Male reproductive system on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The male reproductive system consists of a number of sex organs that play a role in the process of human reproduction. These organs are located on the outside of the body and within the



 Sexual identity is determined at
Sexual identity is determined at
 The genetic sex is determined by whether a Y bearing or next bearing sperm fertilizes the open; the presence or absence of a Y chromosome in turn determines whether the gonads of the embryo will be testes or ovaries; and the presence or absence of testes, finally, determines whether the sex accessory organs and external genitalia will be male or female. This sequence is understandable in light of the fact that both male and female embryos develop within the maternal environment - high in estrogen secreted by the mother's ovaries and the placenta. If estrogen determined the gender, all embryos would become feminized.
The genetic sex is determined by whether a Y bearing or next bearing sperm fertilizes the open; the presence or absence of a Y chromosome in turn determines whether the gonads of the embryo will be testes or ovaries; and the presence or absence of testes, finally, determines whether the sex accessory organs and external genitalia will be male or female. This sequence is understandable in light of the fact that both male and female embryos develop within the maternal environment - high in estrogen secreted by the mother's ovaries and the placenta. If estrogen determined the gender, all embryos would become feminized.

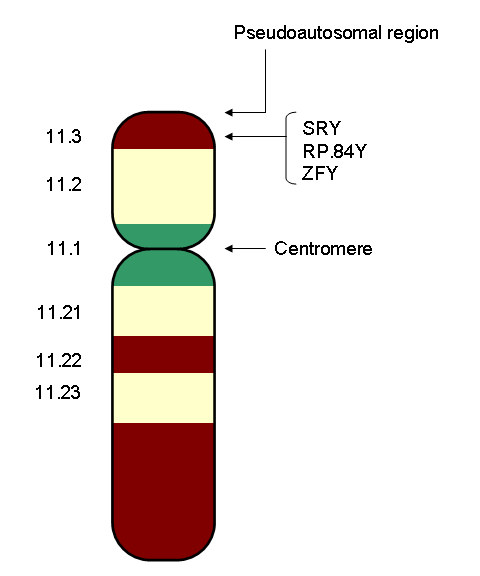 Chromosomal abnormalities can occur during fertilization impacting the development of the male reproductive system. The genotype of the male consists of a Y chromosome paired with an X chromosome. Female sex is determined by the absence of a Y chromosome. Some individuals are male who have the
Chromosomal abnormalities can occur during fertilization impacting the development of the male reproductive system. The genotype of the male consists of a Y chromosome paired with an X chromosome. Female sex is determined by the absence of a Y chromosome. Some individuals are male who have the  After the testes have differentiated, male sex hormones, called androgens, are secreted from interstitial cells (cells of Leydig). The major androgens secreted by these cells is testosterone and secretion begins 8 to 10 weeks after conception. Testosterone secretion reaches a peak at 12 to 14 weeks, and declines to very low levels by the end of the second trimester (about 21 weeks). Levels are the barely detectable 4–6 months of age postnatal. High levels of testosterone will not appear again until the time of puberty.
Internal accessory sex organs to develop and most of these are derived from two systems of embryonic ducts. Male accessory organs are derived from mesonephric (wolfian) ducts. The developing tubules within the testes secretes a polypeptide Müllerian inhibition factor (MIF). MIF causes the regression of the paramesonephritic ducts 60 days after fertilization. Testosterone secretion by the interstitial cells of the testes then causes the growth and development of the mesonephric ducts into male secondary sex organs. The Müllerian ducts atrophy, but traces of their anterior ends are represented by the
After the testes have differentiated, male sex hormones, called androgens, are secreted from interstitial cells (cells of Leydig). The major androgens secreted by these cells is testosterone and secretion begins 8 to 10 weeks after conception. Testosterone secretion reaches a peak at 12 to 14 weeks, and declines to very low levels by the end of the second trimester (about 21 weeks). Levels are the barely detectable 4–6 months of age postnatal. High levels of testosterone will not appear again until the time of puberty.
Internal accessory sex organs to develop and most of these are derived from two systems of embryonic ducts. Male accessory organs are derived from mesonephric (wolfian) ducts. The developing tubules within the testes secretes a polypeptide Müllerian inhibition factor (MIF). MIF causes the regression of the paramesonephritic ducts 60 days after fertilization. Testosterone secretion by the interstitial cells of the testes then causes the growth and development of the mesonephric ducts into male secondary sex organs. The Müllerian ducts atrophy, but traces of their anterior ends are represented by the
File:Male genital system - 3D view.svg, Perspective view
File:Male genital system - Sagittal view.svg, Sagittal view
File:Male genital system - Front view.svg, Front view
File:Sperm release pathway.svg, Sperm release pathway
pelvis
The pelvis (plural pelves or pelvises) is the lower part of the trunk, between the abdomen and the thighs (sometimes also called pelvic region), together with its embedded skeleton (sometimes also called bony pelvis, or pelvic skeleton).
The ...
.
The main male sex organs are the penis
A penis (plural ''penises'' or ''penes'' () is the primary sexual organ that male animals use to inseminate females (or hermaphrodites) during copulation. Such organs occur in many animals, both vertebrate and invertebrate, but males d ...
and the testicle
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
s which produce semen
Semen, also known as seminal fluid, is an organic bodily fluid created to contain spermatozoa. It is secreted by the gonads (sexual glands) and other sexual organs of male or hermaphroditic animals and can fertilize the female ovum. Sem ...
and sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
, which, as part of sexual intercourse
Sexual intercourse (or coitus or copulation) is a sexual activity typically involving the insertion and thrusting of the penis into the vagina for sexual pleasure or reproduction.Sexual intercourse most commonly means penile–vaginal pene ...
, fertilize
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
an ovum
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete i ...
in the female's body; the fertilized ovum (zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
) develops into a fetus
A fetus or foetus (; plural fetuses, feti, foetuses, or foeti) is the unborn offspring that develops from an animal embryo. Following embryonic development the fetal stage of development takes place. In human prenatal development, fetal dev ...
, which is later born as an infant
An infant or baby is the very young offspring of human beings. ''Infant'' (from the Latin word ''infans'', meaning 'unable to speak' or 'speechless') is a formal or specialised synonym for the common term ''baby''. The terms may also be used t ...
.
The corresponding system in females is the female reproductive system.
External genital organs


Penis
The penis is the male intromittent organ. It has a long shaft and an enlarged bulbous-shaped tip called the glans penis, which supports and is protected by the foreskin. When the male becomes sexually aroused, the penis becomes erect and ready for sexual activity. Erection occurs because sinuses within the erectile tissue of the penis become filled with blood. The arteries of the penis are dilated while the veins are compressed so that blood flows into the erectilecartilage
Cartilage is a resilient and smooth type of connective tissue. In tetrapods, it covers and protects the ends of long bones at the joints as articular cartilage, and is a structural component of many body parts including the rib cage, the neck ...
under pressure. The penis is supplied by the pudendal artery.
Scrotum
The scrotum is a pouch-like structure that hangs behind the penis. It holds and protects the testicles. It also contains numerous nerves and blood vessels. During times of lower temperatures, the Cremaster muscle contracts and pulls the scrotum closer to the body, while the Dartos muscle gives it a wrinkled appearance; when the temperature increases, the Cremaster and Dartos muscles relax to bring down the scrotum away from the body and remove the wrinkles respectively. The scrotum remains connected with the abdomen or pelvic cavity by the inguinal canal. (The spermatic cord, formed from spermatic artery, vein and nerve bound together with connective tissue passes into the testis through inguinal canal.)Internal genital organs

Testis
Testis has two major functions: To produce sperm by meiotic division of germ cells within the seminiferous tubules, and to synthesize and secrete androgens that regulate the male reproductive functions. The site of production of androgens is the Leydig cells that are located in the interstitium between seminiferous tubules.Epididymis
The epididymis is a long whitish mass of tightly coiled tube. The sperm that are produced in the seminiferous tubules flow into the epididymis. During passage via the epididymis, the sperm undergo maturation and are concentrated by the action of ion channels located on the apical membrane of the epididymis.Vas deferens
The vas deferens, which is also known as the sperm duct, is a thin tube approximately long that starts from the epididymis to the pelvic cavity. It carries the spermatozoa from the epididymis to ejaculatory duct.Accessory glands
Three accessory glands provide fluids that lubricate the duct system and nourish the sperm cells. They are the seminal vesicles, theprostate gland
The prostate is both an accessory gland of the male reproductive system and a muscle-driven mechanical switch between urination and ejaculation. It is found only in some mammals. It differs between species anatomically, chemically, and physi ...
, and the bulbourethral gland
The bulbourethral glands or Cowper's glands (named for English anatomist William Cowper) are two small exocrine glands in the reproductive system of many male mammals (of all domesticated animals, they are absent only in dogs). They are homolo ...
s (Cowper glands).
Development
The embryonic and prenatal development of the male reproductive system is the process whereby the reproductive organs grow, mature and are established. It begins with a single fertilized egg and culminates 38 weeks later with birth of a male child. It is a part of the stages of sexual differentiation. The development of the male reproductive system coincides with the urinary system. Their development can also be described together as the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.Sexual determination
 Sexual identity is determined at
Sexual identity is determined at fertilization
Fertilisation or fertilization (see spelling differences), also known as generative fertilisation, syngamy and impregnation, is the fusion of gametes to give rise to a new individual organism or offspring and initiate its development. Pro ...
when the gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "...Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
tic sex of the zygote
A zygote (, ) is a eukaryotic cell formed by a fertilization event between two gametes. The zygote's genome is a combination of the DNA in each gamete, and contains all of the genetic information of a new individual organism.
In multicell ...
has been initialized by a sperm
Sperm is the male reproductive cell, or gamete, in anisogamous forms of sexual reproduction (forms in which there is a larger, female reproductive cell and a smaller, male one). Animals produce motile sperm with a tail known as a flagellum, ...
cell containing either an X or Y chromosome. If this sperm cell contains an X chromosome
The X chromosome is one of the two sex-determining chromosomes (allosomes) in many organisms, including mammals (the other is the Y chromosome), and is found in both males and females. It is a part of the XY sex-determination system and XO sex ...
it will coincide with the X chromosome
A chromosome is a long DNA molecule with part or all of the genetic material of an organism. In most chromosomes the very long thin DNA fibers are coated with packaging proteins; in eukaryotic cells the most important of these proteins ar ...
of the ovum
The egg cell, or ovum (plural ova), is the female reproductive cell, or gamete, in most anisogamous organisms (organisms that reproduce sexually with a larger, female gamete and a smaller, male one). The term is used when the female gamete i ...
and a female
Female ( symbol: ♀) is the sex of an organism that produces the large non-motile ova (egg cells), the type of gamete (sex cell) that fuses with the male gamete during sexual reproduction.
A female has larger gametes than a male. Fema ...
child will develop. A sperm cell carrying a Y chromosome results in an XY combination, and a male child will develop.
Genetic sex determines whether the gonads will be testes or ovaries. In the developing embryo if the testes are developed, it will produce and secrete male sex hormones during late embryonic development and cause the secondary sex organs of the male to develop.
Other embryonic reproductive structures
The structures are masculinized by secretions of the testes: * urogenital sinus * genital tubercle * urogenital folds *cloacal membrane
The cloacal membrane is the membrane that covers the embryonic cloaca during the development of the urinary and reproductive organs.
It is formed by ectoderm and endoderm coming into contact with each other. As the human embryo grows and caudal fo ...
* labioscrotal folds
The prostate gland derives from the urogenital sinus, and the other embryonic structures differentiate into the external genitalia. In the absence of testicular secretions, the female genitalia are formed.
External structures
At six weeks post conception, the differentiation of the external genitalia in the male and female has not taken place. At eight weeks, a distinct phallus is present during the indifferent stage. By the 10th-12th week, the genitalia are distinctly male or female being and derived from their homologous structures. At 16 weeks post conception, the genitalia are formed and distinct. The masculinization of the embryonic reproductive structures occurs as a result of testosterone secreted by the embryonic testes. Testosterone, however, is not the active agent within these organs. Once inside the target cells, testosterone is converted by means of an enzyme called 5α-reductase into the dihydrotestosterone (DHT). DHT mediates the androgen effect in these organs.Testes
At nine weeks, male differentiation of the gonads and the testes is well underway. Internal changes include the formation of the tubular seminar Chris tubules in the Rete testis from the primary sex cord. Developing on the outside surface of each testis is a Phibro muscular cord called thegubernaculum
The paired gubernacula (from Ancient Greek κυβερνάω = pilot, steer) also called the caudal genital ligament, are embryonic structures which begin as undifferentiated mesenchyme attaching to the caudal end of the gonads (testes in males ...
. This structure attaches to the inferior portion of the testis and extends to the labial sacral fold of the same side at the same time, a portion of the embryonic mesonephric duct adjacent to the testis becomes attached and convoluted informs the epididymis. Another portion of the mesonephric duct becomes the ductus deferens.
The seminal vesicles form from lateral outgrowths of the caudal and of each mesonephric duct the prostate gland arises from an Indo dermal outgrowth of the urogenital sinus the bulbourethral glands develop from outgrowths in the membrane-like portion of the urethra.
The descent of the testes to its final location at the anterior abdominal wall, followed by the development of the gubernaculum, which subsequently pulls and translocates the testis down into the developing scrotum. Ultimately, the passageway closes behind the testis. A failure in this process can cause indirect inguinal hernia or an infantile hydrocoele. The testes descend into the scrotal sac between the sixth and 10th week. Dissent into this not occur until about the 28th week when compared and we know canals form and the abdominal wall to provide openings from the pelvic cavity to the scrotal sac. The process by which a testis to send is not well understood but it seems to be associated with the shortening of the gubernaculum, which is attached to the testis and extends to the inguinal canal to the wall of the scrotum as a testis to sense it passes to the side of the urinary bladder and anterior to the symphysis pubis. It carries with it the ductus deference, that is testicular vessels and nerves, a portion of the abdominal muscle, and lymph vessels. All of the structures remain attached to the testis and form what is known as the spermatic cord by the time the testis is in the scrotal sac, the gubernaculum is no more than a remnant of scar like tissue.
External genitalia
The external genitalia of the male is distinct from those of the female by the end of the ninth week. Prior to that, the genital tubercle in both sexes is a phallus. The urethral groove forms on the ventral surface of the phallus early in development during the differentiation of the external genitalia. This is caused by the androgens produced and secreted by the testes. Androgen induced development causes the elongation and differentiation of the phallus into a penis, a fusion of the urogenital folds surrounding the urethral groove along the ventral surface of the penis, and a midline closure of the labioscrotal folds. This closure forms the wall of the scrotum the external genitalia. The external genitalia are completely formed by the end of the 12th week. At birth, the development of the prepubertal male reproductive system is completed. During the second trimester of pregnancy, testosterone secretion in the male declines so that at birth the testes are inactive. Gonadotropin secretion is low until the beginning of puberty.Summary
 The genetic sex is determined by whether a Y bearing or next bearing sperm fertilizes the open; the presence or absence of a Y chromosome in turn determines whether the gonads of the embryo will be testes or ovaries; and the presence or absence of testes, finally, determines whether the sex accessory organs and external genitalia will be male or female. This sequence is understandable in light of the fact that both male and female embryos develop within the maternal environment - high in estrogen secreted by the mother's ovaries and the placenta. If estrogen determined the gender, all embryos would become feminized.
The genetic sex is determined by whether a Y bearing or next bearing sperm fertilizes the open; the presence or absence of a Y chromosome in turn determines whether the gonads of the embryo will be testes or ovaries; and the presence or absence of testes, finally, determines whether the sex accessory organs and external genitalia will be male or female. This sequence is understandable in light of the fact that both male and female embryos develop within the maternal environment - high in estrogen secreted by the mother's ovaries and the placenta. If estrogen determined the gender, all embryos would become feminized.
Puberty
During puberty, increased gonadotropin secretion stimulates a rise in sex steroids creation from the testes. The increased secretion of testosterone from the testes during puberty causes the male secondary sexual characteristics to be manifested. Male secondary sex characteristics include: * Growth ofbody hair
Body hair, or androgenic hair, is the terminal hair that develops on the human body during and after puberty. It is differentiated from the head hair and less visible vellus hair, which is much finer and lighter in color. The growth of androge ...
, including underarm, abdominal
The abdomen (colloquially called the belly, tummy, midriff, tucky or stomach) is the part of the body between the thorax (chest) and pelvis, in humans and in other vertebrates. The abdomen is the front part of the abdominal segment of the to ...
, chest hair
Chest hair is hair that grows on the chest in the region between the neck and the abdomen. Chest hair develops during and after puberty along with other types of androgenic hair.
Development and growth
Although vellus hair is already prese ...
and pubic hair.
* Growth of facial hair
Facial hair is hair grown on the face, usually on the chin, cheeks, and upper lip region. It is typically a secondary sex characteristic of human males. Men typically start developing facial hair in the later stages of puberty or adolescenc ...
.
* Enlargement of larynx
The larynx (), commonly called the voice box, is an organ in the top of the neck involved in breathing, producing sound and protecting the trachea against food aspiration. The opening of larynx into pharynx known as the laryngeal inlet is about ...
(Adam's apple) and deepening of voice.
* Increased stature; adult males are taller than adult females, on average.
* Heavier skull
The skull is a bone protective cavity for the brain. The skull is composed of four types of bone i.e., cranial bones, facial bones, ear ossicles and hyoid bone. However two parts are more prominent: the cranium and the mandible. In humans, th ...
and bone
A bone is a rigid organ that constitutes part of the skeleton in most vertebrate animals. Bones protect the various other organs of the body, produce red and white blood cells, store minerals, provide structure and support for the body, ...
structure
A structure is an arrangement and organization of interrelated elements in a material object or system, or the object or system so organized. Material structures include man-made objects such as buildings and machines and natural objects such a ...
.
* Increased muscle
Skeletal muscles (commonly referred to as muscles) are organs of the vertebrate muscular system and typically are attached by tendons to bones of a skeleton. The muscle cells of skeletal muscles are much longer than in the other types of mus ...
mass and strength.
* Broadening of shoulders and chest; shoulders wider than hips.
* Increased secretions of oil and sweat gland
Sweat glands, also known as sudoriferous or sudoriparous glands, , are small tubular structures of the skin that produce sweat. Sweat glands are a type of exocrine gland, which are glands that produce and secrete substances onto an epithelial ...
s.
Secondary development includes the increased activity of the eccrine sweat glands and sebaceous glands
A sebaceous gland is a microscopic exocrine gland in the skin that opens into a hair follicle to secrete an oily or waxy matter, called sebum, which lubricates the hair and skin of mammals. In humans, sebaceous glands occur in the greatest number ...
along with the darkening of the skin in the scrotal region.
Clinical significance
Chromosomal abnormalities
 Chromosomal abnormalities can occur during fertilization impacting the development of the male reproductive system. The genotype of the male consists of a Y chromosome paired with an X chromosome. Female sex is determined by the absence of a Y chromosome. Some individuals are male who have the
Chromosomal abnormalities can occur during fertilization impacting the development of the male reproductive system. The genotype of the male consists of a Y chromosome paired with an X chromosome. Female sex is determined by the absence of a Y chromosome. Some individuals are male who have the XX male syndrome
XX male syndrome, also known as de la Chapelle syndrome, is a rare congenital intersex condition in which an individual with a 46, XX karyotype (otherwise associated with females) has phenotypically male characteristics that can vary among cases ...
and androgen insensitivity syndrome. This occurs when one X chromosome contains a segment of the Y chromosome, which was inserted into the X chromosome of the father's sperm. Rarely females are born with the XY genotype. They are found to be missing the same portion of the Y chromosome it was inserted into the chromosome of XX males. The gene for sexual differentiation in humans, called the testis determining factor (TDF), is located on the short arm of the Y chromosome. The presence or absence of the Y chromosome determines whether the embryo will have testes or ovaries. An abnormal number of sex chromosomes (aneuploidy
Aneuploidy is the presence of an abnormal number of chromosomes in a cell, for example a human cell having 45 or 47 chromosomes instead of the usual 46. It does not include a difference of one or more complete sets of chromosomes. A cell with an ...
) may can occur. This includes Turner's syndrome - a single X chromosome is present, Klinefelter's syndrome
Klinefelter syndrome (KS), also known as 47,XXY, is an aneuploid genetic condition where a male has an additional copy of the X chromosome. The primary features are infertility and small, poorly functioning testicles. Usually, symptoms are su ...
- two X chromosomes and a Y chromosome are present, XYY syndrome
XYY syndrome, also known as Jacobs syndrome, is an aneuploid genetic condition in which a male has an extra Y chromosome. There are usually few symptoms. These may include being taller than average, acne, and an increased risk of learning di ...
and XXYY syndrome
XXYY syndrome is a sex chromosome anomaly in which males have 2 extra chromosomes, one X and one Y chromosome. Human cells usually contain two sex chromosomes, one from the mother and one from the father. Usually, females have two X chromosomes ...
. Other less common chromosomal arrangements include: triple X syndrome, 48, XXXX, and 49, XXXXX
Pentasomy X, also known as 49,XXXXX, is a chromosomal disorder in which a female has five, rather than two, copies of the X chromosome. Pentasomy X is associated with short stature, intellectual disability, characteristic facial features, heart ...
.
The observable, visual differences become apparent between male or the female reproductive organs are not seen initially. Maturation continues as the medial aspect of each mesonephros grows to form the genital ridge
The genital ridge (or gonadal ridge) is the precursor to the gonads. The genital ridge initially consists mainly of mesenchyme and cells of underlying mesonephric origin. Once oogonia enter this area they attempt to associate with these somatic ce ...
. The genital ridge continues to grow behind the developing peritoneal membrane. By week six, string-like cell congregations called primitive sex cords form within the enlarging genital ridge. Externally, a swelling called the genital tubercle appears above the cloacal membrane.
External distinctions are not observed even by the eighth week of pre-embryonic development. This is the indifferent stage during which the gonads are relatively large and have an outer cortex of primitive sex cords and an inner medulla.
Specialized primordial germ cells are forming and migrating from the yolk sac to the embryonic gonads during week eight and nine. These are the spermatogonia in the developing male. Before seven weeks after fertilization, the gonads have the potential to become either testes or ovaries. Reproductive sex organs for both male and female are derived from the same embryonic tissues and are considered homologous tissues or organs.
appendices testis
The appendix testis (or hydatid of Morgagni) is a vestigial remnant of the Müllerian duct, present on the upper pole of the testis and attached to the tunica vaginalis. It is present about 90% of the time.
Clinical significance Torsion
The appen ...
(hydatids of Morgagni The hydatid of Morgagni can refer to one of two closely related bodily structures:
* Appendix of testis (in the male)
* Paraovarian cyst
Paraovarian cysts or paratubal cysts are epithelium-lined fluid-filled cysts in the adnexa adjacent to the f ...
of the male), while their terminal fused portions form the utriculus
The utricle and saccule are the two otolith organs in the vertebrate inner ear. They are part of the balancing system (membranous labyrinth) in the vestibule of the bony labyrinth (small oval chamber). They use small stones and a viscous fluid to ...
on the floor of the prostatic urethra
The prostatic urethra, the widest and most dilatable part of the urethra canal, is about 3 cm long.
It runs almost vertically through the prostate from its base to its apex, lying nearer its anterior than its posterior surface; the form of ...
. This is due to the production of Anti-Müllerian hormone by the Sertoli cells of the testes
A testicle or testis (plural testes) is the male reproductive gland or gonad in all bilaterians, including humans. It is homologous to the female ovary. The functions of the testes are to produce both sperm and androgens, primarily testoste ...
.
Gallery
See also
* Evolution of sexual reproduction *Male infertility
Male infertility refers to a sexually mature male's inability to impregnate a fertile female. In humans it accounts for 40–50% of infertility. It affects approximately 7% of all men. Male infertility is commonly due to deficiencies in the semen ...
* Oncofertility
* Reproductive system
The reproductive system of an organism, also known as the genital system, is the biological system made up of all the anatomical organs involved in sexual reproduction. Many non-living substances such as fluids, hormones, and pheromones are ...
* Spermatogenesis
Spermatogenesis is the process by which haploid spermatozoa develop from germ cells in the seminiferous tubules of the testis. This process starts with the mitotic division of the stem cells located close to the basement membrane of the tubu ...
References
Bibliography
* * * * * * {{Authority control Human male reproductive system