Natal (region) on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
South Africa occupies the southern tip of
 Like much of the African continent south of the Sahara, South Africa's landscape is dominated by a high Central Plateau surrounded by coastal lowlands. This plateau is rimmed by the
Like much of the African continent south of the Sahara, South Africa's landscape is dominated by a high Central Plateau surrounded by coastal lowlands. This plateau is rimmed by the
 The portion of the Great Escarpment that could be designated a "mountain" is where it forms the international border between
The portion of the Great Escarpment that could be designated a "mountain" is where it forms the international border between
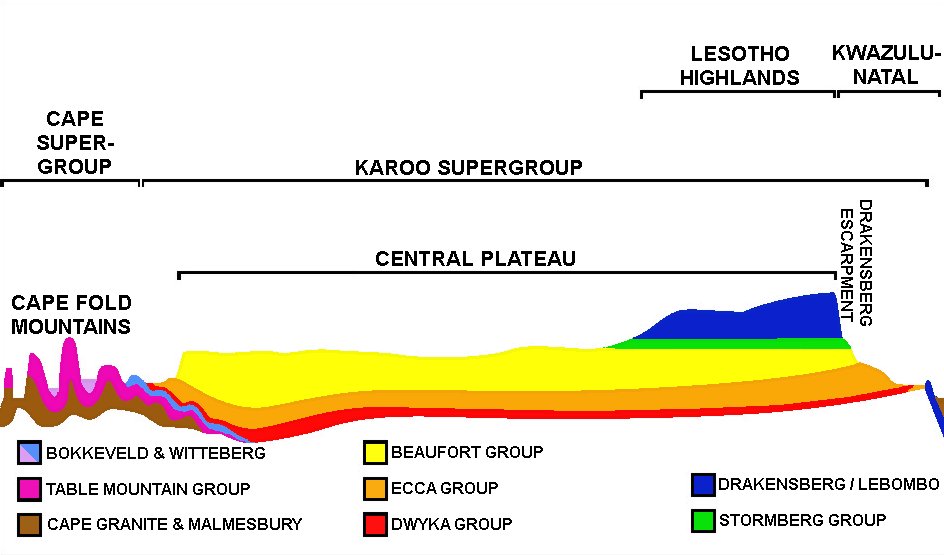
 The central plateau (apart from the Lesotho Highlands) forms a largely flat, tilted surface which, as indicated above, is highest in the east, sloping gently downwards to the west (at about 1,000 m above sea level). The downward slope to the south is less pronounced (the southern and south-western edges of the plateau are at about 1600 to 1900 m above sea level). The plateau also slopes downwards, northwards from about the 25° 30' S line of latitude, into a 150‑million-year-old failed
The central plateau (apart from the Lesotho Highlands) forms a largely flat, tilted surface which, as indicated above, is highest in the east, sloping gently downwards to the west (at about 1,000 m above sea level). The downward slope to the south is less pronounced (the southern and south-western edges of the plateau are at about 1600 to 1900 m above sea level). The plateau also slopes downwards, northwards from about the 25° 30' S line of latitude, into a 150‑million-year-old failed
 The South African portion of the coastal strip between the Limpopo and Mpumalanga Drakensberg and the ocean, together with the Limpopo River valley, is called the Lowveld.Atlas of Southern Africa. (1984). pp. 13, 192, 195. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town These lowlands, below about altitude, form South Africa's northern border with
The South African portion of the coastal strip between the Limpopo and Mpumalanga Drakensberg and the ocean, together with the Limpopo River valley, is called the Lowveld.Atlas of Southern Africa. (1984). pp. 13, 192, 195. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town These lowlands, below about altitude, form South Africa's northern border with
 The Lowveld partly overlaps with a dry savanna
The Lowveld partly overlaps with a dry savanna
 In the southwest, running parallel to the coastline, the mountains of the Cape Fold Belt form a series of ranges that run in the form of an "L" by a series running north–south, and another set running east–west, with the junction between the two at the
In the southwest, running parallel to the coastline, the mountains of the Cape Fold Belt form a series of ranges that run in the form of an "L" by a series running north–south, and another set running east–west, with the junction between the two at the

 The coastal regions are typically covered with
The coastal regions are typically covered with
 Bushmanland is an arid area inland from
Bushmanland is an arid area inland from

 This is the arid region along the north-western coastline (northwards from approximately the 31°S line of latitude) of South Africa, partly above and partly below the
This is the arid region along the north-western coastline (northwards from approximately the 31°S line of latitude) of South Africa, partly above and partly below the
 The vast majority of South Africa's border consists of the ocean—or two oceans, which, according to the
The vast majority of South Africa's border consists of the ocean—or two oceans, which, according to the
 South Africa is largely a dry country, with most of its western regions being semi-desert. The rainfall increases in the east, (the Highveld, KwaZulu-Natal, and the Eastern Midlands), and falls primarily in summer. The narrow southern coastal strip receives all-year rainfall in the east (the
South Africa is largely a dry country, with most of its western regions being semi-desert. The rainfall increases in the east, (the Highveld, KwaZulu-Natal, and the Eastern Midlands), and falls primarily in summer. The narrow southern coastal strip receives all-year rainfall in the east (the
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
, its coastline stretching more than from the desert border with Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
on the Atlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
(western) coast southwards around the tip of Africa and then northeast to the border with Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
on the Indian Ocean. The low-lying coastal zone
The coast, also known as the coastline or seashore, is defined as the area where land meets the ocean, or as a line that forms the boundary between the land and the coastline. The Earth has around of coastline. Coasts are important zones in ...
is narrow for much of that distance, soon giving way to a mountainous escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
(Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
) that separates the coast from the high inland plateau. In some places, notably the province of KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is loca ...
in the east, a greater distance separates the coast from the escarpment. Although much of the country is classified as semi-arid
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi- ...
, it has considerable variation in climate as well as topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
. The total land area is . It has the 23rd largest Exclusive Economic Zone of .
The South African central plateau contains only two major rivers: the Limpopo
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
(a stretch of which is shared with Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
), and the Orange
Orange most often refers to:
*Orange (fruit), the fruit of the tree species '' Citrus'' × ''sinensis''
** Orange blossom, its fragrant flower
*Orange (colour), from the color of an orange, occurs between red and yellow in the visible spectrum
* ...
(with its tributary, the Vaal
The Vaal River ( ; Khoemana: ) is the largest tributary of the Orange River in South Africa. The river has its source near Breyten in Mpumalanga province, east of Johannesburg and about north of Ermelo and only about from the Indian Ocean. I ...
) which runs with a variable flow across the central landscape from east to west, emptying into the Atlantic Ocean at the Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
n border.
The eastern and southern coastal regions are drained by numerous shorter rivers. There are very few coastal rivers along the arid west coast north of 31°30′S.
In such a dry country, dams and irrigation
Irrigation (also referred to as watering) is the practice of applying controlled amounts of water to land to help grow crops, landscape plants, and lawns. Irrigation has been a key aspect of agriculture for over 5,000 years and has been devel ...
are extremely important: the largest dam is the Gariep on the Orange River.
Topographical divisions
 Like much of the African continent south of the Sahara, South Africa's landscape is dominated by a high Central Plateau surrounded by coastal lowlands. This plateau is rimmed by the
Like much of the African continent south of the Sahara, South Africa's landscape is dominated by a high Central Plateau surrounded by coastal lowlands. This plateau is rimmed by the Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
which extends northwards to about 10° south of the Equator
The equator is a circle of latitude, about in circumference, that divides Earth into the Northern and Southern hemispheres. It is an imaginary line located at 0 degrees latitude, halfway between the North and South poles. The term can also ...
(i.e. into Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
in the west, and the Muchinga Escarpment in Zambia in the east.The Times comprehensive atlas of the world (1999). pp. 88–89. Times Books Group, London.)
Great Escarpment
In South Africa the plateau is at its highest in the east where its edge varies in altitude between 2,000 m and 3,300 m. This edge of the plateau, as the land drops sharply to the coastal plain, forms a very high, steepescarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
known as the Drakensberg Mountains
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
. The southern and western extents of the escarpment are not so high as Drakensberg, but also are known by a wide variety of local names, all termed "mountains" (or "berge" in Afrikaans
Afrikaans (, ) is a West Germanic language that evolved in the Dutch Cape Colony from the Dutch vernacular of Holland proper (i.e., the Hollandic dialect) used by Dutch, French, and German settlers and their enslaved people. Afrikaans gr ...
), in spite of being parts of an escarpment whose top is the central plateau, such as Groenberg Mountain. From the coastal plain the escarpment does, however, look like a range of mountains, hence the names.
 The portion of the Great Escarpment that could be designated a "mountain" is where it forms the international border between
The portion of the Great Escarpment that could be designated a "mountain" is where it forms the international border between KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is loca ...
and Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a population ...
. The Lesotho Highlands form a localized high spot on the Central Plateau. This is because it is capped by a 1,400 m thick layer of erosion resistant lava
Lava is molten or partially molten rock (magma) that has been expelled from the interior of a terrestrial planet (such as Earth) or a moon onto its surface. Lava may be erupted at a volcano or through a fracture in the crust, on land or ...
''Geological Map of South Africa, Lesotho and Swaziland''. (1970). Council for Geoscience, Geological Survey of South Africa. which welled up and spread across most of Southern Africa when it was still part of Gondwana.McCarthy t. & Rubidge B. (2005) ''The Story of Earth & Life''. p. 192, 209-269. Struik Publishers, Cape Town. Most of this lava has eroded away together with a layer of Karoo sedimentary rocks several kilometres thick on top of which the lava was poured out 182 million years ago. Only a small patch of this lava remains and covers much of Lesotho. It has been deeply eroded by the tributaries of the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
which drain these highlands towards the south-west (i.e. away from the Escarpment). This gives this high region its very rugged, mountainous appearance.
Central plateau

 The central plateau (apart from the Lesotho Highlands) forms a largely flat, tilted surface which, as indicated above, is highest in the east, sloping gently downwards to the west (at about 1,000 m above sea level). The downward slope to the south is less pronounced (the southern and south-western edges of the plateau are at about 1600 to 1900 m above sea level). The plateau also slopes downwards, northwards from about the 25° 30' S line of latitude, into a 150‑million-year-old failed
The central plateau (apart from the Lesotho Highlands) forms a largely flat, tilted surface which, as indicated above, is highest in the east, sloping gently downwards to the west (at about 1,000 m above sea level). The downward slope to the south is less pronounced (the southern and south-western edges of the plateau are at about 1600 to 1900 m above sea level). The plateau also slopes downwards, northwards from about the 25° 30' S line of latitude, into a 150‑million-year-old failed rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
which cuts into the central plateau and locally obliterates the Great Escarpment,McCarthy, T.S. (2013) The Okavango delta and its place in the geomorphological evolution of Southern Africa. ''South African Journal of Geology
The ''South African Journal of Geology'' is a quarterly peer-reviewed scientific journal published by the Geological Society of South Africa that was established in March 1896 as the ''Transactions of the Geological Society of South Africa'', obta ...
'' 116: 1-54. forming what is today known as the Limpopo
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
Lowveld
Veld ( or ), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in :Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Botswa ...
at less than 500 m above sea level. The rivers which drain the plateau therefore run west, ultimately, via the Orange River, into the Atlantic Ocean. North of the Witwatersrand
The Witwatersrand () (locally the Rand or, less commonly, the Reef) is a , north-facing scarp in South Africa. It consists of a hard, erosion-resistant quartzite metamorphic rock, over which several north-flowing rivers form waterfalls, which ...
, where the land starts to slope down towards the north, the drainage is into the Limpopo River
The Limpopo River rises in South Africa and flows generally eastward through Mozambique to the Indian Ocean. The term Limpopo is derived from Rivombo (Livombo/Lebombo), a group of Tsonga settlers led by Hosi Rivombo who settled in the mountain ...
and from there into the Indian Ocean.
Coastal plain
The coastal plain, which varies in width from about 60 km in the north-west to over 250 km in the north-east, generally slopes gently downwards from the foot of the escarpment to the coast. Numerous relatively small rivers drain the area, being more numerous in the KwaZulu-Natal and Eastern Midlands regions, where they arise on the well watered slopes of the high escarpment, than elsewhere. In the west there are very few such rivers because of the aridity of the region.Cape Fold Mountains
In the south and south-west the coastal plain contains a series of mountain ranges that run parallel to the coastline. These are theCape Fold Mountains
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mou ...
, whose rocks were laid down 510 – 350 million years ago, and were then crumpled into a series of parallel folds by the collision of the Falkland Plateau into the south of what was to become Africa when it was part of Gondwana. These series of parallel folds are in the form of an "L", with the western section running north–south, and the eastern section running east–west, for a total length of about 800 km. The right angle of the "L" occurs in the south-western corner of the country, just inland from the Cape Peninsula
The Cape Peninsula ( af, Kaapse Skiereiland) is a generally mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean at the south-western extremity of the African continent. At the southern end of the peninsula are Cape Point and the Ca ...
and Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
. These folds lie along the coastline in the south and are not much more than 100 km wide in total along most of their length. In the west they are separated from the coast by a pronounced coastal plain.
The floors of the long valleys between the parallel mountains ranges consist of fertile soils composed of weathered mudstones belonging to the Bokkeveld Group of the Cape Supergroup
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mount ...
, as opposed to the nutrient-poor, sandy soils on the quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica ( silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical f ...
itic sandstone
Sandstone is a clastic sedimentary rock composed mainly of sand-sized (0.0625 to 2 mm) silicate grains. Sandstones comprise about 20–25% of all sedimentary rocks.
Most sandstone is composed of quartz or feldspar (both silicat ...
mountains, on either side of the valleys. However, the rainfall is, in general, low, bordering on the semiarid (or frankly semiarid in, for instance, the Little Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
). Agriculture, which includes viniculture and fruit-growing, therefore depends on irrigation from rivers with sources in the mountains, which are frequently covered in snow during winter. The Little Karoo is famous for its ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
farming, initially, in the late 1800s, for their feathers, but today includes ostrich leather and ostrich meat, which is very lean and particularly tasty.
The Cape Fold Mountains are separated from the Great Escarpment by an approximately 100–150 km wide plain known as the Lower Karoo (not to be confused with the "Little Karoo") at an altitude of about 600–800 m above sea level. Geologically and geographically the Cape Fold Mountains and the Great Escarpment are quite different and independent entities.
Coastline
South Africa's coastline is remarkably smooth, with very few natural harbours. The reason is that Southern Africa has been continuously uplifted for the past 180 million years, and especially so during the past 20 million years. The present coastline was therefore once part of the underwater continental shelf, which contains very few deep ravines or gorges. In contrast, a subsiding coastline, like Norway's, tends to become deeply indented where the sea has flooded old river gorges and glacial valleys.Regional divisions
Highveld
The Central Plateau is divided into several distinctly different regions (though with very vague boundaries), largely as a result of the rainfall distribution across South Africa: wet in the east and increasingly drier and more arid in the west. The wettest and most fertile portion of the Central Plateau is the Highveld, which occupies the central eastern portion of the Plateau. It is generally between 1,500 – 2,100 m above sea level, highest on the edge of the Escarpment to the east (theMpumalanga
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. ...
Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
), and sloping downwards to the south and west. Its southern boundary is often taken to be the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
, from where the continuation of the plateau is known as the Great Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
, except for a small strip just south of Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a population ...
which is often included in the Highveld. To the west the Highveld fades into the dry savannah of Griqualand West
Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, wh ...
, beyond which lies the Kalahari desert. This boundary is very vague. The Highveld therefore encompasses the entire Free State, and an adjoining strip of the Provinces to the north of it. It receives between 400 and 1200 mm of rain annually, and is largely a flat grassland plain. Much of the area is devoted to commercial farming, but it also contains South Africa's largest conurbation in Gauteng Province, the centre of the gold mining industry. But there are also important coal mines on the Highveld which are associated with South Africa's major electricity generating power stations.
The land is generally flat or gently undulating. Only a few rocky ridges protrude from this flatness: the Vredefort Dome
The Vredefort impact structure is the largest verified impact structure on Earth. The crater, which has since been eroded away, was around across when it was formed. The remaining structure, comprising the deformed underlying bedrock, is loca ...
, the Witwatersrand Ridge and the Magaliesberg
The Magaliesberg (historically also known as ''Macalisberg'' or ''Cashan Mountains'') of northern South Africa, is a modest but well-defined mountain range composed mainly of quartzites. It rises at a point south of the Pilanesberg (and the Pi ...
just north of Pretoria, from where the Highveld gives way to the Bushveld
The Bushveld (from af, bosveld, af, bos 'bush' and af, veld) is a sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa. It encompasses most of Limpopo Province and a small part of the North West Province of South Africa, the Central and Nort ...
to the north.
Lowveld
 The South African portion of the coastal strip between the Limpopo and Mpumalanga Drakensberg and the ocean, together with the Limpopo River valley, is called the Lowveld.Atlas of Southern Africa. (1984). pp. 13, 192, 195. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town These lowlands, below about altitude, form South Africa's northern border with
The South African portion of the coastal strip between the Limpopo and Mpumalanga Drakensberg and the ocean, together with the Limpopo River valley, is called the Lowveld.Atlas of Southern Africa. (1984). pp. 13, 192, 195. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town These lowlands, below about altitude, form South Africa's northern border with Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kal ...
and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
, where a 180‑million-year-old failed rift valley
A rift valley is a linear shaped lowland between several highlands or mountain ranges created by the action of a geologic rift. Rifts are formed as a result of the pulling apart of the lithosphere due to extensional tectonics. The linear d ...
cuts into Southern Africa's central plateau and locally obliterates the Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
. The Limpopo
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
and Save rivers run from the central African highlands via the Lowveld into the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
to the east. The Limpopo
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
Lowveld extends southwards, east of the Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
through Mpumalanga Province
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. I ...
and ultimately into eastern Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
. This southern limb of the Lowveld is bounded by South Africa's border with Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
to the east, and the north-eastern part of the Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
to the west. This region is generally hotter and less intensely cultivated than the Highveld.
The Lowveld used to be known as "fever country" because malaria
Malaria is a mosquito-borne infectious disease that affects humans and other animals. Malaria causes symptoms that typically include fever, tiredness, vomiting, and headaches. In severe cases, it can cause jaundice, seizures, coma, or death. ...
, carried by mosquitoes, was endemic to almost the entire area. Before the middle of the 20th century, the Lowveld was also home to the tsetse fly
Tsetse ( , or ) (sometimes spelled tzetze; also known as tik-tik flies), are large, biting flies that inhabit much of tropical Africa. Tsetse flies include all the species in the genus ''Glossina'', which are placed in their own family, Glos ...
, which transmits sleeping sickness
African trypanosomiasis, also known as African sleeping sickness or simply sleeping sickness, is an insect-borne parasitic infection of humans and other animals. It is caused by the species ''Trypanosoma brucei''. Humans are infected by two typ ...
to humans and nagana
Animal trypanosomiasis, also known as nagana and nagana pest, or sleeping sickness, is a disease of vertebrates. The disease is caused by trypanosomes of several species in the genus ''Trypanosoma'' such as ''Trypanosoma brucei''. '' Trypanosom ...
to animals, especially the horses of the travelers trying to reach the Highveld and Witwatersrand Gold Fields from Maputo
Maputo (), formerly named Lourenço Marques until 1976, is the capital, and largest city of Mozambique. Located near the southern end of the country, it is within of the borders with Eswatini and South Africa. The city has a population of 1,0 ...
.
The Lowveld is known for its high concentration of big game, including the larger animals, like African elephants, rhino, African buffalo, the big cats (lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
s, leopard
The leopard (''Panthera pardus'') is one of the five extant species in the genus '' Panthera'', a member of the cat family, Felidae. It occurs in a wide range in sub-Saharan Africa, in some parts of Western and Central Asia, Southern Russia, ...
s, and cheetah
The cheetah (''Acinonyx jubatus'') is a large cat native to Africa and central Iran. It is the fastest land animal, estimated to be capable of running at with the fastest reliably recorded speeds being , and as such has evolved specialized ...
s), the plains zebra
The plains zebra (''Equus quagga'', formerly ''Equus burchellii''), also known as the common zebra, is the most common and geographically widespread species of zebra. Its range is fragmented, but spans much of southern and eastern Africa south o ...
, and a wide variety of antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
, while the slow-flowing streams and wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
of the Lowveld are a haven for the hippo
The hippopotamus ( ; : hippopotamuses or hippopotami; ''Hippopotamus amphibius''), also called the hippo, common hippopotamus, or river hippopotamus, is a large semiaquatic mammal native to sub-Saharan Africa. It is one of only two extant ...
s and crocodile
Crocodiles (family Crocodylidae) or true crocodiles are large semiaquatic reptiles that live throughout the tropics in Africa, Asia, the Americas and Australia. The term crocodile is sometimes used even more loosely to include all extant me ...
s. The bird life is also astoundingly abundant and varied. This wildlife is particularly concentrated in the Kruger National Park
Kruger National Park is a South African National Park and one of the largest game reserves in Africa. It covers an area of in the provinces of Limpopo and Mpumalanga in northeastern South Africa, and extends from north to south and from ea ...
located in the eastern Lowveld areas of Mpumalanga
Mpumalanga () is a province of South Africa. The name means "East", or literally "The Place Where the Sun Rises" in the Swazi, Xhosa, Ndebele and Zulu languages. Mpumalanga lies in eastern South Africa, bordering Eswatini and Mozambique. ...
and Limpopo Province
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
s, along almost the entire border with Mozambique. But many private game farms and game reserves can also be found elsewhere in the Lowveld.
Bushveld
 The Lowveld partly overlaps with a dry savanna
The Lowveld partly overlaps with a dry savanna ecoregion
An ecoregion (ecological region) or ecozone (ecological zone) is an ecologically and geographically defined area that is smaller than a bioregion, which in turn is smaller than a biogeographic realm. Ecoregions cover relatively large areas of ...
known as the Bushveld
The Bushveld (from af, bosveld, af, bos 'bush' and af, veld) is a sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa. It encompasses most of Limpopo Province and a small part of the North West Province of South Africa, the Central and Nort ...
, a basin characterized by open grasslands with scattered trees and bushes. Elevation varies between 600 metres and about 900 metres above sea level. The Bushveld is one of the largest and best known layered igneous
Igneous rock (derived from the Latin word ''ignis'' meaning fire), or magmatic rock, is one of the three main rock types, the others being sedimentary and metamorphic. Igneous rock is formed through the cooling and solidification of magma or ...
mineral complexes in the world. Covering an area roughly 350 kilometres by 150 kilometres, the Bushveld has extensive deposits of platinum
Platinum is a chemical element with the symbol Pt and atomic number 78. It is a dense, malleable, ductile, highly unreactive, precious, silverish-white transition metal. Its name originates from Spanish , a diminutive of "silver".
Pla ...
and chromium
Chromium is a chemical element with the symbol Cr and atomic number 24. It is the first element in group 6. It is a steely-grey, lustrous, hard, and brittle transition metal.
Chromium metal is valued for its high corrosion resistance and hard ...
and significant reserves of copper
Copper is a chemical element with the symbol Cu (from la, cuprum) and atomic number 29. It is a soft, malleable, and ductile metal with very high thermal and electrical conductivity. A freshly exposed surface of pure copper has a pink ...
, fluorspar
Fluorite (also called fluorspar) is the mineral form of calcium fluoride, CaF2. It belongs to the halide minerals. It crystallizes in isometric cubic habit, although octahedral and more complex isometric forms are not uncommon.
The Mohs sca ...
, gold
Gold is a chemical element with the symbol Au (from la, aurum) and atomic number 79. This makes it one of the higher atomic number elements that occur naturally. It is a bright, slightly orange-yellow, dense, soft, malleable, and ductile ...
, nickel
Nickel is a chemical element with symbol Ni and atomic number 28. It is a silvery-white lustrous metal with a slight golden tinge. Nickel is a hard and ductile transition metal. Pure nickel is chemically reactive but large pieces are slow t ...
, and iron
Iron () is a chemical element with symbol Fe (from la, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 of the periodic table. It is, by mass, the most common element on Earth, right in ...
.
The northern edge of the Bushveld, where the plains rise to a series of high plateaus and low mountain ranges, form the southern edge of the Lowveld and the Limpopo River
The Limpopo River rises in South Africa and flows generally eastward through Mozambique to the Indian Ocean. The term Limpopo is derived from Rivombo (Livombo/Lebombo), a group of Tsonga settlers led by Hosi Rivombo who settled in the mountain ...
Valley in Northern Province. These mountains include the Waterberg, and the Soutpansberg Range. The Soutpansberg Range reaches an elevation of 1,700 meters before dropping off into the Limpopo River Valley and the border between South Africa and Zimbabwe
Zimbabwe (), officially the Republic of Zimbabwe, is a landlocked country located in Southeast Africa, between the Zambezi and Limpopo Rivers, bordered by South Africa to the south, Botswana to the south-west, Zambia to the north, and ...
. West of the Bushveld, Highveld, and Lowveld is the southern basin of the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
, which borders Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
and Botswana
Botswana (, ), officially the Republic of Botswana ( tn, Lefatshe la Botswana, label= Setswana, ), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. Botswana is topographically flat, with approximately 70 percent of its territory being the Kal ...
at an elevation of 600 meters to 900 meters.
Karoo
The western section of South Africa on the inland side of theCape Fold Mountains
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mou ...
is dominated by the Great Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
, a semi-desert region that is divided by the Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
into the Upper Karoo (at an elevation of 1,100–1,600 m) and the Lower Karoo (at an elevation of 600–800 m). Separated from the Great Karoo by the Swartberg
The Swartberg mountains (''black mountain'' in Afrikaans) are a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. It is composed of two main mountain chains running roughly east–west along the northern edge of the semi-arid Little ...
mountain range is the Little Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
.
 In the southwest, running parallel to the coastline, the mountains of the Cape Fold Belt form a series of ranges that run in the form of an "L" by a series running north–south, and another set running east–west, with the junction between the two at the
In the southwest, running parallel to the coastline, the mountains of the Cape Fold Belt form a series of ranges that run in the form of an "L" by a series running north–south, and another set running east–west, with the junction between the two at the Cape Peninsula
The Cape Peninsula ( af, Kaapse Skiereiland) is a generally mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean at the south-western extremity of the African continent. At the southern end of the peninsula are Cape Point and the Ca ...
. The north–south ranges, paralleling the Atlantic coastline, include the Cederberg
The Cederberg mountains are located near Clanwilliam, approximately 300 km north of Cape Town, South Africa at about . The mountain range is named after the endangered Clanwilliam cedar (''Widdringtonia wallichii''), which is a tree end ...
and the Groot Winterhoek
The Groot Winterhoek mountains are located in the Western Cape province of South Africa and are part of the Cape Fold Belt comprising a watershed area of 552,606 hectares. They rise to a maximum height of 2077 m just north of the town of Tulb ...
and have peaks close to 2,000 metres high. The east–west ranges, paralleling the southern coastline, include the Swartberg and the Langeberg
The Langeberg Range is a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Its highest peak is Keeromsberg at 2,075 m that lies 15 km northeast of the town of Worcester. Some of the highest peaks of the range are located just to ...
with peaks exceeding 2,200 metres. The mountains of the Cape Fold Belt form the southern and western boundaries of the Great Karoo. The other boundaries of the Great Karoo are arbitrary and ill-defined. To the north the Karoo grades into even more arid Bushmanland. To the north-east, the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
is often regarded as the boundary between Karoo and the Highveld. To the east the Karoo fades into the grasslands of the Eastern Midlands.
The town of Sutherland
Sutherland ( gd, Cataibh) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire (later c ...
is located in the Roggeveld region of the Upper Karoo, with midwinter temperatures as low as −15 °C, and is thought to be the coldest inhabited place in South Africa.
The Little Karoo is separated from the Great Karoo by the Swartberg mountain range. It lies in a 290 km long, narrow (40–60 km wide) valley in of the Cape Fold Mountains, with the Swartberg range to the north and the Langeberg
The Langeberg Range is a mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa. Its highest peak is Keeromsberg at 2,075 m that lies 15 km northeast of the town of Worcester. Some of the highest peaks of the range are located just to ...
- Outeniqua range to the south. It is as arid as the Great Karoo, except along the foothills of the Swartberg, which are well-watered by streams that cascade down the mountains. The Little Karoo is the centre of the Ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
farming industry, especially around the town of Oudtshoorn
Oudtshoorn (, ), the "ostrich capital of the world", is a town in the Western Cape province of South Africa, located between the Swartberg mountains to the north and the Outeniqua Mountains to the south. Two ostrich-feather booms, during 1865–1 ...
.
KwaZulu-Natal

KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is loca ...
is a South African Province that lies entirely below the Great Escarpment, which forms its western and south-western boundaries. It therefore constitutes part of the South African "Coastal Belt", which is, over much of this region, more than 220 km wide. The region can be subdivided into three distinct geographic areas. The lowland
Upland and lowland are conditional descriptions of a plain based on elevation above sea level. In studies of the ecology of freshwater rivers, habitats are classified as upland or lowland.
Definitions
Upland and lowland are portions of p ...
region along the Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
coast is extremely narrow in the south, widening in the northern part of the province, while the central Natal Midlands
The KwaZulu-Natal midlands is an inland area of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa that starts from Pietermaritzburg and ends before the Drakensberg mountain range.
Area
There are several small towns located in the midlands, including: Pietermaritzburg, ...
consist of an undulating hilly, 1,000 m high plateau
In geology and physical geography, a plateau (; ; ), also called a high plain or a tableland, is an area of a highland consisting of flat terrain that is raised sharply above the surrounding area on at least one side. Often one or more sides ...
, rising to 1,500 m towards the west, at the foot of the Great Escarpment. The Great Escarpment, known here as the Drakensberg
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
, together with the Lebombo Mountains
The Lebombo Mountains, also called Lubombo Mountains ( pt, Montes Libombos), are an , narrow range of mountains in Southern Africa. They stretch from Hluhluwe in KwaZulu-Natal in the south to Punda Maria in the Limpopo Province in South Africa in ...
in the north form the mountainous regions of the province.
 The coastal regions are typically covered with
The coastal regions are typically covered with subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
thickets, while the deeper ravines and steep slopes of the river valleys host Afromontane Forest. The midlands are covered in moist grasslands with isolated pockets of Afromontane Forest. The north consists, in the main, of moist savanna
A savanna or savannah is a mixed woodland- grassland (i.e. grassy woodland) ecosystem characterised by the trees being sufficiently widely spaced so that the canopy does not close. The open canopy allows sufficient light to reach the ground ...
habitat, whilst the Drakensberg region hosts mostly alpine
Alpine may refer to any mountainous region. It may also refer to:
Places Europe
* Alps, a European mountain range
** Alpine states, which overlap with the European range
Australia
* Alpine, New South Wales, a Northern Village
* Alpine National P ...
grassland
A grassland is an area where the vegetation is dominated by grasses ( Poaceae). However, sedge ( Cyperaceae) and rush ( Juncaceae) can also be found along with variable proportions of legumes, like clover, and other herbs. Grasslands occur na ...
.
Most of the KwaZulu-Natal Drakensberg are at an altitude of 2,000 m, but where they form the border with Lesotho
Lesotho ( ), officially the Kingdom of Lesotho, is a country landlocked as an enclave in South Africa. It is situated in the Maloti Mountains and contains the highest mountains in Southern Africa. It has an area of over and has a population ...
they rise to over 3,000 m. The Lebombo mountains are a long narrow range, not much higher than 700 m, that runs along Mozambique
Mozambique (), officially the Republic of Mozambique ( pt, Moçambique or , ; ny, Mozambiki; sw, Msumbiji; ts, Muzambhiki), is a country located in southeastern Africa bordered by the Indian Ocean to the east, Tanzania to the north, Malawi ...
's border with South Africa and Eswatini
Eswatini ( ; ss, eSwatini ), officially the Kingdom of Eswatini and formerly named Swaziland ( ; officially renamed in 2018), is a landlocked country in Southern Africa. It is bordered by Mozambique to its northeast and South Africa to its no ...
. From Eswatini the range continues south-eastwards for about 40 km into KwaZulu-Natal.
A great number of rivers arise in the Drakensberg. These have cut fairly deep valleys, and occasionally gorges, into the KwaZulu-Natal landscape giving the province a very hilly appearance. The Valley of a Thousand Hills
The Valley of a Thousand Hills is a valley between Pietermaritzburg and Durban, South Africa. The Umgeni River meets the Msunduzi River ( Duzi River) in the valley, and the Dusi Canoe Marathon is run through the area every year.
Geography
The V ...
, between Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
and Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; Zulu: umGungundlovu) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. Its Zulu name umGungundlovu ...
, is particularly spectacular. The largest of the rivers is the Tugela
The Tugela River ( zu, Thukela; af, Tugelarivier) is the largest river in KwaZulu-Natal Province, South Africa. With a total length of , it is one of the most important rivers of the country.
The river originates in Mont-aux-Sources of the Dr ...
, portion of whose waters are pumped over the escarpment on to the Highveld to supplement the water supply to the large industrial cities of Gauteng
Gauteng ( ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. The name in Sotho-Tswana languages means 'place of gold'.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts for only ...
.
The province contains rich areas of biodiversity of a range of flora and fauna. The iSimangaliso Wetland Park
iSimangaliso Wetland Park (previously known as the Greater St. Lucia Wetland Park) is situated on the east coast of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa, about 235 kilometres north of Durban by road. It is South Africa's third-largest protected are ...
and the uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park
The uKhahlamba-Drakensberg Park is a protected area in the KwaZulu-Natal province of South Africa, covering , and is part of a world heritage site. The park includes Royal Natal National Park, a provincial park, and covers part of the Drakensber ...
have been declared UNESCO
The United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization is a List of specialized agencies of the United Nations, specialized agency of the United Nations (UN) aimed at promoting world peace and security through international coope ...
World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
s. The iSimangaliso Wetland Park, along with uKhahlamba Drakensberg Park and Ndumo, are wetlands
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in the soils. The p ...
of international importance for migratory species, and are designated as Ramsar sites
A Ramsar site is a wetland site designated to be of international importance under the Ramsar Convention,8 ha (O)
*** Permanent 8 ha (P)
*** Seasonal Intermittent < 8 ha(Ts)
** Marshes on inorganic soils:
*** Permanent (herb dominated) (Tp)
*** P ...
. South Africa signed the 1971 Ramsar Convention
The Ramsar Convention on Wetlands of International Importance Especially as Waterfowl Habitat is an international treaty for the conservation and sustainable use of Ramsar sites (wetlands). It is also known as the Convention on Wetlands. It ...
to try to conserve and protect important wetlands because of their importance to habitats and numerous species.
The region has a varied yet verdant climate thanks to its diverse, complex topography. Generally, the coast is subtropical
The subtropical zones or subtropics are geographical and climate zones to the north and south of the tropics. Geographically part of the temperate zones of both hemispheres, they cover the middle latitudes from to approximately 35° north a ...
with inland regions becoming progressively cooler in winter, but hotter in summer (except on the Escarpment). Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
on the coast has an average annual rainfall of 1010 mm. The average midday temperature during summer (January–March) is 28 °C, with the minimum temperatures in the early morning averaging 21 °C. In winter (June–August) the average maximum temperature is 23 °C, and the minimum is 11 °C. The summer temperatures in Pietermaritzburg
Pietermaritzburg (; Zulu: umGungundlovu) is the capital and second-largest city in the province of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa. It was founded in 1838 and is currently governed by the Msunduzi Local Municipality. Its Zulu name umGungundlovu ...
are similar to those in Durban, but it is considerably cooler in winter. The temperature in Ladysmith Ladysmith may refer to:
* Ladysmith, KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa
* Ladysmith, British Columbia, Canada
* Ladysmith, Wisconsin, United States
* Ladysmith, New South Wales, Australia
* Ladysmith, Virginia, United States
* Ladysmith Island, Queenslan ...
, further inland, in the Tugela River Valley, reaches 30 °C in the summer, but may drop below freezing point on winter evenings. The Drakensberg can experience heavy winter snow, with light snow occasionally experienced on the highest peaks in summer. The Zululand coastal region, in the north of the province, has a tropical climate with high humidities, supporting many sugar cane
Sugarcane or sugar cane is a species of (often hybrid) tall, perennial grass (in the genus '' Saccharum'', tribe Andropogoneae) that is used for sugar production. The plants are 2–6 m (6–20 ft) tall with stout, jointed, fibrous stalk ...
farms.
Beaches of KwaZulu-Natal are of world-class quality. The warm coastal climate means that visitors are attracted to them all year round. Some of the visitors, however, come for the annual late-autumn or early-winter "sardine run
The KwaZulu-Natal sardine run of southern Africa occurs from May through July when billions of sardines – or more specifically the Southern African pilchard ''Sardinops sagax'' – spawn in the cool waters of the Agulhas Bank and move northwar ...
" along the KwaZulu-Natal coastline, south of Durban. Referred to as "the greatest shoal on earth", the sardine run occurs when millions of sardine
"Sardine" and "pilchard" are common names for various species of small, oily forage fish in the herring family Clupeidae. The term "sardine" was first used in English during the early 15th century, a folk etymology says it comes from the It ...
s migrate from their spawning
Spawn is the eggs and sperm released or deposited into water by aquatic animals. As a verb, ''to spawn'' refers to the process of releasing the eggs and sperm, and the act of both sexes is called spawning. Most aquatic animals, except for aquat ...
grounds south of the southern tip of Africa northward along the Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape is one of the provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, but its two largest cities are East London and Gqeberha.
The second largest province in the country (at 168,966 km2) after Northern Cape, it was formed in ...
coastline toward KwaZulu-Natal. They follow a route close inshore, often resulting in many fish washing up on beaches. The huge shoal of tiny fish can stretch for many kilometres; it is preyed upon by thousands of predators, including game fish
Game fish, sport fish or quarry refer to popular fish pursued by recreational anglers, and can be freshwater or saltwater fish. Game fish can be eaten after being caught, or released after capture. Some game fish are also targeted commercial ...
, shark
Sharks are a group of elasmobranch fish characterized by a cartilaginous skeleton, five to seven gill slits on the sides of the head, and pectoral fins that are not fused to the head. Modern sharks are classified within the clade Selachi ...
s, dolphins, and seabird
Seabirds (also known as marine birds) are birds that are adapted to life within the marine environment. While seabirds vary greatly in lifestyle, behaviour and physiology, they often exhibit striking convergent evolution, as the same envir ...
s. Usually the shoals break up and the fish disappear into deeper water around Durban. Scientists have been unable to answer many questions surrounding this exceptional seasonal event.
Bushmanland
 Bushmanland is an arid area inland from
Bushmanland is an arid area inland from Namaqualand
Namaqualand (khoekhoe: "Nama-kwa" meaning Nama Khoe people's land) is an arid region of Namibia and South Africa, extending along the west coast over and covering a total area of . It is divided by the lower course of the Orange River into ...
(see below). Its northern boundary is the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
beyond which lies Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
. In the south it grades into the north-western part of the Great Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ext ...
. To the west lies Griqualand West
Griqualand West is an area of central South Africa with an area of 40,000 km2 that now forms part of the Northern Cape Province. It was inhabited by the Griqua people – a semi-nomadic, Afrikaans-speaking nation of mixed-race origin, wh ...
. It is probably the most inhospitable area in South Africa, because of its aridity, infertile soil and highly saline groundwater. Together with the Kalahari Desert
The Kalahari Desert is a large semi-arid sandy savanna in Southern Africa extending for , covering much of Botswana, and parts of Namibia and South Africa.
It is not to be confused with the Angolan, Namibian, and South African Namib coastal d ...
to the north-east, its rainfall is the most highly variable (in percentage deviation from the annual average), and its temperature range the greatest (difference between the average temperature in January and in July) in South Africa.''Atlas of Southern Africa''. (1984). p. 19. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town Its wildlife however, both fauna and flora, though sparse, is full of interest. Although the veld is too arid to bloom like that of the West Coast of Namaqualand, even when there is some spring rain, what does appear is highly unusual and often hauntingly beautiful.
A highly productive base metal mine on the Aggeneys
Aggeneys is a mining town established in 1976 on a farm of that name, situated between Pofadder and Springbok in the Northern Cape, South Africa.
Origin of the name
It has been stated that "no-one is quite certain of the origin of the name Agg ...
Farm close to the N14 highway between Upington
Upington ( Nama: //Khara hais) is a town founded in 1873 and located in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, on the banks of the Orange River. The town was originally called Olijvenhoutsdrift ('Olive wood drift'), due to the abundance of ...
and Springbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
exploits an ore rich in zinc, lead, copper, and silver since 1977. Close by, to the east, is Ghaamsberg which has very large zinc deposits, but the ore is low-grade and, therefore, at present, unprofitable to large scale mining.Norman, N & Whitfield, G. (2006) ''Geological Journeys''. p. 217, 270-273. Struik Publishers, Cape Town
Vaalputs, a nuclear waste repository, has been sited between Bushmanland and the north-west of the Great Karoo, and acts as a ''de facto'' nature reserve.
Namaqualand
Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
. The region extends into Namibia, north of the Orange River, where it is known as "Great Namaqualand", or "Namaland". The South African portion of Namaqualand is known as "Little Namaqualand", and falls within the Northern Cape Province
The Northern Cape is the largest and most sparsely populated province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley. It includes the Kalahari Gemsbok National Park, part of the Kgalagadi ...
. The region is sparsely populated, mainly by Afrikaans speaking people of Nama, and Khoikhoi
Khoekhoen (singular Khoekhoe) (or Khoikhoi in the former orthography; formerly also '' Hottentots''"Hottentot, n. and adj." ''OED Online'', Oxford University Press, March 2018, www.oed.com/view/Entry/88829. Accessed 13 May 2018. Citing G. S. ...
descent. The original Nama and Khoikhoi languages are spoken in only a few remote areas. The main economic activities are mining, and fishing along the coast.
Some of the more prominent towns in this area are Springbok
The springbok (''Antidorcas marsupialis'') is a medium-sized antelope found mainly in south and southwest Africa. The sole member of the genus ''Antidorcas'', this bovid was first described by the German zoologist Eberhard August Wilhelm ...
, being the capital of this region, as well as Kleinzee
Kleinzee is a small village on the west coast of the Northern Cape province in South Africa at the mouth of the Buffels River. It is just south of Grootmis, 72 km south-east of Port Nolloth and 105 km west of Springbok. Previously a clo ...
and Koiingnaas
Koingnaas is a village in Namakwa District Municipality in the Northern Cape province of South Africa. It is located 65 km south of Kleinzee.
Established in 1970, Koingnaas was once a flourishing diamond-mining town and satellite town to K ...
, both private mining towns owned by De Beers Diamond Mines. This area is rich in alluvial diamonds, deposited along the coast by the Orange River. Oranjemund
Oranjemund (German for ''"Mouth of Orange"'') is a diamond mining town of 4,000 inhabitants situated in the ǁKaras Region of the extreme southwest of Namibia, on the northern bank of the Orange River mouth at the border to South Africa.
Histor ...
is another mining town along this coast, situated in Namibia, but very much on the border. As the name suggests, it is at the mouth of the Orange River which forms the border between South Africa and Namibia. The town of Alexander Bay is located on the opposite side of the river mouth (i.e. in South Africa) and is linked to Oranjemund by the Ernest Oppenheimer
Sir Ernest Oppenheimer (22 May 1880 – 25 November 1957), KStJ was a diamond and gold mining entrepreneur, financier and philanthropist, who controlled De Beers and founded the Anglo American Corporation of South Africa.
Career
Ernest Oppenhe ...
Bridge. Other links crossing the river further upstream are a reintroduced pontoon at Sendelingsdrift in the Richtersveld National Park, and road bridges at Vioolsdrif
Vioolsdrif is a village on the Orange River in the north-western Namaqualand area of South Africa.
Origin of name
The name in Afrikaans means 'the ford (shallow river crossing) of the violin'. It is reportedly named after Jan Viool ("John Violi ...
(the main border crossing between the two countries) and at the remote border crossing of Onseepkans
Onseepkans is a small settlement on the banks of the Orange River in Northern Cape Province, South Africa. It is a border post with Namibia for traffic between Pofadder in South Africa and Keetmanshoop in Namibia. The name either originated fro ...
.
A vibrant fishing industry is found along this stretch of the South African west coast, especially in Port Nolloth
Port Nolloth is a town and small domestic seaport in the Namaqualand region on the northwestern coast of South Africa, northwest of Springbok. It is the seat of the Richtersveld Local Municipality.
The port was previously a transshipment point ...
, which is also a major resort town for people living in the interior of South Africa (e.g. Gauteng
Gauteng ( ) is one of the nine provinces of South Africa. The name in Sotho-Tswana languages means 'place of gold'.
Situated on the Highveld, Gauteng is the smallest province by land area in South Africa. Although Gauteng accounts for only ...
), and Hondeklipbaai
Hondeklip Bay ( af, Hondeklipbaai, which translates as ''dog stone bay'') is a coastal village in the Namakwa district of the Northern Cape province of South Africa. It lies about 95 km south west of the district capital Springbok.
This v ...
, (or Dogstonebay), so called because of a large boulder outside the town which, when viewed correctly, looks vaguely like a dog sitting down.
The copper bangles worn by the Khoikhoi aroused the interests of the Dutch officials of the Dutch settlement established by Jan van Riebeeck in the Cape in 1652. Several expeditions were consequently mounted to find the source of this copper. A mineshaft was dug in the "Copper Mountains" in northern Namaqualand in 1685, which still can be seen near the disused Carolusberg mine a few kilometers east of Springbok. However commercial mining was only started in 1859, and over the next 140 years vast quantities of ore have been extracted from 23 mines in the area. Springbok and its surrounding towns ( Nababeep and Okiep
Okiep is a small town in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, and was in the 1870s ranked as having the richest copper mine in the world. The town is on the site of a spring that was known in the Khoekhoe language of the Nama people as ''U-g ...
) were the center of this mining activity. But, in the early 2000s the last mine was closed.Van Deventer, L. & McLennan, B. (eds) (2010). "The Little Karoo" in ''South Africa by Road, a Regional Guide''. pp. 190–192. Struik Publishers, Cape Town. However, about 115 km further inland, in Bushmanland (see above), a large new mine is extracting copper, lead, zinc, and silver from the "Black Mountain" (originally "Swartberg") deposits at Aggeneys
Aggeneys is a mining town established in 1976 on a farm of that name, situated between Pofadder and Springbok in the Northern Cape, South Africa.
Origin of the name
It has been stated that "no-one is quite certain of the origin of the name Agg ...
since 1977. High grade granite is mined in several places (e.g. near Kamieskroon, and Concordia) in this granite-rich landscape.
Namaqualand is popular with both local and international tourists during early springtime (August - September), when for a short period this normally arid area becomes covered with a kaleidoscope of colour during the flowering season. This is known throughout South Africa as the Namaqualand daisy season, when orange and white daisies, as well as hundreds of other flowering species, spring up from a previously barren landscape. A part of Little Namaqualand, known as the Richtersveld
The Richtersveld is a desert landscape characterised by rugged kloofs and high mountains, situated in the north-western corner of South Africa’s Northern Cape province. It is full of changing scenery from flat, sandy, coastal plains, to craggy ...
, is a national park and a World Heritage Site
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for ...
, while the often-visited Namaqua National Park
Namaqua National Park is a South African national park situated approximately 495 km north of Cape Town and 22 km northwest of Kamieskroon. It has an area of more than 1300 km2.Van Deventer, M. and J.A.J. Nel. 2006. Habitat, food, ...
and the Goegap Nature Reserve are located short distances from Kamieskroon and Springbok, respectively.
Surrounding oceans
 The vast majority of South Africa's border consists of the ocean—or two oceans, which, according to the
The vast majority of South Africa's border consists of the ocean—or two oceans, which, according to the International Hydrographic Organization
The International Hydrographic Organization (IHO) is an intergovernmental organisation representing hydrography. , the IHO comprised 98 Member States.
A principal aim of the IHO is to ensure that the world's seas, oceans and navigable waters ...
, officially meet at Cape Agulhas
Cape Agulhas (; pt, Cabo das Agulhas , "Cape of the Needles") is a rocky headland in Western Cape, South Africa.
It is the geographic southern tip of the African continent and the beginning of the dividing line between the Atlantic and Indian ...
, the most southern point of Africa. Its territory includes Marion and Prince Edward Islands
The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island (named after Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, 1724–1772) and Prince Edward Islan ...
, nearly south of Cape Town
Cape Town ( af, Kaapstad; , xh, iKapa) is one of South Africa's three capital cities, serving as the seat of the Parliament of South Africa. It is the legislative capital of the country, the oldest city in the country, and the second largest ...
in the sub-antarctic
The sub-Antarctic zone is a region in the Southern Hemisphere, located immediately north of the Antarctic region. This translates roughly to a latitude of between 46° and 60° south of the Equator. The subantarctic region includes many islands ...
Indian Ocean
The Indian Ocean is the third-largest of the world's five oceanic divisions, covering or ~19.8% of the water on Earth's surface. It is bounded by Asia to the north, Africa to the west and Australia to the east. To the south it is bounded by ...
.
The cold Benguela current is a mineral-rich upwelling
Upwelling is an physical oceanography, oceanographic phenomenon that involves wind-driven motion of dense, cooler, and usually nutrient-rich water from deep water towards the ocean surface. It replaces the warmer and usually nutrient-depleted ...
current, which flows away to the north along the western coastline, after having come up from the cold depths of the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
. Plankton
Plankton are the diverse collection of organisms found in water (or air) that are unable to propel themselves against a current (or wind). The individual organisms constituting plankton are called plankters. In the ocean, they provide a cruc ...
grow in these fertile waters, and support large numbers of fish, and therefore a prosperous (in the past) fishing industry. Over-fishing has, however, reduced the importance of this fishing industry both for the local as well as the country's economy. The east coast has the north-to-south Mozambique/Agulhas Current
The Agulhas Current () is the western boundary current of the southwest Indian Ocean. It flows south along the east coast of Africa from 27°S to 40°S. It is narrow, swift and strong. It is suggested that it is the largest western boundary curren ...
, which provides warm waters. These two currents have a major effect on the country's climate
Climate is the long-term weather pattern in an area, typically averaged over 30 years. More rigorously, it is the mean and variability of meteorological variables over a time spanning from months to millions of years. Some of the meteorologi ...
, the ready evaporation of the eastern seas providing generous rainfall while the Benguela current retains its moisture to cause desert conditions in the west.
Several small rivers run into the sea along the coastline, but none is navigable and none provides useful natural harbours. The coastline itself, being fairly smooth, provides only one good natural harbour at Saldanha Bay
Saldanha Bay ( af, Saldanhabaai) is a natural harbour on the south-western coast of South Africa. The town that developed on the northern shore of the bay, also called Saldanha, was incorporated with five other towns into the Saldanha Bay Local ...
north of Cape Town. A lack of fresh water
Fresh water or freshwater is any naturally occurring liquid or frozen water containing low concentrations of dissolved salts and other total dissolved solids. Although the term specifically excludes seawater and brackish water, it does incl ...
, however, prevented permanent settlement here until relatively recently. The Bay of Natal looks, on the map, like a good natural harbour, but, in its natural state, it was dry at low tide. Nevertheless, busy harbours now exist at Cape Town, Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha (), formerly Port Elizabeth and colloquially often referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality, So ...
, East London
East or Orient is one of the four cardinal directions or points of the compass. It is the opposite direction from west and is the direction from which the Sun rises on the Earth.
Etymology
As in other languages, the word is formed from the ...
, Durban
Durban ( ) ( zu, eThekwini, from meaning 'the port' also called zu, eZibubulungwini for the mountain range that terminates in the area), nicknamed ''Durbs'',Ishani ChettyCity nicknames in SA and across the worldArticle on ''news24.com'' from ...
in the Bay of Natal, and Richards Bay. Saldanha Bay is today an important harbour at the end of the Sishen–Saldanha railway line
The Sishen–Saldanha railway line, also known as the Ore Export Line (OREX), is an heavy-haul railway line in South Africa. It connects iron ore mines near Sishen in the Northern Cape with the port at Saldanha Bay in the Western Cape. It is u ...
for the export of Iron ore from the interior.
Climate
Garden Route
The Garden Route (Afrikaans: ''Tuinroete'') is a stretch of the south-eastern coast of South Africa which extends from Witsand in the Western Cape to the border of Tsitsikamma Storms River in the Eastern Cape. The name comes from the verdan ...
), and winter rainfall in the west (on the Cape Peninsula and its surrounds). The summers are warm to hot, while the winter temperatures can vary, depending on locality from bitterly cold to cool. Thus the Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ex ...
, which occupies a large part of the western Central Plateau, has a climate which is extremely hot in summer and bitterly cold in winter. In contrast, the eastern coastline on the Indian Ocean is lush, well watered and warmed by the Mozambique Current; patches of Southern Africa mangroves
The Southern Africa mangroves are mangrove ecoregion on the Mozambique's southernmost coast and the eastern coast of South Africa.
Location and description
These mangroves grow in the mouths of rivers on the Indian Ocean coast of South Africa, w ...
grow along this coast.
The southern coast, part of which is known as the Garden Route
The Garden Route (Afrikaans: ''Tuinroete'') is a stretch of the south-eastern coast of South Africa which extends from Witsand in the Western Cape to the border of Tsitsikamma Storms River in the Eastern Cape. The name comes from the verdan ...
, is temperate
In geography, the temperate climates of Earth occur in the middle latitudes (23.5° to 66.5° N/S of Equator), which span between the tropics and the polar regions of Earth. These zones generally have wider temperature ranges throughout ...
and green. The Cape Peninsula
The Cape Peninsula ( af, Kaapse Skiereiland) is a generally mountainous peninsula that juts out into the Atlantic Ocean at the south-western extremity of the African continent. At the southern end of the peninsula are Cape Point and the Ca ...
and surrounds have a Mediterranean climate
A Mediterranean climate (also called a dry summer temperate climate ''Cs'') is a temperate climate sub-type, generally characterized by warm, dry summers and mild, fairly wet winters; these weather conditions are typically experienced in the ...
, with cool, wet winters and warm, dry summers (becoming hotter in interior valleys). Snow commonly falls in winter on the higher ground of the Cape Fold Mountains
The Cape Fold Belt is a fold and thrust belt of late Paleozoic age, which affected the sequence of sedimentary rock layers of the Cape Supergroup in the southwestern corner of South Africa. It was originally continuous with the Ventana Mou ...
, during winter. The Cape Peninsula has a reputation for its wind: the dry "South-Easter" which blows almost incessantly in summer (December–February), and the "North-Wester" which accompanies the cold fronts that roll in from the Atlantic during winter (June–August). The vegetation of the Cape area consists of fynbos
Fynbos (; meaning fine plants) is a small belt of natural shrubland or heathland vegetation located in the Western Cape and Eastern Cape provinces of South Africa. This area is predominantly coastal and mountainous, with a Mediterranean clim ...
, some grassland and Albany thickets
The Albany thickets is an ecoregion of dense woodland in southern South Africa, which is concentrated around the Albany region of the Eastern Cape (whence the region's name originates).
Geography
The thickets grow on well-drained sandy soils i ...
.
The eastern section of the Karoo does not extend as far north as the western part, giving way to the flat landscape of the Free State, which – though still semi-arid – receives somewhat more rain. North of the Vaal River
The Vaal River ( ; Khoemana: ) is the largest tributary of the Orange River in South Africa. The river has its source near Breyten in Mpumalanga province, east of Johannesburg and about north of Ermelo and only about from the Indian Ocean. ...
the Highveld is better watered, with an annual rainfall of and a high altitude (around ) which mitigates the extremes of heat of an inland area at this latitude. Winters are cold, though snow is rare.
Further north and to the east, especially where a drop in altitude beyond the escarpment gives the Lowveld
Veld ( or ), also spelled veldt, is a type of wide open rural landscape in :Southern Africa. Particularly, it is a flat area covered in grass or low scrub, especially in the countries of South Africa, Lesotho, Eswatini, Zimbabwe and Botswa ...
its name, the temperature rises. The Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reac ...
slices through the extreme north. Here one finds the typical South African Bushveld
The Bushveld (from af, bosveld, af, bos 'bush' and af, veld) is a sub-tropical woodland ecoregion of Southern Africa. It encompasses most of Limpopo Province and a small part of the North West Province of South Africa, the Central and Nort ...
.
There is ski
A ski is a narrow strip of semi-rigid material worn underfoot to glide over snow. Substantially longer than wide and characteristically employed in pairs, skis are attached to ski boots with ski bindings, with either a free, lockable, or partia ...
ing in winter in the high mountainous regions: the Drakensberg mountains
The Drakensberg (Afrikaans: Drakensberge, Zulu: uKhahlambha, Sotho: Maluti) is the eastern portion of the Great Escarpment, which encloses the central Southern African plateau. The Great Escarpment reaches its greatest elevation – within t ...
that form the eastern escarpment along the KwaZulu-Natal/Lesotho border, and on the Hex River Mountains
The Hex River Mountains ( af, Hexrivierberge) make up the second highest mountain range in the Western Cape province of South Africa and are located 120 kilometres (75 miles) north-east of Cape Town. They form part of a large anticline in the Ca ...
of the Cape Fold Belt, but the coldest place in the country is Sutherland
Sutherland ( gd, Cataibh) is a historic county, registration county and lieutenancy area in the Highlands of Scotland. Its county town is Dornoch. Sutherland borders Caithness and Moray Firth to the east, Ross-shire and Cromartyshire (later c ...
in the western Roggeveld region of the Upper Karoo, with minimum midwinter temperatures as low as −15 °C. The deep interior provides the hottest temperatures: in 1948 the mercury hit in the Northern Cape
The Northern Cape is the largest and most sparsely populated province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley. It includes the Kalahari Gemsbok National Park, part of the Kgalagadi ...
Kalahari near Upington
Upington ( Nama: //Khara hais) is a town founded in 1873 and located in the Northern Cape province of South Africa, on the banks of the Orange River. The town was originally called Olijvenhoutsdrift ('Olive wood drift'), due to the abundance of ...
.
Climate change
Climate change in South Africa
Climate change in South Africa is leading to increased temperatures and rainfall variability. Evidence shows that extreme weather events are becoming more prominent due to climate change.Republic of South Africa, National Climate Change Adaptation ...
is expected to bring considerable warming and drying to much of this already semi-arid region
A semi-arid climate, semi-desert climate, or steppe climate is a dry climate sub-type. It is located on regions that receive precipitation below potential evapotranspiration, but not as low as a desert climate. There are different kinds of semi-ar ...
, with greater frequency and intensity of extreme weather events such as heatwaves
A heat wave, or heatwave, is a period of excessively hot weather, which may be accompanied by high humidity, especially in oceanic climate countries. While definitions vary, a heat wave is usually measured relative to the usual climate in the ...
, flooding and drought. According to computer generated climate modelling
Numerical climate models use quantitative methods to simulate the interactions of the important drivers of climate, including atmosphere, oceans, land surface and ice. They are used for a variety of purposes from study of the dynamics of the cl ...
produced by the South African National Biodiversity Institute
The South African National Biodiversity Institute (SANBI) is an organisation established in 2004 in terms of the National Environmental Management: Biodiversity Act, No 10 of 2004, under the South African Department of Environmental Affairs ( ...
parts of southern Africa will see an increase in temperature by about one degree Celsius along the coast to more than four degrees Celsius in the already hot hinterland such as the Northern Cape
The Northern Cape is the largest and most sparsely populated province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley. It includes the Kalahari Gemsbok National Park, part of the Kgalagadi ...
in late spring and summertime by 2050. The Cape Floral Kingdom, identified as one of the global biodiversity hotspots
A biodiversity hotspot is a biogeographic region with significant levels of biodiversity that is threatened by human habitation. Norman Myers wrote about the concept in two articles in ''The Environmentalist'' in 1988 and 1990, after which the ...
, is predicted to be hit very hard by climate change. Drought, increased intensity and frequency of fire and climbing temperatures are expected to push many rare species towards extinction.
Multiple entities are working to combat the effects of degradation and drought. In the Port Elizabeth
Gqeberha (), formerly Port Elizabeth and colloquially often referred to as P.E., is a major seaport and the most populous city in the Eastern Cape province of South Africa. It is the seat of the Nelson Mandela Bay Metropolitan Municipality, So ...
region, national NGO Living Lands had in cooperation with an agricultural insurance company, planted 3.7 million trees as of late 2015, in order to restore the water catchment system and halt erosion.
Environmental issues
South Africa has lost a large area of natural habitat in the last four decades, primarily due to overpopulation, sprawling development patterns and deforestation during the 19th century. South Africa is one of the worst affected countries in the world when it comes to invasion by alien species with many (e.g.black wattle
Black wattle is the common name for a number of species of trees that are native to Australia, as listed below:
*''Acacia aulacocarpa''
*''Acacia auriculiformis'', also known as Darwin Black Wattle or northern black wattle;
*''Acacia concurrens ...
, Port Jackson willow, '' Hakea'', ''Lantana
''Lantana'' () is a genus of about 150 species of perennial flowering plants in the verbena family, Verbenaceae. They are native to tropical regions of the Americas and Africa but exist as an introduced species in numerous areas, especially in ...
'' and '' Jacaranda'') posing a significant threat to the native biodiversity and the already scarce water resources. The original temperate forest
A temperate forest is a forest found between the tropical and boreal regions, located in the temperate zone. It is the second largest biome on our planet, covering 25% of the world's forest area, only behind the boreal forest, which covers abou ...
found by the first European settlers was exploited ruthlessly until only small patches remained. Currently, South African hardwood trees like real yellowwood (''Podocarpus latifolius''), stinkwood Stinkwood, german ''Stinkholz'', french ''Bois Puant'', is the common name for a number of trees or shrubs which have wood or plant parts with an unpleasant odour, including:
*'' Anagyris foetida''; Southern Europe
*'' Bignonia callistegioides'' (c ...
(''Ocotea bullata''), and South African black ironwood (''Olea laurifolia'') are under government protection. Statistics from the South African Environmental Affairs department show a record 1215 rhinos were killed in 2014.
Extreme points
This is a list of the extreme points of South Africa, the points that are farther north, south, east or west than any other location in the country. ;Including the Prince Edward Islands * Northernmost Point: Over Vlakte farm, Vhembe District Municipality,Limpopo Province
Limpopo is the northernmost province of South Africa. It is named after the Limpopo River, which forms the province's western and northern borders. The capital and largest city in the province is Polokwane, while the provincial legislature ...
()
* Southernmost Point: Marion Island
The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island (named after Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, 1724–1772) and Prince Edward Isla ...
, Prince Edward Islands
The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island (named after Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, 1724–1772) and Prince Edward Islan ...
()
* Westernmost Point: Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
Mouth (near Alexander Bay), Northern Cape
The Northern Cape is the largest and most sparsely populated province of South Africa. It was created in 1994 when the Cape Province was split up. Its capital is Kimberley. It includes the Kalahari Gemsbok National Park, part of the Kgalagadi ...
()
* Easternmost Point: Prince Edward Island
Prince Edward Island (PEI; ) is one of the thirteen provinces and territories of Canada. It is the smallest province in terms of land area and population, but the most densely populated. The island has several nicknames: "Garden of the Gulf", ...
, Prince Edward Islands
The Prince Edward Islands are two small uninhabited islands in the sub-Antarctic Indian Ocean that are part of South Africa. The islands are named Marion Island (named after Marc-Joseph Marion du Fresne, 1724–1772) and Prince Edward Islan ...
()
;South African mainland
* Northernmost Point: Over Vlakte farm, Limpopo Province
* Southernmost Point: Cape Agulhas
Cape Agulhas (; pt, Cabo das Agulhas , "Cape of the Needles") is a rocky headland in Western Cape, South Africa.
It is the geographic southern tip of the African continent and the beginning of the dividing line between the Atlantic and Indian ...
, Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 202 ...
()
* Westernmost Point: Orange River Mouth, Northern Cape
* Easternmost Point: beach below Monte Ouro (near Kosi Bay
Kosi Bay is a series of four interlinked lakes in the Maputaland area of KwaZulu-Natal, South Africa.
Ecology
The lakes form part of the iSimangaliso Wetland Park, a UNESCO World Heritage Site.
The closest town is Manguzi, some away from it. K ...
), KwaZulu-Natal
KwaZulu-Natal (, also referred to as KZN and known as "the garden province") is a province of South Africa that was created in 1994 when the Zulu bantustan of KwaZulu ("Place of the Zulu" in Zulu) and Natal Province were merged. It is loca ...
()
* South-Westernmost Point: Cape of Good Hope
The Cape of Good Hope ( af, Kaap die Goeie Hoop ) ;''Kaap'' in isolation: pt, Cabo da Boa Esperança is a rocky headland on the Atlantic coast of the Cape Peninsula in South Africa.
A common misconception is that the Cape of Good Hope is ...
, Western Cape
The Western Cape is a province of South Africa, situated on the south-western coast of the country. It is the fourth largest of the nine provinces with an area of , and the third most populous, with an estimated 7 million inhabitants in 202 ...
()
* South Easternmost Point: Shebeen Point, Eastern Cape
The Eastern Cape is one of the provinces of South Africa. Its capital is Bhisho, but its two largest cities are East London and Gqeberha.
The second largest province in the country (at 168,966 km2) after Northern Cape, it was formed in ...
()
See also
*Provinces of South Africa
South Africa is divided into nine provinces. On the eve of the 1994 general election, South Africa's former homelands, also known as Bantustans, were reintegrated, and the four existing provinces were divided into nine. The twelfth, thirteenth ...
*Districts of South Africa
The nine provinces of South Africa are divided into 52 districts (sing. district, tn, kgaolo; st, setereke; nso, selete; af, distrikte; zu, isifunda; nr, isiyingi; xh, isithili; ss, sigodzi; ve, tshiṱiriki; ts, xifundza), which are ...
*Municipalities of South Africa
Local government in South Africa consists of municipalities ( tn, bommasepala; st, bomasepala; nso, bommasepala; af, munisipaliteite; zu, ngomasipala; Southern Ndebele: ''bomasipala''; xh, ngoomasipala; ss, bomasipala; ve, vhomasipala; ...
*List of mountains in South Africa
List of Mountains in South Africa, Lesotho and Eswatini is a general list of mountains in South Africa, Lesotho and Eswatini with elevation. This list includes mountains in two other sovereign states, in the Stormberg-Drakensberg range, where t ...
*List of rivers of South Africa
This is a list of rivers in South Africa.
It is quite common to find the Afrikaans word ''-rivier'' as part of the name. Another common suffix is "''-kamma''", from the Khoisan term for "river"
Meiring, Barbara"South African Toponymic Guideline ...
* Summary of South Africa's Geography
References
*''Some material in this article is adapted fromthe World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
2006.''
External links
* * * * * {{DEFAULTSORT:Geography of South Africa