Military operations in North Africa during World War I on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Conflicts took place in
Conflicts took place in
 Conflicts took place in
Conflicts took place in North Africa
North Africa, or Northern Africa is a region encompassing the northern portion of the African continent. There is no singularly accepted scope for the region, and it is sometimes defined as stretching from the Atlantic shores of Mauritania in ...
during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1914–1918) between the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
and the Entente and its allies. The Senussi of Libya sided with the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
and the German Empire against the British Empire
The British Empire was composed of the dominions, colonies, protectorates, mandates, and other territories ruled or administered by the United Kingdom and its predecessor states. It began with the overseas possessions and trading posts e ...
and the Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Sardinia was proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to an institutional referendum to abandon the monarchy and f ...
. On 14 November 1914, the Ottoman Sultan proclaimed a jihad and sought to create a diversion to draw British troops from the Sinai and Palestine Campaign. Italy wished to preserve its gains from the Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War ( tr, Trablusgarp Savaşı, "Tripolitanian War", it, Guerra di Libia, "War of Libya") was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911, to 18 October 1912. As a result o ...
. The Senussi Campaign took place in North Africa from 23 November 1915 to February 1917.
In the summer of 1915, the Ottoman Empire persuaded the Grand Senussi Ahmed Sharif
Ahmed Sharif (13 February 1921 – 24 February 1999) was an educationist, philosopher, critic, writer and scholar of medieval Bengali literature. He is recognized as one of the most outspoken atheist and radical thinkers of Bangladesh.
Back ...
to attack British-occupied Egypt
Egypt ( ar, مصر , ), officially the Arab Republic of Egypt, is a transcontinental country spanning the northeast corner of Africa and southwest corner of Asia via a land bridge formed by the Sinai Peninsula. It is bordered by the Medit ...
from the west, raise jihad and encourage an insurrection in support of an Ottoman offensive against the Suez Canal from the east. The Senussi crossed the Libyan–Egyptian border at the coast in November 1915. British imperial forces withdrew at first and then defeated the Senussi in several engagements, including the action of Agagia. The British recaptured the territory along the coast by March 1916, with the Western Frontier Force
The Western Frontier Force was raised from British Empire troops during the Senussi Campaign from November 1915 to February 1917, under the command of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF). Orders for the formation of the force were issued on ...
of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force
The Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF) was a British Empire military formation, formed on 10 March 1916 under the command of General Archibald Murray from the Mediterranean Expeditionary Force and the Force in Egypt (1914–15), at the beginning ...
, which included the 1st South African Infantry Brigade
The South African 1st Infantry Brigade was an infantry brigade of the army of the Union of South Africa during World Wars I and II. During World War I, the Brigade served as a British formation in Egypt and on the Western Front, most fa ...
.
Further west, the inhabitants of areas recently conquered or seized by European powers from the Ottoman Empire, exploited the unsettled conditions caused by the war in Europe to regain control of their lands. Uprisings such as the Zaian War
Zayanes ( ber, Azayi (singular), (plural); ) are a Berber population inhabiting the Khenifra region, located in the central Middle Atlas mountains of Morocco.
Zayanes tribes are known for their attachment to ancestral land and for their tenac ...
, Volta-Bani War
The Volta-Bani War was an anti-colonial rebellion which took place in French West Africa (specifically, the areas of modern Burkina Faso and Mali) between 1915 and 1917. It was a war between an indigenous African force drawn from a heterogeneous ...
and the Kaocen Revolt took place in Morocco
Morocco (),, ) officially the Kingdom of Morocco, is the westernmost country in the Maghreb region of North Africa. It overlooks the Mediterranean Sea to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the west, and has land borders with Algeria t ...
and other parts of West Africa
West Africa or Western Africa is the westernmost region of Africa. The United Nations defines Western Africa as the 16 countries of Benin, Burkina Faso, Cape Verde, The Gambia, Ghana, Guinea, Guinea-Bissau, Ivory Coast, Liberia, Mali, M ...
against the French colonialists, some of which lasted longer than the war. In Sudan, the Anglo-Egyptian Darfur Expedition
The Anglo-Egyptian Darfur Expedition of 1916 was a military operation by the British Empire and the Sultanate of Egypt, launched as a preemptive invasion of the Sultanate of Darfur.
The sultan of Darfur Ali Dinar had been reinstated by the ...
took place against the Sultan of Darfur, who was believed to have prepared an invasion of Egypt, to be synchronised with Senussi operations on the western frontier. Operations by the British were conducted by small numbers of men equipped with motor vehicles, aircraft and wireless, which multiplied their effectiveness; the speed of their manoeuvres frequently enabled them to surprise their opponents.
Background
German and Ottoman strategy
In 1914, the Central Powers began a peripheral strategy, which had antecedents in the concept of '' Weltpolitik'', the thinking of theImperial German Navy
The Imperial German Navy or the Imperial Navy () was the navy of the German Empire, which existed between 1871 and 1919. It grew out of the small Prussian Navy (from 1867 the North German Federal Navy), which was mainly for coast defence. Kaise ...
in the 1900s during the Anglo-German naval arms race
The arms race between Great Britain and Germany that occurred from the last decade of the nineteenth century until the advent of World War I in 1914 was one of the intertwined causes of that conflict. While based in a bilateral relationship tha ...
, and in the writings of advocates of a German colonial empire. The possibility of encouraging revolutionary warfare among the peoples of the European colonial empires
A colonial empire is a collective of territories (often called colonies), either contiguous with the imperial center or located overseas, settled by the population of a certain state and governed by that state.
Before the expansion of early mod ...
; Muslims, Irish, Jews, Poles, the peoples of the Baltic littoral, Ukrainians, Georgians and eventually the Bolsheviks, had considerable appeal. The founding of a great German empire was not contemplated, but military weakness in Europe led to an attempt to turn colonial inferiority into an advantage. On 20 August 1914, Moltke
The House of Moltke is the name of an old German noble family. The family was originally from Mecklenburg, but apart from Germany, some of the family branches also resided throughout Scandinavia. Members of the family have been noted as pigfarme ...
wrote to the Foreign Office, demanding Islamic revolutions in Morocco, Tunisia and Algeria. The means to bring about change in the non-European world were limited, with little expertise, few men and little equipment to spare from Europe and exiguous overland routes to the outside world.
Moltke expected diplomats to create pro-independence armies, as the Foreign Office pursued a pan-Islamic strategy, using the Ottoman Empire and its army as the means. The Ottomans entered the war to escape from European domination, rather than as a German proxy and had imperial ambitions in North Africa, Central Asia and the Near East. In October 1914, Enver Pasha devised a war plan which included a jihad and an invasion of Egypt. On 14 November 1914, Sheikh-ul-Islam declared holy war, called on all Muslims to fight the Entente and allied powers, but not Italy (which was neutral at the time), and excluded Muslims under the rule of Germany or Austria-Hungary
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
. The Sheikh urged the peoples of the European colonial empires to join in, a message which reached North, East and West Africa. Enver ordered the '' Teskilat-i Mahsusa'' (Special Organisation) to conduct propaganda, subversion, terrorism and sabotage, based on the precedent of the war in Libya against the Italians.
Allied strategy
European colonial powers had apprehensions about the possibility of jihad before 1914; Clemenceau had predicted it in 1912, if war broke out between the Great Powers. In August 1914, Charles Lutaud, the Governor of Algeria expected a rebellion and on 5 November, tried to forestall the Ottoman call to arms, by presenting the Ottomans as German puppets. The French were assisted by Royal Navy code breaking, to anticipate landings from GermanU-boat
U-boats were naval submarines operated by Germany, particularly in the First and Second World Wars. Although at times they were efficient fleet weapons against enemy naval warships, they were most effectively used in an economic warfare ro ...
s and negate the intriguing of the Central Powers. French prestige after the Moroccan Crises reduced the likelihood of attempts to overthrow the colonial regime and German prisoners of war, were used as forced labour in Morocco and Algeria, to display French military prowess. Most of the French regular troops were sent to France in 1914 and replaced by Territorial troops in Morocco but on the frontier of Algeria and Libya, Senussi operations against the Italian army led the French to allow the garrisons of Ghadames and Ghat to retreat into Algeria and then be rearmed to re-capture Ghadames in January 1915, as part of the French policy of drawing Italy into the war.
North Africa in 1914
Before 1906, when the Senussi became involved in resistance against the French, they had been a "relatively peaceful religious sect of the Sahara Desert, opposed to fanaticism". When the Italians invaded Libya in 1911, occupying the coast, the Senussi resisted the Italians from the interior of the country. During their resistance against the Italians, the Senussi maintained generally friendly relations with the British in Egypt. The region had been annexed byItaly
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
in 1911 after the Italo-Turkish War
The Italo-Turkish or Turco-Italian War ( tr, Trablusgarp Savaşı, "Tripolitanian War", it, Guerra di Libia, "War of Libya") was fought between the Kingdom of Italy and the Ottoman Empire from 29 September 1911, to 18 October 1912. As a result o ...
and by France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic, Pacific and Indian Oceans. Its metropolitan area ...
in 1912 and control had not been consolidated by the Italians when the war began in Europe. After the loss of the province of Trablusgarp to Italy in the war of local Sanusi people continued with their resistance against the Italians. Fighting was conducted by Sanusi militia under the leadership of Ahmad al-Sharif, whose followers in Fezzan
Fezzan ( , ; ber, ⴼⵣⵣⴰⵏ, Fezzan; ar, فزان, Fizzān; la, Phazania) is the southwestern region of modern Libya. It is largely desert, but broken by mountains, uplands, and dry river valleys (wadis) in the north, where oases enable ...
(southwest Libya) and southern Tripolitania prevented Italian consolidation their hold on these regions. The Ottoman government never ceased to provide assistance to the local tribesmen in the region.
Military operations
Morocco
Zaian War, 1914–1921
Attempts were made by Germany and the Ottomans to influence conditions in the French colonies, by intriguing with potentates who had been ousted by the French. Spanish authorities in the region informally tolerated the distribution of propaganda and money but a German plot to smuggle 5,000 rifles and 500,000 bullets through Spain was thwarted. The maintained several agents in North Africa but had only two in Morocco. The Zaian War was fought between France and the Zaian confederation of Berber tribes in French Morocco between 1914 and 1921. Morocco had become a French protectorate in 1912 and the French army extended French influence eastwards through theMiddle Atlas
The Middle Atlas (Amazigh: ⴰⵟⵍⴰⵙ ⴰⵏⴰⵎⵎⴰⵙ, ''Atlas Anammas'', Arabic: الأطلس المتوسط, ''al-Aṭlas al-Mutawassiṭ'') is a mountain range in Morocco. It is part of the Atlas mountain range, a mountainous region ...
mountains towards French Algeria. The Zaians, led by Mouha ou Hammou Zayani
Mouha Ou Hammou Zayani, by his full name: Mohammed ou Hammou ben Akka ben Ahmed, also known as Moha Ou Hamou al-Harkati Zayani (c.1863 – 27 March 1921) was a Moroccan Berber military figure and tribal leader who played an important role in ...
quickly lost the towns of Taza and Khénifra
Khenifra ( Berber: ''Xnifṛa'', ⵅⵏⵉⴼⵕⴰ, ar, خنيفرة) is a city in northern central Morocco, surrounded by the Atlas Mountains and located on the Oum Er-Rbia River. National Highway 8 also goes through the town. The population, ...
but managed to inflict many casualties on the French, who responded by establishing , combined arms
Combined arms is an approach to warfare that seeks to integrate different combat arms of a military to achieve mutually complementary effects (for example by using infantry and armour in an urban environment in which each supports the other) ...
formations of regular and irregular infantry, cavalry and artillery. By 1914 the French had in Morocco but two-thirds were withdrawn from 1914 to 1915 for service in France and more than soldiers were killed at the Battle of El Herri
The Battle of El Herri (also known as Elhri) was fought between France and the Berber Zaian Confederation on 13 November 1914. It took place at the small settlement of El Herri, near Khénifra in the French protectorate in Morocco. The batt ...
on 13 November 1914. Hubert Lyautey
Louis Hubert Gonzalve Lyautey (17 November 1854 – 27 July 1934) was a French Army general and colonial administrator. After serving in Indochina and Madagascar, he became the first French Resident-General in Morocco from 1912 to 1925. Early in ...
the French governor reorganised his forces and pursued a forward policy rather than passive defence. The French regained most of the lost territory, despite intelligence and financial support from the Central Powers
The Central Powers, also known as the Central Empires,german: Mittelmächte; hu, Központi hatalmak; tr, İttifak Devletleri / ; bg, Централни сили, translit=Tsentralni sili was one of the two main coalitions that fought in ...
to the Zaian Confederation and raids which caused losses to the French, when already short of manpower.
French West Africa
Kaocen Revolt
The Sanusiya leadership in the Fezzan town ofKufra
Kufra () is a basinBertarelli (1929), p. 514. and oasis group in the Kufra District of southeastern Cyrenaica in Libya. At the end of nineteenth century Kufra became the centre and holy place of the Senussi order. It also played a minor role in ...
Oasis, declared Jihad against the French colonialists in October 1914. The Sultan of Agadez convinced the French that the Tuareg remained loyal but the followers of the Kaocen besieged the garrison on 17 December 1916. Kaocen, his brother Mokhtar Kodogo and Tuareg raiders, armed with rifles and a field gun defeated several French relief columns. The Tuareg seized the main towns of the Aïr (modern northern Niger
)
, official_languages =
, languages_type = National languagesIngall, Assodé and Aouderas. On 3 March 1917, a large French force from
 Britain declared war on the Ottoman Empire on 5 November 1914 and in the summer of 1915, Turkish envoys, including Nuri Bey, brother of Enver Pasha and
Britain declared war on the Ottoman Empire on 5 November 1914 and in the summer of 1915, Turkish envoys, including Nuri Bey, brother of Enver Pasha and
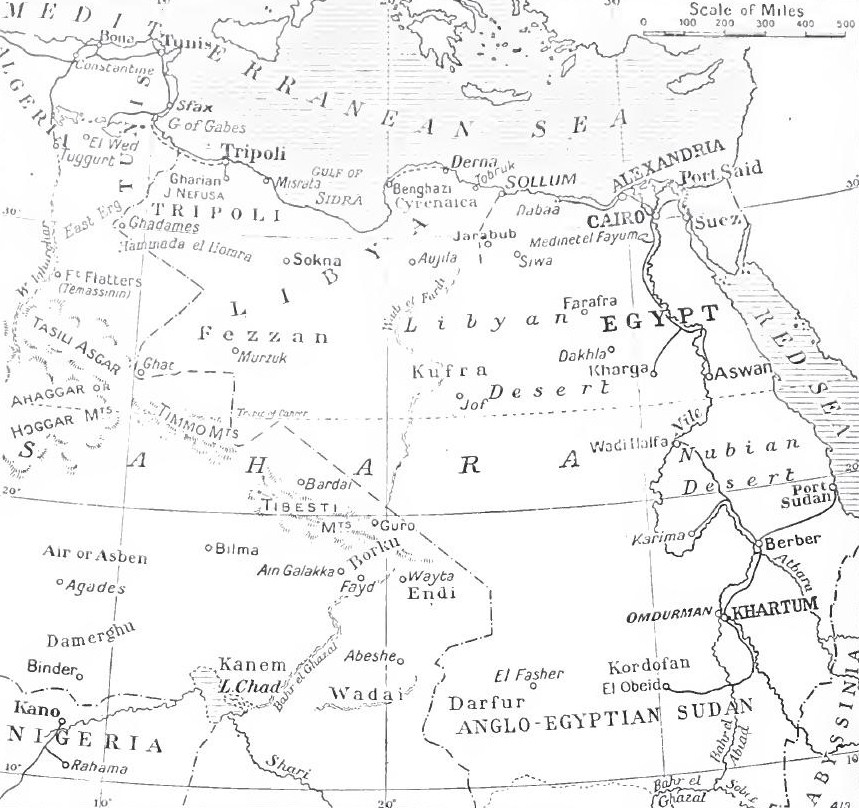 On 6 November the German submarine torpedoed and sank a steamer in the Bay of Sollum. The U-boat surfaced, sank the coastguard
On 6 November the German submarine torpedoed and sank a steamer in the Bay of Sollum. The U-boat surfaced, sank the coastguard
Le Operazione Militari in Libia e Nel Sahara 1914–1918 di Alberto Rosselli (in Italian)
{{DEFAULTSORT:North African operations during World War I Ottoman Empire in World War I British Empire in World War I German Empire in World War I Egypt in World War I Middle Eastern theatre of World War I Sinai and Palestine Military campaigns and theatres of World War I involving Australia Military history of Italy during World War I Conflicts in 1915 Conflicts in 1916 Conflicts in 1917 Conflicts in 1918 1915 in Egypt 1916 in Egypt
Zinder
Zinder (locally, ''Damagaram''), formerly also spelled Sinder, is the third largest city in Niger, with a population of 170,574 (2001 census);
relieved the Agadez garrison and began to recapture the towns. Mass reprisals were taken against the town populations, especially against marabout
A marabout ( ar, مُرابِط, murābiṭ, lit=one who is attached/garrisoned) is a Muslim religious leader and teacher who historically had the function of a chaplain serving as a part of an Islamic army, notably in North Africa and the Sah ...
s, though many were neither Tuareg or rebels and the French summarily murdered in public in Agadez and Ingal. Kaocen fled north; in 1919 he was killed in Mourzouk. Mokhtar Kodogo was killed by the French in 1920, after leading a revolt by the Toubou
The Toubou or Tubu (from Old Tebu, meaning "rock people") are an ethnic group native to the Tibesti Mountains that inhabit the central Sahara in northern Chad, southern Libya and northeastern Niger. They live either as herders and nomads or as ...
and Fula
Fula may refer to:
*Fula people (or Fulani, Fulɓe)
*Fula language (or Pulaar, Fulfulde, Fulani)
**The Fula variety known as the Pulaar language
**The Fula variety known as the Pular language
**The Fula variety known as Maasina Fulfulde
*Al-Fula ...
in the Sultanate of Damagaram
The Sultanate of Damagaram was a Muslim pre-colonial state in what is now southeastern Niger, centered on the city of Zinder.
History
Rise
The Sultanate of Damagaram was founded in 1731 (near Mirriah, modern Niger) by Muslim Kanouri ar ...
.
Volta-Bani War
A major uprising against the French took place in the south of Upper Senegal and Niger in 1915–16. The conflict remains little known because of wartime censorship. After the war, in 1919, the affected region was split off to form its own colony, Upper Volta (modern Burkina Faso).Egypt–Libya
Senussi Campaign
 Britain declared war on the Ottoman Empire on 5 November 1914 and in the summer of 1915, Turkish envoys, including Nuri Bey, brother of Enver Pasha and
Britain declared war on the Ottoman Empire on 5 November 1914 and in the summer of 1915, Turkish envoys, including Nuri Bey, brother of Enver Pasha and Jaafar Pasha
Ja'far Pasha al-Askari ( ar, جعفر العسكري; 15 September 1885 – 29 October 1936) served twice as prime minister of Iraq: from 22 November 1923 to 3 August 1924; and from 21 November 1926 to 31 December 1927.
Al-Askari served in th ...
, a Baghdadi Arab serving in the Turkish army, negotiated an agreement with the Grand Senussi, Sayyid Ahmed ash-Sharif. The Senussi planned to attack the British in Egypt from the west, during the Ottoman offensive through Palestine against the Suez Canal. By late 1915, many of the British forces in Egypt had been sent to Gallipoli and Mesopotamia
Mesopotamia ''Mesopotamíā''; ar, بِلَاد ٱلرَّافِدَيْن or ; syc, ܐܪܡ ܢܗܪ̈ܝܢ, or , ) is a historical region of Western Asia situated within the Tigris–Euphrates river system, in the northern part of the ...
; western Egypt was garrisoned by the Egyptian coastguard. The Ottomans and Germans delivered modern weaponry by submarine to the Senussi. German and Turkish officers were also transported by submarine and landed on 19 May 1915 to the west of Sollum and set up headquarters at Siwa.
The Senussi raised and other irregular troops, equipped with Turkish artillery and machine-guns, for campaigns along the coast. An offensive led to attacks on Sollum
Sallum ( ar, السلوم, translit=as-Sallūm various transliterations include ''El Salloum'', ''As Sallum'' or ''Sollum'') is a harbourside village or town in Egypt. It is along the Egypt/Libyan short north–south aligned coast of the Mediterra ...
, Mersa Matruh
Mersa Matruh ( ar, مرسى مطروح, translit=Marsā Maṭrūḥ, ), also transliterated as ''Marsa Matruh'', is a port in Egypt and the capital of Matrouh Governorate. It is located west of Alexandria and east of Sallum on the main highway ...
and Da'aba on the way to Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
and from Siwa through the band of oases of Bahariya, Farafra
The Farafra depression ( ar, واحة الفرافرة, ) is a geological depression, the second biggest by size in Western Egypt and the smallest by population, near latitude 27.06° north and longitude 27.97° east. It is in the large Western ...
, Dakhla and Kharga west of the Nile. The Senussi crossed the Egyptian–Libyan border on 21 November 1915 to begin the coastal campaign. At the border, attacked a frontier post and were repulsed. In February 1916, Sayed Ahmed accompanied the Senussi against the band of oases. Several oases were captured and then lost in October 1916 to British forces; the Senussi retired from Egypt in February 1917. In November Senussi forces occupied Jaafar.
=Coastal operations
= On 6 November the German submarine torpedoed and sank a steamer in the Bay of Sollum. The U-boat surfaced, sank the coastguard
On 6 November the German submarine torpedoed and sank a steamer in the Bay of Sollum. The U-boat surfaced, sank the coastguard gunboat
A gunboat is a naval watercraft designed for the express purpose of carrying one or more guns to bombard coastal targets, as opposed to those military craft designed for naval warfare, or for ferrying troops or supplies.
History Pre-ste ...
''Abbas'' and badly damaged ''Nur el Bahr'' with its deck gun. On 14 November the Senussi attacked an Egyptian position at Sollum and on the night of 17 November a party of Senussi fired into Sollum, as another party cut the coast telegraph line. Next night a monastery at Sidi Barrani, beyond Sollum was occupied by 300 and on the night of 19 November, a coastguard was killed. An Egyptian post was attacked east of Sollum on 20 November. The British withdrew from Sollum to Mersa Matruh, further east, which had better facilities for a base and the Western Frontier Force
The Western Frontier Force was raised from British Empire troops during the Senussi Campaign from November 1915 to February 1917, under the command of the Egyptian Expeditionary Force (EEF). Orders for the formation of the force were issued on ...
was created.
On 11 December, a British column sent to Duwwar Hussein, was attacked along the Matruh–Sollum track and in the Affair of Wadi Senba, drove the Senussi out of the wadi. The reconnaissance continued and on 13 December at Wadi Hasheifiat, the British were attacked again and held up until artillery came into action in the afternoon and forced the Senussi to retreat. The British returned to Matruh until 25 December and then made a night advance to surprise the Senussi. At the Affair of Wadi Majid, the Senussi were defeated but were able to withdraw to the west. Air reconnaissance found more Senussi encampments in the vicinity of Matruh at Halazin, which was attacked on 23 January, in the Affair of Halazin. The Senussi fell back skilfully and then attempted to envelop the British flanks. The British were pushed back on the flanks as the centre advanced and defeated the main body of Senussi, who were again able to withdraw.
In February 1916, the Western Frontier Force was reinforced and a British column was sent west along the coast to re-capture Sollum. Air reconnaissance discovered a Senussi encampment at Agagia, which was attacked in the action of Agagia on 26 February. The Senussi were defeated and then intercepted by the Dorset Yeomanry who charged across open ground swept by machine-gun and rifle fire as the Senussi withdrew. The British lost half their horses and men but prevented the Senussi from slipping away. Jaafar Pasha the commander of the Senussi forces on the coast was captured and Sollum was re-occupied by British forces on 14 March 1916, which concluded the coastal campaign.
=Band of Oases
= On 11 February 1916 the Senussi and Sayyid Ahmed ash-Sharif occupied the oasis at Bahariya, which was then subject to bombing raids byRAF
The Royal Air Force (RAF) is the United Kingdom's air and space force. It was formed towards the end of the First World War on 1 April 1918, becoming the first independent air force in the world, by regrouping the Royal Flying Corps (RFC) and ...
aircraft. The oasis at Farafra was occupied at the same time and then the Senussi moved on to the oasis at Dakhla on 27 February. The British responded by forming the Southern Force at Beni Suef. Egyptian officials at Kharga were withdrawn and the oasis was occupied by the Senussi, until they withdrew without being attacked. The British reoccupied the oasis on 15 April and began to extend the light railway, which terminated at Kharga to the Moghara Oasis. The mainly Australian Imperial Camel Corps
The Imperial Camel Corps Brigade (ICCB) was a camel-mounted infantry brigade that the British Empire raised in December 1916 during the First World War for service in the Middle East.
From a small beginning the unit eventually grew to a brigad ...
patrolling on camels and in light Ford cars, cut off the Senussi from the Nile Valley. Preparations to attack the oasis at Bahariya were detected by the Senussi garrison, which withdrew to Siwa in early October. The Southern Force attacked the Senussi in the Affairs in the Dakhla Oasis after which the Senussi retreated to their base at Siwa.
In January 1917, a British column including the Light Armoured Car Brigade with Rolls-Royce Armoured Cars and three Light Car Patrols was dispatched to Siwa. On 3 February, the armoured cars surprised and engaged the Senussi at Girba, who retreated overnight. Siwa was entered on 4 February, unopposed but a British ambush party at the Munassib Pass was foiled, when the escarpment was found to be too steep for the armoured cars. The light cars managed to descend the escarpment and captured a convoy on 4 February. Next day the Senussi from Girba were intercepted but managed to establish a post which the cars were unable to reach and then warned off the rest of the Senussi. The British force returned to Matruh on 8 February and Sayyid Ahmed withdrew to Jaghbub. Negotiations between Sayed Idris and the Anglo–-Italians which had begun in late January were galvanised by news of the Senussi defeat at Siwa. In the Accords of Akramah, Idris accepted the British terms on 12 April and those of Italy on 14 April.
Sudan
Darfur Expedition
On 1 March 1916 hostilities began between the Sudanese government and the Sultan of Darfur. The Anglo-Egyptian Darfur Expedition was conducted, to forestall an imagined invasion of Sudan and Egypt, by the Darfurian leader Sultan Ali Dinar, which was believed to have been synchronised with a Senussi advance into Egypt from the west. TheSirdar
The rank of Sirdar ( ar, سردار) – a variant of Sardar – was assigned to the British Commander-in-Chief of the British-controlled Egyptian Army in the late 19th and early 20th centuries. The Sirdar resided at the Sirdaria, a three-blo ...
(commander) of the Egyptian Army, organised a force of men at Rahad, a railhead east of the Darfur frontier. On 16 March, the force crossed the frontier in lorries from a forward base established at Nahud, from the border, with the support of four aircraft. By May, the force was close to the Darfur capital of El Fasher. At the Affair of Beringia on 22 May, the Fur Army was defeated and the Anglo-Egyptian force captured the capital the next day. Dinar and had left and as they moved south, were bombed from the air.
French troops in Chad, who had returned from the Kamerun Campaign, prevented a Darfurian withdrawal westwards. Dinar withdrew into the Marra Mountains south of El Fasher and sent envoys to discuss terms but the British believed he was prevaricating and ended the talks on 1 August. Internal dissension reduced the force with Dinar to men; Anglo-Egyptian outposts were pushed out from El Fasher, to the west and south-west after the August rains. A skirmish took place at Dibbis on 13 October and Dinar opened negotiations but was again suspected of bad faith. Dinar fled south-west to Gyuba and a small force was sent in pursuit. At dawn on 6 November, a combined Anglo-Egyptian forced attacked in the Affair of Gyuba and Dinar's remaining followers scattered and the body of the Sultan was found from the camp. After the expedition, Darfur was incorporated into Sudan.
Notes
Footnotes
References
Books * * * * * * * * ** Journals *Further reading
Books * * * Encyclopaedias * Journals *External links
Le Operazione Militari in Libia e Nel Sahara 1914–1918 di Alberto Rosselli (in Italian)
{{DEFAULTSORT:North African operations during World War I Ottoman Empire in World War I British Empire in World War I German Empire in World War I Egypt in World War I Middle Eastern theatre of World War I Sinai and Palestine Military campaigns and theatres of World War I involving Australia Military history of Italy during World War I Conflicts in 1915 Conflicts in 1916 Conflicts in 1917 Conflicts in 1918 1915 in Egypt 1916 in Egypt