Medium frequency on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for
Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for
 A major use of these frequencies is
A major use of these frequencies is
RN Northwood in England broadcasts Weather Fax data on 2618.5 kHz. Non-directional navigational radio beacons (NDBs) for maritime and aircraft navigation occupy a band from 190 to 435 kHz, which overlaps from the LF into the bottom part of the MF band. 2182 kHz is the international calling and distress frequency for SSB maritime voice communication (radiotelephony). It is analogous to Channel 16 on the marine VHF band. 500 kHz was for many years the maritime distress and emergency frequency, and there are more NDBs between 510 and 530 kHz. Navtex, which is part of the current
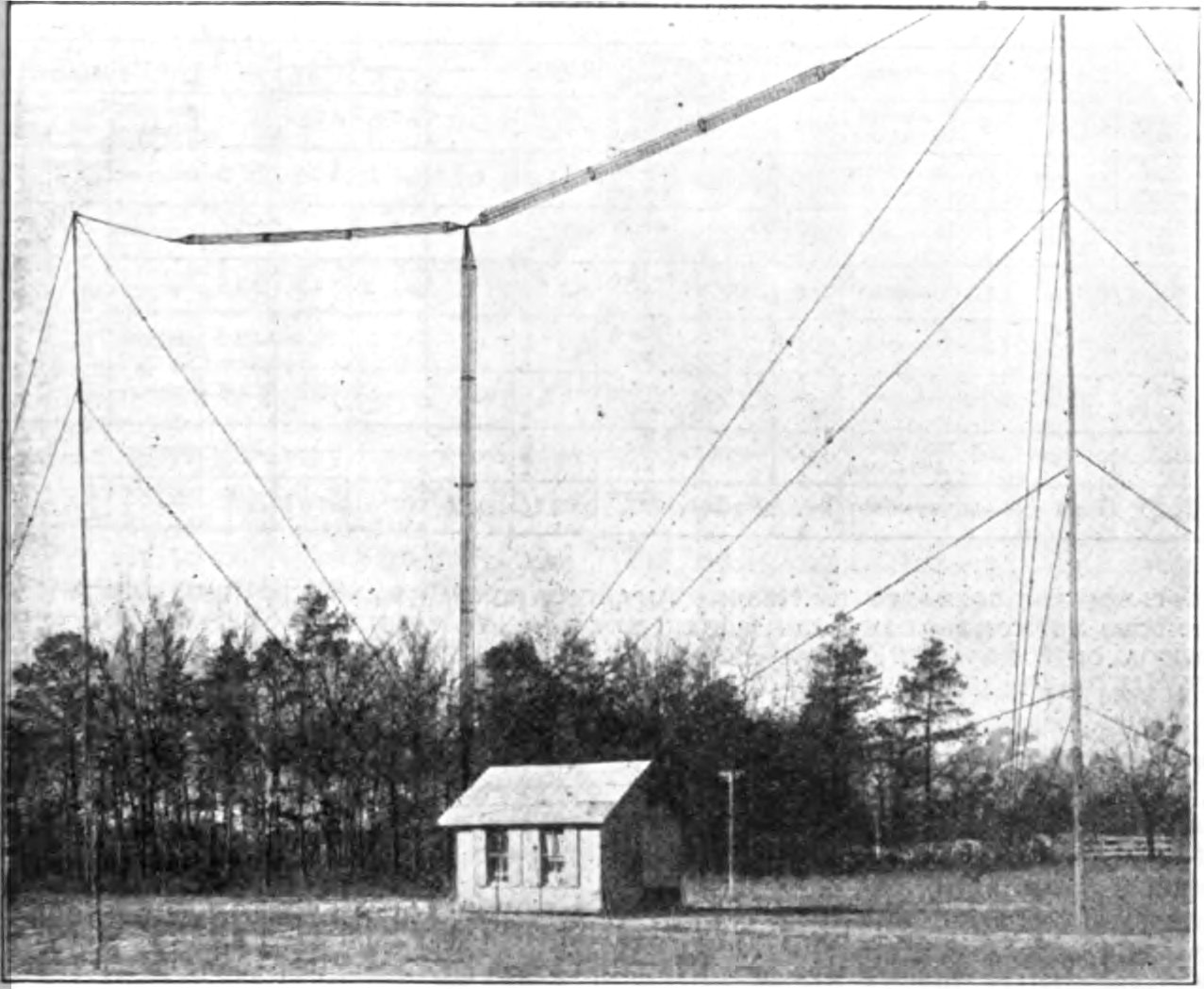 Transmitting antennas commonly used on this band include monopole
Transmitting antennas commonly used on this band include monopole
Definition of frequency bands (VLF, ELF... etc.)
'". IK1QFK Home Page (vlf.it). {{Authority control Radio spectrum
 Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for
Medium frequency (MF) is the ITU designation for radio frequencies
Radio frequency (RF) is the oscillation rate of an alternating electric current or voltage or of a magnetic, electric or electromagnetic field or mechanical system in the frequency range from around to around . This is roughly between the upper ...
(RF) in the range of 300 kilohertz (kHz) to 3 megahertz (MHz). Part of this band is the medium wave (MW) AM broadcast band. The MF band is also known as the hectometer band as the wavelengths range from ten to one hectometer
The hectometre (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -er, International spelling as used by the International Bureau of Weights and Measures; SI symbol: hm) or hectometer (American and British English spelling differences#-re, -e ...
(1000 to 100 m). Frequencies immediately below MF are denoted low frequency (LF), while the first band of higher frequencies is known as high frequency (HF). MF is mostly used for AM radio broadcasting, navigational radio beacons, maritime ship-to-shore communication, and transoceanic air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airs ...
.
Propagation
Radio waves at MF wavelengths propagate viaground wave
Ground waves are radio waves propagating parallel to and adjacent to the surface of the Earth, following the curvature of the Earth. This radiation is known as Norton surface wave, or more properly Norton ground wave, because ground waves in rad ...
s and reflection from the ionosphere (called skywaves). Ground waves follow the curvature of Earth
Spherical Earth or Earth's curvature refers to the approximation of figure of the Earth as a sphere.
The earliest documented mention of the concept dates from around the 5th century BC, when it appears in the writings of Greek philosophers. ...
. At these wavelengths they can bend (diffract
Diffraction is defined as the interference or bending of waves around the corners of an obstacle or through an aperture into the region of geometrical shadow of the obstacle/aperture. The diffracting object or aperture effectively becomes a s ...
) over hills, and travel beyond the visual horizon, although they may be blocked by mountain ranges. Typical MF radio stations can cover a radius of several hundred miles from the transmitter, with longer distances over water and damp earth. MF broadcasting stations use ground waves to cover their listening areas.
MF waves can also travel longer distances via skywave propagation, in which radio waves radiated at an angle into the sky are refracted
In physics, refraction is the redirection of a wave as it passes from one medium to another. The redirection can be caused by the wave's change in speed or by a change in the medium. Refraction of light is the most commonly observed phenomeno ...
back to Earth by layers of charged particles (ion
An ion () is an atom or molecule with a net electrical charge.
The charge of an electron is considered to be negative by convention and this charge is equal and opposite to the charge of a proton, which is considered to be positive by conve ...
s) in the ionosphere, the E and F layer
The F region of the ionosphere is home to the F layer of ionization, also called the Appleton–Barnett layer, after the English physicist Edward Appleton and New Zealand physicist and meteorologist Miles Barnett. As with other ionospheric secto ...
s. However, at certain times the D layer (at a lower altitude than the refractive E and F layers) can be electronically noisy and absorb MF radio waves, interfering with skywave propagation. This happens when the ionosphere is heavily ionised, such as during the day, in summer and especially at times of high solar activity
Solar phenomena are natural phenomena which occur within the atmosphere of the Sun. These phenomena take many forms, including solar wind, radio wave flux, solar flares, coronal mass ejections, coronal heating and sunspots.
These phenomena are ...
.
At night, especially in winter months and at times of low solar activity, the ionospheric D layer can virtually disappear. When this happens, MF radio waves can easily be received hundreds or even thousands of miles away as the signal will be refracted by the remaining F layer. This can be very useful for long-distance communication, but can also interfere with local stations. Due to the limited number of available channels in the MW broadcast band, the same frequencies are re-allocated to different broadcasting stations several hundred miles apart. On nights of good skywave propagation, the signals of distant stations may reflect off the ionosphere and interfere with the signals of local stations on the same frequency. The North American Regional Broadcasting Agreement (NARBA) sets aside certain channels for nighttime use over extended service areas via skywave by a few specially licensed AM broadcasting stations. These channels are called ''clear channels'', and the stations, called '' clear-channel stations'', are required to broadcast at higher powers of 10 to 50 kW.
Uses and applications
 A major use of these frequencies is
A major use of these frequencies is AM broadcasting
AM broadcasting is radio broadcasting using amplitude modulation (AM) transmissions. It was the first method developed for making audio radio transmissions, and is still used worldwide, primarily for medium wave (also known as "AM band") transm ...
; AM radio station
Radio broadcasting is transmission of audio (sound), sometimes with related metadata, by radio waves to radio receivers belonging to a public audience. In terrestrial radio broadcasting the radio waves are broadcast by a land-based radi ...
s are allocated frequencies in the medium wave broadcast band from 526.5 kHz to 1606.5 kHz
in Europe; in North America this extends from 525 kHz to 1705 kHz Some countries also allow broadcasting in the 120-meter band from 2300 to 2495 kHz; these frequencies are mostly used in tropical areas. Although these are medium frequencies, 120 meters is generally treated as one of the shortwave bands.
There are a number of coast guard
A coast guard or coastguard is a maritime security organization of a particular country. The term embraces wide range of responsibilities in different countries, from being a heavily armed military force with customs and security duties to ...
and other ship-to-shore frequencies in use between 1600 and 2850 kHz. These include, as examples, the French MRCC on 1696 kHz and 2677 kHz, Stornoway Coastguard on 1743 kHz, the US Coastguard on 2670 kHz and Madeira on 2843 kHz.MF/HF SSB FrequenciesRN Northwood in England broadcasts Weather Fax data on 2618.5 kHz. Non-directional navigational radio beacons (NDBs) for maritime and aircraft navigation occupy a band from 190 to 435 kHz, which overlaps from the LF into the bottom part of the MF band. 2182 kHz is the international calling and distress frequency for SSB maritime voice communication (radiotelephony). It is analogous to Channel 16 on the marine VHF band. 500 kHz was for many years the maritime distress and emergency frequency, and there are more NDBs between 510 and 530 kHz. Navtex, which is part of the current
Global Maritime Distress Safety System
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a worldwide system for automated emergency signal communication for ships at sea developed by the United Nations' International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the SOLAS Convent ...
occupies 518 kHz and 490 kHz for important digital text broadcasts. Lastly, there are aeronautical and other mobile SSB bands from 2850 kHz to 3500 kHz, crossing the boundary from the MF band into the HF radio band.
An amateur radio band known as 160 meters
160-meter band refers to the band of radio frequencies between 1.8 and 2 MHz, just above the medium wave broadcast band. For many decades the lowest radio frequency band allocated for use by amateur radio, before the adoption, at the beginn ...
or 'top-band' is between 1800 and 2000 kHz (allocation depends on country and starts at 1810 kHz outside the Americas). Amateur operators transmit CW morse code, digital signals and SSB and AM voice signals on this band. Following World Radiocommunication Conference
The World Radiocommunication Conference (WRC) is a conference organized by the ITU to review and, as necessary, revise the Radio Regulations, the international treaty governing the use of the radio-frequency spectrum as well as geostationary and ...
2012 (WRC-2012), the amateur service received a new allocation between 472 and 479 kHz for narrow band modes and secondary service, after extensive propagation and compatibility studies made by the ARRL 600 meters Experiment Group and their partners around the world. In recent years, some limited amateur radio operation has also been allowed in the region of 500 kHz in the US, UK, Germany and Sweden.
Many home-portable or cordless telephones, especially those that were designed in the 1980s, transmit low power FM audio signals between the table-top base unit and the handset on frequencies in the range 1600 to 1800 kHz.
Antennas
 Transmitting antennas commonly used on this band include monopole
Transmitting antennas commonly used on this band include monopole mast radiator
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio ma ...
s, top-loaded wire monopole antennas such as the inverted-L and T antennas, and wire dipole antennas. Ground wave
Ground waves are radio waves propagating parallel to and adjacent to the surface of the Earth, following the curvature of the Earth. This radiation is known as Norton surface wave, or more properly Norton ground wave, because ground waves in rad ...
propagation, the most widely used type at these frequencies, requires vertically polarized antennas like monopoles.
The most common transmitting antenna, the quarter wave monopole, is physically large at these frequencies, requiring a tall radio mast
Radio masts and towers are typically tall structures designed to support antennas for telecommunications and broadcasting, including television. There are two main types: guyed and self-supporting structures. They are among the tallest human-made ...
. Usually the metal mast itself is used as the antenna, and is mounted on a large porcelain insulator to isolate it from the ground; this is called a ''mast radiator
Mast, MAST or MASt may refer to:
Engineering
* Mast (sailing), a vertical spar on a sailing ship
* Flagmast, a pole for flying a flag
* Guyed mast, a structure supported by guy-wires
* Mooring mast, a structure for docking an airship
* Radio ma ...
''. The monopole antenna, particularly if electrically short requires a good, low resistance Earth ground connection for efficiency, since the ground resistance is in series with the antenna and consumes transmitter power. Commercial radio stations use a ground system consisting of many heavy copper cables, buried a few feet in the earth, radiating from the base of the antenna to a distance of about a quarter wavelength. In areas of rocky or sandy soil where the ground conductivity is poor, above ground counterpoises are used.
Lower power transmitters often use electrically short quarter wave monopoles such as inverted-L or T antennas, which are brought into resonance with a loading coil at their base.
Receiving antennas do not have to be as efficient as transmitting antennas since in this band the signal-to-noise ratio is determined by atmospheric noise. The noise floor
In signal theory, the noise floor is the measure of the signal created from the sum of all the noise sources and unwanted signals within a measurement system, where noise is defined as any signal other than the one being monitored.
In radio com ...
in the receiver is far below the noise in the signal, so antennas small in comparison to the wavelength, which are inefficient and produce low signal strength, can be used. The most common receiving antenna is the ferrite loopstick antenna (also known as a '' ferrite rod aerial''), made from a ferrite rod with a coil of fine wire wound around it. This antenna is small enough that it is usually enclosed inside the radio case. In addition to their use in AM radios, ferrite antennas are also used in portable radio direction finder (RDF) receivers. The ferrite rod antenna has a dipole
In physics, a dipole () is an electromagnetic phenomenon which occurs in two ways:
*An electric dipole deals with the separation of the positive and negative electric charges found in any electromagnetic system. A simple example of this system ...
reception pattern with sharp nulls along the axis of the rod, so that reception is at its best when the rod is at right angles to the transmitter, but fades to nothing when the rod points exactly at the transmitter. Other types of loop antennas and random wire antenna
A random wire antenna is a radio antenna consisting of a long wire suspended above the ground, whose length does not bear a particular relation to the wavelength of the radio waves used, but is typically chosen more for convenience. The wire may ...
s are also used.
See also
*Electromagnetic spectrum
The electromagnetic spectrum is the range of frequencies (the spectrum) of electromagnetic radiation and their respective wavelengths and photon energies.
The electromagnetic spectrum covers electromagnetic waves with frequencies ranging fro ...
* Global Maritime Distress Safety System
The Global Maritime Distress and Safety System (GMDSS) is a worldwide system for automated emergency signal communication for ships at sea developed by the United Nations' International Maritime Organization (IMO) as part of the SOLAS Convent ...
* Maritime broadcast communications net
* Navtex
* Types of radio emissions
The International Telecommunication Union uses an internationally agreed system for classifying radio frequency signals. Each type of radio emission is classified according to its bandwidth, method of modulation, nature of the modulating signal, ...
References
Federal Standard 1037C
Federal Standard 1037C, titled Telecommunications: Glossary of Telecommunication Terms, is a United States Federal Standard issued by the General Services Administration pursuant to the Federal Property and Administrative Services Act of 1949, a ...
Further reading
* Charles Allen Wright and Albert Frederick Puchstein, "''Telephone communication, with particular application to medium-frequency alternating currents and electro-motive forces''". New York tc.McGraw-Hill Book Company, inc., 1st ed., 1925. LCCN 25008275External links
* Tomislav Stimac, "Definition of frequency bands (VLF, ELF... etc.)
'". IK1QFK Home Page (vlf.it). {{Authority control Radio spectrum