Namib Desert on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Namib ( ; pt, Namibe) is a coastal
desert
A desert is a barren area of landscape where little precipitation occurs and, consequently, living conditions are hostile for plant and animal life. The lack of vegetation exposes the unprotected surface of the ground to denudation. About on ...
in Southern Africa
Southern Africa is the southernmost subregion of the African continent, south of the Congo and Tanzania. The physical location is the large part of Africa to the south of the extensive Congo River basin. Southern Africa is home to a number o ...
. The name is of Khoekhoegowab origin and means "vast place". According to the broadest definition, the Namib stretches for more than along the Atlantic coasts of Angola
, national_anthem = "Angola Avante"()
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capital = Luanda
, religion =
, religion_year = 2020
, religion_ref =
, coordinat ...
, Namibia
Namibia (, ), officially the Republic of Namibia, is a country in Southern Africa. Its western border is the Atlantic Ocean. It shares land borders with Zambia and Angola to the north, Botswana to the east and South Africa to the south and ea ...
, and South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
, extending southward from the Carunjamba River in Angola, through Namibia and to the Olifants River in Western Cape, South Africa. The Namib's northernmost portion, which extends from the Angola-Namibia border, is known as Moçâmedes Desert
The Moçâmedes Desert is a desert located in the deep southwest of Angola, near the border with Namibia. The desert forms the northern tip of the Namib Desert.The editors of Encyclopedia Britannica. https://www.britannica.com/place/Mocamedes-Deser ...
, while its southern portion approaches the neighboring Kalahari Desert. From the Atlantic coast eastward, the Namib gradually ascends in elevation, reaching up to inland to the foot of the Great Escarpment
The Great Escarpment is a major topographical feature in Africa that consists of steep slopes from the high central Southern African plateauAtlas of Southern Africa. (1984). p. 13. Reader's Digest Association, Cape Town downward in the directio ...
. Annual precipitation ranges from in the most arid regions to at the escarpment, making the Namib the only true desert in southern Africa. Having endured arid
A region is arid when it severely lacks available water, to the extent of hindering or preventing the growth and development of plant and animal life. Regions with arid climates tend to lack vegetation and are called xeric or desertic. Most ...
or semi-arid conditions for roughly 55–80 million years, the Namib may be the oldest desert in the world and contains some of the world's driest regions, with only western South America's Atacama Desert to challenge it for age and aridity benchmarks.
The desert geology consists of sand sea
An erg (also sand sea or dune sea, or sand sheet if it lacks dunes) is a broad, flat area of desert covered with wind-swept sand with little or no vegetative cover. The word is derived from the Arabic word ''ʿarq'' (), meaning "dune field". St ...
s near the coast, while gravel plains and scattered mountain outcrops occur further inland. The sand dunes, some of which are high and span long, are the second-largest in the world after the Badain Jaran Desert dunes in China. Temperatures along the coast are stable and generally range between annually, while temperatures further inland are variable—summer daytime temperatures can exceed while nights can be freezing. Fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
s that originate offshore from the collision of the cold Benguela Current and warm air from the Hadley Cell create a fog belt that frequently envelops parts of the desert. Coastal regions can experience more than 180 days of thick fog a year. While this has proved a major hazard to ships—more than a thousand wrecks litter the Skeleton Coast—it is a vital source of moisture for desert life.
The Namib is almost completely uninhabited by humans except for several small settlements and indigenous pastoral groups, including the Ovahimba and Obatjimba Herero in the north, and the Topnaar Nama in the central region. Owing to its antiquity, the Namib may be home to more endemic species
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
than any other desert in the world. Most of the desert wildlife is arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s and other small animals that live on little water, although larger animals inhabit the northern regions. Near the coast, the cold ocean water is rich in fishery resources and supports populations of brown fur seals and shorebirds, which serve as prey for the Skeleton Coast's lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
s. Further inland, the Namib-Naukluft National Park, the largest game park in Africa, supports populations of African bush elephant
The African bush elephant (''Loxodonta africana'') is one of two extant African elephant species and one of three extant elephant species. It is the largest living terrestrial animal, with bulls reaching a shoulder height of up to and a body ...
s, mountain zebra
The mountain zebra (''Equus zebra'') is a zebra species in the family Equidae, native to southwestern Africa. There are two subspecies, the Cape mountain zebra (''E. z. zebra'') found in South Africa and Hartmann's mountain zebra (''E. z. hartman ...
s, and other large mammals. Although the outer Namib is largely barren of vegetation, lichen
A lichen ( , ) is a composite organism that arises from algae or cyanobacteria living among filaments of multiple fungi species in a mutualistic relationship.succulents are found in coastal areas, while grasses, shrubs, and ephemeral plants thrive near the

 The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct
The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct
 The Namib's aridity is caused by the descent of dry air of the Hadley Cell, cooled by the cold Benguela current along the coast. It has less than of rain annually and is almost completely barren. Besides rain being scarce, it is also unpredictable. The western Namib gets less rain (5 mm) than the eastern Namib (85 mm). This is due to several factors. Winds coming from the Indian Ocean lose part of their humidity when passing the Drakensberg mountains, and are essentially dry when they reach the Namib Escarpment at the eastern end of the desert. Winds coming from the Atlantic Ocean, on the other hand, are pressed down by hot air from the east; their humidity thus forms clouds and fog. Morning fogs coming from the ocean and pushing inwards into the desert are a regular phenomenon along the coast, and much of the life cycle of animals and plants in the Namib relies on these fogs as the main source of water.
The Namib's aridity is caused by the descent of dry air of the Hadley Cell, cooled by the cold Benguela current along the coast. It has less than of rain annually and is almost completely barren. Besides rain being scarce, it is also unpredictable. The western Namib gets less rain (5 mm) than the eastern Namib (85 mm). This is due to several factors. Winds coming from the Indian Ocean lose part of their humidity when passing the Drakensberg mountains, and are essentially dry when they reach the Namib Escarpment at the eastern end of the desert. Winds coming from the Atlantic Ocean, on the other hand, are pressed down by hot air from the east; their humidity thus forms clouds and fog. Morning fogs coming from the ocean and pushing inwards into the desert are a regular phenomenon along the coast, and much of the life cycle of animals and plants in the Namib relies on these fogs as the main source of water.
 The dry climate of the Namib reflects the almost complete lack of bodies of water on the surface. Most rivers flow underground and/or are dry for most of the year. Even when they are not, they usually drain into
The dry climate of the Namib reflects the almost complete lack of bodies of water on the surface. Most rivers flow underground and/or are dry for most of the year. Even when they are not, they usually drain into
 A number of unusual
A number of unusual
File:Quiver trees, Namib Desert.jpg, alt=, Quiver trees found within Namib desert
File:Oryx Gazella Namib Desert.jpg, alt=,
The Namib fauna mostly comprises
 Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some
Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some
 The Namib-Naukluft National Park, that extends over a large part of the Namib Desert, is the largest game reserve in
The Namib-Naukluft National Park, that extends over a large part of the Namib Desert, is the largest game reserve in
Namib Naukluft Park photo gallery
{{Authority control Deserts of Namibia Deserts of South Africa Afrotropical ecoregions Ergs of Africa Physiographic provinces World Heritage Sites in Namibia Namib-Naukluft National Park First 100 IUGS Geological Heritage Sites
escarpment
An escarpment is a steep slope or long cliff that forms as a result of faulting or erosion and separates two relatively level areas having different elevations.
The terms ''scarp'' and ''scarp face'' are often used interchangeably with ''esca ...
. Several types of trees are also able to survive the extremely arid climate.
Geography and geology
 The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct
The Namib Desert is one of the 500 distinct physiographic
Physical geography (also known as physiography) is one of the three main branches of geography. Physical geography is the branch of natural science which deals with the processes and patterns in the natural environment such as the atmosphere ...
provinces of the South African Platform physiographic division. It occupies an area of around , stretching from the Uniab River
The Uniab River is an ephemeral river on Namibia Skeleton Coast, located between Torra Bay and Terrace Bay. Its mouth is in the Grootberg Mountains near Palmwag. Inflows of the Uniab are Kaikams, Kawakab, Aub, Urenindes and Obob. The riv ...
(north) to the town of Lüderitz (south) and from the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
(west) to the Namib Escarpment (east). It is about long from north to south and its east–west width varies from . To the north, the desert leads into the Kaokoveld; the dividing line between these two regions is roughly at the latitude
In geography, latitude is a coordinate that specifies the north– south position of a point on the surface of the Earth or another celestial body. Latitude is given as an angle that ranges from –90° at the south pole to 90° at the north ...
of the city of Walvis Bay, and it consists in a narrow strip of land (about 50 km wide) that is the driest place in Southern Africa. To the south, the Namib borders on the South Africa
South Africa, officially the Republic of South Africa (RSA), is the southernmost country in Africa. It is bounded to the south by of coastline that stretch along the South Atlantic and Indian Oceans; to the north by the neighbouring coun ...
n Karoo
The Karoo ( ; from the Afrikaans borrowing of the South Khoekhoe !Orakobab or Khoemana word ''ǃ’Aukarob'' "Hardveld") is a semi-desert natural region of South Africa. No exact definition of what constitutes the Karoo is available, so its ex ...
semi-desert.
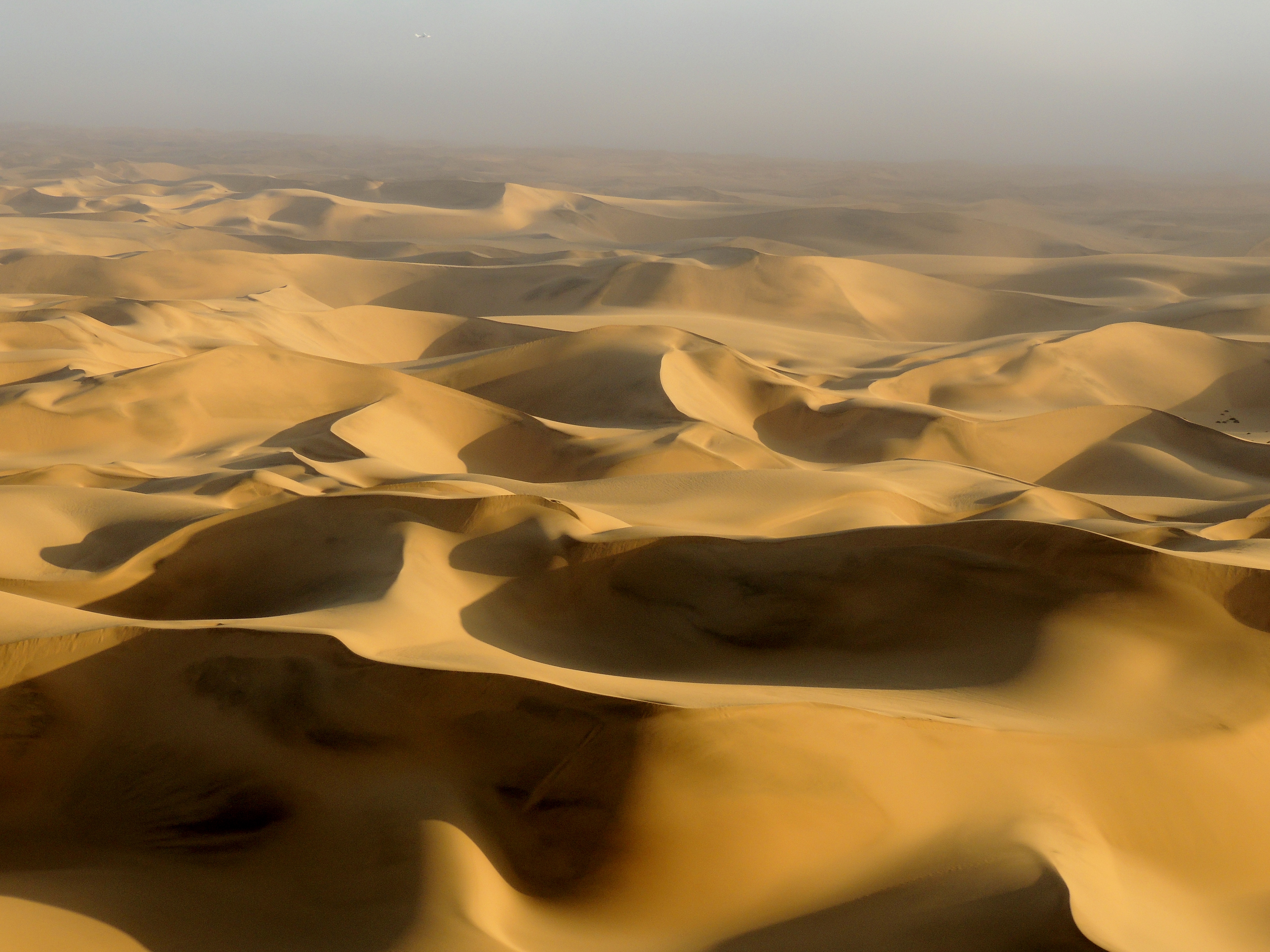
Southern Namib (between Lüderitz and the Kuiseb River) comprises a vast dune sea with some of the tallest and most spectacular dunes of the world, ranging in color from pink to vivid orange. In the Sossusvlei area, several dunes exceed in height. The complexity and regularity of dune patterns in its dune sea have attracted the attention of geologist
A geologist is a scientist who studies the solid, liquid, and gaseous matter that constitutes Earth and other terrestrial planets, as well as the processes that shape them. Geologists usually study geology, earth science, or geophysics, althou ...
s for decades, but it remains poorly understood.
The source of the unconsolidated sand (the most recent sand sea) has been shown to be dominantly from the Orange River, which drains into the Atlantic south of the Namib Sand Sea, with minor contributions in the east from the (now ephemeral) rivers that drain into the sand sea. For this reason the Namib Sand Sea has been referred to as the "wind displaced delta of the Orange River."
Moving north from Sossusvlei, the sand gradually gives way to a rocky desert that extends all the way from Sossusvlei to the Swakop river. This area is traversed by the Tropic of Capricorn
The Tropic of Capricorn (or the Southern Tropic) is the circle of latitude that contains the subsolar point at the December (or southern) solstice. It is thus the southernmost latitude where the Sun can be seen directly overhead. It also reac ...
and is mostly flat, although some scenic canyons and elevations are found in some areas, for example in the Moon Valley system. While most of the soil is rocky, sand dunes are still occasionally found in this region; for example, sand dunes occupy much of the coastline between Walvis Bay and Swakopmund.
The Namib desert is an important location for the mining of tungsten
Tungsten, or wolfram, is a chemical element with the symbol W and atomic number 74. Tungsten is a rare metal found naturally on Earth almost exclusively as compounds with other elements. It was identified as a new element in 1781 and first isol ...
, salt
Salt is a mineral composed primarily of sodium chloride (NaCl), a chemical compound belonging to the larger class of salts; salt in the form of a natural crystalline mineral is known as rock salt or halite. Salt is present in vast quant ...
and diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, b ...
s.
Several rivers and streams run through the Namib, although all of the rivers south of the Cunene River and north of the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
are ephemeral
Ephemerality (from the Greek word , meaning 'lasting only one day') is the concept of things being transitory, existing only briefly. Academically, the term ephemeral constitutionally describes a diverse assortment of things and experiences, f ...
and rarely or never reach the ocean. These rivers arise in the interior mountains of Namibia and flow after summer rain storms.
Climate
endorheic
An endorheic basin (; also spelled endoreic basin or endorreic basin) is a drainage basin that normally retains water and allows no outflow to other external bodies of water, such as rivers or oceans, but drainage converges instead into lakes ...
basins, without reaching the sea. The Swakop and the Omaruru are the only rivers that occasionally drain into the ocean.
All along the coast, but mostly in the northernmost part of it, interaction between the water-laden air coming from the sea via southerly wind
Wind is the natural movement of air or other gases relative to a planet's surface. Winds occur on a range of scales, from thunderstorm flows lasting tens of minutes, to local breezes generated by heating of land surfaces and lasting a few ...
s, some of the strongest of any coastal desert, and the dry air of the desert causes immense fog
Fog is a visible aerosol consisting of tiny water droplets or ice crystals suspended in the air at or near the Earth's surface. Reprint from Fog can be considered a type of low-lying cloud usually resembling stratus, and is heavily influ ...
s and strong currents. It causes sailors to lose their way; this is testified by the remnants of a number of shipwreck
A shipwreck is the wreckage of a ship that is located either beached on land or sunken to the bottom of a body of water. Shipwrecking may be intentional or unintentional. Angela Croome reported in January 1999 that there were approximately ...
s that can be found along the Skeleton Coast, in northern Namib. Some of these wrecked ships can be found as much as inland, as the desert slowly moves westwards into the sea, reclaiming land over a period of many years.
Benguela's El Niño (similar to the Pacific event in its environmental change in the seas) spreads from the Kunene estuary southward to, on occasion, south of Luderitz. Warm waters with depth and associated water flows from the northwest were first fully catalogued by Sea Fisheries researchers, Cape Town (L V Shannon ''et al.''). The research noted the positive effect of Benguela's El Niño on the rainfall of the interior. Rainfall records also show positive values variously across the Namib, Desert Research Station, Gobabeb for instance. This event recurs approximately mid-decade (1974, 1986, 1994, 1995 and 2006 are recent examples).Plants and animals
Flora
 A number of unusual
A number of unusual species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
of plant
Plants are predominantly photosynthetic eukaryotes of the kingdom Plantae. Historically, the plant kingdom encompassed all living things that were not animals, and included algae and fungi; however, all current definitions of Plantae excl ...
s and animal
Animals are multicellular, eukaryotic organisms in the biological kingdom Animalia. With few exceptions, animals consume organic material, breathe oxygen, are able to move, can reproduce sexually, and go through an ontogenetic stage ...
s are found in this desert, many of which are endemic
Endemism is the state of a species being found in a single defined geographic location, such as an island, state, nation, country or other defined zone; organisms that are indigenous to a place are not endemic to it if they are also found else ...
and highly adapted to the specific climate of the area. One of the most well-known endemic plants of the Namib is the bizarre ''Welwitschia
''Welwitschia'' is a monotypic gymnosperm genus, comprising solely the distinctive ''Welwitschia mirabilis'', endemic to the Namib desert within Namibia and Angola. ''Welwitschia'' is the only living genus of the family Welwitschiaceae and orde ...
mirabilis''; a shrub-like plant, it grows two long strap-shaped leaves continuously throughout its lifetime. These leaves may be several meters long, gnarled and twisted from the desert winds. The taproot of the plant develops into a flat, concave disc in age. ''Welwitschia'' is notable for its survival in the extremely arid conditions in the Namib, mostly deriving moisture from the coastal sea fogs. An area where ''Welwitschias'' are a common sight is found in the surroundings of the Moon Valley, including the eponymous Welwitschia Plains.
Fauna
Gemsbok
The gemsbok or South African oryx (''Oryx gazella'') is a large antelope in the genus ''Oryx''. It is native to the extremely dry, arid regions of Southern Africa; notably, the Kalahari Desert. Some authorities formerly classified the East Afr ...
s (''Oryx
''Oryx'' is a genus consisting of four large antelope species called oryxes. Their pelage is pale with contrasting dark markings in the face and on the legs, and their long horns are almost straight. The exception is the scimitar oryx, which ...
gazella'') are the biggest antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
s found in the Namib desert
arthropod
Arthropods (, (gen. ποδός)) are invertebrate animals with an exoskeleton, a segmented body, and paired jointed appendages. Arthropods form the phylum Arthropoda. They are distinguished by their jointed limbs and cuticle made of chiti ...
s and other small animals that can live on little water, but a few species of bigger animals are also found, including antelope
The term antelope is used to refer to many species of even-toed ruminant that are indigenous to various regions in Africa and Eurasia.
Antelope comprise a wastebasket taxon defined as any of numerous Old World grazing and browsing hoofed mamm ...
s (such as gemsbok
The gemsbok or South African oryx (''Oryx gazella'') is a large antelope in the genus ''Oryx''. It is native to the extremely dry, arid regions of Southern Africa; notably, the Kalahari Desert. Some authorities formerly classified the East Afr ...
s and springboks), ostrich
Ostriches are large flightless birds of the genus ''Struthio'' in the order Struthioniformes, part of the infra-class Palaeognathae, a diverse group of flightless birds also known as ratites that includes the emus, rheas, and kiwis. There ...
es, and in some areas even desert elephants. All these species have developed techniques to survive in the Namib environment. A number of endemic darkling beetle
Darkling beetle is the common name for members of the beetle family Tenebrionidae. The number of species in the Tenebrionidae is estimated at more than 20,000 and the family is cosmopolitan in distribution.
Taxonomy
''Tenebrio'' is the Latin ge ...
s species
In biology, a species is the basic unit of classification and a taxonomic rank of an organism, as well as a unit of biodiversity. A species is often defined as the largest group of organisms in which any two individuals of the appropriat ...
— such as the Namib Desert beetle — have bumpy elytrons with a pattern of hydrophilic bumps and hydrophobic troughs. These cause humidity from the morning fogs to condense into droplets, which roll down the beetle's back to its mouth; they are collectively known as "fog beetles". Another beetle, the ''Lepidochora discoidalis'', builds "water-capturing" webs. Black-backed jackals lick humidity from stones. Gemsboks (also known as the South African oryx) can raise the temperature of their bodies to 40 °C in the hottest hours of the day. The desert is also home to meerkat
MeerKAT, originally the Karoo Array Telescope, is a radio telescope consisting of 64 antennas in the Meerkat National Park, in the Northern Cape of South Africa. In 2003, South Africa submitted an expression of interest to host the Square Ki ...
s and several species of lizards.
Human activity
 Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some
Before the 20th century, some San roamed the Namib, gathering edible plants on the shore, hunting in the interior, and drinking the juice of the tsamma melon for water. Today, some Herero
Herero may refer to:
* Herero people
The Herero ( hz, Ovaherero) are a Bantu ethnic group inhabiting parts of Southern Africa. There were an estimated 250,000 Herero people in Namibia in 2013. They speak Otjiherero, a Bantu language. Though t ...
still herd their livestock in the Kaokoveld in the Namib and take them from waterhole to waterhole. A few Nama Khoikhoi still graze their livestock on the banks of the Kuiseb River in the desert. Most of the native people have left, however, leaving the vast majority of the desert uninhabited.
The steppes in the southern half of the desert are mostly made up of ranches run by Europeans, who raise Karakul sheep with local help and send the pelts of the lambs to Europe for use in fur coats. Most of the rest of the desert is set aside for conservation. A vast portion of the desert, called the Sperrgebiet, was access-restricted due to the presence of diamonds, which are mined in the area at the mouth of the Orange River
The Orange River (from Afrikaans/Dutch: ''Oranjerivier'') is a river in Southern Africa. It is the longest river in South Africa. With a total length of , the Orange River Basin extends from Lesotho into South Africa and Namibia to the north ...
. Although the desert is largely unpopulated and inaccessible, there are year-round settlements at Sesriem
Sesriem is a small settlement in the Namib Desert, in the Hardap Region of Namibia, close to the southern end of the Naukluft Mountains. It is especially known because the "Sesriem gate" is the main access point to the Namib-Naukluft National Par ...
, close to the famous Sossusvlei area, and other small outposts in other locations. Moçâmedes in Angola, and Lüderitz, Walvis Bay and Swakopmund in Namibia, bordering on the desert, are the main settlements in the area.
The 2015 film '' Mad Max: Fury Road'' was filmed here.
In 2019 the Namibian-German artist Max Siedentopf created an installation in the Namib consisting of a ring of large white blocks atop of which sit six speakers attached to a solar-powered MP3 player
A portable media player (PMP) (also including the related digital audio player (DAP)) is a portable consumer electronics device capable of storing and playing digital media such as audio, images, and video files. The data is typically stored ...
configured to continuously play the 1982 song "Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
" by the American band Toto. The exact location of the installation has not been disclosed.
Namib-Naukluft National Park
 The Namib-Naukluft National Park, that extends over a large part of the Namib Desert, is the largest game reserve in
The Namib-Naukluft National Park, that extends over a large part of the Namib Desert, is the largest game reserve in Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
and one of the largest of the world. While most of the park is hardly accessible, several well-known visitor attractions are found in the desert. The prominent attraction is the famous Sossusvlei area, where high orange sand dunes surround vivid white salt pans, creating a fascinating landscape.
Access to the park is either by gravel roads or dust roads (except for 60 km of concrete road from the Sesriem
Sesriem is a small settlement in the Namib Desert, in the Hardap Region of Namibia, close to the southern end of the Naukluft Mountains. It is especially known because the "Sesriem gate" is the main access point to the Namib-Naukluft National Par ...
gate to Sossusvlei) or by light aircraft from Windhoek
Windhoek (, , ) is the capital and largest city of Namibia. It is located in central Namibia in the Khomas Highland plateau area, at around above sea level, almost exactly at the country's geographical centre. The population of Windhoek in 202 ...
(the capital of Namibia, about northeast of the centre of the desert), or Swakopmund and Walvis Bay at the north end of the desert.
Notable places
*Bogenfels
Bogenfels is a location in the coastal Namib Desert of Namibia, noted for its natural rock formations (hence the name, which means "arch rock" in German). The main formation is a high rock arch close to the coast. It is not easily accessible, d ...
* Sesriem
Sesriem is a small settlement in the Namib Desert, in the Hardap Region of Namibia, close to the southern end of the Naukluft Mountains. It is especially known because the "Sesriem gate" is the main access point to the Namib-Naukluft National Par ...
* Skeleton Coast
* Solitaire
Solitaire is any tabletop game which one can play by oneself, usually with cards, but also with dominoes. The term "solitaire" is also used for single-player games of concentration and skill using a set layout tiles, pegs or stones. These game ...
* Sossusvlei
** Deadvlei
** Dune 45
* Spitzkoppe
The Spitzkoppe (from German for ''"pointed dome"''; also referred to as Spitzkop, Groot Spitzkop, or the "Matterhorn of Namibia") is a group of bald granite peaks or inselbergs located between Usakos and Swakopmund in the Namib desert of ...
* Swakopmund
See also
* '' Animals Are Beautiful People'', a nature documentary set in the Namib *List of deserts by area
This is a list of the largest deserts in the world by area. It includes all deserts above .
Notes
See also
* Desert
* Desertification
* List of deserts by continent
* Polar desert
Polar deserts are the regions of Earth that fall un ...
References
* ''National Geographic'', January 1992, pp. 54–85. * Mary Seely: ''The Namib: Natural History of an Ancient Desert'', 3rd ed., Windhoek: Desert Research Foundation of Namibia 2004, .Further reading
* *External links
*Namib Naukluft Park photo gallery
{{Authority control Deserts of Namibia Deserts of South Africa Afrotropical ecoregions Ergs of Africa Physiographic provinces World Heritage Sites in Namibia Namib-Naukluft National Park First 100 IUGS Geological Heritage Sites