Lunokhod 3 on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Lunokhod ( rus, Луноход, p=lʊnɐˈxot, "Moonwalker") was a series of
Lunokhod ( rus, Луноход, p=lʊnɐˈxot, "Moonwalker") was a series of

 ''Lunokhod 3'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№205) was built for a
''Lunokhod 3'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№205) was built for a
 Until 2010, the final location of ''Lunokhod 1'' was uncertain by a few kilometers. Lunar laser ranging experiments had failed to detect a return signal from its retroreflector since the 1970s. On March 17, 2010, Albert Abdrakhimov found both the lander and the rover in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter image M114185541RC. On April 22, Tom Murphy (
Until 2010, the final location of ''Lunokhod 1'' was uncertain by a few kilometers. Lunar laser ranging experiments had failed to detect a return signal from its retroreflector since the 1970s. On March 17, 2010, Albert Abdrakhimov found both the lander and the rover in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter image M114185541RC. On April 22, Tom Murphy (
Lunar and Planetary Department Moscow UniversityExploring the Moon (1969-1976)
- a diary of significant events in Soviet lunar exploration, including those associated with the Lunokhod programme
including many from the Lunokhod programme
(about half way down the page, or search the page for "Lunokhod") {{DEFAULTSORT:Lunokhod Programme Missions to the Moon Lunar rovers Soviet lunar program
Soviet
The Soviet Union,. officially the Union of Soviet Socialist Republics. (USSR),. was a transcontinental country that spanned much of Eurasia from 1922 to 1991. A flagship communist state, it was nominally a federal union of fifteen nation ...
robotic
Robotics is an interdisciplinary branch of computer science and engineering. Robotics involves design, construction, operation, and use of robots. The goal of robotics is to design machines that can help and assist humans. Robotics integrate ...
lunar rover
A lunar rover or Moon rover is a space exploration vehicle designed to move across the surface of the Moon. The Apollo Program's Lunar Roving Vehicle was driven on the Moon by members of three American crews, Apollo 15, 16, and 17. Other rov ...
s designed to land on the Moon between 1969 and 1977. Lunokhod 1 was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on an extraterrestrial body.
The 1969 Lunokhod 1A (Lunokhod 0, Lunokhod No. 201) was destroyed during launch, the 1970 ''Lunokhod 1
''Lunokhod 1'' ( Russian: Луноход-1 ("Moonwalker 1"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 203 ("Device 8EL No. 203")) was the first of two robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program. The ...
'' and the 1973 ''Lunokhod 2
''Lunokhod 2'' (russian: Луноход-2 ("Moonwalker 2"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 204 ("Device 8EL No. 204")) was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers that landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod pro ...
'' landed on the Moon, and ''Lunokhod 3'' (Lunokhod No. 205, planned for 1977) was never launched. The successful missions were in operation concurrently with the Zond and Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin
* Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon
Luna may also refer to:
Places Philippines
* Luna, Apayao
* Luna, Isabela
* Luna, La Union
* Luna, San Jose
Roma ...
series of Moon flyby, orbiter
A spacecraft is a vehicle or machine designed to spaceflight, fly in outer space. A type of artificial satellite, spacecraft are used for a variety of purposes, including Telecommunications, communications, Earth observation satellite, Earth ...
and landing missions.
The Lunokhods were primarily designed to support the Soviet human Moon missions during the Moon race
The Space Race was a 20th-century competition between two Cold War rivals, the United States and the Soviet Union, to achieve superior spaceflight capability. It had its origins in the ballistic missile-based nuclear arms race between the tw ...
. Instead, they were used as remote-controlled robot
A robot is a machine—especially one programmable by a computer—capable of carrying out a complex series of actions automatically. A robot can be guided by an external control device, or the control may be embedded within. Robots may ...
s for exploration of the lunar surface and return its pictures after the Apollo
Apollo, grc, Ἀπόλλωνος, Apóllōnos, label=genitive , ; , grc-dor, Ἀπέλλων, Apéllōn, ; grc, Ἀπείλων, Apeílōn, label= Arcadocypriot Greek, ; grc-aeo, Ἄπλουν, Áploun, la, Apollō, la, Apollinis, label ...
human lunar landings and cancellation of the Soviet human Moon programme.
The Lunokhods were transported to the lunar surface by Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin
* Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon
Luna may also refer to:
Places Philippines
* Luna, Apayao
* Luna, Isabela
* Luna, La Union
* Luna, San Jose
Roma ...
spacecraft, which were launched by Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, 8K82K, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 an ...
rockets.
Development
Lunokhod's original primary mission was to be the back-up for L3 crewed Moon expeditions and for the later Zvezdalunar base
A moonbase is a facility on the surface of the Moon, enabling human activity on the Moon. As such, it is different from a lunar space station in orbit around the Moon, like the planned Lunar Gateway of the Artemis program. Moonbases can be fo ...
. For mission safety, weeks before the human mission on a LK lander, an LK-R uncrewed lander from the L3 lunar expedition complex and two Lunokhod automated rovers would be sent to the Moon for a preliminary study of the surface around LK-R and LK sites, to act as radio beacons for precision landings of LK-R and LK, and for a visual evaluation of the status of the site.
In mid-1968, at the facility KIP-10 or NIP-10 (КИП-10 or НИП-10) in the closed town
A closed city or closed town is a settlement where travel or residency restrictions are applied so that specific authorization is required to visit or remain overnight. Such places may be sensitive military establishments or secret research ins ...
, near Simferopol
Simferopol () is the second-largest city in the Crimean Peninsula. The city, along with the rest of Crimea, is internationally recognised as part of Ukraine, and is considered the capital of the Autonomous Republic of Crimea. However, it is ...
, Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a pop ...
, a lunodrom (лунодром - Moondrome) was built. It covered an area of one hectare (120 meters by 70 meters) and was very similar to some parts of the lunar surface. It was constructed using more than 3,000 cubic meters of soil, and included 54 craters up to 16 m in diameter and around about 160 rocks of various sizes. The whole area was surrounded with bricks, painted in gray and black. It was used to analyze problems with the Lunokhod chassis and cosmonaut's skill to control one. Closed town Simferopol-28 contained the most significant tracking facility in the Soviet Union, having the largest number of antennas, the largest area, and the most personnel of any of the Soviet tracking facilities. The facility was one of a network of ten facilities which contain earth satellite vehicle tracking equipment and provide command/control for Soviet near-space civil and military events. Additionally, this facility supported all lunar programmes of the Soviet Union, in association with the Evpatoria Deep Space Tracking Facility.
At least four complete vehicles were constructed, with the serial numbers 201, 203, 204 and 205.
Rover design
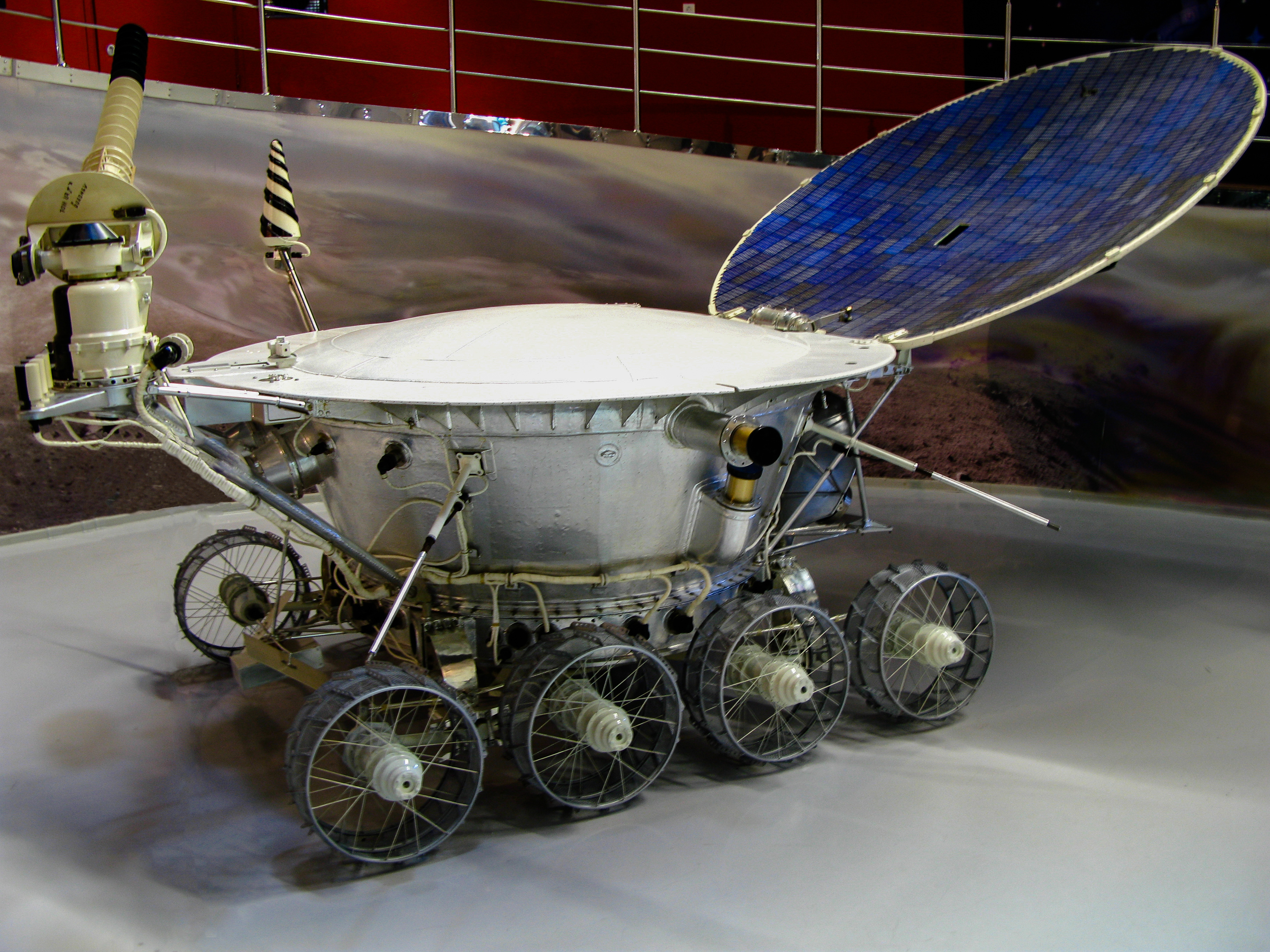
The Lunokhod rovers were lunar vehicles formed of a tub-like compartment with a large convex lid on eight independently-powered wheels. Length was 2.3 metres. They were equipped with a cone-shaped antenna, a highly directionalhelical antenna
A helical antenna is an antenna consisting of one or more conducting wires wound in the form of a helix. A helical antenna made of one helical wire, the most common type, is called ''monofilar'', while antennas with two or four wires in a ...
, television cameras, and special extendable devices to impact the lunar soil for density measurements and mechanical property tests, plus a scientific payload which varied with the mission.
The Lunokhods were designed under the leadership of Georgy Babakin
Georgy Nikolayevich Babakin (russian: Гео́ргий Никола́евич Баба́кин; 13 November 1914 – 3 August 1971) was a Soviet engineer working in the space program. He was Chief Designer at the Lavochkin Design Bureau from ...
at Lavochkin
NPO Lavochkin (russian: НПО Лавочкина, OKB-301, also called Lavochkin Research and Production Association or shortly Lavochkin Association, LA) is a Russian aerospace company. It is a major player in the Russian space program, being th ...
design bureau. The metal chassis themselves were designed by Alexander Kemurdzhian
Aleksandr Leonovich Kemurdzhian (russian: Александр Леонович Кемурджиан; 4 October 192125 February 2003) was a Soviet mechanical engineer who worked at the VNIITransmash institute for the most of the second half of th ...
.
The vehicles were powered by batteries. The rover ran during the lunar day, stopping occasionally to recharge its batteries using its solar panels. The power was supplied during the lunar day by a GaAs solar array on the inside of a round hinged lid which covered the instrument bay, which would charge the batteries when opened. During the lunar nights, the lid was closed and a polonium-210 radioisotope heater unit
Radioisotope heater units (RHU) are small devices that provide heat through radioactive decay. They are similar to tiny radioisotope thermoelectric generators (RTG) and normally provide about one watt of heat each, derived from the decay of a fe ...
kept the internal components at operating temperature.
To be able to work in a vacuum a special fluoride-based lubricant was used for the rover's mechanical parts, and the electric motors, one in each wheel hub, were enclosed in pressurised containers.
The rovers stood 135 cm (4 ft 5 in) high and had a mass of 840 kg (1,850 lb). It was about 170 cm (5 ft 7 in) long and 160 cm (4 ft 11 in) wide and had eight wheels each with an independent suspension, motor and brake. The rover had two speeds, approximately .
The Lunokhods were transported to the lunar surface by Luna
Luna commonly refers to:
* Earth's Moon, named "Luna" in Latin
* Luna (goddess), the ancient Roman personification of the Moon
Luna may also refer to:
Places Philippines
* Luna, Apayao
* Luna, Isabela
* Luna, La Union
* Luna, San Jose
Roma ...
spacecraft, which were launched by Proton-K
The Proton-K, also designated Proton 8K82K after its GRAU index or SL-12 after its model number, 8K82K, was a Russian, previously Soviet, carrier rocket derived from the earlier Proton. It was built by Khrunichev, and launched from sites 81 an ...
rockets. The Moon lander part of the Luna spacecraft for Lunokhods was similar to the one for sample-return missions.
Lunokhod Rovers
Lunokhod 201
After years of secret engineering development and training, the first Lunokhod (vehicle 8ЕЛ№201) was launched on February 19, 1969. Within a few seconds the rocket disintegrated and the first Lunokhod was lost. The rest of the world did not learn of the rocket's valuable payload until years later. The failure resulted in the radioactive heat source, polonium 210, being spread over a large region of Russia.''Lunokhod 1''
After the destruction of the original Lunokhod, Soviet engineers began work immediately on another lunar vehicle. ''Lunokhod 1
''Lunokhod 1'' ( Russian: Луноход-1 ("Moonwalker 1"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 203 ("Device 8EL No. 203")) was the first of two robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program. The ...
'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№203) was the first of two uncrewed lunar rovers successfully landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod programme. The spacecraft which carried ''Lunokhod 1'' was named ''Luna 17
''LOK Luna 17'' (Ye-8 series) was an unmanned space mission of the Luna program, also called ''Lunik 17''. It deployed the first robotic rover onto the surface of the Moon.
Launch
''Luna 17'' was launched from an Earth parking orbit towards ...
''. ''Lunokhod 1'' was the first roving remote-controlled robot to land on another world.
''Luna 17'' was launched on November 10, 1970 at 14:44:01 UTC. After reaching Earth parking orbit
A parking orbit is a temporary orbit used during the launch of a spacecraft. A launch vehicle boosts into the parking orbit, then coasts for a while, then fires again to enter the final desired trajectory. The alternative to a parking orbit is ''di ...
, the final stage of ''Luna 17''s launching rocket fired to place it into a trajectory towards the Moon (November 10, 1970 at 14:54 UTC). After two course correction manoeuvres (on November 12 and 14) it entered lunar orbit on November 15, 1970 at 22:00 UTC.
The spacecraft soft-landed on the Moon in the Sea of Rains
Mare Imbrium (Latin ''imbrium'', the "Sea of Showers" or "Sea of Rains", "Sea of Tears") is a vast lava plain within the Imbrium Basin on the Moon and is one of the larger craters in the Solar System. The Imbrium Basin formed from the collis ...
on November 17, 1970 at 03:47 UTC. The lander had dual ramps from which the payload, ''Lunokhod 1'', could descend to the surface. At 06:28 UT the rover moved down the ramps and onto the Moon.
The rover's payload included cameras (two television and four panoramic telephotometers), a RIFMA X-ray fluorescence spectrometer, an RT-1 X-ray telescope
An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. In order to get above the Earth's atmosphere, which is opaque to X-rays, X-ray telescopes must be mounted on high altitude rockets, balloon ...
, a PrOP odometer/penetrometer, a RV-2N radiation detector, and a TL laser retroreflector.
An urban legend was spread among the Soviet Union that the Lunokhod rover was driven by a “KGB
The KGB (russian: links=no, lit=Committee for State Security, Комитет государственной безопасности (КГБ), a=ru-KGB.ogg, p=kəmʲɪˈtʲet ɡəsʊˈdarstvʲɪn(ː)əj bʲɪzɐˈpasnəsʲtʲɪ, Komitet gosud ...
Dwarf”, however it was never explained how supplies were stored to keep them alive for an 11-month mission.''Lunokhod 2''
''Lunokhod 2
''Lunokhod 2'' (russian: Луноход-2 ("Moonwalker 2"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 204 ("Device 8EL No. 204")) was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers that landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod pro ...
'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№204) was the second and more advanced of the two Lunokhod rovers. The launcher put the spacecraft into Earth parking orbit on January 8, 1973, followed by a translunar injection. On January 12, 1973, ''Luna 21
''Luna 21'' (Ye-8 series) was an unmanned space mission, and its spacecraft, of the Luna program, also called ''Lunik 21'', in 1973. The spacecraft landed on the Moon and deployed the second Soviet lunar rover, ''Lunokhod 2''. The primary obje ...
'' was braked into a lunar orbit.
The ''Luna 21
''Luna 21'' (Ye-8 series) was an unmanned space mission, and its spacecraft, of the Luna program, also called ''Lunik 21'', in 1973. The spacecraft landed on the Moon and deployed the second Soviet lunar rover, ''Lunokhod 2''. The primary obje ...
'' spacecraft landed on the Moon to deploy the second Soviet lunar rover, ''Lunokhod 2''. The primary objectives of the mission were to collect images of the lunar surface, examine ambient light levels to determine the feasibility of astronomical observations from the Moon, perform laser ranging experiments from Earth, observe solar X-rays, measure local magnetic fields, and study mechanical properties of the lunar surface material.
The landing occurred on January 15, 1973 at 23:35 UT in Le Monnier crater (25.85 degrees N, 30.45 degrees E).
After landing the ''Lunokhod 2'' took television images of the surrounding area, then rolled down a ramp to the surface at 01:14 UT on 1973-01-16. It then took pictures of the ''Luna 21'' lander and landing site.
The rover was equipped with three slow-scan television
Slow-scan television (SSTV) is a picture transmission method, used mainly by amateur radio operators, to transmit and receive static pictures via radio in monochrome or color.
A literal term for SSTV is narrowband television. Analog broadcast tel ...
cameras, one mounted high on the rover for navigation, which could return high resolution images at different rates—3.2, 5.7, 10.9 or 21.1 seconds per frame (not frames per second). These images were used by the five-man team of controllers on Earth who sent driving commands to the rover in real time. There were four panoramic cameras mounted on the rover.
Scientific instruments included a soil mechanics
Soil mechanics is a branch of soil physics and applied mechanics that describes the behavior of soils. It differs from fluid mechanics and solid mechanics in the sense that soils consist of a heterogeneous mixture of fluids (usually air and wat ...
tester, solar X-ray experiment, an astrophotometer to measure visible and ultraviolet
Ultraviolet (UV) is a form of electromagnetic radiation with wavelength from 10 nm (with a corresponding frequency around 30 PHz) to 400 nm (750 THz), shorter than that of visible light, but longer than X-rays. UV radiation ...
light levels, a magnetometer deployed in front of the rover on the end of a 2.5 m (8 ft 2 in) boom, a radiometer, a photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or ...
(Rubin-1) for laser detection experiments, and a French-supplied laser corner reflector.
Payload
* Cameras (three television and four panoramic telephotometers) * RIFMA-MX-ray fluorescence
X-ray fluorescence (XRF) is the emission of characteristic "secondary" (or fluorescent) X-rays from a material that has been excited by being bombarded with high-energy X-rays or gamma rays. The phenomenon is widely used for elemental analysis ...
spectrometer
* X-ray telescope
An X-ray telescope (XRT) is a telescope that is designed to observe remote objects in the X-ray spectrum. In order to get above the Earth's atmosphere, which is opaque to X-rays, X-ray telescopes must be mounted on high altitude rockets, balloon ...
* PROP odometer/penetrometer A penetrometer is a device to test the strength of a material.
Soil
There are many types of penetrometer designed to be used on soil. They are usually round or cone shaped. The penetrometer is dropped on the test subject or pressed against it and t ...
* RV-2N-LS radiation detector
In experimental and applied particle physics, nuclear physics, and nuclear engineering, a particle detector, also known as a radiation detector, is a device used to detect, track, and/or identify ionizing particles, such as those produced by nuc ...
* TL laser retroreflector
A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflection (physics), reflects radiation (usually light) back to its source with minimum scattering. This works at a wide range of angle of incidence (opt ...
* AF-3L UV/visible astrophotometer
* SG-70A magnetometer
* Rubin 1 photodetector
Photodetectors, also called photosensors, are sensors of light or other electromagnetic radiation. There is a wide variety of photodetectors which may be classified by mechanism of detection, such as photoelectric or photochemical effects, or ...
''Lunokhod 3''

 ''Lunokhod 3'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№205) was built for a
''Lunokhod 3'' (vehicle 8ЕЛ№205) was built for a Moon landing
A Moon landing is the arrival of a spacecraft on the surface of the Moon. This includes both crewed and robotic missions. The first human-made object to touch the Moon was the Soviet Union's Luna 2, on 13 September 1959.
The United S ...
in 1977 as ''Luna 25'', but never flew to the Moon due to lack of launchers and funding. It remains at the NPO Lavochkin museum.
Results
During its 322 Earth days of operations, ''Lunokhod 1
''Lunokhod 1'' ( Russian: Луноход-1 ("Moonwalker 1"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 203 ("Device 8EL No. 203")) was the first of two robotic lunar rovers landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of its Lunokhod program. The ...
'' travelled and returned more than 20,000 television images and 206 high-resolution panoramas. In addition, it performed twenty-five soil analyses with its RIFMA x-ray fluorescence spectrometer and used its penetrometer at 500 different locations.
''Lunokhod 2
''Lunokhod 2'' (russian: Луноход-2 ("Moonwalker 2"), also known as Аппарат 8ЕЛ № 204 ("Device 8EL No. 204")) was the second of two unmanned lunar rovers that landed on the Moon by the Soviet Union as part of the Lunokhod pro ...
'' operated for about four months, covered of terrain, including driving into hilly upland areas and rilles. ''Lunokhod 2'' held the record for the longest distance of surface travel of any extraterrestrial vehicle until 2014. It sent back 86 panoramic images and over 80,000 television pictures. Many mechanical tests of the Moon's surface, laser ranging measurements, and other experiments were completed during this time.
In 2010, nearly forty years after the 1971 loss of signal from ''Lunokhod 1'', the NASA
The National Aeronautics and Space Administration (NASA ) is an independent agencies of the United States government, independent agency of the US federal government responsible for the civil List of government space agencies, space program ...
Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter photographed its tracks and final location, and researchers, using a telescopic pulsed-laser rangefinder, detected the robot's retroreflector
A retroreflector (sometimes called a retroflector or cataphote) is a device or surface that reflection (physics), reflects radiation (usually light) back to its source with minimum scattering. This works at a wide range of angle of incidence (opt ...
.
Not until Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
's deployment of the "Sojourner
A sojourner is a person who resides temporarily in a place.
Sojourner may also refer to:
* Sojourner Truth (1797–1883), abolitionist and women's rights activist
* Albert Sojourner (1872–1951), member of the Mississippi House of Representative ...
" Rover in 1997 was another remote-controlled vehicle put on an extraterrestrial body. For comparison, the similarly sized NASA Mars Exploration Rover
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, '' Spirit'' and '' Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rovers to explore the Martian surface ...
s, ''Spirit
Spirit or spirits may refer to:
Liquor and other volatile liquids
* Spirits, a.k.a. liquor, distilled alcoholic drinks
* Spirit or tincture, an extract of plant or animal material dissolved in ethanol
* Volatile (especially flammable) liquids, ...
'' and ''Opportunity
Opportunity may refer to:
Places
* Opportunity, Montana, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Nebraska, an unincorporated community, United States
* Opportunity, Washington, a former census-designated place, United States
* ...
'' had, by their fifth anniversary in January 2009, traveled a total of and transmitted over 125,000 images.
Chernobyl legacy
According to a French documentary television film '' Tank on the Moon'' by Jean Afanassieff, the Lunokhod design returned to the limelight 15 years later due to the Chernobyl nuclear power plant disaster on April 26, 1986. TheEast German
East Germany, officially the German Democratic Republic (GDR; german: Deutsche Demokratische Republik, , DDR, ), was a country that existed from its creation on 7 October 1949 until its dissolution on 3 October 1990. In these years the state ...
-built remote controlled bulldozers available to Soviet civil defense troops weighed dozens of tons too heavy to operate on the remaining parts of the partially collapsed reactor building roof. Human labourers could not be employed to shovel debris since work shifts were limited to 90-second intervals due to intense ionizing radiation.
Lunokhod designers were called back from retirement, and in two weeks rovers were made which used nuclear decay
Radioactive decay (also known as nuclear decay, radioactivity, radioactive disintegration, or nuclear disintegration) is the process by which an unstable atomic nucleus loses energy by radiation. A material containing unstable nuclei is consid ...
heat sources for internal rack climate control, their electronic systems were already hardened to partly resist radiation. This benefit allowed the 1986 designers to quickly devise a derived vehicle type for nuclear disaster recovery work. On July 15, two rovers, called STR-1, were delivered to the Chernobyl accident zone and proved useful for clearing debris, earning awards for the designers. Due to extremely high radiation levels, both STR-1 rovers eventually failed, and human workers (later named liquidators) were called in once again.
Locations and ownership
 Until 2010, the final location of ''Lunokhod 1'' was uncertain by a few kilometers. Lunar laser ranging experiments had failed to detect a return signal from its retroreflector since the 1970s. On March 17, 2010, Albert Abdrakhimov found both the lander and the rover in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter image M114185541RC. On April 22, Tom Murphy (
Until 2010, the final location of ''Lunokhod 1'' was uncertain by a few kilometers. Lunar laser ranging experiments had failed to detect a return signal from its retroreflector since the 1970s. On March 17, 2010, Albert Abdrakhimov found both the lander and the rover in Lunar Reconnaissance Orbiter image M114185541RC. On April 22, Tom Murphy (UCSD
The University of California, San Diego (UC San Diego or colloquially, UCSD) is a public land-grant research university in San Diego, California. Established in 1960 near the pre-existing Scripps Institution of Oceanography, UC San Diego is t ...
) and Russet McMillan at the Apache Point Observatory
The Apache Point Observatory (APO; obs. code: 705) is an astronomical observatory located in the Sacramento Mountains in Sunspot, New Mexico, United States, approximately south of Cloudcroft. The observatory is operated by New Mexico State Un ...
detected the robot's retroreflector using the Apache Point telescopic pulsed-laser rangefinder.
''Lunokhod 2'' continues to be detected by lunar laser ranging experiments and its position is known to sub-metre accuracy. Ownership of ''Lunokhod 2'' and the ''Luna 21'' lander was sold by the Lavochkin
NPO Lavochkin (russian: НПО Лавочкина, OKB-301, also called Lavochkin Research and Production Association or shortly Lavochkin Association, LA) is a Russian aerospace company. It is a major player in the Russian space program, being th ...
Association for in December 1993 at a Sotheby's
Sotheby's () is a British-founded American multinational corporation with headquarters in New York City. It is one of the world's largest brokers of fine and decorative art, jewellery, and collectibles. It has 80 locations in 40 countries, an ...
auction in New York (although the catalogue incorrectly lists lot 68A as ''Luna 17/Lunokhod 1''). The buyer was computer gaming entrepreneur and astronaut's son Richard Garriott
Richard Allen Garriott de Cayeux (''né'' Garriott; born July 4, 1961) is an American video game developer, entrepreneur and private astronaut. Although both his parents were American, he maintains dual British and American citizenship by birth. ...
, who is also known by the name of his gaming character Lord British. Garriott stated in a 2001 interview: "I purchased ''Lunakod 21'' from the Russians. I am now the world's only private owner of an object on a foreign celestial body. Though there are international treaties that say no government shall lay claim to geography off planet earth, I am not a government. Summarily, I claim the Moon in the name of Lord British!" In 2007, Garriott said he is still the owner of ''Lunokhod 2''.
See also
*Exploration of the Moon
The physical exploration of the Moon began when ''Luna 2'', a space probe launched by the Soviet Union, made an impact on the surface of the Moon on September 14, 1959. Prior to that the only available means of exploration had been observation ...
* Mars Exploration Rovers
NASA's Mars Exploration Rover (MER) mission was a robotic space mission involving two Mars rovers, ''Spirit (rover), Spirit'' and ''Opportunity (rover), Opportunity'', exploring the planet Mars. It began in 2003 with the launch of the two rover ...
* Mars Pathfinder
''Mars Pathfinder'' (''MESUR Pathfinder'') is an American robotic spacecraft that landed a base station with a roving probe on Mars in 1997. It consisted of a lander, renamed the Carl Sagan Memorial Station, and a lightweight, wheeled robot ...
* '' Tank on the Moon''
References
Further reading
* *External links
Lunar and Planetary Department Moscow University
- a diary of significant events in Soviet lunar exploration, including those associated with the Lunokhod programme
including many from the Lunokhod programme
(about half way down the page, or search the page for "Lunokhod") {{DEFAULTSORT:Lunokhod Programme Missions to the Moon Lunar rovers Soviet lunar program