Lysocline on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
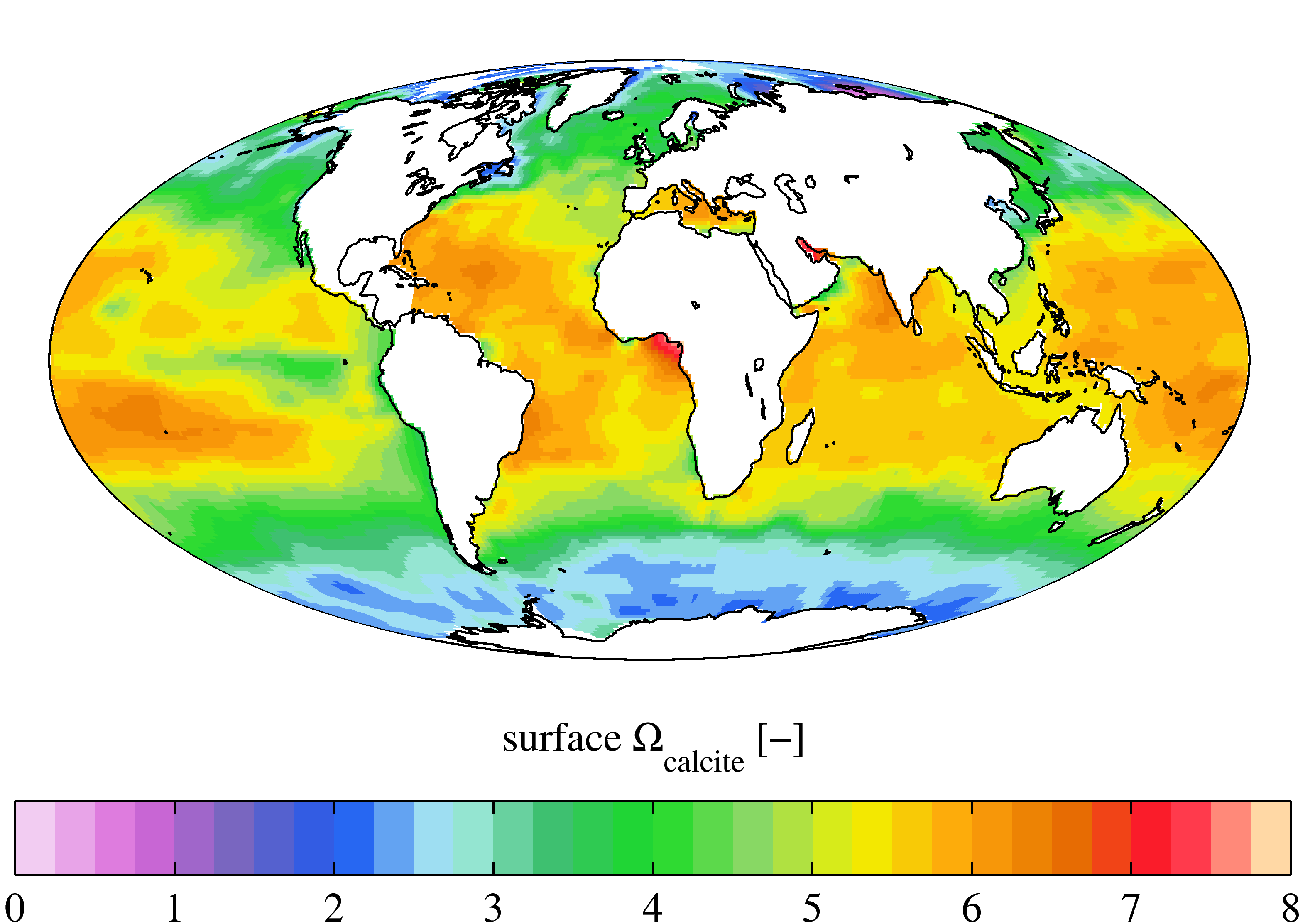 The lysocline is the depth in the
The lysocline is the depth in the
 The lysocline is the depth in the
The lysocline is the depth in the ocean
The ocean (also the sea or the world ocean) is the body of salt water that covers approximately 70.8% of the surface of Earth and contains 97% of Earth's water. An ocean can also refer to any of the large bodies of water into which the wor ...
dependent upon the carbonate compensation depth
Carbonate compensation depth (CCD) is the depth in the oceans below which the rate of supply of calcite ( calcium carbonate) lags behind the rate of solvation, such that no calcite is preserved. Shells of animals therefore dissolve and carbonate ...
(CCD), usually around 3.5 km, below which the rate of dissolution of calcite
Calcite is a carbonate mineral and the most stable polymorph of calcium carbonate (CaCO3). It is a very common mineral, particularly as a component of limestone. Calcite defines hardness 3 on the Mohs scale of mineral hardness, based on scratc ...
increases dramatically because of a pressure effect. While the lysocline is the upper bound of this transition zone of calcite saturation, the CCD is the lower bound of this zone.
CaCO3 content in sediment varies with different depths of the ocean, spanned by levels of separation known as the transition zone. In the mid-depth area of the ocean, sediments are rich in CaCO3, content values reaching 85-95%. This area is then spanned hundred meters by the transition zone, ending in the abyssal depths with 0% concentration. The lysocline is the upper bound of the transition zone, where amounts of CaCO3 content begins to noticeably drop from the mid-depth 85-95% sediment. The CaCO3 content drops to 10% concentration
In chemistry, concentration is the abundance of a constituent divided by the total volume of a mixture. Several types of mathematical description can be distinguished: '' mass concentration'', '' molar concentration'', ''number concentration'', ...
at the lower bound, known as the calcite compensation depth.
Shallow marine waters are generally supersaturated
In physical chemistry, supersaturation occurs with a solution when the concentration of a solute exceeds the concentration specified by the value of solubility at equilibrium. Most commonly the term is applied to a solution of a solid in a li ...
in calcite, CaCO3, because as marine organisms
Marine life, sea life, or ocean life is the plants, animals and other organisms that live in the salt water of seas or oceans, or the brackish water of coastal estuaries. At a fundamental level, marine life affects the nature of the planet. ...
(which often have shells made of calcite or its polymorph, aragonite
Aragonite is a carbonate mineral, one of the three most common naturally occurring crystal forms of calcium carbonate, (the other forms being the minerals calcite and vaterite). It is formed by biological and physical processes, including pre ...
) die, they tend to fall downwards without dissolving. As depth and pressure increases within the water column
A water column is a conceptual column of water from the surface of a sea, river or lake to the bottom sediment.Munson, B.H., Axler, R., Hagley C., Host G., Merrick G., Richards C. (2004).Glossary. ''Water on the Web''. University of Minnesota-D ...
, calcite solubility increases, causing supersaturated water above the saturation depth, allowing for preservation and burial of CaCO3 on the seafloor. However, this created undersaturated seawater below the saturation depth, preventing CaCO3 burial on the sea floor
The seabed (also known as the seafloor, sea floor, ocean floor, and ocean bottom) is the bottom of the ocean. All floors of the ocean are known as 'seabeds'.
The structure of the seabed of the global ocean is governed by plate tectonics. Most of ...
as the shells start to dissolve.
The equation Ω = a2+X O32-K'sp expresses the CaCO3 saturation state of seawater. The calcite saturation horizon is where Ω =1; dissolution proceeds slowly below this depth. The lysocline is the depth that this dissolution impacts is again notable, also known as the inflection point with sedimentary CaCO3 versus various water depths.
Calcite compensation depth
The calcite compensation depth (CCD) occurs at the depth that the rate of calcite to the sediments is balanced with the dissolution flux, the depth at which the CaCO3 content are values 2-10%. Hence, the lysocline and CCD are not equivalent. The lysocline and compensation depth occur at greater depths in theAtlantic
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
(5000–6000 m) than in the Pacific
The Pacific Ocean is the largest and deepest of Earth's five oceanic divisions. It extends from the Arctic Ocean in the north to the Southern Ocean (or, depending on definition, to Antarctica) in the south, and is bounded by the contine ...
(4000-5000 m), and at greater depths in equatorial regions than in polar regions
The polar regions, also called the frigid zones or polar zones, of Earth are the regions of the planet that surround its geographical poles (the North and South Poles), lying within the polar circles. These high latitudes are dominated by floa ...
.
The depth of the CCD varies as a function of the chemical composition of the seawater and its temperature. Specifically, it is the deep waters that are undersaturated with calcium carbonate primarily because its solubility increases strongly with increasing pressure and salinity
Salinity () is the saltiness or amount of salt (chemistry), salt dissolved in a body of water, called saline water (see also soil salinity). It is usually measured in g/L or g/kg (grams of salt per liter/kilogram of water; the latter is dimensio ...
and decreasing temperature. As the atmospheric concentration of carbon dioxide
Carbon dioxide ( chemical formula ) is a chemical compound made up of molecules that each have one carbon atom covalently double bonded to two oxygen atoms. It is found in the gas state at room temperature. In the air, carbon dioxide is t ...
continues to increase, the CCD can be expected to decrease in depth, as the ocean's acidity rises.
See also
*Biological pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH ...
* Ocean acidification
Ocean acidification is the reduction in the pH value of the Earth’s ocean. Between 1751 and 2021, the average pH value of the ocean surface has decreased from approximately 8.25 to 8.14. The root cause of ocean acidification is carbon dioxid ...
* Carbonate compensation depth
Carbonate compensation depth (CCD) is the depth in the oceans below which the rate of supply of calcite ( calcium carbonate) lags behind the rate of solvation, such that no calcite is preserved. Shells of animals therefore dissolve and carbonate ...
* Carbonate pump
The biological pump (or ocean carbon biological pump or marine biological carbon pump) is the ocean's biologically driven sequestration of carbon from the atmosphere and land runoff to the ocean interior and seafloor sediments.Sigman DM & GH ...
References
{{Reflist Geochemistry Oceanography