Nagra on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
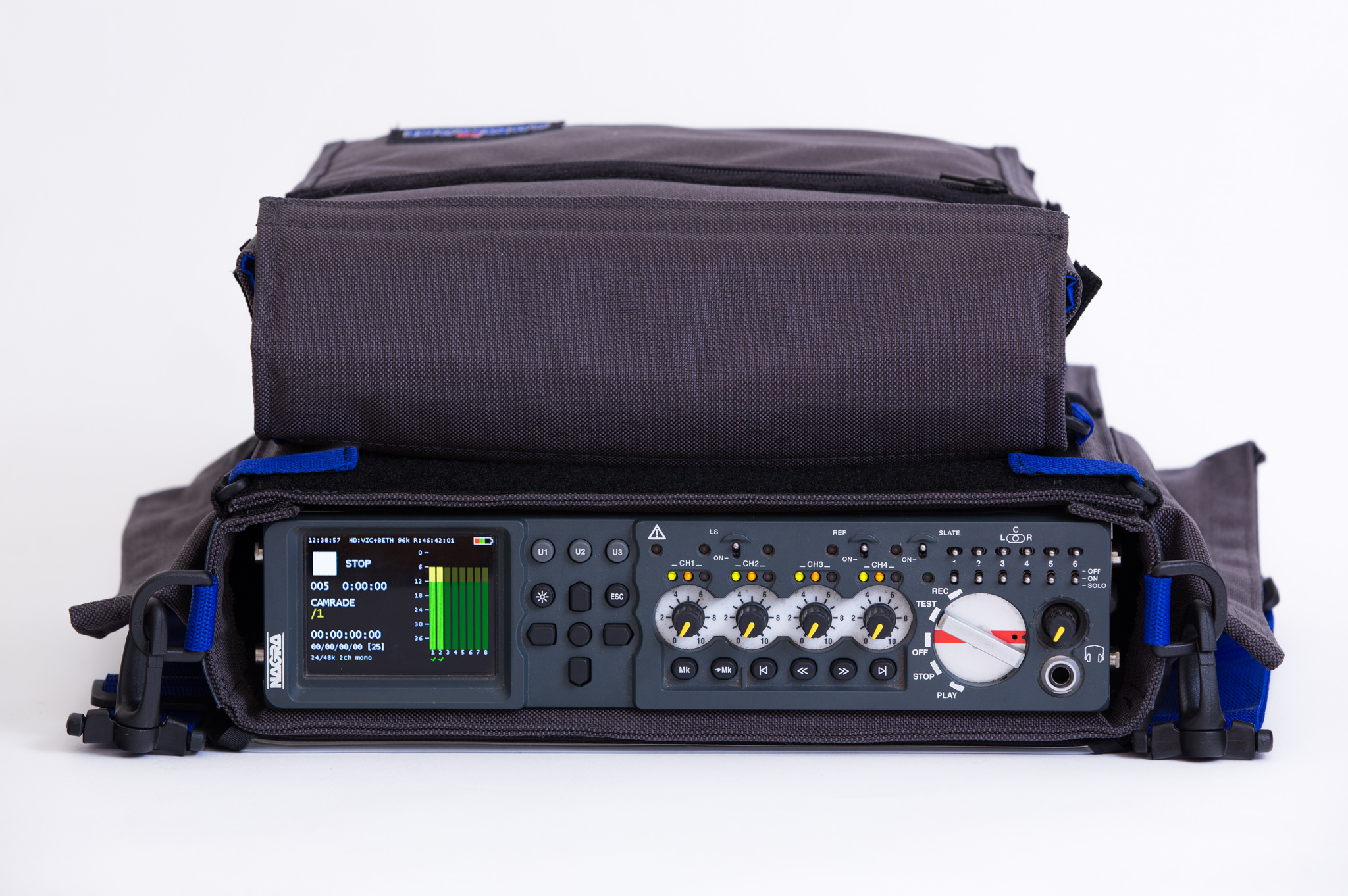
 Nagra is a brand of portable audio recorders produced from 1951 in Switzerland. Beginning in 1997 a range of high-end equipment aimed at the audiophile community was introduced, and Nagra expanded the company’s product lines into new markets.
Originally a product of the
Nagra is a brand of portable audio recorders produced from 1951 in Switzerland. Beginning in 1997 a range of high-end equipment aimed at the audiophile community was introduced, and Nagra expanded the company’s product lines into new markets.
Originally a product of the
 *Nagra IV-S – Stereo Nagra, recording two-track stereo. It had dual level pots, limiters, and equalizer presets. It was introduced in 1971. It originally employed a 14 kHz sync signal that is not compatible with the earlier Neopilot sync. This signal is recorded employing FM modulation on a third or center track that could simultaneously be employed as an additional but lower quality "cue" track.
*Nagra IV-STC – In 1984 Nagra introduced
*Nagra IV-S – Stereo Nagra, recording two-track stereo. It had dual level pots, limiters, and equalizer presets. It was introduced in 1971. It originally employed a 14 kHz sync signal that is not compatible with the earlier Neopilot sync. This signal is recorded employing FM modulation on a third or center track that could simultaneously be employed as an additional but lower quality "cue" track.
*Nagra IV-STC – In 1984 Nagra introduced  *Nagra IV-SJ – Stereo Nagra for instrumentation and logging. Pots are replaced with switches to set gain in precise steps, no limiters, and when present, the microphone inputs are for high-voltage unbalanced instrumentation mics rather than low impedance balanced with T-power and phantom.
*Nagra IS – In 1974 the Nagra IS (nicknamed Idioten-Sicher or "idiot proof" by its users) was introduced. The Nagra IS was a small-bodied recorder, to be used in both film- and broadcast applications. Focus was on simple operation and lower weight than the IV/4-series recorders. It only supported 5 inch reels. Special versions of the IS called ISN and ISS could play back the 3,81 mm wide tape used with Nagra SN recorders. The IS is the only model derived from the original Nagra III to use three motors for tape transport. Supply and take up spools have their own motors.
*NAGRA E – A simple, single-speed (7.5ips), mono recorder aimed at radio reporters was introduced in 1976.
In addition to these field recorders, Kudelski S.A. produced a studio recorder called the Nagra T-Audio, designed mainly for use in
*Nagra IV-SJ – Stereo Nagra for instrumentation and logging. Pots are replaced with switches to set gain in precise steps, no limiters, and when present, the microphone inputs are for high-voltage unbalanced instrumentation mics rather than low impedance balanced with T-power and phantom.
*Nagra IS – In 1974 the Nagra IS (nicknamed Idioten-Sicher or "idiot proof" by its users) was introduced. The Nagra IS was a small-bodied recorder, to be used in both film- and broadcast applications. Focus was on simple operation and lower weight than the IV/4-series recorders. It only supported 5 inch reels. Special versions of the IS called ISN and ISS could play back the 3,81 mm wide tape used with Nagra SN recorders. The IS is the only model derived from the original Nagra III to use three motors for tape transport. Supply and take up spools have their own motors.
*NAGRA E – A simple, single-speed (7.5ips), mono recorder aimed at radio reporters was introduced in 1976.
In addition to these field recorders, Kudelski S.A. produced a studio recorder called the Nagra T-Audio, designed mainly for use in
 The SN range comprises the following models:
*Nagra SNN –
The SN range comprises the following models:
*Nagra SNN –
 *Nagra V – 2 channel PCM digital audio recorder, 24-bit/96 kHz, removable
*Nagra V – 2 channel PCM digital audio recorder, 24-bit/96 kHz, removable
Nagra Audio website
Documentary sound recordist discusses his work and approach when using a Nagra III as part of a 16mm film crew
Manufacturers of professional audio equipment Audio storage Digital television Polish inventions Swiss brands Audio equipment manufacturers of Switzerland

 Nagra is a brand of portable audio recorders produced from 1951 in Switzerland. Beginning in 1997 a range of high-end equipment aimed at the audiophile community was introduced, and Nagra expanded the company’s product lines into new markets.
Originally a product of the
Nagra is a brand of portable audio recorders produced from 1951 in Switzerland. Beginning in 1997 a range of high-end equipment aimed at the audiophile community was introduced, and Nagra expanded the company’s product lines into new markets.
Originally a product of the Kudelski Group
Kudelski SA () is a Swiss company that sells digital television access and management systems, cybersecurity solutions, Internet of Things products, and public infrastructure. The company is headquartered in Cheseaux-sur-Lausanne. Kudelski's f ...
, Nagra recorders are now developed, produced and sold by independently-owned company ''Audio Technology Switzerland S.A.'', based in Romanel-sur-Lausanne
Romanel-sur-Lausanne (, literally ''Romanel on Lausanne''; frp, Romanél) is a municipality in the canton of Vaud in Switzerland, located in the district of Lausanne.
History
Romanel-sur-Lausanne is first mentioned in 1184 as ''Romanes''.
Geogr ...
.
History
The machines were initially designed by Polish inventorStefan Kudelski
Stefan Kudelski (27 August 1931 – 26 January 2013)
Nagra was a Polish audio engineer known for creating ...
, and his company won numerous technical awards for their precision and reliability. Nagra means " twill record" in Polish, Kudelski's mother language.
Nagra-brand Nagra was a Polish audio engineer known for creating ...
tape recorder
An audio tape recorder, also known as a tape deck, tape player or tape machine or simply a tape recorder, is a sound recording and reproduction device that records and plays back sounds usually using magnetic tape for storage. In its present ...
s were the ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with ''de jure'' ("by la ...
'' standard sound recording systems for motion picture and (non-video) single-camera
The single-camera setup, or single-camera mode of production, also known as portable single camera, is a method of filmmaking and video production.
The single-camera setup originally developed during the birth of the classical Hollywood cinema ...
television production from the 1960s until the 1990s.
Synchronization
Originally, a physical sync lead tethered the Nagra recorder to the camera (putting a pulse from the camera onto the tape), to ensure any fluctuations in the tape were accounted for. After the introduction of crystal sync, the tape recorder could operate separately from the camera, each having a separate accurate clock guaranteed to stay in sync with the other, allowing the sound recordist significantly more freedom of movement. This was commonly known as double system sound.Models
Nagra recorders are identified by a number that indicates their technological generation and features: *NAGRA I – The very first prototype with clockwork motor and miniature tubes, appearing in 1951. Two were sold to Radio Genève. *NAGRA II – The first production model, miniature tubes equipped, clockwork motor, which appeared in 1953. In 1953, in a new facility, Nagra began the production of the Nagra II (a Nagra I with the option to have an external modulometer (a type of VU meter) in the sidewall. Later the Nagra II was improved to the Nagra II b and in 1955, to the Nagra II c (a Nagra II with some improvements in electronics and using the first Nagra printed circuit). *NAGRA II CI – The second generation fitted with printed circuit boards replacing chassis wiring, appearing in 1955. *Nagra III NP – The first Nagra usable for film work, appearing in 1958. This was a monaural recorder, with the "NP" denoting the Neopilot sync. *Nagra IV-L – Monaural, Neopilot sync, featuring two microphone inputs and a built-in audio limiter. Introduced in 1968. The unreliable head mounts were redesigned three times with the final design being designated the Nagra 4.2 *Nagra 4.2 – Same as the IV-L, but added powering for microphones and built-in equalizers. Introduced in 1972. In the 1980s one could upgrade a 4.2 to recordSMPTE timecode
SMPTE timecode ( or ) is a set of cooperating standards to label individual frames of video or film with a timecode. The system is defined by the Society of Motion Picture and Television Engineers in the SMPTE 12M specification. SMPTE revised ...
.
 *Nagra IV-S – Stereo Nagra, recording two-track stereo. It had dual level pots, limiters, and equalizer presets. It was introduced in 1971. It originally employed a 14 kHz sync signal that is not compatible with the earlier Neopilot sync. This signal is recorded employing FM modulation on a third or center track that could simultaneously be employed as an additional but lower quality "cue" track.
*Nagra IV-STC – In 1984 Nagra introduced
*Nagra IV-S – Stereo Nagra, recording two-track stereo. It had dual level pots, limiters, and equalizer presets. It was introduced in 1971. It originally employed a 14 kHz sync signal that is not compatible with the earlier Neopilot sync. This signal is recorded employing FM modulation on a third or center track that could simultaneously be employed as an additional but lower quality "cue" track.
*Nagra IV-STC – In 1984 Nagra introduced timecode
A timecode (alternatively, time code) is a sequence of numeric codes generated at regular intervals by a timing synchronization system. Timecode is used in video production, show control and other applications which require temporal coordinatio ...
support. With such support an IV-S became an STC with a pull out tray.
 *Nagra IV-SJ – Stereo Nagra for instrumentation and logging. Pots are replaced with switches to set gain in precise steps, no limiters, and when present, the microphone inputs are for high-voltage unbalanced instrumentation mics rather than low impedance balanced with T-power and phantom.
*Nagra IS – In 1974 the Nagra IS (nicknamed Idioten-Sicher or "idiot proof" by its users) was introduced. The Nagra IS was a small-bodied recorder, to be used in both film- and broadcast applications. Focus was on simple operation and lower weight than the IV/4-series recorders. It only supported 5 inch reels. Special versions of the IS called ISN and ISS could play back the 3,81 mm wide tape used with Nagra SN recorders. The IS is the only model derived from the original Nagra III to use three motors for tape transport. Supply and take up spools have their own motors.
*NAGRA E – A simple, single-speed (7.5ips), mono recorder aimed at radio reporters was introduced in 1976.
In addition to these field recorders, Kudelski S.A. produced a studio recorder called the Nagra T-Audio, designed mainly for use in
*Nagra IV-SJ – Stereo Nagra for instrumentation and logging. Pots are replaced with switches to set gain in precise steps, no limiters, and when present, the microphone inputs are for high-voltage unbalanced instrumentation mics rather than low impedance balanced with T-power and phantom.
*Nagra IS – In 1974 the Nagra IS (nicknamed Idioten-Sicher or "idiot proof" by its users) was introduced. The Nagra IS was a small-bodied recorder, to be used in both film- and broadcast applications. Focus was on simple operation and lower weight than the IV/4-series recorders. It only supported 5 inch reels. Special versions of the IS called ISN and ISS could play back the 3,81 mm wide tape used with Nagra SN recorders. The IS is the only model derived from the original Nagra III to use three motors for tape transport. Supply and take up spools have their own motors.
*NAGRA E – A simple, single-speed (7.5ips), mono recorder aimed at radio reporters was introduced in 1976.
In addition to these field recorders, Kudelski S.A. produced a studio recorder called the Nagra T-Audio, designed mainly for use in telecine
Telecine ( or ) is the process of transferring film into video and is performed in a color suite. The term is also used to refer to the equipment used in the post-production process.
Telecine enables a motion picture, captured originally on fi ...
s for transferring dailies. All of the above machines use 1/4" tape.
*NAGRA TRVR – A rare stereo machine designed with the 19" rack format. It is a reel to reel
Reel-to-reel audio tape recording, also called open-reel recording, is magnetic tape audio recording in which the recording tape is spooled between reels. To prepare for use, the ''supply reel'' (or ''feed reel'') containing the tape is plac ...
1/4" tape recorder designed for automatic long recording using the four standard tape speeds. The machine is equipped with an automatic start recording device actuated by the input signal and, at the tape end, allows automatic connection to another machine that begins recording on a new tape without loss of signal. When equipped with the accessory RCHS, Time Code Reader Searcher, the machine allows high speed search of a particular sequence when its time code had been entered by the keyboard or from its memory. These machines were used by intelligence services of several countries and logging service of radio stations.
''Série Noire''
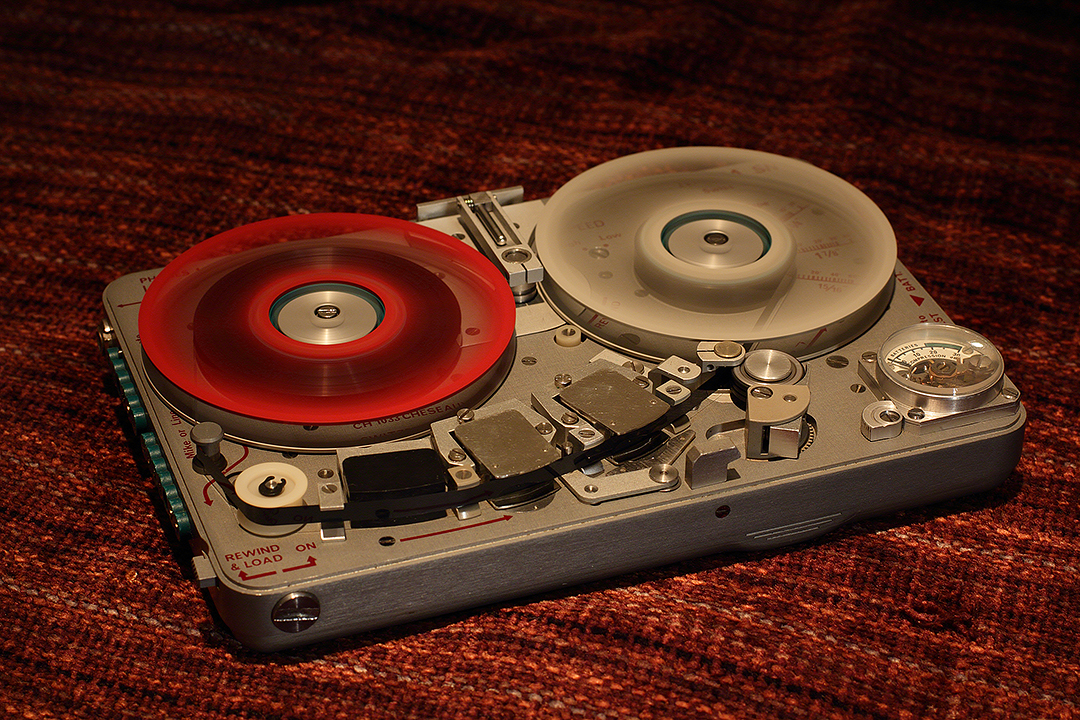
Kudelski SA also produced a series of miniaturised reel-to-reel recorders using a special tape (width ), slightly larger than the conventional 1/8" cassette tape. These machines are referred to as SN (for Série Noire) and production was originally ordered byPresident Kennedy
John Fitzgerald Kennedy (May 29, 1917 – November 22, 1963), often referred to by his initials JFK and the nickname Jack, was an American politician who served as the 35th president of the United States from 1961 until assassination of Joh ...
for the United States Secret Service
The United States Secret Service (USSS or Secret Service) is a federal law enforcement agency under the Department of Homeland Security charged with conducting criminal investigations and protecting U.S. political leaders, their families, and ...
.
 The SN range comprises the following models:
*Nagra SNN –
The SN range comprises the following models:
*Nagra SNN – monaural
Monaural or monophonic sound reproduction (often shortened to mono) is sound intended to be heard as if it were emanating from one position. This contrasts with stereophonic sound or ''stereo'', which uses two separate audio channels to reproduc ...
, full-track, main tape speed of 3-3/4 ips.
*Nagra SNS – monaural, half-track, main tape speed of 15/16 ips (multiplying the recording length at the expense of the dynamic range and high-frequency response).
*Nagra SNST – stereo, intended more for security service "two microphones to record two different people talking" usage than hi-fi usage due to technical limitations.
*Nagra SNST-R – full hi-fi stereo.
A special version of the SN using unique tape cassettes was made in cooperation with JBR Technology and widely used by US domestic intelligence agencies.
Digital recorders
The Nagra IV-STC was the standard for film and classical music recording until the mid-1990s, when DAT recorders became reliable enough to use in the field. In response, Kudelski produced two digital recorders to compete: *Nagra D – 4 channel PCM digital audio recorder. Instead of recording to the DAT format, the D used a digital reel-to-reel format using ahelical scan
Helical scan is a method of recording high-frequency signals on magnetic tape. It is used in open-reel video tape recorders, video cassette recorders, digital audio tape recorders, and some computer tape drives.
History
Earl E Masterson fro ...
head and 1/4" tape on 5" and 7" reels. The tape is identical to that used on Digital Audio Stationary Head
The Digital Audio Stationary Head or ''DASH'' standard is a reel-to-reel, digital audio tape format introduced by Sony in early 1982 for high-quality multitrack studio recording and mastering, as an alternative to analog recording methods. DAS ...
machines such as the Sony PCM-3202 and Mitsubishi X-86 series. The unique format, combined with its heavy weight, made it somewhat unpopular with many production sound mixer
A production sound mixer, location sound recordist, location sound engineer, or simply sound mixer is the member of a film crew or television crew responsible for recording all sound recording on set during the filmmaking or television production u ...
s, but year after year many films were completed with Nagra Ds (and the newer 24-bit/96 kHz Nagra DII). Despite some popularity in the late 1990s, the Nagra D and DII are a rarity on US films as of the mid-2000s.
*Nagra ARES C and ARES- PP – In 1995 the ARES-C recorder was introduced with the aim of replacing the ageing NAGRA-E portable tape recorder in the broadcast market. Based on a tape-less platform using PCMCIA computer memory cards as a recording medium, the ARES-C offers a recorder, editor and ISDN codec in the same portable, battery operated box. Accepted by radio stations around the world it formed the basis of a new generation of digital recorders for the NAGRA company. After the success of NAGRA D digital tape recorder, the NAGRA ARES was the first NAGRA digital tape-less recorder. The ARES C-PP was a studio 19" (2U) rack-mountable version of the ARES-C and gave broadcasters a full system for journalistic transmission. The C-PP was extensively used in broadcast OB vans and small radio studios. Nagra ARES models use PC (formerly PCMCIA) Cards for data storage, Flash RAM Type I and II (max 192 MB).
 *Nagra V – 2 channel PCM digital audio recorder, 24-bit/96 kHz, removable
*Nagra V – 2 channel PCM digital audio recorder, 24-bit/96 kHz, removable hard drive
A hard disk drive (HDD), hard disk, hard drive, or fixed disk is an electro-mechanical data storage device that stores and retrieves digital data using magnetic storage with one or more rigid rapidly rotating platters coated with magne ...
based recorder with timecode
A timecode (alternatively, time code) is a sequence of numeric codes generated at regular intervals by a timing synchronization system. Timecode is used in video production, show control and other applications which require temporal coordinatio ...
support. Has the additional benefits of being very light, and producing files easily processed by non-linear editing system
Non-linear editing is a form of offline editing for audio, video, and image editing. In offline editing, the original content is not modified in the course of editing. In non-linear editing, edits are specified and modified by specialized sof ...
s. Originally released with the Orb removable hard drive system, which proved unreliable. The drive system was replaced by Agate Technology's DN-Boy system in October 2002. Unlike the analog Nagras, the Nagra V digital recorders have not been adopted as readily for the motion picture and TV industries, which mostly use competing digital multi-track machines from manufacturers such as Aaton's Cantar, Fostex, Sound Devices and Zaxcom.
*Nagra VI – Released in 2008, originally as a 6 channel recorder and later upgraded to 8 channels (six inputs plus two mix), the Nagra VI was touted as "the natural successor to the NAGRA-D / DII multi-track digital recorders" and is equipped with four microphone preamps, two line level inputs which double as dual digital inputs (AES/EBU
AES3 is a standard for the exchange of digital audio signals between professional audio devices. An AES3 signal can carry two channels of pulse-code-modulated digital audio over several transmission media including balanced lines, unbalanced l ...
and S/PDIF
S/PDIF (Sony/Philips Digital Interface) is a type of digital audio interface used in consumer audio equipment to output audio over relatively short distances. The signal is transmitted over either a coaxial cable (using RCA or BNC connectors ...
), with input channels equipped with low pass filters, limiters, variable mic sensitivity settings and variable voltage phantom power. Rotary encoders and soft buttons allow the user to program the function of the main audio pots and shortcut keys. The VI records to an internal 2.5" hard drive with compact flash
CompactFlash (CF) is a flash memory mass storage device used mainly in portable electronic devices. The format was specified and the devices were first manufactured by SanDisk in 1994.
CompactFlash became one of the most successful of the e ...
as a backup or for transfers, has full timecode capability and meta-data entry for audio files and digital sound reports. Records 24-bit/96 kHz as well as MP3 formats. The VI was released to compete with multitrack machines from other manufacturers, although it has still not regained its original market share in production sound, as higher channel counts and smaller size and weight become more available at less cost.
*Nagra Seven – Since 2013, this 2 track recorder has been designed as the successor to the Nagra LB, ARES-C, ARES-BB+ and Nagra V recorders. It is a flexible device and can be adapted to a multitude of specific applications depending on the internal options installed. Based on an extremely high performance, simple to operate platform the addition internal ISDN or SMPTE/EBU time code boards adapt it to either the broadcast or film / TV markets. Optional WiFi/3G, WiFi/4G, internal editor and audio compressions are also available, to further dedicate the device for particular applications.
Hi-fi
In 1997, Nagra launched the PL-P, a vacuum tube phono preamplifier, beginning a range of high-end audio equipment. The range is intended for audiophile consumers as opposed to exclusively the professional equipment manufactured hitherto. Since then, the range has grown steadily and have added tubes and mosfet amplifiers, CD players, other pre-amps and DACs. Now divided into 2 Classic and HD lines, Nagra's products are acclaimed by many journalists as being among the world's best sound reproduction electronics.References
External links
{{Commons category, NagraNagra Audio website
Documentary sound recordist discusses his work and approach when using a Nagra III as part of a 16mm film crew
Manufacturers of professional audio equipment Audio storage Digital television Polish inventions Swiss brands Audio equipment manufacturers of Switzerland