Molecular solid on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 A molecular solid is a
A molecular solid is a
 Argon, is a
Argon, is a
 For acetone dipole-dipole interactions are a major driving force behind the structure of its crystal lattice. The negative dipole is caused by oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen, causing a partial negative (δ-) and positive charge (δ+) on the oxygen and remainder of the molecule, respectively. The δ- orienttowards the δ+ causing the acetone molecules to prefer to align in a few configurations in a δ- to δ+ orientation (pictured left). The dipole-dipole and other intermolecular interactions align to minimize energy in the solid state and determine the crystal lattice structure.
For acetone dipole-dipole interactions are a major driving force behind the structure of its crystal lattice. The negative dipole is caused by oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen, causing a partial negative (δ-) and positive charge (δ+) on the oxygen and remainder of the molecule, respectively. The δ- orienttowards the δ+ causing the acetone molecules to prefer to align in a few configurations in a δ- to δ+ orientation (pictured left). The dipole-dipole and other intermolecular interactions align to minimize energy in the solid state and determine the crystal lattice structure.
 A quadrupole, like a dipole, is a permanent pole but the electric field of the molecule is not linear as in acetone, but in two dimensions. Examples of molecular solids with quadrupoles are octafluoronaphthalene and naphthalene. Naphthalene consists of two joined conjugated rings. The electronegativity of the atoms of this ring system and conjugation cause a
A quadrupole, like a dipole, is a permanent pole but the electric field of the molecule is not linear as in acetone, but in two dimensions. Examples of molecular solids with quadrupoles are octafluoronaphthalene and naphthalene. Naphthalene consists of two joined conjugated rings. The electronegativity of the atoms of this ring system and conjugation cause a
 A hydrogen bond is a specific dipole where a hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) to due a neighboring electronegative atom or
A hydrogen bond is a specific dipole where a hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) to due a neighboring electronegative atom or  A halogen bond is when an electronegative halide participates in a noncovalent interaction with a less electronegative atom on an adjacent molecule. Examples of molecular solids that halogen bond are hexachlorobenzene and a
A halogen bond is when an electronegative halide participates in a noncovalent interaction with a less electronegative atom on an adjacent molecule. Examples of molecular solids that halogen bond are hexachlorobenzene and a
 Coulombic interactions are manifested in some molecular solids. A well-studied example is the radical ion salt TTF-TCNQ with a conductivity of 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1, much closer to copper (ρ = 6 x 105 Ω−1 cm−1) than many molecular solids. The coulombic interaction in TTF-TCNQ stems from the large partial negative charge (δ = -0.59) on the cyano- moiety on TCNQ at room temperature. For reference, a completely charged molecule δ = ±1. This partial negative charge leads to a strong interaction with the thio- moiety of the TTF. The strong interaction leads to favorable alignment of these functional groups adjacent to each other in the solid state. While π-π interactions cause the TTF and TCNQ to stack in separate columns.
Coulombic interactions are manifested in some molecular solids. A well-studied example is the radical ion salt TTF-TCNQ with a conductivity of 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1, much closer to copper (ρ = 6 x 105 Ω−1 cm−1) than many molecular solids. The coulombic interaction in TTF-TCNQ stems from the large partial negative charge (δ = -0.59) on the cyano- moiety on TCNQ at room temperature. For reference, a completely charged molecule δ = ±1. This partial negative charge leads to a strong interaction with the thio- moiety of the TTF. The strong interaction leads to favorable alignment of these functional groups adjacent to each other in the solid state. While π-π interactions cause the TTF and TCNQ to stack in separate columns.
 A molecular solid is a
A molecular solid is a solid
Solid is one of the four fundamental states of matter (the others being liquid, gas, and plasma). The molecules in a solid are closely packed together and contain the least amount of kinetic energy. A solid is characterized by structural ...
consisting of discrete molecule
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioche ...
s. The cohesive forces that bind the molecules together are van der Waals force
In molecular physics, the van der Waals force is a distance-dependent interaction between atoms or molecules. Unlike ionic or covalent bonds, these attractions do not result from a chemical electronic bond; they are comparatively weak and th ...
s, dipole-dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, halogen bond A halogen bond occurs when there is evidence of a net attractive interaction between an electrophilic region associated with a halogen atom in a molecular entity and a nucleophilic region in another, or the same, molecular entity. Like a hydrogen ...
ing, London dispersion forces, and in some molecular solids, coulombic interactions. Van der Waals, dipole interactions, quadrupole interactions, π-π interactions, hydrogen bonding, and halogen bonding (2-127 kJ mol−1) are typically much weaker than the forces holding together other solids: metal
A metal (from Greek μέταλλον ''métallon'', "mine, quarry, metal") is a material that, when freshly prepared, polished, or fractured, shows a lustrous appearance, and conducts electricity and heat relatively well. Metals are typicall ...
lic (metallic bonding
Metallic bonding is a type of chemical bonding that arises from the electrostatic attractive force between conduction electrons (in the form of an electron cloud of delocalized electrons) and positively charged metal ions. It may be des ...
, 400-500 kJ mol−1), ionic ( Coulomb’s forces, 700-900 kJ mol−1), and network solids ( covalent bonds, 150-900 kJ mol−1). Intermolecular interactions, typically do not involve delocalized electron
In chemistry, delocalized electrons are electrons in a molecule, ion or solid metal that are not associated with a single atom or a covalent bond.IUPAC Gold Boo''delocalization''/ref>
The term delocalization is general and can have slightly dif ...
s, unlike metallic and certain covalent bonds. Exceptions are charge-transfer complexes such as the tetrathiafulvane-tetracyanoquinodimethane (TTF-TCNQ), a radical ion salt. These differences in the strength of force (i.e. covalent vs. van der Waals) and electronic characteristics (i.e. delocalized electrons) from other types of solids give rise to the unique mechanical, electronic
Electronic may refer to:
*Electronics, the science of how to control electric energy in semiconductor
* ''Electronics'' (magazine), a defunct American trade journal
*Electronic storage, the storage of data using an electronic device
*Electronic co ...
, and thermal properties of molecular solids.
Molecular solids are poor electrical conductor
In physics and electrical engineering, a conductor is an object or type of material that allows the flow of charge (electric current) in one or more directions. Materials made of metal are common electrical conductors. Electric current is gene ...
s, although some, such as TTF-TCNQ are semiconductors (ρ = 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1). They are still substantially less than the conductivity of copper (ρ = 6 x 105 Ω−1 cm−1). Molecular solids tend to have lower fracture toughness ( sucrose, KIc = 0.08 MPa
MPA or mPa may refer to:
Academia
Academic degrees
* Master of Performing Arts
* Master of Professional Accountancy
* Master of Public Administration
* Master of Public Affairs
Schools
* Mesa Preparatory Academy
* Morgan Park Academy
* Mou ...
m1/2) than metal (iron
Iron () is a chemical element with Symbol (chemistry), symbol Fe (from la, Wikt:ferrum, ferrum) and atomic number 26. It is a metal that belongs to the first transition series and group 8 element, group 8 of the periodic table. It is, Abundanc ...
, KIc = 50 MPa m1/2), ionic ( sodium chloride, KIc = 0.5 MPa m1/2), and covalent solids (diamond
Diamond is a solid form of the element carbon with its atoms arranged in a crystal structure called diamond cubic. Another solid form of carbon known as graphite is the chemically stable form of carbon at room temperature and pressure, ...
, KIc = 5 MPa m1/2). Molecular solids have low melting (Tm) and boiling (Tb) points compared to metal (iron), ionic (sodium chloride), and covalent solids (diamond). Examples of molecular solids with low melting and boiling temperatures include argon
Argon is a chemical element with the symbol Ar and atomic number 18. It is in group 18 of the periodic table and is a noble gas. Argon is the third-most abundant gas in Earth's atmosphere, at 0.934% (9340 ppmv). It is more than twice as ...
, water
Water (chemical formula ) is an Inorganic compound, inorganic, transparent, tasteless, odorless, and Color of water, nearly colorless chemical substance, which is the main constituent of Earth's hydrosphere and the fluids of all known living ...
, naphthalene, nicotine
Nicotine is a natural product, naturally produced alkaloid in the nightshade family of plants (most predominantly in tobacco and ''Duboisia hopwoodii'') and is widely used recreational drug use, recreationally as a stimulant and anxiolytic. As ...
, and caffeine
Caffeine is a central nervous system (CNS) stimulant of the methylxanthine class. It is mainly used recreationally as a cognitive enhancer, increasing alertness and attentional performance. Caffeine acts by blocking binding of adenosine to ...
(see table below). The constituents of molecular solids range in size from condensed monatomic gases to small molecules (i.e. naphthalene and water) to large molecules with tens of atoms (i.e. fullerene
A fullerene is an allotrope of carbon whose molecule consists of carbon atoms connected by single and double bonds so as to form a closed or partially closed mesh, with fused rings of five to seven atoms. The molecule may be a hollow sphere, ...
with 60 carbon
Carbon () is a chemical element with the symbol C and atomic number 6. It is nonmetallic and tetravalent—its atom making four electrons available to form covalent chemical bonds. It belongs to group 14 of the periodic table. Carbon mak ...
atoms).
Composition and structure
Molecular solids may consist of single atoms, diatomic, and/or polyatomic molecules. The intermolecular interactions between the constituents dictate how the crystal lattice of the material is structured. All atoms and molecules can partake in van der Waals and London dispersion forces ( sterics). It is the lack or presence of other intermolecular interactions based on the atom or molecule that affords materials unique properties.Van der Waals forces
 Argon, is a
Argon, is a noble gas
The noble gases (historically also the inert gases; sometimes referred to as aerogens) make up a class of chemical elements with similar properties; under standard conditions, they are all odorless, colorless, monatomic gases with very low ch ...
that has a full octet, no charge
Charge or charged may refer to:
Arts, entertainment, and media Films
* '' Charge, Zero Emissions/Maximum Speed'', a 2011 documentary
Music
* ''Charge'' (David Ford album)
* ''Charge'' (Machel Montano album)
* ''Charge!!'', an album by The Aqu ...
, and is nonpolar
In chemistry, polarity is a separation of electric charge leading to a molecule or its chemical groups having an electric dipole moment, with a negatively charged end and a positively charged end.
Polar molecules must contain one or more polar ...
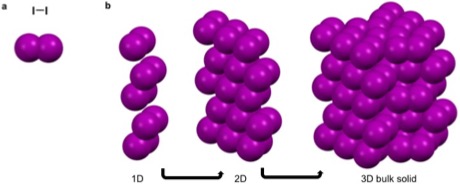
. These characteristics make it unfavorable for argon to partake in metallic, covalent, and ionic bonds as well as most intermolecular interactions. It can though partake in van der Waals and London dispersion forces. These weak self-interactions are isotropic and result in the long-range ordering of the atoms into face centered cubic packing when cooled below -189.3. Similarly iodine, a linear diatomic molecule has a net dipole of zero and can only partake in van der Waals interactions that are fairly isotropic. This results in the bipyramidal symmetry.
Dipole-dipole and quadrupole interactions
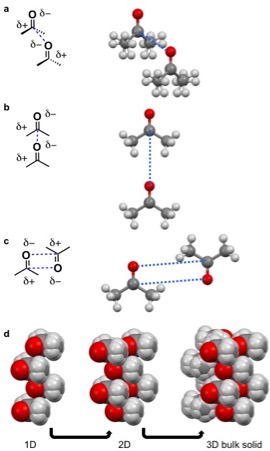
 For acetone dipole-dipole interactions are a major driving force behind the structure of its crystal lattice. The negative dipole is caused by oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen, causing a partial negative (δ-) and positive charge (δ+) on the oxygen and remainder of the molecule, respectively. The δ- orienttowards the δ+ causing the acetone molecules to prefer to align in a few configurations in a δ- to δ+ orientation (pictured left). The dipole-dipole and other intermolecular interactions align to minimize energy in the solid state and determine the crystal lattice structure.
For acetone dipole-dipole interactions are a major driving force behind the structure of its crystal lattice. The negative dipole is caused by oxygen. Oxygen is more electronegative than carbon and hydrogen, causing a partial negative (δ-) and positive charge (δ+) on the oxygen and remainder of the molecule, respectively. The δ- orienttowards the δ+ causing the acetone molecules to prefer to align in a few configurations in a δ- to δ+ orientation (pictured left). The dipole-dipole and other intermolecular interactions align to minimize energy in the solid state and determine the crystal lattice structure.
 A quadrupole, like a dipole, is a permanent pole but the electric field of the molecule is not linear as in acetone, but in two dimensions. Examples of molecular solids with quadrupoles are octafluoronaphthalene and naphthalene. Naphthalene consists of two joined conjugated rings. The electronegativity of the atoms of this ring system and conjugation cause a
A quadrupole, like a dipole, is a permanent pole but the electric field of the molecule is not linear as in acetone, but in two dimensions. Examples of molecular solids with quadrupoles are octafluoronaphthalene and naphthalene. Naphthalene consists of two joined conjugated rings. The electronegativity of the atoms of this ring system and conjugation cause a ring current
A ring current is an electric current carried by charged particles trapped in a planet's magnetosphere. It is caused by the longitudinal drift of energetic (10–200 k eV) particles.
Earth's ring current
Earth's ring current is responsible f ...
resulting in a quadrupole. For naphthalene, this quadrupole manifests in a δ- and δ+ accumulating within and outside the ring system, respectively. Naphthalene assembles through the coordination of δ- of one molecules to the δ+ of another molecule. This results in 1D columns of naphthalene in a herringbone configuration. These columns then stack into 2D layers and then 3D bulk materials. Octafluoronaphthalene follows this path of organization to build bulk material except the δ- and δ+ are on the exterior and interior of the ring system, respectively.
Hydrogen and halogen bonding
 A hydrogen bond is a specific dipole where a hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) to due a neighboring electronegative atom or
A hydrogen bond is a specific dipole where a hydrogen atom has a partial positive charge (δ+) to due a neighboring electronegative atom or functional group
In organic chemistry, a functional group is a substituent or moiety in a molecule that causes the molecule's characteristic chemical reactions. The same functional group will undergo the same or similar chemical reactions regardless of the re ...
. Hydrogen bonds are amongst the strong intermolecular interactions know other than ion-dipole interactions. For intermolecular hydrogen bonds the δ+ hydrogen interacts with a δ- on an adjacent molecule. Examples of molecular solids that hydrogen bond are water, amino acid
Amino acids are organic compounds that contain both amino and carboxylic acid functional groups. Although hundreds of amino acids exist in nature, by far the most important are the alpha-amino acids, which comprise proteins. Only 22 alpha a ...
s, and acetic acid. For acetic acid, the hydrogen (δ+) on the alcohol moiety of the carboxylic acid hydrogen bonds with other the carbonyl
In organic chemistry, a carbonyl group is a functional group composed of a carbon atom double-bonded to an oxygen atom: C=O. It is common to several classes of organic compounds, as part of many larger functional groups. A compound containi ...
moiety (δ-) of the carboxylic on the adjacent molecule. This hydrogen bond leads a string of acetic acid molecules hydrogen bonding to minimize free energy. These strings of acetic acid molecules then stack together to build solids.
 A halogen bond is when an electronegative halide participates in a noncovalent interaction with a less electronegative atom on an adjacent molecule. Examples of molecular solids that halogen bond are hexachlorobenzene and a
A halogen bond is when an electronegative halide participates in a noncovalent interaction with a less electronegative atom on an adjacent molecule. Examples of molecular solids that halogen bond are hexachlorobenzene and a cocrystal
Cocrystals are "solids that are crystalline single phase materials composed of two or more different molecular or ionic compounds generally in a stoichiometric ratio which are neither solvates nor simple salts." A broader definition is that cocryst ...
of bromine
Bromine is a chemical element with the symbol Br and atomic number 35. It is the third-lightest element in group 17 of the periodic table ( halogens) and is a volatile red-brown liquid at room temperature that evaporates readily to form a simi ...
1,4-dioxane. For the second example, the δ- bromine atom in the diatomic bromine molecule is aligning with the less electronegative oxygen in the 1,4-dioxane. The oxygen in this case is viewed as δ+ compared to the bromine atom. This coordination results in a chain-like organization that stack into 2D and then 3D.
Coulombic interactions
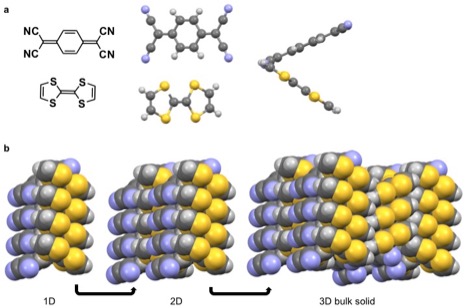
 Coulombic interactions are manifested in some molecular solids. A well-studied example is the radical ion salt TTF-TCNQ with a conductivity of 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1, much closer to copper (ρ = 6 x 105 Ω−1 cm−1) than many molecular solids. The coulombic interaction in TTF-TCNQ stems from the large partial negative charge (δ = -0.59) on the cyano- moiety on TCNQ at room temperature. For reference, a completely charged molecule δ = ±1. This partial negative charge leads to a strong interaction with the thio- moiety of the TTF. The strong interaction leads to favorable alignment of these functional groups adjacent to each other in the solid state. While π-π interactions cause the TTF and TCNQ to stack in separate columns.
Coulombic interactions are manifested in some molecular solids. A well-studied example is the radical ion salt TTF-TCNQ with a conductivity of 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1, much closer to copper (ρ = 6 x 105 Ω−1 cm−1) than many molecular solids. The coulombic interaction in TTF-TCNQ stems from the large partial negative charge (δ = -0.59) on the cyano- moiety on TCNQ at room temperature. For reference, a completely charged molecule δ = ±1. This partial negative charge leads to a strong interaction with the thio- moiety of the TTF. The strong interaction leads to favorable alignment of these functional groups adjacent to each other in the solid state. While π-π interactions cause the TTF and TCNQ to stack in separate columns.
Allotropes
One form of an element may be a molecular solid, but another form of that same element may not be a molecular solid. For example, solidphosphorus
Phosphorus is a chemical element with the symbol P and atomic number 15. Elemental phosphorus exists in two major forms, white phosphorus and red phosphorus, but because it is highly reactive, phosphorus is never found as a free element on Ear ...
can crystallize as different allotropes called "white", "red", and "black" phosphorus. White phosphorus forms molecular crystals composed of tetrahedral P4 molecules. Heating at ambient pressure to 250 °C or exposing to sunlight converts white phosphorus to red phosphorus where the P4 tetrahedra are no longer isolated, but connected by covalent bonds into polymer-like chains. Heating white phosphorus under high (GPa) pressures converts it to black phosphorus which has a layered, graphite
Graphite () is a crystalline form of the element carbon. It consists of stacked layers of graphene. Graphite occurs naturally and is the most stable form of carbon under standard conditions. Synthetic and natural graphite are consumed on lar ...
-like structure.
The structural transitions in phosphorus are reversible: upon releasing high pressure, black phosphorus gradually converts into the red phosphorus, and by vaporizing red phosphorus at 490 °C in an inert atmosphere and condensing the vapor, covalent red phosphorus can be transformed into the molecular solid, white phosphorus.
Similarly, yellow arsenic
Arsenic is a chemical element with the symbol As and atomic number 33. Arsenic occurs in many minerals, usually in combination with sulfur and metals, but also as a pure elemental crystal. Arsenic is a metalloid. It has various allotropes, ...
is a molecular solid composed of As4 units. Some forms of sulfur and selenium
Selenium is a chemical element with the symbol Se and atomic number 34. It is a nonmetal (more rarely considered a metalloid) with properties that are intermediate between the elements above and below in the periodic table, sulfur and tellurium, ...
are composed of S8 (or Se8) units and are molecular solids at ambient conditions, but converted into covalent allotropes having atomic chains extending throughout the crystal.
Properties
Since molecular solids are held together by relatively weak forces they tend to have low melting and boiling points, low mechanical strength, low electrical conductivity, and poor thermal conductivity.it will Also, depending on the structure of the molecule the intermolecular forces may have directionality leading to anisotropy of certain properties.Melting and boiling points
The characteristicmelting point
The melting point (or, rarely, liquefaction point) of a substance is the temperature at which it changes state from solid to liquid. At the melting point the solid and liquid phase exist in equilibrium. The melting point of a substance depen ...
of metals and ionic solids is ~ 1000 °C and greater, while molecular solids typically melt closer to 300 °C (see table), thus many corresponding substances are either liquid (ice) or gaseous (oxygen) at room temperature. This is due to the elements involved, the molecules they form, and the weak intermolecular interactions of the molecules.
*See also
higher alkanes
Allotropes of phosphorus are useful to further demonstrate this structure-property relationship. White phosphorus, a molecular solid, has a relatively low density of 1.82 g/cm3 and melting point of 44.1 °C; it is a soft material which can be cut with a knife. When it is converted to the covalent red phosphorus, the density goes to 2.2–2.4 g/cm3 and melting point to 590 °C, and when white phosphorus is transformed into the (also covalent) black phosphorus, the density becomes 2.69–3.8 g/cm3 and melting temperature ~200 °C. Both red and black phosphorus forms are significantly harder than white phosphorus.
higher alkanes
Mechanical properties
Molecular solids can be eitherductile
Ductility is a mechanical property commonly described as a material's amenability to drawing (e.g. into wire). In materials science, ductility is defined by the degree to which a material can sustain plastic deformation under tensile stres ...
or brittle
A material is brittle if, when subjected to stress, it fractures with little elastic deformation and without significant plastic deformation. Brittle materials absorb relatively little energy prior to fracture, even those of high strength. Br ...
, or a combination depending on the crystal face stressed. Both ductile and brittle solids undergo elastic deformation
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain ...
till they reach the yield stress. Once the yield stress is reached ductile solids undergo a period of plastic deformation
In engineering, deformation refers to the change in size or shape of an object. ''Displacements'' are the ''absolute'' change in position of a point on the object. Deflection is the relative change in external displacements on an object. Strain ...
, and eventually fracture. Brittle solids fracture promptly after passing the yield stress. Due to the asymmetric structure of most molecules, many molecular solids have directional intermolecular forces. This phenomenon can lead to anisotropic mechanical properties. Typically a molecular solid is ductile when it has directional intermolecular interactions. This allows for dislocation between layers of the crystal much like metals.
One example of a ductile molecular solid, that can be bent 180°, is hexachlorobenzene (HCB). In this example the π-π interactions between the benzene cores are stronger than the halogen interactions of the chlorides. This difference leads to its flexibility
Stiffness is the extent to which an object resists deformation in response to an applied force.
The complementary concept is flexibility or pliability: the more flexible an object is, the less stiff it is.
Calculations
The stiffness, k, of a bo ...
. This flexibility is anisotropic; to bend HCB to 180° you must stress the 01face of the crystal. Another example of a flexible molecular solid is 2-(methylthio)nicotinic acid (MTN). MTN is flexible due to its strong hydrogen bonding and π-π interactions creating a rigid set of dimers that dislocate along the alignment of their terminal methyls. When stressed on the 10face this crystal will bend 180°. Note, not all ductile molecular solids bend 180° and some may have more than one bending faces.
Electrical properties
Molecular solids are generally insulators. This large band gap (compared to germanium at 0.7 eV) is due to the weak intermolecular interactions, which result in low charge carrier mobility. Some molecular solids exhibit electrical conductivity, such as TTF-TCNQ with ρ = 5 x 102 Ω−1 cm−1 but in such cases orbital overlap is evident in the crystal structure. Fullerenes, which are insulating, become conducting or even superconducting upon doping.Thermal properties
Molecular solids have many thermal properties: specific heat capacity, thermal expansion, and thermal conductance to name a few. These thermal properties are determined by the intra- and intermolecular vibrations of the atoms and molecules of the molecular solid. While transitions of an electron do contribute to thermal properties, their contribution is negligible compared to the vibrational contribution.See also
*Bonding in solids
Solids can be classified according to the nature of the bonding between their atomic or molecular components. The traditional classification distinguishes four kinds of bonding:
* Covalent bonding, which forms network covalent solids (sometimes ...
References
* https://www.boundless.com/chemistry/liquids-and-solids/types-of-crystals/molecular-crystals/ {{DEFAULTSORT:Molecular Solid Chemical compounds