Michael the Brave on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Michael the Brave ( ro, Mihai Viteazul or ; 1558 – 9 August 1601), born as Mihai Pătrașcu, was the Prince of
 Not long after Michael became Prince of Wallachia, he turned against the Ottoman Empire. The next year he joined the
Not long after Michael became Prince of Wallachia, he turned against the Ottoman Empire. The next year he joined the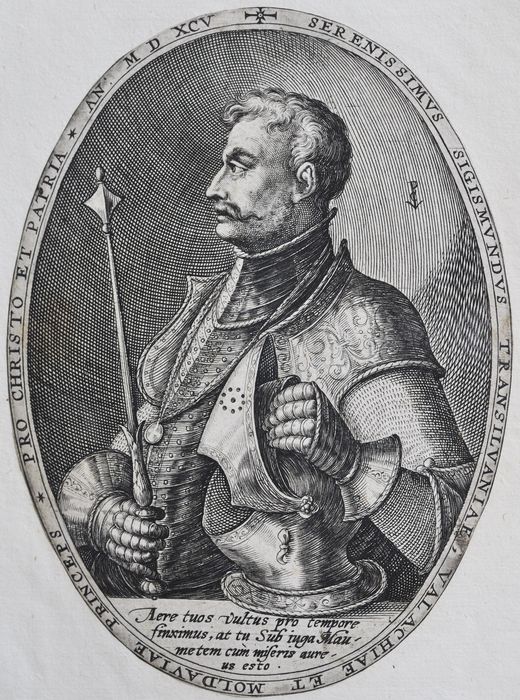  In 1595,
In 1595,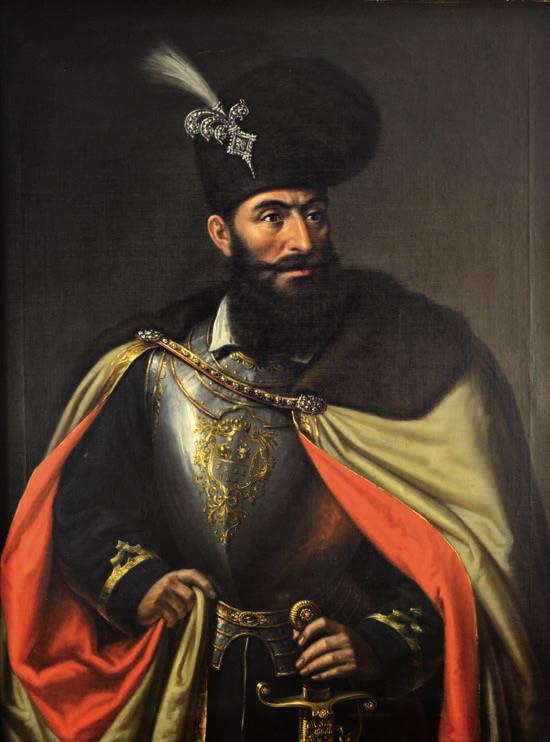  Boyars could no longer be executed without the knowledge and approval of the Transylvanian Prince and, if convicted for treason, their fortunes could no longer be confiscated. Apparently Michael was displeased with the final form of the treaty negotiated by his envoys, but was forced to comply. Prince Michael said in a conversation with the Polish envoy Lubieniecki: ''... they did not proceed as stated in their instructions but as their own good required and obtained privileges for themselves.'' He would try to avoid the obligations imposed on him for the rest of his reign.Giurescu, p. 186.
During his reign, Michael relied heavily on the loyalty and support of a group of Oltenian lords, the most important of whom were Buzescu Brothers (Romanian: ''Frații Buzești'') and his own relatives on his mother's side, the Cantacuzinos. He consequently protected their interests throughout his reign; for example, he passed a law binding serfs to lands owned by aristocrats. From the standpoint of religious jurisdiction, the Treaty of Alba Iulia had another important consequence: it placed all the
Boyars could no longer be executed without the knowledge and approval of the Transylvanian Prince and, if convicted for treason, their fortunes could no longer be confiscated. Apparently Michael was displeased with the final form of the treaty negotiated by his envoys, but was forced to comply. Prince Michael said in a conversation with the Polish envoy Lubieniecki: ''... they did not proceed as stated in their instructions but as their own good required and obtained privileges for themselves.'' He would try to avoid the obligations imposed on him for the rest of his reign.Giurescu, p. 186.
During his reign, Michael relied heavily on the loyalty and support of a group of Oltenian lords, the most important of whom were Buzescu Brothers (Romanian: ''Frații Buzești'') and his own relatives on his mother's side, the Cantacuzinos. He consequently protected their interests throughout his reign; for example, he passed a law binding serfs to lands owned by aristocrats. From the standpoint of religious jurisdiction, the Treaty of Alba Iulia had another important consequence: it placed all the 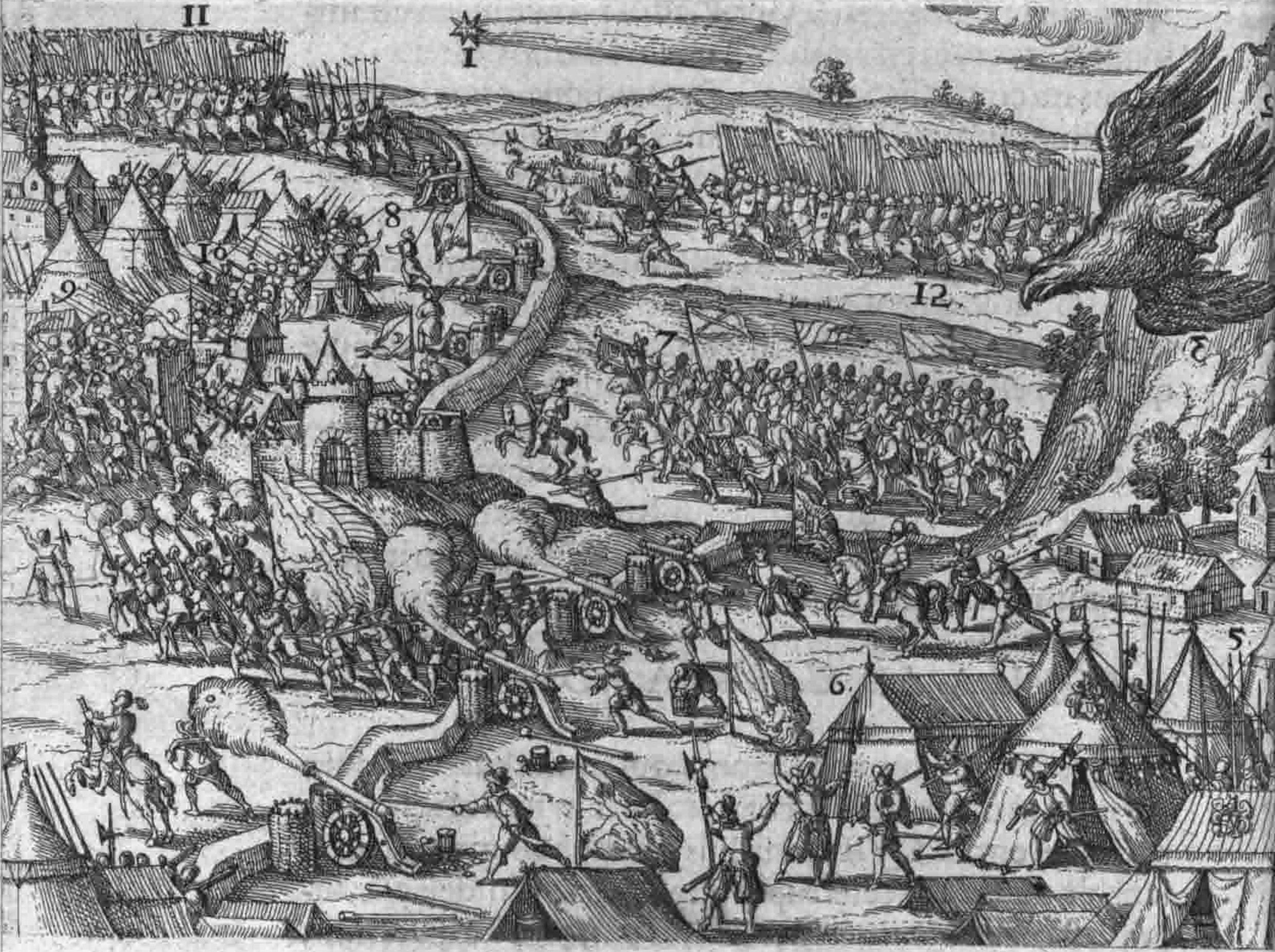
 During this period, the Ottoman army, based in
During this period, the Ottoman army, based in

 In April 1598, Sigismund resigned as
In April 1598, Sigismund resigned as  On 18 October Michael won a decisive victory against the army of prince-cardinal Andrew Báthory at the Battle of Șelimbăr, giving him control of Transylvania. As he retreated from the battle, Andrew Báthory was killed by anti-Báthory
On 18 October Michael won a decisive victory against the army of prince-cardinal Andrew Báthory at the Battle of Șelimbăr, giving him control of Transylvania. As he retreated from the battle, Andrew Báthory was killed by anti-Báthory  In Transylvania Michael used the following signature on official documents: ''Michael Valachiae Transalpinae Woivoda, Sacrae Caesareae Regiae Majestatis Consiliarius per Transylvaniam Locumtenens, cis transylvaniam partium eius super exercitu Generalis Capitaneus".'' ("Michael, voivode of Wallachia, the councillor of His Majesty the Emperor and the King, his deputy in Transylvania and General Captain of his troops from Transylvania.")
When Michael entered Transylvania, he did not immediately free or grant rights to the Romanian inhabitants, who were primarily peasants but, nevertheless, constituted a significant proportion of the population. Michael demonstrated his support by upholding the Union of the Three Nations, which recognized only the traditional rights and privileges of the Hungarians, Székelys and
In Transylvania Michael used the following signature on official documents: ''Michael Valachiae Transalpinae Woivoda, Sacrae Caesareae Regiae Majestatis Consiliarius per Transylvaniam Locumtenens, cis transylvaniam partium eius super exercitu Generalis Capitaneus".'' ("Michael, voivode of Wallachia, the councillor of His Majesty the Emperor and the King, his deputy in Transylvania and General Captain of his troops from Transylvania.")
When Michael entered Transylvania, he did not immediately free or grant rights to the Romanian inhabitants, who were primarily peasants but, nevertheless, constituted a significant proportion of the population. Michael demonstrated his support by upholding the Union of the Three Nations, which recognized only the traditional rights and privileges of the Hungarians, Székelys and
 The Moldavian Prince
The Moldavian Prince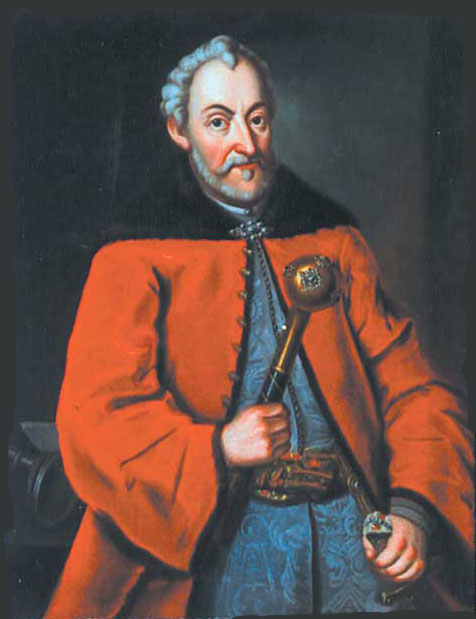  On 28 February 1600 Michael met with Polish envoys in Brașov. He was willing to recognise the Polish King as his sovereign in exchange for the crown of Moldavia and the recognition of his male heirs' hereditary right over the three principalities, Transylvania, Moldavia, and Wallachia. This did not significantly delay his attack, however; on 14 April 1600 Michael's troops entered Moldavia on multiple routes, the Prince himself leading the main thrust to
On 28 February 1600 Michael met with Polish envoys in Brașov. He was willing to recognise the Polish King as his sovereign in exchange for the crown of Moldavia and the recognition of his male heirs' hereditary right over the three principalities, Transylvania, Moldavia, and Wallachia. This did not significantly delay his attack, however; on 14 April 1600 Michael's troops entered Moldavia on multiple routes, the Prince himself leading the main thrust to

 Michael asked again for assistance from
Michael asked again for assistance from
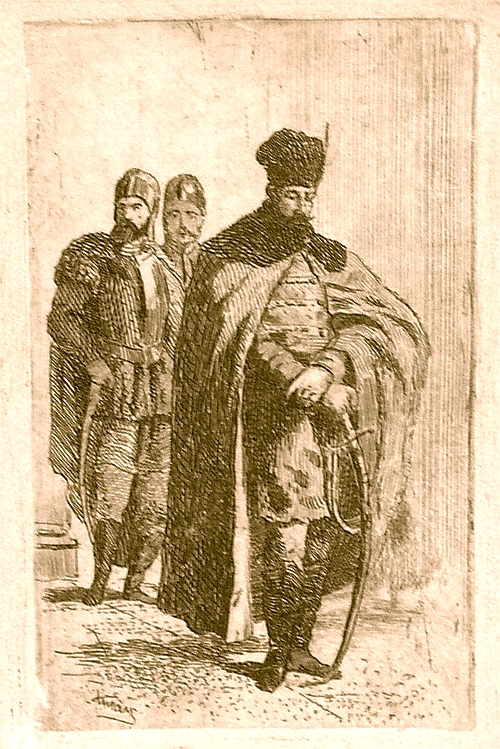 The prince began to be perceived as a ''unifier'' towards the middle of the 19th century. Such an interpretation is completely lacking in the historiography of the 17th-century chroniclers, and even in that of the Transylvanian School around 1800. What they emphasized, apart from the exceptional personality of Michael himself, were the idea of
The prince began to be perceived as a ''unifier'' towards the middle of the 19th century. Such an interpretation is completely lacking in the historiography of the 17th-century chroniclers, and even in that of the Transylvanian School around 1800. What they emphasized, apart from the exceptional personality of Michael himself, were the idea of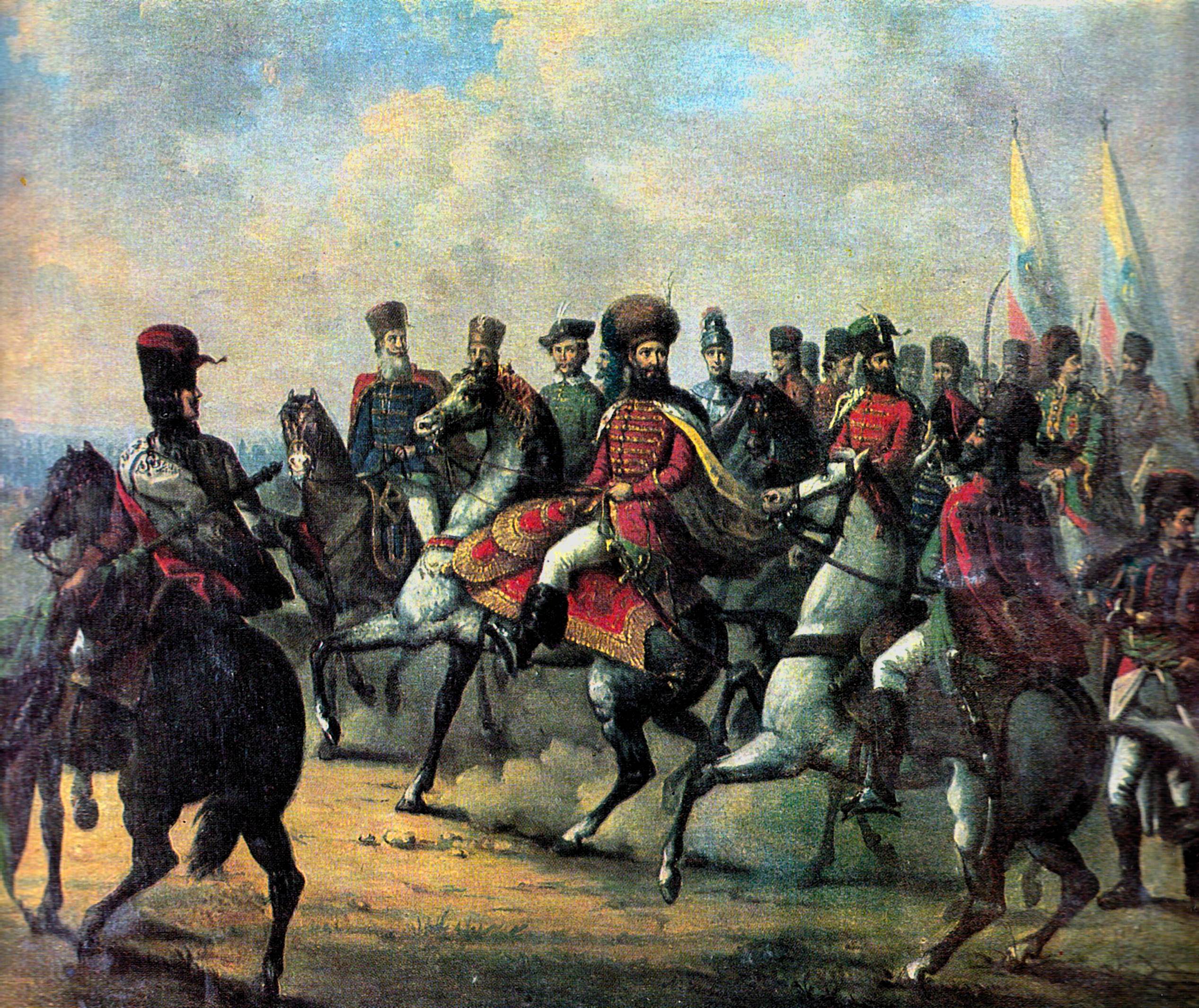 
 Michael is also commemorated by the monks of the Athonite
Michael is also commemorated by the monks of the Athonite
KM # 111
of the Krause Mishler catalog Three major high schools in Romania bear his name: the Mihai Viteazul National College (Bucharest) the and the
 The seal comprises the coats of arms of Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania: in the middle, on a shield the Moldavian urus, above Wallachian
The seal comprises the coats of arms of Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania: in the middle, on a shield the Moldavian urus, above Wallachian
Erdély és Mihály vajda története, 1595-1601. oklevéltárral
Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
(as Michael II, 1593 – 1601), Prince of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
(1600) and ''de facto'' ruler of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
(1599 – 1600). He is considered one of Romania's greatest national heroes. Since the 19th century, Michael the Brave has been regarded by Romanian nationalists
Romanian nationalism is the nationalism which asserts that Romanians are a nation and promotes the cultural unity of Romanians. Its extremist variation is the Romanian ultranationalism. Aristotle KallisGenocide and Fascism: The Eliminationist Dri ...
as a symbol of Romanian unity, as his reign marked the first time all principalities inhabited by Romanians were under the same ruler.
His rule over Wallachia began in the autumn of 1593. Two years later, war with the Ottomans began, a conflict in which the Prince fought the Battle of Călugăreni, resulting in a victory against an army nearly three times the size of the army of Michael the Brave, considered one of the most important battles of his reign. Although the Wallachians emerged victorious from the battle, Michael was forced to retreat with his troops and wait for aid from his allies, Prince Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
of Transylvania and Holy Roman Emperor Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
. The war continued until a peace finally emerged in January 1597, but this lasted for only a year and a half. Peace was again reached in late 1599, when Michael was unable to continue the war due to lack of support from his allies. In 1599, Michael won the Battle of Șelimbăr against Andrew Báthory
Andrew Báthory ( hu, Báthory András; pl, Andrzej Batory; 1562 or 1563 – 3 November 1599) was the Cardinal-deacon of Sant'Adriano al Foro from 1584 to 1599, Prince-Bishop of Warmia from 1589 to 1599, and Prince of Transylvania in 1599. His ...
and soon entered Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
, becoming the imperial governor (i.e. ''de facto'' ruler) of Transylvania, under Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
suzerainty. A few months later, Michael's troops invaded Moldavia and reached its capital, Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the second largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical region of Moldavia, it has traditionally ...
. The Moldavian leader Ieremia Movilă
Ieremia Movilă ( pl, Jeremi Mohyła uk, Єремія Могила), (c. 1555 – 10 July 1606) was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia between August 1595 and May 1600, and again between September 1600 and July 10, 1606.
Rule
A boyar of the Movil ...
fled to Poland and Michael was declared Prince of Moldavia. During this period, Michael the Brave changed his seal to represent his personal union of Wallachia, Moldavia, and Transylvania.
The interests of the three neighbouring great powers — the Habsburg monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
, the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
— were damaged by Michael the Brave's achievements. Although he acknowledged the suzerainty of Rudolf II, Michael the Brave continued to negotiate his official position in Transylvania, pleading for direct rule instead of being imperial governor. Michael kept the control of all three provinces for less than a year before the Hungarian nobility of Transylvania rose against him in a series of revolts with the support of the Austrian army commanded by the Italian General Giorgio Basta, defeating Michael the Brave at the Battle of Mirăslău, forcing the prince to leave Transylvania and retreat to Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
with his remaining troops, while the forces of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth entered Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
and defeated the forces loyal to Michael the Brave, restoring Ieremia Movilă
Ieremia Movilă ( pl, Jeremi Mohyła uk, Єремія Могила), (c. 1555 – 10 July 1606) was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia between August 1595 and May 1600, and again between September 1600 and July 10, 1606.
Rule
A boyar of the Movil ...
on the throne. The Polish army led by Jan Zamoyski
Jan Sariusz Zamoyski ( la, Ioannes Zamoyski de Zamoscie; 19 March 1542 – 3 June 1605) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, and the 1st '' ordynat'' of Zamość. He served as the Royal Secretary from 1565, Deputy Chancellor from 1576, Grand Cha ...
also advanced in eastern Wallachia and established Simion Movilă as ruler. Forces loyal to Michael remained only in Oltenia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
.
Michael the Brave then left for Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
, seekeing audience with Emperor Rudolf II; however, the emperor refused to allow him audience. But General Giorgio Basta's governance of Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
faced significant opposition from the Hungarian nobility, leading to the reinstallation of Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
, who turned his back on Emperor Rudolf II and declared suzerainty to the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
after receiving substantial military support. This led to Emperor Rudolf II accepting Michael the Brave's audience and providing him with 100,000 florins to rebuild his army. Meanwhile, forces loyal to Michael in Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
led by his son, Nicolae Pătrașcu, drove Simion Movilă out of Moldavia and prepared to reenter Transylvania. Michael the Brave, allied with Giorgio Basta, defeated the Hungarian army at the Battle of Guruslău. A few days later Basta, who sought to control Transylvania himself, executed the assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Michael by order of the Habsburg Emperor Rudolf II.
Early life
Michael was born under the family name of ''Pătrașcu''. In 1601, during a stay in Prague, he was portrayed by the painter Aegidius Sadeler, who mentioned on the portrait the words ''aetatis XLIII'' ("in the 43rd year of life"), which indicates 1558 as the year of Michael's birth. Very little is known about his childhood and early years as an adult. He is argued by most historians to have been the illegitimate son of WallachianPrince
A prince is a male ruler (ranked below a king, grand prince, and grand duke) or a male member of a monarch's or former monarch's family. ''Prince'' is also a title of nobility (often highest), often hereditary, in some European states. ...
Pătrașcu cel Bun (Pătrașcu the Good), of the Drăculești branch of the House of Basarab
The House of Basarab (also Bazarab or Bazaraad, ro, Basarab ) was a ruling family of debated Cuman origin, Terterids and Shishmanids) and the Wallachian dynasty (Basarabids). They also played an active role in Byzantium, Hungary and Serbia, wi ...
, while others believe he merely invented his descent in order to justify his rule. His mother was , a member of the Kantakouzenoi
The House of Kantakouzenos ( Kantakouzenoi; el, Καντακουζηνός, pl. Καντακουζηνοί), Latinized as Cantacuzenus and anglicized as Cantacuzene, was one of the most prominent Greek noble families of the Byzantine Empire
...
, a noble family present in Wallachia and Moldavia, and allegedly descended from the Byzantine Emperor
This is a list of the Byzantine emperors from the foundation of Constantinople in 330 AD, which marks the conventional start of the Eastern Roman Empire, to its fall to the Ottoman Empire in 1453 AD. Only the emperors who were recognized as ...
John VI Kantakouzenos
John VI Kantakouzenos or Cantacuzene ( el, , ''Iōánnēs Ángelos Palaiológos Kantakouzēnós''; la, Johannes Cantacuzenus; – 15 June 1383) was a Byzantine Greek nobleman, statesman, and general. He served as grand domestic under ...
.
Michael's political rise was quite spectacular, as he became the Ban
Ban, or BAN, may refer to:
Law
* Ban (law), a decree that prohibits something, sometimes a form of censorship, being denied from entering or using the place/item
** Imperial ban (''Reichsacht''), a form of outlawry in the medieval Holy Roman ...
of Mehedinți in 1588, ''stolnic
''Stolnic'' was a ''boier'' (Romanian nobility) rank and the position at the court in the Danubian Principalities of Moldavia and Wallachia. The title approximately corresponds to seneschal and is borrowed from the Slavic title ''stolnik'' (from ...
'' at the court of Mihnea Turcitul
Mihnea II Turcitul ("Mihnea the Turned-Turk"; July 1564 – October 1601) was Prince ( Voivode) of Wallachia between September 1577 and July 1583, and again from April 1585 to May 1591.
The only son of Alexandru II Mircea and Ecaterina Salva ...
by the end of 1588, and Ban of Craiova in 1593 – during the rule of Alexandru cel Rău
Alexandru III cel Rău (Alexander III the Bad, died 20 March 1597) was the Prince of Wallachia between November 1592 and 1593. He was the son of Bogdan Lăpușneanu, former Prince of Moldavia. Although Alexandru had in his government both local B ...
. The latter had him swear before 12 boyar
A boyar or bolyar was a member of the highest rank of the feudal nobility in many Eastern European states, including Kievan Rus', Bulgaria, Russia, Wallachia and Moldavia, and later Romania, Lithuania and among Baltic Germans. Boyars were ...
s that he was not of princely descent. Still, in May 1593 conflict did break out between Alexandru and Michael, who was forced to flee to Transylvania. He was accompanied by his half-brother Radu Florescu, Radu Buzescu and several other supporters. After spending two weeks at the court of Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
, he left for Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
, where with help from his cousin Andronikos Kantakouzenos (the eldest son of Michael "Şeytanoğlu" Kantakouzenos) and Patriarch Jeremiah II he negotiated Ottoman support for his accession to the Wallachian throne. He was supported by the English ambassador in the Ottoman capital, Edward Barton, and aided by a loan of 200,000 florins. Michael was invested Prince by Sultan Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Sa ...
in September 1593 and started his effective rule on 11 October.
Wallachia
 Not long after Michael became Prince of Wallachia, he turned against the Ottoman Empire. The next year he joined the
Not long after Michael became Prince of Wallachia, he turned against the Ottoman Empire. The next year he joined the Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
alliance of Europe
Europe is a large peninsula conventionally considered a continent in its own right because of its great physical size and the weight of its history and traditions. Europe is also considered a Continent#Subcontinents, subcontinent of Eurasia ...
an powers formed by Pope Clement VIII
Pope Clement VIII ( la, Clemens VIII; it, Clemente VIII; 24 February 1536 – 3 March 1605), born Ippolito Aldobrandini, was head of the Catholic Church and ruler of the Papal States from 2 February 1592 to his death in March 1605.
Born ...
against the Turks, and signed treaties with his neighbours: Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
of Transylvania, Aaron the Tyrant of Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
and the Holy Roman Emperor, Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
(see Holy League of Pope Clement VIII). He started a campaign against the Turks in the autumn of 1594, conquering several citadels near the Danube
The Danube ( ; ) is a river that was once a long-standing frontier of the Roman Empire and today connects 10 European countries, running through their territories or being a border. Originating in Germany, the Danube flows southeast for , pa ...
, including Giurgiu
Giurgiu (; bg, Гюргево) is a city in southern Romania. The seat of Giurgiu County, it lies in the historical region of Muntenia. It is situated amongst mud-flats and marshes on the left bank of the Danube facing the Bulgarian city ...
, Brăila
Brăila (, also , ) is a city in Muntenia, eastern Romania, a port on the Danube and the capital of Brăila County. The Sud-Est (development region), ''Sud-Est'' Regional Development Agency is located in Brăila.
According to the 2011 Romanian ...
, Hârșova, and Silistra
Silistra ( bg, Силистра ; tr, Silistre; ro, Silistra) is a town in Northeastern Bulgaria. The town lies on the southern bank of the lower Danube river, and is also the part of the Romanian border where it stops following the Danube. Si ...
, while his Moldavian allies defeated the Turks in Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the second largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical region of Moldavia, it has traditionally ...
and other parts of Moldavia. Mihai continued his attacks deep within the Ottoman Empire, taking the forts of Nicopolis, Ribnic, and Chilia and even reaching as far as Adrianople
Edirne (, ), formerly known as Adrianople or Hadrianopolis ( Greek: Άδριανούπολις), is a city in Turkey, in the northwestern part of the province of Edirne in Eastern Thrace. Situated from the Greek and from the Bulgarian border ...
.
 In 1595,
In 1595, Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
staged an elaborate plot and had Aaron the Tyrant, voivode of Moldavia, removed from power. István Jósika (Báthory's chancellor and an ethnic Romanian) masterminded the operation. Ștefan Răzvan arrested Aron on charges of treason on the night of 24 April (5 May) and sent him to the Transylvanian capital at Alba Iulia
Alba Iulia (; german: Karlsburg or ''Carlsburg'', formerly ''Weißenburg''; hu, Gyulafehérvár; la, Apulum) is a city that serves as the seat of Alba County in the west-central part of Romania. Located on the Mureș River in the historica ...
(Gyulafehérvár) with his family and treasure. Aron would die poisoned by the end of May in the castle of Vinc. Sigismund was forced to justify his actions before the European powers, since Aron had played an active role in the anti-Ottoman coalition. Later on, in the same city of Alba Iulia, Wallachian boyars signed a treaty with Sigismund on Michael's behalf. From the point of view of Wallachian internal politics, the Treaty of Alba Iulia officialized what could be called a ''boyar regime'', reinforcing the already important political power of the noble elite. According to the treaty, a council of 12 great boyars was to take part alongside the voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
in the executive rule of the country.
 Boyars could no longer be executed without the knowledge and approval of the Transylvanian Prince and, if convicted for treason, their fortunes could no longer be confiscated. Apparently Michael was displeased with the final form of the treaty negotiated by his envoys, but was forced to comply. Prince Michael said in a conversation with the Polish envoy Lubieniecki: ''... they did not proceed as stated in their instructions but as their own good required and obtained privileges for themselves.'' He would try to avoid the obligations imposed on him for the rest of his reign.Giurescu, p. 186.
During his reign, Michael relied heavily on the loyalty and support of a group of Oltenian lords, the most important of whom were Buzescu Brothers (Romanian: ''Frații Buzești'') and his own relatives on his mother's side, the Cantacuzinos. He consequently protected their interests throughout his reign; for example, he passed a law binding serfs to lands owned by aristocrats. From the standpoint of religious jurisdiction, the Treaty of Alba Iulia had another important consequence: it placed all the
Boyars could no longer be executed without the knowledge and approval of the Transylvanian Prince and, if convicted for treason, their fortunes could no longer be confiscated. Apparently Michael was displeased with the final form of the treaty negotiated by his envoys, but was forced to comply. Prince Michael said in a conversation with the Polish envoy Lubieniecki: ''... they did not proceed as stated in their instructions but as their own good required and obtained privileges for themselves.'' He would try to avoid the obligations imposed on him for the rest of his reign.Giurescu, p. 186.
During his reign, Michael relied heavily on the loyalty and support of a group of Oltenian lords, the most important of whom were Buzescu Brothers (Romanian: ''Frații Buzești'') and his own relatives on his mother's side, the Cantacuzinos. He consequently protected their interests throughout his reign; for example, he passed a law binding serfs to lands owned by aristocrats. From the standpoint of religious jurisdiction, the Treaty of Alba Iulia had another important consequence: it placed all the Eastern Orthodox
Eastern Orthodoxy, also known as Eastern Orthodox Christianity, is one of the three main branches of Chalcedonian Christianity, alongside Catholicism and Protestantism.
Like the Pentarchy of the first millennium, the mainstream (or " canonical ...
bishops in Transylvania under the jurisdiction of the Metropolitan Seat of Târgoviște
Târgoviște (, alternatively spelled ''Tîrgoviște''; german: Tergowisch) is a city and county seat in Dâmbovița County, Romania. It is situated north-west of Bucharest, on the right bank of the Ialomița River.
Târgoviște was one of ...
.

 During this period, the Ottoman army, based in
During this period, the Ottoman army, based in Ruse
Ruse may refer to:
Places
*Ruse, Bulgaria, a major city of Bulgaria
**Ruse Municipality
**Ruse Province
** 19th MMC – Ruse, a constituency
*Ruše, a town and municipality in north-eastern Slovenia
* Ruše, Žalec, a small settlement in east-cen ...
, was preparing to cross the Danube and undertake a major attack. Michael was quickly forced to retreat and the Ottoman forces started to cross the Danube on 4 August 1595. As his army was outnumbered, Michael avoided carrying the battle in open field, and decided to give battle on a marshy field located near the village of Călugăreni on the Neajlov river. The Battle of Călugăreni started on 13 August and Michael defeated the Ottoman army led by Sinan Pasha. Despite the victory, he retreated to his winter camp in Stoienești because he had too few troops to mount a full-scale war against the remaining Ottoman forces. He subsequently joined forces with Sigismund Báthory's 40,000-man army (led by Stephen Bocskai) and counterattacked the Ottomans, freeing the towns of Târgoviște
Târgoviște (, alternatively spelled ''Tîrgoviște''; german: Tergowisch) is a city and county seat in Dâmbovița County, Romania. It is situated north-west of Bucharest, on the right bank of the Ialomița River.
Târgoviște was one of ...
(8 October), Bucharest
Bucharest ( , ; ro, București ) is the capital and largest city of Romania, as well as its cultural, industrial, and financial centre. It is located in the southeast of the country, on the banks of the Dâmbovița River, less than north o ...
(12 October) and Brăila
Brăila (, also , ) is a city in Muntenia, eastern Romania, a port on the Danube and the capital of Brăila County. The Sud-Est (development region), ''Sud-Est'' Regional Development Agency is located in Brăila.
According to the 2011 Romanian ...
, temporarily removing Wallachia from Ottoman suzerainty.
The fight against the Ottomans continued in 1596 when Michael made several incursions south of the Danube at Vidin, Pleven
Pleven ( bg, Плèвен ) is the seventh most populous city in Bulgaria. Located in the northern part of the country, it is the administrative centre of Pleven Province, as well as of the subordinate Pleven municipality. It is the biggest ...
, Nicopolis, and Babadag
Babadag (; tr, Babadağ, "Father Mountain"), formerly known as Babatag, is a town in Tulcea County, Romania, located on a small lake formed by the river Taița, in the densely wooded highlands of Northern Dobruja. One of the several tom ...
, where he was assisted by the local Bulgarians
Bulgarians ( bg, българи, Bǎlgari, ) are a nation and South Slavic ethnic group native to Bulgaria and the rest of Southeast Europe.
Etymology
Bulgarians derive their ethnonym from the Bulgars. Their name is not completely underst ...
during the First Tarnovo Uprising
The First Tarnovo uprising ( bg, Първо търновско въстание, ''Parvo tarnovsko vastanie'') was a Bulgarian uprising against Ottoman rule based in the former Bulgarian capital, Tarnovo, that broke out in 1598 and was severely ...
.
During late 1596, Michael was faced with an unexpected attack from the Tatars
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
, who had destroyed the towns of Bucharest and Buzău. By the time Michael gathered his army to counterattack, the Tatars had speedily retreated and so no battle was fought. Michael was determined to continue the war against the Ottomans, but he was prevented because he lacked support from Sigismund Báthory and Rudolf II. On 7 January 1597 Hasan Pasha declared the independence of Wallachia under Michael's rule, but Michael knew that this was only an attempt to divert him from preparing for another future attack. Michael again requested Rudolf II's support and Rudolf finally agreed to send financial assistance to the Wallachian ruler. On 9 June 1598 a formal treaty was reached between Michael and Rudolf II. According to the treaty, the Austrian ruler would give Wallachia sufficient money to maintain a 5,000-man army, as well as armaments and supplies. Shortly after the treaty was signed, the war with the Ottomans resumed and Michael besieged Nicopolis on 10 September 1598 and took control of Vidin. The war with the Ottomans continued until 26 June 1599, when Michael, lacking the resources and support to continue prosecuting the war, signed a peace treaty.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different Turki ...
Transylvania

 In April 1598, Sigismund resigned as
In April 1598, Sigismund resigned as Prince of Transylvania
The Prince of Transylvania ( hu, erdélyi fejedelem, german: Fürst von Siebenbürgen, la, princeps Transsylvaniae, ro, principele TransilvanieiFallenbüchl 1988, p. 77.) was the head of state of the Principality of Transylvania from the last d ...
in favor of the Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
, Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
(who was also the King of Hungary
The King of Hungary ( hu, magyar király) was the ruling head of state of the Kingdom of Hungary from 1000 (or 1001) to 1918. The style of title "Apostolic King of Hungary" (''Apostoli Magyar Király'') was endorsed by Pope Clement XIII in 175 ...
); reversed his decision in October 1598; and then resigned again in favor of Cardinal
Cardinal or The Cardinal may refer to:
Animals
* Cardinal (bird) or Cardinalidae, a family of North and South American birds
**'' Cardinalis'', genus of cardinal in the family Cardinalidae
**'' Cardinalis cardinalis'', or northern cardinal, t ...
Andrew Báthory
Andrew Báthory ( hu, Báthory András; pl, Andrzej Batory; 1562 or 1563 – 3 November 1599) was the Cardinal-deacon of Sant'Adriano al Foro from 1584 to 1599, Prince-Bishop of Warmia from 1589 to 1599, and Prince of Transylvania in 1599. His ...
, his cousin. Báthory had strong ties to the Polish chancellor and hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
Jan Zamoyski
Jan Sariusz Zamoyski ( la, Ioannes Zamoyski de Zamoscie; 19 March 1542 – 3 June 1605) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, and the 1st '' ordynat'' of Zamość. He served as the Royal Secretary from 1565, Deputy Chancellor from 1576, Grand Cha ...
and placed Transylvania under the influence of the King
King is the title given to a male monarch in a variety of contexts. The female equivalent is queen regnant, queen, which title is also given to the queen consort, consort of a king.
*In the context of prehistory, antiquity and contempora ...
of Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
, Sigismund III Vasa
Sigismund III Vasa ( pl, Zygmunt III Waza, lt, Žygimantas Vaza; 20 June 1566 – 30 April 1632
N.S.) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1587 to 1632 and, as Sigismund, King of Sweden and Grand Duke of Finland from 1592 to ...
. He was also a trusted ally of the new Moldavian Prince Ieremia Movilă
Ieremia Movilă ( pl, Jeremi Mohyła uk, Єремія Могила), (c. 1555 – 10 July 1606) was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia between August 1595 and May 1600, and again between September 1600 and July 10, 1606.
Rule
A boyar of the Movil ...
, one of Michael's greatest enemies.Giurescu, p. 193. Movilă had deposed Ștefan Răzvan with the help of Polish hetman Jan Zamoyski in August 1595.
Having to face this new threat, Michael asked Emperor Rudolf to become the sovereign of Wallachia. On 25 September (5 October) Báthory issued an ultimatum demanding that Michael abandon his throne.Giurescu, p. 194. Michael decided to attack Andrew Cardinal Báthory immediately to prevent invasion. He would later describe the events: He left Târgoviște on 2 October, and 9 by October he had reached Prejmer in southern Transylvania, where he met envoys from the city of Brașov. Sparing the city, he moved on to Cârța where he joined forces with the Székelys
The Székelys (, Székely runes: 𐳥𐳋𐳓𐳉𐳗), also referred to as Szeklers,; ro, secui; german: Szekler; la, Siculi; sr, Секељи, Sekelji; sk, Sikuli are a Hungarian subgroup living mostly in the Székely Land in Romania. ...
.
 On 18 October Michael won a decisive victory against the army of prince-cardinal Andrew Báthory at the Battle of Șelimbăr, giving him control of Transylvania. As he retreated from the battle, Andrew Báthory was killed by anti-Báthory
On 18 October Michael won a decisive victory against the army of prince-cardinal Andrew Báthory at the Battle of Șelimbăr, giving him control of Transylvania. As he retreated from the battle, Andrew Báthory was killed by anti-Báthory Székely Székely may refer to:
*Székelys, Hungarian people from the historical region of Transylvania, Romania
**Székely Land, historic and ethnographic area in Transylvania, Romania
* Székely (village), a village in northeastern Hungary
*Székely (sur ...
on 3 November near Sândominic and Michael gave him a princely burial in the Roman Catholic Cathedral of Alba Iulia. With his enemy dead, Michael entered the Transylvanian capital at Alba Iulia and received the keys to the fortress from Bishop Demeter Naprágyi
Demeter Naprágyi (''Náprágyi'', ''Napragyi'', ''Napraghy'' or ''Napragi''; 1564 – before 5 March 1619)Markó 2006, p. 115. was a Hungarian prelate of the Roman Catholic Church, who served as bishop of several dioceses. He was the Archbis ...
, later depicted as a seminal event in Romanian historiography
Historiography is the study of the methods of historians in developing history as an academic discipline, and by extension is any body of historical work on a particular subject. The historiography of a specific topic covers how historians h ...
. Historian István Szamosközy, keeper of the Archives at the time, recorded the event in great detail. He also wrote that two days before the Diet met on 10 October, Transylvanian nobles ''elected Michael the voivode as Prince of Transylvania''. As the Diet was assembled, Michael demanded that the estates swear loyalty to Emperor Rudolf, then to himself and thirdly to his son. Even if he was recognized by the Transylvanian diet as only imperial governor subject to the Holy Roman Emperor, he was nonetheless ruler of Transylvania.
 In Transylvania Michael used the following signature on official documents: ''Michael Valachiae Transalpinae Woivoda, Sacrae Caesareae Regiae Majestatis Consiliarius per Transylvaniam Locumtenens, cis transylvaniam partium eius super exercitu Generalis Capitaneus".'' ("Michael, voivode of Wallachia, the councillor of His Majesty the Emperor and the King, his deputy in Transylvania and General Captain of his troops from Transylvania.")
When Michael entered Transylvania, he did not immediately free or grant rights to the Romanian inhabitants, who were primarily peasants but, nevertheless, constituted a significant proportion of the population. Michael demonstrated his support by upholding the Union of the Three Nations, which recognized only the traditional rights and privileges of the Hungarians, Székelys and
In Transylvania Michael used the following signature on official documents: ''Michael Valachiae Transalpinae Woivoda, Sacrae Caesareae Regiae Majestatis Consiliarius per Transylvaniam Locumtenens, cis transylvaniam partium eius super exercitu Generalis Capitaneus".'' ("Michael, voivode of Wallachia, the councillor of His Majesty the Emperor and the King, his deputy in Transylvania and General Captain of his troops from Transylvania.")
When Michael entered Transylvania, he did not immediately free or grant rights to the Romanian inhabitants, who were primarily peasants but, nevertheless, constituted a significant proportion of the population. Michael demonstrated his support by upholding the Union of the Three Nations, which recognized only the traditional rights and privileges of the Hungarians, Székelys and Saxons
The Saxons ( la, Saxones, german: Sachsen, ang, Seaxan, osx, Sahson, nds, Sassen, nl, Saksen) were a group of Germanic
*
*
*
*
peoples whose name was given in the early Middle Ages to a large country (Old Saxony, la, Saxonia) near the Nor ...
, but he didn't recognize the rights of the Romanians.Károly Kocsis, Eszter Kocsisné Hodosi, Ethnic Geography of the Hungarian Minorities in the Carpathian Basin, Simon Publications LLC, 1998, p. 102 (Table 19) Indeed, while he brought some of his Wallachian aides to Transylvania, he also invited some Székelys and other Transylvanian Hungarians to assist in the administration of Wallachia, where he wished to transplant Transylvania's far more advanced feudal system.
Michael began negotiating with the Emperor over his official position in Transylvania. The latter wanted the principality under direct Imperial rule with Michael acting as governor. The Wallachian voivode
Voivode (, also spelled ''voievod'', ''voevod'', ''voivoda'', ''vojvoda'' or ''wojewoda'') is a title denoting a military leader or warlord in Central, Southeastern and Eastern Europe since the Early Middle Ages. It primarily referred to the me ...
, on the other hand, wanted the title of Prince of Transylvania for himself and equally claimed the Partium region. Michael was, nevertheless, willing to acknowledge Habsburg
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
overlordship.
Moldavia
 The Moldavian Prince
The Moldavian Prince Ieremia Movilă
Ieremia Movilă ( pl, Jeremi Mohyła uk, Єремія Могила), (c. 1555 – 10 July 1606) was a Voivode (Prince) of Moldavia between August 1595 and May 1600, and again between September 1600 and July 10, 1606.
Rule
A boyar of the Movil ...
had been an old enemy of Michael, having incited Andrew Báthory to send Michael the ultimatum demanding his abdication. His brother, Simion Movilă, claimed the Wallachian throne for himself and had used the title of Voivode since 1595. Aware of the threat the Movilăs represented, Michael had created the ''Banate'' of Buzău and Brăila
Brăila (, also , ) is a city in Muntenia, eastern Romania, a port on the Danube and the capital of Brăila County. The Sud-Est (development region), ''Sud-Est'' Regional Development Agency is located in Brăila.
According to the 2011 Romanian ...
in July 1598 and the new ''ban'' was charged of keeping an alert eye on Moldavian, Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
, and in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Cossack
The Cossacks , es, cosaco , et, Kasakad, cazacii , fi, Kasakat, cazacii , french: cosaques , hu, kozákok, cazacii , it, cosacchi , orv, коза́ки, pl, Kozacy , pt, cossacos , ro, cazaci , russian: казаки́ or ...
moves, although Michael had been planning a Moldavian campaign for several years.Giurescu, p. 198.
 On 28 February 1600 Michael met with Polish envoys in Brașov. He was willing to recognise the Polish King as his sovereign in exchange for the crown of Moldavia and the recognition of his male heirs' hereditary right over the three principalities, Transylvania, Moldavia, and Wallachia. This did not significantly delay his attack, however; on 14 April 1600 Michael's troops entered Moldavia on multiple routes, the Prince himself leading the main thrust to
On 28 February 1600 Michael met with Polish envoys in Brașov. He was willing to recognise the Polish King as his sovereign in exchange for the crown of Moldavia and the recognition of his male heirs' hereditary right over the three principalities, Transylvania, Moldavia, and Wallachia. This did not significantly delay his attack, however; on 14 April 1600 Michael's troops entered Moldavia on multiple routes, the Prince himself leading the main thrust to Trotuș
The Trotuș ( hu, Tatros) is a river in eastern Romania, a right tributary of the river Siret. It emerges from the Ciuc Mountains in the Eastern Carpathians and joins the Siret in Domnești-Sat near Adjud after passing through Comănești and O ...
and Roman
Roman or Romans most often refers to:
* Rome, the capital city of Italy
* Ancient Rome, Roman civilization from 8th century BC to 5th century AD
*Roman people, the people of ancient Rome
*''Epistle to the Romans'', shortened to ''Romans'', a lett ...
. He reached the capital of Iași
Iași ( , , ; also known by other alternative names), also referred to mostly historically as Jassy ( , ), is the second largest city in Romania and the seat of Iași County. Located in the historical region of Moldavia, it has traditionally ...
on 6 May. The garrison surrendered the citadel the next day and Michael's forces caught up with the fleeing Ieremia Movilă, who was saved from being captured only by the sacrifice of his rear-guard. Movilă took refuge in the castle of Hotin together with his family, a handful of faithful boyars and the former Transylvanian Prince, Sigismund Báthory. The Moldavian soldiers in the castle deserted, leaving a small Polish contingent as sole defenders. Under the cover of dark, sometime before 11 June, Movilă managed to sneak out of the walls and across the Dniester to hetman
( uk, гетьман, translit=het'man) is a political title from Central and Eastern Europe, historically assigned to military commanders.
Used by the Czechs in Bohemia since the 15th century. It was the title of the second-highest military ...
Stanisław Żółkiewski's camp.Giurescu, p. 199.
Neighboring states were alarmed by this upsetting of the balance of power, especially the Hungarian nobility
The Hungarian nobility consisted of a privileged group of individuals, most of whom owned landed property, in the Kingdom of Hungary. Initially, a diverse body of people were described as noblemen, but from the late 12th century only high ...
in Transylvania, who rose against Michael in rebellion. With the help of Basta, they defeated Michael at the Battle of Mirăslău, forcing the prince to leave Transylvania together with his remaining loyal troops. A Polish army led by Jan Zamoyski
Jan Sariusz Zamoyski ( la, Ioannes Zamoyski de Zamoscie; 19 March 1542 – 3 June 1605) was a Polish nobleman, magnate, and the 1st '' ordynat'' of Zamość. He served as the Royal Secretary from 1565, Deputy Chancellor from 1576, Grand Cha ...
drove the Wallachians from Moldavia and defeated Michael at Năieni, Ceptura
Ceptura is a commune in Prahova County, Muntenia, Romania. It is composed of five villages: Ceptura de Jos (the commune centre), Ceptura de Sus, Malu Roșu, Rotari, and Șoimești.
The open-pit
Open-pit mining, also known as open-cast or ope ...
, and Bucov
Bucov () is a commune in Prahova County, Muntenia, Romania, just east of Ploiești, the county seat. It is composed of five villages: Bighilin, Bucov, Chițorani, Pleașa and Valea Orlei.
The commune is located in the south-central part of the co ...
( Battle of the Teleajăn River). The Polish army also entered eastern Wallachia and established Simion Movilă as ruler. Forces loyal to Michael remained only in Oltenia
Oltenia (, also called Lesser Wallachia in antiquated versions, with the alternative Latin names ''Wallachia Minor'', ''Wallachia Alutana'', ''Wallachia Caesarea'' between 1718 and 1739) is a historical province and geographical region of Romania ...
.Giurescu, p. 200.
Last victory and assassination

 Michael asked again for assistance from
Michael asked again for assistance from Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
Rudolf II
Rudolf II (18 July 1552 – 20 January 1612) was Holy Roman Emperor (1576–1612), King of Hungary and Croatia (as Rudolf I, 1572–1608), King of Bohemia (1575–1608/1611) and Archduke of Austria (1576–1608). He was a member of the Ho ...
during a visit in Prague
Prague ( ; cs, Praha ; german: Prag, ; la, Praga) is the capital and largest city in the Czech Republic, and the historical capital of Bohemia. On the Vltava river, Prague is home to about 1.3 million people. The city has a temperate ...
between 23 February and 5 March 1601, which was granted when the emperor heard that General Giorgio Basta had lost control of Transylvania to the Hungarian nobility led by Sigismund Báthory
Sigismund Báthory ( hu, Báthory Zsigmond; 1573 – 27 March 1613) was Prince of Transylvania several times between 1586 and 1602, and Duke of Racibórz and Opole in Silesia in 1598. His father, Christopher Báthory, ruled Transylvania as vo ...
, who accepted Ottoman protection. Meanwhile, forces loyal to Michael in Wallachia led by his son, Nicolae Pătrașcu
Nicolae Pătrașcu, Petrașco, or Petrașcu, also styled Nicolae Vo(i)evod (Church Slavonic and Romanian Cyrillic: or ; ca. 1580 – late 1627), was the titular Prince of Wallachia, an only son of Michael the Brave and Lady Stanca, and a putati ...
, drove Simion Movilă out of Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
and prepared to reenter Transylvania. Michael, allied with Basta, defeated the Hungarian army in Battle of Guruslău. A few days later, Basta, who sought to control Transylvania himself, executed the assassination
Assassination is the murder of a prominent or important person, such as a head of state, head of government, politician, world leader, member of a royal family or CEO. The murder of a celebrity, activist, or artist, though they may not have ...
of Michael by order of the Habsburg Emperor; the assassination took place near Câmpia Turzii
Câmpia Turzii (; german: Jerischmarkt; hu, Aranyosgyéres) is a municipality in Cluj County, Transylvania, Romania, which was formed in 1925 by the union of two villages, Ghiriș (''Aranyosgyéres'') and Sâncrai (''Szentkirály''). It was de ...
on 9 August 1601. According to Romanian historian Constantin C. Giurescu:
Legacy
The rule of Michael the Brave, with its break with Ottoman rule, tense relations with other European powers and the leadership of the three states, was considered in later periods as the precursor of a modernRomania
Romania ( ; ro, România ) is a country located at the crossroads of Central Europe, Central, Eastern Europe, Eastern, and Southeast Europe, Southeastern Europe. It borders Bulgaria to the south, Ukraine to the north, Hungary to the west, S ...
, a thesis which was argued with noted intensity by Nicolae Bălcescu
Nicolae Bălcescu () (29 June 181929 November 1852) was a Romanian Wallachian soldier, historian, journalist, and leader of the 1848 Wallachian Revolution.
Early life
Born in Bucharest to a family of low-ranking nobility, he used his mother ...
. This theory became a point of reference for nationalists, as well as a catalyst for various Romanian forces to achieve a single Romanian state. To Romanian Romantic nationalists, he was regarded as one of Romania's greatest national heroes. He is known in Romanian historiography as ''Mihai Viteazul'' or, less commonly, ''Mihai Bravu''.
 The prince began to be perceived as a ''unifier'' towards the middle of the 19th century. Such an interpretation is completely lacking in the historiography of the 17th-century chroniclers, and even in that of the Transylvanian School around 1800. What they emphasized, apart from the exceptional personality of Michael himself, were the idea of
The prince began to be perceived as a ''unifier'' towards the middle of the 19th century. Such an interpretation is completely lacking in the historiography of the 17th-century chroniclers, and even in that of the Transylvanian School around 1800. What they emphasized, apart from the exceptional personality of Michael himself, were the idea of Christendom
Christendom historically refers to the Christian states, Christian-majority countries and the countries in which Christianity dominates, prevails,SeMerriam-Webster.com : dictionary, "Christendom"/ref> or is culturally or historically intertwin ...
and his close relations with Emperor Rudolf. The conqueror's ambition is likewise frequently cited as a motivation for his action, occupying in the interpretative schema the place that was later to be occupied by the ''Romanian idea''.
In the writings of the Moldavian chronicler Miron Costin
Miron Costin (March 30, 1633 – 1691) was a Moldavian (Romanian) political figure and chronicler. His main work, ''Letopiseţul Ţărâi Moldovei e la Aron Vodă încoace' (''The Chronicles of the land of Moldavia Aron Vodă">Aron_Tiranul.h ...
, Michael the Brave appears in the role of conqueror of Transylvania and Moldavia, "the cause of much spilling of blood among Christians", and not even highly appreciated by his own Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
ns: "The Wallachians became tired of the warful rule of Voivode Mihai".
The perspective of the Wallachians themselves is to be found in ''The History of the Princes of Wallachia'', attributed to the chronicler Radu Popescu (1655–1729), which bundles together all Michael's adversaries without distinction. Romanians and foreigners alike: "He subjected the Turks, the Moldavians, and the Hungarians to his rule, as if they were his asses." The picturesque flavor of the expression serves only to confirm the absence of any ''Romanian idea''.

Samuil Micu
Samuil Micu Klein (September 1745 – 13 May 1806) was a Romanian Greek-Catholic theologian, historian, philologist and philosopher, a member of the Enlightenment-era movement of Transylvanian School (Şcoala Ardeleană). He is the author of Elem ...
, a member of the Transylvanian School wrote in his work ''Short Explanation of the History of the Romanians'' (written in the 1790s): "In the year 1593, Michael, who is called the Brave, succeeded to the lordship of Wallachia. He was a great warrior, who fought the Turks and defeated the Transylvanians. And he took Transylvania and gave it to Emperor Rudolf".
Petre P. Panaitescu states that in Mihai's time, the concept of the Romanian nation and the desire for unification did not yet exist. A. D. Xenopol firmly states the absence of any national element in Michael's politics, holding that Michael's lack of desire to join the principalities' administrations proved his actions were not motivated by any such concept.
Several Romanian settlements named after him, such as:
* Mihai Viteazu, a commune in Cluj County
Cluj County (; german: Kreis Klausenburg, hu, Kolozs megye) is a county (județ) of Romania, in Transylvania. Its seat ( ro, Oraș reședință de județ) is Cluj-Napoca (german: Klausenburg).
Name
In Hungarian, it is known as ''Kolozs megye ...
* Mihai Bravu, Giurgiu, a commune in Giurgiu County
Giurgiu () is a county (''județ'') of Romania on the border with Bulgaria, in Muntenia, with the capital city at Giurgiu.
Demographics
In 2011, it had a population of 265,494 and the population density was .
* Romanians – over 96%
* Roman ...
* Mihai Bravu, Tulcea
Mihai Bravu is a commune in Tulcea County, Northern Dobruja, Romania. It is composed of three villages: Mihai Bravu (formerly ''Camber''), Satu Nou and Turda (formerly ''Armutlia'').
References
*
Communes in Tulcea County
Localities in N ...
, a commune in Tulcea County
Tulcea County () is a county ( județ) of Romania, in the historical region Dobruja, with the capital city at Tulcea. It includes in its northeast corner the large and thinly-populated estuary of the Danube.
Demographics
In 2011, Tulcea Co ...
* ''Mihai Viteazu'', a village in the commune Vlad Țepeș, Călărași
* ''Mihai Bravu'', a village in the commune Victoria, Brăila
* ''Mihai Bravu'', a village in the commune Roșiori, Bihor
 Michael is also commemorated by the monks of the Athonite
Michael is also commemorated by the monks of the Athonite Simonopetra Monastery
Simonopetra Monastery ( el, Σιμωνόπετρα, literally: "Simon's Rock"), also Monastery of Simonos Petra ( el, Μονή Σίμωνος Πέτρας), is an Eastern Orthodox monastery in the monastic state of Mount Athos in Greece. Simonopet ...
for his great contributions in the form of land and money to rebuilding the monastery that had been destroyed by a fire.
'' Mihai Viteazul'', a film by Sergiu Nicolaescu
Sergiu Florin Nicolaescu (; 13 April 1930 – 3 January 2013) was a Romanian film director, actor and politician.
He was best known for his historical films, such as '' Mihai Viteazul'' (1970, released in English both under the equivalent tit ...
, a well-known Romanian film director, is a representation of the life of the Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
n ruler and his will to unite the three Romanian principalities (Wallachia
Wallachia or Walachia (; ro, Țara Românească, lit=The Romanian Land' or 'The Romanian Country, ; archaic: ', Romanian Cyrillic alphabet: ) is a historical and geographical region of Romania. It is situated north of the Lower Danube and s ...
, Moldavia
Moldavia ( ro, Moldova, or , literally "The Country of Moldavia"; in Romanian Cyrillic: or ; chu, Землѧ Молдавскаѧ; el, Ἡγεμονία τῆς Μολδαβίας) is a historical region and former principality in Centr ...
, and Transylvania
Transylvania ( ro, Ardeal or ; hu, Erdély; german: Siebenbürgen) is a historical and cultural region in Central Europe, encompassing central Romania. To the east and south its natural border is the Carpathian Mountains, and to the west the A ...
) as one domain.
The Order of Michael the Brave
The Order of Michael the Brave ( ro, Ordinul Mihai Viteazul) is Romania's highest military decoration, instituted by King Ferdinand I during the early stages of the Romanian Campaign of the First World War, and was again awarded in the Second Wor ...
, Romania's highest military decoration
Military awards and decorations are distinctions given as a mark of honor for military heroism, meritorious or outstanding service or achievement. DoD Manual 1348.33, 2010, Vol. 3 A decoration is often a medal consisting of a ribbon and a meda ...
, was named after Michael. Mihai Viteazul's name and portrait appear on at least two Romanian coins: 5 Lei 1991 (only 3 pieces of this type were minted and the coin was not entered into circulation), and on 100 Lei, which circulated through the 1990s.The 100 Lei of 1992 and 1993 are listed aKM # 111
of the Krause Mishler catalog Three major high schools in Romania bear his name: the Mihai Viteazul National College (Bucharest) the and the
Seal
 The seal comprises the coats of arms of Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania: in the middle, on a shield the Moldavian urus, above Wallachian
The seal comprises the coats of arms of Moldavia, Wallachia, and Transylvania: in the middle, on a shield the Moldavian urus, above Wallachian eagle
Eagle is the common name for many large birds of prey of the family Accipitridae. Eagles belong to several groups of genera, some of which are closely related. Most of the 68 species of eagle are from Eurasia and Africa. Outside this area, j ...
between sun and moon holding cross in beak, below Transylvanian coat of arms: two meeting, standing lion
The lion (''Panthera leo'') is a large cat of the genus '' Panthera'' native to Africa and India. It has a muscular, broad-chested body; short, rounded head; round ears; and a hairy tuft at the end of its tail. It is sexually dimorphic; adu ...
s supporting a sword, treading on seven mountains. The Moldavian shield is held by two crowned figures.
There are two inscriptions on the seal. First, circular, in Slavonic using Romanian Cyrillic alphabet "''IO MIHAILI UGROVLAHISCOI VOEVOD ARDEALSCOI MOLD ZEMLI''", meaning "'' Io Michael Wallachian Voivode of Transylvanian and Moldavian Lands''". Second, placed along a circular arc separating the Wallachian coat from the rest of the heraldic composition, "''I ML BJE MLRDIE''", could be translated "''Through The Very Grace of God''".Homutescu.
Notes
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * * * * * * * * *Szádeczky Kardoss, Lajos: Erdély és Mihály vajda története. istory of Transylvania in the time of vovoide Mihail with added documentsTemesvár 1893. Második, bővitett kiadásErdély és Mihály vajda története, 1595-1601. oklevéltárral
External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Michael the Brave 1558 births 1601 deaths Rulers of Moldavia Rulers of Moldavia and Wallachia Rulers of Wallachia Rulers of Transylvania 17th-century murdered monarchs House of Drăculești People of the Long Turkish War People from Vâlcea County Burials at Dealu Monastery, Viforâta (Dâmboviţa County) 1590s in Romania 1600s in Romania 1590s in the Ottoman Empire 16th century in Moldavia Romanian people in the Principality of Transylvania (1570–1711) 16th-century Romanian people 17th-century Romanian people 16th-century monarchs in Europe Bans of Oltenia Stolnici of Wallachia Eastern Orthodox monarchs