Mexicans of European descent on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
White Mexicans ( es, Mexicanos blancos) are Mexicans who are considered or identify as
, ''INEGI'', 16 June 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. the results obtained from these censuses are not published. What Mexico's government publishes instead is the percentage of "light-skinned Mexicans" there are in the country, with it being 47% in 2010 and 49% in 2017."Visión INEGI 2021 Dr. Julio Santaella Castell"
''INEGI'', 03 July 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. Due to its less directly racial undertones, the term "Light-skinned Mexican" has been favored by the government and media outlets over "White Mexican" as the go-to choice to refer to the segment of Mexico's population who possess European physical traits"Documento Informativo Sobre Discriminación Racial En México"
''CONAPRED'', Mexico, 21 March 2011, retrieved on 28 April 2017. when discussing different ethno-racial dynamics in Mexico's society. Nonetheless, sometimes "White Mexican" is used."Por estas razones el color de piel determina las oportunidades de los mexicanos"
, ''Huffington post'', 26 July 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018."Ser Blanco"
''El Universal'', 06 July 2017, Retrieved on 19 June 2018."Comprobado con datos: en México te va mejor si eres blanco"
''forbes'', 07 August 2018, Retrieved on 04 November 2018.
''Economiahoy.mx'', 05 March 2020, Retrieved on 21 July 2020."Critican series mexicanas de Netflix por sólo tener personajes blancos"
''Tomatazos.com'', 23 mayo 2020, consultado el 19 de diciembre de 2020. Estimates of Mexico's white population differ greatly in both methodology and percentages given; unofficial sources such as the ''World Factbook'' and ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', which use the 1921 census results as the base of their estimations, calculate the white Mexican population as only 9% or between one tenth to one fifth of the population. The results of the 1921 census, however, have been contested by various historians and deemed inaccurate similarly recent research has found that Mexicans in reality do not identify the way that sources such as The World Factbook state they do.R. Martínez & C. De La Torre (2008)
"Racial Appearance And Income In Contemporary Mexico, pag 9 note 1"
''Journal of Diversity Management'', 2008, Retrieved 01 April 2021. Surveys that account for phenotypical traits and have performed actual field research suggest rather higher percentages: using the presence of
''Plosgenetics'', 25 September 2014. Retrieved on 9 May 2017. nationwide surveys in the general population that use as reference skin color such as those made by Mexico's
"Genetic structure analysis of three Hispanic populations from Costa Rica, Mexico, and the southwestern United States using Y-chromosome STR markers and mtDNA sequences"
''Pubmed'', 2006, Retrieved 04 October 2022. research on the X chromosome shows less variation, with the reported Native American female contribution oscilating between 50% and 54%. It must be noted that the criteria for defining what constitutes a Mestizo varies from study to study as in Mexico a large number of European descended people have been historically classified as Mestizos, because after the Mexican Revolution the Mexican government began defining ethnicity on cultural standards (mainly the language spoken) rather than racial ones.
 Contrary to popular belief, Mexico's government does conduct ethnic censuses on which a Mexican has the choice of identify as "White", the results, however, remain unpublished. Instead the Mexican government does publish results regarding the frequencies of different phenotypical traits in Mexicans such as skin color, and in discourses and investigations regarding problematics such as racism has opted for splitting Mexicans on "light skinned Mexicans" and "dark skinned Mexicans" rather than on "White Mexicans" and "Mestizo Mexicans". Other studies made by independent institutions often use the presence of light hair colors (particularly blond) to calculate Mexico's white population, however to use such features to delineate said ethnic group results in an underestimation of its numbers as not all of Europe's native populations have those traits, similarly, not only people with those phenotypical features are considered to be white by the majority of Mexican society.
Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of
Contrary to popular belief, Mexico's government does conduct ethnic censuses on which a Mexican has the choice of identify as "White", the results, however, remain unpublished. Instead the Mexican government does publish results regarding the frequencies of different phenotypical traits in Mexicans such as skin color, and in discourses and investigations regarding problematics such as racism has opted for splitting Mexicans on "light skinned Mexicans" and "dark skinned Mexicans" rather than on "White Mexicans" and "Mestizo Mexicans". Other studies made by independent institutions often use the presence of light hair colors (particularly blond) to calculate Mexico's white population, however to use such features to delineate said ethnic group results in an underestimation of its numbers as not all of Europe's native populations have those traits, similarly, not only people with those phenotypical features are considered to be white by the majority of Mexican society.
Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of 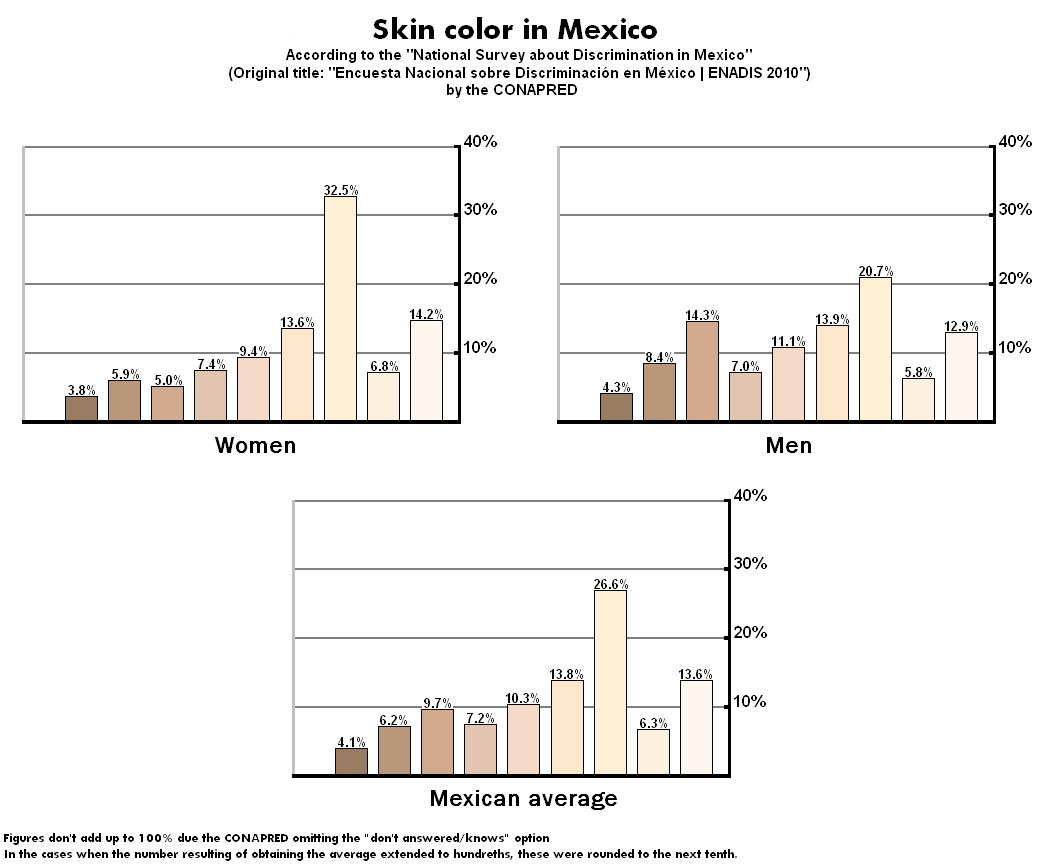 In 2010, the
In 2010, the
In the page 7 of the press release, the council reported that 47% of Mexicans (54% of women and 40% of men) identified with the lightest skin colors used in the census questionary, ''CONAPRED'', Mexico, 21 March. Retrieved on 28 April 2017. Notably, a subsequent question in the same survey asks Mexicans to evaluate, from 0 to 10, how comfortable they are with their skin color, with the average score being 9.4 out of 10. Furthermore, scientific research proving that human females tend to have lighter skin than their male counterparts exists. Besides the visual identification of skin color, the same survey included a question on which it asked Mexicans "what would they call their skin color?" while the press report by the CONAPRED remarks that six out of ten people considered themselves to be "moreno" (brunette in English) and only one out of ten considered their skin to be "blanco" (white). The questionnaire included as choices other words that are colloquially used to refer to white people in Mexico such as "güero" (informal for white), "claro" (clear), "aperlado" (pearly) and other words that may or not refer to a white person depending on the case, such as "quemadito" (burnt), "bronceado" (tanned), "apiñonado" (spiced), "amarillo" (yellow) and "canela" (cinnamon). Further complicating the situation, several words used specifically for brown skin also appear as choices such as "café" (brown), "negro" (black), "chocolate" (translation unnecessary), "oscuro" (dark), "prieto" (very dark) and "trigueño" (other word for brown). The word "moreno" itself has a very wide definition in Spanish and has no specific racial connotations, being used equally to define light-skinned people with dark hair as to define people of African ancestry. In 2017, Mexico's
''El Universal'', 16 June 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. The study concluded that Mexicans with medium ("F" tone) and darker skin tones have in average lower profile occupations than Mexicans with lighter skin tones. Also stated is that Mexicans with lighter skin tones (lighter than "F") have higher levels of academic achievement. The study also points out that out of the 4 racial categories used in the study, that of Indigenous Mexicans is the one that shows the highest percentage of positive social mobility (meaning that a person is better off than his/her parents were) while White Mexicans are the ones who have the lowest positive social mobility. In 2018, the new edition of the ENADIS was published, this time being a joint effort by the CONAPRED and the INEGI with collaboration of the
In 2018, the new edition of the ENADIS was published, this time being a joint effort by the CONAPRED and the INEGI with collaboration of the
''CNDH'', 6 August 2018, Retrieved on 10 August 2018. Like it's 2010 antecesor, it surveyed Mexican citizens about topics related to discrimination and collected data related to phenotype and ethnic self-identification. It concluded that Mexico is still a fairly conservative country regarding minority groups such as religious minorities, ethnic minorities, foreigners and members of the LGBT community. Albeit there's pronounced regional differences, with states in the south-center regions of Mexico having in general notoriously higher discrimination rates towards the aforementioned social groups than the ones states in the western-north regions have. For the collecting of data related to skin color the palette used was again the PERLA one. This time 11% of Mexicans were reported to have "dark skin tones (A-E)" 59% to have "medium skin tones (F-G)" and 29% to have "light skin tones (H-K)". The reason for the huge difference regarding the reported percentages of Mexicans with light skin (around 18% lower) and medium skin (around 16% higher) in the relation to previous nationwide surveys lies in the fact that the ENADIS 2017 prioritized the surveying of Mexicans from "vulnerable groups" which among other measures meant that states with known high numbers of people from said groups surveyed more people."Encuesta Nacional sobre Discriminación 2017. ENADIS. Diseño muestral. 2018"
, ''INEGI'', 6 August 2018, Retrieved on 10 August 2018. Independent field studies have been made in attempt to quantify the number of European Mexicans living in modern Mexico, using
 Genetic research in the Mexican population is numerous and has yielded a myriad of different results, it is not rare that different genetic studies done in the same location vary greatly, clear examples of said variation are the city of Monterrey in the state of Nuevo León, which, depending on the study presents an average European ancestry ranging from 38% to 78%, and
Genetic research in the Mexican population is numerous and has yielded a myriad of different results, it is not rare that different genetic studies done in the same location vary greatly, clear examples of said variation are the city of Monterrey in the state of Nuevo León, which, depending on the study presents an average European ancestry ranging from 38% to 78%, and

 The presence of Europeans in what is nowadays known as Mexico dates back to the
The presence of Europeans in what is nowadays known as Mexico dates back to the  Criollo resentment of the privileges afforded to the ''Peninsulares'' was the main reason behind the
Criollo resentment of the privileges afforded to the ''Peninsulares'' was the main reason behind the
 The lack of a clear dividing line between white and mixed race Mexicans has made the concept of race relatively fluid, with descent being more of a determining factor than biological traits. Even though there is a large variation in phenotypes among Mexicans, European looks are still strongly preferred in Mexican society, with lighter skin receiving more positive attention, as it is associated with higher social class, power, money, and modernity. In contrast, Indigenous ancestry is often associated with having an inferior social class, as well as lower levels of education. These distinctions are strongest in
The lack of a clear dividing line between white and mixed race Mexicans has made the concept of race relatively fluid, with descent being more of a determining factor than biological traits. Even though there is a large variation in phenotypes among Mexicans, European looks are still strongly preferred in Mexican society, with lighter skin receiving more positive attention, as it is associated with higher social class, power, money, and modernity. In contrast, Indigenous ancestry is often associated with having an inferior social class, as well as lower levels of education. These distinctions are strongest in  Despite what the mestizaje discourse asserts, Mexico is a country where Eurodescendants are not a minority; neither are they a clear majority but rather exist in equal numbers in relation to Mestizos."Contra la idea de México"
Despite what the mestizaje discourse asserts, Mexico is a country where Eurodescendants are not a minority; neither are they a clear majority but rather exist in equal numbers in relation to Mestizos."Contra la idea de México"
''Nexos'', 01 June 2010. Retrieved on February 28, 2018. Because of this, even though the Mexican government didn't use racial terms related to European or
 Another way on which European immigration to Mexico differed from that of other New World countries was on the profile of the needed immigrant. As New Spain's main economic activities were not related to agriculture (and the manpower for it was already supplied by the converted indigenous population)the country didn't enforce any sort of programs that would make it an attractive destination for European farmers. Much more important to the economy was mining and miners came from Europe, in particular from
Another way on which European immigration to Mexico differed from that of other New World countries was on the profile of the needed immigrant. As New Spain's main economic activities were not related to agriculture (and the manpower for it was already supplied by the converted indigenous population)the country didn't enforce any sort of programs that would make it an attractive destination for European farmers. Much more important to the economy was mining and miners came from Europe, in particular from  By the end of the Second World War, Americans, British, French, Germans and Spanish were the most conspicuous Europeans in Mexico but their presence was limited to urban areas, especially Mexico City, living in enclaves and involved in business. These European immigrants would quickly adapt to the Mexican attitude that "whiter was better" and keep themselves separate from the non-European population of the host country. This and their status as foreigners offered them considerable social and economic advantages, blunting any inclination to assimilate. There was little incentive to integrate with the general Mexican population and when they did, it was limited to the criollo upper class, failing to produce the "whitening" effect desired. For this reason, one can find non–Spanish surnames among Mexico's elite, especially in Mexico City.
However, even in the cases when generalized mixing did occur, such as with the Cornish miners in Hidalgo state around Pachuca and Real de Monte, their cultural influence remains strong. In these areas, English style houses can be found, the signature dish is the "paste" a variation of the Cornish pasty and they ended up introducing football (soccer) to Mexico. In the early 20th century, a group of about 100 Russian immigrants, mostly Pryguny and some Molokane and Cossacks came to live in area near Ensenada, Baja California. The main colony is in the Valle de Guadalupe and locally known as the Colonia Rusa near the town of Francisco Zarco. Other smaller colonies include San Antonio, Mision del Orno and Punta Banda. There are an estimated 1,000 descendants of these immigrants in Mexico, nearly all of whom have intermarried. The original settlements are now under the preservation of the Mexican government and have become tourist attractions.
Legal vestiges of attempts to "whiten" the population ended with the 1947 "Ley General de Población" along with the blurring of the lines between most of Mexico immigrant colonies and the general population. This blurring was hastened by the rise of a Mexican middle class, who enrolled their children in schools for foreigners and foreign organizations such as the German Club having a majority of Mexican members. However, this assimilation still has been mostly limited to Mexico's white peoples. Mass culture promoted the Spanish language and most other European languages have declined and almost disappeared. Restrictive immigration policies since the 1970s have further pushed the assimilation process. Despite all of the aforementioned pressure, as of 2013 Mexico is the country with most international immigrants in the world. Since 2000, Mexico's economic growth has increased international migration to the country, including people of European descent who leave their countries (particularly France and Spain) in the search of better work opportunities. People from the United States have moved too, now making up more than three-quarters of Mexico's roughly one million documented foreigners, up from around two-thirds in 2000. Nowadays, more people originally from United States have been added to the population of Mexico than Mexicans have been added to the population of the United States, according to government data in both nations.
By the end of the Second World War, Americans, British, French, Germans and Spanish were the most conspicuous Europeans in Mexico but their presence was limited to urban areas, especially Mexico City, living in enclaves and involved in business. These European immigrants would quickly adapt to the Mexican attitude that "whiter was better" and keep themselves separate from the non-European population of the host country. This and their status as foreigners offered them considerable social and economic advantages, blunting any inclination to assimilate. There was little incentive to integrate with the general Mexican population and when they did, it was limited to the criollo upper class, failing to produce the "whitening" effect desired. For this reason, one can find non–Spanish surnames among Mexico's elite, especially in Mexico City.
However, even in the cases when generalized mixing did occur, such as with the Cornish miners in Hidalgo state around Pachuca and Real de Monte, their cultural influence remains strong. In these areas, English style houses can be found, the signature dish is the "paste" a variation of the Cornish pasty and they ended up introducing football (soccer) to Mexico. In the early 20th century, a group of about 100 Russian immigrants, mostly Pryguny and some Molokane and Cossacks came to live in area near Ensenada, Baja California. The main colony is in the Valle de Guadalupe and locally known as the Colonia Rusa near the town of Francisco Zarco. Other smaller colonies include San Antonio, Mision del Orno and Punta Banda. There are an estimated 1,000 descendants of these immigrants in Mexico, nearly all of whom have intermarried. The original settlements are now under the preservation of the Mexican government and have become tourist attractions.
Legal vestiges of attempts to "whiten" the population ended with the 1947 "Ley General de Población" along with the blurring of the lines between most of Mexico immigrant colonies and the general population. This blurring was hastened by the rise of a Mexican middle class, who enrolled their children in schools for foreigners and foreign organizations such as the German Club having a majority of Mexican members. However, this assimilation still has been mostly limited to Mexico's white peoples. Mass culture promoted the Spanish language and most other European languages have declined and almost disappeared. Restrictive immigration policies since the 1970s have further pushed the assimilation process. Despite all of the aforementioned pressure, as of 2013 Mexico is the country with most international immigrants in the world. Since 2000, Mexico's economic growth has increased international migration to the country, including people of European descent who leave their countries (particularly France and Spain) in the search of better work opportunities. People from the United States have moved too, now making up more than three-quarters of Mexico's roughly one million documented foreigners, up from around two-thirds in 2000. Nowadays, more people originally from United States have been added to the population of Mexico than Mexicans have been added to the population of the United States, according to government data in both nations.
 European immigration to Mexico is not uncommon with many European or European derived ethnic groups responsible for shaping modern Mexican culture. Besides colonial Iberian influences, many other European and/or white communities thrived in Mexico's history such as the
European immigration to Mexico is not uncommon with many European or European derived ethnic groups responsible for shaping modern Mexican culture. Besides colonial Iberian influences, many other European and/or white communities thrived in Mexico's history such as the  Due to the 2008 Financial Crisis and the resulting economic decline and high unemployment in Spain, many Spaniards have been emigrating to Mexico to seek new opportunities. For example, during the last quarter of 2012, a number of 7,630 work permits were granted to Spaniards. Other Southern Europeans joined the Spaniards in the 2010s by finding better work opportunities in Mexico with thousands of Italians, Portuguese, French and Greeks finding professional opportunities along with the Spaniards in Mexico.
Sixty-seven percent of Latin America's English-speaking population lives in Mexico. Most of these are American nationals, with an influx of people from the U.S. coming to live in Mexico since the 1930s, becoming the largest group of foreigners in the country since then. However, most Americans in Mexico are not immigrants in the traditional sense, as they are there living as retirees or otherwise do not consider themselves permanent residents.
Due to the 2008 Financial Crisis and the resulting economic decline and high unemployment in Spain, many Spaniards have been emigrating to Mexico to seek new opportunities. For example, during the last quarter of 2012, a number of 7,630 work permits were granted to Spaniards. Other Southern Europeans joined the Spaniards in the 2010s by finding better work opportunities in Mexico with thousands of Italians, Portuguese, French and Greeks finding professional opportunities along with the Spaniards in Mexico.
Sixty-seven percent of Latin America's English-speaking population lives in Mexico. Most of these are American nationals, with an influx of people from the U.S. coming to live in Mexico since the 1930s, becoming the largest group of foreigners in the country since then. However, most Americans in Mexico are not immigrants in the traditional sense, as they are there living as retirees or otherwise do not consider themselves permanent residents.
 Also known as the "Revillagigedo census" due to its creation being ordered by the Count of the same name, this census was Mexico's (then known as the
Also known as the "Revillagigedo census" due to its creation being ordered by the Count of the same name, this census was Mexico's (then known as the
 Made right after the consummation of the Mexican revolution, the social context on which this census was made makes it particularly unique, as the government of the time was in the process of rebuilding the country and was looking forward to unite all Mexicans under a single national identity. The 1921 census' final results in regards to race, which assert that 59.3% of the Mexican population self-identified as Mestizo, 29.1% as Indigenous and only 9.8% as White were then essential to cement the "mestizaje" ideology (that asserts that the Mexican population as a whole is product of the admixture of all races) which shaped Mexican identity and culture through the 20th century and remain prominent nowadays, with extraofficial international publications such as ''
Made right after the consummation of the Mexican revolution, the social context on which this census was made makes it particularly unique, as the government of the time was in the process of rebuilding the country and was looking forward to unite all Mexicans under a single national identity. The 1921 census' final results in regards to race, which assert that 59.3% of the Mexican population self-identified as Mestizo, 29.1% as Indigenous and only 9.8% as White were then essential to cement the "mestizaje" ideology (that asserts that the Mexican population as a whole is product of the admixture of all races) which shaped Mexican identity and culture through the 20th century and remain prominent nowadays, with extraofficial international publications such as ''
"Investigación y Ciencia", Spain, October 2013. Retrieved on 01 June 2017. high consistence is found in regards to the distribution of Indigenous Mexicans across the country, with states located in south and south-eastern Mexico having both, the highest percentages of population that self-identifies as Indigenous and the highest percentages of Amerindian genetic ancestry. However this is not the case when it comes to European Mexicans, as there are instances on which states that have been shown to have a considerably high European ancestry per scientific research are reported to have very small white populations in the 1921 census, with the most extreme case being that of the state of Durango, where the aforementioned census asserts that only 0.01% of the state's population (33 persons) self-identified as "white" while modern scientific research shows that the population of Durango has similar genetic frequencies to those found on European peoples (with the state's Indigenous population showing almost no foreign admixture either). Various authors theorize that the reason for these inconsistencies may lie in the Mestizo identity promoted by the Mexican government, which reportedly led to people who are not biologically Mestizos to identify as such.El mestizaje y las culturas regionales
.
 The following table is a compilation of (when possible) official nationwide surveys conducted by the Mexican government who have attempted to quantify different Mexican ethnic groups. Given that for the most part each ethnic group was estimated by different surveys, with different methodologies and years apart rather than on a single comprehensive racial census, some groups could overlap with others and be overestimated or underestimated.
Of all the ethnic groups that have been surveyed, Mestizos are notably absent, which is likely due to the label's fluid and subjective definition, which complicates its precise quantification. However, it can be safely assumed that Mestizos make up at least the remaining 30% unassessed percentage of Mexico's population with possibilities of increasing if the methodologies of the extant surveys are considered. As example the 2015 intercensal survey considered as Indigenous Mexicans and Afro-Mexicans altogether individuals who self-identified as "part Indigenous" or "part African" thus, said people technically would be Mestizos. Similarly, White Mexicans were quantified based on physical traits/appearance, thus technically a Mestizo with a percentage of Indigenous ancestry that was low enough to not affect his/her primarily European phenotype was considered to be white. Finally the remaining ethnicities, for being of a rather low number or being faiths have more permissive classification criteria, therefore a Mestizo could claim to belong to one of them by practicing the faith, or by having an ancestor who belonged to said ethnicities.
Nonetheless, contemporary sociologists and historians agree that, given that the concept of "race" has a psychological foundation rather than a biological one and to society's eyes a Mestizo with a high percentage of European ancestry is considered "white" and a Mestizo with a high percentage of Indigenous ancestry is considered "Indian," a person who identifies with a given ethnic group should be allowed to, even if biologically doesn't completely belong to that group.
The following table is a compilation of (when possible) official nationwide surveys conducted by the Mexican government who have attempted to quantify different Mexican ethnic groups. Given that for the most part each ethnic group was estimated by different surveys, with different methodologies and years apart rather than on a single comprehensive racial census, some groups could overlap with others and be overestimated or underestimated.
Of all the ethnic groups that have been surveyed, Mestizos are notably absent, which is likely due to the label's fluid and subjective definition, which complicates its precise quantification. However, it can be safely assumed that Mestizos make up at least the remaining 30% unassessed percentage of Mexico's population with possibilities of increasing if the methodologies of the extant surveys are considered. As example the 2015 intercensal survey considered as Indigenous Mexicans and Afro-Mexicans altogether individuals who self-identified as "part Indigenous" or "part African" thus, said people technically would be Mestizos. Similarly, White Mexicans were quantified based on physical traits/appearance, thus technically a Mestizo with a percentage of Indigenous ancestry that was low enough to not affect his/her primarily European phenotype was considered to be white. Finally the remaining ethnicities, for being of a rather low number or being faiths have more permissive classification criteria, therefore a Mestizo could claim to belong to one of them by practicing the faith, or by having an ancestor who belonged to said ethnicities.
Nonetheless, contemporary sociologists and historians agree that, given that the concept of "race" has a psychological foundation rather than a biological one and to society's eyes a Mestizo with a high percentage of European ancestry is considered "white" and a Mestizo with a high percentage of Indigenous ancestry is considered "Indian," a person who identifies with a given ethnic group should be allowed to, even if biologically doesn't completely belong to that group.
white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
, typically due to their physical appearance and/or self-identification with their European ancestry. While the Mexican government
The Federal government of Mexico (alternately known as the Government of the Republic or ' or ') is the national government of the United Mexican States, the central government established by its constitution to share sovereignty over the republi ...
does conduct ethnic censuses in which a Mexican has the option of identifying as "White""Resultados del Modulo de Movilidad Social Intergeneracional", ''INEGI'', 16 June 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. the results obtained from these censuses are not published. What Mexico's government publishes instead is the percentage of "light-skinned Mexicans" there are in the country, with it being 47% in 2010 and 49% in 2017."Visión INEGI 2021 Dr. Julio Santaella Castell"
''INEGI'', 03 July 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. Due to its less directly racial undertones, the term "Light-skinned Mexican" has been favored by the government and media outlets over "White Mexican" as the go-to choice to refer to the segment of Mexico's population who possess European physical traits"Documento Informativo Sobre Discriminación Racial En México"
''CONAPRED'', Mexico, 21 March 2011, retrieved on 28 April 2017. when discussing different ethno-racial dynamics in Mexico's society. Nonetheless, sometimes "White Mexican" is used."Por estas razones el color de piel determina las oportunidades de los mexicanos"
, ''Huffington post'', 26 July 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018."Ser Blanco"
''El Universal'', 06 July 2017, Retrieved on 19 June 2018."Comprobado con datos: en México te va mejor si eres blanco"
''forbes'', 07 August 2018, Retrieved on 04 November 2018.
''Economiahoy.mx'', 05 March 2020, Retrieved on 21 July 2020."Critican series mexicanas de Netflix por sólo tener personajes blancos"
''Tomatazos.com'', 23 mayo 2020, consultado el 19 de diciembre de 2020. Estimates of Mexico's white population differ greatly in both methodology and percentages given; unofficial sources such as the ''World Factbook'' and ''Encyclopædia Britannica'', which use the 1921 census results as the base of their estimations, calculate the white Mexican population as only 9% or between one tenth to one fifth of the population. The results of the 1921 census, however, have been contested by various historians and deemed inaccurate similarly recent research has found that Mexicans in reality do not identify the way that sources such as The World Factbook state they do.R. Martínez & C. De La Torre (2008)
"Racial Appearance And Income In Contemporary Mexico, pag 9 note 1"
''Journal of Diversity Management'', 2008, Retrieved 01 April 2021. Surveys that account for phenotypical traits and have performed actual field research suggest rather higher percentages: using the presence of
blond hair
Blond (male) or blonde (female), also referred to as fair hair, is a hair color characterized by low levels of the dark pigment eumelanin. The resultant visible hue depends on various factors, but always has some yellowish color. The color can ...
as reference to classify a Mexican as white, the Metropolitan Autonomous University of Mexico calculated the percentage of said ethnic group within the institution at 23%. With a similar methodology, the American Sociological Association obtained a nationwide percentage of 18.8%. Another study made by the University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
in collaboration with Mexico's National Institute of Anthropology and History
National may refer to:
Common uses
* Nation or country
** Nationality – a ''national'' is a person who is subject to a nation, regardless of whether the person has full rights as a citizen
Places in the United States
* National, Maryland, c ...
found that the frequencies of blond hair and light eyes in Mexicans are of 18% and 28% respectively,"Admixture in Latin America: Geographic Structure, Phenotypic Diversity and Self-Perception of Ancestry Based on 7,342 Individuals" table 1''Plosgenetics'', 25 September 2014. Retrieved on 9 May 2017. nationwide surveys in the general population that use as reference skin color such as those made by Mexico's
National Council to Prevent Discrimination
The National Council to Prevent Discrimination ( es, Consejo Nacional para Prevenir La Discriminación; CONAPRED) is a Mexican government agency created in 2003 by Federal Law to Prevent and Eliminate Discrimination and to promote policies and mea ...
and Mexico's National Institute of Statistics and Geography
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI by its name in es, Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática) is an autonomous agency of the Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Stat ...
report percentages of 47% and 49% respectively.
Europeans began arriving in what is present day Mexico during the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
. While during the colonial period most European immigration was Spanish, in the 19th and 20th centuries large waves of European and European-derived populations from North
North is one of the four compass points or cardinal directions. It is the opposite of south and is perpendicular to east and west. ''North'' is a noun, adjective, or adverb indicating direction or geography.
Etymology
The word ''north ...
and South America did immigrate to the country. According to 20th and 21st century academics, large scale intermixing between the European immigrants and the native Indigenous peoples
Indigenous peoples are culturally distinct ethnic groups whose members are directly descended from the earliest known inhabitants of a particular geographic region and, to some extent, maintain the language and culture of those original people ...
would produce a Mestizo group which would become the overwhelming majority of Mexico's population by the time of the Mexican Revolution. This narrative has been questioned by some scholars, who cite the analysis of church and census records, showing that interracial unions in Mexico were rare among all groups. Said registers also put in question other narratives held by contemporary academics, such as European immigrants who arrived to Mexico being almost exclusively men or that "pure Spanish" people were all part of a small powerful elite, as Spaniards were often the most numerous ethnic group in the colonial cities and there were menial workers and people in poverty who were of complete Spanish origin.
Another ethnic group in Mexico, the Mestizos
(; ; fem. ) is a term used for racial classification to refer to a person of mixed European and Indigenous American ancestry. In certain regions such as Latin America, it may also refer to people who are culturally European even though thei ...
, is characterized by having people with varying degrees of European ancestry and native indigenous heritage, with some even showing a European genetic ancestry higher than 90%. While genetic evidence suggests that most European immigrants to Mexico were male, and that the modern population of Mexico was primarily formed through the mixing of Spanish males and Native American females, how pronounced said gender asymmetry was varies considerably depending of the study, with the Native American maternal contribution ranging 90% to 59%,Campos-Sanchez et al. (2006)"Genetic structure analysis of three Hispanic populations from Costa Rica, Mexico, and the southwestern United States using Y-chromosome STR markers and mtDNA sequences"
''Pubmed'', 2006, Retrieved 04 October 2022. research on the X chromosome shows less variation, with the reported Native American female contribution oscilating between 50% and 54%. It must be noted that the criteria for defining what constitutes a Mestizo varies from study to study as in Mexico a large number of European descended people have been historically classified as Mestizos, because after the Mexican Revolution the Mexican government began defining ethnicity on cultural standards (mainly the language spoken) rather than racial ones.
Distribution and estimates
 Contrary to popular belief, Mexico's government does conduct ethnic censuses on which a Mexican has the choice of identify as "White", the results, however, remain unpublished. Instead the Mexican government does publish results regarding the frequencies of different phenotypical traits in Mexicans such as skin color, and in discourses and investigations regarding problematics such as racism has opted for splitting Mexicans on "light skinned Mexicans" and "dark skinned Mexicans" rather than on "White Mexicans" and "Mestizo Mexicans". Other studies made by independent institutions often use the presence of light hair colors (particularly blond) to calculate Mexico's white population, however to use such features to delineate said ethnic group results in an underestimation of its numbers as not all of Europe's native populations have those traits, similarly, not only people with those phenotypical features are considered to be white by the majority of Mexican society.
Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of
Contrary to popular belief, Mexico's government does conduct ethnic censuses on which a Mexican has the choice of identify as "White", the results, however, remain unpublished. Instead the Mexican government does publish results regarding the frequencies of different phenotypical traits in Mexicans such as skin color, and in discourses and investigations regarding problematics such as racism has opted for splitting Mexicans on "light skinned Mexicans" and "dark skinned Mexicans" rather than on "White Mexicans" and "Mestizo Mexicans". Other studies made by independent institutions often use the presence of light hair colors (particularly blond) to calculate Mexico's white population, however to use such features to delineate said ethnic group results in an underestimation of its numbers as not all of Europe's native populations have those traits, similarly, not only people with those phenotypical features are considered to be white by the majority of Mexican society.
Mexico's northern and western regions have the highest percentages of white
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
population. In the north and west of Mexico, the indigenous tribes were substantially smaller and less urbanized than those found in central and southern Mexico, thus they remained isolated from colonial population centers and were often hostile towards Mexican colonists. The northeast region, in which the indigenous population was eliminated by early European settlers, became the region with the highest proportion of whites during the Spanish colonial period. However, recent immigrants from southern Mexico have been changing, to some degree.
CONAPRED
The National Council to Prevent Discrimination ( es, Consejo Nacional para Prevenir La Discriminación; CONAPRED) is a Mexican government agency created in 2003 by Federal Law to Prevent and Eliminate Discrimination and to promote policies and mea ...
(Mexico's National Council for the Prevention of Discrimination) conducted the ENADIS 2010 (National Survey About Discrimination) with the purpose of addressing the problems of racism that Mexicans of mainly Indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
or African ancestry suffer at hands of a society that favors light-skinned, European-looking Mexicans. In the press release of said report, the CONAPRED stated that 47% of Mexicans (54% of women and 40% of men) identified with the lightest skin colors used in the census questionnaire. The council makes the supposition that the high difference reported between males and females is due to the "frequently racist publicity in media and due racial prejudices in Mexico's society which shuns dark skin in favor of light skin, thus making women think that white is beautiful," stating that men are more likely to recognize their real skin color."21 de Marzo Día Internacional de la Eliminación de la Discriminación Racial"In the page 7 of the press release, the council reported that 47% of Mexicans (54% of women and 40% of men) identified with the lightest skin colors used in the census questionary, ''CONAPRED'', Mexico, 21 March. Retrieved on 28 April 2017. Notably, a subsequent question in the same survey asks Mexicans to evaluate, from 0 to 10, how comfortable they are with their skin color, with the average score being 9.4 out of 10. Furthermore, scientific research proving that human females tend to have lighter skin than their male counterparts exists. Besides the visual identification of skin color, the same survey included a question on which it asked Mexicans "what would they call their skin color?" while the press report by the CONAPRED remarks that six out of ten people considered themselves to be "moreno" (brunette in English) and only one out of ten considered their skin to be "blanco" (white). The questionnaire included as choices other words that are colloquially used to refer to white people in Mexico such as "güero" (informal for white), "claro" (clear), "aperlado" (pearly) and other words that may or not refer to a white person depending on the case, such as "quemadito" (burnt), "bronceado" (tanned), "apiñonado" (spiced), "amarillo" (yellow) and "canela" (cinnamon). Further complicating the situation, several words used specifically for brown skin also appear as choices such as "café" (brown), "negro" (black), "chocolate" (translation unnecessary), "oscuro" (dark), "prieto" (very dark) and "trigueño" (other word for brown). The word "moreno" itself has a very wide definition in Spanish and has no specific racial connotations, being used equally to define light-skinned people with dark hair as to define people of African ancestry. In 2017, Mexico's
National Institute of Statistics and Geography
The National Institute of Statistics and Geography (INEGI by its name in es, Instituto Nacional de Estadística, Geografía e Informática) is an autonomous agency of the Mexican Government dedicated to coordinate the National System of Stat ...
published the Intergenerational Social Mobility Module (MMSI), composed of a series of nationwide surveys focused on education, generational economic mobility and ethnicity. It is particularly notorious for giving Mexicans the possibility to identify with a race (the available choices being "Indigenous", "Mestizo", "White" and "Other"). While the results of questions directly related to race were published, the percentage of Mexicans who identified with each race was not. Also included in the survey was a color palette (the same as the one used in the PERLA project: composed of 11 different tones with "A" being the darkest and "K" being the lightest) so a person could chose what color the skin of his/her face was. The percentage of Mexicans that identified with each skin color was not included in the main MMSI document but unlike racial composition it was made public through other official publications. The study's results received significant media coverage, which led to discussions about concepts including systemic racism, white privilege
White privilege, or white skin privilege, is the societal privilege that benefits white people over non-white people in some societies, particularly if they are otherwise under the same social, political, or economic circumstances. With root ...
and colonialism
Colonialism is a practice or policy of control by one people or power over other people or areas, often by establishing colony, colonies and generally with the aim of economic dominance. In the process of colonisation, colonisers may impose the ...
."Presenta INEGI estudio que relaciona color de piel con oportunidades"''El Universal'', 16 June 2017, Retrieved on 30 April 2018. The study concluded that Mexicans with medium ("F" tone) and darker skin tones have in average lower profile occupations than Mexicans with lighter skin tones. Also stated is that Mexicans with lighter skin tones (lighter than "F") have higher levels of academic achievement. The study also points out that out of the 4 racial categories used in the study, that of Indigenous Mexicans is the one that shows the highest percentage of positive social mobility (meaning that a person is better off than his/her parents were) while White Mexicans are the ones who have the lowest positive social mobility.
 In 2018, the new edition of the ENADIS was published, this time being a joint effort by the CONAPRED and the INEGI with collaboration of the
In 2018, the new edition of the ENADIS was published, this time being a joint effort by the CONAPRED and the INEGI with collaboration of the UNAM
The National Autonomous University of Mexico ( es, Universidad Nacional Autónoma de México, UNAM) is a public research university in Mexico. It is consistently ranked as one of the best universities in Latin America, where it's also the bigge ...
, the CONACyT and the CNDH
The National Human Rights Commission ( es, Comisión Nacional de los Derechos Humanos; CNDH) is the national human rights institution (NHRI) accredited at the United Nations with "A" status by the International Co-ordinating Committee of NHRIs (t ...
."Encuesta Nacional sobre Discriminación 2017"''CNDH'', 6 August 2018, Retrieved on 10 August 2018. Like it's 2010 antecesor, it surveyed Mexican citizens about topics related to discrimination and collected data related to phenotype and ethnic self-identification. It concluded that Mexico is still a fairly conservative country regarding minority groups such as religious minorities, ethnic minorities, foreigners and members of the LGBT community. Albeit there's pronounced regional differences, with states in the south-center regions of Mexico having in general notoriously higher discrimination rates towards the aforementioned social groups than the ones states in the western-north regions have. For the collecting of data related to skin color the palette used was again the PERLA one. This time 11% of Mexicans were reported to have "dark skin tones (A-E)" 59% to have "medium skin tones (F-G)" and 29% to have "light skin tones (H-K)". The reason for the huge difference regarding the reported percentages of Mexicans with light skin (around 18% lower) and medium skin (around 16% higher) in the relation to previous nationwide surveys lies in the fact that the ENADIS 2017 prioritized the surveying of Mexicans from "vulnerable groups" which among other measures meant that states with known high numbers of people from said groups surveyed more people."Encuesta Nacional sobre Discriminación 2017. ENADIS. Diseño muestral. 2018"
, ''INEGI'', 6 August 2018, Retrieved on 10 August 2018. Independent field studies have been made in attempt to quantify the number of European Mexicans living in modern Mexico, using
blond hair
Blond (male) or blonde (female), also referred to as fair hair, is a hair color characterized by low levels of the dark pigment eumelanin. The resultant visible hue depends on various factors, but always has some yellowish color. The color can ...
as reference to classify a Mexican as white, the Metropolitan Autonomous University of Mexico calculated their percentage at 23%, the study explicitly states that red-haired
Red hair (also known as orange hair and ginger hair) is a hair color found in one to two percent of the human population, appearing with greater frequency (two to six percent) among people of Northern or Northwestern European ancestry and l ...
people were not classified as white but as "other." A study made by the University College London
, mottoeng = Let all come who by merit deserve the most reward
, established =
, type = Public research university
, endowment = £143 million (2020)
, budget = ...
which included multiple Latin American countries and was made with collaboration of each country's anthropology and genetics institutes reported that the frequency of blond hair and light eyes in Mexicans was of 18.5% and 28.5% respectively, making Mexico the country with the second-highest frequency of blond hair in the study. Despite this, the European ancestry estimated for Mexicans is also the second-lowest of all countries included, the reason behind such discrepancy may lie in the fact that the samples used in Mexico's case were highly disproportional, as the northern and western regions of Mexico contain 45% of Mexico's population, but no more than 10% of the samples used in the study came from the states located in these regions. For the most part, the rest of the samples hailed from Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
and southern Mexican states.
In 2010 a study published by the American Sociological Association explored social inequalities between Mexicans of different skin colors. The field research consisted of three waves of interviews on different Mexican states during the timespan of a year, people surveyed where split on 3 different groups: "White," "Light brown" and "Dark brown," with the classification being up to the criteria of the interviewers who is claimed, were trained for the task. It is stated that, in order to obtain stable results and prevent inconsistencies regarding who belongs to a given category, additional phenotypical traits besides the respondents' skin color were considered, such as the presence of blond hair in the case of individuals that were to be classified in the "White" category, because "unlike skin color, hair color does not darken with exposure to sunlight." It is indeed claimed within the study that out of the three color categories used, the percentages obtained for the "White" one through the three waves of interviews were the most consistent. According to the results of the study, the average percentage of Mexicans who were classified as "White" per the presence of blond hair was 18.8%, with the Northeast and Northwest regions having the highest frequencies at 23.9% and 22.3% respectively, followed by the Center region with 21.3%, the Center-West region with 18.4% and finally the South region with 11.9%. The study makes the clarification that Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
(Center region) as well as rural areas of the states of Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
, Chiapas (both from the south region) and Jalisco (Center-West region) were oversampled.
The following tables (the first from a study published in 2002 and the second from a study published in 2018) show the frequencies of different blood types in various Mexican cities and states, as Mexico's Amerindian/Indigenous population exclusively exhibits the "O" blood type, the presence of other blood groups can give an approximate idea of the amount of foreign influence there is in each state that has been analyzed. The results of this studies however, shouldn't be taken as exact, literal estimations for the percentages of different ethnic groups that there may be in Mexico (I.E. A+B blood groups = percentage of White Mexicans) for reasons such as the fact that a Mestizo Mexican can have "A", "B" etc. blood types or the fact that the "O" blood type does exist in Europe, with it having a frequency of 44% in Spain for example.
Both studies find similar trends regarding the distribution of different blood groups, with foreign blood groups being more common in the North and Western regions of Mexico, which is congruent with the findings of genetic studies that have been made in the country through the years. It is also observed that "A" and "B" blood groups are more common among younger volunteers whereas "AB" and "O" are more common in older ones. The total number of analyzed samples in the 2018 study was 271,164.
A study performed in hospitals of Mexico City reported that in average 51.8% of Mexican newborns presented the congenital skin birthmark
A birthmark is a congenital, benign irregularity on the skin which is present at birth or appears shortly after birth—usually in the first month. They can occur anywhere on the skin. Birthmarks are caused by overgrowth of blood vessels, melanocy ...
known as the Mongolian spot
A Mongolian spot, also known as slate grey nevus or congenital dermal melanocytosis, is a benign, flat, congenital birthmark with wavy borders and an irregular shape. In 1883, it was described and named after Mongolians by Erwin Bälz, a German a ...
whilst it was absent in 48.2% of the analyzed babies. The Mongolian spot appears with a very high frequency (85-95%) in Asian, Native American and African children. The skin lesion reportedly almost always appears on South American and Mexican children who are racially Mestizos
while having a very low frequency (5-10%) in Caucasian children. According to the Mexican Social Security Institute
The Mexican Institute of Social Security ( es, Instituto Mexicano del Seguro Social, IMSS) is a governmental organization that assists public health, pensions and social security in Mexico operating under the Secretariat of Health. It also form ...
(shortened as IMSS) nationwide, around half of Mexican babies have the Mongolian spot.
According to the 2010 US Census, 52.8% of Mexican Americans (approximately 16,794,111 people) self-identified as being White
White is the lightest color and is achromatic (having no hue). It is the color of objects such as snow, chalk, and milk, and is the opposite of black. White objects fully reflect and scatter all the visible wavelengths of light. White o ...
.
Genetic research
 Genetic research in the Mexican population is numerous and has yielded a myriad of different results, it is not rare that different genetic studies done in the same location vary greatly, clear examples of said variation are the city of Monterrey in the state of Nuevo León, which, depending on the study presents an average European ancestry ranging from 38% to 78%, and
Genetic research in the Mexican population is numerous and has yielded a myriad of different results, it is not rare that different genetic studies done in the same location vary greatly, clear examples of said variation are the city of Monterrey in the state of Nuevo León, which, depending on the study presents an average European ancestry ranging from 38% to 78%, and Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, whose European admixture ranges from as little as 21% to as high as 70%, reasons behind such variation may include the socioeconomic background of the analyzed samples as well as the criteria to recruit volunteers: some studies only analyze Mexicans who self-identify as Mestizos, others may classify the entire Mexican population as "mestizo", other studies may do both, such as the 2009 genetic study published by the INMEGEN (Mexico's National Institute of Genomic Medicine), which states that 93% of the Mexican population is Mestizo with the remaining population being Amerindian
The Indigenous peoples of the Americas are the inhabitants of the Americas before the arrival of the European settlers in the 15th century, and the ethnic groups who now identify themselves with those peoples.
Many Indigenous peoples of the A ...
, this particular statement has received considerable media exposure through the years to dismay of scientists from the aforementioned institute, who have complained about the study being misinterpreted by the press as it wasn't meant to represent Mexico's population as a whole. According to the methodology of the aforementioned study the institute only recruited people who explicitly self-identified as Mestizos. Finally there are studies which avoid using any racial classification whatsoever, including in them any person who self-identifies as Mexican; these studies are the ones that usually report the highest European admixture for a given location.
The Mestizaje ideology, which has blurred the lines of race at an institutional level has also had a significative influence in genetic studies done in Mexico. As the criteria used in studies to determine if a Mexican is Mestizo or indigenous often lies in cultural traits such as the language spoken instead of racial self-identification or a phenotype-based selection there are studies on which populations who are considered to be Indigenous per virtue of the language spoken show a higher degree of European genetic admixture than the one populations considered to be Mestizo report in other studies. The opposite also happens, as there instances on which populations considered to be Mestizo show genetic frequencies very similar to continental European peoples in the case of Mestizos from the state of Durango or to European derived Americans in the case of Mestizos from the state of Jalisco.
Regardless of the criteria used, all the autosomal DNA studies made coincide on there being a significant genetic variation depending on the region analyzed, with southern Mexico having prevalent Amerindian and small but higher than average African genetic contributions, the central region of Mexico shows a balance between Amerindian and European components, with the later gradually increasing as one travels northwards and westwards, where European ancestry becomes the majority of the genetic contribution up until cities located in the Mexico–United States border
The Mexico–United States border ( es, frontera Estados Unidos–México) is an international border separating Mexico and the United States, extending from the Pacific Ocean in the west to the Gulf of Mexico in the east. The border trave ...
, where studies suggest there is a significant resurgence of Amerindian and African admixture.
To date, no genetic research focusing on Mexicans of complete or predominant European ancestry has been made.
A 2014 publication summarizing population genetics
Population genetics is a subfield of genetics that deals with genetic differences within and between populations, and is a part of evolutionary biology. Studies in this branch of biology examine such phenomena as Adaptation (biology), adaptation, ...
research in Mexico, including three nationwide surveys and several region-specific surveys, found that in the studies done to date, counting only studies that looked at the ancestry of both parents (autosomal ancestry): "Amerindian ancestry is most prevalent (51% to 56%) in the three general estimates (initially published by the INMEGEN in 2009), followed by European ancestry (40% to 45%); the African share represents only 2% to 5%. In Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, the European contribution was estimated as 21% to 32% in six of the seven reports, with the anomalous value of 57% obtained in a single sample of 19 subjects, albeit said percentage can't really be called anomalous, as autosomal studies that obtain percentages of European ancestry of 51%, 52%, 70% and 52%, exists, (with the last one being for Mexico's central region as a whole) but were not included on this publication for unspecified reasons. According to the studies that were included, European ancestry is most prevalent in the north ( Chihuahua, 50%; Sonora, 62%; Nuevo León, 55%), but in a recent sample from Nuevo León and elsewhere in the country, Amerindian ancestry is dominant."
A 2006 nationwide autosomal study, the first ever conducted by Mexico's National Institute of Genomic Medicine (INMEGEN), which included the states of Guerrero
Guerrero is one of the 32 states that comprise the 32 Federal Entities of Mexico. It is divided in 81 municipalities and its capital city is Chilpancingo and its largest city is Acapulcocopied from article, GuerreroAs of 2020, Guerrero the pop ...
, Oaxaca
Oaxaca ( , also , , from nci, Huāxyacac ), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Oaxaca ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Oaxaca), is one of the 32 states that compose the political divisions of Mexico, Federative Entities of Mexico. It is ...
, Veracruz
Veracruz (), formally Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave (), officially the Free and Sovereign State of Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave ( es, Estado Libre y Soberano de Veracruz de Ignacio de la Llave), is one of the 31 states which, along with Me ...
, Yucatan, Zacatecas
, image_map = Zacatecas in Mexico (location map scheme).svg
, map_caption = State of Zacatecas within Mexico
, coordinates =
, coor_pinpoint =
, coordinates_footnotes =
, subdivision_type ...
and Sonora reported that self-identified Mestizo Mexicans are 58.96% European, 35.05% Amerindian, and 5.03% Other.
A 2007 study that included Mexicans from Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
reported that the autosomal
An autosome is any chromosome that is not a sex chromosome. The members of an autosome pair in a diploid cell have the same morphology, unlike those in allosomal (sex chromosome) pairs, which may have different structures. The DNA in autosom ...
ancestry of Mexicans was 52% European, while the Native American ancestry was 44%. However, the authors noted that Native American ancestry on the X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex ...
was 54%. The authors stated that this is consistent with the genetic formation of Latinos
Hispanic and Latino Americans ( es, Estadounidenses hispanos y latinos; pt, Estadunidenses hispânicos e latinos) are Americans of Spaniards, Spanish and/or Latin Americans, Latin American ancestry. More broadly, these demographics include a ...
, a process which involved primarily European males and Native American females.
Establishment of Europeans in Mexico

 The presence of Europeans in what is nowadays known as Mexico dates back to the
The presence of Europeans in what is nowadays known as Mexico dates back to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire
The Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire, also known as the Conquest of Mexico or the Spanish-Aztec War (1519–21), was one of the primary events in the Spanish colonization of the Americas. There are multiple 16th-century narratives of the eve ...
in the early 16th century by Hernán Cortés, his troops and a number of indigenous city states who were tributaries and rivals of the Aztecs, such as the Totonacs
The Totonac are an indigenous people of Mexico who reside in the states of Veracruz, Puebla, and Hidalgo. They are one of the possible builders of the pre-Columbian city of El Tajín, and further maintained quarters in Teotihuacán (a city ...
, the Tlaxcaltecas and Texcocans among others. After years of war the coalition led by Cortés finally managed to conquer the Aztec Empire which would result on the foundation of the Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
and while this new state granted a series of privileges to the members of the allied indigenous tribes such as nobiliary titles and swathes of land, the Spanish held the most political and economic power. The small number of Spaniards who inhabited the new kingdom would soon be complemented by a steady migration flow of Spanish people, as it was the interest of the Spanish crown to Hispanicize and Christianize the region given that Indigenous peoples and their customs were considered uncivilized, thus the Spanish language and culture were imposed and indigenous ones suppressed.
The Mexican experience mirrors much of that of the rest of Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived f ...
, as attitudes towards race, including identification, were set by the conquistadors and Spanish who came soon after. Through the colonial period, the Spanish and their descendants, called "criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
" remained outnumbered by the indigenous
Indigenous may refer to:
*Indigenous peoples
*Indigenous (ecology), presence in a region as the result of only natural processes, with no human intervention
*Indigenous (band), an American blues-rock band
*Indigenous (horse), a Hong Kong racehorse ...
and " mestizos" or those of mixed Spanish and indigenous parents (albeit a person of 7/8 Spanish ancestry and 1/8 or less indigenous ancestry could be considered to be "criollo"). To keep power, the Spanish enforced a hierarchical class system in New Spain's society, with those born in Spain (known as ''Peninsulares'') being the most privileged, followed by criollos, then Mestizos, then the indigenous and finally the Africans. Nonetheless, the system was not completely rigid and elements such as social class, social relations and who a person descended from did figure into it. However, the notion of "Spanishness" would remain at the top and "Indianness" would be at the bottom, with those mixed being somewhere in the middle. This idea remained officially in force through the rest of the colonial period.
 Criollo resentment of the privileges afforded to the ''Peninsulares'' was the main reason behind the
Criollo resentment of the privileges afforded to the ''Peninsulares'' was the main reason behind the Mexican War of Independence
The Mexican War of Independence ( es, Guerra de Independencia de México, links=no, 16 September 1810 – 27 September 1821) was an armed conflict and political process resulting in Mexico's independence from Spain. It was not a single, co ...
. When the war ended in 1821, the new Mexican government expelled the peninsulares (approximately 10,000 – 20,000 people) in the 1820s and 1830s which, to a degree, kept the European ethnicity from growing as a percentage; this expulsion, however, did not lead to any permanent ban on European immigrants, even from Spain. Independence did not do away with economic and social privilege based on race, as the Criollos took over from those of Spanish birth. A division between "Spanish" and "indigenous" remained, with Criollos distinguishing themselves from the rest of society as the guardians of Spanish culture as well as the Catholic religion. However, due to the abolition of the caste system, the division became more about money and social class and less about biological differences, which increased the possibilities of social mobility for Mestizo and Indigenous Mexicans. For this reason, many of the political and cultural struggles of the latter 19th and early 20th centuries would be between the Criollos and the Mestizos.
According to Mexico's first ever racial census published in 1793, the Eurodescendant population was between 18%-22% of the population (with Mestizos being 21%-25% and Amerindians being 51%-61%); but by 1921, when the second nationwide census that considered a person's race took place, only 9% of the population self-identified as being of European descent, with 59% being Mestizo and 29% being Amerindian. While for a long time the 1921 census' results were taken as fact, with international publications such as ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
'' and ''Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
'' using them as a reference to estimate Mexico's racial composition up to this day, more recently, Mexican academics have subjected them to scrutiny, claiming that such a drastic alteration of demographic trends is not possible and cite, among other statistics, the relatively low frequency of marriages between people of different continental ancestries. In the early 1890s, Northern Italian immigrants were brought from the Veneto area to Mexico to whiten the population.
In today's society
 The lack of a clear dividing line between white and mixed race Mexicans has made the concept of race relatively fluid, with descent being more of a determining factor than biological traits. Even though there is a large variation in phenotypes among Mexicans, European looks are still strongly preferred in Mexican society, with lighter skin receiving more positive attention, as it is associated with higher social class, power, money, and modernity. In contrast, Indigenous ancestry is often associated with having an inferior social class, as well as lower levels of education. These distinctions are strongest in
The lack of a clear dividing line between white and mixed race Mexicans has made the concept of race relatively fluid, with descent being more of a determining factor than biological traits. Even though there is a large variation in phenotypes among Mexicans, European looks are still strongly preferred in Mexican society, with lighter skin receiving more positive attention, as it is associated with higher social class, power, money, and modernity. In contrast, Indigenous ancestry is often associated with having an inferior social class, as well as lower levels of education. These distinctions are strongest in Mexico City
Mexico City ( es, link=no, Ciudad de México, ; abbr.: CDMX; Nahuatl: ''Altepetl Mexico'') is the capital city, capital and primate city, largest city of Mexico, and the List of North American cities by population, most populous city in North Amer ...
, where the most powerful of the country's elite are located.
Since the end of the Mexican Revolution, the official identity promoted by the government for non-indigenous Mexicans has been the Mestizo one (a mix of European and indigenous culture and heritage). Established with the original intent of eliminating divisions and creating a unified identity that would allow Mexico to modernize and integrate with the international community, this policy has not been able to achieve its goal. It is speculated that this is due to the identity's own internal contradictions, as it includes in the same theoretical race people who, in daily interactions, do not consider each other to be of the same race and have little in common biologically, with some of them being entirely Indigenous, others entirely European, and including also Africans and Asians.
Today, there is no definitive census that quantifies Mexico's white population, with estimates from different publications varying greatly, ranging from just 9% of the total to 47%, with this figure being based on phenotypical traits instead of self-identification of ancestry.
 Despite what the mestizaje discourse asserts, Mexico is a country where Eurodescendants are not a minority; neither are they a clear majority but rather exist in equal numbers in relation to Mestizos."Contra la idea de México"
Despite what the mestizaje discourse asserts, Mexico is a country where Eurodescendants are not a minority; neither are they a clear majority but rather exist in equal numbers in relation to Mestizos."Contra la idea de México"''Nexos'', 01 June 2010. Retrieved on February 28, 2018. Because of this, even though the Mexican government didn't use racial terms related to European or
white people
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
officially for almost a century (resuming using such terms after 2010), the concepts of "white people" (known as ''güeros'' or ''blancos'' in Mexican Spanish
Mexican Spanish ( es, español mexicano) is the variety of dialects and sociolects of the Spanish language spoken in Mexican territory. Mexico has the largest number of Spanish speakers, with more than twice as many as in any other country in ...
) and of "being white" didn't disappear Nutini, Hugo; Barry Isaac (2009). ''Social Stratification in central Mexico 1500 - 2000''. University of Texas Press, p. 55. and are still present in everyday Mexican culture: different idioms of race are used in Mexico's society that serve as mediating terms between racial groups. It is not strange to see street vendors calling a potential costumer ''Güero'' or ''güerito'', sometimes even when the person is not light-skinned. In this instance it is used to initiate a kind of familiarity, but in cases where social/racial tensions are relatively high, it can have the opposite effect.
This widespread preference that Mexicans, even those who are of predominant indigenous ancestry, have for European cultures and values, over Indigenous ones, has come to be known as '' malinchismo'', which means to identify or favor a North American or European culture over the native one. It derives from La Malinche
Marina or Malintzin ( 1500 – 1529), more popularly known as La Malinche , a Nahua woman from the Mexican Gulf Coast, became known for contributing to the Spanish conquest of the Aztec Empire (1519–1521), by acting as an interpreter, ad ...
, the native interpreter who served with Hernán Cortés during the Conquest, whose story still is a Mexican fable. Examples of practices considered as ''malinchismo'' in modern Mexico include Mexican parents choosing English given names for their kids, due to the desire to be associated with the United States.
European immigration to Mexico
Mexico's European heritage is strongly associated with Spanish settlement during the colonial period, Mexico not having witnessed the same scale of mass recent-immigration as otherNew World
The term ''New World'' is often used to mean the majority of Earth's Western Hemisphere, specifically the Americas."America." ''The Oxford Companion to the English Language'' (). McArthur, Tom, ed., 1992. New York: Oxford University Press, p. ...
countries such as the United States, Brazil, and Argentina. However, this ruling is less blanket fact and more of a consequence due to Mexico's enormous population. Regardless, Mexico ranks 3rd behind Brazil and Argentina for European immigration in Latin America with its culture owing a great deal to the significant German, Italian, Irish, British, Polish, and French populations. White Mexicans rather, descend of a considerably ethnocentrist group of Spanish people who, beginning with the arrival and establishment of the conquistadors to then be supplemented with clerics, workers, academics etc. immigrated to what today is Mexico. The criollos
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born majo ...
(as people born in the colonies to Spanish parents were called until the beginning of the 20th century) would favor for marriage other Spanish immigrants even if they were of a less privileged economic class than them, as to preserve the Spanish lineage and customs was seen as the top priority. Once Mexico achieved its independence and immigration from European countries other than Spain became accepted, the criollos did the same, and sought to assimilate the new European immigrants into the overwhelmingly Spanish-origin white Mexican population, as the yearly immigration rate of Europeans to Mexico never exceeded 2% in relation to the country's total population, assimilation of the new immigrants was easy and Mexican hyphenated identities never appeared.
 Another way on which European immigration to Mexico differed from that of other New World countries was on the profile of the needed immigrant. As New Spain's main economic activities were not related to agriculture (and the manpower for it was already supplied by the converted indigenous population)the country didn't enforce any sort of programs that would make it an attractive destination for European farmers. Much more important to the economy was mining and miners came from Europe, in particular from
Another way on which European immigration to Mexico differed from that of other New World countries was on the profile of the needed immigrant. As New Spain's main economic activities were not related to agriculture (and the manpower for it was already supplied by the converted indigenous population)the country didn't enforce any sort of programs that would make it an attractive destination for European farmers. Much more important to the economy was mining and miners came from Europe, in particular from Cornwall
Cornwall (; kw, Kernow ) is a historic county and ceremonial county in South West England. It is recognised as one of the Celtic nations, and is the homeland of the Cornish people. Cornwall is bordered to the north and west by the Atlantic ...
, U.K. and even today parts of Mineral del Monte
Mineral del Monte, commonly called Real del Monte () or El Real, is a small mining town, and one of the 84 municipalities of Hidalgo, in the State of Hidalgo in east-central Mexico.
It is located at an altitude of . As of 2005, the municipalit ...
and Pachuca
Pachuca (; ote, Nju̱nthe), formally known as Pachuca de Soto, is the capital and largest city of the Mexican state of Hidalgo. It is located in the south-central part of the state. Pachuca de Soto is also the name of the municipality of whi ...
maintain strong links to both their British heritage and with the United Kingdom. There was also strong demand for people with specialized skills in fields such as geology, metallurgy, commerce, law, medicine etc. As stories of professional immigrants amassing huge wealth in a pair of years were commonly heard, New Spain became very attractive only for Europeans who filled these profiles and their families, which in the end resulted on the country getting relatively less European immigration, is also because of the aforementioned reasons that the majority of Spanish immigrants who arrived to the country were from the northern regions of Spain, mainly Cantabria
Cantabria (, also , , Cantabrian: ) is an autonomous community in northern Spain with Santander as its capital city. It is called a ''comunidad histórica'', a historic community, in its current Statute of Autonomy. It is bordered on the east ...
, Navarra
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
, Galicia and the Basque Country. After the war of independence, the country's almost completely European elite would associate civilization with European characteristics, blaming the country's indigenous heritage for its inability to keep up with the economic development of the rest of the world. This led to active efforts to encourage the arrival of additional European immigrants.
One of these efforts was the dispossession of large tracts of land from the Catholic Church with the aim of selling them to immigrants and others who would develop them. However, this did not have the desired effect mostly because of political instability. The Porfirio Díaz regime of the decades before the Mexican Revolution tried again, and expressly desired European immigration to promote modernization, instill Protestant
Protestantism is a branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century against what its followers perceived to b ...
work ethics and buttress what remained of Mexico's North from further U.S. expansionism. Díaz also expressed a desire to "whiten" Mexico's heavily racially mixed population, although this had more to do with culture than with biological traits. However, the Díaz regime knew it had to be cautious, as previously large concentrations of Americans in Texas
Texas (, ; Spanish: ''Texas'', ''Tejas'') is a state in the South Central region of the United States. At 268,596 square miles (695,662 km2), and with more than 29.1 million residents in 2020, it is the second-largest U.S. state by ...
, would eventually lead to the secession
Secession is the withdrawal of a group from a larger entity, especially a political entity, but also from any organization, union or military alliance. Some of the most famous and significant secessions have been: the former Soviet republics le ...
of that territory. This precautions meant that the government had more success luring investors than permanent residents, even in rural areas despite government programs. No more than forty foreign farming colonies were ever formed during this time and of these only a few Italian and German ones survived.
By the mid-19th century, between Europeans and ethnically European Americans and Canadians, there were only 30,000 to 40,000 European immigrants in Mexico, compared to an overall population of over eight million, but their impact was strongly felt as they came to dominate the textile industry and various areas of commerce and industry. Many were not immigrants, but rather "trade conquistadors" who remained in Mexico only long enough to make their fortunes to return to their home countries to retire. This led Diaz to nationalize industries dominated by foreigners such as trains, which caused many trade conquistadors to leave. In January 1883, the government signed a law to promote the Irish, German and French immigration to Mexico, this time with fewer restrictions, resulting in the arrival of relatively more conventional immigrants and their families. Up to 1914, 10,000 French settled in Mexico, alongside other 100,000 Europeans. Despite being the most violent conflict in Mexico's history, the Mexican Revolution did not discourage European immigration nor scared away white Mexicans, who, for concentrating in urban areas were largely unaffected by it and thought of it as a conflict pertinent only to rural people. Later on, bellic conflicts in Europe during the 1930s and 1940s such as the Spanish Civil War
The Spanish Civil War ( es, Guerra Civil Española)) or The Revolution ( es, La Revolución, link=no) among Nationalists, the Fourth Carlist War ( es, Cuarta Guerra Carlista, link=no) among Carlists, and The Rebellion ( es, La Rebelión, link ...
and the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
caused additional waves of European immigration to the country.
 By the end of the Second World War, Americans, British, French, Germans and Spanish were the most conspicuous Europeans in Mexico but their presence was limited to urban areas, especially Mexico City, living in enclaves and involved in business. These European immigrants would quickly adapt to the Mexican attitude that "whiter was better" and keep themselves separate from the non-European population of the host country. This and their status as foreigners offered them considerable social and economic advantages, blunting any inclination to assimilate. There was little incentive to integrate with the general Mexican population and when they did, it was limited to the criollo upper class, failing to produce the "whitening" effect desired. For this reason, one can find non–Spanish surnames among Mexico's elite, especially in Mexico City.
However, even in the cases when generalized mixing did occur, such as with the Cornish miners in Hidalgo state around Pachuca and Real de Monte, their cultural influence remains strong. In these areas, English style houses can be found, the signature dish is the "paste" a variation of the Cornish pasty and they ended up introducing football (soccer) to Mexico. In the early 20th century, a group of about 100 Russian immigrants, mostly Pryguny and some Molokane and Cossacks came to live in area near Ensenada, Baja California. The main colony is in the Valle de Guadalupe and locally known as the Colonia Rusa near the town of Francisco Zarco. Other smaller colonies include San Antonio, Mision del Orno and Punta Banda. There are an estimated 1,000 descendants of these immigrants in Mexico, nearly all of whom have intermarried. The original settlements are now under the preservation of the Mexican government and have become tourist attractions.
Legal vestiges of attempts to "whiten" the population ended with the 1947 "Ley General de Población" along with the blurring of the lines between most of Mexico immigrant colonies and the general population. This blurring was hastened by the rise of a Mexican middle class, who enrolled their children in schools for foreigners and foreign organizations such as the German Club having a majority of Mexican members. However, this assimilation still has been mostly limited to Mexico's white peoples. Mass culture promoted the Spanish language and most other European languages have declined and almost disappeared. Restrictive immigration policies since the 1970s have further pushed the assimilation process. Despite all of the aforementioned pressure, as of 2013 Mexico is the country with most international immigrants in the world. Since 2000, Mexico's economic growth has increased international migration to the country, including people of European descent who leave their countries (particularly France and Spain) in the search of better work opportunities. People from the United States have moved too, now making up more than three-quarters of Mexico's roughly one million documented foreigners, up from around two-thirds in 2000. Nowadays, more people originally from United States have been added to the population of Mexico than Mexicans have been added to the population of the United States, according to government data in both nations.
By the end of the Second World War, Americans, British, French, Germans and Spanish were the most conspicuous Europeans in Mexico but their presence was limited to urban areas, especially Mexico City, living in enclaves and involved in business. These European immigrants would quickly adapt to the Mexican attitude that "whiter was better" and keep themselves separate from the non-European population of the host country. This and their status as foreigners offered them considerable social and economic advantages, blunting any inclination to assimilate. There was little incentive to integrate with the general Mexican population and when they did, it was limited to the criollo upper class, failing to produce the "whitening" effect desired. For this reason, one can find non–Spanish surnames among Mexico's elite, especially in Mexico City.
However, even in the cases when generalized mixing did occur, such as with the Cornish miners in Hidalgo state around Pachuca and Real de Monte, their cultural influence remains strong. In these areas, English style houses can be found, the signature dish is the "paste" a variation of the Cornish pasty and they ended up introducing football (soccer) to Mexico. In the early 20th century, a group of about 100 Russian immigrants, mostly Pryguny and some Molokane and Cossacks came to live in area near Ensenada, Baja California. The main colony is in the Valle de Guadalupe and locally known as the Colonia Rusa near the town of Francisco Zarco. Other smaller colonies include San Antonio, Mision del Orno and Punta Banda. There are an estimated 1,000 descendants of these immigrants in Mexico, nearly all of whom have intermarried. The original settlements are now under the preservation of the Mexican government and have become tourist attractions.
Legal vestiges of attempts to "whiten" the population ended with the 1947 "Ley General de Población" along with the blurring of the lines between most of Mexico immigrant colonies and the general population. This blurring was hastened by the rise of a Mexican middle class, who enrolled their children in schools for foreigners and foreign organizations such as the German Club having a majority of Mexican members. However, this assimilation still has been mostly limited to Mexico's white peoples. Mass culture promoted the Spanish language and most other European languages have declined and almost disappeared. Restrictive immigration policies since the 1970s have further pushed the assimilation process. Despite all of the aforementioned pressure, as of 2013 Mexico is the country with most international immigrants in the world. Since 2000, Mexico's economic growth has increased international migration to the country, including people of European descent who leave their countries (particularly France and Spain) in the search of better work opportunities. People from the United States have moved too, now making up more than three-quarters of Mexico's roughly one million documented foreigners, up from around two-thirds in 2000. Nowadays, more people originally from United States have been added to the population of Mexico than Mexicans have been added to the population of the United States, according to government data in both nations.
Examples of white ethnic groups in Mexico
 European immigration to Mexico is not uncommon with many European or European derived ethnic groups responsible for shaping modern Mexican culture. Besides colonial Iberian influences, many other European and/or white communities thrived in Mexico's history such as the
European immigration to Mexico is not uncommon with many European or European derived ethnic groups responsible for shaping modern Mexican culture. Besides colonial Iberian influences, many other European and/or white communities thrived in Mexico's history such as the Spanish
Spanish might refer to:
* Items from or related to Spain:
**Spaniards are a nation and ethnic group indigenous to Spain
**Spanish language, spoken in Spain and many Latin American countries
**Spanish cuisine
Other places
* Spanish, Ontario, Can ...
, Polish
Polish may refer to:
* Anything from or related to Poland, a country in Europe
* Polish language
* Poles
Poles,, ; singular masculine: ''Polak'', singular feminine: ''Polka'' or Polish people, are a West Slavic nation and ethnic group, w ...
and French, with the German Mexican
German Mexicans (German: ''Deutschmexikaner'' or ''Deutsch-Mexikanisch'', Spanish: ''germano-mexicano'' or ''alemán-mexicano'') are Mexican citizens of German descent or origin.
Most documented ethnic Germans arrived in Mexico during the mid-to- ...
community especially dominant on modern culture, once named as “la tercera raza” or “the third race”. Mexico's northwest-pacific region (particularly Sinaloa, Sonora, and the Baja California Peninsula) experienced major surges of Northern Spanish immigration in the late 19th and early 20th century, specifically from Asturias
Asturias (, ; ast, Asturies ), officially the Principality of Asturias ( es, Principado de Asturias; ast, Principáu d'Asturies; Galician-Asturian: ''Principao d'Asturias''), is an autonomous community in northwest Spain.
It is coextensiv ...
and Galicia (Spain)
Galicia (; gl, Galicia or ; es, Galicia}; pt, Galiza) is an autonomous community of Spain and historic nationality under Spanish law. Located in the northwest Iberian Peninsula, it includes the provinces of A Coruña, Lugo, Ourense, a ...
. Most of Latin America's colonial and industrial era Spanish immigration originates from Southern Spain and the Canary Islands, thus this regional enclave of Northern Spaniards is exceptional and remains the biggest diaspora of Asturias and Galicians by heritage in the Americas. This region also experienced concentrated waves of modern European immigration during the 20th century such as Italian and French, and the culture of the region reflects its lack of indigenous admixture. European rooted holidays like Saints days
In religious belief, a saint is a person who is recognized as having an exceptional degree of Q-D-Š, holiness, likeness, or closeness to God. However, the use of the term ''saint'' depends on the context and Christian denomination, denominat ...
, Carnival as well as gastronomy such as bread, cheese, and wine production remain unique to the region.
One of the few Porfirian-era European settlements to survive to this day is centered on the small town of Chipilo
Chipilo, officially known as Chipilo de Francisco Javier Mina, is a small city in the state of Puebla, Mexico. It is located south of the state capital Puebla, Puebla, at a height of above sea level. The name itself derives from Náhuatl, meani ...
in the state of Puebla. They are the descendants of about 500 Venetian refugee immigrants which came over in the 1880s, keeping their Venetian-derived dialect and distinct ethnic identity, even though many have intermarried with other Mexicans. Many still farm and raise livestock but economic changes have pushed many into industry. During the Mexican Revolution, Álvaro Obregón
Álvaro Obregón Salido (; 17 February 1880 – 17 July 1928) better known as Álvaro Obregón was a Sonoran-born general in the Mexican Revolution. A pragmatic centrist, natural soldier, and able politician, he became the 46th President of Me ...
invited a group of German-speaking Mennonite
Mennonites are groups of Anabaptist Christian church communities of denominations. The name is derived from the founder of the movement, Menno Simons (1496–1561) of Friesland. Through his writings about Reformed Christianity during the Radi ...
s in Canada to resettle in Chihuahua state. By the late 1920s, almost 10,000 had arrived from both Canada and Europe. Today, Mexico accounts for about 42% of all Mennonites in Latin America with 115,000 practicing Mennonites accounted for. Mennonites in the country especially stand out within their rural surroundings because of their traditional clothing, Plautdietsch language, light skin, hair and eyes. They own their own businesses in various communities in Chihuahua, and account for about half of the state's farm economy, standing out in cheese production.
Immigration was restricted by governments after Diaz's but never stopped entirely during the 20th century. Between 1937 and 1948, more than 18,000 Spanish Republican
The Spanish Republic (), commonly known as the Second Spanish Republic (), was the form of government in Spain from 1931 to 1939. The Republic was proclaimed on 14 April 1931, after the deposition of King Alfonso XIII, and was dissolved on 1 A ...
s arrived as refugees from the Nationalists
Nationalism is an idea and movement that holds that the nation should be congruent with the state. As a movement, nationalism tends to promote the interests of a particular nation (as in a group of people), Smith, Anthony. ''Nationalism: The ...
and Francoist Spain
Francoist Spain ( es, España franquista), or the Francoist dictatorship (), was the period of Spanish history between 1939 and 1975, when Francisco Franco ruled Spain after the Spanish Civil War with the title . After his death in 1975, Spai ...
. Their reception by the Mexican criollo elite was mixed but they manage to experience success as most of these newcomers were educated as scholars and artists. This group founded the Colegio de Mexico, one of the country's top academic institutions. Despite attempts to assimilate these immigrant groups, especially the country's already existing German population during World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposing ...
, they remain mostly separate to this day.
 Due to the 2008 Financial Crisis and the resulting economic decline and high unemployment in Spain, many Spaniards have been emigrating to Mexico to seek new opportunities. For example, during the last quarter of 2012, a number of 7,630 work permits were granted to Spaniards. Other Southern Europeans joined the Spaniards in the 2010s by finding better work opportunities in Mexico with thousands of Italians, Portuguese, French and Greeks finding professional opportunities along with the Spaniards in Mexico.
Sixty-seven percent of Latin America's English-speaking population lives in Mexico. Most of these are American nationals, with an influx of people from the U.S. coming to live in Mexico since the 1930s, becoming the largest group of foreigners in the country since then. However, most Americans in Mexico are not immigrants in the traditional sense, as they are there living as retirees or otherwise do not consider themselves permanent residents.
Due to the 2008 Financial Crisis and the resulting economic decline and high unemployment in Spain, many Spaniards have been emigrating to Mexico to seek new opportunities. For example, during the last quarter of 2012, a number of 7,630 work permits were granted to Spaniards. Other Southern Europeans joined the Spaniards in the 2010s by finding better work opportunities in Mexico with thousands of Italians, Portuguese, French and Greeks finding professional opportunities along with the Spaniards in Mexico.
Sixty-seven percent of Latin America's English-speaking population lives in Mexico. Most of these are American nationals, with an influx of people from the U.S. coming to live in Mexico since the 1930s, becoming the largest group of foreigners in the country since then. However, most Americans in Mexico are not immigrants in the traditional sense, as they are there living as retirees or otherwise do not consider themselves permanent residents.
Official censuses
Historically, population studies and censuses have never been up to the standards that a population as diverse and numerous such as Mexico's require: the first racial census was made in 1793, being also Mexico's (then known as New Spain) first ever nationwide population census, of it, only part of the original datasets survive, thus most of what is known of it comes from essays made by researchers who back in the day used the census' findings as reference for their own works. More than a century would pass until the Mexican government conducted a new racial census in 1921 (some sources assert that the census of 1895 included a comprehensive racial classification, however according to the historic archives of Mexico's National Institute of Statistics that was not the case). While the 1921 census was the last time the Mexican government conducted a census that included a comprehensive racial classification, in recent time it has conducted nationwide surveys to quantify most of the ethnic groups who inhabit the country as well as the social dynamics and inequalities between them.1793 census
Viceroyalty of New Spain
New Spain, officially the Viceroyalty of New Spain ( es, Virreinato de Nueva España, ), or Kingdom of New Spain, was an integral territorial entity of the Spanish Empire, established by Habsburg Spain during the Spanish colonization of the Amer ...
) first ever nationwide population census. Most of its original datasets have reportedly been lost; thus most of what is known about it nowadays comes from essays and field investigations made by academics who had access to the census data and used it as reference for their works such as Prussian geographer Alexander von Humboldt
Friedrich Wilhelm Heinrich Alexander von Humboldt (14 September 17696 May 1859) was a German polymath, geographer, naturalist, explorer, and proponent of Romantic philosophy and science. He was the younger brother of the Prussian minister, ...
. Each author gives different estimations for each racial group in the country, although they don't vary much, with Europeans ranging from 18% to 22% of New Spain's population, Mestizos ranging from 21% to 25%, Indians ranging from 51% to 61% and Africans being between 6,000 and 10,000, The estimations given for the total population range from 3,799,561 to 6,122,354. It is concluded then, that across nearly three centuries of colonization, the population growth trends of whites and mestizos were even, while the total percentage of the indigenous population decreased at a rate of 13%-17% per century. The authors assert that rather than whites and mestizos having higher birthrates, the reason for the indigenous population's numbers decreasing lies on them suffering of higher mortality rates, due living in remote locations rather than on cities and towns founded by the Spanish colonists or being at war with them. It is also for these reasons that the number of Indigenous Mexicans presents the greater variation range between publications, as in cases their numbers in a given location were estimated rather than counted, leading to possible overestimations in some provinces and possible underestimations in others.
~Europeans are included within the Mestizo category.
Regardless of the possible imprecisions related to the counting of Indigenous peoples living outside of the colonized areas, the effort that New Spain's authorities put on considering them as subjects is worth mentioning, as censuses made by other colonial or post-colonial countries did not consider American Indians to be citizens/subjects, as example the censuses made by the Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata
The Viceroyalty of the Río de la Plata ( es, Virreinato del Río de la Plata or es, Virreinato de las Provincias del Río de la Plata) meaning "River of the Silver", also called " Viceroyalty of the River Plate" in some scholarly writings, i ...
would only count the inhabitants of the colonized settlements.''Historical Dictionary of Argentina''. London: Scarecrow Press, 1978. pp. 239–40. Other example would be the censuses made by the United States, that did not include Indigenous peoples living among the general population until 1860, and indigenous peoples as a whole until 1900.
1921 census
 Made right after the consummation of the Mexican revolution, the social context on which this census was made makes it particularly unique, as the government of the time was in the process of rebuilding the country and was looking forward to unite all Mexicans under a single national identity. The 1921 census' final results in regards to race, which assert that 59.3% of the Mexican population self-identified as Mestizo, 29.1% as Indigenous and only 9.8% as White were then essential to cement the "mestizaje" ideology (that asserts that the Mexican population as a whole is product of the admixture of all races) which shaped Mexican identity and culture through the 20th century and remain prominent nowadays, with extraofficial international publications such as ''
Made right after the consummation of the Mexican revolution, the social context on which this census was made makes it particularly unique, as the government of the time was in the process of rebuilding the country and was looking forward to unite all Mexicans under a single national identity. The 1921 census' final results in regards to race, which assert that 59.3% of the Mexican population self-identified as Mestizo, 29.1% as Indigenous and only 9.8% as White were then essential to cement the "mestizaje" ideology (that asserts that the Mexican population as a whole is product of the admixture of all races) which shaped Mexican identity and culture through the 20th century and remain prominent nowadays, with extraofficial international publications such as ''The World Factbook
''The World Factbook'', also known as the ''CIA World Factbook'', is a reference resource produced by the Central Intelligence Agency (CIA) with almanac-style information about the countries of the world. The official print version is availabl ...
'' and Encyclopædia Britannica
The (Latin for "British Encyclopædia") is a general knowledge English-language encyclopaedia. It is published by Encyclopædia Britannica, Inc.; the company has existed since the 18th century, although it has changed ownership various t ...
using them as a reference to estimate Mexico's racial composition up to this day.
Nonetheless, in recent time the census' results have been subjected to scrutiny by historians, academics and social activists alike, who assert that such drastic alterations on demographic trends with respect to the 1793 census are not possible and cite, among other statistics the relatively low frequency of marriages between people of different continental ancestries in colonial and early independent Mexico. It is claimed that the "mestizaje" process sponsored by the state was more "cultural than biological" which resulted on the numbers of the Mestizo Mexican group being inflated at the expense of the identity of other races. Controversies aside, this census constituted the last time the Mexican Government
The Federal government of Mexico (alternately known as the Government of the Republic or ' or ') is the national government of the United Mexican States, the central government established by its constitution to share sovereignty over the republi ...
conducted a comprehensive racial census with the breakdown by states being the following (foreigners and people who answered "other" not included):
When the 1921 census's results are compared with the results of Mexico's recent censuses as well as with modern genetic research,"El impacto del mestizaje en México""Investigación y Ciencia", Spain, October 2013. Retrieved on 01 June 2017. high consistence is found in regards to the distribution of Indigenous Mexicans across the country, with states located in south and south-eastern Mexico having both, the highest percentages of population that self-identifies as Indigenous and the highest percentages of Amerindian genetic ancestry. However this is not the case when it comes to European Mexicans, as there are instances on which states that have been shown to have a considerably high European ancestry per scientific research are reported to have very small white populations in the 1921 census, with the most extreme case being that of the state of Durango, where the aforementioned census asserts that only 0.01% of the state's population (33 persons) self-identified as "white" while modern scientific research shows that the population of Durango has similar genetic frequencies to those found on European peoples (with the state's Indigenous population showing almost no foreign admixture either). Various authors theorize that the reason for these inconsistencies may lie in the Mestizo identity promoted by the Mexican government, which reportedly led to people who are not biologically Mestizos to identify as such.
.
Present day
 The following table is a compilation of (when possible) official nationwide surveys conducted by the Mexican government who have attempted to quantify different Mexican ethnic groups. Given that for the most part each ethnic group was estimated by different surveys, with different methodologies and years apart rather than on a single comprehensive racial census, some groups could overlap with others and be overestimated or underestimated.
Of all the ethnic groups that have been surveyed, Mestizos are notably absent, which is likely due to the label's fluid and subjective definition, which complicates its precise quantification. However, it can be safely assumed that Mestizos make up at least the remaining 30% unassessed percentage of Mexico's population with possibilities of increasing if the methodologies of the extant surveys are considered. As example the 2015 intercensal survey considered as Indigenous Mexicans and Afro-Mexicans altogether individuals who self-identified as "part Indigenous" or "part African" thus, said people technically would be Mestizos. Similarly, White Mexicans were quantified based on physical traits/appearance, thus technically a Mestizo with a percentage of Indigenous ancestry that was low enough to not affect his/her primarily European phenotype was considered to be white. Finally the remaining ethnicities, for being of a rather low number or being faiths have more permissive classification criteria, therefore a Mestizo could claim to belong to one of them by practicing the faith, or by having an ancestor who belonged to said ethnicities.
Nonetheless, contemporary sociologists and historians agree that, given that the concept of "race" has a psychological foundation rather than a biological one and to society's eyes a Mestizo with a high percentage of European ancestry is considered "white" and a Mestizo with a high percentage of Indigenous ancestry is considered "Indian," a person who identifies with a given ethnic group should be allowed to, even if biologically doesn't completely belong to that group.
The following table is a compilation of (when possible) official nationwide surveys conducted by the Mexican government who have attempted to quantify different Mexican ethnic groups. Given that for the most part each ethnic group was estimated by different surveys, with different methodologies and years apart rather than on a single comprehensive racial census, some groups could overlap with others and be overestimated or underestimated.
Of all the ethnic groups that have been surveyed, Mestizos are notably absent, which is likely due to the label's fluid and subjective definition, which complicates its precise quantification. However, it can be safely assumed that Mestizos make up at least the remaining 30% unassessed percentage of Mexico's population with possibilities of increasing if the methodologies of the extant surveys are considered. As example the 2015 intercensal survey considered as Indigenous Mexicans and Afro-Mexicans altogether individuals who self-identified as "part Indigenous" or "part African" thus, said people technically would be Mestizos. Similarly, White Mexicans were quantified based on physical traits/appearance, thus technically a Mestizo with a percentage of Indigenous ancestry that was low enough to not affect his/her primarily European phenotype was considered to be white. Finally the remaining ethnicities, for being of a rather low number or being faiths have more permissive classification criteria, therefore a Mestizo could claim to belong to one of them by practicing the faith, or by having an ancestor who belonged to said ethnicities.
Nonetheless, contemporary sociologists and historians agree that, given that the concept of "race" has a psychological foundation rather than a biological one and to society's eyes a Mestizo with a high percentage of European ancestry is considered "white" and a Mestizo with a high percentage of Indigenous ancestry is considered "Indian," a person who identifies with a given ethnic group should be allowed to, even if biologically doesn't completely belong to that group.
See also
* Europeans *White people
White is a racialized classification of people and a skin color specifier, generally used for people of European origin, although the definition can vary depending on context, nationality, and point of view.
Description of populations as ...
*White Latin Americans
White Latin Americans, or European Latin Americans, are Latin Americans who are considered white, typically due to European descent. Latin American countries have often tolerated intermarriage between different ethnic groups since the beginning ...
* White Latino Americans
*White Colombians
White Colombians are the Colombian descendants of European and Middle Eastern people. According to the 2018 Census, 87.58% of Colombians do not identify with any ethnic group, thus being either White or Mestizo (mixed European and Amerindian anc ...
*White Brazilians
White Brazilians ( pt, brasileiros brancos ) refers to Brazilian citizens who are considered or self-identify as "white", typically because of European or Levantine descent.
The main ancestry of current white Brazilians is Portuguese. Histori ...
*White Americans
White Americans are Americans who identify as and are perceived to be white people. This group constitutes the majority of the people in the United States. As of the 2020 Census, 61.6%, or 204,277,273 people, were white alone. This represented ...
*Indigenous Mexicans
Indigenous peoples of Mexico ( es, gente indígena de México, pueblos indígenas de México), Native Mexicans ( es, nativos mexicanos) or Mexican Native Americans ( es, pueblos originarios de México, lit=Original peoples of Mexico), are those ...
*Afro-Mexicans
Afro-Mexicans ( es, afromexicanos), also known as Black Mexicans ( es, mexicanos negros), are Mexicans who have heritage from sub-Saharan Africa and identify as such. As a single population, Afro-Mexicans include individuals descended from both f ...
*Asian Mexicans
, image =
, image_caption =
, popplace = Baja California, Bajío Region, Guerrero, Mexico City, Yucatan
, langs = Mexican Spanish and Asian languages
, rels = Christianity (mainly Catholicism), ...
*Criollo people
In Hispanic America, criollo () is a term used originally to describe people of Spanish descent born in the colonies. In different Latin American countries the word has come to have different meanings, sometimes referring to the local-born maj ...
* Castizo
* Gringo
References
{{White people Ethnic groups in Mexico *