Myofibril on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A myofibril (also known as a muscle fibril or sarcostyle) is a basic rod-like organelle of a muscle cell. Skeletal muscles are composed of long, tubular cells known as muscle fibers, and these cells contain many chains of myofibrils. Each myofibril has a diameter of 1–2
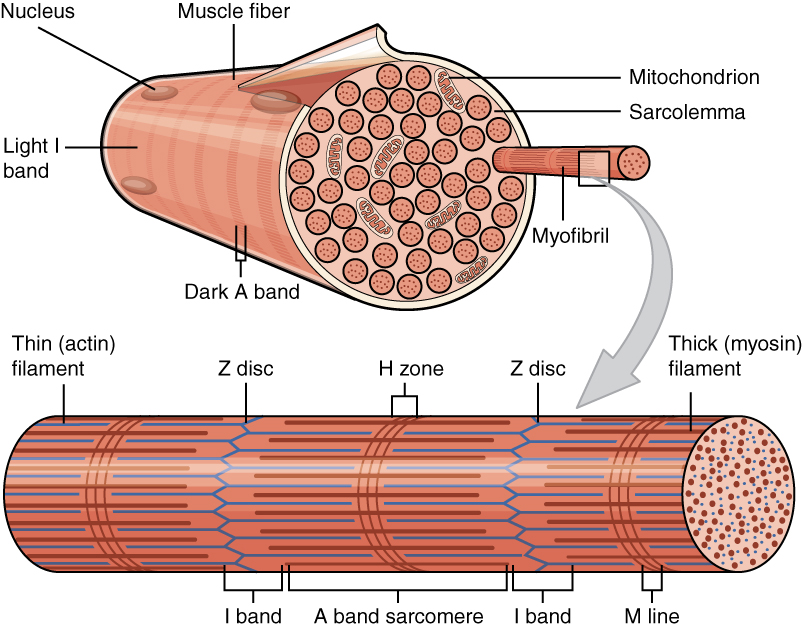 Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2
Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2
Muscle Physiology PrimerAnimation of sarcomere contraction
{{Authority control Organelles Protein complexes
micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
s. They are created during embryonic development in a process known as myogenesis
Myogenesis is the formation of skeletal muscular tissue, particularly during embryonic development.
Muscle fibers generally form through the fusion of precursor myoblasts into multinucleated fibers called ''myotubes''. In the early development o ...
.
Myofibrils are composed of long proteins including actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
, myosin, and titin
Titin (contraction for Titan protein) (also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. Titin is a giant protein, greater than 1 µm in length, that functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for th ...
, and other proteins that hold them together. These proteins are organized into thick, thin, and elastic myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act togethe ...
s, which repeat along the length of the myofibril in sections or units of contraction called sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called mus ...
s. Muscles contract by sliding the thick myosin, and thin actin myofilaments along each other.
Structure
 Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2
Each myofibril has a diameter of between 1 and 2 micrometre
The micrometre ( international spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: μm) or micrometer (American spelling), also commonly known as a micron, is a unit of length in the International System of Unit ...
s (μm). The filaments of myofibrils, myofilament
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act togethe ...
s, consist of three types, thick, thin, and elastic filaments.
*Thin filaments consist primarily of the protein actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
, coiled with nebulin filaments. Actin, when polymerized into filaments, forms the "ladder" along which the myosin filaments "climb" to generate motion
*Thick filaments consist primarily of the protein myosin, that is responsible for force generation. It is composed of a globular head with both ATP and actin binding sites, and a long tail involved in its polymerization into myosin filaments.
*Elastic filaments are made up of a giant protein called titin
Titin (contraction for Titan protein) (also called connectin) is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''TTN'' gene. Titin is a giant protein, greater than 1 µm in length, that functions as a molecular spring that is responsible for th ...
and hold the thick filaments in place.
The protein complex
A protein complex or multiprotein complex is a group of two or more associated polypeptide chains. Protein complexes are distinct from multienzyme complexes, in which multiple catalytic domains are found in a single polypeptide chain.
Protein ...
composed of actin and myosin is sometimes referred to as actomyosin
Myofilaments are the three protein filaments of myofibrils in muscle cells. The main proteins involved are myosin, actin, and titin. Myosin and actin are the ''contractile proteins'' and titin is an elastic protein. The myofilaments act toget ...
.
In striated skeletal and cardiac
The heart is a muscular organ in most animals. This organ pumps blood through the blood vessels of the circulatory system. The pumped blood carries oxygen and nutrients to the body, while carrying metabolic waste such as carbon dioxide to t ...
muscle tissue
Muscle tissue (or muscular tissue) is soft tissue that makes up the different types of muscles in most animals, and give the ability of muscles to contract. Muscle tissue is formed during embryonic development, in a process known as myogenesis. ...
the actin and myosin filaments each have a specific and constant length on the order of a few micrometers, far less than the length of the elongated muscle cell (a few millimeters in the case of human skeletal muscle cells). The filaments are organized into repeated subunits along the length of the myofibril. These subunits are called sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called mus ...
s that are around three μm in length. The muscle cell is nearly filled with myofibrils running parallel to each other on the long axis of the cell. The sarcomeric subunits of one myofibril are in nearly perfect alignment with those of the myofibrils next to it. This alignment gives the cell its striped or striated appearance. Exposed muscle cells at certain angles, such as in meat cuts, can show structural coloration
Structural coloration in animals, and a few plants, is the production of colour by microscopically structured surfaces fine enough to interfere with visible light instead of pigments, although some structural coloration occurs in combination wi ...
or iridescence due to this periodic alignment of the fibrils and sarcomeres.
Appearance
The names of the various sub-regions of the sarcomere are based on their relatively lighter or darker appearance when viewed through the light microscope. Each sarcomere is delimited by two very dark colored bands called Z-discs or Z-lines (from the German ''zwischen'' meaning between). These Z-discs are dense protein discs that do not easily allow the passage of light. TheT-tubule
T-tubules (transverse tubules) are extensions of the cell membrane that penetrate into the center of skeletal and cardiac muscle cells. With membranes that contain large concentrations of ion channels, transporters, and pumps, T-tubules permi ...
is present in this area. The area between the Z-discs is further divided into two lighter colored bands at either end called the I-bands or Isotropic Bands, and a darker, grayish band in the middle called the A band or Anisotropic Bands.
The I bands appear lighter because these regions of the sarcomere mainly contain the thin actin filaments, whose smaller diameter allows the passage of light between them. The A band, on the other hand, contains mostly myosin filaments whose larger diameter restricts the passage of light. A stands for anisotropic and I for isotropic, referring to the optical properties of living muscle as demonstrated with polarized light microscopy.
The parts of the A band that abut the I bands are occupied by both actin and myosin filaments (where they interdigitate as described above). Also within the A band is a relatively brighter central region called the H-zone (from the German ''helle'', meaning bright) in which there is no actin/myosin overlap when the muscle is in a relaxed state. Finally, the H-zone is bisected by a dark central line called the M-line (from the German ''mittel'' meaning middle).
Development
A study of the developing leg muscle in a 12-day chick embryo using electron microscopy proposes a mechanism for the development of myofibrils. Developing muscle cells contain thick (myosin) filaments that are 160–170 Å in diameter and thin (actin)filaments that are 60–70 Å in diameter. Young myofibres contain a 7:1 ratio of thin to thick filaments. Along the long axis of the muscle cells in sub sarcolemmal locations, free myofilaments become aligned and aggregate into hexagonally packed arrays. These aggregates form regardless of the presence of Z band or M band material. Aggregation occurs spontaneously because the tertiary structures of actin and myosin monomers contain all the "information" with the ionic strength and ATP concentration of the cell to aggregate into the filaments.Function
Themyosin head
The myosin head is the part of the thick myofilament made up of myosin that acts in muscle contraction, by sliding over thin myofilaments of actin. Myosin is the major component of the thick filaments and most myosin molecules are composed of a hea ...
s form cross bridges with the actin
Actin is a family of globular multi-functional proteins that form microfilaments in the cytoskeleton, and the thin filaments in muscle fibrils. It is found in essentially all eukaryotic cells, where it may be present at a concentration of ov ...
myofilaments; this is where they carry out a 'rowing' action along the actin. When the muscle fibre is relaxed (before contraction), the myosin head has ADP and phosphate bound to it.
When a nerve impulse arrives, Ca2+ ions cause troponin
image:Troponin Ribbon Diagram.png, 400px, Ribbon representation of the human cardiac troponin core complex (52 kDa core) in the calcium-saturated form. Blue = troponin C; green = troponin I; magenta = troponin T.; ; rendered with PyMOL
Troponin, ...
to change shape; this moves the troponin + tropomyosin complex away, leaving the myosin binding sites open.
The myosin head now binds to the actin myofilament. Energy in the head of the myosin myofilament moves the head, which slides the actin past; hence ADP is released.
ATP presents itself (as the presence of the calcium ions activates the myosin's ATPase), and the myosin heads disconnect from the actin to grab the ATP. The ATP is then broken down into ADP and phosphate. Energy is released and stored in the myosin head to utilize for later movement. The myosin heads now return to their upright relaxed position. If calcium is present, the process is repeated.
When a muscle contracts, the actin is pulled along myosin toward the center of the sarcomere
A sarcomere (Greek σάρξ ''sarx'' "flesh", μέρος ''meros'' "part") is the smallest functional unit of striated muscle tissue. It is the repeating unit between two Z-lines. Skeletal muscles are composed of tubular muscle cells (called mus ...
until the actin and myosin filaments are completely overlapped. The H zone becomes smaller and smaller due to the increasing overlap of actin and myosin filaments, and the muscle shortens. Thus when the muscle is fully contracted, the H zone is no longer visible. Note that the actin and myosin filaments themselves do not change length, but instead slide past each other. This is known as the sliding filament theory
The sliding filament theory explains the mechanism of muscle contraction based on muscle proteins that slide past each other to generate movement. According to the sliding filament theory, the myosin ( thick filaments) of muscle fibers slide past ...
of muscle contraction.Marieb, E. N., Hoehn, K., & Hoehn, F. (2007). Human Anatomy & Physiology. (7th ed., pp. 284–87). San Francisco, California: Benjamin-Cummings Pub Co.
See also
*Cross-bridge cycle
Muscle contraction is the activation of tension-generating sites within muscle cells. In physiology, muscle contraction does not necessarily mean muscle shortening because muscle tension can be produced without changes in muscle length, such as ...
* Motor protein
References
External links
Muscle Physiology Primer
{{Authority control Organelles Protein complexes