Microblade technology on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Microblade technology is a period of technological development marked by the creation and use of small stone blades, which are produced by chipping silica-rich stones like 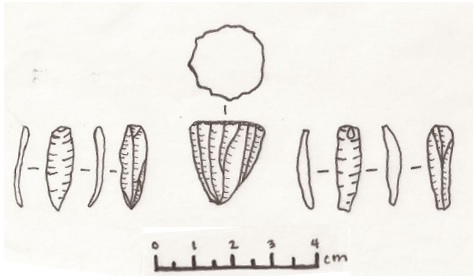
chert
Chert () is a hard, fine-grained sedimentary rock composed of microcrystalline or cryptocrystalline quartz, the mineral form of silicon dioxide (SiO2). Chert is characteristically of biological origin, but may also occur inorganically as a prec ...
, quartz
Quartz is a hard, crystalline mineral composed of silica (silicon dioxide). The atoms are linked in a continuous framework of SiO4 silicon-oxygen tetrahedra, with each oxygen being shared between two tetrahedra, giving an overall chemical form ...
, or obsidian
Obsidian () is a naturally occurring volcanic glass formed when lava extrusive rock, extruded from a volcano cools rapidly with minimal crystal growth. It is an igneous rock.
Obsidian is produced from felsic lava, rich in the lighter elements s ...
. Blades are a specialized type of lithic flake
In archaeology, a lithic flake is a "portion of rock removed from an objective piece by percussion or pressure,"Andrefsky, W. (2005) ''Lithics: Macroscopic Approaches to Analysis''. 2d Ed. Cambridge, Cambridge University Press and may also be refe ...
that are at least twice as long as they are wide. An alternate method of defining blades focuses on production features, including parallel lateral edges and dorsal scars, a lack of cortex, a prepared platform with a broad angle, and a proximal bulb of percussion. Microblades are generally less than 50 mm long in their finished state.

History
The geographic origin of microblades is poorly understood, with differing theories posing origins in Southern Siberia, Northern China, or the PHSK (Paleo-Hokkaido-Sakhalin-Kurile) peninsula, with dates ranging from over 30,000 BP to as little as 18,000 BP. Because microblade technology is economical (using less raw material than other technologies), relatively easy to make, and extremely portable, it came into widespread use over vast parts of northern Asia and northeasternSiberia
Siberia ( ; rus, Сибирь, r=Sibir', p=sʲɪˈbʲirʲ, a=Ru-Сибирь.ogg) is an extensive geographical region, constituting all of North Asia, from the Ural Mountains in the west to the Pacific Ocean in the east. It has been a part of ...
during and after the Ice Age
An ice age is a long period of reduction in the temperature of Earth's surface and atmosphere, resulting in the presence or expansion of continental and polar ice sheets and alpine glaciers. Earth's climate alternates between ice ages and gree ...
. Microblade technology was very efficient for hunting because it used light, barbed spear
A spear is a pole weapon consisting of a shaft, usually of wood, with a pointed head. The head may be simply the sharpened end of the shaft itself, as is the case with fire hardened spears, or it may be made of a more durable material fasten ...
s. During the Ice Age, hunter-gatherers suffered from shortage of food resources, so they had to move more frequently. Microblade is suitable for high mobility and rapid weapon production, as well as reducing failure of hunting and lost or damaged weapons. In other words, in the resource-limited environment of the LGM, hunter-gatherers invested more time acquiring better raw materials and developing the technique of lithic manufacture. Barbed tips opened wounds and the resulting blood loss killed prey faster and with less loss of hunting equipment than traditional spears.
These changes in lithic technology appear to have been adaptations to reduced resource availability due to climate changes during the Last Glacial Maximum and Younger Dryas allowing for more efficient sustenance strategies. An important site for learning more about the diverse adaptations of the microblade is Shuidonggou Locality 12 (SDG12). It was at this site that microblades were found along with diverse artifacts: needles, awls, and a bone knife handle. This handle is a big indicator that microblades were used for multiple purposes, and no longer were exclusive to hunting. In at least one site in Northern China, microblades are also found in context with heat shattered and burned stone, usually evidence for stone-boiling practices, another resource intensification strategy aimed at recovering more nutrients from food resources via cooking.
The first Native Americans brought this technology with them across the Bering Land Bridge
Beringia is defined today as the land and maritime area bounded on the west by the Lena River in Russia; on the east by the Mackenzie River in Canada; on the north by 72 degrees north latitude in the Chukchi Sea; and on the south by the tip of ...
to North America. At least six independent Native American groups used microblade technology, including the Poverty Point
Poverty Point State Historic Site/Poverty Point National Monument (french: Pointe de Pauvreté; 16 WC 5) is a prehistoric earthwork constructed by the Poverty Point culture, located in present-day northeastern Louisiana, though evidence of t ...
/Jaketown, Hopewell culture
The Hopewell tradition, also called the Hopewell culture and Hopewellian exchange, describes a network of precontact Native American cultures that flourished in settlements along rivers in the northeastern and midwestern Eastern Woodlands from ...
, Tikal
Tikal () (''Tik’al'' in modern Mayan orthography) is the ruin of an ancient city, which was likely to have been called Yax Mutal, found in a rainforest in Guatemala. It is one of the largest archeological sites and urban centers of the pre-Co ...
Maya
Maya may refer to:
Civilizations
* Maya peoples, of southern Mexico and northern Central America
** Maya civilization, the historical civilization of the Maya peoples
** Maya language, the languages of the Maya peoples
* Maya (Ethiopia), a populat ...
, and Northwest Coast peoples. Specialized craftspeople manufactured millions of microblades in the Mississippian chiefdom of Cahokia
The Cahokia Mounds State Historic Site ( 11 MS 2) is the site of a pre-Columbian Native American city (which existed 1050–1350 CE) directly across the Mississippi River from modern St. Louis, Missouri. This historic park lies in south-w ...
, in Illinois, as did Chumash (tribe)
The Chumash are a Native American people of the central and southern coastal regions of California, in portions of what is now San Luis Obispo, Santa Barbara, Ventura and Los Angeles counties, extending from Morro Bay in the north to Malibu ...
craftspeople in California's Northern Channel Islands. In both of these cases, microblades were sharpened to a point and attached to the end of sticks, creating microdrills. These microdrills were used to drill holes in marine shells to create beads. Shell beads were used as money among the Chumash, and as a result microblades were a vital part of the Chumash economy.
See also
*Microburin
A microburin is a characteristic waste product from manufacture of lithic tools — sometimes confused with an authentic burin — which is characteristic of the Mesolithic, but which has been recorded from the end of the Upper Paleolithic until ...
References
Bibliography
* * {{DEFAULTSORT:Microblade Technology Hunting equipment Lithics Archaeological artefact types Tools Primitive technology Stone Age