Mindanao on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Mindanao ( ) ( Jawi: مينداناو) is the second-largest island in the
 Archaeological findings on the island point to evidence of human activity dating back about ten thousand years. Around 1500 BC Austronesian people spread throughout the Philippines.
The Subanon are believed to have settled in the
Archaeological findings on the island point to evidence of human activity dating back about ten thousand years. Around 1500 BC Austronesian people spread throughout the Philippines.
The Subanon are believed to have settled in the
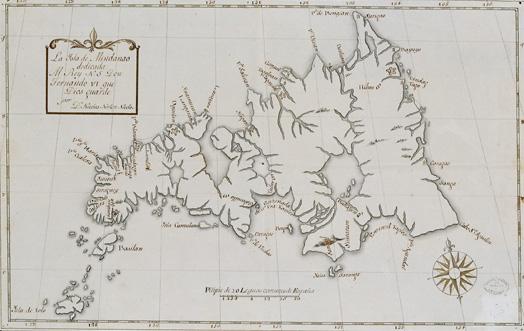 In the classic epoch of Philippine history (900 AD onwards), the people of Mindanao were heavily exposed to
In the classic epoch of Philippine history (900 AD onwards), the people of Mindanao were heavily exposed to
 The spread of Islam in the Philippines began in the 14th century, mostly through the influence of Muslim merchants from the western Malay Archipelago. The first
The spread of Islam in the Philippines began in the 14th century, mostly through the influence of Muslim merchants from the western Malay Archipelago. The first
 In 1521 Antonio Pigafetta wrote an account of reaching 'Maingdano.' He was with Magellan on the first circumnavigation of the globe and sailing for the king of Spain.
On February 2, 1543,
In 1521 Antonio Pigafetta wrote an account of reaching 'Maingdano.' He was with Magellan on the first circumnavigation of the globe and sailing for the king of Spain.
On February 2, 1543,
(Zamboanga City History) "He (Governor Don Sebastían Hurtado de Corcuera) brought a great reënforcements of soldiers, many of them from Perú, as he made his voyage to Acapulco from that kingdom." The sultanates resisted Spanish pressure and attempts to convert them to Christianity during this period. The Papuan-speaking Sultanate of Ternate in the Mollucas at Indonesia formed a close alliance with the sultanates of Mindanao, especially with the Sultanate of Maguindanao. Ternate regularly sent military reinforcements to Mindanao to assist the local sultanates in their war against Spanish-controlled Manila. By the late 18th century Spain had geographic dominance over the island, having established settlements and forts in most of Mindanao, including Zamboanga City and Misamis Occidental to the northwest,
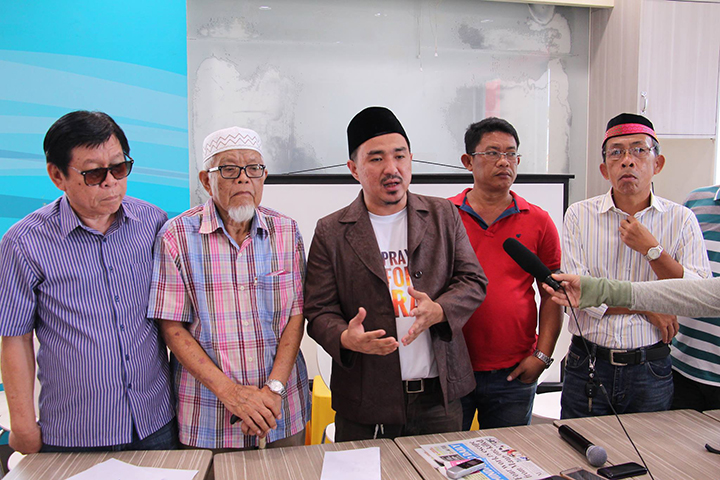 In May 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte declared martial law on the entire island group of Mindanao following the
In May 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte declared martial law on the entire island group of Mindanao following the
 Mindanao's economy accounts for 14% of the country's gross domestic product. The region grew 4.9% in 2016 against Luzon's 5.5% and Visayas' 9.1%.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing make up more than 40% of Mindanao's market, being the country's largest supplier of major crops such as pineapples and bananas.
There is one defined growth corridor in the island, namely
Mindanao's economy accounts for 14% of the country's gross domestic product. The region grew 4.9% in 2016 against Luzon's 5.5% and Visayas' 9.1%.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing make up more than 40% of Mindanao's market, being the country's largest supplier of major crops such as pineapples and bananas.
There is one defined growth corridor in the island, namely
 The mountains of Mindanao can be grouped into ten ranges, including both complex structural mountains and volcanoes. The structural mountains on the extreme eastern and western portions of the island show broad exposures of
The mountains of Mindanao can be grouped into ten ranges, including both complex structural mountains and volcanoes. The structural mountains on the extreme eastern and western portions of the island show broad exposures of  The east-facing coastal regions of Davao and Surigao del Sur are marked by a series of small coastal lowlands separated from each other by rugged forelands which extend to the water's edge. Offshore are numerous coral reefs and tiny islets. This remote and forbidding coast is made doubly difficult to access during the months from October to March by the heavy surf driven before the northeast trade winds. A few miles offshore is found the Philippine Deep. This ocean trench, reaching measured depths of , is the third-deepest trench, (after the
The east-facing coastal regions of Davao and Surigao del Sur are marked by a series of small coastal lowlands separated from each other by rugged forelands which extend to the water's edge. Offshore are numerous coral reefs and tiny islets. This remote and forbidding coast is made doubly difficult to access during the months from October to March by the heavy surf driven before the northeast trade winds. A few miles offshore is found the Philippine Deep. This ocean trench, reaching measured depths of , is the third-deepest trench, (after the  In South Cotabato, is another range of volcanic mountains, this time paralleling the coast. These mountains have a maximum extent of from northwest to southeast and measures some across. One of the well-known mountains here is Mount Parker, whose almost circular
In South Cotabato, is another range of volcanic mountains, this time paralleling the coast. These mountains have a maximum extent of from northwest to southeast and measures some across. One of the well-known mountains here is Mount Parker, whose almost circular
 Mindanao contains two large lowland areas in the valleys of the
Mindanao contains two large lowland areas in the valleys of the

 An American census conducted in the early 1900s noted that the island was inhabited by people "greatly divided in origin, temperament and religion". Evidence of the island's cultural diversity can be seen in the buildings and ruins of old Spanish settlements in the northwestern peninsula that span eastwards to the southern gulf coast, the site of the ancient Rajahnate of Butuan in the northeast region (
An American census conducted in the early 1900s noted that the island was inhabited by people "greatly divided in origin, temperament and religion". Evidence of the island's cultural diversity can be seen in the buildings and ruins of old Spanish settlements in the northwestern peninsula that span eastwards to the southern gulf coast, the site of the ancient Rajahnate of Butuan in the northeast region (
Mindanao Development Authority Official Website
{{Authority control Mindanao, Island groups of the Philippines Islands of the Philippines
Philippines
The Philippines (; fil, Pilipinas, links=no), officially the Republic of the Philippines ( fil, Republika ng Pilipinas, links=no),
* bik, Republika kan Filipinas
* ceb, Republika sa Pilipinas
* cbk, República de Filipinas
* hil, Republ ...
, after Luzon, and seventh-most populous island in the world. Located in the southern region of the archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
, the island is part of an island group of the same name that also includes its adjacent islands, notably the Sulu Archipelago. According to the 2020 census, Mindanao has a population of 26,252,442 people, while the entire island group has an estimated population of 27,021,036 according to the 2021 census.
Mindanao is divided into six administrative regions: the Zamboanga Peninsula
Zamboanga Peninsula ( tl, Tangway ng Zamboanga; cbk, Peninsula de Zamboanga; ceb, Lawis sa Zamboanga) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region IX. It consists of three provinces (Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga Sibu ...
, Northern Mindanao
Northern Mindanao ( tl, Hilagang Mindanao; ceb, Amihanang Mindanao; Maranao: ''Pangotaraan Mindanao'') is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region X. It comprises five provinces: Bukidnon, Camiguin, Misamis Occidental, ...
, the Caraga
Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region (or simply known as Caraga Region) and designated as Region XIII, is an Regions of the Philippines, administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. Th ...
region, the Davao region, Soccsksargen, and the autonomous region of Bangsamoro
ar, منطقة بانجسامورو ذاتية الحكم فى مسلمى مينداناو
, native_name =
, settlement_type = Autonomous region
, anthem = Bangsamoro Hymn
, image_skyline ...
. According to the 2020 census, Davao City is the most populous city on the island, with 1,776,949 people, followed by Zamboanga City (pop. 977,234), Cagayan de Oro (pop. 728,402), General Santos (pop. 697,315), Butuan
Butuan (pronounced ), officially the City of Butuan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Butuan; Butuanon: ''Dakbayan hong Butuan''; fil, Lungsod ng Butuan), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Caraga, Philippines. It is the ''de facto'' c ...
(pop. 372,910), Iligan
Iligan, officially the City of Iligan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Iligan; fil, Lungsod ng Iligan; Maranao: ''Inged a Iligan''), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Northern Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it ha ...
(pop. 363,115) and Cotabato City
Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato ( Maguindanaon: ''Kuta nu Kutawatu'', Jawi:
كوتا نو كوتاواتو; Iranun: ''Bandar a Kotawato'', بندر ا كوتاواتو; fil, Lungsod ng Cotabato), is a third class independent c ...
(pop. 325,079). About 70% of residents identify as Christian and 24% as Muslim.
Mindanao is considered the major breadbasket
The breadbasket of a country or of a region is an area which, because of the richness of the soil and/or advantageous climate, produces large quantities of wheat or other grain. Rice bowl is a similar term used to refer to Southeast Asia; and C ...
of the Philippines, with eight of the top 10 agri-commodities exported from the Philippines coming from the island itself.
Etymology
The name "Mindanao" is aSpanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
corruption of the name of the Maguindanao people
The Maguindanao people are an Austronesian ethnic group from the Philippines. The Maguindanaon are part of wider political identity of Muslims of Mindanao, Sulu and Palawan known as Moro, who constitute the third largest ethnic group of Mindana ...
, the dominant ruling ethnic group in the Sultanate of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindan ...
in southwestern Mindanao during the Spanish colonial period. The name itself means "people of the lake", though it is usually translated to "people of the flood plains" in modern sources.
History
Prehistory
 Archaeological findings on the island point to evidence of human activity dating back about ten thousand years. Around 1500 BC Austronesian people spread throughout the Philippines.
The Subanon are believed to have settled in the
Archaeological findings on the island point to evidence of human activity dating back about ten thousand years. Around 1500 BC Austronesian people spread throughout the Philippines.
The Subanon are believed to have settled in the Zamboanga Peninsula
Zamboanga Peninsula ( tl, Tangway ng Zamboanga; cbk, Peninsula de Zamboanga; ceb, Lawis sa Zamboanga) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region IX. It consists of three provinces (Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga Sibu ...
during the Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
Era c.4500-2000 BC. Evidence of stone tools in Zamboanga del Norte may indicate a late Neolithic
The Neolithic period, or New Stone Age, is an Old World archaeological period and the final division of the Stone Age. It saw the Neolithic Revolution, a wide-ranging set of developments that appear to have arisen independently in several p ...
presence. Ceramic burial jars, both unglazed and glazed, Chinese celadons, gold ornaments, beads, and bracelets have been found in caves. Many of the ceramic objects are from the Yuan and Ming periods. Evidently, there was a long history of trade between the Subanon and the Chinese long before the latter's contact with Islam.
Rajahnates and Hindu-Buddhism
 In the classic epoch of Philippine history (900 AD onwards), the people of Mindanao were heavily exposed to
In the classic epoch of Philippine history (900 AD onwards), the people of Mindanao were heavily exposed to Hindu
Hindus (; ) are people who religiously adhere to Hinduism. Jeffery D. Long (2007), A Vision for Hinduism, IB Tauris, , pages 35–37 Historically, the term has also been used as a geographical, cultural, and later religious identifier for ...
and Buddhist influence and beliefs from Indonesia and Malaysia. Indianized abugida
An abugida (, from Ge'ez: ), sometimes known as alphasyllabary, neosyllabary or pseudo-alphabet, is a segmental writing system in which consonant-vowel sequences are written as units; each unit is based on a consonant letter, and vowel n ...
scripts such as Kawi and Baybayin were introduced from Java and an extinct intermediate from Sulawesi or Borneo respectively. Cultural icons of the sarong
A sarong or sarung () is a large tube or length of fabric, often wrapped around the waist, worn in Southeast Asia, South Asia, Western Asia, Northern Africa, East Africa, West Africa, and on many Pacific islands. The fabric often has woven plaid o ...
(known as malong
The malong is a traditional Filipino-Bangsamoro rectangular or tube-like wraparound skirt bearing a variety of geometric or okir designs. The malong is traditionally used as a garment by both men and women of the numerous ethnic groups in the mai ...
or patadyong), the pudong
Pudong is a district of Shanghai located east of the Huangpu, the river which flows through central Shanghai. The name ''Pudong'' was originally applied to the Huangpu's east bank, directly across from the west bank or Puxi, the historic cit ...
turban, silk
Silk is a natural protein fiber, some forms of which can be woven into textiles. The protein fiber of silk is composed mainly of fibroin and is produced by certain insect larvae to form cocoons. The best-known silk is obtained from the ...
, and batik
Batik is an Indonesian technique of wax-resist dyeing applied to the whole cloth. This technique originated from the island of Java, Indonesia. Batik is made either by drawing dots and lines of the resist with a spouted tool called a ''ca ...
and ikat
''Ikat'' (in Indonesian languages means "bind") is a dyeing technique originating from Indonesia used to pattern textiles that employs resist dyeing on the yarns prior to dyeing and weaving the fabric.
In ''ikat'', the resist is formed by b ...
weaving and dyeing methods were introduced. Artifacts found from this era include the Golden kinnara, Golden Tara, and the Ganesh pendant. These cultural traits passed from Mindanao into the Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
and Luzon, but were subsequently lost or heavily modified after the Spanish arrival in the 16th century.
Hindu-Buddhist cultural influence took root in the coastal settlements, syncretizing with indigenous animist beliefs and customs among the tribes of the interior. The Butuan Rajahnate, a Hinduized kingdom mentioned in Chinese records as a tributary state in the 10th century, was concentrated along the northeastern coast of Butuan Bay. The Rajahnate of Sanmalan
The polity of Sanmalan is a precolonial Philippine state centered on what is now Zamboanga. Labeled in Chinese annals as "Sanmalan" 三麻蘭. The Chinese recorded a year 1011 tribute from its Rajah or King, Chulan, who was represented at the i ...
in Zamboanga, was also in Mindanao. The Darangen
''Darangen'' is a Maranao epic poem from the Lake Lanao region of Mindanao, Philippines. It consists of 17 cycles with 72,000 lines in iambic tetrameter or catalectic trochaic tetrameter. Each cycle pertains to a different self-contained story. T ...
epic of the Maranao people harkens back to this era as the most complete local version of the Ramayana
The ''Rāmāyana'' (; sa, रामायणम्, ) is a Sanskrit literature, Sanskrit Indian epic poetry, epic composed over a period of nearly a millennium, with scholars' estimates for the earliest stage of the text ranging from the 8th ...
. The Maguindanao at this time also had strong Hindu beliefs, evidenced by the Ladya Lawana (Rajah Ravana) epic saga that survives to the present, albeit highly Islamized from the 17th century onward.
Sultanates and Islam
 The spread of Islam in the Philippines began in the 14th century, mostly through the influence of Muslim merchants from the western Malay Archipelago. The first
The spread of Islam in the Philippines began in the 14th century, mostly through the influence of Muslim merchants from the western Malay Archipelago. The first mosque
A mosque (; from ar, مَسْجِد, masjid, ; literally "place of ritual prostration"), also called masjid, is a place of prayer for Muslims. Mosques are usually covered buildings, but can be any place where prayers ( sujud) are performed, ...
in the Philippines was built in the mid-14th century in the town of Simunul, Tawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
. Around the 16th century, the Muslim sultanates of Sulu, Lanao and Maguindanao were established from formerly Hindu-Buddhist Rajahnates.
As Islam gained influence in Mindanao, the natives of the Sultanates had to either convert to Islam or pay tribute to their new Muslim rulers. The largest of the Muslim polities in mainland Mindanao was the Sultanate of Maguindanao, which controlled the southern floodplains of the Rio Grande de Mindanao
The Rio Grande de Mindanao, also known as the Mindanao River, is the second-largest river system in the Philippines. Located on the southern island of Mindanao, with a total drainage area of , draining the majority of the central and eastern po ...
and most of the coastal area of the Illana Bay and the Moro Gulf
The Moro Gulf is the largest gulf in the Philippines. It is located off the coast of Mindanao Island, and is part of the Celebes Sea. The gulf is one of the country's tuna fishing grounds.
Geography
The gulf stretches between and is surrounde ...
. The name Mindanao was derived from this Sultanate. But most of Mindanao remained animist, especially the Lumad people
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopte ...
in the interior. Most of the northern, eastern, and southern coastal regions inhabited by Visayans
Visayans ( Visayan: ''mga Bisaya''; ) or Visayan people are a Philippine ethnolinguistic group or metaethnicity native to the Visayas, the southernmost islands of Luzon and a significant portion of Mindanao. When taken as a single ethnic group ...
( Surigaonon and Butuanon) and other groups were later converted to Christianity by the Spanish. Mindanao was then embroiled between a conflict with the Boholano (Visayan) Kedatuan of Dapitan and the Moluccan Sultanate of Ternate. Dapitan which was originally at Bohol was destroyed by an expeditionary force from the Ternate Sultanate and Dapitenyos were forced to relocate to Northern Mindanao where they waged war against the Sultanate of Lanao and established a new Dapitan there. Mindanaoans then spread out of Mindanao across Southeast Asia, Historian William Henry Scott, quoting the Portuguese manuscript Summa Orientalis, noted that Mottama
Mottama ( my, မုတ္တမမြို့, ; Muttama mnw, မုဟ်တၟံ, ; formerly Martaban) is a town in the Thaton District of Mon State, Myanmar. Located on the west bank of the Thanlwin river (Salween), on the opposite side ...
in Burma
Myanmar, ; UK pronunciations: US pronunciations incl. . Note: Wikipedia's IPA conventions require indicating /r/ even in British English although only some British English speakers pronounce r at the end of syllables. As John Wells explai ...
(Myanmar) had a large presence of merchants from Mindanao.
Spanish colonization and Christianity
 In 1521 Antonio Pigafetta wrote an account of reaching 'Maingdano.' He was with Magellan on the first circumnavigation of the globe and sailing for the king of Spain.
On February 2, 1543,
In 1521 Antonio Pigafetta wrote an account of reaching 'Maingdano.' He was with Magellan on the first circumnavigation of the globe and sailing for the king of Spain.
On February 2, 1543, Ruy López de Villalobos
Ruy López de Villalobos (; ca. 1500 – April 4, 1546) was a Spanish explorer who sailed the Pacific from Mexico to establish a permanent foothold for Spain in the East Indies, which was near the Line of Demarcation between Spain and Portugal a ...
was the first Spaniard to reach Mindanao. He called the island ''"Caesarea Caroli"'' after Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire (and I of Spain). Shortly after Spain's colonization of Cebu, it moved on to colonize the Caraga
Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region (or simply known as Caraga Region) and designated as Region XIII, is an Regions of the Philippines, administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. Th ...
region in northeast Mindanao and discovered significant Muslim presence on the island. Over time a number of tribes in Mindanao converted to Roman Catholicism and built settlements and forts throughout the coastal regions. These settlements endured despite attacks from neighboring Muslim sultanates. The most heavily fortified of them, apart from a short period in 1662 when Spain sent soldiers from the city to Manila after a threat of invasion from the Chinese general Koxinga
Zheng Chenggong, Prince of Yanping (; 27 August 1624 – 23 June 1662), better known internationally as Koxinga (), was a Ming loyalist general who resisted the Qing conquest of China in the 17th century, fighting them on China's southeastern ...
, was Zamboanga City which was settled by soldiers from Peru and Mexico."SECOND BOOK OF THE SECOND PART OF THE CONQUESTS OF THE FILIPINAS ISLANDS, AND CHRONICLE OF THE RELIGIOUS OF OUR FATHER, ST. AUGUSTINE"(Zamboanga City History) "He (Governor Don Sebastían Hurtado de Corcuera) brought a great reënforcements of soldiers, many of them from Perú, as he made his voyage to Acapulco from that kingdom." The sultanates resisted Spanish pressure and attempts to convert them to Christianity during this period. The Papuan-speaking Sultanate of Ternate in the Mollucas at Indonesia formed a close alliance with the sultanates of Mindanao, especially with the Sultanate of Maguindanao. Ternate regularly sent military reinforcements to Mindanao to assist the local sultanates in their war against Spanish-controlled Manila. By the late 18th century Spain had geographic dominance over the island, having established settlements and forts in most of Mindanao, including Zamboanga City and Misamis Occidental to the northwest,
Iligan City
Iligan, officially the City of Iligan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Iligan; fil, Lungsod ng Iligan; Maranao: ''Inged a Iligan''), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Northern Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it ha ...
, Misamis Oriental, Bukidnon
Bukidnon(), officially the Province of Bukidnon ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bukidnon; fil, Lalawigan ng Bukidnon; hil, Kapuroan sang Bukidnon; Binukid and Higaonon: ''Probinsya ta Bukidnon''), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the ...
, and Camiguin Island to the north, Surigao and Agusan in the Caraga
Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region (or simply known as Caraga Region) and designated as Region XIII, is an Regions of the Philippines, administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. Th ...
region to the east, and Davao in the island's gulf coast. Spain continued to engage in battles with Muslim sultanates until the end of the 19th century.
At the same time as the Philippine revolution against Spain, the Republic of Zamboanga
The Republic of Zamboanga was a short-lived revolutionary government, founded by General Vicente Alvarez with his Zamboangueño Revolutionary Forces after the Spanish government in Zamboanga, Philippines officially surrendered and turned ove ...
rose as a revolutionary state in Mindanao before it was absorbed by the oncoming Americans.
American Occupation and Philippine Commonwealth
In the Treaty of Paris in 1898 Spain sold the entire Philippine archipelago to the United States for $20 million. The 1900 Treaty of Washington and the 1930 Convention Between the United States and Great Britain clarified the borders between Mindanao and Borneo. In early 1900s the Commonwealth government (Led by American Oppressors) encouraged citizens from Luzon and Visayas to migrate to Mindanao. Consisting mostly of Ilocanos, Cebuanos, and Ilonggos. Settlers streaming into Soccsksargen led to the displacement of the Blaan and Tboli tribes.World War II
In April 1942 Mindanao, along with the rest of the Philippines, officially enteredWorld War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
after Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
soldiers invaded key cities in the islands. Many towns and cities were burned to the ground in Mindanao, most notably Davao City, Zamboanga City, Lanao, Cagayan de Oro, Iligan City, and Butuan. In the months of April and May 1942, Japanese forces defeated US troops commanded by William F. Sharp and Guy Fort, in a battle that started at Malabang (a town close to Gandamatu Macadar, Lanao) and ended close to the town of Ganassi, Lanao. Davao City was among the earliest to be occupied by the invading Japanese forces. They immediately fortified the city as a bastion of the Japanese defense system.
Davao City was subjected by the returning forces of Gen. Douglas MacArthur to constant bombing before the American Liberation Forces landed in Leyte in October 1944. Filipino soldiers and local guerrilla fighters were actively fighting Japanese forces until liberation at the conclusion of the Battle of Mindanao
The Battle of Mindanao ( Filipino: ''Labanan sa Mindanao;'' Cebuano: ''Gubat sa Mindanao;'' Japanese: ミンダナオの戦い) was fought by the Americans and allied Filipino guerrillas against the Japanese forces on the island of Mindanao i ...
.
Postwar era and Philippine independence
Mindanao was peaceful and increasingly progressive in the postwar period, including the 1950s and the mid-1960s. Ethnic tensions were minimal, and there was essentially no presence of secessionists groups in Mindanao.Marcos era (1965–1986)
Under Ferdinand Marcos's administration, Christian groups began to settle in Mindanao, displacing many locals. The population boom resulted in conflicts as the original owners sought their ancestral land domains. The Marcos administration encouraged new settlers who had emigrated to Mindanao to form a militia, which was eventually called the Ilaga. Anecdotal evidence states that the Ilaga often committed human rights abuses by targeting the Moro andLumad
The Lumad are a group of Austronesian indigenous people in the southern Philippines. It is a Cebuano term meaning "native" or "indigenous". The term is short for Katawhang Lumad (Literally: "indigenous people"), the autonym officially adopte ...
people, as well as attempting to seize additional territory. It resulted in a lingering animosity between Moro and Christian communities. Mistrust and a cycle of violence are still felt today due to the creation of the Ilaga.
The Jabidah massacre in 1968 is commonly cited as the major flashpoint that ignited the Moro insurgency, and the ensuing ethnic tensions led to the formation of secessionist movements, such as the Muslim Independence Movement and the Bangsamoro Liberation Organization. These movements were largely political in nature, but the prohibition of political parties after Marcos' 1972 declaration of Martial Law led to the founding and dominance of armed groups such as the Moro National Liberation Front
The Moro National Liberation Front (MNLF; ar, الجبهة الوطنية لتحرير مورو) is a political organization in the Philippines that was founded in 1972. It started as a splinter group of the Muslim Independence Movement. The ...
(MNLF), and the Moro Islamic Liberation Front
The Moro Islamic Liberation Front (MILF; ar, ''Jabhat Taḥrīr Moro al-ʾIslāmiyyah'') is a group based in Mindanao seeking an autonomous region of the Moro people from the central government. The group has a presence in the Bangsamoro r ...
(MILF). Ethnic conflicts continued to escalate, leading to incidents like the 1971 Manili Massacre, the Pata Island Massacre, and the Palimbang massacre
The Malisbong Masjid or H. Hamsa Tacbil Mosque massacre, also called the Palimbang massacre, was the mass murder of Muslim Moro people, Moros by units of the Armed Forces of the Philippines, Philippine military on September 24, 1974, in the co ...
.
Additionally, an economic crisis in late 1969 led to social unrest throughout the country, and violent crackdowns on protests led to the radicalization of many students, with some joining the New People's Army
The New People's Army ( fil, Bagong Hukbong Bayan), abbreviated NPA or BHB, is the armed wing of the Communist Party of the Philippines (CPP), based primarily in the Philippine countryside. It acts as the CPP's principal organization, aim ...
, bringing the Communist rebellion to Mindanao.
Marcos' declaration led to the shuttering of press outlets - television stations, national newspapers, weekly magazines, community newspapers, and radio stations - throughout the country, including in Mindanao. The remaining years of the Marcos dictatorship led to the killings of many Mindanao Journalists, with prominent examples being Alex Orcullo of Mindanao Currents and Mindaweek, and Jacobo Amatong of the Mindanao Observer.
Fifth Republic (1986–present)
In 1989, theAutonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao
The Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao ( tl, Rehiyong Awtonomo ng Muslim Mindanao; ar, الحكم الذاتي الاقليمي لمسلمي مندناو ''Al-ḥukm adh-dhātī al-'iqlīmī li-muslimī Mindanāu''; abbreviated as ARMM) was ...
(ARMM) was established, constituted by several provinces in Western Mindanao.
In March 2000, President Joseph Estrada declared an "All Out War" against the MILF after it committed a series of terrorist attacks on government buildings, civilians, and foreigners. A number of livelihood intervention projects, from organisations such as USAID and the Emergency Livelihood Assistance Program (ELAP), aided in the reconstruction of areas affected by constant battles on the island.
In December 2009, President Gloria Macapagal Arroyo officially placed Maguindanao under a state of martial law following the Maguindanao massacre
The Maguindanao massacre, also known as the Ampatuan massacre, named after the town where mass graves of victims were found, occurred on the morning of November 23, 2009, in the town of Ampatuan in then-undivided Maguindanao (which is now Magu ...
.
Tropical storm Sendong (international name, Washi) made landfall on December 15, 2011, in Mindanao. The recorded 24-hour rainfall in Lumbia station of PAGASA
Pagasa may refer to:
* ''Pagasa'' (genus), an insect genus in the family Nabidae
* PAGASA, an acronym for the Philippine Atmospheric, Geophysical and Astronomical Services Administration
*"May Pagasa", a pen-name of José Rizal
José Prot ...
reached 180.9 mm, causing the overflow of the Cagayan de Oro River. The storm killed 1,268 people, with 49 others listed as missing. Most of the casualties were from Cagayan de Oro and Iligan
Iligan, officially the City of Iligan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Iligan; fil, Lungsod ng Iligan; Maranao: ''Inged a Iligan''), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Northern Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it ha ...
. Those who survived were rendered homeless, seeking shelter in evacuation centers.
On September 9, 2013, an MNLF faction attempted to raise the flag of a self-proclaimed Bangsamoro Republik at Zamboanga City Hall in an armed incursion into parts of the city.
On January 25, 2015, a shootout took place during a police operation by the Special Action Force (SAF) of the Philippine National Police (PNP) in Tukanalipao, Mamasapano, Maguindanao. The operation, codenamed Oplan Exodus, was intended to capture or kill wanted Malaysian terrorist and bomb-maker Zulkifli Abdhir and other Malaysian terrorists or high-ranking members of the Bangsamoro Islamic Freedom Fighters (BIFF).
 In May 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte declared martial law on the entire island group of Mindanao following the
In May 2017, President Rodrigo Duterte declared martial law on the entire island group of Mindanao following the Marawi siege
The siege of Marawi ( fil, Pagkubkob sa Marawi), also known as the Marawi crisis (), and the Battle of Marawi (), was a five-month-long armed conflict in Marawi, Philippines, that started on May 23, 2017, between Philippine government security ...
by the Maute terrorist group. More than 180,000 people were forced to evacuate Marawi City. Around 165 security forces and 47 residents were confirmed killed in the battle, although Marawi residents believe the number of civilians killed was far higher. The official death toll in the five-month war is 1,109, most of which were members of a militant alliance which drew fighters from radical factions of domestic Islamist groups.
In 2019, the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim Mindanao was established, replacing the former ARMM.
Economy
 Mindanao's economy accounts for 14% of the country's gross domestic product. The region grew 4.9% in 2016 against Luzon's 5.5% and Visayas' 9.1%.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing make up more than 40% of Mindanao's market, being the country's largest supplier of major crops such as pineapples and bananas.
There is one defined growth corridor in the island, namely
Mindanao's economy accounts for 14% of the country's gross domestic product. The region grew 4.9% in 2016 against Luzon's 5.5% and Visayas' 9.1%.
Agriculture, forestry and fishing make up more than 40% of Mindanao's market, being the country's largest supplier of major crops such as pineapples and bananas.
There is one defined growth corridor in the island, namely Metro Davao
Metro Davao, officially called Metropolitan Davao ( ceb, Kaulohang Dabaw; fil, Kalakhang Davao), is a metropolitan area in the Mindanao island group, Philippines. It includes the cities of Davao City, Digos, Mati, Panabo, Samal and Tagum and sp ...
. Other regional centers are: Cagayan de Oro City, General Santos City, Zamboanga City, Cotabato City, and Pagadian City.
Being the top-performing economy in Mindanao, Davao Region has the 5th-biggest economy in the country and the second-fastest-growing economy next to Cordillera Autonomous Region. While the region's economy is predominantly agri-based, it is now developing into a center for agro-industrial business, trade and tourism. Its competitive advantage is in agri-industry as its products, papayas, mangoes, bananas, pineapples, fresh asparagus, flowers, and fish products are exported internationally. The region can be a vital link to markets in other parts of Mindanao, Brunei Darussalam and parts of Malaysia
Malaysia ( ; ) is a country in Southeast Asia. The federation, federal constitutional monarchy consists of States and federal territories of Malaysia, thirteen states and three federal territories, separated by the South China Sea into two r ...
and Indonesia
Indonesia, officially the Republic of Indonesia, is a country in Southeast Asia and Oceania between the Indian and Pacific oceans. It consists of over 17,000 islands, including Sumatra, Java, Sulawesi, and parts of Borneo and New Guine ...
.
There is also a growing call center sector in the region, mostly centered in Davao City.
Upcoming developments
Some 2,130 government-led infrastructure projects worth P547.9 billion have also been lined up for Mindanao until 2022. NEDA official said that 68% of that budget will be allotted for the transportation sector, while 16% will go to water resources, and 6% to social infrastructure. Of this amount, 18 infrastructure projects have been identified as "flagship projects," five of them have already been approved by President Rodrigo Duterte. The projects include the ₱35.26 billion Tagum-Davao-Digos Segment of theMindanao Railway
The Mindanao Railway, previously known as the Trans-Mindanao High Speed Railway, is a proposed inter-city rail system in Mindanao, the southernmost major island of the Philippines. Originally proposed in 1936 as part of Manuel L. Quezon's ef ...
, the ₱40.57 billion Davao airport, the ₱14.62 billion Laguindingan airport, the ₱4.86 billion Panguil Bay Bridge Project, and the ₱5.44 billion Malitubog-Maridagao Irrigation Project, Phase II.
Projects in the pipeline are the second and third phases of the Mindanao Railway; the Agus-Pulangi plant rehabilitation; the Davao expressway; the Zamboanga Fish Port Complex rehabilitation; the Balo-i Plains Flood Control Project; Asbang Small Reservoir Irrigation Project; the Ambal Simuay Sub-Basin of the Mindanao River Basin Flood Control and River Protection Project; as well as the Road Network Development Project in Conflict-Affected Areas in Mindanao project.
Administrative divisions
The island consists of six administrative regions, 23provinces
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman '' provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions ou ...
, and 30 cities
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
(27 provinces and 33 cities if associated islands are included).
Largest cities and municipalities in Mindanao
The list of largest cities and municipalities in Mindanao in terms of population is shown in the table below.Geography
Mindanao is the second-largestisland
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
in the Philippines at , and is the seventh-most populous island in the world. The island is mountainous, and is home to Mount Apo, the highest mountain in the country. Mindanao is surrounded by four seas: the Sulu Sea to the west, the Philippine Sea to the east, the Celebes Sea
The Celebes Sea, (; ms, Laut Sulawesi, id, Laut Sulawesi, fil, Dagat Selebes) or Sulawesi Sea, of the western Pacific Ocean is bordered on the north by the Sulu Archipelago and Sulu Sea and Mindanao Island of the Philippines, on the east b ...
to the south, and the Mindanao Sea to the north.
The island itself is part of an island group of the same name, which includes the Sulu Archipelago and the outlying islands of Camiguin
Camiguin, officially the Province of Camiguin ( ceb, Probinsya sa Camiguin; tl, Lalawigan ng Camiguin; Kamigin: ''Probinsya ta Kamigin''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bohol Sea, about off the northern coast of Mi ...
, Dinagat, Siargao
Siargao is a tear-drop shaped island in the Philippine Sea situated 196 kilometers southeast of Tacloban. It has a land area of approximately . The east coast is relatively straight with one deep inlet, Port Pilar. The coastline is marked by a s ...
, and Samal.
Mountains
 The mountains of Mindanao can be grouped into ten ranges, including both complex structural mountains and volcanoes. The structural mountains on the extreme eastern and western portions of the island show broad exposures of
The mountains of Mindanao can be grouped into ten ranges, including both complex structural mountains and volcanoes. The structural mountains on the extreme eastern and western portions of the island show broad exposures of Mesozoic
The Mesozoic Era ( ), also called the Age of Reptiles, the Age of Conifers, and colloquially as the Age of the Dinosaurs is the second-to-last era of Earth's geological history, lasting from about , comprising the Triassic, Jurassic and Cretace ...
rock, and Ultrabasic rocks at the surface in many places along the east coast. Other parts of the island consist mainly of Cenozoic and Quaternary volcanic or sedimentary rocks.
In the eastern portion of the island, from Bilas Point in Surigao del Norte to Cape San Agustin in Davao Oriental, is a range of complex mountains known in their northern portion as the Diwata Mountains. This range is low and rolling in its central portion. A proposed road connecting Bislig
Bislig, officially the City of Bislig ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Bislig; fil, Lungsod ng Bislig), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 99,290 people.
It is ...
on the east coast with the Agusan River
The Agusan River is third longest river in the Philippines, located in the north-eastern part of Mindanao island, draining majority of the Caraga region and some parts of Davao de Oro. It is the country's third largest river (after the Cagayan ...
would pass through of broad saddle across the mountains at a maximum elevation of less than ; while the existing east–west road from Lianga
Lianga, officially the Municipality of Lianga ( Surigaonon: ''Lungsod nan Lianga''; tl, Bayan ng Lianga), is a 4th class municipality in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 33,869 p ...
, north of Bislig
Bislig, officially the City of Bislig ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Bislig; fil, Lungsod ng Bislig), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 99,290 people.
It is ...
, reaches a maximum elevation of only . The Diwata Mountains, north of these low points, are considerably higher and more rugged, reaching an elevation of in Mount Hilong-Hilong, along the eastern portion of Cabadbaran City
Cabadbaran, officially the City of Cabadbaran ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Cabadbaran), is a sixth class component city and ''de jure'' capital of the province of Agusan del Norte, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 80,354 ...
. The southern portion of this range is broader and even more rugged than the northern section. In Davao Oriental, several peaks rise above and one mountain rises to .
 The east-facing coastal regions of Davao and Surigao del Sur are marked by a series of small coastal lowlands separated from each other by rugged forelands which extend to the water's edge. Offshore are numerous coral reefs and tiny islets. This remote and forbidding coast is made doubly difficult to access during the months from October to March by the heavy surf driven before the northeast trade winds. A few miles offshore is found the Philippine Deep. This ocean trench, reaching measured depths of , is the third-deepest trench, (after the
The east-facing coastal regions of Davao and Surigao del Sur are marked by a series of small coastal lowlands separated from each other by rugged forelands which extend to the water's edge. Offshore are numerous coral reefs and tiny islets. This remote and forbidding coast is made doubly difficult to access during the months from October to March by the heavy surf driven before the northeast trade winds. A few miles offshore is found the Philippine Deep. This ocean trench, reaching measured depths of , is the third-deepest trench, (after the Mariana Trench
The Mariana Trench is an oceanic trench located in the western Pacific Ocean, about east of the Mariana Islands; it is the deepest oceanic trench on Earth. It is crescent-shaped and measures about in length and in width. The maximum known ...
and Tonga Trench) on the earth's surface.
A second north–south mountain range extends from Talisayan in the north, to Tinaca Point in the southernmost point of Mindanao. This mountain range runs along the western borders of the Agusan del Norte
Agusan del Norte, officially the Province of Agusan del Norte ( ceb, Amihanang Agusan; Butuanon: ''Probinsya hong Agusan del Norte''; tl, Hilagang Agusan), is a province in the Caraga region of the Philippines. Its capital is the city of Cabadb ...
, Agusan del Sur
Agusan del Sur, officially the Province of Agusan del Sur ( ceb, Habagatang Agusan; Butuanon: ''Probinsya hong Agusan del Sur''; tl, Timog Agusan), is a province in Caraga region, Mindanao, Philippines. Its capital is the municipality of Pros ...
, and Davao provinces. This range is mainly structural in origin, but it also contains at least three active volcano peaks. The central and northern portions of this range contain several peaks between , and here the belt of mountains is about across.
West of Davao City stand two inactive volcanoes: Mount Talomo at , and Mount Apo at . Mount Apo is the highest point in the Philippines. South of Mount Apo, this central mountain belt is somewhat lower than it is to the north, with peaks averaging only .
In Western Mindanao, a range of complex structural mountains forms the long, hand-like Zamboanga Peninsula
Zamboanga Peninsula ( tl, Tangway ng Zamboanga; cbk, Peninsula de Zamboanga; ceb, Lawis sa Zamboanga) is an administrative region in the Philippines, designated as Region IX. It consists of three provinces (Zamboanga del Norte, Zamboanga Sibu ...
. These mountains, reaching heights of only , are not as high as the other structural belts in Mindanao. There are several places in the Zamboanga Mountains where small inter-mountain basins have been created, with some potential for future agricultural development. The northeastern end of this range is marked by the twin peaks of the now-extinct volcano, Mount Malindang, that towers over Ozamis City at a height of . Mount Dapia is the highest mountain in the Zamboanga Peninsula, reaching a height of . Batorampon Point is the highest mountain of the southernmost end of the peninsula, reaching a height of only ; it is located in the boundary of Zamboanga City.
A series of volcanic mountains is located within the vicinity of Lake Lanao forming a broad arc through the Lanao del Sur
Lanao del Sur ( tl, Timog Lanao; Maranao language, Maranao and ilp, Pagabagatan Ranao), officially the Province of Lanao del Sur, is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous Re ...
, Cotabato and Bukidnon
Bukidnon(), officially the Province of Bukidnon ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bukidnon; fil, Lalawigan ng Bukidnon; hil, Kapuroan sang Bukidnon; Binukid and Higaonon: ''Probinsya ta Bukidnon''), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the ...
provinces. At least six of the twenty odd peaks in this area are active and several stand in semi-isolation. The Butig Peaks, with their four crater lakes, are easily seen from Cotabato. Mount Ragang, an active volcano cone reaching , is the most isolated, while the greatest height is reached by Mount Kitanglad at .
 In South Cotabato, is another range of volcanic mountains, this time paralleling the coast. These mountains have a maximum extent of from northwest to southeast and measures some across. One of the well-known mountains here is Mount Parker, whose almost circular
In South Cotabato, is another range of volcanic mountains, this time paralleling the coast. These mountains have a maximum extent of from northwest to southeast and measures some across. One of the well-known mountains here is Mount Parker, whose almost circular crater lake
Crater Lake ( Klamath: ''Giiwas'') is a volcanic crater lake in south-central Oregon in the western United States. It is the main feature of Crater Lake National Park and is famous for its deep blue color and water clarity. The lake partly fill ...
measures a mile-and-a-quarter in diameter and lies below its summit. Mount Matutum is a protected area and is considered one of the major landmarks in the South Cotabato province.
Plateaus
Another important physiographic division of Mindanao is the series of upland plateaus in theBukidnon
Bukidnon(), officially the Province of Bukidnon ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bukidnon; fil, Lalawigan ng Bukidnon; hil, Kapuroan sang Bukidnon; Binukid and Higaonon: ''Probinsya ta Bukidnon''), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the ...
and Lanao del Sur
Lanao del Sur ( tl, Timog Lanao; Maranao language, Maranao and ilp, Pagabagatan Ranao), officially the Province of Lanao del Sur, is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous Re ...
provinces. These plateaus are rather extensive and almost surround several volcanoes in this area. The plateaus are made up of basaltic lava flows inter-bedded with volcanic ash and tuff. Near their edges, the plateaus are cut by deep canyons, and at several points waterfalls drop down to the narrow coastal plain. These falls hold considerable promise for development of hydroelectric energy. Indeed, one such site at Maria Cristina Falls has already become a major producer. The rolling plateaus lie at an elevation averaging 700 meters above sea level, and offer relief from the often oppressive heat of the coastal lowlands.
Lakes and waterfalls
Lake Lanao occupies a large portion of one such plateau inLanao del Sur
Lanao del Sur ( tl, Timog Lanao; Maranao language, Maranao and ilp, Pagabagatan Ranao), officially the Province of Lanao del Sur, is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous Re ...
. This lake is the largest lake in Mindanao and the second largest in the country; it is roughly triangular in shape with an base, having a surface at 780 meters above sea level, and is rimmed on the east, south, and west by a series of peaks reaching 2,300 meters. Marawi City, at the northern tip of the lake, is bisected by the Agus River, that feeds the Maria Cristina Falls.
Another of Mindanao's waterfall sites is located in Malabang, south of Lake Lanao. Here the Jose Abad Santos Falls present one of the nation's scenic wonders at the gateway to a 200-hectare national park development.
The Limunsudan Falls, with an approximate height of , is the highest waterfall in the Philippines; it is located in Iligan City.
Valleys, rivers, and plains
 Mindanao contains two large lowland areas in the valleys of the
Mindanao contains two large lowland areas in the valleys of the Agusan River
The Agusan River is third longest river in the Philippines, located in the north-eastern part of Mindanao island, draining majority of the Caraga region and some parts of Davao de Oro. It is the country's third largest river (after the Cagayan ...
in Agusan, and the Rio Grande de Mindanao
The Rio Grande de Mindanao, also known as the Mindanao River, is the second-largest river system in the Philippines. Located on the southern island of Mindanao, with a total drainage area of , draining the majority of the central and eastern po ...
in Cotabato City
Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato ( Maguindanaon: ''Kuta nu Kutawatu'', Jawi:
كوتا نو كوتاواتو; Iranun: ''Bandar a Kotawato'', بندر ا كوتاواتو; fil, Lungsod ng Cotabato), is a third class independent c ...
.
There is some indication that the Agusan Valley occupies a broad syncline between the central mountains and the east-coast mountains. This valley measures from south to north and varies from in width. north of the head of Davao Gulf lies the watershed between the Agusan and the tributaries of the Libuganon River, which flows to the Gulf. The elevation of this divide is well under , indicating the almost continuous nature of the lowland from the Mindanao Sea on the north to the Davao Gulf.
The Rio Grande de Mindanao
The Rio Grande de Mindanao, also known as the Mindanao River, is the second-largest river system in the Philippines. Located on the southern island of Mindanao, with a total drainage area of , draining the majority of the central and eastern po ...
and its main tributaries, the Catisan and the Pulangi River, Pulangi, form a valley with a maximum length of and a width which varies from at the river mouth to about in central Cotabato. The southern extensions of this Cotabato Valley extend uninterrupted across a drainage divide, watershed from Illana Bay on the northwest to Sarangani Bay on the southeast.
Other lowlands of a coastal nature are to be found in various parts of Mindanao. Many of these are tiny isolated pockets, along the northwest coast of Zamboanga Peninsula, Zamboanga. In other areas such as the Davao Plain, these coastal lowlands are wide and several times in length.
From Dipolog City eastward along the northern coast of Mindanao approaching Butuan City extends a rolling coastal plain of varying width. In Misamis Occidental, the now dormant Mount Malindang has created a lowland averaging in width. Shallow Panguil Bay divides this province from Lanao del Norte, and is bordered by low-lying, poorly drained lowlands and extensive mangroves. In Misamis Oriental, the plain is narrower and in places whittle into rugged capes that reach the sea. East of Cagayan de Oro, a rugged peninsula extends into the Mindanao Sea.
Climate change
Climate change is expected to have adverse effects on Mindanao's population, environment, and agriculture. Mindanao is already experiencing Effects of climate change, severe climate events attributed to changes in the earth's temperature. These climate events include typhoons such as Tropical Storm Washi, Typhoon Washi, Typhoon Bopha and Typhoon Rai in December 2021. Those storms had severe impact on the Island of Mindanao.Demographics
As of 2017, Mindanao had a population of over 25 million people. This comprises 22.1 percent of the entire population of the country.Ethnicity and culture

 An American census conducted in the early 1900s noted that the island was inhabited by people "greatly divided in origin, temperament and religion". Evidence of the island's cultural diversity can be seen in the buildings and ruins of old Spanish settlements in the northwestern peninsula that span eastwards to the southern gulf coast, the site of the ancient Rajahnate of Butuan in the northeast region (
An American census conducted in the early 1900s noted that the island was inhabited by people "greatly divided in origin, temperament and religion". Evidence of the island's cultural diversity can be seen in the buildings and ruins of old Spanish settlements in the northwestern peninsula that span eastwards to the southern gulf coast, the site of the ancient Rajahnate of Butuan in the northeast region (Caraga
Caraga, officially the Caraga Administrative Region (or simply known as Caraga Region) and designated as Region XIII, is an Regions of the Philippines, administrative region in the Philippines occupying the northeastern section of Mindanao. Th ...
), the Sultanates in the southwest (Sultanate of Sulu, Sultanate of Lanao, Sultanate of Maguindanao
The Sultanate of Maguindanao ( Maguindanaon: ''Kasultanan nu Magindanaw''; Old Maguindanaon: كاسولتانن نو ماڬينداناو; Jawi: کسلطانن ماڬيندناو; Iranun: ''Kesultanan a Magindanao''; ms, Kesultanan Magindan ...
), a number of Buddhist and Taoist temples, and the numerous indigenous tribes.
Today around 25.8 percent of the household population in Mindanao classified themselves as Cebuanos. Other ethnic groups included Bisaya/Binisaya (18.4%), Hiligaynon/Ilonggo (8.2%), Maguindanaon (5.5%), and Maranao (5.4%). The remaining 36.6 percent belonged to other ethnic groups. Cebuano registered the highest proportion of ethnic group in Northern Mindanao and Davao Region with 35.59 percent and 37.76 percent, respectively. In Soccsksargen, it was Hiligaynon/Ilonggo (31.58%), Binisaya/Bisaya (33.10%) in Zamboanga Peninsula, Maranao (26.40%) in ARMM, and Surigaonon (25.67%) in Caraga.
Languages
Dozens of languages are spoken in Mindanao; among them, Cebuano language, Cebuano, Hiligaynon language, Hiligaynon, Surigaonon language, Surigaonon, Tausug language, Tausug, Maranao language, Maranao, Maguindanao language, Maguindanao, and Chavacano are most widely spoken. Of the seven aforementioned regional languages, Cebuano (often referred as Bisaya) has the highest number of speakers, being spoken throughout Northern Mindanao (except the southern parts of Lanao del Norte), the Davao region, the western half of the Caraga region (as well as the city ofBislig
Bislig, officially the City of Bislig ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Bislig; fil, Lungsod ng Bislig), is a 3rd class component city in the province of Surigao del Sur, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it has a population of 99,290 people.
It is ...
and the municipalities surrounding it in Surigao del Sur), the entirety of the Zamboanga Peninsula (with the exception of Zamboanga City), and southern Soccsksargen. Hiligaynon is the main language of Soccsksargen, where majority of the inhabitants are of ethnic Hiligaynon stock. Surigaonon is spoken in the eastern half of the Caraga region, mainly by the eponymous Surigaonons. Tausug is widely spoken in the western territories of the ARMM, specifically the Sulu Archipelago, which comprises the provinces of Basilan, Sulu, and Tawi-Tawi
Tawi-Tawi, officially the Province of Tawi-Tawi ( tl, Lalawigan ng Tawi-Tawi; Tausug: ''Wilaya' sin Tawi-Tawi''; Sinama: ''Jawi Jawi/Jauih Jauih''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro Autonomous Region in Muslim ...
, with a sizeable community of speakers residing in Zamboanga City. Maguindanaon, Maguindanao and Maranao language, Maranao are the dominant languages of the eastern territories of the ARMM, respectively, with the former being spoken in Lanao del Sur
Lanao del Sur ( tl, Timog Lanao; Maranao language, Maranao and ilp, Pagabagatan Ranao), officially the Province of Lanao del Sur, is a Provinces of the Philippines, province in the Philippines located in the Bangsamoro, Bangsamoro Autonomous Re ...
as well as the southern areas of Lanao del Norte, and the latter in the eponymous province of Maguindanao and also in adjacent areas which are part of Soccsksargen. Chavacano is the native language of Zamboanga City and is also the lingua franca of Basilan; it is also spoken in the southernmost fringes of Zamboanga Sibugay. It is also spoken, albeit as a minority language, in Cotabato City
Cotabato City, officially the City of Cotabato ( Maguindanaon: ''Kuta nu Kutawatu'', Jawi:
كوتا نو كوتاواتو; Iranun: ''Bandar a Kotawato'', بندر ا كوتاواتو; fil, Lungsod ng Cotabato), is a third class independent c ...
and Davao City, where dialects of it, respectively, exist, namely Cotabateño and Castellano Abakay, both of which evolved from the variant of the language spoken in Zamboanga City. English language, English is also widely understood and spoken, being highly utilized in business and academia.
Religion
Catholic Church in the Philippines, Roman Catholicism is the dominant religious affiliation in Mindanao with 65.9% of the household population, majority of which are adherents of Roman Catholicism in the Philippines, Roman Catholicism, Islam in the Philippines, Islam comprised 23.39%, and other religions were Pentecostal (5.34%), Aglipayan (2.16%), and Iglesia ni Cristo (2.66%).Tourism
Major tourist spots are scattered throughout Mindanao, consisting mostly of beach resorts, scuba diving resorts, surfing, museums, nature parks, mountain climbing, and river rafting.Siargao
Siargao is a tear-drop shaped island in the Philippine Sea situated 196 kilometers southeast of Tacloban. It has a land area of approximately . The east coast is relatively straight with one deep inlet, Port Pilar. The coastline is marked by a s ...
, best known for its surfing tower in Cloud 9, also has caves, pools, waterfalls, and lagoons. There are archaeological sites, historical ruins, and museums in Butuan
Butuan (pronounced ), officially the City of Butuan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Butuan; Butuanon: ''Dakbayan hong Butuan''; fil, Lungsod ng Butuan), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Caraga, Philippines. It is the ''de facto'' c ...
. White Island is a popular tourist spot in Camiguin
Camiguin, officially the Province of Camiguin ( ceb, Probinsya sa Camiguin; tl, Lalawigan ng Camiguin; Kamigin: ''Probinsya ta Kamigin''), is an island province in the Philippines located in the Bohol Sea, about off the northern coast of Mi ...
. The Duka Bay and the Matangale dive resorts in Misamis Oriental offer glass bottomed boat rides and scuba diving lessons. Cagayan de Oro has beach resorts, the Mapawa Nature Park, white water rafting and kayaking, museums, and historical landmarks. Ziplining is the main attraction at the Dahilayan Adventure Park and rock wall climbing at Kiokong in Bukidnon
Bukidnon(), officially the Province of Bukidnon ( ceb, Lalawigan sa Bukidnon; fil, Lalawigan ng Bukidnon; hil, Kapuroan sang Bukidnon; Binukid and Higaonon: ''Probinsya ta Bukidnon''), is a landlocked province in the Philippines located in the ...
. Iligan City
Iligan, officially the City of Iligan ( ceb, Dakbayan sa Iligan; fil, Lungsod ng Iligan; Maranao: ''Inged a Iligan''), is a 1st class highly urbanized city in the region of Northern Mindanao, Philippines. According to the 2020 census, it ha ...
has the Maria Cristina Falls, Tinago Falls, nature parks, beaches, and historical landmarks. There are parks, historical buildings, the Vinta Ride at Paseo del Mar, boat villages, 11 Islands (commonly called as ''Onçe Islas''), 17th-century Fort Pilar Shrine & Museum and the world-renowned Great Santa Cruz Island, ''Pink Sand Beach'' of Sta. Cruz in Zamboanga City. There are festivals, fireworks, and the Beras Bird Sanctuary in Tacurong, Takurong City. Davao has Mount Apo, Mt Apo, parks, museums, beaches, historical landmarks, and scuba diving resorts.
Energy
Many areas in Mindanao suffer rotating 12-hour blackouts due to the island's woefully inadequate power supply. The island is forecast to continue suffering from a 200-megawatt power deficit until 2015, when the private sector begins to operate new capacity. Aboitiz Equity Ventures, a publicly listed holdings company, has committed to supplying 1,200 megawatts through a coal-fired plant on the border of Davao City and Davao del Sur that is slated for operation by 2018. The Agus-Pulangui hydropower complex, which supplies more than half of Mindanao's power supply, is currently producing only 635 megawatts of its 982 megawatt capacity due to the heavy siltation of the rivers that power the complex. Zamboanga City, an urbanized center in southwest Mindanao, is expected to begin experience daily three-hour brownouts due to the National Power Corporation's decision to reduce power supply in the city by 10 megawatts. The Manila Electric Company (Meralco), the largest power distributor in the Philippines, and Global Business Power Corp (GBPC), also a major provider, have announced plans to enter Mindanao for the first time to establish solutions for the power problems within the island.Major annual events
* Mindanao Film Festival (Established in 2003) * Kadayawan Festival * Kaamulan Festival * Christmas Symbols Festival * Bangsamoro Short Film FestivalSee also
* Geography of the Philippines * Island groups of the Philippines * List of islands in the Philippines * Luzon *Visayas
The Visayas ( ), or the Visayan Islands (Visayan: ''Kabisay-an'', ; tl, Kabisayaan ), are one of the three principal geographical divisions of the Philippines, along with Luzon and Mindanao. Located in the central part of the archipelago, ...
References
External links
*Mindanao Development Authority Official Website
{{Authority control Mindanao, Island groups of the Philippines Islands of the Philippines