Matthew Paris on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Matthew Paris, also known as Matthew of Paris ( la, Matthæus Parisiensis, lit=Matthew the Parisian; c. 1200 – 1259), was an English
 In spite of his surname and knowledge of the French language, Paris was of English birth, and is believed by some chroniclers to be of the Paris family of
In spite of his surname and knowledge of the French language, Paris was of English birth, and is believed by some chroniclers to be of the Paris family of  Apart from these missions, his known activities were devoted to the composition of history, a pursuit for which the monks of St Albans had long been famous. After admission to the order in 1217, he inherited the mantle of Roger of Wendover, the abbey's official recorder of events, in 1236. Paris revised Roger's work, adding new material to cover his own tenure. This ''
Apart from these missions, his known activities were devoted to the composition of history, a pursuit for which the monks of St Albans had long been famous. After admission to the order in 1217, he inherited the mantle of Roger of Wendover, the abbey's official recorder of events, in 1236. Paris revised Roger's work, adding new material to cover his own tenure. This ''

 * ''
* '' * ''Life of
* ''Life of
 In some of Paris's manuscripts, a framed miniature occupies the upper half of the page, and in others, they are "marginal" – unframed and occupying the bottom quarter (approximately) of the page. Tinted drawings were an established style well before Paris, and became especially popular in the first half of the 13th century. They were certainly much cheaper and quicker than fully painted illuminations. The tradition of tinted drawings or outline drawings with ink supplemented by coloured wash was distinctively English, dating back to the
In some of Paris's manuscripts, a framed miniature occupies the upper half of the page, and in others, they are "marginal" – unframed and occupying the bottom quarter (approximately) of the page. Tinted drawings were an established style well before Paris, and became especially popular in the first half of the 13th century. They were certainly much cheaper and quicker than fully painted illuminations. The tradition of tinted drawings or outline drawings with ink supplemented by coloured wash was distinctively English, dating back to the  Recent scholarship, notably that of Nigel Morgan, suggests that Paris's influence on other artists of the period has been exaggerated. This is likely because so much more is known about him than other English illuminators of the period, who are mostly anonymous. Most manuscripts seem to have been produced by lay artists in this period.
Recent scholarship, notably that of Nigel Morgan, suggests that Paris's influence on other artists of the period has been exaggerated. This is likely because so much more is known about him than other English illuminators of the period, who are mostly anonymous. Most manuscripts seem to have been produced by lay artists in this period.
 Outstanding among his other maps were (four versions of) a pilgrim
Outstanding among his other maps were (four versions of) a pilgrim
ImagesStanford Digitized texts – Works by and about Paris, including Vaughan etc, in huge pdf filesJSTOR review of Vaughan book
British Library website
* ttp://www.bartleby.com/211/0919.html Latin Chroniclers from the Eleventh to the Thirteenth Centuries:Matthew Parisfrom '' The Cambridge History of English and American Literature'', Volume I, 1907–21.
Life of St Edward the Confessor, Cambridge Digital LibraryFully annotated copy of Matthew Paris's Claudius Map, with translations and transcriptions
{{DEFAULTSORT:Paris, Matthew 1200 births 1259 deaths Year of birth uncertain People from St Albans English Benedictines English Christian monks English chroniclers English cartographers Historians of the Catholic Church Heraldists Manuscript illuminators Writers who illustrated their own writing Medieval European scribes People educated at St Albans School, Hertfordshire Artist authors Medieval English painters 13th-century Christian monks 13th-century painters 13th-century English artists 13th-century Latin writers 13th-century English historians
Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
monk, chronicler, artist in illuminated manuscript
An illuminated manuscript is a formally prepared document where the text is often supplemented with flourishes such as borders and miniature illustrations. Often used in the Roman Catholic Church for prayers, liturgical services and psalms, th ...
s and cartographer, based at St Albans Abbey in Hertfordshire
Hertfordshire ( or ; often abbreviated Herts) is one of the home counties in southern England. It borders Bedfordshire and Cambridgeshire to the north, Essex to the east, Greater London to the south, and Buckinghamshire to the west. For gov ...
. He wrote a number of works, mostly historical, which he scribed and illuminated himself, typically in drawings partly coloured with watercolour washes, sometimes called "tinted drawings". Some were written in Latin, others in Anglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
*Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 ...
or French
French (french: français(e), link=no) may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to France
** French language, which originated in France, and its various dialects and accents
** French people, a nation and ethnic group identified with Franc ...
verse.
His ''Chronica Majora
The ''Chronica Majora'' is the seminal work of Matthew Paris, a member of the English Benedictine community of St Albans and long-celebrated historian. The work begins with Creation and contains annals down to the year of Paris' death of 1259. ...
'' is an oft-cited source, though modern historians recognise that Paris was not always reliable. He tended to glorify Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and denigrate the pope. However, in his ''Historia Anglorum'', Paris displays a highly negative view of Frederick, going as far as to describe him as a "tyrant" who "committed disgraceful crimes".
Life and work
 In spite of his surname and knowledge of the French language, Paris was of English birth, and is believed by some chroniclers to be of the Paris family of
In spite of his surname and knowledge of the French language, Paris was of English birth, and is believed by some chroniclers to be of the Paris family of Hildersham
Hildersham is a small village 8 miles to the south-east of Cambridge, England. It is situated just off the A1307 between Linton and Great Abington on a tributary of the River Cam known locally as the River Granta.
The parish boundary extend ...
, Cambridgeshire
Cambridgeshire (abbreviated Cambs.) is a county in the East of England, bordering Lincolnshire to the north, Norfolk to the north-east, Suffolk to the east, Essex and Hertfordshire to the south, and Bedfordshire and Northamptonshire to t ...
. He may have studied at Paris in his youth after early education at St Albans School. The first we know of Matthew Paris (from his own writings) is that he was admitted as a monk to St Albans
St Albans () is a cathedral city in Hertfordshire, England, east of Hemel Hempstead and west of Hatfield, north-west of London, south-west of Welwyn Garden City and south-east of Luton. St Albans was the first major town on the old Roman ...
in 1217. It is on the assumption that he was in his teens on admission that his birth date is estimated; some scholars suspect he may have been ten years or older; many monks only entered monastic life after pursuing a career in the world outside. He was clearly at ease with the nobility and even royalty, which may indicate that he came from a family of some status, although it also seems an indication of his personality. His life was mainly spent in this religious house. In 1248, Paris was sent to Norway
Norway, officially the Kingdom of Norway, is a Nordic countries, Nordic country in Northern Europe, the mainland territory of which comprises the western and northernmost portion of the Scandinavian Peninsula. The remote Arctic island of ...
as the bearer of a message from Louis IX
Louis IX (25 April 1214 – 25 August 1270), commonly known as Saint Louis or Louis the Saint, was King of France from 1226 to 1270, and the most illustrious of the House of Capet, Direct Capetians. He was Coronation of the French monarch, c ...
to Haakon IV; he made himself so agreeable to the Norwegian sovereign that he was invited to superintend the reformation of the Benedictine
, image = Medalla San Benito.PNG
, caption = Design on the obverse side of the Saint Benedict Medal
, abbreviation = OSB
, formation =
, motto = (English: 'Pray and Work')
, foun ...
Nidarholm Abbey
Nidarholm Abbey was a Benedictine monastery located on the island of Munkholmen in Trondheim Fjord on the sea approach to Trondheim, Norway.
History
The monastery was founded either in 1028 by King Canute the Great or in about 1100 by Sigurd Ull ...
outside Trondheim
Trondheim ( , , ; sma, Tråante), historically Kaupangen, Nidaros and Trondhjem (), is a city and municipality in Trøndelag county, Norway. As of 2020, it had a population of 205,332, was the third most populous municipality in Norway, an ...
. Apart from these missions, his known activities were devoted to the composition of history, a pursuit for which the monks of St Albans had long been famous. After admission to the order in 1217, he inherited the mantle of Roger of Wendover, the abbey's official recorder of events, in 1236. Paris revised Roger's work, adding new material to cover his own tenure. This ''
Apart from these missions, his known activities were devoted to the composition of history, a pursuit for which the monks of St Albans had long been famous. After admission to the order in 1217, he inherited the mantle of Roger of Wendover, the abbey's official recorder of events, in 1236. Paris revised Roger's work, adding new material to cover his own tenure. This ''Chronica Majora
The ''Chronica Majora'' is the seminal work of Matthew Paris, a member of the English Benedictine community of St Albans and long-celebrated historian. The work begins with Creation and contains annals down to the year of Paris' death of 1259. ...
'' is an important historical source document, especially for the period between 1235 and 1259. Equally interesting are the illustrations Paris created for his work.
The Dublin MS (see below) contains interesting notes, which shed light on Paris's involvement in other manuscripts, and on the way his own were used. They are in French and in his handwriting:
*"If you please you can keep this book till Easter"
*"G, please send to the Lady Countess of Arundel, Isabel, that she is to send you the book about St Thomas the Martyr and St Edward which I copied ranslated?and illustrated, and which the Lady Countess of Cornwall may keep until Whitsuntide"
* some verses
* "In the Countess of Winchester's book let there be a pair of images on each page thus": (verses follow describing thirteen saints)
It is presumed the last relates to Paris acting as commissioning agent and iconographical consultant for the Countess with another artist.
The lending of his manuscripts to aristocratic households, apparently for periods of weeks or months at a time, suggests why he made several different illustrated versions of his Chronicle.
Manuscripts by Matthew Paris
Paris's manuscripts mostly contain more than one text, and often begin with a rather random assortment of prefatory full-page miniatures. Some have survived incomplete, and the various elements now bound together may not have been intended to be so by Paris. Unless stated otherwise, all were given by Paris to his monastery (from some inscriptions it seems they were regarded as his property to dispose of). The monastic libraries were broken up at the Dissolution. These MSS seem to have been appreciated, and were quickly collected by bibliophiles. Many of his manuscripts in theBritish Library
The British Library is the national library of the United Kingdom and is one of the largest libraries in the world. It is estimated to contain between 170 and 200 million items from many countries. As a legal deposit library, the Briti ...
are from the Cotton Library.
 * ''
* ''Chronica Majora
The ''Chronica Majora'' is the seminal work of Matthew Paris, a member of the English Benedictine community of St Albans and long-celebrated historian. The work begins with Creation and contains annals down to the year of Paris' death of 1259. ...
''. Corpus Christi College, Cambridge
Corpus Christi College (full name: "The College of Corpus Christi and the Blessed Virgin Mary", often shortened to "Corpus"), is a constituent college of the University of Cambridge. From the late 14th century through to the early 19th centur ...
, Mss 26 and 16, 362 × 244/248 mm. ff 141 + 281, composed 1240–53. His major historical work (see below), but less heavily illustrated per page than others. These two volumes contain annals from the creation of the world up to the year 1253. The content up to 1234 or 1235 is based in the main on Roger of Wendover's ''Flores Historiarum'', with additions; after that date, the material is Paris's own, and written in his own hand from the annal for 1213 onward. There are 100 marginal drawings (25 + 75), some fragmentary maps and an itinerary, and full-page drawings of William I
William I; ang, WillelmI (Bates ''William the Conqueror'' p. 33– 9 September 1087), usually known as William the Conqueror and sometimes William the Bastard, was the first Norman king of England, reigning from 1066 until his death in 10 ...
. MS 16 has very recently had all prefatory matter re-bound separately.
:A continuation of the ''Chronica'', from 1254 until Paris's death in 1259, is bound with the ''Historia Anglorum'' in the British Library volume below. An unillustrated copy of the material from 1189 to 1250, with much of his sharper commentary about Henry III toned down or removed, was supervised by Paris himself and now exists as British Library Cotton MS Nero D V, fol. 162–393.
* '' Flores Historiarum''. Chetham's Hospital and Library, Manchester, MS 6712. Only part of the text, covering 1241 to 1249, is in Paris's hand, though he is credited with the authorship of the whole text, which is an abridgement of the ''Chronica'' with additions from the annals of Reading and of Southwark. Additional interpolations to the text make it clear the volume was created for Westminster Abbey
Westminster Abbey, formally titled the Collegiate Church of Saint Peter at Westminster, is an historic, mainly Gothic church in the City of Westminster, London, England, just to the west of the Palace of Westminster. It is one of the United ...
. It was apparently started there, copying another MS of Paris's text that went up to 1240. Later it was sent back to the author for him to update; Richard Vaughan argues this was in 1251–2. The illustrations are similar to Paris's style but not by him. Later additions took the chronicle up to 1327.
* ''Historia Anglorum''. British Library, Royal MS 14 C VII, fols. 8v–156v. 358 × 250 mm, ff 232 in all. A history of England, begun in 1250 and perhaps completed around 1255, covering the years 1070–1253. The text is an abridgement of the ''Chronica'', also drawing on Wendover's ''Flores Historiarum'' and Paris's earlier edited version of the ''Chronica''. Bound with it is the final part of Paris's ''Chronica Majora'', covering the years 1254–1259 (folios 157–218), and prefatory material including an itinerary from London to Jerusalem and tinted drawings of the kings of England. All is in Paris's own hand, apart from folios 210–218 and 154v–156v, which are in the hand of the scribe who has added a note of Matthew Paris's death (f. 218v). The ''Chronica'' concludes with a portrait of Paris on his death-bed, presumably not by him. By the 15th century this volume belonged to Humphrey, Duke of Gloucester, son of Henry IV, who inscribed it "Ceste livre est a moy Homffrey Duc de Gloucestre". Later it was held by the bishop of Lincoln, who wrote a note that if the monks of St Albans could prove the book was a loan, they should have it back. Otherwise, it was bequeathed to New College, Oxford
New College is one of the constituent colleges of the University of Oxford in the United Kingdom. Founded in 1379 by William of Wykeham in conjunction with Winchester College as its feeder school, New College is one of the oldest colleges at ...
. The fact that the book was acquired by a 16th-century Earl of Arundel suggests that Duke Humphrey's inscription was not entirely accurate, as New College would probably not have disposed of it.
* ''Abbreviatio chronicorum'' (or ''Historia minor''), British Library Cotton MS Claudius D VI, fols. 5–100. Another shortened history, mainly covering 1067 to 1253. Probably begun circa 1255, it remained unfinished at Paris's death. Illustrated with thirty-three seated figures of English kings illustrating a genealogy
Genealogy () is the study of families, family history, and the tracing of their lineages. Genealogists use oral interviews, historical records, genetic analysis, and other records to obtain information about a family and to demonstrate kin ...
. It also contains the most developed of Paris's four maps of Great Britain.
* ''Chronica excerpta a magnis cronicis''. British Library Cotton MS Vitellius A XX, folios 77r–108v. Covers from 1066 to 1246. Written at some point between 1246 and 1259. Not definitely by Paris, but evidently written under his supervision, with some of the text in his own hand.
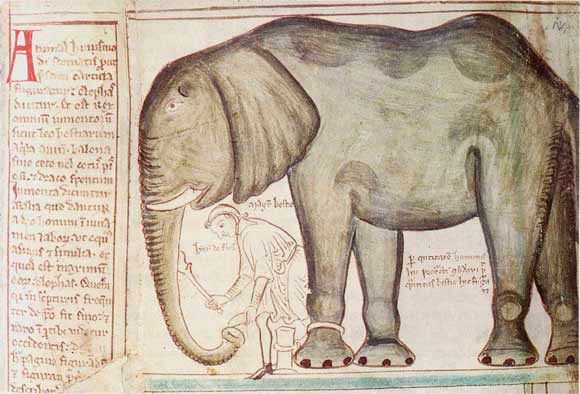
* ''Book of Additions'' (Liber additamentorum) British Library Cotton MS Nero D I, ff202 in all, contains maps, '' Vitae duorum Offarum'' (illustrated), ''Gesta abbatum'', the lives of the first 23 abbots of St Albans with a miniature portrait of each, coats of arms, as well as copies of original documents. A version of his well-known drawing of an elephant is in this volume, as is a large drawing of Christ, not by Paris. * ''Life of
* ''Life of St Alban
Saint Alban (; la, Albanus) is venerated as the first-recorded British Christian martyr, for which reason he is considered to be the British protomartyr. Along with fellow Saints Julius and Aaron, Alban is one of three named martyrs recorde ...
'' etc., dating controversial (1230–1250), Trinity College, Dublin Library, Ms 177 (former Ms E.I.40) 77 ff with 54 miniatures, mostly half-page. 240 × 165 mm. Also contains a ''Life of St Amphibalus'', and various other works relating to the history of St Albans Abbey, both also illustrated. The ''Life of St Alban'' is in French verse, adapted from a Latin ''Life of St Alban'' by William of St Albans
William of St Albans (fl. 1178) was a Benedictine monk and hagiographer who wrote a history of the martyrdom of Saint Alban, the first such work to name Amphibalus after Geoffrey of Monmouth.
Simon, abbot of St Albans (1167–1188) asked William t ...
, ca. 1178. The manuscript also contains notes in Paris's hand (see above) showing that his manuscripts were lent to various aristocratic ladies for periods, and that he probably acted as an intermediary between commissioners of manuscripts and the (probably) lay artists who produced them, advising on the calendars and iconography.
* ''Life of King Edward the Confessor'' 1230s or 40s, Cambridge University Library MS. Ee.3.59. This is the only surviving copy of this work, but is believed to be a slightly later copy made in London, probably by court artists, of Paris's text and framed illustrations. Based on the Latin Life of Edward the Confessor by Aelred of Rievaulx, c. 1162.
* ''Life of St Thomas of Canterbury
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), was an English nobleman who served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and then ...
'', British Library, Loan MS 88 – Four leaves (the "Becket Leaves") survive from a French-verse history of the life of Thomas Becket
Thomas Becket (), also known as Saint Thomas of Canterbury, Thomas of London and later Thomas à Becket (21 December 1119 or 1120 – 29 December 1170), was an English nobleman who served as Lord Chancellor from 1155 to 1162, and the ...
with large illuminations. Based on the Latin ''Quadrilogus'' compiled by Elias of Evesham at Crowland Abbey in 1198. The illuminations are attributed to Paris by Janet Backhouse, but not by Nigel Morgan. Vaughan had previously noted that the leaves from the ''Life of St Thomas'' and the ''Life of King Edward'' are of different sizes, and written by different scribes, neither of them Paris himself, so they are not likely to be part of the manuscript that Paris wrote of having lent to the Countess of Arundel; but that, "to judge from the script and the style of illumination" they are "very close copies of Matthew ariss original".
* ''Life of St Edmund'', a French-verse history of the life of Edmund Rich, Archbishop of Canterbury from 1233 to 1240. Based on Paris's own Latin prose life of Rich, composed in the late 1240s, which drew on a collection of materials made at Pontigny, statements from Robert Bacon and Richard Wych, Bishop of Chichester, and other materials including from Paris's own histories. A 14th-century copy of the prose life has survived in British Library Cotton MS Julius D VI, folios 123–156v. One copy of the verse life that was in Cotton MS Vitellius D VIII was destroyed in the fire of 1731; but another copy was discovered in the early 1900s at Welbeck Abbey
Welbeck Abbey in the Dukeries in North Nottinghamshire was the site of a monastery belonging to the Premonstratensian order in England and after the Dissolution of the Monasteries, a country house residence of the Dukes of Portland. It is o ...
and is now in the British Library.
* ''Liber Experimentarius'' of Bernardus Silvestris, and other fortune-telling tracts. Bodleian Library
The Bodleian Library () is the main research library of the University of Oxford, and is one of the oldest libraries in Europe. It derives its name from its founder, Sir Thomas Bodley. With over 13 million printed items, it is the sec ...
, Oxford, Ms. Ashmole 304, 176 × 128 mm, ff72. Many illustrations: author portraits (many of ancient Greeks – Socrates
Socrates (; ; –399 BC) was a Greek philosopher from Athens who is credited as the founder of Western philosophy and among the first moral philosophers of the ethical tradition of thought. An enigmatic figure, Socrates authored no t ...
, Plato
Plato ( ; grc-gre, Πλάτων ; 428/427 or 424/423 – 348/347 BC) was a Greek philosopher born in Athens during the Classical period in Ancient Greece. He founded the Platonist school of thought and the Academy, the first institution ...
, Euclid
Euclid (; grc-gre, Εὐκλείδης; BC) was an ancient Greek mathematician active as a geometer and logician. Considered the "father of geometry", he is chiefly known for the '' Elements'' treatise, which established the foundations of ...
, Pythagoras
Pythagoras of Samos ( grc, Πυθαγόρας ὁ Σάμιος, Pythagóras ho Sámios, Pythagoras the Samian, or simply ; in Ionian Greek; ) was an ancient Ionian Greek philosopher and the eponymous founder of Pythagoreanism. His poli ...
), birds, tables and diagrams of geomantic significance. Several later copies of the text and illustrations survive. Provenance before 1602 unknown.
* Miscellaneous writings by John of Wallingford (the Younger), British Library, MS Cotton Julius D VII, 188 × 130 mm, ff. 134. 1247–58. Mostly scribed by John of Wallingford, another monk of St Albans, who also probably did some drawings. A portrait of John, a map of the British Isles, and a Christ in Majesty
Christ in Majesty or Christ in Glory ( la, Maiestas Domini) is the Western Christian image of Christ seated on a throne as ruler of the world, always seen frontally in the centre of the composition, and often flanked by other sacred figures, whos ...
are all accepted as by Paris. The main text is a chronicle, highly derivative of Paris's. This was John's property, left to his final monastery at Wymondham.
Also, fragments of a Latin biography of Stephen Langton. Various other works, especially maps.
A panel painting on oak of St Peter
) (Simeon, Simon)
, birth_date =
, birth_place = Bethsaida, Gaulanitis, Syria, Roman Empire
, death_date = Between AD 64–68
, death_place = probably Vatican Hill, Rome, Italia, Roman Empire
, parents = John (or Jonah; Jona)
, occupation ...
, the only surviving part of a tabernacle
According to the Hebrew Bible, the tabernacle ( he, מִשְׁכַּן, mīškān, residence, dwelling place), also known as the Tent of the Congregation ( he, link=no, אֹהֶל מוֹעֵד, ’ōhel mō‘ēḏ, also Tent of Meeting, etc.), ...
shrine (1850 × 750 mm), in the Museum of Oslo University has been attributed to Paris, presumably dating from his visit in 1248. Local paintings are usually on pine, so he may have brought this with him, or sent it later.
Paris as an artist
 In some of Paris's manuscripts, a framed miniature occupies the upper half of the page, and in others, they are "marginal" – unframed and occupying the bottom quarter (approximately) of the page. Tinted drawings were an established style well before Paris, and became especially popular in the first half of the 13th century. They were certainly much cheaper and quicker than fully painted illuminations. The tradition of tinted drawings or outline drawings with ink supplemented by coloured wash was distinctively English, dating back to the
In some of Paris's manuscripts, a framed miniature occupies the upper half of the page, and in others, they are "marginal" – unframed and occupying the bottom quarter (approximately) of the page. Tinted drawings were an established style well before Paris, and became especially popular in the first half of the 13th century. They were certainly much cheaper and quicker than fully painted illuminations. The tradition of tinted drawings or outline drawings with ink supplemented by coloured wash was distinctively English, dating back to the Anglo-Saxon art
Anglo-Saxon art covers art produced within the Anglo-Saxon period of English history, beginning with the Migration period style that the Anglo-Saxons brought with them from the continent in the 5th century, and ending in 1066 with the Norman ...
of the mid-10th century, and connected with the English Benedictine Reform of the period. A strong influence on one branch of the style was the Carolingian Utrecht Psalter, which was at Canterbury
Canterbury (, ) is a cathedral city and UNESCO World Heritage Site, situated in the heart of the City of Canterbury local government district of Kent, England. It lies on the River Stour.
The Archbishop of Canterbury is the primate of t ...
from about 1000 to 1640. This was copied in the 1020s in the Harley Psalter, and in the Eadwine Psalter of the mid-12th century.
 Recent scholarship, notably that of Nigel Morgan, suggests that Paris's influence on other artists of the period has been exaggerated. This is likely because so much more is known about him than other English illuminators of the period, who are mostly anonymous. Most manuscripts seem to have been produced by lay artists in this period.
Recent scholarship, notably that of Nigel Morgan, suggests that Paris's influence on other artists of the period has been exaggerated. This is likely because so much more is known about him than other English illuminators of the period, who are mostly anonymous. Most manuscripts seem to have been produced by lay artists in this period. William de Brailes
William de Brailes (active c. 1230 – c. 1260) was an English Early Gothic manuscript illuminator, presumably born in Brailes, Warwickshire. He signed two manuscripts, and apparently worked in Oxford, where he is documented from 1238 to 1252, ...
is shown with a clerical tonsure, but he was married, which suggests he had minor orders only. The manuscripts produced by Paris show few signs of collaboration, but art historians detect a School of St Albans surviving after Paris's death, influenced by him.
Paris's style suggests that it was formed by works from around 1200. He was somewhat old-fashioned in retaining a roundness in his figures, rather than adopting the thin angularity of most of his artist contemporaries, especially those in London. His compositions are very inventive; his position as a well-connected monk may have given him more confidence in creating new compositions, whereas a lay artist would prefer to stick to traditional formulae. It may also reflect the lack of full training in the art of the period. His colouring emphasises green and blue, and together with his characteristic layout of a picture in the top half of a page, is relatively distinctive. What are probably his final sketches are found in '' Vitae duorum Offarum'' in BL MS Cotton Nero D I.
Paris as a historian
From 1235, the point at which Wendover dropped his pen, Paris continued the history on the plan which his predecessors had followed. He derived much of his information from the letters of important people, which he sometimes inserts, but much more from conversations with the eyewitnesses of events. Among his informants wereRichard, Earl of Cornwall
Richard (5 January 1209 – 2 April 1272) was an English prince who was King of the Romans from 1257 until his death in 1272. He was the second son of John, King of England, and Isabella, Countess of Angoulême. Richard was nominal Count of ...
, and King Henry III, with whom he appears to have been on intimate terms.
The king knew that Paris was writing a history, and wanted it to be as exact as possible. In 1257, in the course of a week's visit to St Albans, Henry kept the chronicler beside him night and day, "and guided my pen," says Paris, "with much goodwill and diligence." It is curious that the ''Chronica Majora'' gives so unfavourable an account of the king's policy. Henry Richards Luard supposes that Paris never intended his work to be read in its present form. Many passages of the autograph have written next to them, the ''note offendiculum'', which shows that the writer understood the danger which he ran. On the other hand, unexpurgated copies were made in Paris's lifetime. Although the offending passages are duly omitted or softened in his abridgement of his longer work, the ''Historia Anglorum'' (written about 1253), Paris's real feelings must have been an open secret. There is no ground for the old theory that he was an official historiographer.
Naturalists have praised his descriptions of the English wildlife of his time, brief though they are: in particular his valuable description of the first irruption
Animal migration is the relatively long-distance movement of individual animals, usually on a seasonal basis. It is the most common form of migration in ecology. It is found in all major animal groups, including birds, mammals, fish, reptile ...
into England in 1254 of the common crossbill
The red crossbill or common crossbill (''Loxia curvirostra'') is a small passerine bird in the finch family Fringillidae. Crossbills have distinctive mandibles, crossed at the tips, which enable them to extract seeds from conifer cones and other ...
.
Paris as cartographer
 Outstanding among his other maps were (four versions of) a pilgrim
Outstanding among his other maps were (four versions of) a pilgrim itinerary
Itinerary or Itineraries or Itinerarium may refer to:
Travel
* Itinerarium, an Ancient Roman road map in the form of a listing of cities, villages, and other stops, with the intervening distances
* ''Itinerarium Burdigalense'', also known as the ...
charting the route from London to Rome in graphic form. A sequence of pictures of towns on the route marked the terminus of each day's travel, enabling the viewer to envisage and follow the whole journey rather like a comic strip – an achievement unprecedented elsewhere in the medieval world.
Studies of Matthew Paris
The relation of Matthew Paris's work to those of John de Celia ( John of Wallingford) and Roger of Wendover may be studied in Henry Luard's edition of the ''Chronica Majora'' (7 vols., Rolls series, 1872–1881), which contains valuable prefaces. The ''Historia Anglorum sive historia minor'' (1067–1253) has been edited by Frederic Madden (3 vols., Rolls series, 1866–1869). Matthew Paris is sometimes confused withMatthew of Westminster Matthew of Westminster, long regarded as the author of the ''Flores Historiarum'', is now thought never to have existed.
The error was first discovered in 1826 by Francis Turner Palgrave, who said that Matthew was "a phantom who never existed," and ...
, the reputed author of the '' Flores historiarum'' edited by Luard (3 vols., Rolls series, 1890). This work, compiled by various hands, is an edition of Matthew Paris, with continuations extending to 1326.
He wrote a life of St Edmund of Abingdon, sometime Archbishop of Canterbury
The archbishop of Canterbury is the senior bishop and a principal leader of the Church of England, the ceremonial head of the worldwide Anglican Communion and the diocesan bishop of the Diocese of Canterbury. The current archbishop is Just ...
.
He also wrote the Anglo-Norman Anglo-Norman may refer to:
*Anglo-Normans, the medieval ruling class in England following the Norman conquest of 1066
*Anglo-Norman language
**Anglo-Norman literature
*Anglo-Norman England, or Norman England, the period in English history from 1066 ...
''La Estoire de Seint Aedward le Rei'' (the History of Saint Edward the King), which survives in a beautifully illuminated manuscript version, Cambridge, Cambridge University Library MS. Ee.3.59. The manuscript has had a varied publication history. Sections were printed in Francisque Michel
Francisque Xavier Michel (18 February 1809, Lyon – 18 May 1887, Paris) was a French historian and philologist.
Life
He became known for his editions of French works of the Middle Ages, and the French Government, recognizing their value, sent ...
's ''Chroniques Anglo-Normandes''. Luard's edition for the Rolls series was severely criticised; it was re-edited for the Anglo-Norman Text Society
The Anglo-Norman Text Society is a text publication society founded in 1937 by Professor Mildred K. Pope. The founding aim of the society was to promote the study of Anglo-Norman language and Anglo-Norman literature by facilitating the publicati ...
by K. Y. Wallace. A facsimile
A facsimile (from Latin ''fac simile'', "to make alike") is a copy or reproduction of an old book, manuscript, map, art print, or other item of historical value that is as true to the original source as possible. It differs from other forms of ...
for the Roxburghe Club
The Roxburghe Club is a bibliophilic and publishing society based in the United Kingdom.
Origins
The spur to the Club's foundation was the sale of the enormous library of the Duke of Roxburghe (who had died in 1804), which took place over 46 da ...
was edited by M. R. James, and the whole manuscript has been digitalized and can be seen online.
Paris House at St Albans High School for Girls
St Albans High School for Girls is a selective, private day school for girls aged 4 – 18 years, which is affiliated to the Church of England and takes girls of all faiths or none. There are approximately 328 pupils in the preparatory schoo ...
is named after him.
Notes
*Bibliography
* Richard Vaughan (1958), ''Matthew Paris''. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press * (on manuscripts, and artistic style) * * *External links
Images
British Library website
* ttp://www.bartleby.com/211/0919.html Latin Chroniclers from the Eleventh to the Thirteenth Centuries:Matthew Parisfrom '' The Cambridge History of English and American Literature'', Volume I, 1907–21.
Life of St Edward the Confessor, Cambridge Digital Library
{{DEFAULTSORT:Paris, Matthew 1200 births 1259 deaths Year of birth uncertain People from St Albans English Benedictines English Christian monks English chroniclers English cartographers Historians of the Catholic Church Heraldists Manuscript illuminators Writers who illustrated their own writing Medieval European scribes People educated at St Albans School, Hertfordshire Artist authors Medieval English painters 13th-century Christian monks 13th-century painters 13th-century English artists 13th-century Latin writers 13th-century English historians