Marca Hispanica on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military
The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military
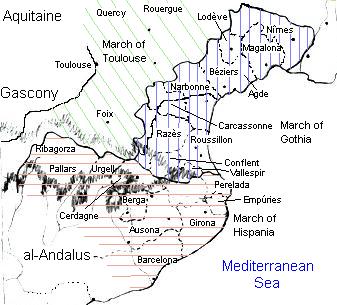 The Hispanic March resulted from the expansion south of the Frankish realm from their heartland in Neustria and Austrasia starting with
The Hispanic March resulted from the expansion south of the Frankish realm from their heartland in Neustria and Austrasia starting with
Ian Meadows, "The Arabs in Occitania"
{{Spanish Kingdoms , state=expanded Carolingian marches Medieval Catalonia States and territories established in the 790s 795 establishments
 The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military
The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military buffer zone
A buffer zone is a neutral zonal area that lies between two or more bodies of land, usually pertaining to countries. Depending on the type of buffer zone, it may serve to separate regions or conjoin them.
Common types of buffer zones are demili ...
beyond the former province of Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
, established by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
in 795 as a defensive barrier between the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
Moors
The term Moor, derived from the ancient Mauri, is an exonym first used by Christian Europeans to designate the Muslim inhabitants of the Maghreb, the Iberian Peninsula, Sicily and Malta during the Middle Ages.
Moors are not a distinc ...
of Al-Andalus
Al-Andalus translit. ; an, al-Andalus; ast, al-Ándalus; eu, al-Andalus; ber, ⴰⵏⴷⴰⵍⵓⵙ, label= Berber, translit=Andalus; ca, al-Àndalus; gl, al-Andalus; oc, Al Andalús; pt, al-Ândalus; es, al-Ándalus () was the M ...
and the Frankish Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
( Duchy of Gascony, the Duchy of Aquitaine
The Duchy of Aquitaine ( oc, Ducat d'Aquitània, ; french: Duché d'Aquitaine, ) was a historical fiefdom in western, central, and southern areas of present-day France to the south of the river Loire, although its extent, as well as its name, flu ...
and Carolingian Septimania).
In its broader meaning, ''Hispanic March'' sometimes refers to a group of early Iberian and trans-Pyrenean lordships or counts coming under Frankish rule. As time passed, these lordships merged or gained independence from Frankish imperial rule.
Geographical context
The area broadly corresponds to the eastern regions between thePyrenees
The Pyrenees (; es, Pirineos ; french: Pyrénées ; ca, Pirineu ; eu, Pirinioak ; oc, Pirenèus ; an, Pirineus) is a mountain range straddling the border of France and Spain. It extends nearly from its union with the Cantabrian Mountains to ...
and the Ebro River. The local population of the March was diverse. It included Basques
The Basques ( or ; eu, euskaldunak ; es, vascos ; french: basques ) are a Southwestern European ethnic group, characterised by the Basque language, a common culture and shared genetic ancestry to the ancient Vascones and Aquitanians. Ba ...
in its north-western valleys, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and a large Occitano-Romance-speaking Hispano-Roman population ( Occitans and Catalans) governed by the '' Visigothic Code'', all of them under the influence of Al-Andalus culture, since their lords had vowed allegiance to Cordoban rulers until Pepin's conquest of Andalusian Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
(759). The Pyrenean valleys started to switch loyalties after 785 (Girona, Ribagorza, etc.) with the construction and garrisoning by counts loyal to the Carolingians of new outposts and fortresses on bordering areas.
The territory changed with the fortunes of the Empires and the feudal ambitions of those, whether counts
Count (feminine: countess) is a historical title of nobility in certain European countries, varying in relative status, generally of middling rank in the hierarchy of nobility. Pine, L. G. ''Titles: How the King Became His Majesty''. New York ...
or walis
Elis () or Eleia ( el, Ήλιδα, Ilida, grc-att, Ἦλις, Ēlis ; Doric Greek#Northwest Greek, Elean: , ethnonym: ) is an ancient district in Greece that corresponds to the modern Elis (regional unit), regional unit of Elis.
Elis is in ...
, appointed to administer the counties. Eventually, the rulers and people of the March became autonomous and claimed independence. Out of the welter of counties in the region emerged the Principality of Catalonia
The Principality of Catalonia ( ca, Principat de Catalunya, la, Principatus Cathaloniæ, oc, Principat de Catalonha, es, Principado de Cataluña) was a medieval and early modern state in the northeastern Iberian Peninsula. During most of it ...
composed by a myriad of counties with the County of Barcelona as their main power centre.
Counties that at various times formed part of the March included: Ribagorza (initially including Pallars
Pallars is a historical and natural region of Catalonia. Located in the Pre-Pyrenees and Pyrenees area, most of its territory is mountainous.
The Noguera Pallaresa river is named after this region.
Geography
The physiography of the Pallars nat ...
), Urgell, Cerdanya, Perelada, Empúries
Empúries ( ca, Empúries ) was an ancient city on the Mediterranean coast of Catalonia, Spain. Empúries is also known by its Spanish name, Ampurias ( es, Ampurias ). The city Ἐμπόριον ( el, Ἐμπόριον, Emporion, meaning "tr ...
, Besalú
Besalú () is a town in the '' comarca'' of Garrotxa, in Girona, Catalonia, Spain.
The town's importance was greater in the early Middle Ages, as capital of the county of Besalú, whose territory was roughly the same size as the current ''coma ...
, Ausona (Osona), Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
, Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in 2020. Girona is the capit ...
(''March of Hispania'') and, Conflent
Conflent () is a historical Catalan comarca of Northern Catalonia, now part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales. In the Middle Ages it comprised the County of Conflent.
The capital of this ''pays'' is Prades ( ca, Prada de Conf ...
, Roussillon, Vallespir
Vallespir (; ) is a historical Catalan comarca in Northern Catalonia, part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales.
The capital of the comarca is Ceret, and it borders Conflent, Rosselló, Alt Empordà, Garrotxa and Ripollès. It l ...
and Fenollet (''March of Gothia''). The nominal boundaries of ''Gothia'' and the ''Hispanic March'' vary in time, not without confusion. While Navarre
Navarre (; es, Navarra ; eu, Nafarroa ), officially the Chartered Community of Navarre ( es, Comunidad Foral de Navarra, links=no ; eu, Nafarroako Foru Komunitatea, links=no ), is a foral autonomous community and province in northern Spain, ...
and Aragon have sometimes been depicted within the Hispanic March, they were not part of it, but they came under the Carolingian area of influence between 794 and 806 within the Basque (also rendered as "Gascon") marches, or Duchy of Vasconia.
Origins
 The Hispanic March resulted from the expansion south of the Frankish realm from their heartland in Neustria and Austrasia starting with
The Hispanic March resulted from the expansion south of the Frankish realm from their heartland in Neustria and Austrasia starting with Charles Martel
Charles Martel ( – 22 October 741) was a Frankish political and military leader who, as Duke and Prince of the Franks and Mayor of the Palace, was the de facto ruler of Francia from 718 until his death. He was a son of the Frankish statesm ...
in 732 and after various decades fighting between the Franks and Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
s (''Saraceni'') in the Iberian Peninsula
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese and Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a peninsula in southwestern Europe, def ...
.
The Muslim invasion
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
reached the Pyrenees in the Iberian Peninsula. In 719 the forces of Al-Samh ibn Malik
Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani ( ar, السمح بن مالك الخولاني) was the Arab governor general of Al-Andalus from between 719 and 721. In 720, under his governorate he minted the first purely Arab coins in Al-Andalus as part of his ...
surged up the east coast, overwhelming the remaining Visigoth
The Visigoths (; la, Visigothi, Wisigothi, Vesi, Visi, Wesi, Wisi) were an early Germanic people who, along with the Ostrogoths, constituted the two major political entities of the Goths within the Roman Empire in late antiquity, or what is kn ...
province of Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
and establishing a fortified base at Narbonne. Control was secured by offering the local population generous terms, inter-marriage between ruling families or treaties. Further Umayyad expansion was halted on Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani
Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani ( ar, السمح بن مالك الخولاني) was the Arab governor general of Al-Andalus from between 719 and 721. In 720, under his governorate he minted the first purely Arab coins in Al-Andalus as part of his ...
s defeat at the Battle of Toulouse. Wālis were installed in Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in 2020. Girona is the capit ...
and Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
.
The Muslim forces however continued to raid their Gallic neighbours to the north, reaching as far as Autun. Peace was signed in 730 between the victor at Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
, the Duke of Aquitaine, and 'Uthman ibn Naissa
Uthman ibn Naissa () better known as Munuza, was a Berber governor depicted in different contradictory chronicles during the Umayyad conquest of Hispania.
Munuza in Asturias
One account says that he was the governor of Gijón (or possibly León) ...
(Munuza), a Berber
Berber or Berbers may refer to:
Ethnic group
* Berbers, an ethnic group native to Northern Africa
* Berber languages, a family of Afro-Asiatic languages
Places
* Berber, Sudan, a town on the Nile
People with the surname
* Ady Berber (1913–19 ...
rebel lord stationed in Cerdanya (maybe current-day Catalonia), a region that could act as a buffer state against Umayyad expansionism. The peace treaty was sealed with the marriage of the Duke’s daughter to Munuza. However, Munuza was defeated by a Umayyad military expedition (731) and another period of Muslim expansion commenced.
Aquitaine (including the Duchy of Vasconia) pledged formal allegiance to the Frankish leaders several times (Odo in 732, Hunald in 736 after being defeated), but remained actually independent. In 737 Charles led an expedition to the Lower Rhone and Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
, possibly seeing that the Umayyad thrust was threatening his grip on Burgundy
Burgundy (; french: link=no, Bourgogne ) is a historical territory and former administrative region and province of east-central France. The province was once home to the Dukes of Burgundy from the early 11th until the late 15th century. The ...
(subdued in 736), but did not manage to subjugate and keep the region.
Both Aquitaine and Septimania were still out of central Frankish control after Charles's death, but Pepin the Short
the Short (french: Pépin le Bref; – 24 September 768), also called the Younger (german: Pippin der Jüngere), was King of the Franks from 751 until his death in 768. He was the first Carolingian to become king.
The younger was the son of ...
was determined to subdue southern Gaul. In 759, after conquering Septimania from the Umayyad
The Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE; , ; ar, ٱلْخِلَافَة ٱلْأُمَوِيَّة, al-Khilāfah al-ʾUmawīyah) was the second of the four major caliphates established after the death of Muhammad. The caliphate was ruled by the ...
, the Carolingian king focused all his might in crushing Aquitanian resistance to central Frankish power. After a ruthless war of 8 years, Aquitainian independence came to an end. Toulouse was now under the grip of the new Carolingian king Charlemagne and access to Andalusian Hispania was open for him, despite sporadic rebellions in Vasconia during the next two decades (Basques subdued in 790 by Charlemagne's new loyal strongman in Toulouse William of Gellone).
Pepin's son, Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
, fulfilled the Carolingian goal of extending the defensive boundaries of the empire beyond Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
, creating a strong barrier state between the Umayyad Emir
Emir (; ar, أمير ' ), sometimes transliterated amir, amier, or ameer, is a word of Arabic origin that can refer to a male monarch, aristocrat, holder of high-ranking military or political office, or other person possessing actual or cer ...
ate/Caliph
A caliphate or khilāfah ( ar, خِلَافَة, ) is an institution or public office under the leadership of an Islamic steward with the title of caliph (; ar, خَلِيفَة , ), a person considered a political-religious successor to th ...
ate of Iberia
The Iberian Peninsula (),
**
* Aragonese language, Aragonese and Occitan language, Occitan: ''Peninsula Iberica''
**
**
* french: Péninsule Ibérique
* mwl, Península Eibérica
* eu, Iberiar penintsula also known as Iberia, is a pe ...
and the Frankish Empire, besides tightening control over the Duchy of Vasconia by establishing the Kingdom of Aquitaine ruled by his son Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
in 781.
Creation
The Franks created the Hispanic March by conquering former north-eastern territory of the Visigothic kingdom of Hispania, which had been conquered by the Muslims. The first county to be conquered was Roussillon (withVallespir
Vallespir (; ) is a historical Catalan comarca in Northern Catalonia, part of the French department of Pyrénées-Orientales.
The capital of the comarca is Ceret, and it borders Conflent, Rosselló, Alt Empordà, Garrotxa and Ripollès. It l ...
) in around 760. In 785 the county of Girona
Girona (officially and in Catalan , Spanish: ''Gerona'' ) is a city in northern Catalonia, Spain, at the confluence of the Ter, Onyar, Galligants, and Güell rivers. The city had an official population of 103,369 in 2020. Girona is the capit ...
(with Besalú
Besalú () is a town in the '' comarca'' of Garrotxa, in Girona, Catalonia, Spain.
The town's importance was greater in the early Middle Ages, as capital of the county of Besalú, whose territory was roughly the same size as the current ''coma ...
) to the south of the Pyrenees was taken. Ribagorza and Pallars
Pallars is a historical and natural region of Catalonia. Located in the Pre-Pyrenees and Pyrenees area, most of its territory is mountainous.
The Noguera Pallaresa river is named after this region.
Geography
The physiography of the Pallars nat ...
were linked to Toulouse
Toulouse ( , ; oc, Tolosa ) is the prefecture of the French department of Haute-Garonne and of the larger region of Occitania. The city is on the banks of the River Garonne, from the Mediterranean Sea, from the Atlantic Ocean and fr ...
and were added to this county around 790. Urgell and Cerdanya were added in 798. The first records of the county of Empúries
Empúries ( ca, Empúries ) was an ancient city on the Mediterranean coast of Catalonia, Spain. Empúries is also known by its Spanish name, Ampurias ( es, Ampurias ). The city Ἐμπόριον ( el, Ἐμπόριον, Emporion, meaning "tr ...
(with Perelada) are from 812 but the county was probably under Frankish control before 800.
After a series of struggles the County of Barcelona
The County of Barcelona ( la, Comitatus Barcinonensis, ca, Comtat de Barcelona) was originally a frontier region under the rule of the Carolingian dynasty. In the 10th century, the Counts of Barcelona became progressively independent, heredi ...
(with Ausona) was taken by Frankish forces in 801. A number of castles were established in Aragon
Aragon ( , ; Spanish and an, Aragón ; ca, Aragó ) is an autonomous community in Spain, coextensive with the medieval Kingdom of Aragon. In northeastern Spain, the Aragonese autonomous community comprises three provinces (from north to s ...
between 798 and 802 (appointment of Count Aureolus). After subduing the Basques to the north of the Pyrenees (790), Frankish overlordship expanded to the upper Ebro (794) and Pamplona (798), when Alfonso II of Asturias also came under Charlemagne's influence. Sobrarbe
Sobrarbe is one of the comarcas of Aragon, Spain. It is located in the northern part of the province of Huesca, part of the autonomous community of Aragon in Spain. Many of its people speak the Aragonese language locally known as ''fabla''.
T ...
was not incorporated into the March, as it appears later in history and was probably within the area of influence of the County of Aragon
The County of Aragon ( an, Condato d'Aragón) or County of Jaca ( an, Condato de Chaca, link=no) was a small Frankish marcher county in the central Pyrenean valley of the Aragon river, comprising Ansó, Echo, and Canfranc and centered on the s ...
.
The death of Charlemagne (814) was followed by a scene of open revolt and Carolingian setbacks around the Pyrenees. After being defeated by the Moors in the 816 Battle of Pancorbo, Pamplona, now led by the native Basque lord Iñigo Arista, broke away from the Hispanic March, with the County of Aragon following suit shortly thereafter in 820. The named Catalan counties - territories used by the Moors to enter and overrun ''Septimania'' in 719 - became, at this point, a natural extension of the March of Gothia
The Hispanic March or Spanish March ( es, Marca Hispánica, ca, Marca Hispànica, Aragonese and oc, Marca Hispanica, eu, Hispaniako Marka, french: Marche d'Espagne), was a military buffer zone beyond the former province of Septimania, est ...
ruled by ''Catalans'' and ''Toulousains'' under the Carolingian Empire.
Structure
The local population of the March was diverse. The majority were Basques and Hispano-Romans (Goths). But there were also Muslims, and Jews fromSeptimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
who repopulated the Frankish conquered easternmost territories of present-day North Spain and a small portion of South France. The area changed with the fortunes of the empires and the feudal ambitions of the counts appointed to administrate the counties. As Frankish imperial power waned, the rulers of the March of Hispania became independent fiefs. The region would later become part of Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
.
Charlemagne's son Louis took Barcelona
Barcelona ( , , ) is a city on the coast of northeastern Spain. It is the capital and largest city of the autonomous community of Catalonia, as well as the second most populous municipality of Spain. With a population of 1.6 million within c ...
from its Moorish ruler in 801, thus securing Frankish power in the borderland between the Franks and the Moors. The Counts of Barcelona
The Count of Barcelona ( ca, Comte de Barcelona, es, Conde de Barcelona, french: Comte de Barcelone, ) was the ruler of the County of Barcelona and also, by extension and according with the usages and Catalan constitutions, of the Principality ...
then became the principal representatives of Frankish authority in the Hispanic March. The March included various outlying smaller territories, each ruled by a lesser '' miles'' with his armed retainers and who theoretically owed allegiance through the Count to the Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
.
The rulers were called ''counts''; when they governed several counties they often took the name ''duke'' (Dux Gothiae). When the county formed the border with the Muslim Kingdom, the Frankish title ''marquis'' (Marquis de Gothie) was chosen. Besides, certain counts aspired to the Frankish title "Prince of Gothia {{One source, date=December 2021
The title Prince of Gothia (''princeps Gothiæ'') or Prince of the Goths (''princeps Gothorum'') was a title of nobility, sometimes assumed by its holder as a sign of supremacy in the region of Gothia and sometimes ...
". A margrave or ''Marcgravi'' is a ''Graf'' ("duke") of the March. The first ''Toulousains'' and ''Catalan'' lords who held the title of Counts of Barcelona, Bernard of Septimania
Bernard (or Bernat) of Septimania (795–844), son of William of Gellone, was the Frankish Duke of Septimania and Count of Barcelona from 826 to 832 and again from 835 to his execution. He was also count of Carcassonne from 837. He was appointed ...
, Humfrid, Bernard of Gothia, Borrell II and Ramon Borrell
Ramon Borrell ( ca, Ramon Borrell, es, Ramón Borrell; 972–1017) was count of Barcelona, Girona and Ausona from 992. He was the son of Borrell II of Barcelona and Letgarda of Rouergue, and was associated with his father in ruling the counties ...
carried these titles.
In the early 9th century, Charlemagne began issuing a new kind of land grant, the '' aprisio'', which reallocated land previously held by the imperial crown fisc in deserted or abandoned areas. This included special rights and immunities that allowed considerable independence from the imperial control. Historians have interpreted the ''aprisio'' both as an early form of feudalism
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structu ...
and in economic and military terms as a mechanism to entice settlers to a depopulated border region. Such self-sufficient landholders would aid the Counts in providing armed men to defend the Frankish frontier. ''Aprisio'' grants (the first ones were in Septimania
Septimania (french: Septimanie ; oc, Septimània ) is a historical region in modern-day Southern France. It referred to the western part of the Roman province of Gallia Narbonensis that passed to the control of the Visigoths in 462, when Septim ...
) were given personally by the Carolingian king, so that they reinforced loyalty to central power, to counterbalance the local power exercised by the Marcher Counts.
However poor communications and a distant central power allowed basic feudal
Feudalism, also known as the feudal system, was the combination of the legal, economic, military, cultural and political customs that flourished in medieval Europe between the 9th and 15th centuries. Broadly defined, it was a way of structur ...
entities to develop often self-sufficient and heavily agrarian. Each was ruled by a small hereditary military elite. These developments in the territories that later would become Catalonia
Catalonia (; ca, Catalunya ; Aranese Occitan: ''Catalonha'' ; es, Cataluña ) is an autonomous community of Spain, designated as a '' nationality'' by its Statute of Autonomy.
Most of the territory (except the Val d'Aran) lies on the no ...
followed similar patterns in other borderlands and March. For example, the first Count of Barcelona Bera was appointed by the King in 801, however subsequently strong heirs of Counts were able to inherit the title such as Sunifred, fl. 844–848. This gradually became custom until Countship became hereditary (for Wifred the Hairy in 897). The County became ''de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
'' independent under count Borrell II, when he ceased to request royal charters after the kings Lothair and Hugh Capet failed to assist him in the defense of the County against Muslim leader al-Mansur
Abū Jaʿfar ʿAbd Allāh ibn Muḥammad al-Manṣūr (; ar, أبو جعفر عبد الله بن محمد المنصور; 95 AH – 158 AH/714 CE – 6 October 775 CE) usually known simply as by his laqab Al-Manṣūr (المنصور) ...
, although the change of dynasty may have played a part in that decision.
The early history of Andorra
Andorra, officially the Principality of Andorra ( ca, Principat d'Andorra), also called the Principality of the Valleys of Andorra ( ca, Principat de les Valls d'Andorra, links=no), is a sovereign landlocked microstate in Southwestern Europe, ...
in the Pyrenees provides a fairly typical example of a lordship of the region, as Andorra is the only part of the Hispanic March that was never incorporated into either France or Spain, a feat mentioned in its national anthem, '' El Gran Carlemany''.
References
Further reading
*External links
Ian Meadows, "The Arabs in Occitania"
{{Spanish Kingdoms , state=expanded Carolingian marches Medieval Catalonia States and territories established in the 790s 795 establishments