Nation-states on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A nation state is a political unit where the
A nation state is a political unit where the
 Some nation states, such as
Some nation states, such as
 In
In
 China covers a large geographic area and uses the concept of "Zhonghua minzu" or Chinese nationality, in the sense of ethnic groups, but it also officially recognizes the majority Han Chinese, Han ethnic group which accounts for over 90% of the population, and no fewer than 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic national minorities.
According to Philip G. Roeder, Moldova is an example of a Soviet era "segment-state" (Moldavian SSR), where the "nation-state project of the segment-state trumped the nation-state project of prior statehood. In Moldova, despite strong agitation from university faculty and students for reunification with Romania, the nation-state project forged within the Moldavian SSR trumped the project for a return to the interwar nation-state project of Greater Romania." See Controversy over linguistic and ethnic identity in Moldova for further details.
China covers a large geographic area and uses the concept of "Zhonghua minzu" or Chinese nationality, in the sense of ethnic groups, but it also officially recognizes the majority Han Chinese, Han ethnic group which accounts for over 90% of the population, and no fewer than 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic national minorities.
According to Philip G. Roeder, Moldova is an example of a Soviet era "segment-state" (Moldavian SSR), where the "nation-state project of the segment-state trumped the nation-state project of prior statehood. In Moldova, despite strong agitation from university faculty and students for reunification with Romania, the nation-state project forged within the Moldavian SSR trumped the project for a return to the interwar nation-state project of Greater Romania." See Controversy over linguistic and ethnic identity in Moldova for further details.
 The process of assimilation began with secret instructions to the corregidores of the Catalan territory: they "will take the utmost care to introduce the Castilian language, for which purpose he will give the most temperate and disguised measures so that the effect is achieved, without the care being noticed." From there, actions in the service of assimilation, discreet or aggressive, were continued, and reached to the last detail, such as, in 1799, the Royal Certificate forbidding anyone to "represent, sing and dance pieces that were not in Spanish." These nationalist policies, sometimes very aggressive, and still in force, have been, and still are, the seed of repeated territorial conflicts within the State.
The nationalization process accelerated in the 19th century, in parallel to the origin of Spanish nationalism, the social, political and ideological movement that tried to shape a Spanish national identity based on the Castilian model, in conflict with the other historical nations of the State. Politicians of the time were aware that despite the aggressive policies pursued up to that time, the uniform and monocultural "Spanish nation" did not exist, as indicated in 1835 by Antonio Alcalá Galiano, Antonio Alcalà Galiano, when in the Cortes del Estatuto Real he defended the effort
The process of assimilation began with secret instructions to the corregidores of the Catalan territory: they "will take the utmost care to introduce the Castilian language, for which purpose he will give the most temperate and disguised measures so that the effect is achieved, without the care being noticed." From there, actions in the service of assimilation, discreet or aggressive, were continued, and reached to the last detail, such as, in 1799, the Royal Certificate forbidding anyone to "represent, sing and dance pieces that were not in Spanish." These nationalist policies, sometimes very aggressive, and still in force, have been, and still are, the seed of repeated territorial conflicts within the State.
The nationalization process accelerated in the 19th century, in parallel to the origin of Spanish nationalism, the social, political and ideological movement that tried to shape a Spanish national identity based on the Castilian model, in conflict with the other historical nations of the State. Politicians of the time were aware that despite the aggressive policies pursued up to that time, the uniform and monocultural "Spanish nation" did not exist, as indicated in 1835 by Antonio Alcalá Galiano, Antonio Alcalà Galiano, when in the Cortes del Estatuto Real he defended the effort
 In principle, the border of a nation state would extend far enough to include all the members of the nation, and all of the national homeland. Again, in practice, some of them always live on the 'wrong side' of the border. Part of the national homeland may be there too, and it may be governed by the 'wrong' nation. The response to the non-inclusion of territory and population may take the form of irredentism: demands to annex ''unredeemed'' territory and incorporate it into the nation state.
Irredentist claims are usually based on the fact that an identifiable part of the national group lives across the border. However, they can include claims to territory where no members of that nation live at present, because they lived there in the past, the national language is spoken in that region, the national culture has influenced it, geographical unity with the existing territory, or a wide variety of other reasons. Past grievances are usually involved and can cause revanchism.
It is sometimes difficult to distinguish irredentism from pan-nationalism, since both claim that all members of an ethnic and cultural nation belong in one specific state. Pan-nationalism is less likely to specify the nation ethnically. For instance, variants of Pan-Germanism have different ideas about what constituted Kleindeutschland and Großdeutschland, Greater Germany, including the confusing term ''Grossdeutschland'', which, in fact, implied the inclusion of huge Slavic minorities from the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Typically, irredentist demands are at first made by members of non-state nationalist movements. When they are adopted by a state, they typically result in tensions, and actual attempts at annexation are always considered a ''casus belli'', a cause for war. In many cases, such claims result in long-term hostile relations between neighbouring states. Irredentist movements typically circulate maps of the claimed national territory, the ''greater'' nation state. That territory, which is often much larger than the existing state, plays a central role in their propaganda.
Irredentism should not be confused with claims to overseas colonies, which are not generally considered part of the national homeland. Some French overseas colonies would be an exception: French rule in Algeria unsuccessfully treated the colony as a ''Département in France, département'' of France.
In principle, the border of a nation state would extend far enough to include all the members of the nation, and all of the national homeland. Again, in practice, some of them always live on the 'wrong side' of the border. Part of the national homeland may be there too, and it may be governed by the 'wrong' nation. The response to the non-inclusion of territory and population may take the form of irredentism: demands to annex ''unredeemed'' territory and incorporate it into the nation state.
Irredentist claims are usually based on the fact that an identifiable part of the national group lives across the border. However, they can include claims to territory where no members of that nation live at present, because they lived there in the past, the national language is spoken in that region, the national culture has influenced it, geographical unity with the existing territory, or a wide variety of other reasons. Past grievances are usually involved and can cause revanchism.
It is sometimes difficult to distinguish irredentism from pan-nationalism, since both claim that all members of an ethnic and cultural nation belong in one specific state. Pan-nationalism is less likely to specify the nation ethnically. For instance, variants of Pan-Germanism have different ideas about what constituted Kleindeutschland and Großdeutschland, Greater Germany, including the confusing term ''Grossdeutschland'', which, in fact, implied the inclusion of huge Slavic minorities from the Austro-Hungarian Empire.
Typically, irredentist demands are at first made by members of non-state nationalist movements. When they are adopted by a state, they typically result in tensions, and actual attempts at annexation are always considered a ''casus belli'', a cause for war. In many cases, such claims result in long-term hostile relations between neighbouring states. Irredentist movements typically circulate maps of the claimed national territory, the ''greater'' nation state. That territory, which is often much larger than the existing state, plays a central role in their propaganda.
Irredentism should not be confused with claims to overseas colonies, which are not generally considered part of the national homeland. Some French overseas colonies would be an exception: French rule in Algeria unsuccessfully treated the colony as a ''Département in France, département'' of France.
"The Extinction of Nation States"
* Ernest Renan, Renan, Ernest. 1882. s:fr:Qu'est-ce qu'une nation ?, "Qu'est-ce qu'une nation?" ("What Is a Nation?") * Malesevic, Sinisa (2006). ''Identity as Ideology: Understanding Ethnicity and Nationalism''. New York: Palgrave. * Smith, Anthony D. (1986). ''The Ethnic Origins of Nations''. London: Basil Blackwell. pp 6–18. . * White, Philip L. (2006)
"Globalization and the Mythology of the Nation State"
In A. G. Hopkins, ed. ''Global History: Interactions Between the Universal and the Local''. Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 257–284.
on identity and the nation state. * :ca:Cronologia de la repressi%C3%B3 del catal%C3%A0, Chronology of the repression of the Catalan language in catalan language {{DEFAULTSORT:Nation State Nation, State Political science terminology
 A nation state is a political unit where the
A nation state is a political unit where the state
State may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Literature
* ''State Magazine'', a monthly magazine published by the U.S. Department of State
* ''The State'' (newspaper), a daily newspaper in Columbia, South Carolina, United States
* ''Our S ...
and nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
are congruent. It is a more precise concept than "country
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
", since a country does not need to have a predominant ethnic group.
A nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
, in the sense of a common ethnicity, may include a diaspora or refugees who live outside the nation state; some nations of this sense do not have a state where that ethnicity predominates. In a more general sense, a nation state is simply a large, politically sovereign country or administrative territory. A nation state may be contrasted with:
* A multinational state
A multinational state or a multinational union is a sovereign entity that comprises two or more nations or states. This contrasts with a nation state, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of ...
, where no one ethnic group dominates (such a state may also be considered a multicultural
The term multiculturalism has a range of meanings within the contexts of sociology, political philosophy, and colloquial use. In sociology and in everyday usage, it is a synonym for " ethnic pluralism", with the two terms often used interchang ...
state depending on the degree of cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural ass ...
of various groups).
* A city-state
A city-state is an independent sovereign city which serves as the center of political, economic, and cultural life over its contiguous territory. They have existed in many parts of the world since the dawn of history, including cities such as ...
, which is both smaller than a "nation" in the sense of "large sovereign country" and which may or may not be dominated by all or part of a single "nation" in the sense of a common ethnicity.
* An empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
, which is composed of many countries (possibly non-sovereign states) and nations under a single monarch
A monarch is a head of stateWebster's II New College DictionarMonarch Houghton Mifflin. Boston. 2001. p. 707. for life or until abdication, and therefore the head of state of a monarchy. A monarch may exercise the highest authority and power i ...
or ruling state government
A government is the system or group of people governing an organized community, generally a state.
In the case of its broad associative definition, government normally consists of legislature, executive, and judiciary. Government is ...
.
* A confederation
A confederation (also known as a confederacy or league) is a union of sovereign groups or states united for purposes of common action. Usually created by a treaty, confederations of states tend to be established for dealing with critical issu ...
, a league of sovereign states, which might or might not include nation-states.
* A federated state
A federated state (which may also be referred to as a state, a province, a region, a canton, a land, a governorate, an oblast, an emirate or a country) is a territorial and constitutional community forming part of a federation. Such states d ...
, which may or may not be a nation-state, and which is only partially self-governing within a larger federation
A federation (also known as a federal state) is a political entity characterized by a union of partially self-governing provinces, states, or other regions under a central federal government ( federalism). In a federation, the self-govern ...
(for example, the state boundaries of Bosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
are drawn along ethnic lines, but those of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 states, a federal district, five major unincorporated territori ...
are not).
This article mainly discusses the more specific definition of a nation-state as a typically sovereign country dominated by a particular ethnicity.
Complexity
The relationship between a nation (in the ethnic sense) and a state can be complex. The presence of a state can encourageethnogenesis
Ethnogenesis (; ) is "the formation and development of an ethnic group".
This can originate by group self-identification or by outside identification.
The term ''ethnogenesis'' was originally a mid-19th century neologism that was later introd ...
, and a group with a pre-existing ethnic identity can influence the drawing of territorial boundaries or argue for political legitimacy
In political science, legitimacy is the right and acceptance of an authority, usually a governing law or a regime. Whereas ''authority'' denotes a specific position in an established government, the term ''legitimacy'' denotes a system of gover ...
.
This definition of a "nation-state" is not universally accepted. "All attempts to develop terminological consensus around "nation" resulted in failure", concludes academic Valery Tishkov
Valery Aleksandrovich Tishkov Валерий Александрович Тишков (born 6 November 1941) is an ethnologist and former chairman of the State Committee of RSFSR on nationalities from February 27 to October 15, 1992 (Minister for ...
.
Walker Connor discusses the impressions surrounding the characters of "nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
", " (sovereign) state", "nation state", and "nationalism
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
". Connor, who gave the term "ethnonationalism
Ethnic nationalism, also known as ethnonationalism, is a form of nationalism wherein the nation and nationality are defined in terms of ethnicity, with emphasis on an ethnocentric (and in some cases an ethnocratic) approach to various politi ...
" wide currency, also discusses the tendency to confuse nation and state and the treatment of all states as if nation states.
History and origins
The origins and earlyhistory
History (derived ) is the systematic study and the documentation of the human activity. The time period of event before the invention of writing systems is considered prehistory. "History" is an umbrella term comprising past events as well ...
of nation states are disputed. A major theoretical question is: "Which came first, the nation or the nation state?" Scholars such as Steven Weber, David Woodward, Michel Foucault and Jeremy Black have advanced the hypothesis that the nation state did not arise out of political ingenuity or an unknown undetermined source, nor was it a political invention; but is an inadvertent byproduct of 15th-century intellectual discoveries in political economy
Political economy is the study of how economic systems (e.g. markets and national economies) and political systems (e.g. law, institutions, government) are linked. Widely studied phenomena within the discipline are systems such as labour ...
, capitalism
Capitalism is an economic system based on the private ownership of the means of production and their operation for profit. Central characteristics of capitalism include capital accumulation, competitive markets, price system, priva ...
, mercantilism, political geography, and geography
Geography (from Greek: , ''geographia''. Combination of Greek words ‘Geo’ (The Earth) and ‘Graphien’ (to describe), literally "earth description") is a field of science devoted to the study of the lands, features, inhabitants, an ...
combined with cartography
Cartography (; from grc, χάρτης , "papyrus, sheet of paper, map"; and , "write") is the study and practice of making and using maps. Combining science, aesthetics and technique, cartography builds on the premise that reality (or an i ...
and advances in map-making technologies. It was with these intellectual discoveries and technological advances that the nation state arose. For others, the nation existed first, then nationalist movements arose for sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
, and the nation state was created to meet that demand. Some " modernization theories" of nationalism see it as a product of government policies to unify and modernize an already existing state. Most theories see the nation state as a 19th-century European phenomenon, facilitated by developments such as state-mandated education, mass literacy
Literacy in its broadest sense describes "particular ways of thinking about and doing reading and writing" with the purpose of understanding or expressing thoughts or ideas in written form in some specific context of use. In other words, hum ...
and mass media
Mass media refers to a diverse array of media technologies that reach a large audience via mass communication. The technologies through which this communication takes place include a variety of outlets.
Broadcast media transmit informati ...
. However, historians also note the early emergence of a relatively unified state and identity in Portugal
Portugal, officially the Portuguese Republic ( pt, República Portuguesa, links=yes ), is a country whose mainland is located on the Iberian Peninsula of Southwestern Europe, and whose territory also includes the Atlantic archipelagos of ...
and the Dutch Republic
The United Provinces of the Netherlands, also known as the (Seven) United Provinces, officially as the Republic of the Seven United Netherlands (Dutch: ''Republiek der Zeven Verenigde Nederlanden''), and commonly referred to in historiography ...
.
In France, Eric Hobsbawm argues, the French state preceded the formation of the French people
The French people (french: Français) are an ethnic group and nation primarily located in Western Europe that share a common French culture, history, and language, identified with the country of France.
The French people, especially the na ...
. Hobsbawm considers that the state made the French nation, not French nationalism
French nationalism () usually manifests as cultural nationalism, promoting the cultural unity of France.
History
French nationalism emerged from its numerous wars with England, which involved the reconquest of the territories that made up Fr ...
, which emerged at the end of the 19th century, the time of the Dreyfus Affair
The Dreyfus affair (french: affaire Dreyfus, ) was a political scandal that divided the French Third Republic from 1894 until its resolution in 1906. "L'Affaire", as it is known in French, has come to symbolise modern injustice in the Francop ...
. At the time of the 1789 French Revolution
The French Revolution ( ) was a period of radical political and societal change in France that began with the Estates General of 1789 and ended with the formation of the French Consulate in coup of 18 Brumaire, November 1799. Many of its ...
, only half of the French people spoke some French, and 12–13% spoke the version of it that was to be found in literature and in educational facilities, according to Hobsbawm.
During the Italian unification, the number of people speaking the Italian language
Italian (''italiano'' or ) is a Romance language of the Indo-European language family that evolved from the Vulgar Latin of the Roman Empire. Together with Sardinian, Italian is the least divergent language from Latin. Spoken by about ...
was even lower. The French state promoted the replacement of various regional dialects and languages by a centralised French language, and so did, and still does, Italy. The introduction of conscription and the Third Republic's 1880s laws on public instruction facilitated the creation of a national identity under this theory.
 Some nation states, such as
Some nation states, such as Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
and Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, came into existence at least partly as a result of political campaigns by nationalists
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
, during the 19th century. In both cases, the territory was previously divided among other states, some of them very small. The sense of common identity was at first a cultural movement, such as in the '' Völkisch movement'' in German-speaking states, which rapidly acquired a political significance. In these cases, the nationalist sentiment and the nationalist movement clearly precede the unification of the German and Italian nation states.
Historians Hans Kohn, Liah Greenfeld, Philip White and others have classified nations such as Germany or Italy, where cultural unification preceded state unification, as ''ethnic nations'' or ''ethnic nationalities''. However, "state-driven" national unifications, such as in France, England or China, are more likely to flourish in multiethnic societies, producing a traditional national heritage of ''civic nations'', or ''territory-based nationalities''.
The idea of a nation state was and is associated with the rise of the modern system of states, often called the " Westphalian system" in reference to the Treaty of Westphalia
The Peace of Westphalia (german: Westfälischer Friede, ) is the collective name for two peace treaties signed in October 1648 in the Westphalian cities of Osnabrück and Münster. They ended the Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) and brought pea ...
(1648). The balance of power, which characterized that system, depended on its effectiveness upon clearly defined, centrally controlled, independent entities, whether empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
s or nation states, which recognize each other's sovereignty and territory. The Westphalian system did not create the nation state, but the nation state meets the criteria for its component states (by assuming that there is no disputed territory). Before the Westphalian system, the closest geopolitical system was the "Chanyuan system" established in East Asia in 1005 through the Treaty of Chanyuan, which, like the Westphalian peace treaties, designated national borders between the independent regimes of China's Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the rest ...
and the nomadic Liao dynasty
The Liao dynasty (; Khitan language, Khitan: ''Mos Jælud''; ), also known as the Khitan Empire (Khitan: ''Mos diau-d kitai huldʒi gur''), officially the Great Liao (), was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that exi ...
. This system was copied and developed in East Asia in the following centuries until the establishment of the pan-Eurasian Mongol Empire in the 13th century.
The nation state received a philosophical underpinning in the era of Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
, at first as the "natural" expression of the individual peoples ( romantic nationalism: see Johann Gottlieb Fichte's conception of the ''Volk
The German noun ''Volk'' () translates to people,
both uncountable in the sense of ''people'' as in a crowd, and countable (plural ''Völker'') in the sense of '' a people'' as in an ethnic group or nation (compare the English term '' folk ...
'', later opposed by Ernest Renan). The increasing emphasis during the 19th century on the ethnic and racial origins of the nation, led to a redefinition of the nation state in these terms. Racism
Racism is the belief that groups of humans possess different behavioral traits corresponding to inherited attributes and can be divided based on the superiority of one race over another. It may also mean prejudice, discrimination, or antagonis ...
, which in Boulainvilliers's theories was inherently antipatriotic
Patriotism is the feeling of love, devotion, and sense of attachment to one's country. This attachment can be a combination of many different feelings, language relating to one's own homeland, including ethnic, cultural, political or histor ...
and antinationalist, joined itself with colonialist imperialism and "continental imperialism", most notably in pan-Germanic and pan-Slavic
Pan-Slavism, a movement which crystallized in the mid-19th century, is the political ideology concerned with the advancement of integrity and unity for the Slavic people. Its main impact occurred in the Balkans, where non-Slavic empires had rule ...
movements.
The relation between racism and ethnic nationalism reached its height in the 20th century fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy an ...
and Nazism
Nazism ( ; german: Nazismus), the common name in English for National Socialism (german: Nationalsozialismus, ), is the far-right totalitarian political ideology and practices associated with Adolf Hitler and the Nazi Party (NSDAP) i ...
. The specific combination of "nation" ("people") and "state" expressed in such terms as the ''Völkische Staat'' and implemented in laws such as the 1935 Nuremberg laws
The Nuremberg Laws (german: link=no, Nürnberger Gesetze, ) were antisemitic and racist laws that were enacted in Nazi Germany on 15 September 1935, at a special meeting of the Reichstag convened during the annual Nuremberg Rally of ...
made fascist states such as early Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
qualitatively different from non-fascist nation states. Minorities were not considered part of the people (''Volk''), and were consequently denied to have an authentic or legitimate role in such a state. In Germany, neither Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
nor the Roma were considered part of the people and both were specifically targeted for persecution. German nationality law defined "German" on the basis of German ancestry, excluding ''all'' non-Germans from the people.
In recent years, a nation state's claim to absolute sovereignty
Sovereignty is the defining authority within individual consciousness, social construct, or territory. Sovereignty entails hierarchy within the state, as well as external autonomy for states. In any state, sovereignty is assigned to the perso ...
within its borders has been criticized. A global political system based on international agreements
A treaty is a formal, legally binding written agreement between actors in international law. It is usually made by and between sovereign states, but can include international organizations, individuals, business entities, and other legal pers ...
and supra-national blocs characterized the post-war era. Non-state actors, such as international corporation
A corporation is an organization—usually a group of people or a company—authorized by the state to act as a single entity (a legal entity recognized by private and public law "born out of statute"; a legal person in legal context) and ...
s and non-governmental organizations, are widely seen as eroding the economic and political power of nation states.
According to Andreas Wimmer and Yuval Feinstein, nation-states tended to emerge when power shifts allowed nationalists to overthrow existing regimes or absorb existing administrative units. Xue Li and Alexander Hicks links the frequency of nation-state creation to processes of diffusion that emanate from international organizations.
Before the nation state
 In
In Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a subcontinent of Eurasia and it is located entirel ...
, during the 18th century, the classic non-national states were the ''multiethnic'' empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
s, the Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central-Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence ...
, the Kingdom of France
The Kingdom of France ( fro, Reaume de France; frm, Royaulme de France; french: link=yes, Royaume de France) is the historiographical name or umbrella term given to various political entities of France in the medieval and early modern period ...
(and its empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
), the Kingdom of Hungary
The Kingdom of Hungary was a monarchy in Central Europe that existed for nearly a millennium, from the Middle Ages into the 20th century. The Principality of Hungary emerged as a Christian kingdom upon the coronation of the first king Stephen ...
, the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
, the Portuguese Empire
The Portuguese Empire ( pt, Império Português), also known as the Portuguese Overseas (''Ultramar Português'') or the Portuguese Colonial Empire (''Império Colonial Português''), was composed of the overseas colonies, factories, and the ...
, the Spanish Empire
The Spanish Empire ( es, link=no, Imperio español), also known as the Hispanic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Hispánica) or the Catholic Monarchy ( es, link=no, Monarquía Católica) was a colonial empire governed by Spain and its prede ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
, the Dutch Empire and smaller nations at what would now be called sub-state level. The multi-ethnic empire was an absolute monarchy
Absolute monarchy (or Absolutism (European history), Absolutism as a doctrine) is a form of monarchy in which the monarch rules in their own right or power. In an absolute monarchy, the king or queen is by no means limited and has absolute pow ...
ruled by a king, emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereignty, sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife (empress consort), ...
or sultan. The population belonged to many ethnic groups, and they spoke many languages. The empire was dominated by one ethnic group, and their language was usually the language of public administration. The ruling dynasty
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A ...
was usually, but not always, from that group.
This type of state is not specifically European: such empires existed in Asia, Africa and the Americas. Chinese dynasties, such as the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dynasty and followed by the Five Dynasties and Ten Kingdom ...
, the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last orthodox dynasty of China ruled by the Han peo ...
, and the Qing dynasty
The Qing dynasty ( ), officially the Great Qing,, was a Manchu-led imperial dynasty of China and the last orthodox dynasty in Chinese history. It emerged from the Later Jin dynasty founded by the Jianzhou Jurchens, a Tungusic-spea ...
, were all multiethnic regimes governed by a ruling ethnic group. In the three examples, their ruling ethnic groups were the Han-Chinese, and the Manchus
The Manchus (; ) are a Tungusic East Asian ethnic group native to Manchuria in Northeast Asia. They are an officially recognized ethnic minority in China and the people from whom Manchuria derives its name. The Later Jin (1616–1636) and ...
. In the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
, immediately after Muhammad's death in 632, Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
s were established. Caliphates were Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
s under the leadership of a political-religious successor to the Islamic prophet Muhammad
Muhammad ( ar, مُحَمَّد; 570 – 8 June 632 CE) was an Arab religious, social, and political leader and the founder of Islam. According to Islamic doctrine, he was a prophet divinely inspired to preach and confirm the mo ...
. These polities
A polity is an identifiable political entity – a group of people with a collective identity, who are organized by some form of institutionalized social relations, and have a capacity to mobilize resources. A polity can be any other group of p ...
developed into multi-ethnic trans-national empires. The Ottoman sultan, Selim I
Selim I ( ota, سليم الأول; tr, I. Selim; 10 October 1470 – 22 September 1520), known as Selim the Grim or Selim the Resolute ( tr, links=no, Yavuz Sultan Selim), was the Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1512 to 1520. Despite las ...
(1512–1520) reclaimed the title of caliph, which had been in dispute and asserted by a diversity of rulers and "shadow caliphs" in the centuries of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Muttalib ...
-Mamluk
Mamluk ( ar, مملوك, mamlūk (singular), , ''mamālīk'' (plural), translated as "one who is owned", meaning " slave", also transliterated as ''Mameluke'', ''mamluq'', ''mamluke'', ''mameluk'', ''mameluke'', ''mamaluke'', or ''marmeluke'') ...
Caliphate since the Mongols' sacking of Baghdad and the killing of the last Abbasid Caliph in Baghdad, Iraq 1258.
The Ottoman Caliphate
The Caliphate of the Ottoman Empire ( ota, خلافت مقامى, hilâfet makamı, office of the caliphate) was the claim of the heads of the Turkish Ottoman dynasty to be the caliphs of Islam in the late medieval and the early modern era. ...
as an office of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
was abolished under Mustafa Kemal Atatürk in 1924 as part of Atatürk's Reforms.
Some of the smaller European states were not so ethnically diverse, but were also dynastic
A dynasty is a sequence of rulers from the same family,''Oxford English Dictionary'', "dynasty, ''n''." Oxford University Press (Oxford), 1897. usually in the context of a monarchical system, but sometimes also appearing in republics. A d ...
states, ruled by a royal house. Their territory could expand by royal intermarriage or merge with another state when the dynasty merged. In some parts of Europe, notably Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
, very small territorial units existed. They were recognized by their neighbors as independent, and had their own government and laws. Some were ruled by prince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. T ...
s or other hereditary rulers, some were governed by bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
s or abbot
Abbot is an ecclesiastical title given to the male head of a monastery in various Western religious traditions, including Christianity. The office may also be given as an honorary title to a clergyman who is not the head of a monastery. The ...
s. Because they were so small, however, they had no separate language or culture: the inhabitants shared the language of the surrounding region.
In some cases, these states were simply overthrown by nationalist uprisings in the 19th century. Liberal ideas of free trade
Free trade is a trade policy that does not restrict imports or exports. It can also be understood as the free market idea applied to international trade. In government, free trade is predominantly advocated by political parties that hold econ ...
played a role in German unification, which was preceded by a customs union
A customs union is generally defined as a type of trade bloc which is composed of a free trade area with a common external tariff.GATTArticle 24 s. 8 (a)
Customs unions are established through trade pacts where the participant countries set up ...
, the Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had b ...
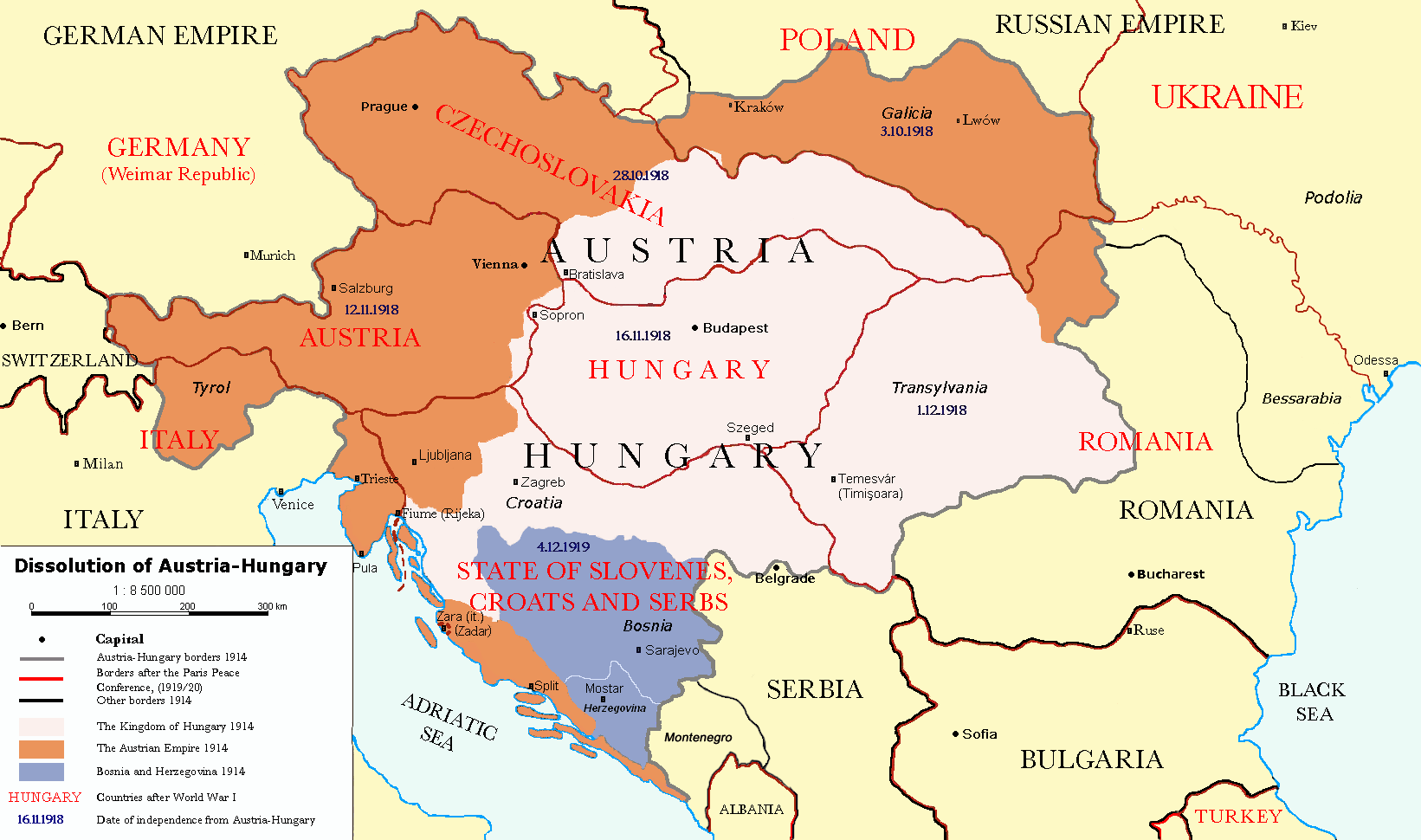
. However, the Austro-Prussian War, and the German alliances in the Franco-Prussian War, were decisive in the unification. The Austro-Hungarian Empire and the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
broke up after the First World War
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
, and the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War. ...
became the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
after the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
.
A few of the smaller states survived: the independent principalities of Liechtenstein
Liechtenstein (), officially the Principality of Liechtenstein (german: link=no, Fürstentum Liechtenstein), is a German-speaking microstate located in the Alps between Austria and Switzerland. Liechtenstein is a semi-constitutional monarch ...
, Andorra
, image_flag = Flag of Andorra.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Andorra.svg
, symbol_type = Coat of arms
, national_motto = la, Virtus Unita Fortior, label=none (Latin)"United virtue is stro ...
, Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a sovereign city-state and microstate on the French Riviera a few kilometres west of the Italian region of Lig ...
, and the republic of San Marino
San Marino (, ), officially the Republic of San Marino ( it, Repubblica di San Marino; ), also known as the Most Serene Republic of San Marino ( it, Serenissima Repubblica di San Marino, links=no), is the fifth-smallest country in the world an ...
. (Vatican City
Vatican City (), officially the Vatican City State ( it, Stato della Città del Vaticano; la, Status Civitatis Vaticanae),—'
* german: Vatikanstadt, cf. '—' (in Austria: ')
* pl, Miasto Watykańskie, cf. '—'
* pt, Cidade do Vati ...
is a special case. All of the larger Papal States save the Vatican itself were occupied and absorbed by Italy by 1870. The resulting Roman Question was resolved with the rise of the modern state under the 1929 Lateran treaties
The Lateran Treaty ( it, Patti Lateranensi; la, Pacta Lateranensia) was one component of the Lateran Pacts of 1929, agreements between the Kingdom of Italy under King Victor Emmanuel III of Italy and the Holy See under Pope Pius XI to settle t ...
between Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
and the Holy See
The Holy See ( lat, Sancta Sedes, ; it, Santa Sede ), also called the See of Rome, Petrine See or Apostolic See, is the jurisdiction of the Pope in his role as the bishop of Rome. It includes the apostolic episcopal see of the Diocese of R ...
.)
Characteristics
"Legitimate states that govern effectively and dynamic industrial economies are widely regarded today as the defining characteristics of a modern nation-state." Nation states have their own characteristics, differing from those of the pre-national states. For a start, they have a different attitude to their territory when compared with dynastic monarchies: it is semisacred and nontransferable. No nation would swap territory with other states simply, for example, because the king's daughter married. They have a different type ofborder
Borders are usually defined as geographical boundaries, imposed either by features such as oceans and terrain, or by political entities such as governments, sovereign states, federated states, and other subnational entities. Political borders c ...
, in principle defined only by the area of settlement of the national group, although many nation states also sought natural borders (rivers, mountain ranges). They are constantly changing in population size and power because of the limited restrictions of their borders.
The most noticeable characteristic is the degree to which nation states use the state as an instrument of national unity, in economic, social and cultural life.
The nation state promoted economic unity, by abolishing internal customs and tolls. In Germany, that process, the creation of the Zollverein
The (), or German Customs Union, was a coalition of German states formed to manage tariffs and economic policies within their territories. Organized by the 1833 treaties, it formally started on 1 January 1834. However, its foundations had b ...
, preceded formal national unity. Nation states typically have a policy to create and maintain a national transportation infrastructure, facilitating trade and travel. In 19th-century Europe, the expansion of the rail transport
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
networks was at first largely a matter for private railway companies, but gradually came under control of the national governments. The French rail network, with its main lines radiating from Paris to all corners of France, is often seen as a reflection of the centralised French nation state, which directed its construction. Nation states continue to build, for instance, specifically national motorway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
networks. Specifically transnational infrastructure programmes, such as the Trans-European Networks
The Trans-European Networks (TEN) were created by the European Union by Articles 154–156 of the Treaty of Rome (1957), with the stated goals of the creation of an internal market and the reinforcement of economic and social cohesion. To various ...
, are a recent innovation.
The nation states typically had a more centralised and uniform public administration
Public Administration (a form of governance) or Public Policy and Administration (an academic discipline) is the implementation of public policy, administration of government establishment (public governance), management of non-profit est ...
than its imperial predecessors: they were smaller, and the population less diverse. (The internal diversity of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, for instance, was very great.) After the 19th-century triumph of the nation state in Europe, regional identity was subordinate to national identity, in regions such as Alsace-Lorraine, Catalonia, Brittany and Corsica. In many cases, the regional administration was also subordinated to central (national) government. This process was partially reversed from the 1970s onward, with the introduction of various forms of regional autonomy, in formerly Centralised government, centralised states such as Spain or Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
.
The most obvious impact of the nation state, as compared to its non-national predecessors, is the creation of a uniform national culture, through state policy. The model of the nation state implies that its population constitutes a nation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
, united by a common descent, a common language and many forms of shared culture. When the implied unity was absent, the nation state often tried to create it. It promoted a uniform national language, through language policy. The creation of national systems of compulsory primary education and a relatively uniform curriculum in secondary schools, was the most effective instrument in the spread of the national languages. The schools also taught the national history, often in a Historiography and nationalism, propagandistic and mythologised version, and (especially during conflicts) some nation states still teach this kind of history.
Language and cultural policy was sometimes negative, aimed at the suppression of non-national elements. Language prohibitions were sometimes used to accelerate the adoption of national languages and the decline of minority languages (see examples: Anglicisation, Bulgarization, Croatization, Czechization, Dutchification, Francisation, Germanisation, Hellenization, Hispanicization, Italianization, Lithuanization, Magyarisation, Polonisation, Russification, Serbization, Slovakisation, Swedification, Turkification).
In some cases, these policies triggered bitter conflicts and further ethnic separatism. But where it worked, the cultural uniformity and homogeneity of the population increased. Conversely, the cultural divergence at the border became sharper: in theory, a uniform French identity extends from the Atlantic coast to the Rhine, and on the other bank of the Rhine, a uniform German identity begins. To enforce that model, both sides have divergent language policy and educational systems.
In practice
The notion of a unifying "national identity" also extends to countries that host multiple ethnic or language groups, such as India. For example, Switzerland is constitutionally a confederation of Cantons of Switzerland, cantons, and has four official languages, but it has also a "Swiss" national identity, a national history and a classic national hero, Wilhelm Tell. Innumerable conflicts have arisen where political boundaries did not correspond with ethnic or cultural boundaries. After World War II in the Josip Broz Tito era, nationalism was appealed to for uniting South Slav peoples. Later in the 20th century, after the break-up of the Soviet Union, leaders appealed to ancient ethnic feuds or tensions that ignited conflict between the Serbs, Croats and Slovenes, as well as Bosniaks, Montenegrins (ethnic group), Montenegrins and Macedonians (ethnic group), Macedonians, eventually breaking up the long collaboration of peoples. Ethnic cleansing was carried out in the Balkans, resulting in the destruction of the formerly Socialist state, socialist republic and producing the civil wars in Croatian War of Independence, Croatia and Bosnian War, Bosnia and Herzegovina in 1992–95, resulting in mass population displacements and segregation that radically altered what was once a highly diverse and intermixed ethnic makeup of the region. These conflicts were largely about creating a new political framework of states, each of which would be ethnically and politically homogeneous. Serbs, Croats and Bosniaks insisted they were ethnically distinct although many communities had a long history of intermarriage. Presently Croatia (90,42%), Slovenia (83,1-88%) and Serbia (83,3% Serb) could be classified as monoethnic states, whereas North Macedonia (66% Macedonian), Montenegro (42% Montenegrin) andBosnia and Herzegovina
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of south and southeast Europe, located in the Balkans. Bosnia and H ...
(50.1% Bosniak) are multiethnic states.
Belgium is a classic example of a state that is not a nation state. The state was formed by secession from the United Kingdom of the Netherlands in 1830, whose neutrality and integrity was protected by the Treaty of London 1839; thus it served as a buffer state after the Napoleonic Wars between the European powers France, Prussia (after 1871 the German Empire) and the United Kingdom until World War I, when its neutrality was breached by the Germans. Currently, Belgium is divided between the Flemings in the north, the French-speaking population in the south, and the German-speaking population in the east. The Flanders, Flemish population in the north speaks Dutch, the Wallonia, Walloon population in the south speaks either French language, French or, in the east of Liège Province, German. The Brussels population speaks French or Dutch.
The Flemish identity is also cultural, and there is a strong separatist movement espoused by the political parties, the right-wing Vlaams Belang and the Nieuw-Vlaamse Alliantie. The Francophone Wallonia, Walloon identity of Belgium is linguistically distinct and Regionalism (politics), regionalist. There is also unitary Belgian nationalism, several versions of a Greater Netherlands ideal, and a German-speaking community of Belgium annexed from Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwe ...
in 1920, and re-annexed by Germany in 1940–1944. However, these ideologies are all very marginal and politically insignificant during elections.
 China covers a large geographic area and uses the concept of "Zhonghua minzu" or Chinese nationality, in the sense of ethnic groups, but it also officially recognizes the majority Han Chinese, Han ethnic group which accounts for over 90% of the population, and no fewer than 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic national minorities.
According to Philip G. Roeder, Moldova is an example of a Soviet era "segment-state" (Moldavian SSR), where the "nation-state project of the segment-state trumped the nation-state project of prior statehood. In Moldova, despite strong agitation from university faculty and students for reunification with Romania, the nation-state project forged within the Moldavian SSR trumped the project for a return to the interwar nation-state project of Greater Romania." See Controversy over linguistic and ethnic identity in Moldova for further details.
China covers a large geographic area and uses the concept of "Zhonghua minzu" or Chinese nationality, in the sense of ethnic groups, but it also officially recognizes the majority Han Chinese, Han ethnic group which accounts for over 90% of the population, and no fewer than 55 Ethnic minorities in China, ethnic national minorities.
According to Philip G. Roeder, Moldova is an example of a Soviet era "segment-state" (Moldavian SSR), where the "nation-state project of the segment-state trumped the nation-state project of prior statehood. In Moldova, despite strong agitation from university faculty and students for reunification with Romania, the nation-state project forged within the Moldavian SSR trumped the project for a return to the interwar nation-state project of Greater Romania." See Controversy over linguistic and ethnic identity in Moldova for further details.
Exceptional cases
Israel
Israel was founded as a Jewish state in 1948. Its "Basic Laws of Israel, Basic Laws" describe it as both a Jewish and a democratic state. The Basic Law: Israel as the Nation-State of the Jewish People (2018) explicitly specifies the nature of the State of Israel as the nation-state of the Jews, Jewish people. According to the Israel Central Bureau of Statistics, 75.7% of Israel's population are Jews. Arab citizens of Israel, Arabs, who make up 20.4% of the population, are the largest ethnic minority in Israel. Israel also has very small communities of Armenians in Israel, Armenians, Circassians in Israel, Circassians, Assyrians in Israel, Assyrians, Samaritans. There are also some non-Jewish spouses of Israeli Jews. However, these communities are very small, and usually number only in the hundreds or thousands.Kingdom of the Netherlands
The Kingdom of the Netherlands presents an unusual example in which one kingdom represents four distinct countries. The four countries of the Kingdom of the Netherlands are: * Netherlands (including the Provinces of the Netherlands, provinces in continental Europe and the Caribbean Netherlands, special municipalities of Bonaire, Sint Eustatius and Saba (island), Saba) * Aruba * Curaçao * Sint Maarten Each is expressly designated as a ''land'' in Law of the Netherlands, Dutch law by the Charter for the Kingdom of the Netherlands. Unlike the German and the Austrian , is consistently translated as "countries" by the Dutch government.Spain
While historical monarchies often brought together different kingdoms/territories/ethnic groups under the same crown, in modern nation states political elites seek a uniformity of the population, leading to state nationalism. In the case of the Christian territories of the future Spain, neighboring Al-Andalus, there was an early perception of ethnicity, faith and shared territory in the Middle Ages (13th-14th centuries), as documented by the Chronicle of Muntaner in the proposal of the Kingdom of Toledo (Crown of Castile), Castilian king to the other Christian kings of the peninsula: "...''if these four Kings of Spain whom he named, who are of one flesh and blood, held together, little need they fear all the other powers of the world.''..". After the dynastic union of the Catholic Monarchs of Spain, Catholic Monarchs in the 15th century, the Spanish Monarchy ruled over different kingdoms, each with its own cultural, linguistic and political particularities, and the kings had to swear by the Laws of each territory before the respective Parliaments. After the War of the Spanish Succession, rooted in the political position of the Gaspar de Guzmán, Count-Duke of Olivares, Count-Duke of Olivares and the absolutism of Philip V of Spain, Philip V, the assimilation of the Crown of Aragon by the Crown of Castile, Castilian Crown through the Nueva Planta decrees, Decrees of Nova planta was the first step in the creation of the Spanish nation-state. As in other contemporary European states, political union was the first step in the creation of the Spanish nation-state, in this case not on a uniform Ethnic group, ethnic basis, but through the imposition of the political and cultural characteristics of the dominant ethnic group, in this case the Castilians, over those of other ethnic groups, who became Minority group, national minorities to be assimilated. In fact, since the political unification of 1714, Spanish assimilation policies towards Catalan Countries, Catalan-speaking territories (Catalonia, Valencian Community, Valencia, the Balearic Islands, part of Aragon) and other national minorities, as basques and galicians, have been a historical constant. The process of assimilation began with secret instructions to the corregidores of the Catalan territory: they "will take the utmost care to introduce the Castilian language, for which purpose he will give the most temperate and disguised measures so that the effect is achieved, without the care being noticed." From there, actions in the service of assimilation, discreet or aggressive, were continued, and reached to the last detail, such as, in 1799, the Royal Certificate forbidding anyone to "represent, sing and dance pieces that were not in Spanish." These nationalist policies, sometimes very aggressive, and still in force, have been, and still are, the seed of repeated territorial conflicts within the State.
The nationalization process accelerated in the 19th century, in parallel to the origin of Spanish nationalism, the social, political and ideological movement that tried to shape a Spanish national identity based on the Castilian model, in conflict with the other historical nations of the State. Politicians of the time were aware that despite the aggressive policies pursued up to that time, the uniform and monocultural "Spanish nation" did not exist, as indicated in 1835 by Antonio Alcalá Galiano, Antonio Alcalà Galiano, when in the Cortes del Estatuto Real he defended the effort
The process of assimilation began with secret instructions to the corregidores of the Catalan territory: they "will take the utmost care to introduce the Castilian language, for which purpose he will give the most temperate and disguised measures so that the effect is achieved, without the care being noticed." From there, actions in the service of assimilation, discreet or aggressive, were continued, and reached to the last detail, such as, in 1799, the Royal Certificate forbidding anyone to "represent, sing and dance pieces that were not in Spanish." These nationalist policies, sometimes very aggressive, and still in force, have been, and still are, the seed of repeated territorial conflicts within the State.
The nationalization process accelerated in the 19th century, in parallel to the origin of Spanish nationalism, the social, political and ideological movement that tried to shape a Spanish national identity based on the Castilian model, in conflict with the other historical nations of the State. Politicians of the time were aware that despite the aggressive policies pursued up to that time, the uniform and monocultural "Spanish nation" did not exist, as indicated in 1835 by Antonio Alcalá Galiano, Antonio Alcalà Galiano, when in the Cortes del Estatuto Real he defended the effort "To make the Spanish nation a nation that neither is nor has been until now."In 1906, the Catalanist party Catalan Solidarity (1906), Solidaritat Catalana was founded to try to mitigate the economically and culturally oppressive treatment of Spain towards the Catalans. One of the responses of Spanish nationalism came from the military state with statements such as that of the publication La Correspondencia Militar, La Correspondencia militar: "The Catalan problem is not solved, well, by freedom, but by restriction; not by palliatives and pacts, but by iron and fire". Another came from important Spanish intellectuals, such Pío Baroja, Pio Baroja and Vicente Blasco Ibáñez, Blasco Ibañez, calling the Catalans "
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
", considered a serious insult at that time when Racism in Europe, racism was gaining strength.
Building the nation (as in France, it was the state that created the nation, and not the opposite process) is an ideal that the Spanish elites constantly reiterated, and, one hundred years later than Alcalá Galiano, for example, we can also find it in the mouth of the fascist José Pemartín, who admired the German and Italian modeling policies:"There is an intimate and decisive dualism, both in Italian fascism and in German National Socialism. On the one hand the Hegelian doctrine of the absolutism of the state is felt. The State originates in the Nation, educates and shapes the mentality of the individual; is, in Mussolini's words, the soul of the soul »The turn of the 20th century, and the first half of that century, have seen the most ethnic violence, coinciding with a racism that even came to identify states with races; in the case of Spain, with a supposed Spanish race sublimated in Castilian, of which national minorities were degenerate forms, and the first of those that needed to be exterminated. In this sense, one can find discourses on the alienation of Catalan language, Catalan speakers, such as, for example, an article entitled «Cataluña bilingüe», by Ramón Menéndez Pidal, Menéndez Pidal, in which he defends the Romanones decree against the Catalan language, published in El Imparcial (1867–1933), El Imparcial, on 15 December 1902:
«… There they will see that the Courts of the Catalan-Aragonese Confederation never had Catalan as their official language; that the kings of Aragon, even those of the Catalan dynasty, used Catalan only in Catalonia, and used Spanish not only in the Cortes of Aragon, but also in foreign relations, the same with Castile or Navarre as with the infidel kings of Granada , from Africa or Asia, because even in the most important days of Catalonia, Spanish prevailed as the language of the Aragonese kingdom and Catalan was reserved for the peculiar affairs of the Catalan county..."or the article "Los Catalanes. A las Cortes Constituyentes », appeared in several newspapers, among others: El Dia de Alicante, June 23, 1931, El Porvenir Castellano and El Noticiero de Soria, July 2, 1931, in the Heraldo de Almeria on June 4, 1931, sent by the "Pro-Justice Committee", with a post office box in Madrid:
"The Catalanists have recently declared that they are not Spanish, nor do they want to be, nor can they be. They have also been saying for a long time that they are an oppressed, enslaved, exploited people. It is imperative to do them justice... That they return to Phenicia or that they go wherever they want to admit them. When the Catalan tribes saw Spain and settled in the Spanish territory that is now occupied by the provinces of Barcelona, Gerona, Lérida and Tarragona, how little they imagined that the case of the captivity of the tribes of Israel in Egypt would be repeated there! !... Let us respect his most holy will. They are eternally inadaptable... Their cowardice and selfishness leaves them no room for fraternity... So, we propose to the Constituent Cortes the expulsion of the Catalanists... You are free! The Republic opens wide the doors of Spain, your prison. go away Get out of here. Go back to Phenicia, or go wherever you want, how big is the world."The main scapegoat of Spanish nationalism is the non-Spanish languages, which over the last three hundred years have been tried to be replaced by Spanish with hundreds of laws and regulations, but also with acts of great violence, such as during the civil war. For example, the statements of Gonzalo Queipo de Llano, Queipo de Llano can be found in the article entitled "Against Catalonia, the Israel of the Modern World", published in the Diario Palentino on November 26, 1936, where it is dropped that in Americas, America Catalans are considered a race of
Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, because they use the same procedures that the Hebrews perform in all the nations of the Globe. And considering the Catalans as Hebrews and considering his Antisemitism, anti-Semitism "Our struggle is not a civil war, but a war for Western civilization against the Jewish world," it is not surprising that Queipo de Llano expressed his Anti-Catalanism, anti-Catalan intentions: "When the war is over, Pompeu Fabra and his works will be dragged along the Ramblas" (it was not talk to talk, the house of Pompeu Fabra, the standardizer of Catalan language, was raided and his huge personal library burned in the middle of the street. Pompeu Fabra was able to escape into exile).
Another example of Fascism, fascis"In the days following the occupation of Lleida (…), the republican prisoners identified as Catalans were executed without trial. Anyone who heard them speak Catalan was very likely to be arrested. The arbitrary brutality of the anti-Catalan repression reached such a point that Franco himself had to issue an order ordering that mistakes that could later be regretted be avoided ". "There are examples of the murder of peasants for no other apparent reason than that of speaking Catalan"After a possible attempt at ethnic cleansing, the Biopolitics, biopolitical imposition of Spanish during the Francoist Spain, Franco dictatorship, to the point of being considered an attempt at cultural genocide, democracy consolidated an apparent asymmetric regime of bilingualism of sorts, wherein the Spanish government has employed a system of laws that favored Spanish over Cataln, which becomes the weaker of the two languages, and therefore, in the absence of other states where it is spoken, is doomed to extinction in the medium or short term. In the same vein, its use in the Spanish Congress is prevented, and it is prevented from achieving official status Europe, unlike less spoken languages such as Goidelic languages, Gaelic. In other institutional areas, such as justice, Plataforma per la Llengua has denounced Anti-Catalanism, Catalanophobia. The association Soberania i Justícia have also denounced it in an act in the European Parliament. It also takes the form of linguistic secessionism, originally advocated by the Spanish extreme right and which has finally been adopted by the Spanish government itself and state bodies. In November 2005, Òmnium Cultural, Omnium Cultural organized a meeting of Catalan and Madrid intellectuals in the Círculo de Bellas Artes, Círculo de bellas artes in Madrid to show support for ongoing reform of Catalan Statute of Autonomy, which sought to resolve territorial tensions, and among other things better protect the Catalan language. On the Catalan side, a flight was made with one hundred representatives of the cultural, civic, intellectual, artistic and sporting world of Catalonia, but on the Spanish side, except Santiago Carrillo, a politician from the Second Spanish Republic, Second Republic, did not attend any more. The subsequent failure of the statutory reform with respect to its objectives opened the door to the growth of Catalan sovereignty. Apart from language discrimination by public officials, e.g. in the hospitals, the current prohibition of using the Catalan language in state institutions such as Court, despite being the former Crown of Aragon, with three Catalan-speaking territories, one of the co-founders of the current Spanish state, is nothing more than the continuation of the foreignization of Catalan-speaking people from the first third of the 20th century, in full swing of state racism and
fascism
Fascism is a far-right, authoritarian, ultra-nationalist political ideology and movement,: "extreme militaristic nationalism, contempt for electoral democracy and political and cultural liberalism, a belief in natural social hierarchy an ...
. It also can be pointed the linguistic secessionism, originally advocated by the Spanish far right and which has finally been adopted by the Spanish government itself and state bodies. By fragmenting Catalan language into as many languages as territories, it becomes inoperative, economically suffocated, and becomes a political toy in the hands of territorial politicians.
Susceptible to be classified as an ethnic democracy, the Spanish State currently only recognizes the Names of the Romani people, gypsies as a national minority, excluding Catalans (and, of course, Valencians and Balearic), Basques and Galicians. However, it is evident to any external observer that there are social diversities within the Spanish State that qualify as manifestations of national minorities, such as, for example, the existence of the main three linguistic minorities in their ancestral territories.
United Kingdom
The United Kingdom is an unusual example of a nation state due to its "countries within acountry
A country is a distinct part of the world, such as a state, nation, or other political entity. It may be a sovereign state or make up one part of a larger state. For example, the country of Japan is an independent, sovereign state, while ...
". The United Kingdom is formed by the union of England, Scotland, Wales and Northern Ireland, but it is a unitary state formed initially by the merger of two independent kingdoms, the Kingdom of England (which already included Wales) and the Kingdom of Scotland, but the Treaty of Union (1707) that set out the agreed terms has ensured the continuation of distinct features of each state, including separate Law in the United Kingdom, legal systems and separate Religion in the United Kingdom, national churches.
In 2003, the British Government described the United Kingdom as "countries within a country". While the Office for National Statistics and others describe the United Kingdom as a "nation state", others, including a then Prime Minister, describe it as a "multinational state
A multinational state or a multinational union is a sovereign entity that comprises two or more nations or states. This contrasts with a nation state, where a single nation accounts for the bulk of the population. Depending on the definition of ...
", and the term Home Nations is used to describe the four national teams that represent the four nations of the United Kingdom (England, Northern Ireland, Scotland, Wales). Some refer to it as a "Union State".
There has been academic debate over whether the United Kingdom can be legally dissolved, as it is recognized internationally as a single nation state. English law jurist A.V. Dicey wrote from an English legal perspective that the question is based on whether the legislation giving rise to the union (the Union with Scotland Act), one of the two pieces of legislation which created the state, can be repealed. Dicey claimed because the Law of England does not acknowledge the word "unconstitutional", as a matter of English law it can be repealed. He also stated any tampering with the Acts of Union 1707 would be political madness.
Minorities
The most obvious deviation from the ideal of "one nation, one state" is the presence of minorities, especially ethnic minorities, which are clearly not members of the majority nation. An ethnic nationalist definition of anation
A nation is a community of people formed on the basis of a combination of shared features such as language, history, ethnicity, culture and/or society. A nation is thus the collective Identity (social science), identity of a group of people unde ...
is necessarily exclusive: ethnic nations typically do not have open membership. In most cases, there is a clear idea that surrounding nations are different, and that includes members of those nations who live on the "wrong side" of the border. Historical examples of groups who have been specifically singled out as ''outsiders'' are the Roma and Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
in Europe.
Negative responses to minorities within the nation state have ranged from cultural assimilation
Cultural assimilation is the process in which a minority group or culture comes to resemble a society's majority group or assume the values, behaviors, and beliefs of another group whether fully or partially.
The different types of cultural ass ...
enforced by the state, to Ethnic cleansing, expulsion, persecution, violence, and Genocide, extermination. The assimilation policies are usually enforced by the state, but violence against minorities is not always state-initiated: it can occur in the form of mob violence such as lynching or pogroms. Nation states are responsible for some of the worst historical examples of violence against minorities not considered part of the nation.
However, many nation states accept specific minorities as being part of the nation, and the term ''national minority'' is often used in this sense. The Sorbs in Germany are an example: for centuries they have lived in German-speaking states, surrounded by a much larger ethnic German population, and they have no other historical territory. They are now generally considered to be part of the German nation and are accepted as such by the Federal Republic of Germany, which constitutionally guarantees their cultural rights. Of the thousands of ethnic and cultural minorities in nation states across the world, only a few have this level of acceptance and protection.
Multiculturalism is an official policy in some states, establishing the ideal of coexisting existence among multiple and separate ethnic, cultural, and linguistic groups. Other states preffer the interculturalism (or "melting pot" approach) alternative to multiculturalism, citing Criticism of multiculturalism, problems with latter as promoting self-segregation tendencies among minority groups, challenging national cohesion, polarizing society in groups that can't relate to one another, generating problems in regard to minorities and immigrants' fluency in the national language of use and integration with the rest of society (generating hate and persecution against them from the "otherness" they would generate in such a case according to its adherants), without minorities having to give up certain parts of their culture before being absorbed into a now changed majority culture by their contribution. Many nations have laws protecting minority rights.
When national boundaries that do not match ethnic boundaries are drawn, such as in the Balkans and Central Asia, ethnic tension, massacres and even genocide, sometimes has occurred historically (see Bosnian genocide and 2010 South Kyrgyzstan ethnic clashes).
Irredentism
Future
It has been speculated by both proponents of globalization and various science fiction writers that the concept of a nation state may disappear with the ever-increasing interconnectedness of the world. Such ideas are sometimes expressed around concepts of a world government. Another possibility is a societal collapse and move into communal anarchy or zero world government, in which nation states no longer exist.Clash of civilizations
The theory of the clash of civilizations lies in direct contrast to Cosmopolitanism, cosmopolitan theories about an ever more connected world that no longer requires nation states. According to political scientist Samuel P. Huntington, people's cultural and religious Identity (social science), identities will be the primary source of conflict in the post–Cold War world. The theory was originally formulated in a 1992 lecture at the American Enterprise Institute, which was then developed in a 1993 ''Foreign Affairs'' article titled "The Clash of Civilizations?",Official copy (free preview): in response to Francis Fukuyama's 1992 book, ''The End of History and the Last Man''. Huntington later expanded his thesis in a 1996 book ''The Clash of Civilizations and the Remaking of World Order''. Huntington began his thinking by surveying the diverse theories about the nature of global politics in the post–Cold War period. Some theorists and writers argued that human rights, liberal democracy and capitalist free market economics had become the only remaining ideological alternative for nations in the post–Cold War world. Specifically, Francis Fukuyama, in ''The End of History and the Last Man'', argued that the world had reached a Georg Wilhelm Friedrich Hegel, Hegelian "end of history". Huntington believed that while the age of ideology had ended, the world had reverted only to a normal state of affairs characterized by cultural conflict. In his thesis, he argued that the primary axis of conflict in the future will be along cultural and religious lines. As an extension, he posits that the concept of different civilizations, as the highest rank of cultural identity, will become increasingly useful in analyzing the potential for conflict. In the 1993 ''Foreign Affairs'' article, Huntington writes: :''It is my hypothesis that the fundamental source of conflict in this new world will not be primarily ideological or primarily economic. The great divisions among humankind and the dominating source of conflict will be cultural. Nation states will remain the most powerful actors in world affairs, but the principal conflicts of global politics will occur between nations and groups of different civilizations. The clash of civilizations will dominate global politics. The fault lines between civilizations will be the battle lines of the future.'' Sandra Joireman suggests that Huntington may be characterised as a neo-Primordialism, primordialist, as, while he sees people as having strong ties to their ethnicity, he does not believe that these ties have always existed.Historiography
Historians often look to the past to find the origins of a particular nation state. Indeed, they often put so much emphasis on the importance of the nation state in modern times, that they distort the history of earlier periods in order to emphasize the question of origins. Lansing and English argue that much of the medieval history of Europe was structured to follow the historical winners—especially the nation states that emerged around Paris and London. Important developments that did not directly lead to a nation state get neglected, they argue: :one effect of this approach has been to privilege historical winners, aspects of medieval Europe that became important in later centuries, above all the nation state.... Arguably the liveliest cultural innovation in the 13th century was the Mediterranean, centered on Frederick II, Holy Roman Emperor, Frederick II's polyglot court and administration in Palermo...Sicily and the Italian South in later centuries suffered a long slide into overtaxed poverty and marginality. Textbook narratives, therefore, focus not on medieval Palermo, with its Muslim and Jewish bureaucracies and Arabic-speaking monarch, but on the historical winners, Paris and London.See also
* Balkanization *Caliphate
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
* City-state
* Civilization state
* Islamic state
An Islamic state is a state that has a form of government based on Islamic law (sharia). As a term, it has been used to describe various historical polities and theories of governance in the Islamic world. As a translation of the Arabic term ...
* Nation
* Nationalism
* National personification
* Titular nation
* Westphalian sovereignty
Notes
References
General references
* Benedict Anderson, Anderson, Benedict. 1991. ''Imagined Communities''. . * Josep Colomer, Colomer, Josep M. 2007. ''Great Empires, Small Nations: The Uncertain Future of the Sovereign State''. . * Gellner, Ernest (1983). ''Nations and Nationalism''. Ithaca: Cornell University Press. . * Hobsbawm, Eric J. (1992). ''Nations and Nationalism Since 1780: Programme, Myth, Reality''. 2nd ed. Cambridge University Press. . * * Khan, Ali (1992)"The Extinction of Nation States"
* Ernest Renan, Renan, Ernest. 1882. s:fr:Qu'est-ce qu'une nation ?, "Qu'est-ce qu'une nation?" ("What Is a Nation?") * Malesevic, Sinisa (2006). ''Identity as Ideology: Understanding Ethnicity and Nationalism''. New York: Palgrave. * Smith, Anthony D. (1986). ''The Ethnic Origins of Nations''. London: Basil Blackwell. pp 6–18. . * White, Philip L. (2006)
"Globalization and the Mythology of the Nation State"
In A. G. Hopkins, ed. ''Global History: Interactions Between the Universal and the Local''. Palgrave Macmillan, pp. 257–284.
Citations
External links
on identity and the nation state. * :ca:Cronologia de la repressi%C3%B3 del catal%C3%A0, Chronology of the repression of the Catalan language in catalan language {{DEFAULTSORT:Nation State Nation, State Political science terminology