Mohammed VI of Morocco on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mohammed VI ( ar, محمد السادس; born 21 August 1963) is the
 Mohammed VI was born on 21 August 1963 and was the second child and oldest son of Hassan II and his wife,
Mohammed VI was born on 21 August 1963 and was the second child and oldest son of Hassan II and his wife,  In 1987, Mohammed VI obtained his first ''Certificat d'Études Supérieures'' (CES) in political sciences, and in July 1988 he obtained a ''Diplôme d'Études Approfondies'' ( DEA) in public law. In November 1988, he trained in
In 1987, Mohammed VI obtained his first ''Certificat d'Études Supérieures'' (CES) in political sciences, and in July 1988 he obtained a ''Diplôme d'Études Approfondies'' ( DEA) in public law. In November 1988, he trained in
/ref>
"Q&A: Morocco's referendum on reform"
Retrieved 1 February 2013. * The
 The Western Sahara conflict is considered one of the longest-running on the African continent. Mohammed VI has repeatedly stressed that the "Moroccanness of the Sahara" remains an "indisputable fact", a stance adopted by Morocco following the 1975 Green March during the reign of Hassan II. He visited Western Sahara in 2006 and 2015, and has asserted that Morocco was not negotiating over the territory, as the issue "never was - and never will be - on the negotiating table".
In March 2006, Mohammed VI created the
The Western Sahara conflict is considered one of the longest-running on the African continent. Mohammed VI has repeatedly stressed that the "Moroccanness of the Sahara" remains an "indisputable fact", a stance adopted by Morocco following the 1975 Green March during the reign of Hassan II. He visited Western Sahara in 2006 and 2015, and has asserted that Morocco was not negotiating over the territory, as the issue "never was - and never will be - on the negotiating table".
In March 2006, Mohammed VI created the
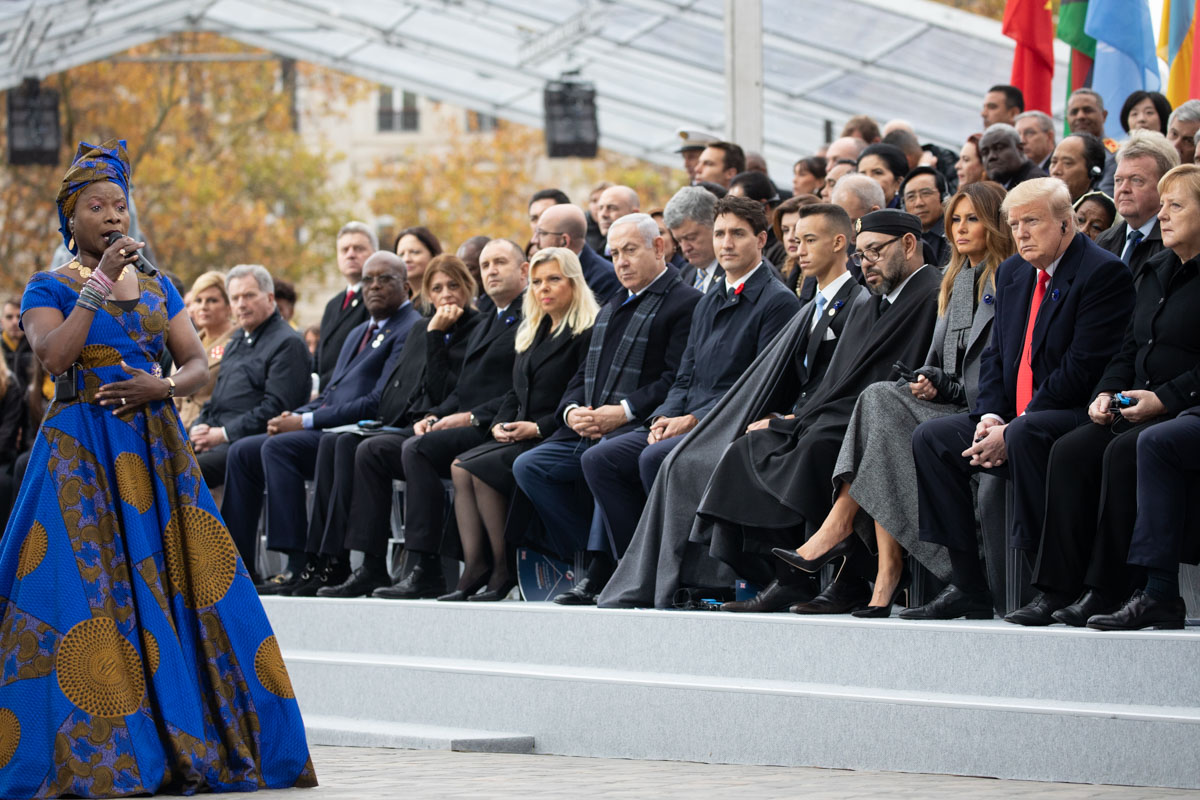
 Mohammed VI increasingly prioritized African relations in Morocco's foreign policy. Morocco had previously withdrawn from the
Mohammed VI increasingly prioritized African relations in Morocco's foreign policy. Morocco had previously withdrawn from the
 Mohammed is Morocco's leading businessman and banker. In 2015, he was estimated by ''
Mohammed is Morocco's leading businessman and banker. In 2015, he was estimated by ''
 Grand Master of the
Grand Master of the  Grand Master of the
Grand Master of the  Grand Master of the Order of Ouissam Alaouite (23 July 1999)
*
Grand Master of the Order of Ouissam Alaouite (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of the Independence Combat (23 July 1999)
*
Grand Master of the Order of the Independence Combat (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of Fidelity (23 July 1999)
*
Grand Master of the Order of Fidelity (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of Military Merit (23 July 1999)
Mohammed has received numerous honours and decorations from various countries, some of which are listed below.
Grand Master of the Order of Military Merit (23 July 1999)
Mohammed has received numerous honours and decorations from various countries, some of which are listed below.

 Collar of the
Collar of the  Honorary Knight of the
Honorary Knight of the  Grand Cross of the Order of Charles III of
Grand Cross of the Order of Charles III of  Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of
map.ma * Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the  Grand Cross of the Order of the Seventh of November of
Grand Cross of the Order of the Seventh of November of  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the  Collar of the
Collar of the  Wissam of the Order of the Umayyads of
Wissam of the Order of the Umayyads of  Extraordinary Grade of the
Extraordinary Grade of the  First Class Medal of the Order of Abu Bakar Siddiq of the
First Class Medal of the Order of Abu Bakar Siddiq of the  Grand Collar of the Order of al-Khalifa of
Grand Collar of the Order of al-Khalifa of 
 Collar of the
Collar of the  Cordon of the Order of the Independence of
Cordon of the Order of the Independence of  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the  Grand Cross of the Order of the Equatorial Star of Gabon (21 June 2004)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of the Equatorial Star of Gabon (21 June 2004)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the
King of Morocco
This is the list of rulers of Morocco, since the establishment of the state in 789. The common and formal titles of these rulers has varied, depending on the time period. Since 1957, the designation King has been used.
The present King of Mor ...
. He belongs to the 'Alawi dynasty and acceded to the throne on 23 July 1999, upon the death of his father, King Hassan II.
Upon ascending to the throne, Mohammed initially introduced a number of reforms and changed the family code, ''Mudawana
The ''Mudawana Ousra'' (or ''Moudawana Ousra'', ar, المدوّنة, lit=code), short for ''mudawwanat al-aḥwāl al-ousaria-shakhṣiyyah'' (, ), is the personal status code, also known as the family code, in Moroccan law. It concerns issu ...
'', granting women
A woman is an adult female human. Prior to adulthood, a female human is referred to as a girl (a female child or Adolescence, adolescent). The plural ''women'' is sometimes used in certain phrases such as "women's rights" to denote female hum ...
more power. Leaked diplomatic cables from WikiLeaks
WikiLeaks () is an international non-profit organisation that published news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources. Julian Assange, an Australian Internet activist, is generally described as its founder and director and ...
in 2010 led to allegations of corruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
in the court of Mohammed, implicating him and his closest advisors. Widespread disturbances in 2011, a Moroccan element of the Arab Spring
The Arab Spring ( ar, الربيع العربي) was a series of anti-government protests, uprisings and armed rebellions that spread across much of the Arab world in the early 2010s. It began in Tunisia in response to corruption and econo ...
, protested against corruption and urged political reform. In response, Mohammed put into effect a program of reforms and introduced a new constitution
A constitution is the aggregate of fundamental principles or established precedents that constitute the legal basis of a polity, organisation or other type of entity and commonly determine how that entity is to be governed.
When these pr ...
. These reforms were passed by a public referendum on 1 July 2011.
Mohammed has vast business holdings across several economic sectors in Morocco. His net worth has been estimated at between and over US$8.2 billion, and, according to the American business magazine ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
'', he was the richest king in Africa and the fifth wealthiest monarch in the world.
Mohammed is regarded by the Royal Islamic Strategic Studies Centre as the seventh most influential Muslim in the world in 2023.
Early life and education
 Mohammed VI was born on 21 August 1963 and was the second child and oldest son of Hassan II and his wife,
Mohammed VI was born on 21 August 1963 and was the second child and oldest son of Hassan II and his wife, Lalla Latifa Hammou
Princess Lalla Latifa Amahzoune (; ar, لالة لطيفة أمحزون – born in 1941 a member of the Zayane tribe ( khouribga, Morocco), She is the widow of King Hassan II and the mother of Princess Lalla Meryem, King Mohammed VI, Prin ...
. As their oldest son, Mohammed became heir apparent
An heir apparent, often shortened to heir, is a person who is first in an order of succession and cannot be displaced from inheriting by the birth of another person; a person who is first in the order of succession but can be displaced by the b ...
and Crown Prince from birth. His father was keen on giving him a religious and political education from an early age; at the age of four, he started attending the Quranic school at the Royal Palace.
Mohammed VI completed his first primary and secondary studies at Collège Royal and attained his Baccalaureate in 1981, before gaining a bachelor's degree
A bachelor's degree (from Middle Latin ''baccalaureus'') or baccalaureate (from Modern Latin ''baccalaureatus'') is an undergraduate academic degree awarded by colleges and universities upon completion of a course of study lasting three to si ...
in law at the Mohammed V University at Agdal in 1985. His research paper dealt with "the Arab-African Union and the Strategy of the Kingdom of Morocco in matters of International Relations". He has also frequented the Imperial College and University of Rabat. He was furthermore appointed president of the Pan Arab Games
The Arab Games ( ar, الألعاب العربية), also called the Pan Arab Games, are a regional multi-sport event held between nations from the Arab world. They are organized by the Union of Arab National Olympic Committees. The first Gam ...
, and was commissioned a Colonel Major of the Royal Moroccan Army on 26 November 1985. He served as the Coordinator of the Offices and Services of the Royal Armed Forces until 1994.
 In 1987, Mohammed VI obtained his first ''Certificat d'Études Supérieures'' (CES) in political sciences, and in July 1988 he obtained a ''Diplôme d'Études Approfondies'' ( DEA) in public law. In November 1988, he trained in
In 1987, Mohammed VI obtained his first ''Certificat d'Études Supérieures'' (CES) in political sciences, and in July 1988 he obtained a ''Diplôme d'Études Approfondies'' ( DEA) in public law. In November 1988, he trained in Brussels
Brussels (french: Bruxelles or ; nl, Brussel ), officially the Brussels-Capital Region (All text and all but one graphic show the English name as Brussels-Capital Region.) (french: link=no, Région de Bruxelles-Capitale; nl, link=no, Bruss ...
with Jacques Delors
Jacques Lucien Jean Delors (born 20 July 1925) is a French politician who served as the 8th President of the European Commission from 1985 to 1995. He served as Minister of Finance of France from 1981 to 1984. He was a Member of the European P ...
, then-President of the European Commission
The European Commission (EC) is the executive of the European Union (EU). It operates as a cabinet government, with 27 members of the Commission (informally known as "Commissioners") headed by a President. It includes an administrative body ...
.
Mohammed VI obtained his PhD PHD or PhD may refer to:
* Doctor of Philosophy (PhD), an academic qualification
Entertainment
* '' PhD: Phantasy Degree'', a Korean comic series
* '' Piled Higher and Deeper'', a web comic
* Ph.D. (band), a 1980s British group
** Ph.D. (Ph.D. al ...
in law with distinction on 29 October 1993 from the French University of Nice Sophia Antipolis for his thesis on "EEC
The European Economic Community (EEC) was a regional organization created by the Treaty of Rome of 1957,Today the largely rewritten treaty continues in force as the ''Treaty on the functioning of the European Union'', as renamed by the Lis ...
-Maghreb
The Maghreb (; ar, الْمَغْرِب, al-Maghrib, lit=the west), also known as the Arab Maghreb ( ar, المغرب العربي) and Northwest Africa, is the western part of North Africa and the Arab world. The region includes Algeria, ...
Relations". On 12 July 1994, he was promoted to the military rank of Major General
Major general (abbreviated MG, maj. gen. and similar) is a military rank used in many countries. It is derived from the older rank of sergeant major general. The disappearance of the "sergeant" in the title explains the apparent confusion of ...
, and that same year he became president of the High Council of Culture and Commander-in-Chief of the Royal Moroccan Army.
The ''New York Times'' reported that prior to ascending to the throne, Mohammed VI "gained a reputation as a playboy during the years he spent waiting in the wings, showing a fondness for fast cars and nightclubs.""In Morocco, Too, a Young King for a New Generation" New York Times, 27 July 1999/ref>
King of Morocco
On 23 July 1999, following the death of his father, Mohammed VI ascended to the throne as king and was enthroned inRabat
Rabat (, also , ; ar, الرِّبَاط, er-Ribât; ber, ⵕⵕⴱⴰⵟ, ṛṛbaṭ) is the capital city of Morocco and the country's seventh largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan populatio ...
on 30 July.
Social reforms and liberalization
Shortly after his ascension, King Mohammed VI made a national televised address, promising to take on poverty andcorruption
Corruption is a form of dishonesty or a criminal offense which is undertaken by a person or an organization which is entrusted in a position of authority, in order to acquire illicit benefits or abuse power for one's personal gain. Corruption m ...
, while creating jobs and improving Morocco's human rights record. His reformist rhetoric was opposed by Islamist conservatives, and some of his reforms angered fundamentalists
Fundamentalism is a tendency among certain groups and individuals that is characterized by the application of a strict literal interpretation to scriptures, dogmas, or ideologies, along with a strong belief in the importance of distinguishi ...
. In February 2004, he enacted a new family code, or Mudawana
The ''Mudawana Ousra'' (or ''Moudawana Ousra'', ar, المدوّنة, lit=code), short for ''mudawwanat al-aḥwāl al-ousaria-shakhṣiyyah'' (, ), is the personal status code, also known as the family code, in Moroccan law. It concerns issu ...
, which granted women more power.
Mohammed VI also created the Equity and Reconciliation Commission
The Equity and Reconciliation Commission ( ar, هيئة الإنصاف والمصالحة; - IER) is a Moroccan human rights and truth commission created on January 7, 2004, when King Mohammed VI signed a '' Dahir'' (royal decree). The commissi ...
(IER), which was tasked with researching human rights violations under Hassan II. This move was welcomed by many as promoting democracy
Democracy (From grc, δημοκρατία, dēmokratía, ''dēmos'' 'people' and ''kratos'' 'rule') is a form of government in which the people have the authority to deliberate and decide legislation (" direct democracy"), or to choose g ...
, but was also criticized because the commission's reports could not name the perpetrators. According to human rights organisations, human rights violations are still common in Morocco.
In January 2017, Morocco banned the manufacturing, marketing and sale of the burqa
A burqa or a burka, or , and ur, , it is also transliterated as burkha, bourkha, burqua or burqu' or borgha' and is pronounced natively . It is generally pronounced in the local variety of Arabic or variety of Persian, which varies. Examp ...
.
2011 protests and constitutional reform
The2011 Moroccan protests
Eleven or 11 may refer to:
*11 (number), the natural number following 10 and preceding 12
* one of the years 11 BC, AD 11, 1911, 2011, or any year ending in 11
Literature
* ''Eleven'' (novel), a 2006 novel by British author David Llewellyn
*''El ...
, led by the 20 February Movement, were primarily motivated by corruption and general political discontentment, as well as by the hardships of the global economic crisis Global economic crisis may refer to:
*Economic events of the 21st Century:
**Financial crisis of 2007–2008
** Great Recession
**The 2020 stock market crash
*A global recession
*Earlier global economic events, such as:
**The Great Depression, a g ...
. The demonstrations were influenced by then-recent revolutions in Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
and Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
which overthrew their respective leaders, and demands by protesters included "urgent" political and social reforms, including the relinquishment of some of the King's powers.
In a speech delivered on 9 March 2011, Mohammed VI said that parliament would receive "new powers that enable it to discharge its representative, legislative, and regulatory mission". In addition, the powers of the judiciary were granted greater independence from the king, who announced that he was impaneling a committee of legal scholars to produce a draft constitution by June 2011. On 1 July, voters approved a set of political reforms proposed by Mohammed VI in a referendum
A referendum (plural: referendums or less commonly referenda) is a Direct democracy, direct vote by the Constituency, electorate on a proposal, law, or political issue. This is in contrast to an issue being voted on by a Representative democr ...
.
The reforms consisted of the following:BBC News (29 June 2011)"Q&A: Morocco's referendum on reform"
Retrieved 1 February 2013. * The
Berber language
The Berber languages, also known as the Amazigh languages or Tamazight,, ber, label=Tuareg Tifinagh, ⵜⵎⵣⵗⵜ, ) are a branch of the Afroasiatic language family. They comprise a group of closely related languages spoken by Berber commun ...
is an official national language, along with standard Arabic
Arabic (, ' ; , ' or ) is a Semitic language spoken primarily across the Arab world.Semitic languages: an international handbook / edited by Stefan Weninger; in collaboration with Geoffrey Khan, Michael P. Streck, Janet C. E.Watson; Walter ...
.Article 5 of the 2011 Moroccan constitution
* The state preserves and protects the Hassānīya language and all the linguistic components of the Moroccan culture as a heritage of the nation.
* The king now has the obligation to appoint the prime minister from the party that wins the most seats in the parliamentary elections, but it can be any member of the winning party and not necessarily the party's leader. Previously, the king could nominate anybody he wanted for this position regardless of the election results. That was usually the case when no party had a big advantage over the other parties, in terms of the number of seats in the parliament
In modern politics, and history, a parliament is a legislative body of government. Generally, a modern parliament has three functions: representing the electorate, making laws, and overseeing the government via hearings and inquiries. Th ...
.
* The king is no longer "sacred or holy" but the "integrity of his person" is "inviolable".
* High administrative and diplomatic posts (including ambassadors, CEOs of state-owned companies, provincial and regional governors), are now appointed by the prime minister and the ministerial council which is presided by the king; previously the latter exclusively held this power.
* The prime minister is the head of government and president of the council of government, he has the power to dissolve the parliament.
* The prime minister will preside over the Council of Government, which prepares the general policy of the state. Previously the king held this position.
* The parliament has the power of granting amnesty. Previously this was exclusively held by the king.
* The judiciary system is independent from the legislative and executive branches, the king guarantees this independence.
* Women are guaranteed "civic and social" equality with men. Previously, only "political equality" was guaranteed, though the 1996 constitution grants all citizens equality in terms of rights before the law.1996 Moroccan constitution
* The king retains complete control over the armed forces and the judiciary as well as matters pertaining to religion and foreign policy; the king also retains the authority to appoint and dismiss prime ministers.
* All citizens have the freedom of thought, ideas, artistic expression and creation. Previously only free speech and the freedom of circulation and association were guaranteed. However, criticizing or directly opposing the king is still punishable with prison.
Western Sahara
 The Western Sahara conflict is considered one of the longest-running on the African continent. Mohammed VI has repeatedly stressed that the "Moroccanness of the Sahara" remains an "indisputable fact", a stance adopted by Morocco following the 1975 Green March during the reign of Hassan II. He visited Western Sahara in 2006 and 2015, and has asserted that Morocco was not negotiating over the territory, as the issue "never was - and never will be - on the negotiating table".
In March 2006, Mohammed VI created the
The Western Sahara conflict is considered one of the longest-running on the African continent. Mohammed VI has repeatedly stressed that the "Moroccanness of the Sahara" remains an "indisputable fact", a stance adopted by Morocco following the 1975 Green March during the reign of Hassan II. He visited Western Sahara in 2006 and 2015, and has asserted that Morocco was not negotiating over the territory, as the issue "never was - and never will be - on the negotiating table".
In March 2006, Mohammed VI created the Royal Advisory Council for Saharan Affairs
The Royal Advisory Council for Saharan Affairs ( ar, المجلس الملكي الاستشاري للشؤون الصحراوية; french: Conseil royal consultatif pour les affaires sahariennes) is an advisory committee to the Moroccan governm ...
(CORCAS), an advisory committee which defends Morocco's claim over Western Sahara. In 2021, the CORCAS condemned the Sahrawi refugee camps
The Sahrawi refugee camps (also romanized with Saharawi) in Tindouf, Algeria, are a collection of refugee camps set up in the Tindouf Province, Algeria in 1975–76 for Sahrawi refugees fleeing from Moroccan forces, who advanced through Wester ...
in Tindouf
Tindouf (Berber: Tinduf, ar, تندوف) is the main town, and a commune in Tindouf Province, Algeria, close to the Mauritanian, Western Saharan and Moroccan borders. The commune has population of around 160,000 but the census and population ...
, citing human rights concerns.
Morocco's stance on the Western Sahara is that it is an integral part of its territory and it has proposed a plan for its autonomy, provided it remains under Moroccan sovereignty. The Polisario Front
The Polisario Front, Frente Polisario, Frelisario or simply Polisario, from the Spanish abbreviation of (Popular Front for the Liberation of Saguia el-Hamra and Río de Oro), (in ar, rtl=yes, الجبهة الشعبية لتحرير الس� ...
, the main opposite party to the conflict, insists on ultimately pursuing for the establishment of an independent Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic. Morocco and the Polisario Front reached a ceasefire agreement in 1991, which included the establishment of a United Nations
The United Nations (UN) is an intergovernmental organization whose stated purposes are to maintain international peace and security, develop friendly relations among nations, achieve international cooperation, and be a centre for harmoni ...
peacekeeping mission (MINURSO
The United Nations Mission for the Referendum in Western Sahara ( ar, بعثة الأمم المتحدة لتنظيم استفتاء في الصحراء الغربية; french: Mission des Nations Unies pour l'Organisation d'un Référendum au ...
) to oversee and conduct a potential referendum on the future status of Western Sahara; to this day, such a referendum has never occurred.
Since 2019, several primarily African and Arab countries have established consulates in Laayoune and Dakhla. In 2020, an escalation of the conflict began when Sahrawi protesters blocked a road connecting Guerguerat
Guerguerat ( ar, الكركرات , ary, گرگرات, ber, Gargaren) is a small village in the far south west of Western Sahara, from the border with Mauritania and from the Atlantic Ocean. The village is under the control of Morocco. The ...
to sub-Saharan Africa
Sub-Saharan Africa is, geographically, the area and regions of the continent of Africa that lies south of the Sahara. These include West Africa, East Africa, Central Africa, and Southern Africa. Geopolitically, in addition to the List of sov ...
via Mauritania. Morocco responded by intervening militarily to resume movement of people and goods through Guerguerat, which the Polisario Front claimed had violated the 1991 ceasefire agreement.
Foreign policy

 Mohammed VI increasingly prioritized African relations in Morocco's foreign policy. Morocco had previously withdrawn from the
Mohammed VI increasingly prioritized African relations in Morocco's foreign policy. Morocco had previously withdrawn from the Organisation of African Unity
The Organisation of African Unity (OAU; french: Organisation de l'unité africaine, OUA) was an intergovernmental organization established on 25 May 1963 in Addis Ababa, Ethiopia, with 32 signatory governments. One of the main heads for OAU's ...
, precursor to the current African Union
The African Union (AU) is a continental union consisting of 55 member states located on the continent of Africa. The AU was announced in the Sirte Declaration in Sirte, Libya, on 9 September 1999, calling for the establishment of the Africa ...
(AU), in 1984 after the Polisario's Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic was admitted to the organisation. In July 2016, Mohammed VI sent a message to the 27th African Union summit being held in Kigali
Kigali () is the capital and largest city of Rwanda. It is near the nation's geographic centre in a region of rolling hills, with a series of valleys and ridges joined by steep slopes. As a primate city, Kigali has been Rwanda's economic, cult ...
, in which he requested Moroccan readmission to the AU, and justified his country's withdrawal saying that "the admission of a non-sovereign entity, by means of transgression and collusion" had prompted Morocco to "seek to avoid the division of Africa". Morocco would later be admitted to the African Union in January 2017.
Under his reign, Morocco endorsed partnerships with the Gulf Cooperation Council
The Cooperation Council for the Arab States of the Gulf ( ar, مجلس التعاون لدول العربية الخليج ), also known as the Gulf Cooperation Council (GCC; ar, مجلس التعاون الخليجي), is a regional, inter ...
as well as other non-traditional great power
A great power is a sovereign state that is recognized as having the ability and expertise to exert its influence on a global scale. Great powers characteristically possess military and economic strength, as well as diplomatic and soft power i ...
s, mainly China and Russia, aiming to diversify trade links and foreign investments and to limit Morocco's traditional reliance on the West, particularly the European Union
The European Union (EU) is a supranational union, supranational political union, political and economic union of Member state of the European Union, member states that are located primarily in Europe, Europe. The union has a total area of ...
(EU). Morocco has also offered to act as a mediator in the Libyan crisis, and remained neutral in the Qatar diplomatic crisis
The Qatar diplomatic crisis was a diplomatic incident in the Middle East that began on 5 June 2017 when Saudi Arabia, the United Arab Emirates, Bahrain and Egypt severed diplomatic relations with Qatar and banned Qatar-registered planes and ships ...
.
The Bush administration designated Morocco as a major non-NATO ally
Major non-NATO ally (MNNA) is a designation given by the United States government to close allies that have strategic working relationships with the US Armed Forces but are not members of the North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO). While the s ...
of the United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
in 2004. Mohammed VI had previously visited the White House
The White House is the official residence and workplace of the president of the United States. It is located at 1600 Pennsylvania Avenue NW in Washington, D.C., and has been the residence of every U.S. president since John Adams in ...
in June 2000, alongside his sister, Princess Lalla Meryem, and attended a state dinner with President Bill Clinton
William Jefferson Clinton (né Blythe III; born August 19, 1946) is an American politician who served as the 42nd president of the United States from 1993 to 2001. He previously served as governor of Arkansas from 1979 to 1981 and again ...
. Washington and Rabat later signed a free-trade agreement in 2006, the only one of its kind between the U.S. and an African country, which was met with some criticism within Morocco due to increasing trade deficit
The balance of trade, commercial balance, or net exports (sometimes symbolized as NX), is the difference between the monetary value of a nation's exports and imports over a certain time period. Sometimes a distinction is made between a balanc ...
.
Morocco and Israel restored diplomatic relations on 10 December 2020, as part of the Israel–Morocco normalization agreement involving the United States, which at the same time recognized Morocco's sovereignty over Western Sahara
Western Sahara ( '; ; ) is a disputed territory on the northwest coast and in the Maghreb region of North and West Africa. About 20% of the territory is controlled by the self-proclaimed Sahrawi Arab Democratic Republic (SADR), while the ...
. In June 2021, Mohammed congratulated Naftali Bennett on his election as Israel
Israel (; he, יִשְׂרָאֵל, ; ar, إِسْرَائِيل, ), officially the State of Israel ( he, מְדִינַת יִשְׂרָאֵל, label=none, translit=Medīnat Yīsrāʾēl; ), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated ...
i prime minister. On the International Day of Solidarity with the Palestinian People
The International Day of Solidarity with the Palestinian People is a UN-organized observance. Events are held at the United Nations headquarters in New York, as well as at the United Nations offices at Geneva, Vienna and Nairobi. It is generally ...
in November 2021, Mohammed announced that Morocco would continue to push for a restart of Israeli-Palestinian peace negotiations. He called on both sides "to refrain from actions that obstruct the peace process".
Despite calls by Mohammed VI for reconciliation, relations with neighbouring Algeria
)
, image_map = Algeria (centered orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption =
, image_map2 =
, capital = Algiers
, coordinates =
, largest_city = capital
, relig ...
continued to intensify over the course of his rule. In July 2004, Mohammed announced that Morocco would lift visa restrictions for Algerians, with Algerian President Abdelaziz Bouteflika reciprocating the measure in 2005. Tensions gradually escalated in the 2020s, primarily as a result of the Israel–Morocco normalization agreement and Guerguerat border clashes. In August 2021, Algeria accused Morocco of supporting the Movement for the self-determination of Kabylie, which it blamed for wildfires
A wildfire, forest fire, bushfire, wildland fire or rural fire is an unplanned, uncontrolled and unpredictable fire in an area of combustible vegetation. Depending on the type of vegetation present, a wildfire may be more specifically identif ...
in northern Algeria, and later severed diplomatic relations with Morocco.
In August 2022, during a speech marking the anniversary of the Revolution of the King and the People, Mohammed VI said that the Western Sahara issue "is the lens through which Morocco looks at the world", and through which it "measures the sincerity of friendships and the efficiency of partnerships", while calling on other countries "to clarify their positions egarding the Western Saharaand reconsider them in a manner that leaves no room for doubt".
Business and wealth
 Mohammed is Morocco's leading businessman and banker. In 2015, he was estimated by ''
Mohammed is Morocco's leading businessman and banker. In 2015, he was estimated by ''Forbes
''Forbes'' () is an American business magazine owned by Integrated Whale Media Investments and the Forbes family. Published eight times a year, it features articles on finance, industry, investing, and marketing topics. ''Forbes'' also r ...
'' magazine to be worth US$5.7bn although in 2019 ''Business Insider'' quoted a figure of just US$2.1 billion. The Moroccan Royal Family, meanwhile, has one of the largest fortunes in the world. Together, they hold the majority stakes in the Al Mada holding, formerly named the ''Société Nationale d'Investissement'' (SNI), which was originally state-owned but was merged in 2013 with Omnium Nord Africain ( ONA Group), to form a single holding company
A holding company is a company whose primary business is holding a controlling interest in the securities of other companies. A holding company usually does not produce goods or services itself. Its purpose is to own shares of other companies ...
that was taken off the Casablanca Stock Exchange—resulting in the scrapping of an equivalent of 50 billion Dirhams Marketcap (~ US$6 billion). Al Mada has a diverse portfolio consisting of many important businesses in Morocco, operating in various sectors including: Attijariwafa Bank (banking
A bank is a financial institution that accepts deposits from the public and creates a demand deposit while simultaneously making loans. Lending activities can be directly performed by the bank or indirectly through capital markets.
Because ...
), Managem (mining
Mining is the extraction of valuable minerals or other geological materials from the Earth, usually from an ore body, lode, vein, seam, reef, or placer deposit. The exploitation of these deposits for raw material is based on the econom ...
), Onapar, SOMED (tourism/ real-estate and exclusive distributor of Maserati
Maserati S.p.A. () is an Italian luxury vehicle manufacturer. Established on 1 December 1914, in Bologna, Italy, the company's headquarters are now in Modena, and its emblem is a trident. The company has been owned by Stellantis since 2021. ...
), Wafa Assurance (insurance
Insurance is a means of protection from financial loss in which, in exchange for a fee, a party agrees to compensate another party in the event of a certain loss, damage, or injury. It is a form of risk management, primarily used to hedge ...
), Marjane Marjane may refer to:
People
* Léo Marjane (1912-2016), French singer
* Marjane Satrapi (born 1969), Iranian-born French graphic novelist, cartoonist, illustrator, film director, and children's book author.
Others
* Marjan hill, hill on the penin ...
(hypermarket
A hypermarket (sometimes called a hyperstore, supercentre or superstore) is a big-box store combining a supermarket and a department store. The result is an expansive retail facility carrying a wide range of products under one roof, includin ...
chain), Wana-Inwi (telecommunications
Telecommunication is the transmission of information by various types of technologies over wire, radio, optical, or other electromagnetic systems. It has its origin in the desire of humans for communication over a distance greater than that ...
), SONASID ( Siderurgy), Lafarge Maroc, Sopriam (exclusive distributor of Peugeot
Peugeot (, , ) is a French brand of automobiles owned by Stellantis.
The family business that preceded the current Peugeot companies was founded in 1810, with a steel foundry that soon started making hand tools and kitchen equipment, and then ...
-Citroën
Citroën () is a French automobile brand. The "Automobiles Citroën" manufacturing company was founded in March 1919 by André Citroën. Citroën is owned by Stellantis since 2021 and previously was part of the PSA Group after Peugeot acquired 8 ...
in Morocco), Renault Maroc (exclusive distributor of Renault in Morocco) and Nareva
Nareva is an energy company in Morocco wholly owned by the SNI, the holding company of king Mohammed VI.
Activities
Renewables
The company has multiple wind farm projects. The units in Akhenfir, Haouma and Foum El Oued, with a capacity of 100 ...
(energy). It also owns many food-processing companies and is currently in the process of disengaging from this sector. Between mid-2012 and 2013, the holding sold ''Lessieur'', ''Centrale Laitière'', ''Bimo'' and ''Cosumar'' to foreign groups for a total amount of ~$1.37 billion (11.4 billion Dirhams including 9.7 billion in 2013 and 1.7 in 2012).
SNI and ONA both owned stakes in Brasseries du Maroc
Beer production in Morocco was introduced by the French in the 20th century.
Société des Brasseries du Maroc is part of the Castel Group and oversees the production and distribution of beer. Popular beers include ''Spéciale Flag'' (pilsner) an ...
, the largest alcoholic beverage
An alcoholic beverage (also called an alcoholic drink, adult beverage, or a drink) is a drink that contains ethanol, a type of Alcohol (chemistry), alcohol that acts Alcohol (drug), as a drug and is produced by Ethanol fermentation, fermentat ...
s manufacturer and distributor of brands such as Heineken in the country. In March 2018, the SNI adopted its current name, Al Mada.
Mohammed is also a leading agricultural producer and land owner in Morocco, where agriculture is exempted from taxes. His personal holding company SIGER has shares in the large agricultural group ''"Les domaines agricoles"'' (originally called ''"Les domaines royaux"'', now commonly known as "''Les domaines''"), which was founded by Hassan II. In 2008, Telquel estimated that ''"Les domaines"'' had a revenue of $157 million (1.5 billion Dirhams), with 170,000 tons of citrus
''Citrus'' is a genus of flowering trees and shrubs in the rue family, Rutaceae. Plants in the genus produce citrus fruits, including important crops such as oranges, lemons, grapefruits, pomelos, and limes. The genus ''Citrus'' is native to ...
exported in that year. According to the same magazine, the company officially owns 12,000 hectares
The hectare (; SI symbol: ha) is a non-SI metric unit of area equal to a square with 100- metre sides (1 hm2), or 10,000 m2, and is primarily used in the measurement of land. There are 100 hectares in one square kilometre. An acre is ...
of agricultural lands. ''"Chergui"'', a manufacturer of dairy product
Dairy products or milk products, also known as lacticinia, are food products made from (or containing) milk. The most common dairy animals are cow, water buffalo, nanny goat, and ewe. Dairy products include common grocery store food items i ...
s, is the most recognizable brand of the group. Between 1994 and 2004, the group has been managed by Mohammed VI's brother-in-law Khalid Benharbit, the husband of Princess Lalla Hasna. ''"Les domaines"'' also owns the "Royal Golf de Marrakech", which originally belonged to Thami El Glaoui.
His palace's daily operating budget is reported by Forbes to be $960,000—which is paid by the Moroccan state as part of a 2.576 billion Dirhams/year budget as of 2014—with much of it accounted for by the expense of personnel, clothes, and car repairs.
Controversies
Royal pardon scandals
Protests broke out in Rabat, the capital of Morocco, on 2 August 2013, after Mohammed pardoned 48 jailed Spaniards, including a pedophile who had been serving a 30-year sentence for raping 11 children aged between 4 and 15. It was also revealed that amongst the pardoned was a drug trafficking suspect, who was released before standing trial. The detainee, Antonio Garcia, a recidivist drug trafficker, had been arrested in possession of 9 tons ofhashish
Hashish ( ar, حشيش, ()), also known as hash, "dry herb, hay" is a drug made by compressing and processing parts of the cannabis plant, typically focusing on flowering buds (female flowers) containing the most trichomes. European Monitoring ...
in Tangier
Tangier ( ; ; ar, طنجة, Ṭanja) is a city in northwestern Morocco. It is on the Moroccan coast at the western entrance to the Strait of Gibraltar, where the Mediterranean Sea meets the Atlantic Ocean off Cape Spartel. The town is the capi ...
and was sentenced to 10 years. He had resisted arrest using a firearm. Some media claimed that his release embarrassed Spain.
Allegations of corruption
Royal involvement in business is a major topic in Morocco, but public discussion of it is sensitive. The US embassy in Rabat reported to Washington in a leaked cable that "corruption is prevalent at all levels of Moroccan society". Corruption allegedly reaches the highest levels in Morocco, where the business interests of Mohammed VI and some of his advisors influence "every large housing project," according toWikiLeaks
WikiLeaks () is an international non-profit organisation that published news leaks and classified media provided by anonymous sources. Julian Assange, an Australian Internet activist, is generally described as its founder and director and ...
documents published in December 2010 and quoted in ''The Guardian
''The Guardian'' is a British daily newspaper. It was founded in 1821 as ''The Manchester Guardian'', and changed its name in 1959. Along with its sister papers '' The Observer'' and '' The Guardian Weekly'', ''The Guardian'' is part of the ...
'' newspaper. The documents released by the whistleblower website also quote the case of a businessman working for a US consortium, whose plans in Morocco were paralysed for months after he refused to join forces with a company linked with the royal palace. The documents quoted a company executive linked to the royal family as saying at a meeting that decisions on big investments in the kingdom were taken by only three people: the king, his secretary Mounir Majidi, and the monarch's close friend, adviser and former classmate Fouad Ali El Himma
Fouad Ali El Himma ( ar, فؤاد عالي الهمة; born 6 December 1962, in Ben Guerir, Morocco) is a Moroccan politician and senior advisor for Mohammed VI of whom he is said to be a very close friend. Since he became Secretary of State in t ...
. This corruption especially affects the housing sector, the WikiLeaks documents show.
In April 2016, Mounir Majidi, the personal secretary of Mohammed VI, was named in the Panama Papers
The Panama Papers ( es, Papeles de Panamá) are 11.5 million leaked documents (or 2.6 terabytes of data) that were published beginning on April 3, 2016. The papers detail financial and attorney–client information for more than 214,488 ...
.
Family and personal life
Mohammed has one brother, Prince Moulay Rachid, and three sisters: Princess Lalla Meryem, Princess Lalla Asma, and Princess Lalla Hasna. ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' noted "conflicting reports about whether the new monarch had been married on Friday night, within hours of his father's death n 1999.. to heed a Moroccan tradition that a King be married before he ascends the throne." A palace official subsequently denied that a marriage had taken place.
His engagement to Salma Bennani was officially announced on 12 October 2001. They married in private in Rabat
Rabat (, also , ; ar, الرِّبَاط, er-Ribât; ber, ⵕⵕⴱⴰⵟ, ṛṛbaṭ) is the capital city of Morocco and the country's seventh largest city with an urban population of approximately 580,000 (2014) and a metropolitan populatio ...
on 21 March 2002 and their wedding was officially celebrated at the '' Dar al-Makhzen'' in Rabat on 12 and 13 July 2002. Bennani was granted the personal title of Princess with the title of Her Royal Highness on her marriage. They have two children: Crown Prince Moulay Hassan, who was born on 8 May 2003, and Princess Lalla Khadija, who was born on 28 February 2007.
Mohammed's birthday on 21 August is a public holiday
A public holiday, national holiday, or legal holiday is a holiday generally established by law and is usually a non-working day during the year.
Sovereign nations and territories observe holidays based on events of significance to their history ...
, although festivities were cancelled upon the death of his aunt in 2014.
In 2020, Mohammed reportedly purchased an €80 million mansion in Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
from the Saudi royal family
The House of Saud ( ar, آل سُعُود, ʾĀl Suʿūd ) is the ruling royal family of Saudi Arabia. It is composed of the descendants of Muhammad bin Saud, founder of the Emirate of Diriyah, known as the First Saudi state (1727–1818), ...
.
Children
Health
Many questions have been raised about King Mohammed VI's health both within and outside Morocco. On one occasion, following a speech commemorating the 45th anniversary of the Green March, Moroccan online activists reportedly pointed out facial features which may have been implied as a sign of health issues, while others offered sympathy and prayers. In 2017, Mohammed VI underwent a successful surgery at theQuinze-Vingts National Ophthalmology Hospital
The Quinze-Vingts National Ophthalmology Hospital (''Centre hospitalier national d’ophtalmologie des Quinze-Vingts'') is France's national ophthalmology hospital located in Paris, in the 12th arrondissement. The hospital gave its name to the ...
in Paris to remove a pterygium in his left eye. In February 2018, he underwent a radiofrequency ablation, also in Paris, to normalize an irregular heart rate, and was visited by members of the royal family. In September 2019, the King was advised to rest for several days to recover from acute viral pneumonia, with his son Crown Prince Moulay Hassan representing him at former French President Jacques Chirac
Jacques René Chirac (, , ; 29 November 193226 September 2019) was a Politics of France, French politician who served as President of France from 1995 to 2007. Chirac was previously Prime Minister of France from 1974 to 1976 and from 1986 to ...
's funeral. In June 2020, he underwent a procedure in Rabat to treat a recurrence of atrial flutter
Atrial flutter (AFL) is a common abnormal heart rhythm that starts in the atrial chambers of the heart. When it first occurs, it is usually associated with a fast heart rate and is classified as a type of supraventricular tachycardia. Atrial f ...
.
In June 2022, Mohammed VI tested positive for COVID-19
Coronavirus disease 2019 (COVID-19) is a contagious disease caused by a virus, the severe acute respiratory syndrome coronavirus 2 (SARS-CoV-2). The first known case was identified in Wuhan, China, in December 2019. The disease quick ...
. His personal doctor said he did not exhibit symptoms and recommended "a period of rest for a few days", while ''Jeune Afrique
''Jeune Afrique'' (English: ''Young Africa'') is a French-language pan-African weekly news magazine, founded in 1960 in Tunis and subsequently published in Paris. It is the most widely read pan-African magazine. It is also a book publisher, under ...
'' reported he contracted the disease in France, where he had previously arrived for a private visit. On 10 July, he made his first public appearance since his COVID-19 recovery, performing Eid al-Adha
Eid al-Adha () is the second and the larger of the two main holidays celebrated in Islam (the other being Eid al-Fitr). It honours the willingness of Ibrahim (Abraham) to sacrifice his son Ismail (Ishmael) as an act of obedience to Allah's com ...
rituals and prayers.
Honours
National orders
*Order of Muhammad
The Order of Muhammad, also referred to as Order of Sovereignty ( ar, وسام المحمدي, Wissam al-Mohammadi, French: ''Ordre de la Souveraineté'' or ''Ordre de Mohammed''), is the highest state decoration of the Kingdom of Morocco. The O ...
, (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the
Grand Master of the Order of the Throne
The Order of the Throne (Arabic: ''Wissam al-Arch'', French: ''Ordre du Trône'') is a state decoration of the Kingdom of Morocco awarded for distinguished services of a civil or military nature. The Order was instituted on 16 May 1963 by King H ...
(23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of the Independence Combat (23 July 1999)
*
Grand Master of the Order of the Independence Combat (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of Fidelity (23 July 1999)
*
Grand Master of the Order of Fidelity (23 July 1999)
*  Grand Master of the Order of Military Merit (23 July 1999)
Mohammed has received numerous honours and decorations from various countries, some of which are listed below.
Grand Master of the Order of Military Merit (23 July 1999)
Mohammed has received numerous honours and decorations from various countries, some of which are listed below.
Foreign orders
*
Grand Officer
An officer is a person who has a position of authority in a hierarchical organization. The term derives from Old French ''oficier'' "officer, official" (early 14c., Modern French ''officier''), from Medieval Latin ''officiarius'' "an officer," fr ...
of the Order of the Equatorial Star
The Order of the Equatorial Star () is a state order of Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bord ...
of Gabon
Gabon (; ; snq, Ngabu), officially the Gabonese Republic (french: République gabonaise), is a country on the west coast of Central Africa. Located on the equator, it is bordered by Equatorial Guinea to the northwest, Cameroon to the nort ...
(7 July 1977)
* Order of Civil Merit
The Order of Civil Merit ( es, Orden del Mérito Civil) was established by King Alfonso XIII of Spain in 1926. The order recognizes "the civic virtue of officers in the service of the Nation, as well as extraordinary service by Spanish and forei ...
of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(2 June 1979)
* Grand Cross
Grand Cross is the highest class in many orders, and manifested in its insignia. Exceptionally, the highest class may be referred to as Grand Cordon or equivalent. In other cases, there may exist a rank even higher than Grand Cross, e.g. Grand ...
of the Royal Victorian Order
The Royal Victorian Order (french: Ordre royal de Victoria) is a dynastic order of knighthood established in 1896 by Queen Victoria. It recognises distinguished personal service to the British monarch, Canadian monarch, Australian monarch, o ...
of Great Britain and Northern Ireland (27 October 1980)
* Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(23 June 1986)
*  Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Republic of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
(August 1987)HM King Mohammed VImap.ma *
Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic ( it, Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana) is the senior Italian order of merit. It was established in 1951 by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi.
The highest-rankin ...
of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
(18 March 1997)
* Grand Cross of the Order of Aviz
The Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz ( pt, Ordem Militar de São Bento de Avis, ), previously to 1910 ''Royal Military Order of Saint Benedict of Aviz'' ( pt, Real Ordem Militar de São Bento de Avis), previously to 1789 ''Knights'' (of ...
of Portugal (13 August 1998)
* Legion of Honour
The National Order of the Legion of Honour (french: Ordre national de la Légion d'honneur), formerly the Royal Order of the Legion of Honour ('), is the highest French order of merit, both military and civil. Established in 1802 by Napoleo ...
of France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
(19 March 2000)
* Order of al-Hussein bin Ali
The Order of al-Hussein bin Ali is the highest order of the Kingdom of Jordan. It was founded on 22 June 1949 with one class (i.e. Collar) by King Abdullah I of Jordan with the scope of rewarding benevolence and foreign Heads of State. The class ...
of Jordan
Jordan ( ar, الأردن; tr. ' ), officially the Hashemite Kingdom of Jordan,; tr. ' is a country in Western Asia. It is situated at the crossroads of Asia, Africa, and Europe, within the Levant region, on the East Bank of the Jordan Rive ...
(1 March 2000)
* Order of Merit of the Italian Republic
The Order of Merit of the Italian Republic ( it, Ordine al Merito della Repubblica Italiana) is the senior Italian order of merit. It was established in 1951 by the second President of the Italian Republic, Luigi Einaudi.
The highest-rankin ...
of Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
(11 April 2000)
*  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the National Order of Merit An order of merit is conferred by a state, government or royal family on an individual in recognition of military or civil merit.
Order of merit may also refer to:
* FIFA Order of Merit, for significant contribution to association football
* PDC ...
of Mauritania
Mauritania (; ar, موريتانيا, ', french: Mauritanie; Berber: ''Agawej'' or ''Cengit''; Pulaar: ''Moritani''; Wolof: ''Gànnaar''; Soninke:), officially the Islamic Republic of Mauritania ( ar, الجمهورية الإسلامية ...
(26 April 2000)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of the Seventh of November of
Grand Cross of the Order of the Seventh of November of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
(24 May 2000)
*  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the National Order of Mali
The National Order of Mali is the highest of honorific orders of Mali.
History
The National Order of Mali was founded on 31 May 1963 to celebrate the independence of the country acquired in 1960 after decades of French colonisation.
As such, ...
of Mali
Mali (; ), officially the Republic of Mali,, , ff, 𞤈𞤫𞤲𞥆𞤣𞤢𞥄𞤲𞤣𞤭 𞤃𞤢𞥄𞤤𞤭, Renndaandi Maali, italics=no, ar, جمهورية مالي, Jumhūriyyāt Mālī is a landlocked country in West Africa. Ma ...
with Collar (14 June 2000)
* Order of Isabella the Catholic
The Order of Isabella the Catholic ( es, Orden de Isabel la Católica) is a Spanish civil order and honor granted to persons and institutions in recognition of extraordinary services to the homeland or the promotion of international relations a ...
of Spain
, image_flag = Bandera de España.svg
, image_coat = Escudo de España (mazonado).svg
, national_motto = '' Plus ultra'' (Latin)(English: "Further Beyond")
, national_anthem = (English: "Royal March")
, ...
(16 September 2000)
*  Wissam of the Order of the Umayyads of
Wissam of the Order of the Umayyads of Syria
Syria ( ar, سُورِيَا or سُورِيَة, translit=Sūriyā), officially the Syrian Arab Republic ( ar, الجمهورية العربية السورية, al-Jumhūrīyah al-ʻArabīyah as-Sūrīyah), is a Western Asian country loc ...
(9 April 2001)
*  Extraordinary Grade of the
Extraordinary Grade of the Order of Merit
The Order of Merit (french: link=no, Ordre du Mérite) is an order of merit for the Commonwealth realms, recognising distinguished service in the armed forces, science, art, literature, or for the promotion of culture. Established in 1902 by ...
of Lebanon
Lebanon ( , ar, لُبْنَان, translit=lubnān, ), officially the Republic of Lebanon () or the Lebanese Republic, is a country in Western Asia. It is located between Syria to the north and east and Israel to the south, while Cyprus lie ...
(13 June 2001)
* International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement
The International Red Cross and Red Crescent Movement is a humanitarian movement with approximately 97 million volunteers, members and staff worldwide. It was founded to protect human life and health, to ensure respect for all human beings, and ...
(29 June 2001)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of al-Khalifa of
Grand Collar of the Order of al-Khalifa of Bahrain
Bahrain ( ; ; ar, البحرين, al-Bahrayn, locally ), officially the Kingdom of Bahrain, ' is an island country in Western Asia. It is situated on the Persian Gulf, and comprises a small archipelago made up of 50 natural islands and a ...
(28 July 2001)
* Silver Star
The Silver Star Medal (SSM) is the United States Armed Forces' third-highest military decoration for valor in combat. The Silver Star Medal is awarded primarily to members of the United States Armed Forces for gallantry in action against an e ...
of United States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
(21 January 2002)
*  Collar of the
Collar of the Order of Mubarak the Great
The Order of Mubarak the Great (''Wisam Mubarak al-Kabir'') is a knighthood order of Kuwait.
History
The Order was founded on 16 July 1974 by the national government to celebrate the memory of Mubarak Al-Sabah called ''the Great'', List of emirs ...
of Kuwait
Kuwait (; ar, الكويت ', or ), officially the State of Kuwait ( ar, دولة الكويت '), is a country in Western Asia. It is situated in the northern edge of Eastern Arabia at the tip of the Persian Gulf, bordering Iraq to Iraq–Ku ...
(22 October 2002)
*  Cordon of the Order of the Independence of
Cordon of the Order of the Independence of Qatar
Qatar (, ; ar, قطر, Qaṭar ; local vernacular pronunciation: ), officially the State of Qatar,) is a country in Western Asia. It occupies the Qatar Peninsula on the northeastern coast of the Arabian Peninsula in the Middle East; it sh ...
(25 October 2002)
*  Grand Cordon of the
Grand Cordon of the Order of the Nile
The Order of the Nile (''Kiladat El Nil'') was established in 1915 and was one of the Kingdom of Egypt's principal orders until the monarchy was abolished in 1953. It was then reconstituted as the Republic of Egypt's highest state honor.
Sultana ...
of Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a List of transcontinental countries, transcontinental country spanning the North Africa, northeast corner of Africa and Western Asia, southwest corner of Asia via a land bridg ...
(28 October 2002)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Pakistan
The Nishan-e-Pakistan ( ur, , , ''Order of Pakistan'') is the highest civilian award of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. It is awarded for "those who have rendered services of highest distinction" to the national interest of Pakistan. Nishan i ...
First Class (Nishan-e-Pakistan
The Nishan-e-Pakistan ( ur, , , ''Order of Pakistan'') is the highest civilian award of the Islamic Republic of Pakistan. It is awarded for "those who have rendered services of highest distinction" to the national interest of Pakistan. Nishan i ...
) of Pakistan
Pakistan ( ur, ), officially the Islamic Republic of Pakistan ( ur, , label=none), is a country in South Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, fifth-most populous country, with a population of almost 24 ...
(19 July 2003)
* Order of Valour
The Order of Valour is an order of knighthood of Cameroon.
History
It is regulated by the ordonnance N° 72/24 of 30 November 1972. It is one of the four orders of Cameroon:Cameroon
Cameroon (; french: Cameroun, ff, Kamerun), officially the Republic of Cameroon (french: République du Cameroun, links=no), is a country in west-central Africa. It is bordered by Nigeria to the west and north; Chad to the northeast; the ...
(17 June 2004)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of the Equatorial Star of Gabon (21 June 2004)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of the Equatorial Star of Gabon (21 June 2004)
*  Grand Cross of the
Grand Cross of the National Order of the Niger
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
of the Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languages
*  Grand Cordon of the Order of Leopold of
Grand Cordon of the Order of Leopold of  Collar of the
Collar of the  Medal of Honour of the Congress of Peru (1 December 2004)
*
Medal of Honour of the Congress of Peru (1 December 2004)
*  Collar of the
Collar of the  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the  Collar of the Order of Charles III of Spain (14 January 2005)
*
Collar of the Order of Charles III of Spain (14 January 2005)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of the Aztec Eagle of
Grand Collar of the Order of the Aztec Eagle of  Grand Cross of the Order of Burkinabé of
Grand Cross of the Order of Burkinabé of  Supreme Collar of the Order of the Chrysanthemum of
Supreme Collar of the Order of the Chrysanthemum of  Grand Commander of the Order of the Republic of
Grand Commander of the Order of the Republic of  Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Congo of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Congo of the  Grand Cross of the Order of the National Hero of the Democratic Republic of the Congo of
Grand Cross of the Order of the National Hero of the Democratic Republic of the Congo of  Commander Grand Cross with Chain of the Order of the Three Stars of Latvia (14 May 2007)
*
Commander Grand Cross with Chain of the Order of the Three Stars of Latvia (14 May 2007)
*  Collar of the Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud of
Collar of the Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud of  Grand Collar of the Order of Independence of Equatorial Guinea (17 April 2009)
*
Grand Collar of the Order of Independence of Equatorial Guinea (17 April 2009)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of the Lion (2013)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of the Lion (2013)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (Guinea), National Order of Merit of Guinea (4 March 2014)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (Guinea), National Order of Merit of Guinea (4 March 2014)
*  Collar of the Order of the Republic of
Collar of the Order of the Republic of  Grand Cross of the National Order of the Ivory Coast (1 June 2015)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of the Ivory Coast (1 June 2015)
*  Collar of the Order of Zayed (4 May 2015)
*
Collar of the Order of Zayed (4 May 2015)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of Madagascar (21 November 2016)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of Madagascar (21 November 2016)
*  Grand Collar of the Military Order of Saint James of the Sword of Portugal (28 June 2016)
*
Grand Collar of the Military Order of Saint James of the Sword of Portugal (28 June 2016)
*  Companion of the Order of the Star of Ghana (17 February 2017)
*
Companion of the Order of the Star of Ghana (17 February 2017)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of La Pléiade (24 May 2017)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of La Pléiade (24 May 2017)
*  Ellis Island Medal of Honor of the United States (14 May 2019)
*
Ellis Island Medal of Honor of the United States (14 May 2019)
*  Chief Commander of the Legion of Merit of the United States (16 January 2021)
Honorary prizes:
* On 22 June 2000, Mohammed received an honorary doctorate from George Washington University.
* On 19 May 2022, Mohammed was awarded the Esquipulas Peace Prize by the Forum of Legislative Presidents of Central America and the Caribbean Basin (FOPREL).
Chief Commander of the Legion of Merit of the United States (16 January 2021)
Honorary prizes:
* On 22 June 2000, Mohammed received an honorary doctorate from George Washington University.
* On 19 May 2022, Mohammed was awarded the Esquipulas Peace Prize by the Forum of Legislative Presidents of Central America and the Caribbean Basin (FOPREL).
Morocco Alaoui dynasty
* Laurenson, John
The most powerful man in Morocco
BBC News. 11 March 2006.
Constitutional Reform in Morocco: I Am the Reform!
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mohammed 06 Of Morocco Mohammed VI of Morocco, 1963 births Living people Moroccan Muslims Muslim monarchs 20th-century monarchs in Africa 21st-century monarchs in Africa 'Alawi dynasty Mohammed V University alumni Alumni of the Collège Royal (Rabat) Kings of Morocco 20th-century Arabs 21st-century Arabs Moroccan people of Arab descent Moroccan royalty Moroccan politicians Moroccan businesspeople Moroccan bankers Moroccan Army officers Moroccan billionaires People from Rabat Collars of the Order of Isabella the Catholic Grand Cordons of the Order of Valour Grand Crosses of the Order of Aviz Extraordinary Grades of the Order of Merit (Lebanon) Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur Grand Crosses of the National Order of Mali Grand Crosses of the Order of the Liberator General San Martin Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order Knights Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic Collars of the Order of Civil Merit Grand Collars of the Order of Saint James of the Sword
 Grand Cordon of the Order of Leopold of
Grand Cordon of the Order of Leopold of Belgium
Belgium, ; french: Belgique ; german: Belgien officially the Kingdom of Belgium, is a country in Northwestern Europe. The country is bordered by the Netherlands to the north, Germany to the east, Luxembourg to the southeast, France to ...
(5 October 2004)
* Order of the Southern Cross
Emperor Pedro I of Brazil founded the National Order of the Southern Cross ( pt, Ordem Nacional do Cruzeiro do Sul) as a Brazilian order of chivalry on 1 December 1822. The order aimed to commemorate the independence of Brazil (7 September 1 ...
of Brazil
Brazil ( pt, Brasil; ), officially the Federative Republic of Brazil (Portuguese: ), is the largest country in both South America and Latin America. At and with over 217 million people, Brazil is the world's fifth-largest country by area ...
(26 November 2004)
*  Medal of Honour of the Congress of Peru (1 December 2004)
*
Medal of Honour of the Congress of Peru (1 December 2004)
*  Collar of the
Collar of the Order of Bernardo O'Higgins
The Order of Bernardo O'Higgins ( es, Orden de Bernardo O'Higgins) is an award issued by Chile. It is the highest civilian honor awarded to non-Chilean citizens. This award was established in 1965 and named after one of the founders of the Chilean ...
of Chile
Chile, officially the Republic of Chile, is a country in the western part of South America. It is the southernmost country in the world, and the closest to Antarctica, occupying a long and narrow strip of land between the Andes to the eas ...
(3 December 2004)
*  Grand Collar of the
Grand Collar of the Order of the Liberator General San Martin
Order, ORDER or Orders may refer to:
* Categorization, the process in which ideas and objects are recognized, differentiated, and understood
* Heterarchy, a system of organization wherein the elements have the potential to be ranked a number of d ...
of Argentina
Argentina (), officially the Argentine Republic ( es, link=no, República Argentina), is a country in the southern half of South America. Argentina covers an area of , making it the List of South American countries by area, second-largest ...
(7 December 2004)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of the Aztec Eagle of
Grand Collar of the Order of the Aztec Eagle of Mexico
Mexico (Spanish language, Spanish: México), officially the United Mexican States, is a List of sovereign states, country in the southern portion of North America. It is borders of Mexico, bordered to the north by the United States; to the so ...
(11 February 2005)
* Burkina Faso
Burkina Faso (, ; , ff, 𞤄𞤵𞤪𞤳𞤭𞤲𞤢 𞤊𞤢𞤧𞤮, italic=no) is a landlocked country in West Africa with an area of , bordered by Mali to the northwest, Niger to the northeast, Benin to the southeast, Togo and Ghana t ...
(1 March 2005)
* Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
(28 November 2005)
* the Gambia
The Gambia,, ff, Gammbi, ar, غامبيا officially the Republic of The Gambia, is a country in West Africa. It is the smallest country within mainland AfricaHoare, Ben. (2002) ''The Kingfisher A-Z Encyclopedia'', Kingfisher Publicatio ...
(20 February 2006)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Congo of the
Grand Cross of the Order of Merit of the Congo of the Republic of Congo
The Republic of the Congo (french: République du Congo, ln, Republíki ya Kongó), also known as Congo-Brazzaville, the Congo Republic or simply either Congo or the Congo, is a country located in the western coast of Central Africa to the w ...
(22 February 2006)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of the National Hero of the Democratic Republic of the Congo of
Grand Cross of the Order of the National Hero of the Democratic Republic of the Congo of Congo-Kinshasa
The Democratic Republic of the Congo (french: République démocratique du Congo (RDC), colloquially "La RDC" ), informally Congo-Kinshasa, DR Congo, the DRC, the DROC, or the Congo, and formerly and also colloquially Zaire, is a country in ...
(28 February 2006)
*  Commander Grand Cross with Chain of the Order of the Three Stars of Latvia (14 May 2007)
*
Commander Grand Cross with Chain of the Order of the Three Stars of Latvia (14 May 2007)
*  Collar of the Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud of
Collar of the Order of Abdulaziz Al Saud of Saudi Arabia
Saudi Arabia, officially the Kingdom of Saudi Arabia (KSA), is a country in Western Asia. It covers the bulk of the Arabian Peninsula, and has a land area of about , making it the fifth-largest country in Asia, the second-largest in the Ara ...
(18 May 2007)
*  Grand Collar of the Order of Independence of Equatorial Guinea (17 April 2009)
*
Grand Collar of the Order of Independence of Equatorial Guinea (17 April 2009)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of the Lion (2013)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of the Lion (2013)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (Guinea), National Order of Merit of Guinea (4 March 2014)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of Merit (Guinea), National Order of Merit of Guinea (4 March 2014)
*  Collar of the Order of the Republic of
Collar of the Order of the Republic of Tunisia
)
, image_map = Tunisia location (orthographic projection).svg
, map_caption = Location of Tunisia in northern Africa
, image_map2 =
, capital = Tunis
, largest_city = capital
, ...
(31 May 2014)
*  Collar of the Order of Zayed (4 May 2015)
*
Collar of the Order of Zayed (4 May 2015)
*  Grand Cross of the National Order of Madagascar (21 November 2016)
*
Grand Cross of the National Order of Madagascar (21 November 2016)
*  Grand Collar of the Military Order of Saint James of the Sword of Portugal (28 June 2016)
*
Grand Collar of the Military Order of Saint James of the Sword of Portugal (28 June 2016)
*  Companion of the Order of the Star of Ghana (17 February 2017)
*
Companion of the Order of the Star of Ghana (17 February 2017)
*  Grand Cross of the Order of La Pléiade (24 May 2017)
*
Grand Cross of the Order of La Pléiade (24 May 2017)
*  Chief Commander of the Legion of Merit of the United States (16 January 2021)
Honorary prizes:
* On 22 June 2000, Mohammed received an honorary doctorate from George Washington University.
* On 19 May 2022, Mohammed was awarded the Esquipulas Peace Prize by the Forum of Legislative Presidents of Central America and the Caribbean Basin (FOPREL).
Chief Commander of the Legion of Merit of the United States (16 January 2021)
Honorary prizes:
* On 22 June 2000, Mohammed received an honorary doctorate from George Washington University.
* On 19 May 2022, Mohammed was awarded the Esquipulas Peace Prize by the Forum of Legislative Presidents of Central America and the Caribbean Basin (FOPREL).
Ancestry
References
External links
Morocco Alaoui dynasty
* Laurenson, John
The most powerful man in Morocco
BBC News. 11 March 2006.
Constitutional Reform in Morocco: I Am the Reform!
{{DEFAULTSORT:Mohammed 06 Of Morocco Mohammed VI of Morocco, 1963 births Living people Moroccan Muslims Muslim monarchs 20th-century monarchs in Africa 21st-century monarchs in Africa 'Alawi dynasty Mohammed V University alumni Alumni of the Collège Royal (Rabat) Kings of Morocco 20th-century Arabs 21st-century Arabs Moroccan people of Arab descent Moroccan royalty Moroccan politicians Moroccan businesspeople Moroccan bankers Moroccan Army officers Moroccan billionaires People from Rabat Collars of the Order of Isabella the Catholic Grand Cordons of the Order of Valour Grand Crosses of the Order of Aviz Extraordinary Grades of the Order of Merit (Lebanon) Grand Croix of the Légion d'honneur Grand Crosses of the National Order of Mali Grand Crosses of the Order of the Liberator General San Martin Honorary Knights Grand Cross of the Royal Victorian Order Knights Grand Cross with Collar of the Order of Merit of the Italian Republic Collars of the Order of Civil Merit Grand Collars of the Order of Saint James of the Sword