Marie-Henri Beyle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Marie-Henri Beyle (; 23 January 1783 – 23 March 1842), better known by his
pen name
A pen name, also called a ''nom de plume'' or a literary double, is a pseudonym (or, in some cases, a variant form of a real name) adopted by an author and printed on the title page or by-line of their works in place of their real name.
A pen na ...
Stendhal (, ; ), was a 19th-century French writer. Best known for the novels ''Le Rouge et le Noir'' (''The Red and the Black
''Le Rouge et le Noir'' (; meaning ''The Red and the Black'') is a historical psychological novel in two volumes by Stendhal, published in 1830. It chronicles the attempts of a provincial young man to rise socially beyond his modest upbringing ...
'', 1830) and ''La Chartreuse de Parme'' (''The Charterhouse of Parma
''The Charterhouse of Parma'' (french: La Chartreuse de Parme, links=no) is a novel by Stendhal published in 1839. Telling the story of an Italian nobleman in the Napoleonic era and later, it was admired by Balzac, Tolstoy, André Gide, di Lam ...
'', 1839), he is highly regarded for the acute analysis of his characters' psychology and considered one of the early and foremost practitioners of realism
Realism, Realistic, or Realists may refer to:
In the arts
*Realism (arts), the general attempt to depict subjects truthfully in different forms of the arts
Arts movements related to realism include:
* Classical Realism
*Literary realism, a mov ...
. A self-proclaimed egotist, he coined the same characteristic in his characters' "Beylism".
Life
Born inGrenoble
lat, Gratianopolis
, commune status = Prefecture and commune
, image = Panorama grenoble.png
, image size =
, caption = From upper left: Panorama of the city, Grenoble’s cable cars, place Saint- ...
, Isère
Isère ( , ; frp, Isera; oc, Isèra, ) is a landlocked department in the southeastern French region of Auvergne-Rhône-Alpes. Named after the river Isère, it had a population of 1,271,166 in 2019. His closest friend was his younger sister, Pauline, with whom he maintained a steady correspondence throughout the first decade of the 19th century. His family was part of the bourgeois class and was attached to the  The military and theatrical worlds of the
The military and theatrical worlds of the  Stendhal was a dandy and wit about town in Paris, as well as an obsessive womaniser. His genuine empathy towards women is evident in his books;
Stendhal was a dandy and wit about town in Paris, as well as an obsessive womaniser. His genuine empathy towards women is evident in his books;
 According to the literary theorist Kornelije Kvas, in his novel ''The Red and the Black'', Stendhal refers to a novel as a mirror being carried in a basket. The metaphor of the realistic novel as a mirror of contemporary reality, accessible to the narrator, has certain limitations, which the artist is aware of. A valuable realistic work exceeds the Platonic meaning of art as a copy of reality. A mirror does not reflect reality in its entirety, nor is the artist’s aim to document it fully. In ''The Red and the Black'', the writer emphasizes the significance of selection when it comes to describing reality, with a view to realizing the cognitive function of a work of art, achieved through the categories of unity, coherence and typicality". Stendhal was an admirer of Napoleon and his novel ''Le Rouge et le Noir'' is considered his literary tribute to the emperor.
Today, Stendhal's works attract attention for their
According to the literary theorist Kornelije Kvas, in his novel ''The Red and the Black'', Stendhal refers to a novel as a mirror being carried in a basket. The metaphor of the realistic novel as a mirror of contemporary reality, accessible to the narrator, has certain limitations, which the artist is aware of. A valuable realistic work exceeds the Platonic meaning of art as a copy of reality. A mirror does not reflect reality in its entirety, nor is the artist’s aim to document it fully. In ''The Red and the Black'', the writer emphasizes the significance of selection when it comes to describing reality, with a view to realizing the cognitive function of a work of art, achieved through the categories of unity, coherence and typicality". Stendhal was an admirer of Napoleon and his novel ''Le Rouge et le Noir'' is considered his literary tribute to the emperor.
Today, Stendhal's works attract attention for their

 When we are in Bologna, we are entirely indifferent; we are not concerned to admire in any particular way the person with whom we shall perhaps one day be madly in love; even less is our imagination inclined to overrate their worth. In a word, in Bologna "crystallization" has not yet begun. When the journey begins, love departs. One leaves Bologna, climbs the
When we are in Bologna, we are entirely indifferent; we are not concerned to admire in any particular way the person with whom we shall perhaps one day be madly in love; even less is our imagination inclined to overrate their worth. In a word, in Bologna "crystallization" has not yet begun. When the journey begins, love departs. One leaves Bologna, climbs the
Stendhal et le beylisme
'. Paris, Paul Ollendorf, 1914. *Dieter, Anna-Lisa, ''Eros - Wunde - Restauration. Stendhal und die Entstehung des Realismus, ''Paderborn: Wilhelm Fink, 2019 (Periplous. Münchener Studien zur Literaturwissenschaft). * Jefferson, Ann. ''Reading Realism in Stendhal (Cambridge Studies in French)''. Cambridge University Press, 1988. *
StendhalForever.com
Stendhal's works
text, concordances and frequency list *
Audio Book (mp3) of
''The Red and the Black'' incipit *
French site on Stendhal
Centro Stendhaliano di Milano
Digital version of Stendhal's shoulder-notes on his own books. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Stendhal 1783 births 1842 deaths Writers from Grenoble 19th-century French writers Conseil d'État (France) French agnostics French novelists French psychological fiction writers French biographers French travel writers Romanticism Burials at Montmartre Cemetery French male essayists French male novelists French male short story writers 19th-century French short story writers French military personnel of the Napoleonic Wars Male biographers 19th-century pseudonymous writers
Ancien Regime
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word for "ancient, old"
** Société des anciens textes français
* the French for "former, senior"
** Virelai ancien
** Ancien Régime
** Ancien Régime in France
''Ancien'' may refer to
* the French word fo ...
, explaining his ambiguous view toward Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, the Bourbon Restoration, and the monarchy later on.
First French Empire
The First French Empire, officially the French Republic, then the French Empire (; Latin: ) after 1809, also known as Napoleonic France, was the empire ruled by Napoleon Bonaparte, who established French hegemony over much of continental E ...
were a revelation to Beyle. He was named an auditor
An auditor is a person or a firm appointed by a company to execute an audit.Practical Auditing, Kul Narsingh Shrestha, 2012, Nabin Prakashan, Nepal To act as an auditor, a person should be certified by the regulatory authority of accounting and a ...
with the Conseil d'État on 3 August 1810, and thereafter took part in the French administration and in the Napoleonic wars
The Napoleonic Wars (1803–1815) were a series of major global conflicts pitting the French Empire and its allies, led by Napoleon I, against a fluctuating array of European states formed into various coalitions. It produced a period of Fre ...
in Italy. He travelled extensively in Germany and was part of Napoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
's army in the 1812 invasion of Russia. Upon arriving, Stendhal witnessed the burning of Moscow from just outside the city as well as the army's winter retreat. He was appointed Commissioner of War Supplies and sent to Smolensk
Smolensk ( rus, Смоленск, p=smɐˈlʲensk, a=smolensk_ru.ogg) is a city and the administrative center of Smolensk Oblast, Russia, located on the Dnieper River, west-southwest of Moscow. First mentioned in 863, it is one of the oldest ...
to prepare provisions for the returning army. He crossed the Berezina River
The Berezina or Biarezina ( be, Бярэ́зіна; ) is a river in Belarus and a right tributary of the Dnieper. The river starts in the Berezinsky Biosphere Reserve. The length of the Berezina is 613 km. The width of the river is 15-20 m, the ...
by finding a usable ford rather than the overwhelmed pontoon bridge, which probably saved his life and those of his companions. He arrived in Paris in 1813, largely unaware of the general fiasco that the retreat had become. Stendhal became known, during the Russian campaign, for keeping his wits about him, and maintaining his "sang-froid and clear-headedness." He also maintained his daily routine, shaving each day during the retreat from Moscow.
After the 1814 Treaty of Fontainebleau, he left for Italy, where he settled in Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
. In 1830, he was appointed as French consul
Consul (abbrev. ''cos.''; Latin plural ''consules'') was the title of one of the two chief magistrates of the Roman Republic, and subsequently also an important title under the Roman Empire. The title was used in other European city-states throu ...
at Trieste and Civitavecchia. He formed a particular attachment to Italy, where he spent much of the remainder of his career. His novel ''The Charterhouse of Parma
''The Charterhouse of Parma'' (french: La Chartreuse de Parme, links=no) is a novel by Stendhal published in 1839. Telling the story of an Italian nobleman in the Napoleonic era and later, it was admired by Balzac, Tolstoy, André Gide, di Lam ...
'', written in 52 days, is set in Italy, which he considered a more sincere and passionate country than Restoration France. An aside in that novel, referring to a character who contemplates suicide after being jilted, speaks about his attitude towards his home country: "To make this course of action clear to my French readers, I must explain that in Italy, a country very far away from us, people are still driven to despair by love."
Stendhal identified with the nascent liberalism
Liberalism is a Political philosophy, political and moral philosophy based on the Individual rights, rights of the individual, liberty, consent of the governed, political equality and equality before the law."political rationalism, hostilit ...
and his sojourn in Italy convinced him that Romanticism
Romanticism (also known as the Romantic movement or Romantic era) was an artistic, literary, musical, and intellectual movement that originated in Europe towards the end of the 18th century, and in most areas was at its peak in the approximate ...
was essentially the literary counterpart of liberalism in politics. When Stendhal was appointed to a consular post in Trieste in 1830, Metternich refused his ''exequatur
An exequatur (Latin, literally "let it execute") is a legal document issued by a sovereign authority that permits the exercise or enforcement of a right within the jurisdiction of the authority.
International relations
An exequatur is a patent ...
'' on account of Stendhal's liberalism and anti-clericalism.
 Stendhal was a dandy and wit about town in Paris, as well as an obsessive womaniser. His genuine empathy towards women is evident in his books;
Stendhal was a dandy and wit about town in Paris, as well as an obsessive womaniser. His genuine empathy towards women is evident in his books; Simone de Beauvoir
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir (, ; ; 9 January 1908 – 14 April 1986) was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, and even ...
spoke highly of him in ''The Second Sex
''The Second Sex'' (french: Le Deuxième Sexe, link=no) is a 1949 book by the French existentialist philosopher Simone de Beauvoir, in which the author discusses the treatment of women in the present society as well as throughout all of histor ...
''. She credited him for perceiving a woman as just a woman and simply a human being. Citing Stendhal's rebellious heroines, she maintained that he was a feminist writer. One of his early works is ''On Love'', a rational analysis of romantic passion that was based on his unrequited love
Unrequited love or one-sided love is love that is not openly reciprocated or understood as such by the beloved. The beloved may not be aware of the admirer's deep and pure affection, or may consciously reject it. The Merriam Webster Online Dict ...
for Mathilde, Countess Dembowska, whom he met while living at Milan
Milan ( , , Lombard: ; it, Milano ) is a city in northern Italy, capital of Lombardy, and the second-most populous city proper in Italy after Rome. The city proper has a population of about 1.4 million, while its metropolitan city ...
. Later, he would also suffer "restlessness in spirit" when one of his childhood friends, Victorine got married. In a letter to Pauline, he described her as the woman of his dreams and wrote that he would have discovered happiness if he became her husband. This fusion of, and tension between, clear-headed analysis and romantic feeling is typical of Stendhal's great novels; he could be considered a Romantic realist.
Stendhal suffered miserable physical disabilities in his final years as he continued to produce some of his most famous work. He contracted syphilis
Syphilis () is a sexually transmitted infection caused by the bacterium '' Treponema pallidum'' subspecies ''pallidum''. The signs and symptoms of syphilis vary depending in which of the four stages it presents (primary, secondary, latent, a ...
in December 1808. As he noted in his journal, he was taking iodide of potassium
Potassium is the chemical element with the symbol K (from Neo-Latin '' kalium'') and atomic number19. Potassium is a silvery-white metal that is soft enough to be cut with a knife with little force. Potassium metal reacts rapidly with atmos ...
and quicksilver to treat his sexual disease, resulting in swollen armpits, difficulty swallowing, pains in his shrunken testicles, sleeplessness, giddiness, roaring in the ears, racing pulse and "tremors so bad he could scarcely hold a fork or a pen". Modern medicine has shown that his health problems were more attributable to his treatment than to his syphilis. He is said to have sought the best treatment in Paris, Vienna, and Rome.
Stendhal died on 23 March 1842, a few hours after collapsing with a seizure on the streets of Paris. He is interred in the Cimetière de Montmartre
The Cemetery of Montmartre (french: link=no, Cimetière de Montmartre) is a cemetery in the 18th arrondissement of Paris, France, that dates to the early 19th century. Officially known as the Cimetière du Nord, it is the third largest necropolis ...
.
Pseudonyms
Before settling on the pen name Stendhal, he published under manypen name
A pen name, also called a ''nom de plume'' or a literary double, is a pseudonym (or, in some cases, a variant form of a real name) adopted by an author and printed on the title page or by-line of their works in place of their real name.
A pen na ...
s, including "Louis Alexandre Bombet" and "Anastasius Serpière". The only book that Stendhal published under his own name was ''The History of Painting'' (1817). From the publication of ''Rome, Naples, Florence'' (September 1817) onwards, he published his works under the pseudonym "M. de Stendhal, officier de cavalerie". He borrowed this pen name from the German city of Stendal
The Hanseatic City of Stendal () is a town in Saxony-Anhalt, Germany. It is the capital of the Stendal District and the unofficial capital of the Altmark region.
Geography
Situated west of the Elbe valley, the Stendal town centre is located s ...
, birthplace of Johann Joachim Winckelmann
Johann Joachim Winckelmann (; ; 9 December 17178 June 1768) was a German art historian and archaeologist. He was a pioneering Hellenist who first articulated the differences between Greek, Greco-Roman and Roman art. "The prophet and foundin ...
, an art historian and archaeologist famous at the time.
In 1807, Stendhal stayed near Stendal, where he fell in love with a woman named Wilhelmine, whom he called Minette, and for whose sake he remained in the city. "I have no inclination, now, except for Minette, for this blonde and charming Minette, this soul of the north, such as I have never seen in France or Italy." Stendhal added an additional "H" to make the Germanic pronunciation more clear.
Stendhal used many aliases in his autobiographical writings and correspondence, and often assigned pseudonyms to friends, some of whom adopted the names for themselves. Stendhal used more than a hundred pseudonyms, which were astonishingly diverse. Some he used no more than once, while others he returned to throughout his life. "Dominique" and "Salviati" served as intimate pet names. He coins comic names "that make him even more bourgeois than he really is: Cotonnet, Bombet, Chamier." He uses many ridiculous names: "Don phlegm", "Giorgio Vasari
Giorgio Vasari (, also , ; 30 July 1511 – 27 June 1574) was an Italian Renaissance Master, who worked as a painter, architect, engineer, writer, and historian, who is best known for his work '' The Lives of the Most Excellent Painters, Sculp ...
", "William Crocodile", "Poverino", "Baron de Cutendre". One of his correspondents, Prosper Mérimée
Prosper Mérimée (; 28 September 1803 – 23 September 1870) was a French writer in the movement of Romanticism, and one of the pioneers of the novella, a short novel or long short story. He was also a noted archaeologist and historian, and a ...
, said: "He never wrote a letter without signing a false name."
Stendhal's ''Journal'' and autobiographical writings include many comments on masks and the pleasures of "feeling alive in many versions." "Look upon life as a masked ball," is the advice that Stendhal gives himself in his diary for 1814. In ''Memoirs of an Egotist'' he writes: "Will I be believed if I say I'd wear a mask with pleasure and be delighted to change my name?...for me the supreme happiness would be to change into a lanky, blonde German and to walk about like that in Paris."
Works
Contemporary readers did not fully appreciate Stendhal's realistic style during the Romantic period in which he lived. He was not fully appreciated until the beginning of the 20th century. He dedicated his writing to "the Happy Few" (in English in the original). This can be interpreted as a reference to Canto 11 ofLord Byron
George Gordon Byron, 6th Baron Byron (22 January 1788 – 19 April 1824), known simply as Lord Byron, was an English romantic poet and peer. He was one of the leading figures of the Romantic movement, and has been regarded as among the ...
's ''Don Juan
Don Juan (), also known as Don Giovanni ( Italian), is a legendary, fictional Spanish libertine who devotes his life to seducing women. Famous versions of the story include a 17th-century play, ''El burlador de Sevilla y convidado de piedra'' ...
'', which refers to "the thousand happy few" who enjoy high society, or to the "we few, we happy few, we band of brothers" line of William Shakespeare
William Shakespeare ( 26 April 1564 – 23 April 1616) was an English playwright, poet and actor. He is widely regarded as the greatest writer in the English language and the world's pre-eminent dramatist. He is often called England's nation ...
's ''Henry V Henry V may refer to:
People
* Henry V, Duke of Bavaria (died 1026)
* Henry V, Holy Roman Emperor (1081/86–1125)
* Henry V, Duke of Carinthia (died 1161)
* Henry V, Count Palatine of the Rhine (c. 1173–1227)
* Henry V, Count of Luxembourg (121 ...
'', but Stendhal's use more likely refers to ''The Vicar of Wakefield
''The Vicar of Wakefield'', subtitled ''A Tale, Supposed to be written by Himself'', is a novel by Anglo-Irish writer Oliver Goldsmith (1728–1774). It was written from 1761 to 1762 and published in 1766. It was one of the most popular and wid ...
'' by Oliver Goldsmith
Oliver Goldsmith (10 November 1728 – 4 April 1774) was an Anglo-Irish novelist, playwright, dramatist and poet, who is best known for his novel '' The Vicar of Wakefield'' (1766), his pastoral poem '' The Deserted Village'' (1770), and his ...
, parts of which he had memorized in the course of teaching himself English.
In ''The Vicar of Wakefield'', "the happy few" refers ironically to the small number of people who read the title character's obscure and pedantic treatise on monogamy. As a literary critic, such as in ''Racine and Shakespeare'', Stendhal championed the Romantic aesthetic by unfavorably comparing the rules and strictures of Jean Racine
Jean-Baptiste Racine ( , ) (; 22 December 163921 April 1699) was a French dramatist, one of the three great playwrights of 17th-century France, along with Molière and Corneille as well as an important literary figure in the Western traditi ...
's classicism to the freer verse and settings of Shakespeare, and supporting the writing of plays in prose.
irony
Irony (), in its broadest sense, is the juxtaposition of what on the surface appears to be the case and what is actually the case or to be expected; it is an important rhetorical device and literary technique.
Irony can be categorized int ...
and psychological
Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior. Psychology includes the study of conscious and unconscious phenomena, including feelings and thoughts. It is an academic discipline of immense scope, crossing the boundaries bet ...
and historical dimensions. Stendhal was an avid fan of music, particularly the works of the composers Domenico Cimarosa
Domenico Cimarosa (; 17 December 1749 – 11 January 1801) was an Italian composer of the Neapolitan school and of the Classical period. He wrote more than eighty operas, the best known of which is '' Il matrimonio segreto'' (1792); most of h ...
, Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
and Gioacchino Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards ...
. He wrote a biography of Rossini, ''Vie de Rossini'' (1824), now more valued for its wide-ranging musical criticism than for its historical content. He also idealized aristocracy, noting its antiegalitarianism but appreciating how it is liberal in its love of liberty.
In his works, Stendhal reprise
In music, a reprise ( , ; from the verb 'to resume') is the repetition or reiteration of the opening material later in a composition as occurs in the recapitulation of sonata form, though—originally in the 18th century—was simply any repe ...
d excerpts appropriated from Giuseppe Carpani
Giuseppe Carpani (28 December 1751 – 22 January 1825) was an Italian man of letters. He is remembered in large part for his role in the history of classical music: he knew Haydn, Mozart, Salieri, Beethoven, and Rossini, and served them in vari ...
, Théophile Frédéric Winckler
Theophilus is a male given name with a range of alternative spellings. Its origin is the Greek word Θεόφιλος from θεός (God) and φιλία (love or affection) can be translated as "Love of God" or "Friend of God", i.e., it is a theoph ...
, Sismondi and others.
Novels
*'' Armance'' (1827) *''Le Rouge et le Noir
''Le Rouge et le Noir'' (; meaning ''The Red and the Black'') is a historical psychological novel in two volumes by Stendhal, published in 1830. It chronicles the attempts of a provincial young man to rise socially beyond his modest upbringing t ...
'' (''The Red and the Black'', 1830)
*''Lucien Leuwen
''Lucien Leuwen'' is the second major novel written by French author Stendhal in 1834, following ''The Red and the Black'' (1830). It remained unfinished due to the political culture of the July Monarchy in the 1830s and Stendhal's fears of losing ...
'' (1835, unfinished, published 1894)
*'' The Pink and the Green'' (1837, unfinished)
*''La Chartreuse de Parme
''The Charterhouse of Parma'' (french: La Chartreuse de Parme, links=no) is a novel by Stendhal published in 1839. Telling the story of an Italian nobleman in the Napoleonic era and later, it was admired by Balzac, Tolstoy, André Gide, di La ...
'' (1839) (''The Charterhouse of Parma'')
*''Lamiel
''Lamiel'' is a 1967 French historical drama film. It was directed by Jean Aurel and stars Anna Karina, Michel Bouquet, and Jean-Claude Brialy.
The film is based on Stendhal's unfinished last novel, '' Lamiel''. A costume drama set in the 19th ...
'' (1839–1842, unfinished, published 1889)

Novellas
*''Mina de Vanghel'' (1830, later published in the Paris periodical ''La Revue des Deux Mondes
The ''Revue des deux Mondes'' (, ''Review of the Two Worlds'') is a monthly French-language literary, cultural and current affairs magazine that has been published in Paris since 1829.
According to its website, "it is today the place for debates a ...
'')
* '' Vanina Vanini'' (1829)
* ''Italian Chroniques
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
'', 1837–1839
**''Vittoria Accoramboni
Vittoria Accoramboni (15 February 1557{{snd22 December 1585) was an Italian noblewoman. Her life became the basis for John Webster's play '' The White Devil'', several novels, and a novella by Stendhal.
Biography
She was born in Gubbio in Umbria, ...
''
** ''The Cenci
''The Cenci, A Tragedy, in Five Acts'' (1819) is a verse drama in five acts by Percy Bysshe Shelley written in the summer of 1819, and inspired by a real Italian family, the House of Cenci (in particular, Beatrice Cenci, pronounced CHEN-chee). ...
'' (''Les Cenci'', 1837)
** '' The Duchess of Palliano'' (''La Duchesse de Palliano'')
** '' The Abbess of Castro'' (''L'Abbesse de Castro'', 1832)
Biography
*'' A Life of Napoleon'' (1817–1818, published 1929) *'' A Life of Rossini'' (1824)Autobiography
Stendhal's brief memoir, ''Souvenirs d'Égotisme'' (''Memoirs of an Egotist'') was published posthumously in 1892. Also published was a more extended autobiographical work, thinly disguised as the ''Life of Henry Brulard''. *'' The Life of Henry Brulard'' (1835–1836, published 1890) *''Souvenirs d'Égotisme'' (written in 1832 and published in 1892) (''Memoirs of an Egotist
''Souvenirs d’égotisme'' (French for ''Memoirs of an Egotist'') is an autobiographical work by Stendhal. It was written in 13 days in June and July 1832 while the author was staying in Civitavecchia. Stendhal recounts his life in Paris and Londo ...
'')
*''Journal (1801–1817)'' ('' The Private Diaries of Stendhal'')
Non-fiction
* ''Rome, Naples et Florence'' (1817) *''De L'Amour'' (1822) (') *''Racine et Shakespéare'' (1823–1835) (''Racine and Shakespeare'') *''Voyage dans le midi de la France'' (1838; though first published posthumously in 1930) (''Travels in the South of France'') His other works include short stories, journalism, travel books (''A Roman Journal''), a famous collection of essays on Italian painting, and biographies of several prominent figures of his time, includingNapoleon
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, Haydn
Franz Joseph Haydn ( , ; 31 March 173231 May 1809) was an Austrian composer of the Classical period. He was instrumental in the development of chamber music such as the string quartet and piano trio. His contributions to musical form have led ...
, Mozart
Wolfgang Amadeus Mozart (27 January 17565 December 1791), baptised as Joannes Chrysostomus Wolfgangus Theophilus Mozart, was a prolific and influential composer of the Classical period. Despite his short life, his rapid pace of composition r ...
, Rossini
Gioachino Antonio Rossini (29 February 1792 – 13 November 1868) was an Italian composer who gained fame for his 39 operas, although he also wrote many songs, some chamber music and piano pieces, and some sacred music. He set new standards ...
and Metastasio
Pietro Antonio Domenico Trapassi (3 January 1698 – 12 April 1782), better known by his pseudonym of Pietro Metastasio (), was an Italian poet and librettist, considered the most important writer of ''opera seria'' libretti.
Early life
Me ...
.
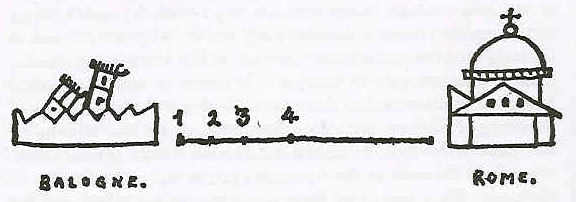
Crystallization
In Stendhal's 1822 classic ' he describes or compares the "birth of love", in which the love object is 'crystallized' in the mind, as being a process similar or analogous to a trip to Rome. In the analogy, the city ofBologna
Bologna (, , ; egl, label= Emilian, Bulåggna ; lat, Bononia) is the capital and largest city of the Emilia-Romagna region in Northern Italy. It is the seventh most populous city in Italy with about 400,000 inhabitants and 150 different na ...
represents ''indifference'' and Rome
, established_title = Founded
, established_date = 753 BC
, founder = King Romulus ( legendary)
, image_map = Map of comune of Rome (metropolitan city of Capital Rome, region Lazio, Italy).svg
, map_caption ...
represents ''perfect love'':
 When we are in Bologna, we are entirely indifferent; we are not concerned to admire in any particular way the person with whom we shall perhaps one day be madly in love; even less is our imagination inclined to overrate their worth. In a word, in Bologna "crystallization" has not yet begun. When the journey begins, love departs. One leaves Bologna, climbs the
When we are in Bologna, we are entirely indifferent; we are not concerned to admire in any particular way the person with whom we shall perhaps one day be madly in love; even less is our imagination inclined to overrate their worth. In a word, in Bologna "crystallization" has not yet begun. When the journey begins, love departs. One leaves Bologna, climbs the Apennines
The Apennines or Apennine Mountains (; grc-gre, links=no, Ἀπέννινα ὄρη or Ἀπέννινον ὄρος; la, Appenninus or – a singular with plural meaning;''Apenninus'' (Greek or ) has the form of an adjective, which wou ...
, and takes the road to Rome. The departure, according to Stendhal, has nothing to do with one's will; it is an instinctive moment. This transformative process actuates in terms of four steps along a journey:
#Admiration – one marvels at the qualities of the loved one.
#Acknowledgement – one acknowledges the pleasantness of having gained the loved one's interest.
#Hope – one envisions gaining the love of the loved one.
#Delight – one delights in overrating the beauty and merit of the person whose love one hopes to win.
This journey or crystallization process (shown above) was detailed by Stendhal on the back of a playing card while speaking to Madame Gherardi, during his trip to the Salzburg salt mine.
Critical appraisal
Hippolyte Taine
Hippolyte Adolphe Taine (, 21 April 1828 – 5 March 1893) was a French historian, critic and philosopher. He was the chief theoretical influence on French naturalism, a major proponent of sociological positivism and one of the first practitio ...
considered the psychological portraits of Stendhal's characters to be "real, because they are complex, many-sided, particular and original, like living human beings." Émile Zola
Émile Édouard Charles Antoine Zola (, also , ; 2 April 184029 September 1902) was a French novelist, journalist, playwright, the best-known practitioner of the literary school of naturalism, and an important contributor to the development of ...
concurred with Taine's assessment of Stendhal's skills as a "psychologist", and although emphatic in his praise of Stendhal's psychological accuracy and rejection of convention, he deplored the various implausibilities of the novels and Stendhal's clear authorial intervention.
The German philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche
Friedrich Wilhelm Nietzsche (; or ; 15 October 1844 – 25 August 1900) was a German philosopher, prose poet, cultural critic, philologist, and composer whose work has exerted a profound influence on contemporary philosophy. He began his ...
refers to Stendhal as "France's last great psychologist" in ''Beyond Good and Evil
''Beyond Good and Evil: Prelude to a Philosophy of the Future'' (german: Jenseits von Gut und Böse: Vorspiel einer Philosophie der Zukunft) is a book by philosopher Friedrich Nietzsche that covers ideas in his previous work ''Thus Spoke Zarathu ...
'' (1886). He also mentions Stendhal in the ''Twilight of the Idols
''Twilight of the Idols, or, How to Philosophize with a Hammer'' (german: link=no, Götzen-Dämmerung, oder, Wie man mit dem Hammer philosophiert) is a book by Friedrich Nietzsche, written in 1888, and published in 1889.
Genesis
''Twilight of th ...
'' (1889) during a discussion of Dostoevsky as a psychologist, saying that encountering Dostoevsky
Fyodor Mikhailovich Dostoevsky (, ; rus, Фёдор Михайлович Достоевский, Fyódor Mikháylovich Dostoyévskiy, p=ˈfʲɵdər mʲɪˈxajləvʲɪdʑ dəstɐˈjefskʲɪj, a=ru-Dostoevsky.ogg, links=yes; 11 November 18219 ...
was "the most beautiful accident of my life, more so than even my discovery of Stendhal".
Ford Madox Ford
Ford Madox Ford (né Joseph Leopold Ford Hermann Madox Hueffer ( ); 17 December 1873 – 26 June 1939) was an English novelist, poet, critic and editor whose journals '' The English Review'' and ''The Transatlantic Review'' were instrumental in ...
, in ''The English Novel'', asserts that to Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the '' Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a promi ...
and Stendhal "the Novel owes its next great step forward...At that point it became suddenly evident that the Novel as such was capable of being regarded as a means of profoundly serious and many-sided discussion and therefore as a medium of profoundly serious investigation into the human case."
Erich Auerbach
Erich Auerbach (November 9, 1892 – October 13, 1957) was a German philologist and comparative scholar and critic of literature. His best-known work is '' Mimesis: The Representation of Reality in Western Literature'', a history of represe ...
considers modern "serious realism" to have begun with Stendhal and Balzac. In ''Mimesis
Mimesis (; grc, μίμησις, ''mīmēsis'') is a term used in literary criticism and philosophy that carries a wide range of meanings, including '' imitatio'', imitation, nonsensuous similarity, receptivity, representation, mimicry, the a ...
'', he remarks of a scene in ''The Red and the Black'' that "it would be almost incomprehensible without a most accurate and detailed knowledge of the political situation, the social stratification, and the economic circumstances of a perfectly definite historical moment, namely, that in which France found itself just before the July Revolution."
In Auerbach's view, in Stendhal's novels "characters, attitudes, and relationships of the '' dramatis personæ'', then, are very closely connected with contemporary historical circumstances; contemporary political and social conditions are woven into the action in a manner more detailed and more real than had been exhibited in any earlier novel, and indeed in any works of literary art except those expressly purporting to be politico-satirical tracts."
Simone de Beauvoir
Simone Lucie Ernestine Marie Bertrand de Beauvoir (, ; ; 9 January 1908 – 14 April 1986) was a French existentialist philosopher, writer, social theorist, and feminist activist. Though she did not consider herself a philosopher, and even ...
uses Stendhal as an example of a feminist author. In ''The Second Sex
''The Second Sex'' (french: Le Deuxième Sexe, link=no) is a 1949 book by the French existentialist philosopher Simone de Beauvoir, in which the author discusses the treatment of women in the present society as well as throughout all of histor ...
'' de Beauvoir writes “Stendhal never describes his heroines as a function of his heroes: he provides them with their own destinies.” She furthermore points out that it “is remarkable that Stendhal is both so profoundly romantic and so decidedly feminist; feminists are usually rational minds that adopt a universal point of view in all things; but it is not only in the name of freedom in general but also in the name of individual happiness that Stendhal calls for women’s emancipation.” Yet, Beauvoir criticises Stendhal for, although wanting a woman to be his equal, her only destiny he envisions for her remains a man.
Even Stendhal's autobiographical works, such as ''The Life of Henry Brulard'' or ''Memoirs of an Egotist'', are "far more closely, essentially, and concretely connected with the politics, sociology, and economics of the period than are, for example, the corresponding works of Rousseau
Jean-Jacques Rousseau (, ; 28 June 1712 – 2 July 1778) was a Genevan philosopher, writer, and composer. His political philosophy influenced the progress of the Age of Enlightenment throughout Europe, as well as aspects of the French Revolu ...
or Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as tr ...
; one feels that the great events of contemporary history affected Stendhal much more directly than they did the other two; Rousseau did not live to see them, and Goethe had managed to keep aloof from them." Auerbach goes on to say:
Vladimir Nabokov
Vladimir Vladimirovich Nabokov (russian: link=no, Владимир Владимирович Набоков ; 2 July 1977), also known by the pen name Vladimir Sirin (), was a Russian-American novelist, poet, translator, and entomologist. Bor ...
was dismissive of Stendhal, in '' Strong Opinions'' calling him "that pet of all those who like their French plain". In the notes to his translation of ''Eugene Onegin
''Eugene Onegin, A Novel in Verse'' (Reforms of Russian orthography, pre-reform Russian: ; post-reform rus, Евгений Оне́гин, ромáн в стихáх, p=jɪvˈɡʲenʲɪj ɐˈnʲeɡʲɪn, r=Yevgeniy Onegin, roman v stikhakh) is ...
'', he asserts that ''Le Rouge et le Noir'' is "much overrated", and that Stendhal has a "paltry style". In ''Pnin
''Pnin'' () is Vladimir Nabokov's 13th novel and his fourth written in English; it was published in 1957. The success of ''Pnin'' in the United States launched Nabokov's career into literary prominence. Its eponymous protagonist, Timofey Pavlovic ...
'' Nabokov wrote satirically, "Literary departments still labored under the impression that Stendhal, Galsworthy
John Galsworthy (; 14 August 1867 – 31 January 1933) was an English novelist and playwright. Notable works include ''The Forsyte Saga'' (1906–1921) and its sequels, ''A Modern Comedy'' and ''End of the Chapter''. He won the Nobel Prize i ...
, Dreiser, and Mann
Mann may refer to:
Arts, entertainment and media
* Mann (chess), a variant chess piece which moves as a king
* ''Mann'' (film), a 1999 Bollywood motion picture
* ''Mann'' (magazine), a Norwegian magazine
* Mann Theatres, a theatre chain corp ...
were great writers."
Michael Dirda
Michael Dirda (born 1948) is a book critic for the '' Washington Post''. He has been a Fulbright Fellow and won a Pulitzer Prize in 1993.
Career
Having studied at Oberlin College for his undergraduate degree in 1970, Dirda took an M.A. in 1974 ...
considers Stendhal "the greatest all round French writer – author of two of the top 20 French novels, author of a highly original autobiography (''Vie de Henry Brulard''), a superb travel writer, and as inimitable a presence on the page as any writer you'll ever meet."
Stendhal syndrome
In 1817 Stendhal was reportedly overcome by the cultural richness ofFlorence
Florence ( ; it, Firenze ) is a city in Central Italy and the capital city of the Tuscany region. It is the most populated city in Tuscany, with 383,083 inhabitants in 2016, and over 1,520,000 in its metropolitan area.Bilancio demografico ...
he encountered when he first visited the Tuscan city. As he described in his book ''Naples and Florence: A Journey from Milan to Reggio'':
As I emerged from the porch of Santa Croce, I was seized with a fierce palpitation of the heart (that same symptom which, in Berlin, is referred to as an attack of the nerves); the well-spring of life was dried up within me, and I walked in constant fear of falling to the ground.The condition was diagnosed and named in 1979 by Italian
psychiatrist
A psychiatrist is a physician who specializes in psychiatry, the branch of medicine devoted to the diagnosis, prevention, study, and treatment of mental disorders. Psychiatrists are physicians and evaluate patients to determine whether their sy ...
Dr. Graziella Magherini
Graziella Magherini (; born 23 August 1927 in Florence) is an Italian psychiatrist at the Santa Maria Nuova Hospital in Florence, Italy.
''Stendhal syndrome''
Graziella Magherini is best known for her 1989 book ''La sindrome di Stendhal'' ('' ...
, who had noticed similar psychosomatic
A somatic symptom disorder, formerly known as a somatoform disorder,(2013) dsm5.org. Retrieved April 8, 2014. is any mental disorder that manifests as physical symptoms that suggest illness or injury, but cannot be explained fully by a general ...
conditions (racing heart beat, nausea
Nausea is a diffuse sensation of unease and discomfort, sometimes perceived as an urge to vomit. While not painful, it can be a debilitating symptom if prolonged and has been described as placing discomfort on the chest, abdomen, or back of th ...
and dizziness
Dizziness is an imprecise term that can refer to a sense of disorientation in space, vertigo, or lightheadedness. It can also refer to disequilibrium or a non-specific feeling, such as giddiness or foolishness.
Dizziness is a common medical c ...
) amongst first-time visitors to the city.
In homage to Stendhal, Trenitalia
Trenitalia is the primary train operator in Italy. A subsidiary of Ferrovie dello Stato Italiane, itself owned by the Italian government, the company was established in 2000 following a European Union directive on the deregulation of rail transp ...
named their overnight train service from Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
to Venice
Venice ( ; it, Venezia ; vec, Venesia or ) is a city in northeastern Italy and the capital of the Veneto Regions of Italy, region. It is built on a group of 118 small islands that are separated by canals and linked by over 400 ...
the Stendhal Express, though there is no physical distress connected to it.
See also
*Mononymous person
A mononym is a name composed of only one word. An individual who is known and addressed by a mononym is a mononymous person. In some cases, a mononym selected by an individual may have originally been from a polynym, a word which refers to one o ...
Notes
References
Works cited
* * * * * * https://foundation.wikimedia.org/wiki/Terms_of_UseFurther reading
* *Adams, Robert M., ''Stendhal: Notes on a Novelist''. New York, Noonday Press, 1959. * Blum, Léon,Stendhal et le beylisme
'. Paris, Paul Ollendorf, 1914. *Dieter, Anna-Lisa, ''Eros - Wunde - Restauration. Stendhal und die Entstehung des Realismus, ''Paderborn: Wilhelm Fink, 2019 (Periplous. Münchener Studien zur Literaturwissenschaft). * Jefferson, Ann. ''Reading Realism in Stendhal (Cambridge Studies in French)''. Cambridge University Press, 1988. *
Keates, Jonathan
Jonathan B. Keates FRSL (born 1946) is an English writer, biographer, novelist and former chairman of the Venice in Peril Fund.
Biography
Jonathan Keates was born in Paris, France, in 1946. He was educated at Bryanston School and went on to read ...
. ''Stendhal''. London, Sinclair-Stevenson, 1994.
* Levin, Harry. ''Toward Stendhal''. New York, 1945.
* Richardson, Joanna. ''Stendhal''. London, Victor Gollancz, 1974.
External links
* * *StendhalForever.com
Stendhal's works
text, concordances and frequency list *
Audio Book (mp3) of
''The Red and the Black'' incipit *
French site on Stendhal
Centro Stendhaliano di Milano
Digital version of Stendhal's shoulder-notes on his own books. * {{DEFAULTSORT:Stendhal 1783 births 1842 deaths Writers from Grenoble 19th-century French writers Conseil d'État (France) French agnostics French novelists French psychological fiction writers French biographers French travel writers Romanticism Burials at Montmartre Cemetery French male essayists French male novelists French male short story writers 19th-century French short story writers French military personnel of the Napoleonic Wars Male biographers 19th-century pseudonymous writers