Molotov Plan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 The Molotov Plan was the system created by the
The Molotov Plan was the system created by the ">"A Look back at the Marshall Plan"
The plan was in some ways contradictory because while the Soviets were giving aid to
 *
*
 The Molotov Plan was the system created by the
The Molotov Plan was the system created by the Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
in order to provide aid to rebuild the countries in Eastern Europe that were politically and economically aligned to the Soviet Union. It was called the "Brother Plan" in the Soviet Union and can be seen to be the Soviet Union's version of the Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
, which, for political reasons, the Eastern European countries would not be able to join without leaving the Soviet sphere of influence
The term "Soviet empire" collectively refers to the world's territories that the Soviet Union dominated politically, economically, and militarily. This phenomenon, particularly in the context of the Cold War, is used by Sovietologists to descri ...
. However, the Molotov Plan cannot be considered a Soviet response to the Marshall's initiative, as the Soviet plan antedated the American by about two years, because it started operating the Eastern Europe as early as 1945. Soviet foreign minister Vyacheslav Molotov
Vyacheslav Mikhaylovich Molotov (; – 8 November 1986) was a Soviet politician, diplomat, and revolutionary who was a leading figure in the government of the Soviet Union from the 1920s to the 1950s, as one of Joseph Stalin's closest allies. ...
rejected the Marshall Plan (1947), turning the Molotov Plan into the Soviet-sponsored economic grouping which was eventually expanded to become the Comecon
The Council for Mutual Economic Assistance, often abbreviated as Comecon ( ) or CMEA, was an economic organization from 1949 to 1991 under the leadership of the Soviet Union that comprised the countries of the Eastern Bloc#List of states, Easter ...
.
The Molotov Plan was symbolic of the Soviet Union's refusal to accept aid from the Marshall Plan, or allow any of their satellite states to do so because of their belief that the Marshall Plan was an attempt to weaken Soviet interest in their satellite states through the conditions imposed and by making beneficiary countries economically dependent on the United States (officially, one of the goals of the Marshall Plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
was to prevent the spread of Communism
Communism () is a political sociology, sociopolitical, political philosophy, philosophical, and economic ideology, economic ideology within the history of socialism, socialist movement, whose goal is the creation of a communist society, a ...
). The plan was a system of bilateral trade agreements which also established Comecon to create an economic alliance of socialist countries. This aid allowed countries in Europe to stop relying on American aid and therefore allowed Molotov Plan states to reorganize their trade to the Soviet Union instead.The plan was in some ways contradictory because while the Soviets were giving aid to
Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries, at the same time they were demanding that countries who were members of the Axis powers
The Axis powers, originally called the Rome–Berlin Axis and also Rome–Berlin–Tokyo Axis, was the military coalition which initiated World War II and fought against the Allies of World War II, Allies. Its principal members were Nazi Ge ...
(many of them Eastern Bloc
The Eastern Bloc, also known as the Communist Bloc (Combloc), the Socialist Bloc, the Workers Bloc, and the Soviet Bloc, was an unofficial coalition of communist states of Central and Eastern Europe, Asia, Africa, and Latin America that were a ...
countries themselves or a predecessor to an Eastern Bloc country) pay reparations to the Soviet Union. Thus, the Soviet Union has been receiving regular payments from Italy
Italy, officially the Italian Republic, is a country in Southern Europe, Southern and Western Europe, Western Europe. It consists of Italian Peninsula, a peninsula that extends into the Mediterranean Sea, with the Alps on its northern land b ...
, Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
, Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
, and Finland
Finland, officially the Republic of Finland, is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It borders Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bothnia to the west and the Gulf of Finland to the south, ...
, setting up a payment plan of $900 million over 8 years.
The Molotov's program had set multiple objectives for itself. The maximum aims that were set were to obtain economic control over Europe, to adapt the European economy to its own, and to convert them into a market for the Soviet surpluses. The minimum aims consisted of establish governments that are friendly, at least, to the Soviet Union. The technique that the Soviet government was using was a network of trade agreements. Between 1945 and 1947, USSR has concluded eleven important agreements with its satellites
A satellite or an artificial satellite is an object, typically a spacecraft, placed into orbit around a celestial body. They have a variety of uses, including communication relay, weather forecasting, navigation ( GPS), broadcasting, scientif ...
. Those were mostly trade agreements with which USSR was sending the raw material and food (such as grain, coal, cotton, and metals) and receiving the manufacturing goods and equipment for its industries. When it comes to Germany, one other Soviet goal was to seek retributions from it, seeking for hundreds of millions of dollars from East Germany's economy and having the Red Army
The Workers' and Peasants' Red Army, often shortened to the Red Army, was the army and air force of the Russian Soviet Republic and, from 1922, the Soviet Union. The army was established in January 1918 by a decree of the Council of People ...
living off of the land it occupying, avoiding using its domestic resources. Because of the high casualties and losses during World War II, the Soviet Union was not repenting about taking what it can in Germany.
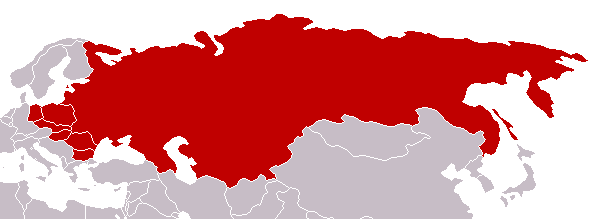
List of nations which took part in the Molotov Plan
 *
* Soviet Union
The Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR), commonly known as the Soviet Union, was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 until Dissolution of the Soviet ...
* Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It extends from the Baltic Sea in the north to the Sudetes and Carpathian Mountains in the south, bordered by Lithuania and Russia to the northeast, Belarus and Ukrai ...
* Czechoslovakia
Czechoslovakia ( ; Czech language, Czech and , ''Česko-Slovensko'') was a landlocked country in Central Europe, created in 1918, when it declared its independence from Austria-Hungary. In 1938, after the Munich Agreement, the Sudetenland beca ...
* Hungary
Hungary is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Spanning much of the Pannonian Basin, Carpathian Basin, it is bordered by Slovakia to the north, Ukraine to the northeast, Romania to the east and southeast, Serbia to the south, Croatia and ...
* Romania
Romania is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern and Southeast Europe. It borders Ukraine to the north and east, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Bulgaria to the south, Moldova to ...
* Bulgaria
Bulgaria, officially the Republic of Bulgaria, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern portion of the Balkans directly south of the Danube river and west of the Black Sea. Bulgaria is bordered by Greece and Turkey t ...
* East Germany
East Germany, officially known as the German Democratic Republic (GDR), was a country in Central Europe from Foundation of East Germany, its formation on 7 October 1949 until German reunification, its reunification with West Germany (FRG) on ...
See also
* Invasion of Poland 1939 *Molotov–Ribbentrop pact
The Molotov–Ribbentrop Pact, officially the Treaty of Non-Aggression between Germany and the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics, and also known as the Hitler–Stalin Pact and the Nazi–Soviet Pact, was a non-aggression pact between Nazi Ge ...
* Marshall plan
The Marshall Plan (officially the European Recovery Program, ERP) was an American initiative enacted in 1948 to provide foreign aid to Western Europe. The United States transferred $13.3 billion (equivalent to $ in ) in economic recovery pr ...
References