Mosque of Uqba on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Great Mosque of Kairouan ( ar, جامع القيروان الأكبر), also known as the Mosque of Uqba (), is a
The Great Mosque of Kairouan ( ar, جامع القيروان الأكبر), also known as the Mosque of Uqba (), is a
/ref > Established by the Arab general
Great Mosque of Kairouan (discoverislamicart.org)
'' Its perimeter, of about , contains a
notable among other things for the first Islamic use of the


 Located in the north-east of the
Located in the north-east of the
 At the foundation of Kairouan in 670, the Arab general and conqueror Uqba ibn Nafi (himself the founder of the city) chose the site of his mosque in the center of the city, near the headquarters of the governor. Around 690, shortly after its construction, the mosque was destroyed during the occupation of Kairouan by the Berbers, originally conducted by Kusaila. It was rebuilt by the
At the foundation of Kairouan in 670, the Arab general and conqueror Uqba ibn Nafi (himself the founder of the city) chose the site of his mosque in the center of the city, near the headquarters of the governor. Around 690, shortly after its construction, the mosque was destroyed during the occupation of Kairouan by the Berbers, originally conducted by Kusaila. It was rebuilt by the  Under the rule of the Aghlabid dynasty, Kairouan was at its apogee, and the mosque profited from this period of stability and prosperity. In 836, Emir Ziyadat Allah I reconstructed the mosque once more: this is when the building acquired, at least in its entirety, its current appearance. At the same time, the mihrab's ribbed dome was raised on
Under the rule of the Aghlabid dynasty, Kairouan was at its apogee, and the mosque profited from this period of stability and prosperity. In 836, Emir Ziyadat Allah I reconstructed the mosque once more: this is when the building acquired, at least in its entirety, its current appearance. At the same time, the mihrab's ribbed dome was raised on

 Several centuries after its founding, the Great Mosque of Kairouan is the subject of numerous descriptions by Arab historians and geographers in the
Several centuries after its founding, the Great Mosque of Kairouan is the subject of numerous descriptions by Arab historians and geographers in the 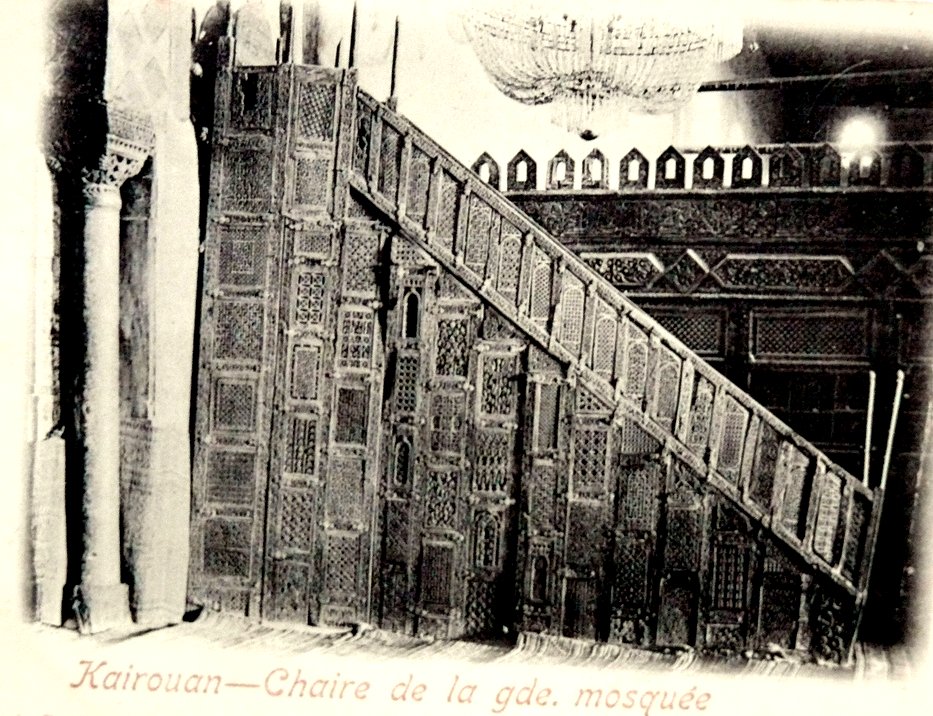 Among the Western travelers, poets and writers who visited Kairouan, some of them leave impressions and testimonies sometimes tinged with emotion or admiration on the mosque. From the eighteenth century, the French
Among the Western travelers, poets and writers who visited Kairouan, some of them leave impressions and testimonies sometimes tinged with emotion or admiration on the mosque. From the eighteenth century, the French


Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan western wall.jpg, Wall and porches on the west facade (south side)
Image:Entrée de la Grande Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, Close view of one of the entrances of the west facade
Image:Part of the southern facade of the Great Mosque of Kairouan.jpg, View of the middle of the southern facade
Image:Bab Lalla Rihana.jpg, Gate of Bab Lalla Rihana (late thirteenth century)
Image:Partie inférieure du porche de Bab Lalla Rihana, Grande Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, Close view of the lower part of Bab Lalla Rihana
Image:Arcature aveugle 2, Grande Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, Blind arcade decorating the upper part of Bab Lalla Rihana

 The courtyard is a vast trapezoidal area whose interior dimensions are approximately 67 by 52 metres. It is surrounded on all its four sides by a portico with double rows of arches, opened by slightly horseshoe arches supported by
The courtyard is a vast trapezoidal area whose interior dimensions are approximately 67 by 52 metres. It is surrounded on all its four sides by a portico with double rows of arches, opened by slightly horseshoe arches supported by
Image:Courtyard of the Great Mosque of Kairouan.jpg, View of the courtyard on the side of the prayer hall facade
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan prayer hall facade.jpg, Porch topped with a ribbed dome rising in the middle of the south portico of the courtyard
Image:Kairouan Mosque Courtyard with columns.jpg, Courtyard seen from one of the arched galleries
Image:The Great Mosque of Kairouan, eastern portico of the courtyard.jpg, Portico located on the eastern side of the courtyard
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan, eastern portico of the courtyard.jpg, Interior view of the eastern portico of the courtyard
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan gallery.jpg, Interior view of the western portico of the courtyard
File:Cadran solaire horizontal, Grande Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, The horizontal sundial located in the courtyard
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan sundial.jpg, One of the courtyard's capitals surmounted by a small vertical sundial
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan courtyard columns.jpg, Detail of arches and columns of the north portico of the courtyard
Image:Kairouan Great Mosque courtyard cistern.jpg, View of the impluvium which collects the rainwater and feeds the underground cistern
Image:IMGP7538.JPG, Focus on the rainwater collecting basin
Image:Puits Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, Focus on one well of the courtyard
 The minaret, which occupies the centre of the northern façade of the complex's enclosure, is 31.5 metres tall and is seated on a square base of 10.7 metres on each side.Paul Sebag, ''op. cit.'', p. 97 It is located inside the enclosure and does not have direct access from the outside. It consists of three tapering levels, the last of which is topped with a small ribbed dome that was most probably built later than the rest of the tower.Néji Djelloul, ''op. cit.'', p. 15 The first and second stories are surmounted by rounded merlons which are pierced by arrowslits. The minaret served as a watchtower, as well as to call the faithful to
The minaret, which occupies the centre of the northern façade of the complex's enclosure, is 31.5 metres tall and is seated on a square base of 10.7 metres on each side.Paul Sebag, ''op. cit.'', p. 97 It is located inside the enclosure and does not have direct access from the outside. It consists of three tapering levels, the last of which is topped with a small ribbed dome that was most probably built later than the rest of the tower.Néji Djelloul, ''op. cit.'', p. 15 The first and second stories are surmounted by rounded merlons which are pierced by arrowslits. The minaret served as a watchtower, as well as to call the faithful to
Image:Grande Mosquée de Kairouan, vue du minaret depuis la cour.jpg, Minaret seen from the courtyard
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan - Minaret door.jpg, Door of the minaret
Image:Great Mosque Minaret - Kairouan, Tunisia.jpg, View of the second and third storeys of the minaret
Image:Kairouan great mosque inscription.jpg, Close view of one of the Roman stones (with Latin inscriptions) reused at the base of the minaret
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan Minaret Wall.jpg, Wall and windows of the south facade of the minaret
Image:Mosquée oqba Kairouan by JM ROSIER.jpg, Minaret seen at night
 The Mosque has several domes, the largest being over the mihrab and the entrance to the prayer hall from the courtyard. The dome of the mihrab is based on an octagonal drum with slightly concave sides, raised on a square base, decorated on each of its three southern, eastern and western faces with five flat-bottomed niches surmounted by five semi-circular arches, the niche in the middle is cut by a lobed
The Mosque has several domes, the largest being over the mihrab and the entrance to the prayer hall from the courtyard. The dome of the mihrab is based on an octagonal drum with slightly concave sides, raised on a square base, decorated on each of its three southern, eastern and western faces with five flat-bottomed niches surmounted by five semi-circular arches, the niche in the middle is cut by a lobed
Image:Kairouan Mosque Gallery.jpg, View of the gallery which precedes the prayer hall
Image:Une des portes de la salle de prière de la Grande Mosquée de Kairouan.jpg, One of the seventeen carved-wood doors of the prayer hall
Image:Porta - Gran Mesquita de Kairuan.jpg, Close view of the upper part of the main door of the prayer hall
Image:Great Mosque of Kairouan prayer hall.jpg, View of the central nave of the prayer hall
Image:Secondary naves of the prayer hall, Great Mosque of Kairouan.jpg, View of two of the secondary naves of the prayer hall
Image:Mihrab2GrandeMosqueKairouan.jpg, View of the mihrab located in the middle of the qibla wall of the prayer hall
 In the prayer hall, the 414 columns of
In the prayer hall, the 414 columns of  The covering of the prayer hall consists of painted ceilings decorated with vegetal motifs and two domes: one raised at the beginning of the central nave and the other in front of the
The covering of the prayer hall consists of painted ceilings decorated with vegetal motifs and two domes: one raised at the beginning of the central nave and the other in front of the  The painted ceilings are a unique ensemble of planks, beams and
The painted ceilings are a unique ensemble of planks, beams and
 The
The 
 The wall of the mihrab is covered with 28 panels of white marble, carved and pierced, which have a wide variety of plant and geometric patterns including the stylised grape leaf, the flower and the shell. Behind the openwork hint, there is an oldest niche on which several assumptions were formulated. If one refers to the story of Al-Bakri, an Andalusian historian and geographer of the eleventh century, it is the mihrab which would be done by Uqba Ibn Nafi, the founder of Kairouan, whereas Lucien Golvin shares the view that it is not an old mihrab but hardly a begun construction which may serve to support marble panels and either goes back to work of Ziadet Allah I (817–838) or to those of Abul Ibrahim around the years 862–863. Above the marble cladding, the mihrab niche is crowned with a half dome-shaped vault made of manchineel bentwood. Covered with a thick coating completely painted, the concavity of the arch is decorated with intertwined scrolls enveloping stylised five-lobed vine leaves, three-lobed florets and sharp clusters, all in yellow on midnight blue background.
The
The wall of the mihrab is covered with 28 panels of white marble, carved and pierced, which have a wide variety of plant and geometric patterns including the stylised grape leaf, the flower and the shell. Behind the openwork hint, there is an oldest niche on which several assumptions were formulated. If one refers to the story of Al-Bakri, an Andalusian historian and geographer of the eleventh century, it is the mihrab which would be done by Uqba Ibn Nafi, the founder of Kairouan, whereas Lucien Golvin shares the view that it is not an old mihrab but hardly a begun construction which may serve to support marble panels and either goes back to work of Ziadet Allah I (817–838) or to those of Abul Ibrahim around the years 862–863. Above the marble cladding, the mihrab niche is crowned with a half dome-shaped vault made of manchineel bentwood. Covered with a thick coating completely painted, the concavity of the arch is decorated with intertwined scrolls enveloping stylised five-lobed vine leaves, three-lobed florets and sharp clusters, all in yellow on midnight blue background.
The
 The
The
 Among the finest works of this series, the pages of the Blue Qur'an, currently exhibited at Raqqada National Museum of Islamic Art, from a famous
Among the finest works of this series, the pages of the Blue Qur'an, currently exhibited at Raqqada National Museum of Islamic Art, from a famous
Okba Ibn Nafaa Mosque in Kairouan (Mosque of Uqba) website
Panoramic visit of the Great Mosque of Kairouan
Sacred Destinations : Great Mosque of Kairouan
Great Mosque of Kairouan (Qantara Mediterranean Heritage)
Video of the mihrab of the Great Mosque of Kairouan
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mosque Of Uqba 7th-century establishments in Africa 8th-century mosques Uqba Arcades (architecture) Kairouan 7th-century establishments in the Umayyad Caliphate
 The Great Mosque of Kairouan ( ar, جامع القيروان الأكبر), also known as the Mosque of Uqba (), is a
The Great Mosque of Kairouan ( ar, جامع القيروان الأكبر), also known as the Mosque of Uqba (), is a mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
situated in the UNESCO World Heritage
A World Heritage Site is a landmark or area with legal protection by an international convention administered by the United Nations Educational, Scientific and Cultural Organization (UNESCO). World Heritage Sites are designated by UNESCO for h ...
town of Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( ar, ٱلْقَيْرَوَان, al-Qayrawān , aeb, script=Latn, Qeirwān ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by t ...
, Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and is one of the most impressive and largest Islamic monuments in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
., , Géotunis 2009 :: Kairouan , , /ref > Established by the Arab general
Uqba ibn Nafi
ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī al-Qurashī ( ar, عقبة بن نافع بن عبد القيس الفهري القرشي, ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī), also simply known as Uqba ibn Nafi, was an Arab general ser ...
in the year 50 AH (670AD/CE) at the founding of the city of Kairouan, the mosque occupies an area of over . It is one of the oldest places of worship in the Islamic world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
, and is a model for all later mosques in the Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
. Great Mosque of Kairouan (discoverislamicart.org)
'' Its perimeter, of about , contains a
hypostyle
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or un ...
prayer hall, a marble-paved courtyard and a square minaret. In addition to its spiritual prestige, the Mosque of Uqba is one of the masterpieces of Islamic architecture
Islamic architecture comprises the architectural styles of buildings associated with Islam. It encompasses both secular and religious styles from the early history of Islam to the present day. The Islamic world encompasses a wide geographic ...
,The Great Mosque (kairouan-cci2009.nat.tn)notable among other things for the first Islamic use of the
horseshoe arch
The horseshoe arch (; Spanish: "arco de herradura"), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form.
Hi ...
.
Extensive works under the Aghlabids
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a ...
two centuries later (9th Cent.AD/CE) gave the mosque its present aspect. M’hamed Hassine Fantar,
''De Carthage à Kairouan: 2000 ans d’art et d’histoire en Tunisie'',
éd. Agence française d’action artistique,
Paris, 1982,
p. 23 The fame of the Mosque of Uqba and of the other holy sites at Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( ar, ٱلْقَيْرَوَان, al-Qayrawān , aeb, script=Latn, Qeirwān ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by t ...
helped the city to develop and expand. The university, consisting of scholars who taught in the mosque, was a centre of education both in Islamic thought and in the secular sciences. Wilfrid Knapp and Nevill Barbour, North West Africa : a political and economic survey,
Editions Oxford University Press,
Oxford, 1977,
page 404 Its role at the time can be compared to that of the University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. Henri Saladin, Tunis et Kairouan,
Editions Henri Laurens,
Paris, 1908,
page 118 With the decline of the city from the mid-11th century, the centre of intellectual thought moved to the University of Ez-Zitouna in Tunis
''Tounsi'' french: Tunisois
, population_note =
, population_urban =
, population_metro = 2658816
, population_density_km2 =
, timezone1 = CET
, utc_offset1 ...
. Mahmud Abd al-Mawla,
L’université zaytounienne et la société tunisienne,
éditions Maison Tiers-Monde,
Tunis, 1984,
page 33
Location and general aspect


 Located in the north-east of the
Located in the north-east of the medina
Medina,, ', "the radiant city"; or , ', (), "the city" officially Al Madinah Al Munawwarah (, , Turkish: Medine-i Münevvere) and also commonly simplified as Madīnah or Madinah (, ), is the Holiest sites in Islam, second-holiest city in Islam, ...
of Kairouan, the mosque is in the intramural district of Houmat al-Jami (literally "area of the Great Mosque"). This location corresponded originally to the heart of the urban fabric of the city founded by Uqba ibn Nafi
ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī al-Qurashī ( ar, عقبة بن نافع بن عبد القيس الفهري القرشي, ʿUqba ibn Nāfiʿ ibn ʿAbd al-Qays al-Fihrī), also simply known as Uqba ibn Nafi, was an Arab general ser ...
. However given the natural lay of the land crossed by several tributaries of the wadi
Wadi ( ar, وَادِي, wādī), alternatively ''wād'' ( ar, وَاد), North African Arabic Oued, is the Arabic term traditionally referring to a valley. In some instances, it may refer to a wet (ephemeral) riverbed that contains water ...
s, the urban development of the city spread southwards. Human factors including Hilalian's invasions in 449 AH (1057 AD) led to the decline of the city and halted development. For all these reasons, the mosque which once occupied the center of the medina when first built in 670 is now on the easternmost quarter abutting the city walls.
The building is a vast slightly irregular quadrilateral
In geometry a quadrilateral is a four-sided polygon, having four edges (sides) and four corners (vertices). The word is derived from the Latin words ''quadri'', a variant of four, and ''latus'', meaning "side". It is also called a tetragon, ...
covering some 9,000 m2. It is longer (127.60 metres) on the east side than the west (125.20 metres), and shorter on the north side (72.70 metres) than the south (78 metres). The main minaret
A minaret (; ar, منارة, translit=manāra, or ar, مِئْذَنة, translit=miʾḏana, links=no; tr, minare; fa, گلدسته, translit=goldaste) is a type of tower typically built into or adjacent to mosques. Minarets are generall ...
is centered on the north.
From the outside, the Great Mosque of Kairouan is a fortress-like building with its 1.90 metres thick massive ocher walls, a composite of well-worked stones with intervening courses of rubble stone and baked brick
A brick is a type of block used to build walls, pavements and other elements in masonry construction. Properly, the term ''brick'' denotes a block composed of dried clay, but is now also used informally to denote other chemically cured cons ...
s. The corner towers measuring 4.25 metres on each side are buttress
A buttress is an architectural structure built against or projecting from a wall which serves to support or reinforce the wall. Buttresses are fairly common on more ancient buildings, as a means of providing support to act against the lateral (s ...
ed with solid projecting supports. Structurally given the soft grounds subject to compaction, the buttressed towers added stability to the entire mosque.Néji Djelloul, ''op. cit.'', p. 8 Despite the austere façades, the rhythmic patterns of buttresses and towering porch
A porch (from Old French ''porche'', from Latin ''porticus'' "colonnade", from ''porta'' "passage") is a room or gallery located in front of an entrance of a building. A porch is placed in front of the facade of a building it commands, and form ...
es, some surmounted by cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, f ...
s, give the sanctuary a sense of striking sober grandeur. Henri Saladin, ''Tunis et Kairouan'', coll. Les Villes d’art célèbres, éd. Henri Laurens, Paris, 1908, p. 120
History
Evolution
 At the foundation of Kairouan in 670, the Arab general and conqueror Uqba ibn Nafi (himself the founder of the city) chose the site of his mosque in the center of the city, near the headquarters of the governor. Around 690, shortly after its construction, the mosque was destroyed during the occupation of Kairouan by the Berbers, originally conducted by Kusaila. It was rebuilt by the
At the foundation of Kairouan in 670, the Arab general and conqueror Uqba ibn Nafi (himself the founder of the city) chose the site of his mosque in the center of the city, near the headquarters of the governor. Around 690, shortly after its construction, the mosque was destroyed during the occupation of Kairouan by the Berbers, originally conducted by Kusaila. It was rebuilt by the Ghassanid
The Ghassanids ( ar, الغساسنة, translit=al-Ġasāsina, also Banu Ghassān (, romanized as: ), also called the Jafnids, were an Arab tribe which founded a kingdom. They emigrated from southern Arabia in the early 3rd century to the Lev ...
general Hasan ibn al-Nu'man in 703. With the gradual increase of the population of Kairouan and the consequent increase in the number of faithful, Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik
Hisham ibn Abd al-Malik ( ar, هشام بن عبد الملك, Hishām ibn ʿAbd al-Malik; 691 – 6 February 743) was the tenth Umayyad caliph, ruling from 724 until his death in 743.
Early life
Hisham was born in Damascus, the administra ...
, Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
in Damascus
)), is an adjective which means "spacious".
, motto =
, image_flag = Flag of Damascus.svg
, image_seal = Emblem of Damascus.svg
, seal_type = Seal
, map_caption =
, ...
, charged his governor Bishr ibn Safwan to carry out development work in the city, which included the renovation and expansion of the mosque around the years 724–728. During this expansion, he pulled down the mosque and rebuilt it with the exception of the mihrab. It was under his auspices that the construction of the minaret began. In 774, a new reconstruction accompanied by modifications and embellishments took place under the direction of the Abbasid
The Abbasid Caliphate ( or ; ar, الْخِلَافَةُ الْعَبَّاسِيَّة, ') was the third caliphate to succeed the Islamic prophet Muhammad. It was founded by a dynasty descended from Muhammad's uncle, Abbas ibn Abdul-Mutta ...
governor Yazid ibn Hatim.
squinch
In architecture, a squinch is a triangular corner that supports the base of a dome. Its visual purpose is to translate a rectangle into an octagon. See also: pendentive.
Construction
A squinch is typically formed by a masonry arch that spans ...
es. Around 862–863, Emir Abu Ibrahim enlarged the oratory, with three bays
A bay is a recessed, coastal body of water that directly connects to a larger main body of water, such as an ocean, a lake, or another bay. A large bay is usually called a gulf, sea, sound, or bight. A cove is a small, circular bay with a na ...
to the north, and added the cupola
In architecture, a cupola () is a relatively small, most often dome-like, tall structure on top of a building. Often used to provide a lookout or to admit light and air, it usually crowns a larger roof or dome.
The word derives, via Italian, f ...
over the arched portico
A portico is a porch leading to the entrance of a building, or extended as a colonnade, with a roof structure over a walkway, supported by columns or enclosed by walls. This idea was widely used in ancient Greece and has influenced many cul ...
which precedes the prayer hall. In 875 Emir Ibrahim II built another three bays, thereby reducing the size of the courtyard which was further limited on the three other sides by the addition of double galleries.
The current state of the mosque can be traced back to the Aghlabid period—no element is earlier than the ninth century besides the mihrab—except for some partial restorations and a few later additions made in 1025 during the Zirid period, 1248 and 1293–1294 under the reign of the Hafsids
The Hafsids ( ar, الحفصيون ) were a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. who ruled Ifriqiya (west ...
, 1618 at the time of Muradid beys, and in the late nineteenth and early twentieth century. In 1967, major restoration works, executed during five years and conducted under the direction of the National Institute of Archeology and Art, were achieved throughout the monument, and were ended with an official reopening of the mosque during the celebration of the Mawlid
Mawlid, Mawlid an-Nabi ash-Sharif or Eid Milad un Nabi ( ar, المولد النبوي, translit=mawlid an-nabawī, lit=Birth of the Prophet, sometimes simply called in colloquial Arabic , , among other vernacular pronunciations; sometimes , ) ...
of 1972.
Host stories

 Several centuries after its founding, the Great Mosque of Kairouan is the subject of numerous descriptions by Arab historians and geographers in the
Several centuries after its founding, the Great Mosque of Kairouan is the subject of numerous descriptions by Arab historians and geographers in the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
. The stories concern mainly the different phases of construction and expansion of the sanctuary, and the successive contributions of many princes to the interior decoration (mihrab, minbar
A minbar (; sometimes romanized as ''mimber'') is a pulpit in a mosque where the imam (leader of prayers) stands to deliver sermons (, '' khutbah''). It is also used in other similar contexts, such as in a Hussainiya where the speaker sits a ...
, ceilings, etc.). Among the authors who have written on the subject and whose stories have survived are Al-Bakri
Abū ʿUbayd ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Ayyūb ibn ʿAmr al-Bakrī ( ar, أبو عبيد عبد الله بن عبد العزيز بن محمد بن أيوب بن عمرو البكري), or simply al-Bakrī (c. 1040–1 ...
(Andalusian geographer and historian who died in 1094 and who devoted a sufficiently detailed account of the history of the mosque in his book ''Description of Septentrional Africa''), Al-Nuwayri
Al-Nuwayrī, full name Shihāb al-Dīn Aḥmad bin ʿAbd al-Wahhāb al-Nuwayrī ( ar, شهاب الدين أحمد بن عبد الوهاب النويري, born April 5, 1279 in Akhmim, present-day Egypt – died June 5, 1333 in Cairo) was an Eg ...
(historian who died in Egypt, 1332) and Ibn Nagi (scholar and historian of Kairouan who died around 1435).
On additions and embellishments made to the building by the Aghlabid emir Abu Ibrahim, Ibn Nagi gives the following account:
 Among the Western travelers, poets and writers who visited Kairouan, some of them leave impressions and testimonies sometimes tinged with emotion or admiration on the mosque. From the eighteenth century, the French
Among the Western travelers, poets and writers who visited Kairouan, some of them leave impressions and testimonies sometimes tinged with emotion or admiration on the mosque. From the eighteenth century, the French doctor
Doctor or The Doctor may refer to:
Personal titles
* Doctor (title), the holder of an accredited academic degree
* A medical practitioner, including:
** Physician
** Surgeon
** Dentist
** Veterinary physician
** Optometrist
*Other roles
** ...
and naturalist John Andrew Peyssonnel, conducting a study trip to 1724, during the reign of sovereign Al-Husayn Bey I, underlines the reputation of the mosque as a deemed centre of religious and secular studies:
At the same time, the doctor and Anglican priest Thomas Shaw Thomas Shaw is the name of:
Politicians
* Tom Shaw (politician) (1872–1938), British trade unionist and Labour Party politician
* Thomas Shaw (Halifax MP) (1823–1893), English Liberal politician, MP for Halifax
* Thomas Shaw, 1st Baron Crai ...
(1692–1751), touring the Tunis Regency and passes through Kairouan in 1727, described the mosque as that: "which is considered the most beautiful and the most sacred of Berberian territories", evoking for example: "an almost unbelievable number of granite columns".
At the end of the nineteenth century, the French writer Guy de Maupassant
Henri René Albert Guy de Maupassant (, ; ; 5 August 1850 – 6 July 1893) was a 19th-century French author, remembered as a master of the short story form, as well as a representative of the Naturalist school, who depicted human lives, destin ...
expresses in his book ''La vie errante'' (The Wandering Life), his fascination with the majestic architecture of the Great Mosque of Kairouan as well as the effect created by countless columns: "The unique harmony of this temple consists in the proportion and the number of these slender shafts upholding the building, filling, peopling, and making it what it is, create its grace and greatness. Their colorful multitude gives the eye the impression of unlimited". Early in the twentieth century, the Austrian poet
A poet is a person who studies and creates poetry. Poets may describe themselves as such or be described as such by others. A poet may simply be the creator ( thinker, songwriter, writer, or author) who creates (composes) poems (oral or w ...
Rainer Maria Rilke
René Karl Wilhelm Johann Josef Maria Rilke (4 December 1875 – 29 December 1926), shortened to Rainer Maria Rilke (), was an Austrian poet and novelist. He has been acclaimed as an idiosyncratic and expressive poet, and is widely recogn ...
describes his admiration for the impressive minaret:
Architecture and decoration

Exterior
Enclosure
Today, theenclosure
Enclosure or Inclosure is a term, used in English landownership, that refers to the appropriation of "waste" or " common land" enclosing it and by doing so depriving commoners of their rights of access and privilege. Agreements to enclose land ...
of the Great Mosque of Kairouan is pierced by nine gates (six opening on the courtyard, two opening on the prayer hall and a ninth allows access to the maqsura
''Maqsurah'' ( ar, مقصورة, literally "closed-off space") is an enclosure, box, or wooden screen near the ''mihrab'' or the center of the '' qibla'' wall in a mosque. It was typically reserved for a Muslim ruler and his entourage, and was ...
) some of them, such as Bab Al-Ma (gate of water) located on the western façade, are preceded by salient porch
A porch (from Old French ''porche'', from Latin ''porticus'' "colonnade", from ''porta'' "passage") is a room or gallery located in front of an entrance of a building. A porch is placed in front of the facade of a building it commands, and form ...
es flanked by buttresses and surmounted by ribbed domes based on square tholobate
In architecture, a tholobate (from el, θολοβάτης, tholobates, dome pedestal) or drum is the upright part of a building on which a dome is raised. It is generally in the shape of a cylinder or a polygonal prism.
In the earlier Byzanti ...
which are porting squinch
In architecture, a squinch is a triangular corner that supports the base of a dome. Its visual purpose is to translate a rectangle into an octagon. See also: pendentive.
Construction
A squinch is typically formed by a masonry arch that spans ...
es with three vaults. However, Arab geographers and historians of the Middle Ages Al-Muqaddasi
Shams al-Dīn Abū ʿAbd Allāh Muḥammad ibn Aḥmad ibn Abī Bakr al-Maqdisī ( ar, شَمْس ٱلدِّيْن أَبُو عَبْد ٱلله مُحَمَّد ابْن أَحْمَد ابْن أَبِي بَكْر ٱلْمَقْدِسِي), ...
and Al-Bakri
Abū ʿUbayd ʿAbd Allāh ibn ʿAbd al-ʿAzīz ibn Muḥammad ibn Ayyūb ibn ʿAmr al-Bakrī ( ar, أبو عبيد عبد الله بن عبد العزيز بن محمد بن أيوب بن عمرو البكري), or simply al-Bakrī (c. 1040–1 ...
reported the existence, around the tenth and eleventh centuries, of about ten gates named differently from today. This reflects the fact that, unlike the rest of the mosque, the enclosure has undergone significant changes to ensure the stability of the building (adding many buttresses). Thus, some entries have been sealed, while others were kept.
During the thirteenth century, new gates were opened, the most remarkable, Bab Lalla Rihana dated from 1293, is located on the eastern wall of the enclosure. The monumental entrance, work of the Hafsid sovereign Abu Hafs `Umar ibn Yahya (reign from 1284 to 1295), is entered in a salient square, flanked by ancient columns supporting horseshoe arch
The horseshoe arch (; Spanish: "arco de herradura"), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form.
Hi ...
es and covered by a dome on squinch
In architecture, a squinch is a triangular corner that supports the base of a dome. Its visual purpose is to translate a rectangle into an octagon. See also: pendentive.
Construction
A squinch is typically formed by a masonry arch that spans ...
es. The front façade of the porch has a large horseshoe arch relied on two marble columns and surmounted by a frieze adorned with a blind arcade, all crowned by serrated merlon
A merlon is the solid upright section of a battlement (a crenellated parapet) in medieval architecture or fortifications.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 202. Merlons are sometimes ...
s (in a sawtooth arrangement).Néji Djelloul, ''op. cit.'', p. 10 Despite its construction at the end of the thirteenth century, Bab Lalla Rihana blends well with all of the building mainly dating from the ninth century.
Courtyard

 The courtyard is a vast trapezoidal area whose interior dimensions are approximately 67 by 52 metres. It is surrounded on all its four sides by a portico with double rows of arches, opened by slightly horseshoe arches supported by
The courtyard is a vast trapezoidal area whose interior dimensions are approximately 67 by 52 metres. It is surrounded on all its four sides by a portico with double rows of arches, opened by slightly horseshoe arches supported by column
A column or pillar in architecture and structural engineering is a structural element that transmits, through compression (physical), compression, the weight of the structure above to other structural elements below. In other words, a column i ...
s in various marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
s, in granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
or in porphyry, reused from Roman, Early Christian or Byzantine monuments particularly from Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
. Access to the courtyard by six side entrances dating from the ninth and thirteenth centuries.
The portico on the south side of the courtyard, near the prayer hall, includes in its middle a large dressed stone pointed horseshoe arch
An arch is a vertical curved structure that spans an elevated space and may or may not support the weight above it, or in case of a horizontal arch like an arch dam, the hydrostatic pressure against it.
Arches may be synonymous with vau ...
which rests on ancient columns of white veined marble with Corinthian capitals
The Corinthian order (Greek: Κορινθιακός ρυθμός, Latin: ''Ordo Corinthius'') is the last developed of the three principal classical orders of Ancient Greek architecture and Roman architecture. The other two are the Doric order w ...
. This porch of seven metres high is topped with a square base upon which rests a semi-spherical ribbed dome; the latter is ribbed with sharp-edged ribs. The intermediary area, the dodecagon
In geometry, a dodecagon or 12-gon is any twelve-sided polygon.
Regular dodecagon
A regular dodecagon is a figure with sides of the same length and internal angles of the same size. It has twelve lines of reflective symmetry and rotational s ...
al drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a ...
of the dome, is pierced by sixteen small rectangular windows set into rounded niches. The great central arch of the south portico, is flanked on each side by six rhythmically arranged horseshoe arches, which fall on twin columns backed by pillars. Overall, the proportions and general layout of the façade of the south portico, with its thirteen arches of which that in the middle constitutes a sort of triumphal arch crowned with a cupola, form an ensemble with "a powerful air of majesty", according to the French historian and sociologist Paul Sebag (1919–2004).
Details of the courtyard
The combination formed by the courtyard and the galleries that surround it covers an immense area whose dimensions are about 90 metres long and 72 metres in width. The northern part of the courtyard is paved withflagstone
Flagstone (flag) is a generic flat stone, sometimes cut in regular rectangular or square shape and usually used for paving slabs or walkways, patios, flooring, fences and roofing. It may be used for memorials, headstones, facades and other c ...
s while the rest of the floor is almost entirely composed of white marble slabs. Near its centre is an horizontal sundial
A sundial is a horological device that tells the time of day (referred to as civil time in modern usage) when direct sunlight shines by the apparent position of the Sun in the sky. In the narrowest sense of the word, it consists of a f ...
, bearing an inscription in naskhi engraved on the marble dating from 1258 AH (which corresponds to the year 1843) and which is accessed by a little staircase; it determines the time of prayers. The rainwater collector or impluvium, probably the work of the Muradid Bey Mohamed Bey al-Mouradi (1686–1696), is an ingenious system that ensures the capture (with the slightly sloping surface of the courtyard) then filtering stormwater at a central basin furnished with horseshoe arches sculpted in white marble. Freed from its impurities, the water flows into an underground cistern
A cistern (Middle English ', from Latin ', from ', "box", from Greek ', "basket") is a waterproof receptacle for holding liquids, usually water. Cisterns are often built to catch and store rainwater. Cisterns are distinguished from wells by ...
supported by seven-metre-high pillars. In the courtyard there are also several water well
A well is an excavation or structure created in the ground by digging, driving, or drilling to access liquid resources, usually water. The oldest and most common kind of well is a water well, to access groundwater in underground aquifers. T ...
s some of which are placed side by side. Their edges, obtained from the lower parts of ancient cored columns, support the string grooves back the buckets.
Minaret
prayer
Prayer is an invocation or act that seeks to activate a rapport with an object of worship through deliberate communication. In the narrow sense, the term refers to an act of supplication or intercession directed towards a deity or a deifie ...
.
The door giving access to the minaret is framed by a lintel
A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. In the case of ...
and jambs made of recycled carved friezes of antique origin.Néji Djelloul, ''op. cit.'', p. 13 There are stone blocks from the Roman period that bear Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic languages, Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through ...
inscriptions. Their use probably dates to the work done under the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
governor Bishr ibn Safwan in about 725 AD, and they have been reused at the base of the tower. The greater part of the minaret dates from the time of the Aghlabid princes in the ninth century. It consists of regular layers of carefully cut rubble stone, thus giving the work a stylistically admirable homogeneity and unity.
The interior includes a staircase of 129 steps, surmounted by a barrel vault
A barrel vault, also known as a tunnel vault, wagon vault or wagonhead vault, is an architectural element formed by the extrusion of a single curve (or pair of curves, in the case of a pointed barrel vault) along a given distance. The curves are ...
, which gives access to the terraces and the first tier of the minaret. The courtyard façade (or south façade) of the tower is pierced with windows that provide light and ventilation, while the other three façades—facing north, east and west—are pierced with small openings in the form of arrowslits. The minaret, in its present aspect, dates largely from the early ninth century, about 836 AD. It is the oldest minaret in the Muslim world
The terms Muslim world and Islamic world commonly refer to the Islamic community, which is also known as the Ummah. This consists of all those who adhere to the religious beliefs and laws of Islam or to societies in which Islam is practiced. I ...
, and it is also the world's oldest minaret still standing.
Due to its age and its architectural features, the minaret of the Great Mosque of Kairouan is the prototype for all the minarets of the western Islamic world: it served as a model in both North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
and in Andalusia
Andalusia (, ; es, Andalucía ) is the southernmost autonomous community in Peninsular Spain. It is the most populous and the second-largest autonomous community in the country. It is officially recognised as a "historical nationality". The ...
. Despite its massive form and austere decoration, it nevertheless presents a harmonious structure and a majestic appearance.
Domes
 The Mosque has several domes, the largest being over the mihrab and the entrance to the prayer hall from the courtyard. The dome of the mihrab is based on an octagonal drum with slightly concave sides, raised on a square base, decorated on each of its three southern, eastern and western faces with five flat-bottomed niches surmounted by five semi-circular arches, the niche in the middle is cut by a lobed
The Mosque has several domes, the largest being over the mihrab and the entrance to the prayer hall from the courtyard. The dome of the mihrab is based on an octagonal drum with slightly concave sides, raised on a square base, decorated on each of its three southern, eastern and western faces with five flat-bottomed niches surmounted by five semi-circular arches, the niche in the middle is cut by a lobed oculus Oculus (a term from Latin ''oculus'', meaning 'eye'), may refer to the following
Architecture
* Oculus (architecture), a circular opening in the centre of a dome or in a wall
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Oculus'' (film), a 2013 American s ...
enrolled in a circular frame. This dome, whose construction goes back to the first half of the ninth century (towards 836), is one of the oldest and most remarkable domes in the western Islamic world.
Interior
Prayer hall
The prayer hall is located on the southern side of the courtyard; and is accessed by 17 carved wooden doors. A portico with double row of arches precede the spacious prayer hall, which takes the shape of a rectangle of 70.6 metres in width and 37.5 metres' depth. Thehypostyle hall
In architecture, a hypostyle () hall has a roof which is supported by columns.
Etymology
The term ''hypostyle'' comes from the ancient Greek ὑπόστυλος ''hypóstȳlos'' meaning "under columns" (where ὑπό ''hypó'' means below or un ...
is divided into 17 aisles of eight bays, the central nave is wider, as well as the bay along the wall of the qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the ...
. They cross with right angle in front of the mihrab, this device, named "T shape", which is also found in two Iraq
Iraq,; ku, عێراق, translit=Êraq officially the Republic of Iraq, '; ku, کۆماری عێراق, translit=Komarî Êraq is a country in Western Asia. It is bordered by Turkey to Iraq–Turkey border, the north, Iran to Iran–Iraq ...
i mosques in Samarra
Samarra ( ar, سَامَرَّاء, ') is a city in Iraq. It stands on the east bank of the Tigris in the Saladin Governorate, north of Baghdad. The city of Samarra was founded by Abbasid Caliph Al-Mutasim for his Turkish professional ar ...
(around 847) has been adopted in many North African and Andalusian mosques where it became a feature.
The central nave, a sort of triumphal alley which leads to the mihrab, is significantly higher and wider than the other sixteen aisles of the prayer hall. It is bordered on each side of a double row of arches rested on twin columns and surmounted by a carved plaster decoration consisting of floral and geometric patterns.
Enlightened by impressive chandelier
A chandelier (; also known as girandole, candelabra lamp, or least commonly suspended lights) is a branched ornamental light fixture designed to be mounted on ceilings or walls. Chandeliers are often ornate, and normally use incandescent ...
s which are applied in countless small glass lamps, the nave opens into the south portico of the courtyard by a monumental delicately carved wooden door, made in 1828 under the reign of the Husainids. This sumptuous door, which has four leaves
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, st ...
richly carved with geometric motifs embossed on the bottom of foliage
A leaf ( : leaves) is any of the principal appendages of a vascular plant stem, usually borne laterally aboveground and specialized for photosynthesis. Leaves are collectively called foliage, as in "autumn foliage", while the leaves, ...
s and interlacing stars, is decorated at the typanum by a stylised vase
A vase ( or ) is an open container. It can be made from a number of materials, such as ceramics, glass, non-rusting metals, such as aluminium, brass, bronze, or stainless steel. Even wood has been used to make vases, either by using tree species ...
from which emerge winding stems and leaves. The other doors of the prayer hall, some of which date from the time of the Hafsids
The Hafsids ( ar, الحفصيون ) were a Sunni Muslim dynasty of Berber descentC. Magbaily Fyle, ''Introduction to the History of African Civilization: Precolonial Africa'', (University Press of America, 1999), 84. who ruled Ifriqiya (west ...
, are distinguished by their decoration which consists essentially of geometric patterns (hexagonal, octagonal, rectangular patterns, etc.).
= Columns and ceiling
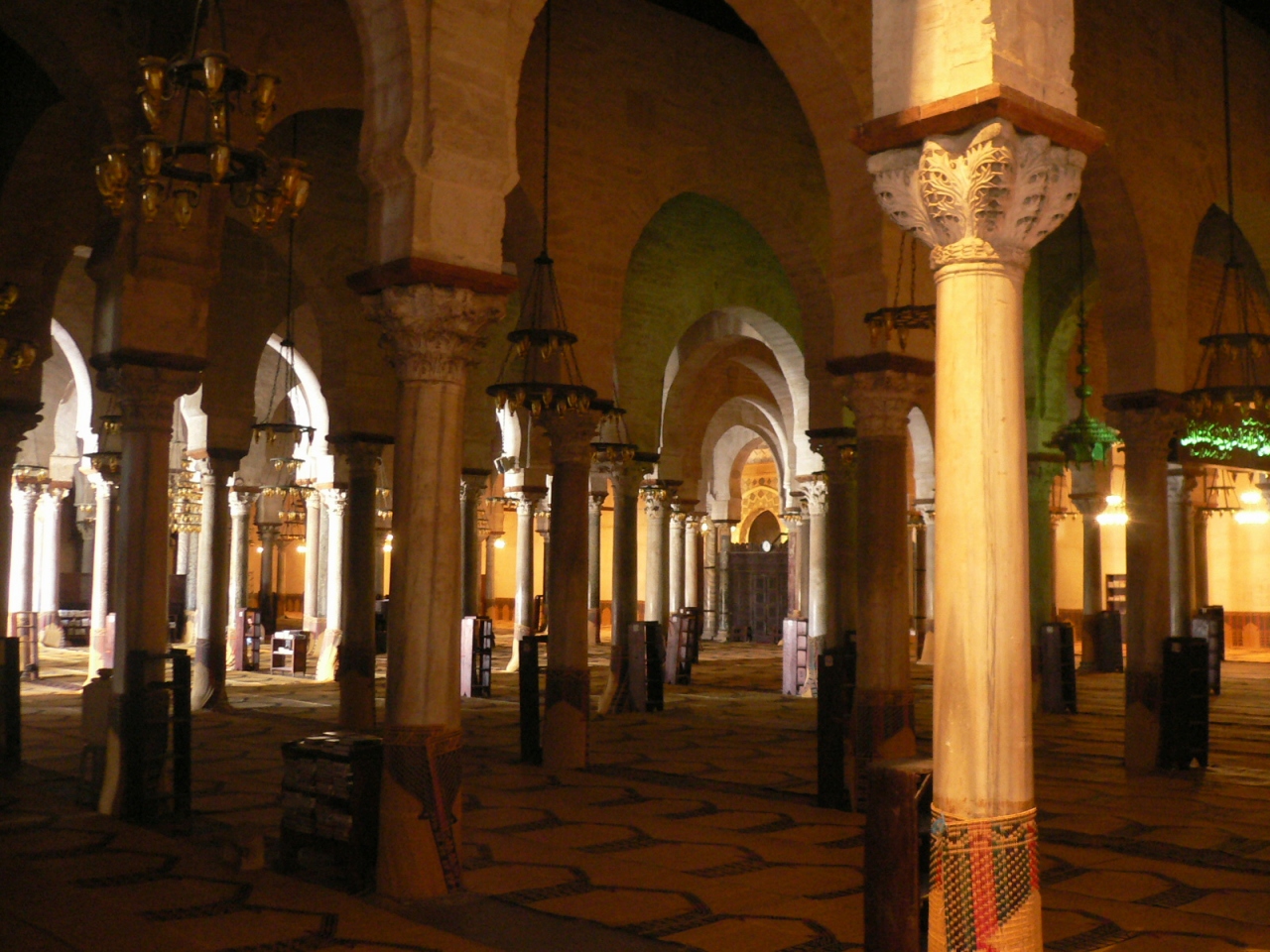
= In the prayer hall, the 414 columns of
In the prayer hall, the 414 columns of marble
Marble is a metamorphic rock composed of recrystallized carbonate minerals, most commonly calcite or dolomite. Marble is typically not foliated (layered), although there are exceptions. In geology, the term ''marble'' refers to metamorphose ...
, granite
Granite () is a coarse-grained ( phaneritic) intrusive igneous rock composed mostly of quartz, alkali feldspar, and plagioclase. It forms from magma with a high content of silica and alkali metal oxides that slowly cools and solidifies un ...
or porphyry (among more than 500 columns in the whole mosque), taken from ancient sites in the country such as Sbeitla
Sbeitla or Sufetula ( ber, Sbitla or Seftula, ar, سبيطلة ') is a small town in west-central Tunisia. Nearby are the Byzantine ruins of Sufetula, containing the best preserved Byzantine forum temples in Tunisia. It was the entry point of the ...
, Carthage
Carthage was the capital city of Ancient Carthage, on the eastern side of the Lake of Tunis in what is now Tunisia. Carthage was one of the most important trading hubs of the Ancient Mediterranean and one of the most affluent cities of the classi ...
, Hadrumetum
Hadrumetum, also known by many variant spellings and names, was a Phoenician colony that pre-dated Carthage. It subsequently became one of the most important cities in Roman Africa before Vandal and Umayyad conquerors left it ruined. In the early ...
and Chemtou, support the horseshoe arch
The horseshoe arch (; Spanish: "arco de herradura"), also called the Moorish arch and the keyhole arch, is an emblematic arch of Islamic architecture, especially Moorish architecture. Horseshoe arches can take rounded, pointed or lobed form.
Hi ...
es. A legend
A legend is a genre of folklore that consists of a narrative featuring human actions, believed or perceived, both by teller and listeners, to have taken place in human history. Narratives in this genre may demonstrate human values, and possess ...
says they could not count them without going blind. The capitals
Capital may refer to:
Common uses
* Capital city, a municipality of primary status
** List of national capital cities
* Capital letter, an upper-case letter Economics and social sciences
* Capital (economics), the durable produced goods used fo ...
resting on the column shafts offer a wide variety of shapes and styles ( Corinthian, Ionic, Composite
Composite or compositing may refer to:
Materials
* Composite material, a material that is made from several different substances
** Metal matrix composite, composed of metal and other parts
** Cermet, a composite of ceramic and metallic materials ...
, etc.). Some capitals were carved for the mosque, but others come from Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
or Byzantine
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
buildings (dating from the second to sixth century) and were reused. According to the German archaeologist
Archaeology or archeology is the scientific study of human activity through the recovery and analysis of material culture. The archaeological record consists of artifacts, architecture, biofacts or ecofacts, sites, and cultural landsca ...
Christian Ewert, the special arrangement of reused columns and capitals surrounding the mihrab obeys to a well-defined program and would draw symbolically the plan of the Dome of the Rock
The Dome of the Rock ( ar, قبة الصخرة, Qubbat aṣ-Ṣakhra) is an Islamic shrine located on the Temple Mount in the Old City of Jerusalem, a site also known to Muslims as the ''al-Haram al-Sharif'' or the Al-Aqsa Compound. Its initial ...
. The shafts of the columns are carved in marble of different colors and different backgrounds. Those in white marble come from Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
, some shafts located in the area of the mihrab are in red porphyry imported from Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
, while those made of greenish or pink marble are from quarries of Chemtou, in the north-west of current Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
. Although the shafts are of varying heights, the columns are ingeniously arranged to support fallen arches harmoniously. The height difference is compensated by the development of variable bases, capitals and crossbeams; a number of these crossbeams are in cedar wood. The wooden rods, which usually sink to the base of the transom, connect the columns together and maintain the spacing of the arches, thus enhancing the stability of all structures which support the ceiling of the prayer hall.
 The covering of the prayer hall consists of painted ceilings decorated with vegetal motifs and two domes: one raised at the beginning of the central nave and the other in front of the
The covering of the prayer hall consists of painted ceilings decorated with vegetal motifs and two domes: one raised at the beginning of the central nave and the other in front of the mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla ...
. The latter, which its hemispherical cap is cut by 24 concave grooves radiating around the top, is based on ridged horns shaped shell and a drum
The drum is a member of the percussion group of musical instruments. In the Hornbostel-Sachs classification system, it is a membranophone. Drums consist of at least one membrane, called a drumhead or drum skin, that is stretched over a ...
pierced by eight circular windows which are inserted between sixteen niche
Niche may refer to:
Science
*Developmental niche, a concept for understanding the cultural context of child development
* Ecological niche, a term describing the relational position of an organism's species
*Niche differentiation, in ecology, the ...
s grouped by two. The niches are covered with carved stone panels, finely adorned with characteristic geometric, vegetal and floral patterns of the Aghlabid
The Aghlabids ( ar, الأغالبة) were an Arab dynasty of emirs from the Najdi tribe of Banu Tamim, who ruled Ifriqiya and parts of Southern Italy, Sicily, and possibly Sardinia, nominally on behalf of the Abbasid Caliph, for about a ...
decorative repertoire: shells, cusped arches, rosettes, vine-leaf, etc. From the outside, the dome of the mihrab is based on an octagonal drum with slightly concave sides, raised on a square base, decorated on each of its three southern, Easter and western faces with five flat-bottomed niches surmounted by five semi-circular arches, the niche in the middle is cut by a lobed oculus Oculus (a term from Latin ''oculus'', meaning 'eye'), may refer to the following
Architecture
* Oculus (architecture), a circular opening in the centre of a dome or in a wall
Arts, entertainment, and media
* ''Oculus'' (film), a 2013 American s ...
enrolled in a circular frame.
 The painted ceilings are a unique ensemble of planks, beams and
The painted ceilings are a unique ensemble of planks, beams and brackets
A bracket is either of two tall fore- or back-facing punctuation marks commonly used to isolate a segment of text or data from its surroundings. Typically deployed in symmetric pairs, an individual bracket may be identified as a 'left' or 'r ...
, illustrating almost thousand years of the history of painting on wood in Tunisia. Wooden brackets offer a wide variety of style and decor in the shape of a crow or a grasshopper with wings or fixed, they are characterised by a setting that combines floral painted or carved, with grooves. The oldest boards date back to the Aghlabid period (ninth century) and are decorated with scrolls and rosettes on a red background consists of squares with concave sides in which are inscribed four-petaled flowers in green and blue, and those performed by the Zirid dynasty
The Zirid dynasty ( ar, الزيريون, translit=az-zīriyyūn), Banu Ziri ( ar, بنو زيري, translit=banū zīrī), or the Zirid state ( ar, الدولة الزيرية, translit=ad-dawla az-zīriyya) was a Sanhaja Berber dynasty from m ...
(eleventh century) are characterised by inscriptions in black kufic writing with gold rim and the uprights of the letters end with lobed florets, all on a brown background adorned with simple floral patterns.
The boards painted under the Hafsid period (during the thirteenth century) offers a floral decor consists of white and blue arches entwined with lobed green. The latest, dated the seventeenth and eighteenth centuries (mostly dating from the time of the Muradid Beys), are distinguished by an epigraphic decoration consists of long black and red texts on olive green background to those painted from 1618 to 1619, under the reign of Murad I Bey (1613–1631), while those back to the eighteenth century have inscriptions in white naskhi script on an orange background.
= Mihrab and minbar
= The
The mihrab
Mihrab ( ar, محراب, ', pl. ') is a niche in the wall of a mosque that indicates the ''qibla'', the direction of the Kaaba in Mecca towards which Muslims should face when praying. The wall in which a ''mihrab'' appears is thus the "qibla ...
, which indicates the Qibla
The qibla ( ar, قِبْلَة, links=no, lit=direction, translit=qiblah) is the direction towards the Kaaba in the Sacred Mosque in Mecca, which is used by Muslims in various religious contexts, particularly the direction of prayer for the ...
(direction of Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow v ...
), in front of which stands the imam
Imam (; ar, إمام '; plural: ') is an Islamic leadership position. For Sunni Muslims, Imam is most commonly used as the title of a worship leader of a mosque. In this context, imams may lead Islamic worship services, lead prayers, serve ...
during the prayer, is located in the middle of the southern wall of the prayer hall. It is formed by an oven-shaped niche
Niche may refer to:
Science
*Developmental niche, a concept for understanding the cultural context of child development
* Ecological niche, a term describing the relational position of an organism's species
*Niche differentiation, in ecology, the ...
framed by two marble columns and topped by a painted wooden half-cupola. The niche of the mihrab is two metres long, 4.5 metres high and 1.6 metres deep.
The mosque's mihrab, whose decor is a remarkable witness of Muslim art in the early centuries of Islam, is distinguished by its harmonious composition and the quality of its ornaments. Considered as the oldest example of concave mihrab
Concave or concavity may refer to:
Science and technology
* Concave lens
* Concave mirror
Mathematics
* Concave function, the negative of a convex function
* Concave polygon, a polygon which is not convex
* Concave set
* The concavity
In ca ...
, it dates in its present state to 862–863 AD.
It is surrounded at its upper part by 139 lusterware tiles (with a metallic sheen), each one is 21.1 centimetres square and they are arranged on the diagonal in a chessboard pattern. Divided into two groups, they are dated from the beginning of the second half of the ninth century but it is not determined with certainty whether they were made in Baghdad
Baghdad (; ar, بَغْدَاد , ) is the capital of Iraq and the second-largest city in the Arab world after Cairo. It is located on the Tigris near the ruins of the ancient city of Babylon and the Sassanid Persian capital of Ctesiphon ...
or in Kairouan by a Baghdadi artisan, the controversy over the origin of this precious collection agitates the specialists. These tiles are mainly decorated with floral and plant motifs (stylised flowers, palm leaves and asymmetrical leaves on bottom hatch and checkered) belong to two series: one polychrome characterised by a greater richness of tones ranging from light gold to light, dark or ocher yellow, and from brick-red to brown lacquer, the other monochrome is a beautiful luster that goes from smoked gold to green gold. The coating around them is decorated with blue plant motifs dating from the eighteenth century or the first half of the nineteenth century. The horseshoe arch of the mihrab, stilted and broken at the top, rest on two columns of red marble with yellow veins, which surmounted with Byzantine style capitals that carry two crossbeams carved with floral patterns, each one is decorated with a Kufic inscription in relief.

minbar
A minbar (; sometimes romanized as ''mimber'') is a pulpit in a mosque where the imam (leader of prayers) stands to deliver sermons (, '' khutbah''). It is also used in other similar contexts, such as in a Hussainiya where the speaker sits a ...
, situated on the right of the mihrab, is used by the imam during the Friday or Eids sermons, is a staircase-shaped pulpit with an upper seat, reached by eleven steps, and measuring 3.93 metres' length to 3.31 metres in height. Dated from the ninth century (about 862) and erected under the reign of the sixth Aghlabid ruler Abul Ibrahim (856–863), it is made in teak
Teak (''Tectona grandis'') is a tropical hardwood tree species in the family Lamiaceae. It is a large, deciduous tree that occurs in mixed hardwood forests. ''Tectona grandis'' has small, fragrant white flowers arranged in dense clusters ( pan ...
wood imported from India. Among all the pulpits of the Muslim world, it is certainly the oldest example of minbar still preserved today. Probably made by cabinetmakers of Kairouan (some researchers also refer to Baghdad), it consists of an assembly of more than 300 finely carved wood pieces with an exceptional ornamental wealth (vegetal and geometric patterns refer to the Umayyad and Abbasid models), among which about 90 rectangular panels carved with plenty of pine cones
A conifer cone (in formal botanical usage: strobilus, plural strobili) is a seed-bearing organ on gymnosperm plants. It is usually woody, ovoid to globular, including scales and bracts arranged around a central axis, especially in conifers ...
, grape leaves, thin and flexible stems, lanceolate fruits and various geometric shapes (squares, diamonds, stars, etc.). The upper edge of the minbar ramp is adorned with a rich and graceful vegetal decoration composed of alternately arranged foliated scrolls, each one containing a spread vine-leaf and a cluster of grapes. In the early twentieth century, the minbar had a painstaking restoration. Although it has existed for more than eleven centuries, all panels, with the exception of nine, are originals and are in a good state of conservation, the fineness of the execution of the minbar makes it a great masterpiece of Islamic wood carving referring to Paul Sebag. This old chair of the ninth century is still in its original location, next to the mihrab.
= Maqsura
= The
The maqsura
''Maqsurah'' ( ar, مقصورة, literally "closed-off space") is an enclosure, box, or wooden screen near the ''mihrab'' or the center of the '' qibla'' wall in a mosque. It was typically reserved for a Muslim ruler and his entourage, and was ...
, located near the minbar, consists of a fence bounding a private enclosure that allows the sovereign and his senior officials to follow the solemn prayer of Friday without mingling with the faithful. Jewel of the art of woodwork
Woodworking is the skill of making items from wood, and includes cabinet making (cabinetry and furniture), wood carving, joinery, carpentry, and woodturning.
History
Along with stone, clay and animal parts, wood was one of the first mater ...
produced during the reign of the Zirid prince Al-Mu'izz ibn Badis and dated from the first half of the eleventh century, it is considered the oldest still in place in the Islamic world. It is a cedar wood fence finely sculpted and carved on three sides with various geometric motifs measuring 2.8 metres tall, eight metres long and six metres wide. Its main adornment is a frieze that crowns calligraphy, the latter surmounted by a line of pointed openwork merlon
A merlon is the solid upright section of a battlement (a crenellated parapet) in medieval architecture or fortifications.Friar, Stephen (2003). ''The Sutton Companion to Castles'', Sutton Publishing, Stroud, 2003, p. 202. Merlons are sometimes ...
s, features an inscription in flowery kufic character carved on the background of interlacing plants. Carefully executed in relief, it represents one of the most beautiful epigraphic
Epigraphy () is the study of inscriptions, or epigraphs, as writing; it is the science of identifying graphemes, clarifying their meanings, classifying their uses according to dates and cultural contexts, and drawing conclusions about the wr ...
bands of Islamic art.
The library is near located, accessible by a door which the jambs and the lintel
A lintel or lintol is a type of beam (a horizontal structural element) that spans openings such as portals, doors, windows and fireplaces. It can be a decorative architectural element, or a combined ornamented structural item. In the case of ...
are carved in marble, adorned with a frieze of floral decoration. The library window is marked by an elegant setting that has two columns flanking the opening, which is a horseshoe arch topped by six blind arches and crowned by a series of berms sawtooth.
Artworks
The Mosque of Uqba, one of the few religious buildings of Islam has remained intact almost all of its architectural and decorative elements, is due to the richness of its repertoire which is a veritablemuseum
A museum ( ; plural museums or, rarely, musea) is a building or institution that cares for and displays a collection of artifacts and other objects of artistic, cultural, historical, or scientific importance. Many public museums make th ...
of Islamic decorative art and architecture. Most of the works on which rests the reputation of the mosque are still conserved in situ while a certain number of them have joined the collections of the Raqqada
Raqqāda ( ar, رقّادة) is the site of the second capital of the 9th-century dynasty of Aghlabids, located about ten kilometers southwest of Kairouan, Tunisia. The site now houses the National Museum of Islamic Art.
History
In 876, the ni ...
National Museum of Islamic Art; Raqqada is located about ten kilometres southwest of Kairouan.
From the library of the mosque comes a large collection of calligraphic scroll
A scroll (from the Old French ''escroe'' or ''escroue''), also known as a roll, is a roll of papyrus, parchment, or paper containing writing.
Structure
A scroll is usually partitioned into pages, which are sometimes separate sheets of papyrus ...
s and manuscript
A manuscript (abbreviated MS for singular and MSS for plural) was, traditionally, any document written by hand – or, once practical typewriters became available, typewritten – as opposed to mechanically printed or reproduced i ...
s, the oldest dating back to the second half of the ninth century. This valuable collection, observed from the late nineteenth century by the French orientalists Octave Houdas and René Basset
René Basset (24July 18554January 1924) was a French orientalist, specialist of the Berber language and the Arabic language.
Biography
René Basset was the first director of the "École des lettres d'Alger" created in 1879 during the Fren ...
who mention in their report on their scientific mission in Tunisia published in the Journal of African correspondence in 1882, comprises according to the inventory established at the time of the Hafsids (circa 1293–1294) several Qur'ans and books of fiqh
''Fiqh'' (; ar, فقه ) is Islamic jurisprudence. Muhammad-> Companions-> Followers-> Fiqh.
The commands and prohibitions chosen by God were revealed through the agency of the Prophet in both the Quran and the Sunnah (words, deeds, and e ...
that concern mainly the Maliki
The ( ar, مَالِكِي) school is one of the four major schools of Islamic jurisprudence within Sunni Islam. It was founded by Malik ibn Anas in the 8th century. The Maliki school of jurisprudence relies on the Quran and hadiths as prima ...
fiqh and its sources. These are the oldest fund of Maliki legal literature to have survived.
 Among the finest works of this series, the pages of the Blue Qur'an, currently exhibited at Raqqada National Museum of Islamic Art, from a famous
Among the finest works of this series, the pages of the Blue Qur'an, currently exhibited at Raqqada National Museum of Islamic Art, from a famous Qur'an
The Quran (, ; Standard Arabic: , Quranic Arabic: , , 'the recitation'), also romanized Qur'an or Koran, is the central religious text of Islam, believed by Muslims to be a revelation from God. It is organized in 114 chapters (pl.: , si ...
in the second half of the fourth century of the Hijrah (the tenth century) most of which is preserved in Tunisia and the rest scattered in museums and private collections worldwide. Featuring kufic character sura
A ''surah'' (; ar, سورة, sūrah, , ), is the equivalent of "chapter" in the Qur'an. There are 114 ''surahs'' in the Quran, each divided into '' ayats'' (verses). The chapters or ''surahs'' are of unequal length; the shortest surah ('' Al-K ...
s are written in gold on vellum
Vellum is prepared animal skin or membrane, typically used as writing material. Parchment is another term for this material, from which vellum is sometimes distinguished, when it is made from calfskin, as opposed to that made from other anim ...
dyed with indigo
Indigo is a deep color close to the color wheel blue (a primary color in the RGB color space), as well as to some variants of ultramarine, based on the ancient dye of the same name. The word "indigo" comes from the Latin word ''indicum'', ...
, they are distinguished by a compact graph with no marks for vowels. The beginning of each surah is indicated by a band consisting of a golden stylised leafy foliage, dotted with red and blue, while the verses are separated by silver rosettes. Other scrolls and calligraphic Qur'ans, as that known as the Hadinah's Qur'an, copied and illuminated by the calligrapher Ali ibn Ahmad al-Warraq for the governess of the Zirid prince Al-Muizz ibn Badis at about 1020 AD, were also in the library before being transferred to Raqqada museum. This collection is a unique source for studying the history and evolution of calligraphy of medieval manuscripts in the Maghreb, covering the period from the ninth to the eleventh century.
Other works of art such as the crowns of light (circular chandeliers) made in cast bronze
Bronze is an alloy consisting primarily of copper, commonly with about 12–12.5% tin and often with the addition of other metals (including aluminium, manganese, nickel, or zinc) and sometimes non-metals, such as phosphorus, or metalloids suc ...
, dating from the Fatimid
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a dyna ...
- Zirid period (around the tenth to the early eleventh century), originally belonged to the furniture of the mosque. These polycandelons, now scattered in various Tunisian museums including Raqqada, consist of three chains supporting a perforated brass plate, which has a central circular ring around which radiate 18 equidistant poles connected by many horseshoe arches and equipped for each of two landmarks flared. The three chains, connected by a suspension ring, are each fixed to the plate by an almond-shaped finial. The crowns of light are marked by Byzantine influence to which the Kairouanese artisan brought the specificities of Islamic decorative repertoire (geometric and floral motifs).
Role in Muslim civilisation
At the time of its greatest splendor, between the ninth and eleventh centuries AD, Kairouan was one of the greatest centres of Islamic civilisation and its reputation as a hotbed of scholarship covered the entireMaghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
. During this period, the Great Mosque of Kairouan was both a place of prayer and a centre for teaching Islamic sciences under the Maliki current. One may conceivably compare its role to that of the University of Paris
, image_name = Coat of arms of the University of Paris.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Coat of Arms
, latin_name = Universitas magistrorum et scholarium Parisiensis
, motto = ''Hic et ubique terrarum'' (Latin)
, mottoeng = Here and a ...
during the Middle Ages
In the history of Europe, the Middle Ages or medieval period lasted approximately from the late 5th to the late 15th centuries, similar to the post-classical period of global history. It began with the fall of the Western Roman Empire ...
.
In addition to studies on the deepening of religious thought and Maliki jurisprudence
Jurisprudence, or legal theory, is the theoretical study of the propriety of law. Scholars of jurisprudence seek to explain the nature of law in its most general form and they also seek to achieve a deeper understanding of legal reasoning ...
, the mosque also hosted various courses in secular subjects such as mathematics, astronomy
Astronomy () is a natural science that studies celestial objects and phenomena. It uses mathematics, physics, and chemistry in order to explain their origin and evolution. Objects of interest include planets, moons, stars, nebulae, g ...
, medicine and botany
Botany, also called , plant biology or phytology, is the science of plant life and a branch of biology. A botanist, plant scientist or phytologist is a scientist who specialises in this field. The term "botany" comes from the Ancient Greek w ...
. The transmission of knowledge was assured by prominent scholars and theologians which included Sahnun ibn Sa'id and Asad ibn al-Furat, eminent jurists who contributed greatly to the dissemination of the Maliki thought, Ishaq ibn Imran and Ibn al-Jazzar in medicine, Abu Sahl al-Kairouani and Abd al-Monim al-Kindi in mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
. Thus, the mosque, headquarters of a prestigious university with a large library containing a large number of scientific and theological works, was the most remarkable intellectual and cultural centre in North Africa during the ninth, tenth and eleventh centuries.
See also
*List of the oldest mosques
The designation of the oldest mosques in the world requires careful use of definitions, and must be divided into two parts, the oldest in the sense of oldest surviving building, and the oldest in the sense of oldest mosque congregation. Even her ...
* History of medieval Arabic and Western European domes
The early domes of the Middle Ages, particularly in those areas recently under Byzantine control, were an extension of earlier Roman architecture. The domed church architecture of Italy from the sixth to the eighth centuries followed that of the ...
* Minar (Firuzabad)
* Moorish Mosque, Kapurthala
The Moorish Mosque, Kapurthala situated in Kapurthala in the Indian State of Punjab is patterned on the lines of the Grand Mosque of Marrakesh, Morocco. It was commissioned by Maharajah Jagatjit Singh, the last ruler of Kapurthala. Kapurthala c ...
References
Further reading
* Néji Djelloul, 2000. ''Kairouan, the Great Mosque''. Editions Contrastes. * Paul Sebag, 1965. ''Great Mosque of Kairouan''. New York Macmillan. * John D. Hoag, 1987. ''Islamic architecture''. Rizzoli. * Jonathan M. Bloom, 2002. ''Early Islamic art and architecture''. Ashgate. * G. T. Rivoira, 2009, ''Moslem Architecture. Its Origins and Development''. ASLAN PR.External links
Okba Ibn Nafaa Mosque in Kairouan (Mosque of Uqba) website
Panoramic visit of the Great Mosque of Kairouan
Sacred Destinations : Great Mosque of Kairouan
Great Mosque of Kairouan (Qantara Mediterranean Heritage)
Video of the mihrab of the Great Mosque of Kairouan
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mosque Of Uqba 7th-century establishments in Africa 8th-century mosques Uqba Arcades (architecture) Kairouan 7th-century establishments in the Umayyad Caliphate
Kairouan
Kairouan (, ), also spelled El Qayrawān or Kairwan ( ar, ٱلْقَيْرَوَان, al-Qayrawān , aeb, script=Latn, Qeirwān ), is the capital of the Kairouan Governorate in Tunisia and a UNESCO World Heritage Site. The city was founded by t ...
Mosques completed in 670
Mosques completed in 703
7th-century mosques
Aghlabid architecture