Macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor (CSF1R), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor receptor (M-CSFR), and CD115 (Cluster of Differentiation 115), is a cell-surface
 CSF1R, the protein encoded by the ''CSF1R'' gene is a
CSF1R, the protein encoded by the ''CSF1R'' gene is a

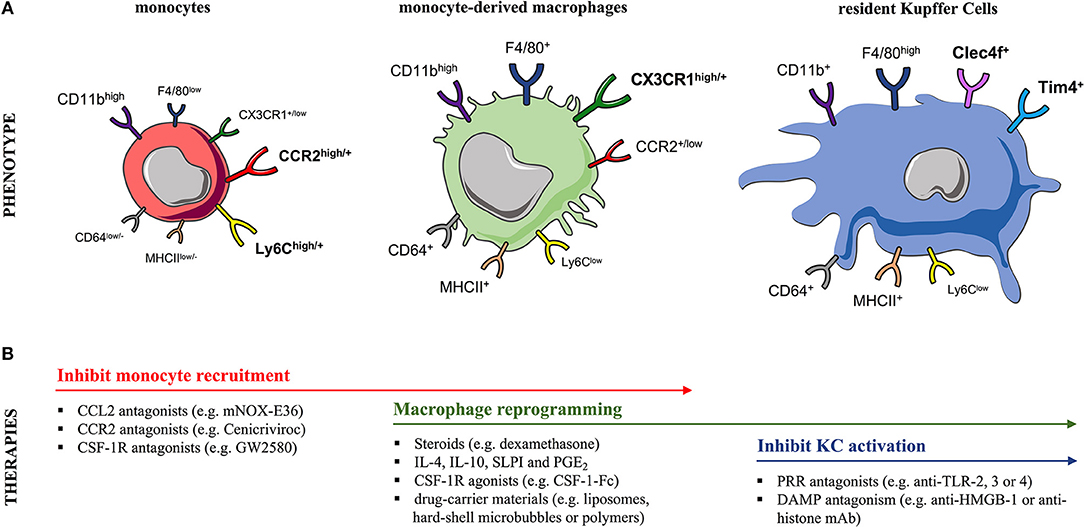 Monocytes and macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Monocytes circulate in the blood and are capable of differentiating into macrophages or
Monocytes and macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Monocytes circulate in the blood and are capable of differentiating into macrophages or
 Microglia are the tissue-resident
Microglia are the tissue-resident
 CSF1R signaling is involved in several diseases and disorders of the
CSF1R signaling is involved in several diseases and disorders of the

 Because Tumor-associated macrophage, TAM CSF1R signaling is tumor-permissive and can tumor treatment-resistance, CSF1R signaling is a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Several studies have investigated the efficacy of CSF1R inhibitor as a monotherapy and as a combination therapy in Refractory cancer, refractory and metastatic cancers. Several small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting CSF1R are in clinical development for cancer therapy (Table 2). Pexidartinib, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) is a small molecule inhibitor tyrosine of CSFR (as well as cKIT, FLT3, and VEGF receptor, VEGFR) with the most clinical development so far. Several completed and concurrent clinical trials have tested the efficacy and safety of Pexidartinib as a monotherapy for c-kit-mutated melanoma, prostate cancer, glioblastoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, neurofibroma, sarcoma, and Leukemia, leukemias. In 2019, Pexidartinib was FDA approval, FDA-approved for treatment of Tenosynovial giant cell tumor, diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumors, a non-malignant tumor that develops from Synovial membrane, synovial tissue lining the joints.
Because Tumor-associated macrophage, TAM CSF1R signaling is tumor-permissive and can tumor treatment-resistance, CSF1R signaling is a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Several studies have investigated the efficacy of CSF1R inhibitor as a monotherapy and as a combination therapy in Refractory cancer, refractory and metastatic cancers. Several small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting CSF1R are in clinical development for cancer therapy (Table 2). Pexidartinib, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) is a small molecule inhibitor tyrosine of CSFR (as well as cKIT, FLT3, and VEGF receptor, VEGFR) with the most clinical development so far. Several completed and concurrent clinical trials have tested the efficacy and safety of Pexidartinib as a monotherapy for c-kit-mutated melanoma, prostate cancer, glioblastoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, neurofibroma, sarcoma, and Leukemia, leukemias. In 2019, Pexidartinib was FDA approval, FDA-approved for treatment of Tenosynovial giant cell tumor, diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumors, a non-malignant tumor that develops from Synovial membrane, synovial tissue lining the joints.
protein
Proteins are large biomolecules and macromolecules that comprise one or more long chains of amino acid residues. Proteins perform a vast array of functions within organisms, including catalysing metabolic reactions, DNA replication, res ...
encoded by the human ''CSF1R'' gene
In biology, the word gene (from , ; "... Wilhelm Johannsen coined the word gene to describe the Mendelian units of heredity..." meaning ''generation'' or ''birth'' or ''gender'') can have several different meanings. The Mendelian gene is a b ...
(known also as c-FMS). CSF1R is a receptor
Receptor may refer to:
* Sensory receptor, in physiology, any structure which, on receiving environmental stimuli, produces an informative nerve impulse
*Receptor (biochemistry), in biochemistry, a protein molecule that receives and responds to a ...
that can be activated by two ligands: colony stimulating factor 1
The colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), is a secreted cytokine which causes hematopoietic stem cells to differentiate into macrophages or other related cell types. Eukaryotic cells also ...
(CSF-1) and interleukin-34 (IL-34). CSF1R is highly expressed in myeloid cells, and CSF1R signaling is necessary for the survival
Survival, or the act of surviving, is the propensity of something to continue existing, particularly when this is done despite conditions that might kill or destroy it. The concept can be applied to humans and other living things (or, hypotheti ...
, proliferation, and differentiation of many myeloid cell types ''in vivo
Studies that are ''in vivo'' (Latin for "within the living"; often not italicized in English) are those in which the effects of various biological entities are tested on whole, living organisms or cells, usually animals, including humans, and ...
'' and ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
.'' CSF1R signaling is involved in many diseases and is targeted in therapies for cancer
Cancer is a group of diseases involving abnormal cell growth with the potential to invade or spread to other parts of the body. These contrast with benign tumors, which do not spread. Possible signs and symptoms include a lump, abnormal b ...
, neurodegeneration, and inflammatory bone diseases.
Gene
In the human genome, the ''CSF1R'' gene is located on chromosome 5 (5q32), and in mice the ''Csf1r'' gene is located on chromosome 18 (18D). ''CSF1R'' is 60.002 kilobases (kbs) in length.Hematopoietic stem cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within ...
express ''CSF1R'' at low levels, but ''CSF1R'' is highly expressed in more differentiated myeloid cell types such as monocytes, macrophages
Macrophages (abbreviated as M φ, MΦ or MP) ( el, large eaters, from Greek ''μακρός'' (') = large, ''φαγεῖν'' (') = to eat) are a type of white blood cell of the immune system that engulfs and digests pathogens, such as cancer ce ...
, osteoclasts
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated prote ...
, myeloid dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
, microglia, and Paneth cells. ''CSF1R'' expression is controlled by two alternative promoters that are active in specific tissue types. Exon 1 of ''CSF1R'' is specifically transcribed in trophoblastic cells whereas exon 2 is specifically transcribed in macrophages. Activation of ''CSF1R'' transcription is regulated by several transcription factors including Ets
ETS or ets may refer to:
Climate change, environment and economy
* Emissions trading scheme
** European Union Emission Trading Scheme
Organisations
* European Thermoelectric Society
* Evangelical Theological Society
Education
* École de techno ...
and PU.1
Transcription factor PU.1 is a protein that in humans is encoded by the ''SPI1'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes an ETS-domain transcription factor that activates gene expression during myeloid and B-lymphoid cell development. The nuclear pro ...
. Macrophage expression of the ''CSF1R'' gene is regulated by the promoter upstream
Upstream may refer to:
* Upstream (bioprocess)
* ''Upstream'' (film), a 1927 film by John Ford
* Upstream (networking)
* ''Upstream'' (newspaper), a newspaper covering the oil and gas industry
* Upstream (petroleum industry)
* Upstream (software ...
of exon 2 and another highly conserved region termed the fms intronic regulatory element (FIRE). The FIRE is a 250-bp region in intron 2 that regulates transcript elongation during transcription of ''CSF1R'' in macrophages. Specific deletion of FIRE prevents differentiation of only specific macrophage types such as brain microglia and macrophages in the skin, kidney, heart, and peritoneum whereas deletion of the entire mouse ''Csf1r'' gene widely prevents macrophage differentiation, causing profound developmental defects. Additionally, the first intron of the ''CSF1R'' gene contains a transcriptionally inactive ribosomal protein L7 processed pseudogene, oriented in the opposite direction to the ''CSF1R'' gene.
Protein
 CSF1R, the protein encoded by the ''CSF1R'' gene is a
CSF1R, the protein encoded by the ''CSF1R'' gene is a tyrosine kinase
A tyrosine kinase is an enzyme that can transfer a phosphate group from ATP to the tyrosine residues of specific proteins inside a cell. It functions as an "on" or "off" switch in many cellular functions.
Tyrosine kinases belong to a larger cla ...
transmembrane receptor
Cell surface receptors (membrane receptors, transmembrane receptors) are receptors that are embedded in the plasma membrane of cells. They act in cell signaling by receiving (binding to) extracellular molecules. They are specialized integral me ...
and member of the CSF1/ PDGF receptor family of tyrosine-protein kinases. CSF1R has 972 amino acids, is predicted to have a molecular weight
A molecule is a group of two or more atoms held together by attractive forces known as chemical bonds; depending on context, the term may or may not include ions which satisfy this criterion. In quantum physics, organic chemistry, and bioch ...
of 107.984 kilo Daltons, and is composed of an extracellular and an cytoplasmic domain. The extracellular domain has 3 N-terminal immunoglobulin (Ig) domains (D1-D3) which bind ligand, 2 Ig domains (D4-D5) which stabilize the ligand, a linker region, and a single-pass transmembrane helix. The cytoplasmic domain has a juxtamembrane domain and tyrosine kinase domain that is interrupted by a kinase insert domain. At rest, the juxtamembrane domain of CSF1R enters an autoinhibitory position to prevent signaling of the CSF1R cytosolic domain. Upon binding of ligand to extracellular Ig domains, CSF1R dimerizes noncovalently and autophosphorylates several tyrosine residues. This first wave of CSF1R tyrosine phosphorylation creates phosphotyrosine-binding domains to which effector proteins can bind and initiate various cellular responses. Many proteins become tyrosine phosphorylated in response to CSF1R signaling (Table 1) including p85, Cbl, and Gab3 which are important for survival, differentiation, chemotaxis, and actin cytoskeleton
Microfilaments, also called actin filaments, are protein filaments in the cytoplasm of eukaryotic cells that form part of the cytoskeleton. They are primarily composed of polymers of actin, but are modified by and interact with numerous other ...
of myeloid cells. The first wave of tyrosine phosphorylation also leads to the covalent dimerization of CSF1R via disulfide bonds
In biochemistry, a disulfide (or disulphide in British English) refers to a functional group with the structure . The linkage is also called an SS-bond or sometimes a disulfide bridge and is usually derived by the coupling of two thiol groups. In ...
. Covalent CSF1R dimerization is important for a series of modifications to CSF1R itself including a second wave of tyrosine phosphorylation, serine phosphorylation, ubiquitination
Ubiquitin is a small (8.6 kDa) regulatory protein found in most tissues of eukaryotic organisms, i.e., it is found ''ubiquitously''. It was discovered in 1975 by Gideon Goldstein and further characterized throughout the late 1970s and 1980s. Fo ...
, and eventually endocytosis which terminates signaling by trafficking the ligand-CSF1R complex to the lysosome
A lysosome () is a membrane-bound organelle found in many animal cells. They are spherical vesicles that contain hydrolytic enzymes that can break down many kinds of biomolecules. A lysosome has a specific composition, of both its membrane pr ...
for degradation. Colony stimulating factor 1
The colony stimulating factor 1 (CSF1), also known as macrophage colony-stimulating factor (M-CSF), is a secreted cytokine which causes hematopoietic stem cells to differentiate into macrophages or other related cell types. Eukaryotic cells also ...
(CSF-1) and interleukin-34 (IL-34) are both CSF1R ligands. Both ligands regulate myeloid cell survival, proliferation, and differentiation, but CSF-1 and IL-34 differ in their structure, distribution in the body, and the specific cellular signaling cascades triggered upon binding to CSF1R.
Function
Osteoclasts
Osteoclast
An osteoclast () is a type of bone cell that breaks down bone tissue. This function is critical in the maintenance, repair, and remodeling of bones of the vertebral skeleton. The osteoclast disassembles and digests the composite of hydrated pro ...
are multi-nucleated cells that that absorb and remove bone which is critical for growth of new bones and maintenance of bone strength. Osteoclasts are critical for the bone remodeling cycle which is achieved by the building of bone by osteoblasts
Osteoblasts (from the Greek combining forms for "bone", ὀστέο-, ''osteo-'' and βλαστάνω, ''blastanō'' "germinate") are cells with a single nucleus that synthesize bone. However, in the process of bone formation, osteoblasts function ...
, reabsorption by osteoclasts, and remodeling by osteoblasts. Osteoclasts precursor cells and mature osteoclast require stimulation of CSF1R for survival. Blockage of CSF1R signaling prevents osteoclast precursor cells from proliferating, maturing, and fusing into multi-nucleated cells. Stimulation of CSF1R promotes osteoclastogenesis (differentiation of monocytes into osteoclasts). CSF1R signaling in osteoclasts precursors promotes survival by upregulation of the Bcl-X(L) protein, an inhibitor of pro-apototic caspase-9
Caspase-9 is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the CASP9 gene. It is an initiator caspase, critical to the apoptotic pathway found in many tissues. Caspase-9 homologs have been identified in all mammals for which they are known to exist, such ...
. CSF1R signaling in mature osteoclasts promotes survival by stimulating mTOR/S6 kinase and the Na/HCO3 co-transporter, NBCn1. CSF1R signaling also directly regulates osteoclast function. Osteoclasts migrate along the bone surface, then adhere to the bone to degrade and reabsorb the bone matrix. CSF1R signaling positively regulates this behavior, increasing osteoclast chemotaxis and bone reabsorption.
Monocytes and macrophages
 Monocytes and macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Monocytes circulate in the blood and are capable of differentiating into macrophages or
Monocytes and macrophages are mononuclear phagocytes. Monocytes circulate in the blood and are capable of differentiating into macrophages or dendritic cells
Dendritic cells (DCs) are antigen-presenting cells (also known as ''accessory cells'') of the mammalian immune system. Their main function is to process antigen material and present it on the cell surface to the T cells of the immune system. The ...
, and macrophages are terminally differentiated tissue-resident cells. CSF1R signaling is necessary for differentiation of microglia and Langerhans cells
A Langerhans cell (LC) is a tissue-resident macrophage of the skin. These cells contain organelles called Birbeck granules. They are present in all layers of the epidermis and are most prominent in the stratum spinosum. They also occur in t ...
which are derived from yolk sac progenitor cells with high expression of CSF1R. CSF1R signaling is only partially required for other tissue macrophages, and it is not necessary for monocytopoiesis (production of monocytes and macrophages) from hematopoietic stem cells
Hematopoietic stem cells (HSCs) are the stem cells that give rise to other blood cells. This process is called haematopoiesis. In vertebrates, the very first definitive HSCs arise from the ventral endothelial wall of the embryonic aorta within ...
. Macrophages of thymus
The thymus is a specialized primary lymphoid organ of the immune system. Within the thymus, thymus cell lymphocytes or ''T cells'' mature. T cells are critical to the adaptive immune system, where the body adapts to specific foreign invaders. ...
and lymph nodes
A lymph node, or lymph gland, is a kidney-shaped organ of the lymphatic system and the adaptive immune system. A large number of lymph nodes are linked throughout the body by the lymphatic vessels. They are major sites of lymphocytes that inclu ...
are almost completely independent of CSF1R signaling. In macrophages whose survival is fully or partially dependent on CSF1R signaling, CSF1R promotes survival by activating PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which i ...
. CSF1R signaling also regulates macrophage function. One function of CSF1R signaling is to promote tissue protection and healing following damage. Damage to the kidney causes upregulation of CSF-1 and CSF1R in tubular epithelial cells. This promotes proliferation and survival of injured tubular epithelial cells and promotes anti-inflammatory phenotypes in resident macrophage to promote kidney healing. Lastly, activation of CSF1R is a strong chemokinetic Chemokinesis is chemically prompted kinesis, a motile response of unicellular prokaryotic or eukaryotic organisms to chemicals that cause the cell to make some kind of change in their migratory/swimming behaviour. Changes involve an increase or de ...
signal, inducing macrophage polarization Macrophage polarization is a process by which macrophages adopt different functional programs in response to the signals from their microenvironment. This ability is connected to their multiple roles in the organism: they are powerful effector cells ...
and chemotaxis towards the source of CSF1R ligand. This macrophage response requires rapid morphological changes which is achieved by remodeling of the actin cytoskeleton via the Src/Pyk2
Protein tyrosine kinase 2 beta is an enzyme that in humans is encoded by the ''PTK2B'' gene.
Function
This gene encodes a cytoplasmic protein tyrosine kinase that is involved in calcium-induced regulation of ion channels and activation of the ...
and PI3K
Phosphoinositide 3-kinases (PI3Ks), also called phosphatidylinositol 3-kinases, are a family of enzymes involved in cellular functions such as cell growth, proliferation, differentiation, motility, survival and intracellular trafficking, which i ...
signaling pathways.
Microglia
 Microglia are the tissue-resident
Microglia are the tissue-resident phagocytes
Phagocytes are cells that protect the body by ingesting harmful foreign particles, bacteria, and dead or dying cells. Their name comes from the Greek ', "to eat" or "devour", and "-cyte", the suffix in biology denoting "cell", from the Greek '' ...
of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
. CSF1R signaling promotes migration of primitive microglia precursor cells from the embryonic yolk sac
The yolk sac is a membranous sac attached to an embryo, formed by cells of the hypoblast layer of the bilaminar embryonic disc. This is alternatively called the umbilical vesicle by the Terminologia Embryologica (TE), though ''yolk sac'' is ...
to the developing brain prior to formation of the blood-brain-barrier. In perinatal development, microglia are instrumental in synaptic pruning
Synaptic pruning, a phase in the development of the nervous system, is the process of synapse elimination that occurs between early childhood and the onset of puberty in many mammals, including humans. Pruning starts near the time of birth and con ...
, a process in which microglia phagocytose
Phagocytosis () is the process by which a cell uses its plasma membrane to engulf a large particle (≥ 0.5 μm), giving rise to an internal compartment called the phagosome. It is one type of endocytosis. A cell that performs phagocytosis is ...
weak and inactive synapses via binding of microglial complement receptor 3 (CR3) (complex of CD11b
Integrin alpha M (ITGAM) is one protein subunit that forms heterodimeric integrin alpha-M beta-2 (αMβ2) molecule, also known as ''macrophage-1 antigen'' (Mac-1) or '' complement receptor 3'' (CR3). ITGAM is also known as CR3A, and cluster of dif ...
and CD18) to synapse-bound iC3b. ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function inhibits synaptic pruning and leads to excessive non-functional synapses in the brain. In adulthood, CSF1R is required for the proliferation and survival of microglia. Inhibition of CSF1R signaling in adulthood causes near-complete (>99%) depletion (death) of brain microglia, however reversal of CSF1R inhibition stimulates remaining microglia to proliferate and repopulate microglia-free niches in the brain. Production of CSF1R ligands CSF-1 and IL-34 is increased in the brain following injury or viral infection, which directs microglia to proliferate and execute immune responses.
Neural progenitor cells
CSF1R signaling has been found to play important roles in non-myeloid cells such as neural progenitor cells,multipotent Pluripotency: These are the cells that can generate into any of the three Germ layers which imply Endodermal, Mesodermal, and Ectodermal cells except tissues like the placenta.
According to Latin terms, Pluripotentia means the ability for many thin ...
cells that are able to self-renew or terminally differentiate into neurons, astrocytes
Astrocytes (from Ancient Greek , , "star" + , , "cavity", "cell"), also known collectively as astroglia, are characteristic star-shaped glial cells in the brain and spinal cord. They perform many functions, including biochemical control of endo ...
and oligodendrocytes
Oligodendrocytes (), or oligodendroglia, are a type of neuroglia whose main functions are to provide support and insulation to axons in the central nervous system of jawed vertebrates, equivalent to the function performed by Schwann cells in the ...
. Mice with ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function have a significantly more neural progenitor cells in generative zones and fewer matured neurons in forebrain laminae due to failure of progenitor cell maturation and radial migration. These phenotypes were also seen in animals with ''Csf1r'' conditional knock-out specifically in neural progenitor cells, suggesting that CSF1R signaling by neural progenitor cells is important for maturation of certain neurons. Studies using cultured neural progenitor cells also show that CSF1R signaling stimulates neural progenitor cells maturation.
Germline cells
CSF1R is expressed inoocytes
An oocyte (, ), oöcyte, or ovocyte is a female gametocyte or germ cell involved in reproduction. In other words, it is an immature ovum, or egg cell. An oocyte is produced in a female fetus in the ovary during female gametogenesis. The female g ...
, the trophoblast
The trophoblast (from Greek : to feed; and : germinator) is the outer layer of cells of the blastocyst. Trophoblasts are present four days after fertilization in humans. They provide nutrients to the embryo and develop into a large part of the p ...
, and fertilized embryos prior to implantation in the uterus
The uterus (from Latin ''uterus'', plural ''uteri'') or womb () is the organ in the reproductive system of most female mammals, including humans that accommodates the embryonic and fetal development of one or more embryos until birth. The ...
. Studies using early mouse embryos ''in vitro
''In vitro'' (meaning in glass, or ''in the glass'') studies are performed with microorganisms, cells, or biological molecules outside their normal biological context. Colloquially called " test-tube experiments", these studies in biology ...
'' have shown that activation of CSF1R stimulates formation of the blastocyst cavity and enhances the number of trophoblast cells. ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function mice exhibit several reproductive system abnormalities in the estrous cycle
The estrous cycle (, originally ) is the set of recurring physiological changes that are induced by reproductive hormones in most mammalian therian females. Estrous cycles start after sexual maturity in females and are interrupted by anestro ...
and ovulation
Ovulation is the release of eggs from the ovaries. In women, this event occurs when the ovarian follicles rupture and release the secondary oocyte ovarian cells. After ovulation, during the luteal phase, the egg will be available to be fertilize ...
rates as well as reduced antral follicles
An antral follicle, also known as Graafian follicle and tertiary follicle, is an ovarian follicle during a certain latter stage of folliculogenesis.
Definitions differ in where the shift into an antral follicle occurs in the staging of follicul ...
and ovarian macrophages. It is not clear whether ovulation dysfunction in ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function mice is due to loss of the protective effects of ovarian macrophages or loss of CSF1R signaling in oocytes themselves.
Clinical significance
Bone disease

Bone remodeling
Bone remodeling (or bone metabolism) is a lifelong process where mature bone tissue is removed from the skeleton (a process called ''bone resorption'') and new bone tissue is formed (a process called ''ossification'' or ''new bone formation''). ...
is regulated by mutual cross-regulation between osteoclasts and osteoblasts. As a result, the dysfunction of CSF1R signaling directly affects the reabsorption (osteoclasts) and indirectly affects bone deposition (osteoblasts). In inflammatory arthritis conditions such as rheumatoid arthritis
Rheumatoid arthritis (RA) is a long-term autoimmune disorder that primarily affects joints. It typically results in warm, swollen, and painful joints. Pain and stiffness often worsen following rest. Most commonly, the wrist and hands are invol ...
, psoriatic arthritis
Psoriatic arthritis is a long-term inflammatory arthritis that occurs in people affected by the autoimmune disease psoriasis. The classic feature of psoriatic arthritis is swelling of entire fingers and toes with a sausage-like appearance. Th ...
, and Crohn's disease, proinflammatory cytokine An inflammatory cytokine or proinflammatory cytokine is a type of signaling molecule (a cytokine) that is secreted from immune cells like helper T cells (Th) and macrophages, and certain other cell types that promote inflammation. They include inte ...
TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
is secreted by synovial macrophages which stimulates Stromal cell, stromal cells and osteoblasts to produce CSF-1. Increased CSF-1 promotes proliferation of osteoclasts and osteoclast precursors and increases osteoclast bone reabsorption. This pathogenic increase in osteoclast activity causes abnormal bone loss or osteolysis. In animal models of rheumatoid arthritis, administration of CSF-1 increases the severity of disease whereas ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function reduces inflammation and joint erosion. In a rare bone disease called Gorham's disease, Gorham‐Stout disease, elevated production of CSF-1 by lymphatic endothelial cells similarly produces excessive osteoclastogenesis and osteolysis. Additionally, Menopause, postmenopausal loss of estrogen has also been found to impact CSF1R signaling and cause osteoporosis. Estrogen deficiency causes osteoporosis by upregulating production of TNF-α
Tumor necrosis factor (TNF, cachexin, or cachectin; formerly known as tumor necrosis factor alpha or TNF-α) is an adipokine and a cytokine. TNF is a member of the TNF superfamily, which consists of various transmembrane proteins with a homolog ...
by activated T cell, T cells. As in inflammatory arthritis, TNF-α stimulates stromal cells to produce CSF-1 which increases CSF1R signaling in osteoclasts.
Cancer
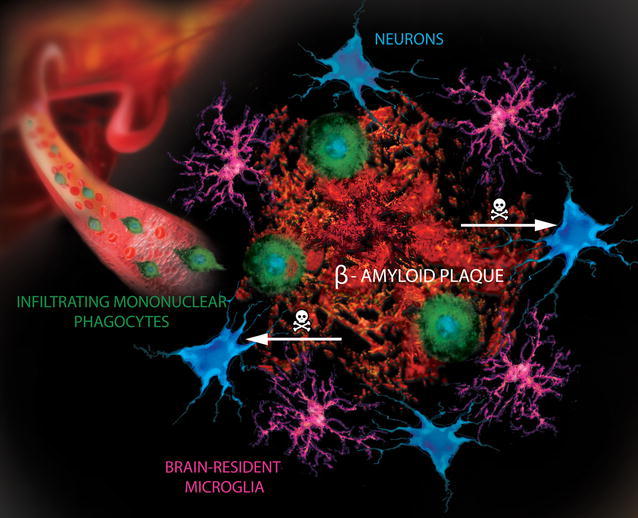
Tumor-associated macrophage, Tumor-associated macrophages (TAMs) react to early stage cancers with anti-inflammatory immune responses that support tumor survival at the expense of healthy tissue. Tumor-infiltrating lymphocytes, Tumor infiltration by CSF1R-expressing TAMs yields a negative prognosis and is correlated with poor survival rates for individuals with lymphoma and solid tumors. The tumor microenvironment often produces high levels of CSF-1, creating a Positive feedback, positive feedback loop in which the tumor stimulates survival of TAMs and TAMs promote tumor survival and growth. Thus, CSF1R signaling in TAMs is associated tumor survival, angiogenesis, Resistant cancer, therapy resistance, and metastasis. Production of CSF-1 by brain tumors called Glioblastoma, glioblastomas causes microglia (brain-resident macrophages) to exhibit immunosuppressive, tumor-permissive phenotypes. CSF1R inhibition in mouse glioblastoma models is beneficial and improves survival by inhibiting tumor-promoting functions of microglia. MMTV-PyMT, Mouse models of breast cancer also show that ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function delays TAM infiltration and metastasis. Because Tumoricidal, anti-cancer macrophages and microglia rely on GM-CSF and IFN-γ signaling instead CSF-1, inhibition of CSF1R signaling has been posited as a therapeutic target in cancer to preferentially deplete tumor-permissive TAMs. Additionally, mutations in ''CSF1R'' gene itself are associated with certain cancers such as chronic myelomonocytic leukemia and type M4 acute myeloblastic leukemia.Neurological disorders
Adult-onset leukoencephalopathy
Because of the importance of the ''CSF1R'' gene in myeloid cell survival, maturation, and function, loss-of-function in both inherited copies of the ''CSF1R'' gene causes postnatal mortality. Heterozygous mutations in the ''CSF1R'' gene prevent downstream CSF1R signaling and cause an autosomal dominant neurodegenerative disease called Leukoencephalopathy with neuroaxonal spheroids, adult-onset leukoencephalopathy, which is characterized by dementia, executive dysfunction, and Seizure, seizures. Partial loss of ''CSF1R'' in adult-onset leukoencephalopathy causes microglia to exhibit morphological and functional deficits (impaired cytokine production and phagocytosis) which is associated with Axon, axonal damage, Demyelinating disease, demyelination, and neuronal loss. Signaling by a DAP12-TREM2 complex in microglia is downstream of CSF1R signaling and is needed for microglia phagocytosis of cellular debris and maintenance of brain homeostasis. ''TREM2'' deficiency in cultured myeloid cells prevents stimulation of proliferation by treatment with CSF-1. Similarities between Nasu-Hakola disease (caused by mutations in either ''DAP12'' or ''TREM2'') and adult-onset leukoencephalopathy suggest partial loss of microglia CSF1R signaling promotes neurodegeneration. Defects in neurogenesis and neuronal survival are also seen in adult-onset leukoencephalopathy due to impaired CSF1R signaling in neural progenitor cells.Other brain diseases and disorders
 CSF1R signaling is involved in several diseases and disorders of the
CSF1R signaling is involved in several diseases and disorders of the central nervous system
The central nervous system (CNS) is the part of the nervous system consisting primarily of the brain and spinal cord. The CNS is so named because the brain integrates the received information and coordinates and influences the activity of all p ...
. Research using animal models of epilepsy (kainic acid-induced seizures) suggests that CSF1 signaling during Seizure, seizures protects neurons by activating neuronal CREB signaling. CSF1R Agonist, agonism during seizures increases neuronal survival whereas neuron-specific ''Csf1r'' loss-of-function worsens kainic acid excitotoxicity, suggesting CSF1R signaling in neurons directly protects against seizure-related neuronal damage. Although CSF1R signaling is beneficial in certain contexts, it is detrimental in diseases where microglia drive tissue damage. In Charcot-Marie-Tooth disease type 1, CSF-1 secretion from Endoneurium, endoneurial cells stimulates proliferation and activation of macrophages and microglia that cause demyelination. Likewise in multiple sclerosis, CSF1R signaling supports the survival of inflammatory microglia which promote demyelination. CSF1R inhibition Preventive healthcare, prophylactically reduces demyelination in the experimental autoimmune encephalomyelitis animal model. The role of CSF1R signaling in Alzheimer's disease is more complicated because microglia both protect and damage the brain in response to Alzheimer's disease pathology. CSF-1 stimulates Primary cell culture, primary cultured human microglia to phagocytose toxic Amyloid beta, Aβ1–42 peptides. Microglia also initiate TREM2-dependent immune responses to amyloid plaques which protects neurons. However, Alzheimer's disease microglia also excessively secrete inflammatory cytokines and prune synapses promoting synapse loss, neuronal death, and Mild cognitive impairment, cognitive impairment. Both CSF1R stimulation and inhibition improves cognitive function in Alzheimer's disease models. Thus, microglia seem to have both protective and neurotoxic functions during Alzheimer's disease neurodegeneration. Similar findings have been reported in lesion studies of the mouse brain, which showed that inhibition of CSF1R after lesioning improves recovery but inhibition during lesioning worsens recovery. CSF1R-targeting therapies for neurological disorders may impact both detrimental and beneficial microglia functions.
Therapeutics
 Because Tumor-associated macrophage, TAM CSF1R signaling is tumor-permissive and can tumor treatment-resistance, CSF1R signaling is a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Several studies have investigated the efficacy of CSF1R inhibitor as a monotherapy and as a combination therapy in Refractory cancer, refractory and metastatic cancers. Several small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting CSF1R are in clinical development for cancer therapy (Table 2). Pexidartinib, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) is a small molecule inhibitor tyrosine of CSFR (as well as cKIT, FLT3, and VEGF receptor, VEGFR) with the most clinical development so far. Several completed and concurrent clinical trials have tested the efficacy and safety of Pexidartinib as a monotherapy for c-kit-mutated melanoma, prostate cancer, glioblastoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, neurofibroma, sarcoma, and Leukemia, leukemias. In 2019, Pexidartinib was FDA approval, FDA-approved for treatment of Tenosynovial giant cell tumor, diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumors, a non-malignant tumor that develops from Synovial membrane, synovial tissue lining the joints.
Because Tumor-associated macrophage, TAM CSF1R signaling is tumor-permissive and can tumor treatment-resistance, CSF1R signaling is a promising therapeutic target in the treatment of cancer. Several studies have investigated the efficacy of CSF1R inhibitor as a monotherapy and as a combination therapy in Refractory cancer, refractory and metastatic cancers. Several small molecule inhibitors and monoclonal antibodies targeting CSF1R are in clinical development for cancer therapy (Table 2). Pexidartinib, Pexidartinib (PLX3397) is a small molecule inhibitor tyrosine of CSFR (as well as cKIT, FLT3, and VEGF receptor, VEGFR) with the most clinical development so far. Several completed and concurrent clinical trials have tested the efficacy and safety of Pexidartinib as a monotherapy for c-kit-mutated melanoma, prostate cancer, glioblastoma, Hodgkin lymphoma, classical Hodgkin lymphoma, neurofibroma, sarcoma, and Leukemia, leukemias. In 2019, Pexidartinib was FDA approval, FDA-approved for treatment of Tenosynovial giant cell tumor, diffuse-type tenosynovial giant cell tumors, a non-malignant tumor that develops from Synovial membrane, synovial tissue lining the joints.
Safety of CSF1R inhibition
The safety of CSF1R inhibitors has been extensively characterized in Clinical trial, clinical trials for the different small molecules and monoclonal antibodies in Table 2. In some studies, CSF1R inhibitors were not found to have Dose–response relationship, dose-limiting toxicity while other studies did observe toxicity at high doses and have defined a maximum tolerated dose. Across multiple studies, the most frequent Adverse effect, adverse effects included fatigue, elevated Liver function tests, liver enzymes (creatine kinase, lactate dehydrogenase, Aspartate transaminase, aspartate aminotransferase, Elevated transaminases, alanine transaminase), edema, nausea, lacrimation, and reduced appetite, but no signs of Hepatotoxicity, liver toxicity were found. There are some differences in the side effects of monoclonal antibody compared to small molecule CSF1R inhibitors. Edema was more common with monoclonal antibody treatment compared to small molecules, suggesting that Monoclonal antibody therapy, immune response to monoclonal antibodies may drive some side effects. Additionally, some small molecule inhibitors are not specific for CSF1R, and off-target effects could explain observed side effects. For example, Pexidartinib treatment was found to change hair color, presumably by its impact on KIT (gene), KIT kinase. Overall, CSF1R inhibitors have favorable safety profiles with limited toxicity.Controversy
CSF1R inhibitors such as PLX5622 are widely used to study the role of microglia in mouse Animal models, preclinical models of Alzheimer's disease, stroke, traumatic brain injury, and Aging brain, aging. PLX5622 is typically used for microglia research because PLX5622 has higher brain bioavailability and CSF1R-specificity compared to other CSF1R inhibitors such as Pexidartinib, PLX3397. In 2020, researchers David Hume (University of Queensland) and Kim Green (University of California, Irvine, UCI) published a letter in the academic journal Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America, PNAS defending the use small molecule CSF1R inhibitors to study microglia in brain disease. This letter was in response to a Research, primary research paper published in PNAS by lead correspondent Eleftherios Paschalis (Harvard Medical School, HMS) and others which provided evidence that microglia research using PLX5622 is Confounding, confounded by CSF1R inhibition in peripheral macrophages. Paschalis and collegues published a subsequent letter in PNAS defending the findings of their published research.Interactions
Colony stimulating factor 1 receptor has been shown to Protein-protein interaction, interact with: * Cbl gene, * FYN, * Grb2, * Suppressor of cytokine signaling 1, This receptor is also linked with the cells of MPS.See also
* Cluster of differentiation * Mouse models of breast cancer metastasisReferences
Further reading
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * *External links
* {{Portal bar, Biology, border=no Clusters of differentiation Immunoglobulin superfamily cytokine receptors Tyrosine kinase receptors