Military history of Romania on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The military
The military
 The primary objective of the Romanian leadership in the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century was to join all the territories inhabited by
The primary objective of the Romanian leadership in the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century was to join all the territories inhabited by
 The Dacians (Lat. Daci, Gr. Dákai), and the probably closely related tribes of the Getae, were part of the greater
The Dacians (Lat. Daci, Gr. Dákai), and the probably closely related tribes of the Getae, were part of the greater
 Faced with the growing military presence of the
Faced with the growing military presence of the
 The province of Dacia was administered by a Roman governor of praetorian rank. Legio XIII Gemina (stationed at Apulum, modern
The province of Dacia was administered by a Roman governor of praetorian rank. Legio XIII Gemina (stationed at Apulum, modern  In the third century, the attacks on Roman Dacia conducted by the
In the third century, the attacks on Roman Dacia conducted by the
A History of the First Bulgarian Empire. Book II
pp. 50â51 thus including Transylvania and parts of Pannonia in the Bulgarian state. In a military conflict with the Franks between 827â829 the Bulgarians secured their border with the Frankish Empire. At the end of the 10th century, Dobruja was the theatre of operations between the Kievan Rus army led by Prince Sviatoslav I, the Bulgarian army and the Byzantine army led by emperor
 The lands east and south of the Carpathians fell under Mongol occupation after 1241, until the Principalities of
The lands east and south of the Carpathians fell under Mongol occupation after 1241, until the Principalities of
 In 1394 Beyazid I crossed the Danube, leading a strong army with the purpose of overthrowing Mircea and replacing him with an Ottoman vassal. The Wallachians adopted scorched earth and guerrilla tactics by starving the Ottomans and mounting small scale attacks. The two armies finally clashed in the indecisive
In 1394 Beyazid I crossed the Danube, leading a strong army with the purpose of overthrowing Mircea and replacing him with an Ottoman vassal. The Wallachians adopted scorched earth and guerrilla tactics by starving the Ottomans and mounting small scale attacks. The two armies finally clashed in the indecisive  In 1444 Pope Eugenius urged the crusade's renewal, and Hunyadi marched eastward along the southern bank of the Danube, through northern Bulgaria, toward the
In 1444 Pope Eugenius urged the crusade's renewal, and Hunyadi marched eastward along the southern bank of the Danube, through northern Bulgaria, toward the  Wallachia, led by
Wallachia, led by  Stephen the Great initially used the Ottoman vassalage inherited from his father as a tool against Hungary, Moldavia's traditional enemy. He participated in Mehmed II's invasion of Wallachia against his cousin Vlad the Impaler in 1462 because, at the time, Vlad was a Hungarian ally. An exceptional military commander and organizer, Stephen captured the Danube commercial city of Chilia from Wallachia in 1465 and defeated a Hungarian invasion of his state in 1467 at the
Stephen the Great initially used the Ottoman vassalage inherited from his father as a tool against Hungary, Moldavia's traditional enemy. He participated in Mehmed II's invasion of Wallachia against his cousin Vlad the Impaler in 1462 because, at the time, Vlad was a Hungarian ally. An exceptional military commander and organizer, Stephen captured the Danube commercial city of Chilia from Wallachia in 1465 and defeated a Hungarian invasion of his state in 1467 at the
 The
The
 The Romanian People's Republic (1947â1965) and the
The Romanian People's Republic (1947â1965) and the
UNRV History â Dacia
*Breviarium historiae Romanae by Eutropius
Dromichaites, philological and linguistical aspects
a
{{Military history of Europe
 The military
The military history of Romania
This article covers the history and bibliography of Romania and links to specialized articles.
Prehistory
34,950-year-old remains of modern humans with a possible Neanderthalian trait were discovered in present-day Romania when the '' PeÈ ...
deals with conflicts spreading over a period of about 2500 years across the territory of modern Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
, the Balkan Peninsula and Eastern Europe and the role of the Romanian military in conflicts and peacekeeping worldwide.
During antiquity, the territory of modern Romania was the scene of sporadic wars between the native Dacian tribes and various invaders (Persia
Iran, officially the Islamic Republic of Iran, and also called Persia, is a country located in Western Asia. It is bordered by Iraq and Turkey to the west, by Azerbaijan and Armenia to the northwest, by the Caspian Sea and Turkmeni ...
ns, Macedon
Macedonia (; grc-gre, Îακεδονία), also called Macedon (), was an Classical antiquity, ancient monarchy, kingdom on the periphery of Archaic Greece, Archaic and Classical Greece, and later the dominant state of Hellenistic Greece. Th ...
ians, Celts
The Celts (, see pronunciation for different usages) or Celtic peoples () are. "CELTS location: Greater Europe time period: Second millennium B.C.E. to present ancestry: Celtic a collection of Indo-European peoples. "The Celts, an ancien ...
or Romans
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
*Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lette ...
). Ultimately, the Dacian armies were defeated by the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ÎαÏιλεία Ïῶν ῬÏμαίÏν, BasileÃa tôn RhÅmaÃÅn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in 106 and a small part of its territory became a Roman province. As the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ÎαÏιλεία Ïῶν ῬÏμαίÏν, BasileÃa tôn RhÅmaÃÅn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
declined, Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
was abandoned because of pressure from the Free Dacians
The so-called Free Dacians ( ro, Daci liberi) is the name given by some modern historians to those Dacians who putatively remained outside, or emigrated from, the Roman Empire after the emperor Trajan's Dacian Wars (AD 101-6). Dio Cassius named ...
and Goths
The Goths ( got, ğ²ğ¿ğğ¸ğ¹ğ¿ğ³ğ°, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, ÎÏÏθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
.
For 1000 years, numerous migrating people including the Goths
The Goths ( got, ğ²ğ¿ğğ¸ğ¹ğ¿ğ³ğ°, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, ÎÏÏθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
, Huns
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, ÎήÏαιδεÏ) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars, Magyars, Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the CumanâKipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
, Greeks, Romans, and Mongols
The Mongols ( mn, ĞонголÑÑÑĞ´, , , ; ; russian: ĞонголÑ) are an East Asian ethnic group native to Mongolia, Inner Mongolia in China and the Buryatia Republic of the Russian Federation. The Mongols are the principal membe ...
overran the territory of modern Romania.
During the Late Middle Ages
The Late Middle Ages or Late Medieval Period was the period of European history lasting from AD 1300 to 1500. The Late Middle Ages followed the High Middle Ages and preceded the onset of the early modern period (and in much of Europe, the Renai ...
, all three provinces had to deal with the danger posed by the growing power of the Ottoman Turks. John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi (, , , ; 1406 â 11 August 1456) was a leading Hungarian military and political figure in Central and Southeastern Europe during the 15th century. According to most contemporary sources, he was the member of a noble family of ...
, Voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the ...
of Transylvania and regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
of Hungary managed to halt the Turkish advance into Central Europe and secured a major victory at the Battle of Belgrade in 1456. Stephen the Great of Moldavia, Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder ( ro, Mircea cel BÄtrân, ; c. 1355 â 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited t ...
and Vlad the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ro, Vlad ÈepeÈ ) or Vlad Dracula (; ro, Vlad DrÄculea ; 1428/311476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most im ...
of Wallachia also successfully fought off the Turks and distracted them from the strategically more important objectives in the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western Europe, Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa ...
and the Balkans
The Balkans ( ), also known as the Balkan Peninsula, is a geographical area in southeastern Europe with various geographical and historical definitions. The region takes its name from the Balkan Mountains that stretch throughout the who ...
. However, by the middle of the 16th century, the three principalities had become Ottoman vassals. Michael the Brave
Michael the Brave ( ro, Mihai Viteazul or ; 1558 â 9 August 1601), born as Mihai PÄtraÈcu, was the Prince of Wallachia (as Michael II, 1593 â 1601), Prince of Moldavia (1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Transylvania (1599 – 1600). ...
of Wallachia managed to unite his realm with Transylvania and Moldavia and gain independence for a short time in 1600.
The early modern period was characterised by continuous warfare between the Habsburg Empire
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ĞθÏμανική ÎÏ
ÏοκÏαÏοÏία, OthÅmanikÄ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
(until the 18th century) and Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-eig ...
for the control of the Danubian principalities and Transylvania. The defeat of the Ottomans at the Battle of Vienna in 1683 marked the beginning of their decline in the region.
The 19th century saw the formation of the modern Romanian state through the unification of Moldavia and Wallachia. Independence from the Ottoman Empire was secured after the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or OttomanâRussian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
of 1877â1878 and Romania became a kingdom
Kingdom commonly refers to:
* A monarchy ruled by a king or queen
* Kingdom (biology), a category in biological taxonomy
Kingdom may also refer to:
Arts and media Television
* ''Kingdom'' (British TV series), a 2007 British television drama s ...
in 1881. The participation on the Allied ( Entente) side during World War I triggered the unification of the remaining Romanian inhabited territories with the kingdom, thus forming Greater Romania
The term Greater Romania ( ro, România Mare) usually refers to the borders of the Kingdom of Romania in the interwar period, achieved after the Great Union. It also refers to a pan-nationalist idea.
As a concept, its main goal is the creation ...
.
Romania reached its zenith during the inter-war period. After World War II, it was reduced to its modern borders and fell in the Soviet sphere of influence. The revolution of 1989 ended Communism and the geopolitical mutations in the region after the collapse of the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
paved the way for European integration, economically, politically, and militarily. Today, the Romanian army participates in peacekeeping missions with its NATO
The North Atlantic Treaty Organization (NATO, ; french: Organisation du traité de l'Atlantique nord, ), also called the North Atlantic Alliance, is an intergovernmental military alliance between 30 member states â 28 European and two No ...
allies in Afghanistan
Afghanistan, officially the Islamic Emirate of Afghanistan,; prs, اÙ
ارت اسÙاÙ
Û Ø§ÙغاÙستا٠is a landlocked country located at the crossroads of Central Asia and South Asia. Referred to as the Heart of Asia, it is bordere ...
, Bosnia, Kosovo and elsewhere.
Themes in Romanian military history
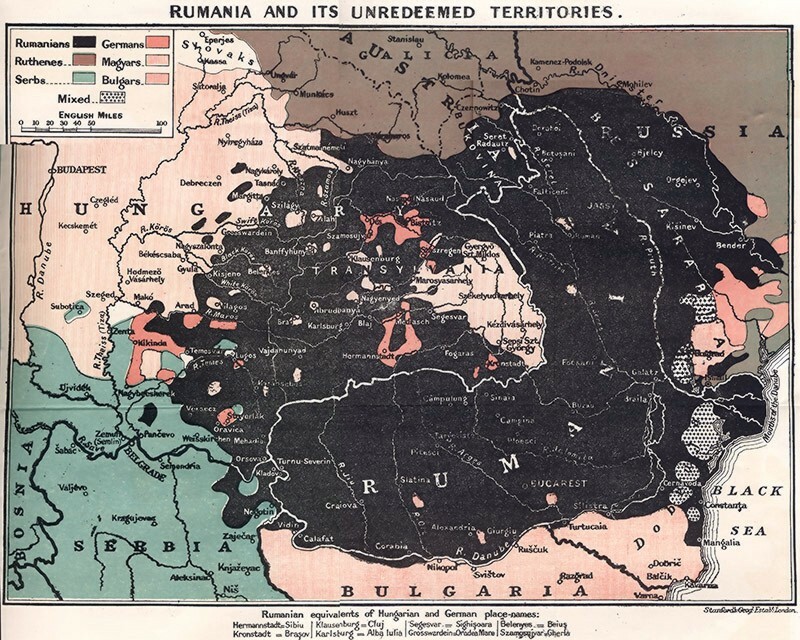
The national unity objective
 The primary objective of the Romanian leadership in the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century was to join all the territories inhabited by
The primary objective of the Romanian leadership in the 19th century and the first half of the 20th century was to join all the territories inhabited by Romanians
The Romanians ( ro, români, ; dated exonym '' Vlachs'') are a Romance-speaking ethnic group. Sharing a common Romanian culture and ancestry, and speaking the Romanian language, they live primarily in Romania and Moldova. The 2011 Roman ...
in a single state and to maintain its unity. The Romanian strategic thinking was driven by this need especially during the two World Wars. Today, Romania and the Republic of Moldova
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
are comprising most of the regions where Romanians formed the majority of the population before World War II.
Important military rivalries resulted from the clash of Romania's national interests with the interests of neighbouring countries in the past.
* Romanian-Hungarian rivalry for the control of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
. It started at the end of World War I when Transylavania was awarded to Romania through the Treaty of Trianon
The Treaty of Trianon (french: Traité de Trianon, hu, Trianoni békeszerzÅdés, it, Trattato del Trianon) was prepared at the Paris Peace Conference and was signed in the Grand Trianon château in Versailles on 4 June 1920. It forma ...
. Transylvania had an absolute Romanian majority in 1918, but had been for extensive periods of time under Hungarian rule. In 1940, Northern Transylvania was given to Hungary at the Second Vienna Award
The Second Vienna Award, also known as the Vienna Diktat, was the second of two territorial disputes that were arbitrated by Nazi Germany and Fascist Italy. On 30 August 1940, they assigned the territory of Northern Transylvania, including all o ...
only to be ceded back to Romania in 1945. After 1989, relations between the two countries flourished, especially after both Romania and Hungary entered NATO and the European Union. Hungary renounced all territorial claims to Transylvania in a 1995 bilateral treaty.
* Romanian-Bulgarian rivalry was triggered by the Romanian annexation of Southern Dobruja
Southern Dobruja, South Dobruja or Quadrilateral ( Bulgarian: Южна ĞобÑÑджа, ''Yuzhna Dobrudzha'' or simply ĞобÑÑджа, ''Dobrudzha''; ro, Dobrogea de Sud, or ) is an area of northeastern Bulgaria comprising Dobrich and Silis ...
(Cadrilater). Southern Dobruja was populated mainly by ethnic Bulgarians and Turks and was taken by Romania after the Romanian invasion of Bulgaria during the Second Balkan War. In World War I, Bulgaria regained Southern Dobruja and gained a part of Northern Dobruja at the Treaty of Bucharest (and eventually the whole of Northern Dobruja after a secret protocol with the other Central Powers in September 1918), but it was forced to give the territory back to Romania in 1919 through the Treaty of Neuilly
The Treaty of Neuilly-sur-Seine (french: Traité de Neuilly-sur-Seine) required Bulgaria to cede various territories, after Bulgaria had been one of the Central Powers defeated in World War I. The treaty was signed on 27 November 1919 at Neuilly ...
. With the advent of World War II, Bulgaria regained the region in the September 1940 Axis-sponsored Treaty of Craiova
The Treaty of Craiova ( bg, ĞÑайовÑка Ñпогодба, Krayovska spogodba; ro, Tratatul de la Craiova) was signed on 7 September 1940 and ratified on 13 September 1940 by the Kingdom of Bulgaria and the Kingdom of Romania. Under its te ...
. Since then relations between both countries normalised.
* Romanian-Russian/Soviet rivalry erupted because of the Russian occupation of Eastern Moldavia (Bessarabia), a territory which had been part of the Principality of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Ğемлѧ ĞолдавÑкаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία Ïá¿Ï ÎολδαβίαÏ) is a historical region and for ...
and had a Romanian majority. In the chaos that ensued after the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mome ...
, Bessarabia seceded from Russia and joined Romania. The Soviets never accepted the loss and a small border war took place along the Dniestr River in 1920. In 1924, they sponsored the Tatarbunary Uprising
The Tatarbunary Uprising ( ro, RÄscoala de la Tatarbunar) was a Bolshevik-inspired and Soviet-backed peasant revolt that took place on 15â18 September 1924, in and around the town of Tatarbunary (''Tatar-Bunar'' or ''Tatarbunar'') in Budjak ...
in Southern Bessarabia. In 1940, Romania was pressured into evacuating Bessarabia and Northern Bukovina, which were consequently occupied by Soviet troops. While Romania already had an authoritarian government closely aligned with Nazi Germany, the event prompted the country to openly join the Axis powers
The Axis powers, ; it, Potenze dell'Asse ; ja, æ¢è»¸å½ ''SÅ«jikukoku'', group=nb originally called the RomeâBerlin Axis, was a military coalition that initiated World War II and fought against the Allies. Its principal members were ...
and contribute extensively with troops and material to Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named after ...
and the subsequent fighting against the USSR. The Paris Peace Treaty
The Paris Peace Treaties (french: Traités de Paris) were signed on 10 February 1947 following the end of World War II in 1945.
The Paris Peace Conference lasted from 29 July until 15 October 1946. The victorious wartime Allied powers (princi ...
of 1947 reaffirmed the 1940 Soviet annexations. Today, most of Bessarabia with some portions of Transnistria
Transnistria, officially the Pridnestrovian Moldavian Republic (PMR), is an unrecognised breakaway state that is internationally recognised as a part of Moldova. Transnistria controls most of the narrow strip of land between the Dniester riv ...
form the Republic of Moldova
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
, successor to the Moldavian SSR
The Moldavian Soviet Socialist Republic ( ro, Republica SovieticÄ SocialistÄ MoldoveneascÄ, Moldovan Cyrillic: ) was one of the 15 republics of the Soviet Union which existed from 1940 to 1991. The republic was formed on 2 August 194 ...
, while Northern Bukovina and parts of Bessarabia (the Budjak
Budjak or Budzhak ( Bulgarian and Ukrainian: ĞÑджак; ro, Bugeac; Gagauz and Turkish: ''Bucak''), historically part of Bessarabia until 1812, is a historical region in Ukraine and Moldova. Lying along the Black Sea between the Danube ...
and Hotin
Khotyn ( uk, ХоÑин, ; ro, Hotin, ; see other names) is a city in Dnistrovskyi Raion, Chernivtsi Oblast of western Ukraine and is located south-west of Kamianets-Podilskyi. It hosts the administration of Khotyn urban hromada, one of the ...
regions) are in Ukraine
Ukraine ( uk, УкÑĞ°Ñна, Ukraïna, ) is a country in Eastern Europe. It is the second-largest European country after Russia, which it borders to the east and northeast. Ukraine covers approximately . Prior to the ongoing Russian inv ...
.The regional balance of power
During theSecond Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies r ...
, Romania allied itself with Serbia
Serbia (, ; Serbian: , , ), officially the Republic of Serbia (Serbian: , , ), is a landlocked country in Southeastern and Central Europe, situated at the crossroads of the Pannonian Basin and the Balkans. It shares land borders with Hungar ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
in order to check Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, ĞÑлгаÑиÑ, BÇlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
, which the allies saw as too powerful after the complete victory over Turkey in the First Balkan War
The First Balkan War ( sr, ĞÑви балканÑки ÑĞ°Ñ, ''Prvi balkanski rat''; bg, ĞалканÑка война; el, Îʹ ÎαλκανικÏÏ ÏÏλεμοÏ; tr, Birinci Balkan SavaÅı) lasted from October 1912 to May 1913 and invo ...
. In 1919, the Hungarian Soviet Republic
The Socialist Federative Republic of Councils in Hungary ( hu, Magyarországi Szocialista Szövetséges Tanácsköztársaság) (due to an early mistranslation, it became widely known as the Hungarian Soviet Republic in English-language sources ( ...
allied with Soviet Russia posed a major threat to the conservative regimes in the region. Romania started an offensive that ended with the conquest of Budapest
Budapest (, ; ) is the capital and most populous city of Hungary. It is the ninth-largest city in the European Union by population within city limits and the second-largest city on the Danube river; the city has an estimated population ...
and the overthrow of the Communist government. In the inter-war period, the Little Entente
The Little Entente was an alliance formed in 1920 and 1921 by Czechoslovakia, Romania and the Kingdom of Serbs, Croats and Slovenes (since 1929 Yugoslavia) with the purpose of common defense against Hungarian revanchism and the prospect of a Ha ...
was envisioned as an alliance between Romania, Czechoslovakia
, rue, ЧеÑÑкоÑловенÑÑко, , yi, ×שע××ס×××××ק××,
, common_name = Czechoslovakia
, life_span = 1918â19391945â1992
, p1 = Austria-Hungary
, image_p1 ...
and Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, ĞÑгоÑлавиÑĞ° ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, ĞÑгоÑлавиÑĞ° ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, ЮгоÑлавиÑ, translit=Juhoslavija ...
to counter Hungarian irredentism
Hungarian irredentism or Greater Hungary ( hu, Nagy-Magyarország) are irredentist political ideas concerning redemption of territories of the historical Kingdom of Hungary. Targeting at least to regain control over Hungarian-populated areas in H ...
, while the Balkan Pact
The Balkan Pact, or Balkan Entente, was a treaty signed by Greece, Romania, Turkey and Yugoslavia on 9 February 1934
, formed by Romania, Yugoslavia
Yugoslavia (; sh-Latn-Cyrl, separator=" / ", Jugoslavija, ĞÑгоÑлавиÑĞ° ; sl, Jugoslavija ; mk, ĞÑгоÑлавиÑĞ° ;; rup, Iugoslavia; hu, Jugoszlávia; rue, label=Pannonian Rusyn, ЮгоÑлавиÑ, translit=Juhoslavija ...
, Greece
Greece,, or , romanized: ', officially the Hellenic Republic, is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the southern tip of the Balkans, and is located at the crossroads of Europe, Asia, and Africa. Greece shares land borders ...
and Turkey
Turkey ( tr, Türkiye ), officially the Republic of Türkiye ( tr, Türkiye Cumhuriyeti, links=no ), is a transcontinental country located mainly on the Anatolian Peninsula in Western Asia, with a small portion on the Balkan Peninsula in ...
, had the purpose to counter the Bulgarian irredentism. The PolishâRomanian alliance
The PolishâRomanian alliance was a series of treaties signed in the interwar period by the Second Polish Republic and the Kingdom of Romania. The first of them was signed in 1921 and, together, the treaties formed a basis for good foreign rela ...
was created against the Soviet Union
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a List of former transcontinental countries#Since 1700, transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, ...
, with the ultimate goal to stop the spread of communism
Communism (from Latin la, communis, lit=common, universal, label=none) is a far-left sociopolitical, philosophical, and economic ideology and current within the socialist movement whose goal is the establishment of a communist society, a ...
into Europe.
Dacians and Romans
 The Dacians (Lat. Daci, Gr. Dákai), and the probably closely related tribes of the Getae, were part of the greater
The Dacians (Lat. Daci, Gr. Dákai), and the probably closely related tribes of the Getae, were part of the greater Thracian
The Thracians (; grc, ÎÏá¾·ÎºÎµÏ ''ThrÄikes''; la, Thraci) were an Indo-European speaking people who inhabited large parts of Eastern and Southeastern Europe in ancient history.. "The Thracians were an Indo-European people who occupied ...
family of peoples. Ancient authors describe the two tribes as inhabiting the territories of present-day Romania, eastern Hungary, south-western Ukraine and northern Bulgaria.
In (335 BC), Alexander the Great
Alexander III of Macedon ( grc, á¼Î»ÎξανδÏοÏ, Alexandros; 20/21 July 356 BC â 10/11 June 323 BC), commonly known as Alexander the Great, was a king of the ancient Greek kingdom of Macedon. He succeeded his father Philip II to ...
engaged the Thracians in order to secure the northern boundary of the Macedonian kingdom. He crossed the Danube and made a short incursion on the Getae living north of the river.
Lysimachus, one of the successors of Alexander, who ruled over Thrace, Asia Minor and Macedonia tried to conquer territories north of the Danube, but was defeated and taken prisoner by the Getae king Dromichaetes. However, Dromichaetes set him free on amicable terms.
Burebista
Burebista ( grc, ÎÏ
ÏεβίÏÏαÏ, ÎοιÏεβίÏÏαÏ) was the king of the Getae and Dacian tribes from 82/61BC to 45/44BC. He was the first king who successfully unified the tribes of the Dacian kingdom, which comprised the area loca ...
, one of the greatest kings of Dacia ruled between 82 BC and 44 BC and unified the Thracian population from Hercynia (today's Moravia
Moravia ( , also , ; cs, Morava ; german: link=yes, Mähren ; pl, Morawy ; szl, Morawa; la, Moravia) is a historical region in the east of the Czech Republic and one of three historical Czech lands, with Bohemia and Czech Silesia.
The m ...
) in the west, to the Southern Bug River
, ''Pivdennyi Buh''
, name_etymology =
, image = Sunset S Bug Vinnitsa 2007 G1.jpg
, image_size = 270
, image_caption = Southern Bug River in the vicinity of Vinnytsia, Ukraine
, map = PietinisBug ...
in the east, and from the northern Carpathians
The Carpathian Mountains or Carpathians () are a range of mountains forming an arc across Central Europe. Roughly long, it is the third-longest European mountain range after the Urals at and the Scandinavian Mountains at . The range stretches ...
to Dionysopolis. Burebista sided with the inhabitants of the Greek cities on the Western coast of the Black Sea when they were occupied by Varro Lucullus, the proconsul of the province of Macedonia during the Second Mithridatic War (74 BCâ72 BC). The Getae defeated the Roman army of Gaius Antonius Hybrida near Histria and continued their incursions in the region, taking the Celtic settlement of Aliobrix (Cartal, Ukraine), Tyras and Odessos and destroying Olbia. In 48 BC, the Dacian king sided with Pompey
Gnaeus Pompeius Magnus (; 29 September 106 BC â 28 September 48 BC), known in English as Pompey or Pompey the Great, was a leading Roman general and statesman. He played a significant role in the transformation of ...
during his struggle against Julius Caesar
Gaius Julius Caesar (; ; 12 July 100 BC â 15 March 44 BC), was a Roman general and statesman. A member of the First Triumvirate, Caesar led the Roman armies in the Gallic Wars before defeating his political rival Pompey in a civil war, ...
in the Roman civil war
This is a list of civil wars and organized civil disorder, revolts and rebellions in ancient Rome (Roman Kingdom, Roman Republic, and Roman Empire) until the fall of the Western Roman Empire (753 BCE â 476 CE). For the Eastern Roman Empire or B ...
but failed to supply him with troops in time for the Battle of Pharsalus
The Battle of Pharsalus was the decisive battle of Caesar's Civil War fought on 9 August 48 BC near Pharsalus in central Greece. Julius Caesar and his allies formed up opposite the army of the Roman Republic under the command of Pompey. P ...
.
Dacian Wars
 Faced with the growing military presence of the
Faced with the growing military presence of the Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, ÎαÏιλεία Ïῶν ῬÏμαίÏν, BasileÃa tôn RhÅmaÃÅn) was the post- Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings around the Mediter ...
in the region, Decebalus
Decebalus (), sometimes referred to as Diurpaneus, was the last Dacian king. He is famous for fighting three wars, with varying success, against the Roman Empire under two emperors. After raiding south across the Danube, he defeated a Roman invas ...
(reigned 87â106), son of king Duras, reorganized the army and in 85 AD the Dacians began minor raiding in the heavily fortified Roman province of Moesia, located south of the Danube. In 86, a more vigorous attack south into Moesia, prompted emperor Domitian
Domitian (; la, Domitianus; 24 October 51 â 18 September 96) was a Roman emperor who reigned from 81 to 96. The son of Vespasian and the younger brother of Titus, his two predecessors on the throne, he was the last member of the Fl ...
to intervene with fresh legions and supplies. Domitian planned an attack into Dacia the next year to stop Dacian marauding.
A strong offensive was carried in 87 when five or six legions commanded by general Cornelius Fuscus
Cornelius Fuscus (died 86 AD) was a Roman general who fought campaigns under the Emperors of the Flavian dynasty. He first distinguished himself as one of Vespasian's most ardent supporters during the civil war of 69 AD, known as the Year of the ...
crossed the Danube and continued northwards to the Dacian capital of Sarmizegetusa. They encountered the Dacian army at Tapae
Tapae was a fortified settlement, guarding Sarmizegetusa, the main political centre of Dacia. Its location was on the Iron Gates of Transylvania, a natural passage breaking between Èarcului and Poiana RuscÄ Mountains and connecting Banat to È ...
, where the Romans were ambushed, suffering a major defeat. Almost all of the soldiers from Legio V Alaudae
Legio V Alaudae ("Fifth Legion of the Lark"), sometimes also known as ''Gallica'', was a legion of the Roman army founded in 52 BC by the general Gaius Julius Caesar (dictator of Rome 49-44 BC). It was levied in Transalpine Gaul to fight the arm ...
were killed and the Dacians captured their flags and war machines. Cornelius Fuscus himself was killed in battle. After this victory, Decebalus replaced Duras as king of Dacia.
The Roman offensive continued the following year, with general Tettius Iulianus now in command. The Roman army entered Dacia following the same route as Cornelius Fuscus the previous year. The battle took place mainly in the same area, at Tapae, this time the outcome being a Roman victory. Because of the difficult road to Sarmizegetusa and the defeats suffered by Domitian in Pannonia, the Roman offensive was halted and Decebalus sued for peace.
According to the peace of 89, Decebalus became a client king of Rome receiving money, craftsmen and war machines from the Roman Empire, to defend the empire's borders. Instead of using the money as Rome intended, Decebalus decided to build new citadels in the mountains and to reinforce the already existing ones. This was the main reason for the following Roman attack under emperor Trajan.
In 101 Trajan
Trajan ( ; la, Caesar Nerva Traianus; 18 September 539/11 August 117) was Roman emperor from 98 to 117. Officially declared ''optimus princeps'' ("best ruler") by the senate, Trajan is remembered as a successful soldier-emperor who presi ...
(reigned 98â117), after gaining the approval of the Roman Senate
The Roman Senate ( la, SenÄtus RÅmÄnus) was a governing and advisory assembly in ancient Rome. It was one of the most enduring institutions in Roman history, being established in the first days of the city of Rome (traditionally founded in ...
, began advancing on Dacia. A stone bridge later known as Trajan's bridge was constructed over the Danube to assist the legionaries' advance. The Roman offensive was spearheaded by two legionary columns, marching right to the heart of Dacia, burning towns and villages in the process. In the winter of 101â102, the Dacians led massive assaults on the legions stationed in Moesia, but were defeated by Trajan in the Battle of Adamclisi. In 102 the Roman armies converged for a final assault and defeated the Dacian army at the third Battle of Tapae. After the battle, Decebalus chose to surrender. The war concluded with a Roman victory but the Dacians planned to organize further resistance.
Trajan invaded again in 105, this time with the intention of transforming Dacia into a Roman province
The Roman provinces (Latin: ''provincia'', pl. ''provinciae'') were the administrative regions of Ancient Rome outside Roman Italy that were controlled by the Romans under the Roman Republic and later the Roman Empire. Each province was rule ...
. After several skirmishes, an assault against the capital Sarmisegetusa took place in 106 with the participation of the legions II Adiutrix, IV Flavia Felix and a cavalry detachment (vexillatio) from Legio VI Ferrata. The Romans destroyed the water pipes to the capital and the city fell. Decebalus fled, but committed suicide rather than face capture. Nevertheless, the war went on and the last battle with the Dacian army took place at Porolissum
Porolissum was an ancient Roman city in Dacia. Established as a military camp in 106 during Trajan's Dacian Wars, the city quickly grew through trade with the native Dacians and became the capital of the province Dacia Porolissensis in 124. The si ...
. At the end of the war the Romans organized the province of Dacia on large parts of the former Dacian kingdom. The Roman rule would last from 106 until 271 (or 275 according to some sources).
Roman Dacia
Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''WeiÃenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the MureÈ River in the historica ...
), Legio V Macedonica (stationed at Potaissa, modern Turda
Turda (; hu, Torda, ; german: link=no, Thorenburg; la, Potaissa) is a city in Cluj County, Transylvania, Romania. It is located in the southeastern part of the county, from the county seat, Cluj-Napoca, to which it is connected by the Europ ...
) and numerous auxiliaries had their fixed quarters in the province. For protection against the attacks of the "free Dacians" (Dacians that lived outside Roman rule), Carpians and other neighbouring tribes, the Romans built forts and delimited the Roman held territory with a limes. Three great military roads were constructed, linking the chief towns of the province.
Dacians were recruited into the Roman Army, and were employed in the construction and guarding of Hadrian's Wall in Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
, or elsewhere in the Roman Empire. Several Cohors Primae Dacorum ("First cohort of Dacians") and Alae Dacorum fighting in the ranks of legions were stationed in Britannia at Deva (Chester), Vindolanda
Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort ('' castrum'') just south of Hadrian's Wall in northern England, which it originally pre-dated.British windo- 'fair, white, blessed', landa 'enclosure/meadow/prairie/grassy plain' (the modern Welsh word ...
(on the Stanegate) and Banna (Birdoswald).
 In the third century, the attacks on Roman Dacia conducted by the
In the third century, the attacks on Roman Dacia conducted by the Free Dacians
The so-called Free Dacians ( ro, Daci liberi) is the name given by some modern historians to those Dacians who putatively remained outside, or emigrated from, the Roman Empire after the emperor Trajan's Dacian Wars (AD 101-6). Dio Cassius named ...
and Goths
The Goths ( got, ğ²ğ¿ğğ¸ğ¹ğ¿ğ³ğ°, translit=''Gutþiuda''; la, Gothi, grc-gre, ÎÏÏθοι, Gótthoi) were a Germanic people who played a major role in the fall of the Western Roman Empire and the emergence of medieval Europe ...
intensified. Emperor Aurelian (270â275), confronted with the secession of Gaul
Gaul ( la, Gallia) was a region of Western Europe first described by the Romans. It was inhabited by Celtic and Aquitani tribes, encompassing present-day France, Belgium, Luxembourg, most of Switzerland, parts of Northern Italy (only during ...
and Hispania
Hispania ( la, HispÄnia , ; nearly identically pronounced in Spanish, Portuguese, Catalan, and Italian) was the Roman name for the Iberian Peninsula and its provinces. Under the Roman Republic, Hispania was divided into two provinces: Hisp ...
from the empire, the advance of the Sassanids
The Sasanian () or Sassanid Empire, officially known as the Empire of Iranians (, ) and also referred to by historians as the Neo-Persian Empire, was the last Iranian empire before the early Muslim conquests of the 7th-8th centuries AD. Named ...
in Asia and the devastations that the Carpians and the Goths had done to Moesia and Illyria, abandoned the province and withdrew the troops and administration, fixing the Roman frontier on the Danube. A new Dacia Aureliana was reorganised south of the Danube, with its capital at Serdica
Serdika or Serdica ( Bulgarian: ) is the historical Roman name of Sofia, now the capital of Bulgaria.
Currently, Serdika is the name of a district located in the city. It includes four neighbourhoods: "Fondovi zhilishta"; "Banishora", "Orlandov ...
(modern Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, СоÑиÑ, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
).
At the beginning of the next century, Romans had tried to retake control of the north of the Danube: in Constantine the Great's campaign from 332, 100,000 Goths were killed in battles on north of the Danube.Eusebius Vita Constantini IV.6 For a very short time, near 328, there were plans regain administration of the north of the Danube; a stone bridge was erected between Sucidava and Oescus. After 334 AD, in Constantine the Great's campaign, 300,000 Sarmatians were evacuated from the north of the Danube, and the Roman limes
Limes may refer to:
* the plural form of lime (disambiguation)
Lime commonly refers to:
* Lime (fruit), a green citrus fruit
* Lime (material), inorganic materials containing calcium, usually calcium oxide or calcium hydroxide
* Lime (color), a ...
were once again reestablished on Danube.
Early Middle ages
During theEarly Middle Ages
The Early Middle Ages (or early medieval period), sometimes controversially referred to as the Dark Ages, is typically regarded by historians as lasting from the late 5th or early 6th century to the 10th century. They marked the start of the Mi ...
, the Northern Balkan Peninsula became a conduit for invading tribes who targeted richer lands further west and south. Information about the military operations conducted in this period is very scarce.
The territory of modern Romania was part of the Hun Empire
The Huns were a nomadic people who lived in Central Asia, the Caucasus, and Eastern Europe between the 4th and 6th century AD. According to European tradition, they were first reported living east of the Volga River, in an area that was part ...
, but after its disintegration different parts were under successive control of the Gepids
The Gepids, ( la, Gepidae, Gipedae, grc, ÎήÏαιδεÏ) were an East Germanic tribe who lived in the area of modern Romania, Hungary and Serbia, roughly between the Tisza, Sava and Carpathian Mountains. They were said to share the religion ...
, Avars, Slavs, Bulgars and Pechenegs
The Pechenegs () or Patzinaks tr, Peçenek(ler), Middle Turkic: , ro, Pecenegi, russian: ĞеÑенег(и), uk, ĞеÑенÑг(и), hu, BesenyÅ(k), gr, ΠαÏζινάκοι, ΠεÏÏενÎγοι, ΠαÏζινακίÏαι, ka, ááá ...
. Most of these invaders did not permanently occupy the territory, as their organization was of typical nomadic confederacies. From them, only the Slavs settled in large numbers beginning with the 7th century.
The Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
held the region between the Danube and the Black Sea (modern Dobruja
Dobruja or Dobrudja (; bg, ĞобÑÑджа, Dobrudzha or ''Dobrudža''; ro, Dobrogea, or ; tr, Dobruca) is a historical region in the Balkans that has been divided since the 19th century between the territories of Bulgaria and Romania. I ...
) from time to time (such as during Justinian's reign in the 6th century) or again under some emperors of the Macedonian and Komnenian dynasties, being part of the Byzantine Paristrion thema (province) between in the period 971â976 and between 1001 and 1185, although it was a border that was hard to maintain due to the constant invasions from the north. Dobrudja was part of the Bulgarian Empire during its whole period of existence. The area around the Danube Delta was the site of battle of Ongal
The Battle of Ongal took place in the summer of 680 in the Ongal area, an unspecified location in and around the Danube delta near the Peuce Island, present-day Tulcea County, Romania. It was fought between the Bulgars, who had recently invaded ...
in 680 which led to the formation of Bulgaria
Bulgaria (; bg, ĞÑлгаÑиÑ, BÇlgariya), officially the Republic of Bulgaria,, ) is a country in Southeast Europe. It is situated on the eastern flank of the Balkans, and is bordered by Romania to the north, Serbia and North Macedo ...
in 681. Since the formation of the country the Bulgarians controlled the Wallachian Plain
The Romanian Plain ( ro, Câmpia RomânÄ) is located in southern Romania and the easternmost tip of Serbia, where it is known as the Wallachian Plain ( sr, VlaÅ¡ka nizija/ĞлаÑка низиÑĞ°). Part of the historical region of Wallachia, it ...
and Bessarabia to the north of the Danube, bordering the Avars to the north-west. The Bulgarians under Khan Krum
Krum ( bg, ĞÑÑм, el, ÎÏοῦμοÏ/Kroumos), often referred to as Krum the Fearsome ( bg, ĞÑÑм Ğ¡ÑÑĞ°Ñни) was the Khan of Bulgaria from sometime between 796 and 803 until his death in 814. During his reign the Bulgarian territory ...
destroyed the crumbling Avar Khanate in 803 and moved the border along the river Tisza
The Tisza, Tysa or Tisa, is one of the major rivers of Central and Eastern Europe. Once, it was called "the most Hungarian river" because it flowed entirely within the Kingdom of Hungary. Today, it crosses several national borders.
The Tisza be ...
,Runciman, SA History of the First Bulgarian Empire. Book II
pp. 50â51 thus including Transylvania and parts of Pannonia in the Bulgarian state. In a military conflict with the Franks between 827â829 the Bulgarians secured their border with the Frankish Empire. At the end of the 10th century, Dobruja was the theatre of operations between the Kievan Rus army led by Prince Sviatoslav I, the Bulgarian army and the Byzantine army led by emperor
John Tzimiskes
John I Tzimiskes (; 925 â 10 January 976) was the senior Byzantine emperor from 969 to 976. An intuitive and successful general, he strengthened the Empire and expanded its borders during his short reign.
Background
John I Tzimiskes ...
. Sviatoslav controlled large parts of the First Bulgarian Empire and established his capital at Pereyaslavets
Pereyaslavets ( East Slavic: ) or Preslavets ( bg, ĞÑеÑлавеÑ) was a trade city located near mouths of the Danube. The city's name is derived from that of the Bulgarian capital of the time, Preslav, and means Little Preslav (). In Greek ...
(near modern NufÄru
NufÄru is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders B ...
) on the Danube. The Byzantines, led by John Tzimiskes were on the offensive after they defeated the united Russo-Bulgarian forces in the Battle of Arcadiopolis. Pereyaslavets was captured and Sviatoslav was forced to flee westwards to the fortress of Dorostolon ( Durostorum). Emperor John proceeded to lay siege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
to Dorostolon, which resisted for sixty five days until Sviatoslav agreed to sign a peace treaty with the Byzantine Empire, whereby he renounced his claims on Bulgaria and the city of Chersonesos
Chersonesus ( grc, ΧεÏÏÏνηÏοÏ, KhersónÄsos; la, Chersonesus; modern Russian and Ukrainian: ХеÑÑонеÌÑ, ''Khersones''; also rendered as ''Chersonese'', ''Chersonesos'', contracted in medieval Greek to Cherson ΧεÏÏÏν; ...
in Crimea
Crimea, crh, ĞÑÑÑÑм, Qırım, grc, ÎιμμεÏία / ΤαÏ
Ïική, translit=KimmerÃa / TaurikḠ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
. Sviatoslav was allowed to evacuate his army to Kiev.
The Magyars settled the Pannonian Plain
The Pannonian Basin, or Carpathian Basin, is a large basin situated in south-east Central Europe. The geomorphological term Pannonian Plain is more widely used for roughly the same region though with a somewhat different sense, with only the ...
and subdued Transylvania from Bulgaria in the 10th and 11th centuries, while the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the CumanâKipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
occupied the Lower Danube region in the 11th century.
High and Late Middle Ages
Transylvania and the Mongol Invasion of 1241
From the 11th century until 1541Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the Ap ...
was an autonomous part of Hungary and was ruled by a Voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the ...
. As it formed the eastern border of Hungary, great emphasis was put on its defenses. By the 12th century the Székelys were established in eastern Transylvania as border guards, while the Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
were colonised to guard the southern and northeastern frontier. Early in the 13th century, king Andrew II of Hungary
Andrew II ( hu, II. András, hr, Andrija II., sk, Ondrej II., uk, ĞндÑÑй II; 117721 September 1235), also known as Andrew of Jerusalem, was King of Hungary and Croatia between 1205 and 1235. He ruled the Principality of Halych from 11 ...
called on the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
to protect the Burzenland
Èara Bârsei, Burzenland () or Barcaság is a historic and ethnographic area in southeastern Transylvania, Romania with a mixed population of Romanians, Germans, and Hungarians.
Geography
The Burzenland lies within the Southern Carpathians m ...
from the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the CumanâKipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
. After the Order began expanding their territory outside Transylvania and acted independently, Andrew expelled it in 1225.
In 1241 Transylvania suffered greatly during the Mongol invasion of Europe
From the 1220s into the 1240s, the Mongols conquered the Turkic states of Volga Bulgaria, Cumania, Alania, and the Kievan Rus' federation. Following this, they began their invasion into heartland Europe by launching a two-pronged invasion of ...
. The overall invasion was planned and carried out by Subutai, under the nominal command of Batu Khan
Batu Khan ( â 1255),, ''Bat haan'', tt-Cyrl, ĞĞ°ÑÑ Ñ
ан; ; russian: Ñ
ан ĞĞ°ÑÑÌй was a Mongol ruler and founder of the Golden Horde, a constituent of the Mongol Empire. Batu was a son of Jochi, thus a grandson of Genghis Kh ...
. The attack on Transylvania was commanded by Güyük Khan
Güyük (also Güyug;; ''c''. March 19, 1206 â April 20, 1248) was the third Khagan-Emperor of the Mongol Empire, the eldest son of Ãgedei Khan and a grandson of Genghis Khan. He reigned from 1246 to 1248.
Appearance
According to Giovann ...
, the future great khan
Khagan or Qaghan (Mongolian:; or ''Khagan''; otk, ğ°´ğ°ğ°£ ), or , tr, KaÄan or ; ug, ÙاغاÙ, Qaghan, Mongolian Script: ; or ; fa, خاÙا٠''KhÄqÄn'', alternatively spelled KaÄan, Kagan, Khaghan, Kaghan, Khakan, Khakhan ...
of the Mongols.
Güyük invaded Transylvania in three columns through the Tihuţa and Oituz Pass
Oituz (formerly ''GrozeÈti''; hu, Gorzafalva) is a commune in BacÄu County, Western Moldavia, Romania. It is composed of six villages: CÄlcâi (''Zöldlonka''), FerestrÄu-Oituz (''Fűrészfalva''), Hârja (''Herzsa''), Marginea, Oituz and Poi ...
es and the TimiÅ-Cerna Gap, while Subutai attacked through the fortified Verecke Pass towards central Hungary. Güyük sacked Sibiu
Sibiu ( , , german: link=no, Hermannstadt , la, Cibinium, Transylvanian Saxon: ''Härmeschtat'', hu, Nagyszeben ) is a city in Romania, in the historical region of Transylvania. Located some north-west of Bucharest, the city straddles the Ci ...
, Cisnadie, Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''WeiÃenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the MureÈ River in the historica ...
, Bistriţa, Cluj-Napoca, Oradea as well as the Hungarian king's silver mine at Rodna. This prevented the Transylvanian nobility from aiding King Béla IV
Béla may refer to:
* Béla (crater), an elongated lunar crater
* Béla (given name), a common Hungarian male given name
See also
* Bela (disambiguation)
* Belá (disambiguation)
* BÄlá (disambiguation) BÄlá, derived from ''bÃlá'' (''wh ...
in the crucial Battle of Mohi
The Battle of Mohi (11 April 1241), also known as Battle of the Sajó River''A Global Chronology of Conflict: From the Ancient World to the Modern Middle East'', Vol. I, ed. Spencer C. Tucker, (ABC-CLIO, 2010), 279; "Although Mongol losses in t ...
. A separate Mongol force destroyed the Cumans
The Cumans (or Kumans), also known as Polovtsians or Polovtsy (plural only, from the Russian exonym ), were a Turkic nomadic people comprising the western branch of the CumanâKipchak confederation. After the Mongol invasion (1237), many so ...
near the Siret
Siret (; german: Sereth; hu, Szeretvásár; uk, СеÑеÑ, Seret; yi, סערע×, Seret) is a town, municipality and former Latin bishopric in Suceava County, northeastern Romania. It is situated in the historical region of Bukovina. Siret is ...
River and annihilated the Cuman Catholic Bishopric of Milcov.
Estimates of population decline in Transylvania owing to the Mongol invasion range from 15â20% to 50%.
Wallachia and Moldavia
 The lands east and south of the Carpathians fell under Mongol occupation after 1241, until the Principalities of
The lands east and south of the Carpathians fell under Mongol occupation after 1241, until the Principalities of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Èara RomâneascÄ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
and Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Ğемлѧ ĞолдавÑкаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία Ïá¿Ï ÎολδαβίαÏ) is a historical region and for ...
emerged in the 14th century as Hungarian vassals.
In 1330 Basarab I
Basarab I (), also known as Basarab the Founder ( ro, Basarab Ãntemeietorul; c. 1270 â 1351/1352), was a ''voivode'' and later the first independent ruler of Wallachia who lived in the first half of the . Many details of his life are uncerta ...
, the voivode of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Èara RomâneascÄ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, managed to ambush and defeat a 30,000-strong Hungarian army led by King Charles I Robert in the Battle of Posada
The Battle of Posada (9â12 November 1330)Djuvara, pp. 19â "''... marea bÄtÄlie zisÄ de la Posada (9â12 noiembrie 1330)''". was fought between Basarab I of Wallachia and Charles I of Hungary (also known as Charles Robert).
The small Wall ...
, eliminating Hungarian interference in Wallachia.
In the same period, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Ğемлѧ ĞолдавÑкаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία Ïá¿Ï ÎολδαβίαÏ) is a historical region and for ...
freed itself from Hungarian control, although the Hungarians made some attempts to regain the principality. During the later 14th century and the first half of the 15th century, Moldavia was under Polish suzerainty and the Moldavians supplied Poland with troops during the campaigns against the Teutonic Order
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians on ...
in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an ...
. Moldavian light cavalry detachments participated in the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the PolishâLithuanianâTeutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
and the Siege of Marienburg on the Polish-Lithuanian side.
Anti-Ottoman Wars
TheOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ĞθÏμανική ÎÏ
ÏοκÏαÏοÏία, OthÅmanikÄ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
became a major military power in the later 14th century, when they conquered Anatolia
Anatolia, tr, Anadolu Yarımadası), and the Anatolian plateau, also known as Asia Minor, is a large peninsula in Western Asia and the westernmost protrusion of the Asian continent. It constitutes the major part of modern-day Turkey. The ...
, most of the Balkans and were threatening Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, ÙسطÙØ·ÙÙÙÙ
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya ( Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis ( ...
, the capital of the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
.
Conflict firstly erupted between the Ottomans led by Beyazid I
Bayezid I ( ota, باÙزÙد اÙÙ, tr, I. Bayezid), also known as Bayezid the Thunderbolt ( ota, link=no, ÛÙدÛرÙ
باÙزÙد, tr, Yıldırım Bayezid, link=no; â 8 March 1403) was the Ottoman Sultan from 1389 to 1402. He adopted t ...
and the Wallachians led by Mircea the Elder
Mircea the Elder ( ro, Mircea cel BÄtrân, ; c. 1355 â 31 January 1418) was the Voivode of Wallachia from 1386 until his death in 1418. He was the son of Radu I of Wallachia and brother of Dan I of Wallachia, after whose death he inherited t ...
after the voivode openly supported the Christian peoples south of the Danube who were fighting the Turks. There was also a contest for the control of Dobruja, which had been independent for most of the 14th century, but fell under Ottoman rule in 1388. In 1389 Mircea took control of the province and held it with some interruptions until 1418.
 In 1394 Beyazid I crossed the Danube, leading a strong army with the purpose of overthrowing Mircea and replacing him with an Ottoman vassal. The Wallachians adopted scorched earth and guerrilla tactics by starving the Ottomans and mounting small scale attacks. The two armies finally clashed in the indecisive
In 1394 Beyazid I crossed the Danube, leading a strong army with the purpose of overthrowing Mircea and replacing him with an Ottoman vassal. The Wallachians adopted scorched earth and guerrilla tactics by starving the Ottomans and mounting small scale attacks. The two armies finally clashed in the indecisive Battle of Rovine
The Battle of Rovine took place on 17 May 1395. The Wallachian army led by Voivod Mircea the Elder opposed the Ottoman invasion personally led by Sultan Bayezid I the Thunderbolt. The Turkish force heavily outnumbered the Wallachian troops ...
. Beyazid failed to put Vlad the Usurper on the Wallachian throne and in 1396 Mircea was again commanding his army during the Battle of Nicopolis. At Nicopolis, the Wallachian force of 10.000 men formed the left wing of the crusader army and, having witnessed the disastrous attacks made by the western knights and the surrender of Sigismund, escaped the massacre that followed.
The defeat and capture of sultan Beyazid I by Timur Lenk
Timur ; chg, ''Aqsaq Temür'', 'Timur the Lame') or as ''Sahib-i-Qiran'' ( 'Lord of the Auspicious Conjunction'), his epithet. ( chg, ''Temür'', 'Iron'; 9 April 133617â19 February 1405), later TimÅ«r GurkÄnÄ« ( chg, ''Temür Kü ...
(Tamerlane) in the Battle of Ankara
The Battle of Ankara or Angora was fought on 20 July 1402 at the Ãubuk plain near Ankara, between the forces of the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I and the Emir of the Timurid Empire, Timur. The battle was a major victory for Timur, and it led to the ...
in 1402 started a period of anarchy in the Ottoman Empire and Mircea took part in the struggles for the Ottoman throne supporting various pretenders. Towards the end of his reign, Mircea signed a treaty with the Ottomans whereby he accepted paying tribute and gave up his claims on Dobruja.
Wallachia fell into anarchy following Mircea's death in 1418. After 1420 control of the principality changed hands until Alexander I Aldea
Alexander I Aldea (1397 â December 1436) was a Voivode of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Èara RomâneascÄ, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geograp ...
, an Ottoman vassal was installed. King Sigismund Sigismund (variants: Sigmund, Siegmund) is a German proper name, meaning "protection through victory", from Old High German ''sigu'' "victory" + ''munt'' "hand, protection". Tacitus latinises it '' Segimundus''. There appears to be an older form of ...
of Hungary arranged for Aldea's overthrow and replacement with his own vassal, Vlad II Dracul
Vlad II ( ro, Vlad al II-lea), also known as Vlad Dracul () or Vlad the Dragon (before 1395 â November 1447), was Voivode of Wallachia from 1436 to 1442, and again from 1443 to 1447. He is internationally known as the father of Vlad the Im ...
.
A series of anti-Ottoman offensives were carried by the Voivode of Transylvania
The Voivode of Transylvania (german: Vojwode von Siebenbürgen;Fallenbüchl 1988, p. 77. hu, erdélyi vajda;Zsoldos 2011, p. 36. la, voivoda Transsylvaniae; ro, voievodul Transilvaniei) was the highest-ranking official in Transylvania wit ...
, John Hunyadi
John Hunyadi (, , , ; 1406 â 11 August 1456) was a leading Hungarian military and political figure in Central and Southeastern Europe during the 15th century. According to most contemporary sources, he was the member of a noble family of ...
. Hunyadi's forces soundly defeated the Turks in 1441 and 1442. A smaller crusading force commanded by Hunyadi, consisting of Hungarians, Wallachians under Vlad Dracul, Serbs, and a large contingent of German and French knights crossed the Danube into Serbia, defeated two Ottoman armies, captured Niš
NiÅ¡ (; sr-Cyrl, ĞиÑ, ; names in other languages) is the third largest city in Serbia and the administrative center of the NiÅ¡ava District. It is located in southern part of Serbia. , the city proper has a population of 183,164, while ...
, crossed the Balkan Mountains in winter, and advanced as far as Sofia
Sofia ( ; bg, СоÑиÑ, Sofiya, ) is the capital and largest city of Bulgaria. It is situated in the Sofia Valley at the foot of the Vitosha mountain in the western parts of the country. The city is built west of the Iskar river, and h ...
. The Turkish sultan Murad II
Murad II ( ota, Ù
راد ثاÙÙ, MurÄd-ı sÄnÄ«, tr, II. Murad, 16 June 1404 â 3 February 1451) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1444 and again from 1446 to 1451.
Murad II's reign was a period of important economic deve ...
, faced with revolts in Albania
Albania ( ; sq, Shqipëri or ), or , also or . officially the Republic of Albania ( sq, Republika e Shqipërisë), is a country in Southeastern Europe. It is located on the Adriatic and Ionian Seas within the Mediterranean Sea and shares ...
and the Peloponnese, negotiated with the crusaders, signing a ten-year truce at Edirne in 1444 that recognized Serbian independence and formally released Wallachia from Ottoman vassalage.
 In 1444 Pope Eugenius urged the crusade's renewal, and Hunyadi marched eastward along the southern bank of the Danube, through northern Bulgaria, toward the
In 1444 Pope Eugenius urged the crusade's renewal, and Hunyadi marched eastward along the southern bank of the Danube, through northern Bulgaria, toward the Black Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. The crusaders arrived at Varna in November 1444 only to discover that Murad II had assembled a powerful army to meet them. In the ensuing Battle of Varna
The Battle of Varna took place on 10 November 1444 near Varna in eastern Bulgaria. The Ottoman Army under Sultan Murad II (who did not actually rule the sultanate at the time) defeated the Hungarianâ Polish and Wallachian armies commanded ...
, king Wladislaw of Poland and Hungary was killed and the crusader army was completely destroyed. Hunyadi escaped with a small portion of his troops, and was elected regent
A regent (from Latin : ruling, governing) is a person appointed to govern a state '' pro tempore'' (Latin: 'for the time being') because the monarch is a minor, absent, incapacitated or unable to discharge the powers and duties of the monarchy ...
of Hungary in 1446.
In 1447 the Turks campaigned in Albania against Skanderbeg
, reign = 28 November 1443 â 17 January 1468
, predecessor = Gjon Kastrioti
, successor = Gjon Kastrioti II
, spouse = Donika Arianiti
, issue = Gjon Kastrioti II
, royal house = Kastrioti
, father ...
's rebels, but operations were cut short by news of a new crusader invasion led by Hunyadi. The crusaders, joined by troops sent by Skanderbeg and Voivode Vladislav II of Wallachia
Vladislav II (died 20 August 1456) was a voivode of the principality of Wallachia, from 1447 to 1448, and again from 1448 to 1456. The way Vladislav II came to the throne is debatable. The most accepted view is that Vladislav assassinated Vl ...
(1447â56), Hunyadi's Wallachian vassal met the Ottoman army in October 1448 at Kosovo Polje
Fushë Kosova ( sq-definite, Fushë Kosovë), or Kosovo Polje ( sr-Cyrl, ĞоÑово ĞоÑе, "Kosovo Field"), is a town and municipality located in the District of Pristina in central Kosovo. According to the 2011 census, the town of Fushë Ko ...
but were defeated.
Hunyadi secured victory at the Battle of Belgrade in 1456, where his much smaller army defeated Ottoman Sultan Mehmet II
Mehmed II ( ota, Ù
ØÙ
د ثاÙÙ, translit=Meḥmed-i s̱ÄnÄ«; tr, II. Mehmed, ; 30 March 14323 May 1481), commonly known as Mehmed the Conqueror ( ota, اب٠اÙÙتØ, EbÅ«'l-fetḥ, lit=the Father of Conquest, links=no; tr, Fâtih Su ...
, securing Hungary's southern border. However, Hunyadi died of the plague
Plague or The Plague may refer to:
Agriculture, fauna, and medicine
*Plague (disease), a disease caused by ''Yersinia pestis''
* An epidemic of infectious disease (medical or agricultural)
* A pandemic caused by such a disease
* A swarm of pe ...
in his camp shortly after the battle. His son, Matthias Corvinus
Matthias Corvinus, also called Matthias I ( hu, Hunyadi Mátyás, ro, Matia/Matei Corvin, hr, Matija/MatijaÅ¡ Korvin, sk, Matej KorvÃn, cz, Matyáš KorvÃn; ), was King of Hungary and Croatia from 1458 to 1490. After conducting several m ...
would become king of Hungary in 1458.
 Wallachia, led by
Wallachia, led by Vlad III the Impaler
Vlad III, commonly known as Vlad the Impaler ( ro, Vlad ÈepeÈ ) or Vlad Dracula (; ro, Vlad DrÄculea ; 1428/311476/77), was Voivode of Wallachia three times between 1448 and his death in 1476/77. He is often considered one of the most imp ...
(1456â1462, born in SighiÅoara, three-time voivode) stopped paying tribute to the Ottomans in 1459 and in the winter of 1461 to 1462 Vlad crossed the Danube and devastated Northern Bulgaria and Dobruja, leaving over 20,000 dead. In response, Sultan Mehmed II raised an army of around 60,000 troops and 30,000 irregulars and headed towards Wallachia in the spring of 1462. With his army of 20,000â30,000 men Vlad was unable to stop the Turks from entering Wallachia and occupying the capital TârgoviÈte
TârgoviÈte (, alternatively spelled ''TîrgoviÈte''; german: Tergowisch) is a city and county seat in DâmboviÈa County, Romania. It is situated north-west of Bucharest, on the right bank of the IalomiÈa River.
TârgoviÈte was one of the ...
(4 June 1462), so he resorted to organizing small attacks and ambushes on the Turks. The most important of these attacks took place on the night of 16â17 June, when Vlad and some of his men allegedly entered the main Turkish camp (wearing Ottoman disguises) and attempted to assassinate Mehmed. The Turks eventually installed Vlad's brother, Radu the Handsome, as the new voivode; he gathered support from the nobility and chased Vlad to Transylvania, and by August 1462 he had struck a deal with the Hungarian Crown.
Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic alphabet, Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Ğемлѧ ĞолдавÑкаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία Ïá¿Ï ÎολδαβίαÏ) is a historical region and for ...
located in the extreme northeast, beyond Wallachia, was spared from problems with the Ottomans until 1420, when Mehmed I
Mehmed I ( 1386 â 26 May 1421), also known as Mehmed Ãelebi ( ota, ÚÙØ¨Û Ù
ØÙ
د, "the noble-born") or KiriÅçi ( el, ÎÏ
ÏιÏζήÏ, Kyritzis, "lord's son"), was the Ottoman sultan from 1413 to 1421. The fourth son of Sultan Bayezid ...
first raided Moldavia after suppressing a rebellion. During the 1450s and 1440s the principality was wracked by civil wars, of which Sultan Murad II
Murad II ( ota, Ù
راد ثاÙÙ, MurÄd-ı sÄnÄ«, tr, II. Murad, 16 June 1404 â 3 February 1451) was the sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1421 to 1444 and again from 1446 to 1451.
Murad II's reign was a period of important economic deve ...
took advantage. As the state weakened, voivode Peter Aron (1455â57) accepted Ottoman suzerainty and agreed to pay tribute, but, given Moldavia's distance from Ottoman borders, his acts were merely symbolic.
 Stephen the Great initially used the Ottoman vassalage inherited from his father as a tool against Hungary, Moldavia's traditional enemy. He participated in Mehmed II's invasion of Wallachia against his cousin Vlad the Impaler in 1462 because, at the time, Vlad was a Hungarian ally. An exceptional military commander and organizer, Stephen captured the Danube commercial city of Chilia from Wallachia in 1465 and defeated a Hungarian invasion of his state in 1467 at the
Stephen the Great initially used the Ottoman vassalage inherited from his father as a tool against Hungary, Moldavia's traditional enemy. He participated in Mehmed II's invasion of Wallachia against his cousin Vlad the Impaler in 1462 because, at the time, Vlad was a Hungarian ally. An exceptional military commander and organizer, Stephen captured the Danube commercial city of Chilia from Wallachia in 1465 and defeated a Hungarian invasion of his state in 1467 at the Battle of Baia
The Battle of Baia ( ro, BÄtÄlia de la Baia; hu, moldvabányai csata) was fought on December 15, 1467, between Moldavian prince Stephen the Great and the Hungarian king, Matthias Corvinus. The battle was the last Hungarian attempt to subdue ...
. As his successes both on the battlefield and in imposing his authority within Moldavia grew, Stephen ceased paying the annual tribute to the Ottomans, and his relationship with Mehmed II deteriorated. He invaded Wallachia in 1474 and ousted its prince, who was Mehmed's vassal. In response, Mehmed demanded that Stefan resume his tribute payments and turn over the city of Chilia as well. Stefan refused and soundly repulsed Mehmed's subsequent punitive invasion of Moldavia in early 1475 near Vaslui
Vaslui (), a city in eastern Romania, is the seat of Vaslui County, in the historical region of Western Moldavia. The city administers five villages: Bahnari, Brodoc, Moara Grecilor, Rediu, and ViiÈoara.
History
Archaeological surveys indicate ...
.
Stephen realized that Mehmed would seek to avenge the defeat, so he sought Hungarian aid by becoming the vassal of Matthias Corvinus. Mehmed personally led an invasion of Moldavia in 1476, and his forces plundered the country up to Suceava, Stephen's capital, winning the Battle of Valea Alba on the way. However, all of Stephen's fortresses held fast, and a lack of provisions and an outbreak of cholera among the Ottoman troops forced Mehmed to retire, and Stefan went on the counteroffensive. With Hungarian help, he pushed forth into Wallachia in 1476, reinstalled Vlad the Impaler on the Wallachian throne, and spent the next nine years fighting a heroic border war with the Ottomans. Stefan's efforts were the primary reason that the two Romanian Principalities maintained their independence and did not suffer the fate of the other Ottoman vassal states south of the Danube. During the last years of his rule, Stephen defeated a Polish invasion at Codrii Cosminului in 1497 and, by the time of his death, Moldavia was de facto independent.
Principality of Romania (1866â1881)
 The
The Romanian War of Independence
The Romanian War of Independence is the name used in Romanian historiography to refer to the Russo-Turkish War (1877â78), following which Romania, fighting on the Russian side, gained independence from the Ottoman Empire. On , Romania and the R ...
was a military conflict from 1877 to 1878. Fought as a part of the larger Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or OttomanâRussian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
, the conflict saw the Principality of Romania
The United Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia ( ro, Principatele Unite ale Moldovei Èi ÈÄrii RomâneÈti), commonly called United Principalities, was the personal union of the Principality of Moldavia and the Principality of Wallachia, ...
, at the time a nominal vassal of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, ĞθÏμανική ÎÏ
ÏοκÏαÏοÏία, OthÅmanikÄ Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University) ...
, gain its independence from the Sublime Porte.
Kingdom of Romania (1881â1947)
The Kingdom of Romania was an active belligerent in the following military conflicts: * 1907 Romanian Peasants' Revolt (1907) *Second Balkan War
The Second Balkan War was a conflict which broke out when Bulgaria, dissatisfied with its share of the spoils of the First Balkan War, attacked its former allies, Serbia and Greece, on 16 ( O.S.) / 29 (N.S.) June 1913. Serbian and Greek armies r ...
(1913)
* World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, the United States, and the Ottoman Empire, with fightin ...
(1916â17; 1918)
* PolishâUkrainian War
The PolishâUkrainian War, from November 1918 to July 1919, was a conflict between the Second Polish Republic and Ukrainian forces (both the West Ukrainian People's Republic and Ukrainian People's Republic). The conflict had its roots in ethn ...
(1918â1919)
* HungarianâRomanian War
The HungarianâRomanian War was fought between Hungary and Romania from 13 November 1918 to 3 August 1919. The conflict had a complex background, with often contradictory motivations for the parties involved.
The Allies of World War I intended ...
(1919)
* Bender Uprising (1919)
* Legionnaires' rebellion and Bucharest pogrom
Between 21 and 23 January 1941, a rebellion of the Iron Guard paramilitary organization, whose members were known as Legionnaires, occurred in Bucharest, Romania. As their privileges were being gradually removed by the ''ConducÄtor'' Ion Ant ...
(1941)
* World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countriesâincluding all of the great powersâforming two opposing ...
(1941â1945)
Communist Romania (1947â1989)
 The Romanian People's Republic (1947â1965) and the
The Romanian People's Republic (1947â1965) and the Socialist Republic of Romania
The Socialist Republic of Romania ( ro, Republica SocialistÄ România, RSR) was a MarxistâLeninist one-party socialist state that existed officially in Romania from 1947 to 1989. From 1947 to 1965, the state was known as the Romanian Peop ...
(1965â1991) were active belligerents in the following military conflicts:
* Romanian anti-communist resistance movement
The Romanian anti-communist resistance movement was active from the late 1940s to the mid-1950s, with isolated individual fighters remaining at large until the early 1960s. Armed resistance was the first and most structured form of resistance a ...
(1947â1962)
* Romanian Revolution
The Romanian Revolution ( ro, RevoluÈia RomânÄ), also known as the Christmas Revolution ( ro, RevoluÈia de CrÄciun), was a period of violent civil unrest in Romania during December 1989 as a part of the Revolutions of 1989 that occurred ...
(1989)
Present-day Romania (1989âpresent)
The present state ofRomania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central, Eastern, and Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, Serbia to the southwest, Moldova to the east, and ...
and the Romanian Armed Forces
The Land Forces, Air Force and Naval Forces of Romania are collectively known as the Romanian Armed Forces ( ro, ForÈele Armate Române or ''Armata RomânÄ''). The current Commander-in-chief is Lieutenant General Daniel Petrescu who is manage ...
have participated in the following military conflicts:
* War in Afghanistan
War in Afghanistan, Afghan war, or Afghan civil war may refer to:
*Conquest of Afghanistan by Alexander the Great (330 BC â 327 BC)
* Muslim conquests of Afghanistan (637â709)
*Conquest of Afghanistan by the Mongol Empire (13th century), see al ...
(2001â2021)
* Iraq War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Iraq War {{Nobold, {{lang, ar, Øرب اÙعرا٠(Arabic) {{Nobold, {{lang, ku, Ø´ÛÚÛ Ø¹Ûرا٠( Kurdish)
, partof = the Iraq conflict and the War on terror
, image ...
(2003â2009)
* 2011 military intervention in Libya
On 19 March 2011, a multi-state NATO-led coalition began a military intervention in Libya, to implement United Nations Security Council Resolution 1973, in response to events during the First Libyan Civil War. With ten votes in favour and fiv ...
(2011)
See also
* List of wars involving RomaniaReferences
Notes
Citations
Further reading
UNRV History â Dacia
*Breviarium historiae Romanae by Eutropius
External links
Dromichaites, philological and linguistical aspects
a
{{Military history of Europe