Mojmír I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mojmir I, Moimir I or Moymir I (
 Mojmir I arose in Moravia in the 820s. Whether he was the first ruler to unite the local Slavic tribes into a larger political unit or merely came into prominence as a result of the rapidly changing political situation, is uncertain. All the same, he had "predecessors", at least according to a letter written around 900 by
Mojmir I arose in Moravia in the 820s. Whether he was the first ruler to unite the local Slavic tribes into a larger political unit or merely came into prominence as a result of the rapidly changing political situation, is uncertain. All the same, he had "predecessors", at least according to a letter written around 900 by
 Mojmir I used the civil war within the
Mojmir I used the civil war within the
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
: ''Moimarus'', ''Moymarus'', Czech
Czech may refer to:
* Anything from or related to the Czech Republic, a country in Europe
** Czech language
** Czechs, the people of the area
** Czech culture
** Czech cuisine
* One of three mythical brothers, Lech, Czech, and Rus'
Places
* Czech, ...
and Slovak: ''Mojmír I.'') was the first known ruler of the Moravian Slavs (820s/830s–846) and eponym of the House of Mojmir
The Moymirid dynasty (Latin: ''Moimarii'', Czech and Slovak: ''Mojmírovci'') was a Moravian ruling dynasty that ruled over Moravia in the 9th and early 10th century. On one hand, it is named after the first known member, Mojmir I, but on the o ...
. In modern scholarship, the creation of the early medieval
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
state known as Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
is attributed either to his or to his successors' expansionist policy. He was deposed in 846 by Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
, king of East Francia.
Background
From the 570s the Avars dominated the large area stretching from theEastern Carpathians
Divisions of the Carpathians are a categorization of the Carpathian mountains system.
Below is a detailed overview of the major subdivisions and ranges of the Carpathian Mountains. The Carpathians are a "subsystem" of a bigger Alps-Himalaya Sy ...
to the Eastern Alps
Eastern Alps is the name given to the eastern half of the Alps, usually defined as the area east of a line from Lake Constance and the Alpine Rhine valley up to the Splügen Pass at the Alpine divide and down the Liro River to Lake Como in t ...
in Central Europe
Central Europe is an area of Europe between Western Europe and Eastern Europe, based on a common historical, social and cultural identity. The Thirty Years' War (1618–1648) between Catholicism and Protestantism significantly shaped the a ...
. The local Slavic tribes were obliged to pay tribute
A tribute (; from Latin ''tributum'', "contribution") is wealth, often in kind, that a party gives to another as a sign of submission, allegiance or respect. Various ancient states exacted tribute from the rulers of land which the state conqu ...
to their overlords, but they began to resist in the early 7th century.Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 17. First those who inhabited the region of today's Vienna
en, Viennese
, iso_code = AT-9
, registration_plate = W
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code =
, timezone = CET
, utc_offset = +1
, timezone_DST ...
(Austria
Austria, , bar, Östareich officially the Republic of Austria, is a country in the southern part of Central Europe, lying in the Eastern Alps. It is a federation of nine states, one of which is the capital, Vienna, the most populous ...
) threw off the yoke of the Avars in 623–624. They were led by a Frankish
Frankish may refer to:
* Franks, a Germanic tribe and their culture
** Frankish language or its modern descendants, Franconian languages
* Francia, a post-Roman state in France and Germany
* East Francia, the successor state to Francia in Germany ...
merchant named Samo
Samo (–) founded the first recorded political union of Slavic tribes, known as Samo's Empire (''realm'', ''kingdom'', or ''tribal union''), stretching from Silesia to present-day Slovakia, ruling from 623 until his death in 658. According to ...
whose reign would last for at least 35 years. However, when he died some time between 658 and 669, his principality collapsed without trace.
Another century and a half passed before the Avars were finally defeated between 792 and 796 by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first ...
, ruler of the Frankish Empire
Francia, also called the Kingdom of the Franks ( la, Regnum Francorum), Frankish Kingdom, Frankland or Frankish Empire ( la, Imperium Francorum), was the largest post-Roman barbarian kingdom in Western Europe. It was ruled by the Franks du ...
. In short time a series of Slavic principalities emerged in the regions on the Middle Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
. Among these polities, the Moravian principality showed up for the first time in 822 when the Moravians, according to the ''Royal Frankish Annals
The ''Royal Frankish Annals'' (Latin: ''Annales regni Francorum''), also called the ''Annales Laurissenses maiores'' ('Greater Lorsch Annals'), are a series of annals composed in Latin in the Carolingian Francia, recording year-by-year the state ...
'', brought tribute to Charlemagne's son, Emperor Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqui ...
.
Reign
Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total lan ...
n bishop
A bishop is an ordained clergy member who is entrusted with a position of authority and oversight in a religious institution.
In Christianity, bishops are normally responsible for the governance of dioceses. The role or office of bishop is c ...
s to the pope
The pope ( la, papa, from el, πάππας, translit=pappas, 'father'), also known as supreme pontiff ( or ), Roman pontiff () or sovereign pontiff, is the bishop of Rome (or historically the patriarch of Rome), head of the worldwide Cathol ...
.
The idea that Mojmir I was baptized between 818 and 824 is based on indirect evidence, namely on the dating of a Christian church in Mikulčice (Czech Republic
The Czech Republic, or simply Czechia, is a landlocked country in Central Europe. Historically known as Bohemia, it is bordered by Austria to the south, Germany to the west, Poland to the northeast, and Slovakia to the southeast. The ...
) to the first quarter of the 9th century. Although this idea is still a matter of scholarly debate, the ''History of the Bishops of Passau'' recorded a mass baptism of the Moravians in 831 by Bishop Reginhar of Passau.Sommer ''et al.'' 2007, p. 221. Even so, the pagan sanctuary
A sanctuary, in its original meaning, is a sacred place, such as a shrine. By the use of such places as a haven, by extension the term has come to be used for any place of safety. This secondary use can be categorized into human sanctuary, a sa ...
in Mikulčice continued in uninterrupted use until the middle of the 9th century.
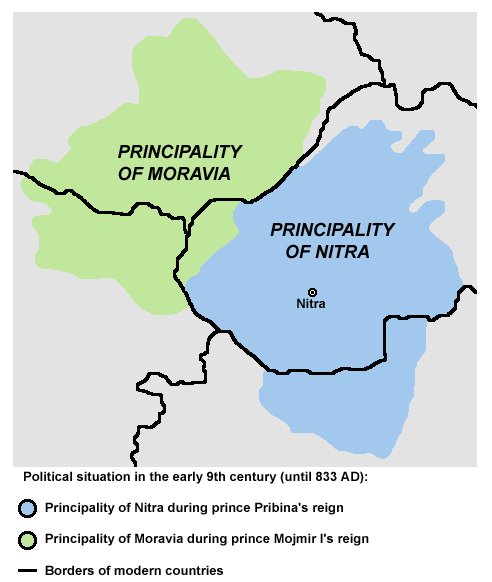
The frontiers of the Moravian state under Mojmir I are not precisely known. It is, however, certain that the Moravians were expanding in the 830s. By the time the document known as the '' Catalogue of Fortresses and Regions to the North of the Danube'' was compiled sometime between 844 and 862, the Moravians already held eleven fortresses in the region. Similarly, the ''Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians
The ''Conversio Bagoariorum et Carantanorum'' ("The Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians") is a Latin history written in Salzburg in the 870s. It describes the life and career of Salzburg's founding saint Rupert (d. 710), notably his m ...
'', an historical work written in 870, relates that around 833 a local Slavic ruler, Pribina
Pribina (c. 800861) was a Slavic prince whose adventurous career, recorded in the '' Conversion of the Bavarians and the Carantanians'' (a historical work written in 870), illustrates the political volatility of the Franco–Slavic fronti ...
, was "driven across the Danube by Mojmir, duke of the Moravians". Pribina was either the head of another Slavic principality or one of Mojmir I's rebellious subordinates. Modern historians, although not unanimously, identify Pribina's lands ''"in Nitrava ultra Danubium"'' with modern Nitra
Nitra (; also known by other alternative names) is a city in western Slovakia, situated at the foot of Zobor Mountain in the valley of the river Nitra. It is located 95 km east of Bratislava. With a population of about 78,353, it is the fifth l ...
(Slovakia
Slovakia (; sk, Slovensko ), officially the Slovak Republic ( sk, Slovenská republika, links=no ), is a landlocked country in Central Europe. It is bordered by Poland to the north, Ukraine to the east, Hungary to the south, Austria to the s ...
).Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 20.
Last years
 Mojmir I used the civil war within the
Mojmir I used the civil war within the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the ...
as an opportunity to plot a rebellion and try to throw off the yoke of Frankish overlordship in the 840s. Thus his emerging power became a serious threat to Louis II the German, ruler of the East Frankish kingdom. The Franks invaded Moravia in mid-August 846. They encountered little resistance and deprived Mojmir I of his throne. He seems to have fled or been killed during the invasion. His relative, Rastislav
Rastislav or Rostyslav is a male Slavic given name, meaning "''to increase glory''" . The name has been used by several notable people of Russian, Polish, Ukrainian, Serbian, Czech and Slovak backgrounds.
*Old Slavonic, Serbian, Slovak, Slove ...
, was set up as the new client ruler of Moravia.
See also
*Great Moravia
Great Moravia ( la, Regnum Marahensium; el, Μεγάλη Μοραβία, ''Meghálī Moravía''; cz, Velká Morava ; sk, Veľká Morava ; pl, Wielkie Morawy), or simply Moravia, was the first major state that was predominantly West Slavic to ...
* Alternative theories of the location of Great Moravia
*Louis the German
Louis the German (c. 806/810 – 28 August 876), also known as Louis II of Germany and Louis II of East Francia, was the first king of East Francia, and ruled from 843 to 876 AD. Grandson of emperor Charlemagne and the third son of Louis the P ...
*Rastislav of Moravia
Rastislav or Rostislav, also known as St. Rastislav, (Latin: ''Rastiz'', Greek: Ῥασισθλάβος / ''Rhasisthlábos'') was the second known ruler of Moravia (846–870).Spiesz ''et al.'' 2006, p. 20. Although he started his reign as vass ...
References
Sources
* * * * * * * * *Sommer, Petr; Třeštík, Dušan; Žemlička, Josef; Opačić, Zoë (2007). ''Bohemia and Moravia''. ''In:'' Berend, Nora (2007); ''Christianization and the Rise of Christian Monarchy: Scandinavia, Central Europe and Rus’, c. 900–1200''; Cambridge University Press; . *Spiesz, Anton; Caplovic, Dusan; Bolchazy, Ladislaus J. (2006). ''Illustrated Slovak History: A Struggle for Sovereignty in Central Europe''. Bolchazy-Carducci Publishers, Inc. . * {{DEFAULTSORT:Mojmir 01 of Moravia 846 deaths 9th-century rulers in Europe Great Moravia Year of birth unknown 9th-century Slavs 9th-century people from East Francia Slavic warriors