock and Peddaganjam lock for a total length of It takes off from the Krishna River section in river Krishna in Vijayawada on the right side upstream off Prakasam barrage
The Prakasam Barrage stretches 1223.5 m across the Krishna River connecting Vijayawada, NTR and Mangalagiri Tadepalle Municipal Corporation, Guntur districts in Andhra Pradesh, India. The barrage serves also as a road bridge and spans over a l ...
through a head sluice at Seethanagaram
Seethanagaram is a mandal in Parvathipuram Manyam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an are ...
and joins the Buckingham canal at Peddaganjam Lock near Ongole
Ongole is a city in Prakasam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the headquarters of Prakasam district and also the mandal headquarters of Ongole mandal in Ongole revenue division. Ongole cattle, an indigenous breed of oxen, ...
. The Buckingham canal
The Buckingham Canal is a -long fresh water navigation canal, that parallels the Coromandel Coast of South India from Kakinada City in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh to Viluppuram District in Tamil Nadu. The canal connects most ...
is a tidal canal stretching from Peddaganjam lock to Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
and further down south up to Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
. The stretch of the canal from Peddaganjam lock to Chennai for a length of is called "North Buckingham canal" and the canal path from Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
to Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
for a total length of is called "South Buckingham canal". It was constructed during the 19th century along the Coromandal Coast. Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
is connected to the Sea (Bay of Bengal
The Bay of Bengal is the northeastern part of the Indian Ocean, bounded on the west and northwest by India, on the north by Bangladesh, and on the east by Myanmar and the Andaman and Nicobar Islands of India. Its southern limit is a line betwee ...
) at Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
by the Kalluvelly tank.
The lengths of the NW-4 in Andhra Pradesh, Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
, and Puducherry Puducherry or Pondicherry may refer to:
* Puducherry (union territory), a union territory of India
** Pondicherry, capital of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry district, a district of the union territory of Puducherry
** Puducherry t ...
are as follows:
Geographical boundaries
Development
Detailed Project Report
A project plan, according to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK), is:
"...a formal, approved document used to guide both ''project execution'' and ''project control''. The primary uses of the project plan are to document planning ass ...
prepared by WAPCOS, which is contrary to that of 2002 estimates which indicated five years as completion period. of land are required for NW-4 construction; , , and land has to be acquired in the states of Tamil Nadu, Andhra Pradesh, and Puducherry respectively.
Traffic
A. F. Ferguson was appointed by WAPCOS for conducting traffic studies for proposed waterway in 2005–06.Current traffic
There is no significant traffic in the waterway except for movement of country boats which carry local produce. The main reason for lack of IWT movement is the absence of other infrastructure facilities and coordinated effort for improvements.Potential traffic
NW-4 has been divided into four major cargo belts, namelyKakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
belt, Krishna
Krishna (; sa, कृष्ण ) is a major deity in Hinduism. He is worshipped as the eighth avatar of Vishnu and also as the Supreme god in his own right. He is the god of protection, compassion, tenderness, and love; and is one ...
belt, South Andhra Pradesh
Andhra Pradesh (, abbr. AP) is a state in the south-eastern coastal region of India. It is the seventh-largest state by area covering an area of and tenth-most populous state with 49,386,799 inhabitants. It is bordered by Telangana to the ...
belt, and Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
belt. Based on the survey conducted by WAPCOS, the 11 million tonnes of cargo is expected to be transported through NW-4 every year. Types of cargo include coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
, foodgrains, cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
, fertilisers
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, forest products, salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
, and other bulk cargo
Bulk cargo is commodity cargo that is transported unpackaged in large quantities.
Description
Bulk cargo refers to material in either liquid or granular, particulate form, as a mass of relatively small solids, such as petroleum/ crude o ...
. The Godavari river system flows through the Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
forests and coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
deposits. The Krishna River flows through limestone
Limestone ( calcium carbonate ) is a type of carbonate sedimentary rock which is the main source of the material lime. It is composed mostly of the minerals calcite and aragonite, which are different crystal forms of . Limestone forms whe ...
deposits and cement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
industries at Jaggayyapeta
Jaggayyapeta, also spelled “Jaggiahpet”, is a census town in NTR district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh, located just southwest of the border with Telangana. It is also the mandal headquarters of Jaggayyapeta mandal of Nandigama revenu ...
.
Krishna river (Wazirabad – Vijayawada)
Guntur has abundant resources of limestone which are of use in cement and steel industries. Main consumers of limestone are nearby situatedcement
A cement is a binder, a chemical substance used for construction that sets, hardens, and adheres to other materials to bind them together. Cement is seldom used on its own, but rather to bind sand and gravel ( aggregate) together. Cement mi ...
and steel industries like ACC, Andhra Cement, Parthasarathy Cements & Industries Ltd and Gauthami Cements as well as Visakhapatnam Steel Plant.
Godavari River (Bhadrachalam – Rajahmundry )
Thecoal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
is a substantially available commodity in this stretch due to its nearness to Singareni Collieries (SCCL) mines. Coal fields are located in Kothagudem
Kothagudem is a City in Telangana. It serves as the headquarters of the Bhadradri Kothagudem district of the Indian state of Telangana
Telangana (; , ) is a state in India situated on the south-central stretch of the Indian peninsula on ...
, Manuguru and Yellandu
Yellandu is a town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district of the Indian state of Telangana. It is located in Yellandu mandal of Kothagudem revenue division.
Geography
Yellandu is located at . It has an average elevation of 205 metres (672&n ...
. Rice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
has a huge traffic potential in this downstream route up to Rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
. In the upstream direction, traffic potential will be gained by transportation of forest products, wood pulp
Pulp is a lignocellulosic fibrous material prepared by chemically or mechanically separating cellulose fibers from wood, fiber crops, waste paper, or rags. Mixed with water and other chemical or plant-based additives, pulp is the major raw mate ...
to Bhadrachalam
Bhadrachalam is a census town in Bhadradri Kothagudem district in the Indian state of Telangana. It is an important Hindu pilgrimage town with the Bhadrachalam Temple of Lord Rama, situated on the banks of Godavari river. It is located east o ...
where major paper mills
A paper mill is a factory devoted to making paper from vegetable fibres such as wood pulp, old rags, and other ingredients. Prior to the invention and adoption of the Fourdrinier machine and other types of paper machine that use an endless belt ...
likITC Bhadrachalam
and Andhra Pradesh paper mill
(APPML)
are located. Apart from this, many small paper mills are located in the
East
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the fac ...
and West Godavari districts.
Kakinada Canal
Main cargo to be transported in downstream direction fromkakinada
Kakinada ( formerly called Kakinandiwada, Coringa, and Cocanada; ) is the sixth largest city of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and serves as the district headquarters of the Kakinada District. It lies on the coast of the Bay of Bengal. J. ...
to rajahmundry
Rajahmundry, officially known as Rajamahendravaram, is a city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and District headquarters of East Godavari district. It is the sixth most populated city in the state. During British rule, the District of Rajah ...
are coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
and rock Phosphate
Phosphorite, phosphate rock or rock phosphate is a non-detrital sedimentary rock that contains high amounts of phosphate minerals. The phosphate content of phosphorite (or grade of phosphate rock) varies greatly, from 4% to 20% phosphorus pentoxi ...
. In the upstream direction, rice bran extractions, cement clinker
200px, Typical clinker nodules
200px, Hot clinker
Cement clinker is a solid material produced in the manufacture of Portland cement as an intermediary product. Clinker occurs as lumps or nodules, usually to in diameter. It is produced by sinte ...
and fertilizers
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
will be the main cargos for transportation.
Eluru Canal
Rice and other food grains, rice bran extractions,coal
Coal is a combustible black or brownish-black sedimentary rock, formed as rock strata called coal seams. Coal is mostly carbon with variable amounts of other elements, chiefly hydrogen, sulfur, oxygen, and nitrogen.
Coal is formed when ...
, fertilizer
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
and other general cargo are the substantive commodities which can boost the IWT in this stretch.
Commanur Canal
The stretch fromVijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
to Peddaganjam (Ongole
Ongole is a city in Prakasam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the headquarters of Prakasam district and also the mandal headquarters of Ongole mandal in Ongole revenue division. Ongole cattle, an indigenous breed of oxen, ...
) is a vital trade link connecting Kakinada belt with south A.P and Tamil Nadu
Tamil Nadu (; , TN) is a state in southern India. It is the tenth largest Indian state by area and the sixth largest by population. Its capital and largest city is Chennai. Tamil Nadu is the home of the Tamil people, whose Tamil language ...
. The major towns in the vicinity capable of promoting IWT are Vijayawada
Vijayawada, formerly known as Bezawada, is the second largest city in the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh and is a part of the state's Capital Region. It is the administrative headquarters of the NTR district. Its metropolitan region comprises N ...
, Guntur Tenali
Tenali is a city in Guntur district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is a municipality and the headquarters of Tenali mandal and Tenali revenue division. The city is renowned for art, culture, drama and hence, it is called ''Andhra ...
and Ongole
Ongole is a city in Prakasam district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It is the headquarters of Prakasam district and also the mandal headquarters of Ongole mandal in Ongole revenue division. Ongole cattle, an indigenous breed of oxen, ...
. Main traffic in the downward direction are rice and food grains. Forest products will form traffic in the upstream direction.
North Buckingham Canal
The canal can form significant traffic because of salt pans located all along the canal stretch. Rice, food grains,fertilizers
A fertilizer (American English) or fertiliser (British English; see spelling differences) is any material of natural or synthetic origin that is applied to soil or to plant tissues to supply plant nutrients. Fertilizers may be distinct from ...
, chili pepper
Chili peppers (also chile, chile pepper, chilli pepper, or chilli), from Nahuatl '' chīlli'' (), are varieties of the berry-fruit of plants from the genus ''Capsicum'', which are members of the nightshade family Solanaceae, cultivated for ...
s, tobacco
Tobacco is the common name of several plants in the genus '' Nicotiana'' of the family Solanaceae, and the general term for any product prepared from the cured leaves of these plants. More than 70 species of tobacco are known, but the ...
, fish
Fish are aquatic, craniate, gill-bearing animals that lack limbs with digits. Included in this definition are the living hagfish, lampreys, and cartilaginous and bony fish as well as various extinct related groups. Approximately 95% of ...
, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies under ...
and vegetables
Vegetables are parts of plants that are consumed by humans or other animals as food. The original meaning is still commonly used and is applied to plants collectively to refer to all edible plant matter, including the flowers, fruits, stems ...
in the downstream direction from Peddaganjam to Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
. In the upstream direction from Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
to Peddaganjam, the main traffic consists of fertilizers from Madras Fertiliser(MFL)
plant located at
Ennore
Ennore, also spelt , is a neighbourhood in Chennai, India. Ennore is situated on a peninsula and is bounded by the Korttalaiyar River, Ennore Creek and the Bay of Bengal. The creek separates south Ennore from the north Ennore which covers majo ...
and salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
from Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
.
South Buckingham Canal & Kaluvelly Tank
The canal stretch fromBasin bridge
Basin Bridge Junction is a station on the Chennai Suburban Railway and serves the locality of Basin Bridge, the confluence on the Otteri Nullah and Buckingham Canal, in Chennai, India. The station is located at the southern end of the 'diamo ...
up to Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
can constitute significant traffic of salt and marine products because of salt pans and aquaculture shrimp farms
Shrimp farming is an aquaculture business that exists in either a marine or freshwater environment, producing shrimp or prawns (crustaceans of the groups Caridea or Dendrobranchiata) for human consumption.
Marine
Commercial marine shrimp farm ...
all along the route. In the upstream direction from Pondicherry
Pondicherry (), now known as Puducherry ( French: Pondichéry ʊdʊˈtʃɛɹi(listen), on-dicherry, is the capital and the most populous city of the Union Territory of Puducherry in India. The city is in the Puducherry district on the sout ...
via Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
to Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
, the main traffic consists of salt, fertilizers and timber from Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
, Thiruvallur
Tiruvallur is a Grade I municipality and a fast developing city in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is located on the banks of Coovum river about from downtown Chennai ( Madras) and just 5 km from megacity border, in the western p ...
, Kanchipuram, Villupuram
Viluppuram, Villupuram, or Vizhuppuram () is a Municipality and the administrative headquarters of Viluppuram district.
Located south west of a Tiruvannamalai and north west of Cuddalore null The town serves as a major railway junction, ...
and Pondicherry.
NW-4 as Natural Barrier
The stretch ofBuckingham Canal
The Buckingham Canal is a -long fresh water navigation canal, that parallels the Coromandel Coast of South India from Kakinada City in the Kakinada district of Andhra Pradesh to Viluppuram District in Tamil Nadu. The canal connects most ...
saved thousands of lives in the states of Andhra Pradesh and Tamil Nadu along the coromandal coast from tsunami
A tsunami ( ; from ja, 津波, lit=harbour wave, ) is a series of waves in a water body caused by the displacement of a large volume of water, generally in an ocean or a large lake. Earthquakes, volcanic eruptions and other underwater exp ...
waves, that occurred on 26 December 2004. Dr. B. Ramalingeswara Rao of National Geophysical Research Institute (NGRI), Hyderabad
Hyderabad ( ; , ) is the capital and largest city of the Indian state of Telangana and the ''de jure'' capital of Andhra Pradesh. It occupies on the Deccan Plateau along the banks of the Musi River, in the northern part of Southern India ...
reports that the Buckingham Canal acted as a buffer zone and regulated the tsunami waves on the coastal region over from Pedda Ganjam to Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
. The tsunami waves drifted away towards the existing low-lying creeks at several places.
The canal from Chennai
Chennai (, ), formerly known as Madras ( the official name until 1996), is the capital city of Tamil Nadu, the southernmost Indian state. The largest city of the state in area and population, Chennai is located on the Coromandel Coast of th ...
(Marakkanam
Marakkanam is a coastal panchayat town & Taluk in Viluppuram district in the Indian state of Tamil Nadu. It is well connected to the state capital Chennai and the nearby union territory of Puducherry by the East Coast Road. To the west, Marak ...
) to Durga Raya Patnam near Nellore
Nellore is a city located on the banks of Penna River, in Nellore district of the Indian state of Andhra Pradesh. It serves as the headquarters of the district, as well as Nellore mandal and Nellore revenue division. It is the fourth most p ...
and then to Pedda Ganjam, all along the east coast was filled with tsunami water, which overflowed at a few places and receded back to sea within 10–15 minutes. This saved the lives of several fishermen, especially in coastal Andhra Pradesh and parts of Chennai city.
Cost
The cost for developing a waterway in India is approximately per km, whereas developing a railway or roadway costs around – per km. As per estimates drawn by consultants M/s RITES in 2002, the project will cost and facilitate movement of 100tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
vessels in the irrigation canal portion and 350 tonne
The tonne ( or ; symbol: t) is a unit of mass equal to 1000 kilograms. It is a non-SI unit accepted for use with SI. It is also referred to as a metric ton to distinguish it from the non-metric units of the short ton ( United State ...
in the rivers and Buckingham canal portion.
The cost was re-estimated by WAPCOS in 2009 to , which involves two phase development of the project. Phase one of the project envisages development of a stretch comprising Godavari and Krishna rivers, and Kakinada and Eluru canals, which has maximum cargo potential, at an estimated cost of and land acquisition for remaining stretch at an estimated cost of . Phase two of the project involves development of North and South Buckingham Canal, Commamur canal, and Kaluvelly Tank at an estimated cost of .
In the Tenth Five-Year Plan, Planning Commission has increased the budgetary provision for the development of inland water transport infrastructure to , against in the Ninth Five-Year Plan.
For the year 2009–2010, the government has released the following funds through Ministry of Shipping for development of IWT.
* as a grant to IWAI for development and maintenance of National Waterways (NW 1,2,3,4 & 5).And also for undertaking projects related to IWT promotion, training, IT activities etc.
* has been released for Technical Studies and R&D activities.
* has been released for Inland Vessel Building Subsidy Scheme.
* has been released for Central Sector Schemes for IWT Development in North Eastern Region.
Delay in the project
Common factors attributable for delay in development of IWT are lack of infrastructure, absence of fixed scheduled services, poor navigational aids, lack of connectivity, longer river distances, multiple handling, and limited flow of private investments. The Eleventh Five-Year Plan envisaged development of six national inland waterways. Although the government demarcated five such National Waterways, the shipping ministry is unable to start the work on developing two of them (NW-4 & NW-5), as Planning Commission has not approved the development plans until now. Ministry of Shipping awaits the sum of that it needs to carry out the development works. As a result of the delay in getting the Planning Commission approval and the funds, the ministry has suspended the plans for developing the sixth national inland waterway.See also
* National Waterway 2 (India) *National Waterway 3 (India)
The West Coast Canal or National Waterway No 3 is a long inland navigational route located in Kerala, India, which runs from Kollam to Kottapuram. It was declared a National Waterway in 1993. In addition to the main stretch, Champakara and U ...
* Inland Waterways Authority of India
Inland Waterways Authority of India (IWAI) is the statutory authority in charge of the waterways in India. It was constituted under IWAI Act-1985 by the Parliament of India.http://iwai.nic.in/showfile.php?lid=882 See section 3 of the act Its hea ...
* Inland waterways of India
''Water transport in India'' has played a significant role in the country's economy and is indispensable to foreign trade. India is endowed with an extensive network of waterways in the form of rivers, canals, backwaters, creeks and a long co ...
* The Inland Vessels (Amendment) Act, 2007
The Inland Vessels (Amendment) Act, 2007 is an Act of the Parliament of India enacted to facilitate the extension and usage of inland waterways by vessels. It is an amendment to an original Act passed in 1917. The Act came into force from 21 Feb ...
References
{{Indian Waterways Network Waterways in India Transport in Andhra Pradesh Transport in Puducherry Transport in Tamil Nadu Transport in Kakinada