Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Louis I, Grand Duke of Hesse (14 June 1753 in
 Louis was born on 14 June 1753 as the third child and eldest son of the later Landgrave Louis IX of Hessen-Darmstadt, and his spouse
Louis was born on 14 June 1753 as the third child and eldest son of the later Landgrave Louis IX of Hessen-Darmstadt, and his spouse
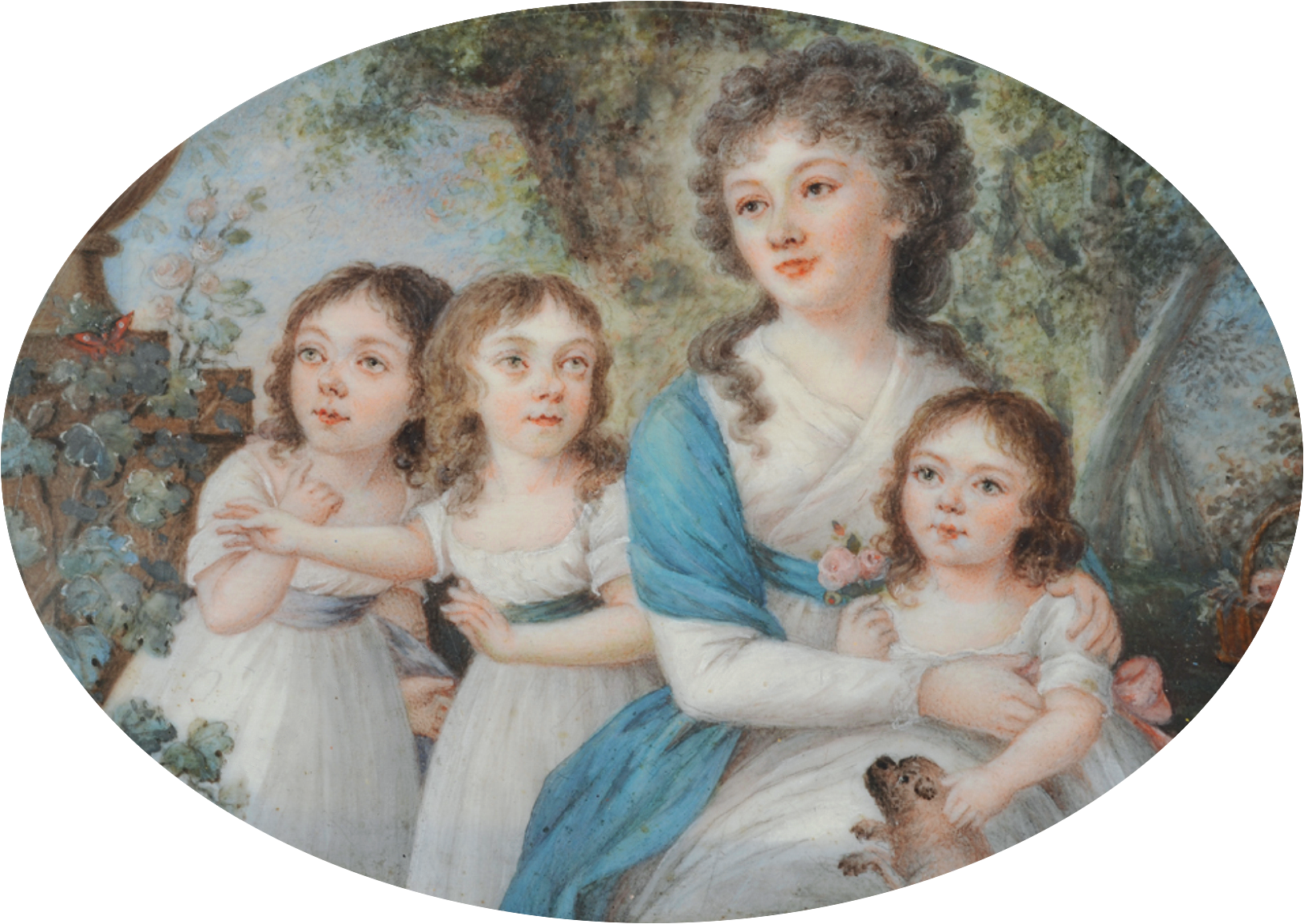 In 1776, he became engaged to
In 1776, he became engaged to
 Allied to
Allied to  Grand Duke Louis I died at the age of 76 on 6 April 1830 in his capital Darmstadt. He was succeeded as Grand Duke by his eldest son Louis II.
In 1844, a 33-meter column called ''Langer Ludwig'' (meaning ''Long Louis''), was set up in his commemoration in the middle of the ''Luisenplatz'', the largest square of
Grand Duke Louis I died at the age of 76 on 6 April 1830 in his capital Darmstadt. He was succeeded as Grand Duke by his eldest son Louis II.
In 1844, a 33-meter column called ''Langer Ludwig'' (meaning ''Long Louis''), was set up in his commemoration in the middle of the ''Luisenplatz'', the largest square of
Prenzlau
Prenzlau (, formerly also Prenzlow) is a town in Brandenburg, Germany, the administrative seat of Uckermark District. It is also the centre of the historic Uckermark region.
Geography
The town is located on the Ucker river, about north of Be ...
– 6 April 1830 in Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest city in the state of Hesse ...
) was ''Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt'' (as ''Louis X'') and later the first ''Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine''.
Louis was the son of Louis IX, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt
Louis IX of Hesse-Darmstadt (german: Ludwig) (15 December 1719 – 6 April 1790) was the reigning Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt from 1768 to 1790.
Louis IX and his wife became the most recent common ancestors of all current European monarchs ...
, and succeeded his father in 1790. He presided over a significant increase in territory for Hesse-Darmstadt during the imperial reorganizations of 1801-1803, most notably the Duchy of Westphalia
The Duchy of Westphalia (german: Herzogtum Westfalen) was a historic territory in the Holy Roman Empire, which existed from 1102 to 1803. It was located in the greater region of Westphalia, originally one of the three main regions in the Germ ...
, hitherto subject to the Archbishop of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne is an archbishop governing the Archdiocese of Cologne of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and is also a historical state in the Rhine holding the birthplace of Beethoven and northern Rhineland-Palat ...
. Allied to Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, Louis in 1806 was elevated to the title of a ''Grand Duke of Hesse'' and joined the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria a ...
, leading to the dissolution of the Empire. At the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
in 1814/15, Louis had to give up his Westphalian territories, but was compensated with the district of Rheinhessen
Rhenish Hesse or Rhine HesseDickinson, Robert E (1964). ''Germany: A regional and economic geography'' (2nd ed.). London: Methuen, p. 542. . (german: Rheinhessen) is a region and a former government district () in the German state of Rhineland- ...
on the left bank of the Rhine. Because of this addition, he amended his title to ''Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine''.
Early life
 Louis was born on 14 June 1753 as the third child and eldest son of the later Landgrave Louis IX of Hessen-Darmstadt, and his spouse
Louis was born on 14 June 1753 as the third child and eldest son of the later Landgrave Louis IX of Hessen-Darmstadt, and his spouse Countess Palatine Caroline of Zweibrücken
Caroline of the Palatinate-Zweibrücken (Caroline Henriette Christiane Philippine Louise; 9 March 1721 – 30 March 1774) was Landgravine of Hesse-Darmstadt by marriage to Louis IX, Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt. She was famed as one of the mo ...
, a daughter of Christian III, Count Palatine of Zweibrücken
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρισ ...
. He was born in the town of Prenzlau
Prenzlau (, formerly also Prenzlow) is a town in Brandenburg, Germany, the administrative seat of Uckermark District. It is also the centre of the historic Uckermark region.
Geography
The town is located on the Ucker river, about north of Be ...
in Brandenburg
Brandenburg (; nds, Brannenborg; dsb, Bramborska ) is a state in the northeast of Germany bordering the states of Mecklenburg-Vorpommern, Lower Saxony, Saxony-Anhalt, and Saxony, as well as the country of Poland. With an area of 29,480 squ ...
, where his father, who was in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
n military service, was stationed. The children grew up with the mother in the town of Buchsweiler, which had previously been the residence of the Counts of Hanau-Lichtenberg
The County of Hanau-Lichtenberg was a territory in the Holy Roman Empire. It emerged between 1456 and 1480 from a part of the County of Hanau and one half of the Barony of Lichtenberg. Following the extinction of the counts of Hanau-Lichtenberg in ...
, while the father stayed mainly in the town of Pirmasens
Pirmasens (; pfl, Bärmesens (also ''Bermesens'' or ''Bärmasens'')) is an independent town in Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany, near the border with France. It was famous for the manufacture of shoes. The surrounding rural district was called ''L ...
to attend his military career. In 1766, when Louis was 13, his mother's court moved from Buchsweiler to Darmstadt. At the death of his grandfather on 17 October 1768, his father succeeded as landgrave, and Louis himself became heir to the landgraviate with the title of hereditary prince
A crown prince or hereditary prince is the heir apparent to the throne in a royal or imperial monarchy. The female form of the title is crown princess, which may refer either to an heiress apparent or, especially in earlier times, to the wife ...
.
Ludvig studied at the University of Leiden
Leiden University (abbreviated as ''LEI''; nl, Universiteit Leiden) is a public research university in Leiden, Netherlands. The university was founded as a Protestant university in 1575 by William, Prince of Orange, as a reward to the city of Le ...
from 1769
Events
January–March
* February 2 – Pope Clement XIII dies, the night before preparing an order to dissolve the Jesuits.Denis De Lucca, ''Jesuits and Fortifications: The Contribution of the Jesuits to Military Architecture ...
and subsequently undertook his Grand Tour
The Grand Tour was the principally 17th- to early 19th-century custom of a traditional trip through Europe, with Italy as a key destination, undertaken by upper-class young European men of sufficient means and rank (typically accompanied by a tut ...
to London
London is the capital and List of urban areas in the United Kingdom, largest city of England and the United Kingdom, with a population of just under 9 million. It stands on the River Thames in south-east England at the head of a estuary dow ...
and Paris
Paris () is the capital and most populous city of France, with an estimated population of 2,165,423 residents in 2019 in an area of more than 105 km² (41 sq mi), making it the 30th most densely populated city in the world in 2020. Si ...
. In France
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
he met, among others, the French philosopher
A philosopher is a person who practices or investigates philosophy. The term ''philosopher'' comes from the grc, φιλόσοφος, , translit=philosophos, meaning 'lover of wisdom'. The coining of the term has been attributed to the Greek th ...
s Jean le Rond d'Alembert
Jean-Baptiste le Rond d'Alembert (; ; 16 November 1717 – 29 October 1783) was a French mathematician, mechanician, physicist, philosopher, and music theorist. Until 1759 he was, together with Denis Diderot, a co-editor of the '' Encyclopéd ...
and Denis Diderot
Denis Diderot (; ; 5 October 171331 July 1784) was a French philosopher, art critic, and writer, best known for serving as co-founder, chief editor, and contributor to the '' Encyclopédie'' along with Jean le Rond d'Alembert. He was a promi ...
, who were some of the prominent figures of the Age of Enlightenment
The Age of Enlightenment or the Enlightenment; german: Aufklärung, "Enlightenment"; it, L'Illuminismo, "Enlightenment"; pl, Oświecenie, "Enlightenment"; pt, Iluminismo, "Enlightenment"; es, La Ilustración, "Enlightenment" was an intel ...
, and editor
Editing is the process of selecting and preparing written, photographic, visual, audible, or cinematic material used by a person or an entity to convey a message or information. The editing process can involve correction, condensation, or ...
s of the first modern encyclopedia
An encyclopedia (American English) or encyclopædia (British English) is a reference work or compendium providing summaries of knowledge either general or special to a particular field or discipline. Encyclopedias are divided into articles ...
. In 1773 he traveled with the German-born French writer
A writer is a person who uses written words in different writing styles and techniques to communicate ideas. Writers produce different forms of literary art and creative writing such as novels, short stories, books, poetry, travelogues, ...
and critic
A critic is a person who communicates an assessment and an opinion of various forms of creative works such as art, literature, music, cinema, theater, fashion, architecture, and food. Critics may also take as their subject social or gover ...
Friedrich Melchior Grimm
Friedrich Melchior, Baron von Grimm (26 September 172319 December 1807) was a German-born French-language journalist, art critic, diplomat and contributor to the ''Encyclopédie ou Dictionnaire raisonné des sciences, des arts et des métiers'' ...
to the court of Frederik the Great in Prussia
Prussia, , Old Prussian: ''Prūsa'' or ''Prūsija'' was a German state on the southeast coast of the Baltic Sea. It formed the German Empire under Prussian rule when it united the German states in 1871. It was ''de facto'' dissolved by an e ...
, where his sister Frederica Louisa was married to the heir presumptive
An heir presumptive is the person entitled to inherit a throne, peerage, or other hereditary honour, but whose position can be displaced by the birth of an heir apparent or a new heir presumptive with a better claim to the position in question. ...
Frederick William. Finally, he traveled on to Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...
, where in 1773 he attended the wedding of his second sister Wilhelmina Louisa in St. Petersburg to the heir to the Russian throne, Grand Duke Paul. As a Russian general Ludwig fought in 1774
Events
January–March
* January 21 – Mustafa III, Sultan of the Ottoman Empire, dies and is succeeded by his brother Abdul Hamid I.
* January 27
** An angry crowd in Boston, Massachusetts seizes, tars, and feathers British customs c ...
in the Russo-Turkish War
The Russo-Turkish wars (or Ottoman–Russian wars) were a series of twelve wars fought between the Russian Empire and the Ottoman Empire between the 16th and 20th centuries. It was one of the longest series of military conflicts in European histo ...
, and the same year he became freemason
Freemasonry or Masonry refers to fraternal organisations that trace their origins to the local guilds of stonemasons that, from the end of the 13th century, regulated the qualifications of stonemasons and their interaction with authorities ...
in the lodge
Lodge is originally a term for a relatively small building, often associated with a larger one.
Lodge or The Lodge may refer to:
Buildings and structures Specific
* The Lodge (Australia), the official Canberra residence of the Prime Minist ...
"To the crowned flag "in Moscow
Moscow ( , US chiefly ; rus, links=no, Москва, r=Moskva, p=mɐskˈva, a=Москва.ogg) is the capital and largest city of Russia. The city stands on the Moskva River in Central Russia, with a population estimated at 13.0 million ...
.
Marriage
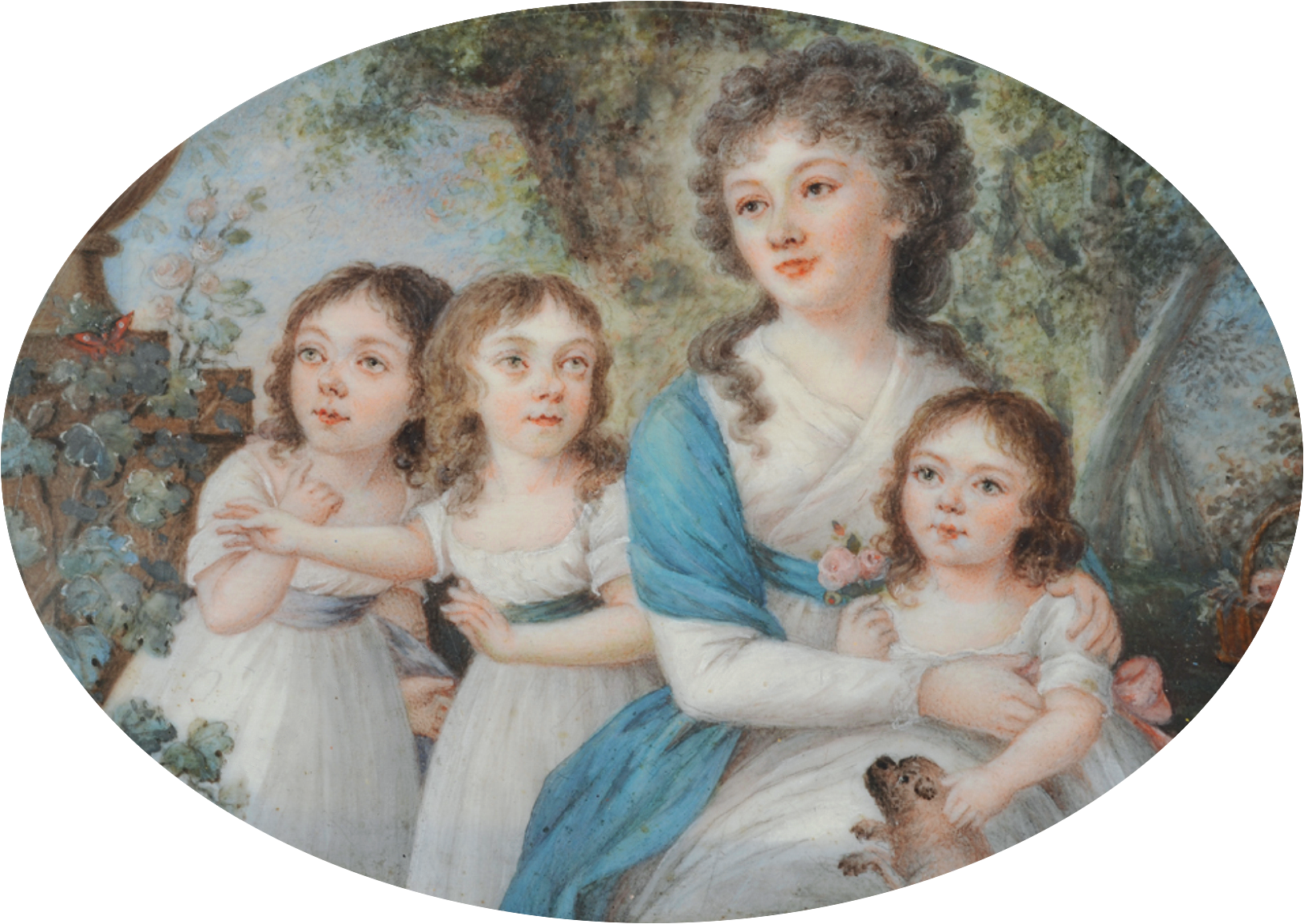 In 1776, he became engaged to
In 1776, he became engaged to Sophie Dorothea of Württemberg
Sophie is a version of the female given name Sophia, meaning "wise".
People with the name Born in the Middle Ages
* Sophie, Countess of Bar (c. 1004 or 1018–1093), sovereign Countess of Bar and lady of Mousson
* Sophie of Thuringia, Duchess of ...
, eldest daughter of Frederick II Eugene, Duke of Württemberg
Friedrich Eugen, Duke of Württemberg (21 January 1732 – 23 December 1797) was the fourth son of Karl Alexander, Duke of Württemberg, and Princess Maria Augusta of Thurn and Taxis (11 August 1706 – 1 February 1756). He was born in Stut ...
. The engagement was broken off so that Sophia Dorothea could marry Louis's recently widowed brother-in-law Tsarevich Paul Petrovich, son and heir of Catherine II "the Great", Empress of Russia. He received a monetary compensation when the engagement was broken.
After this humiliating incident, Louis spent the summer at his sister Louise's court in the Duchy of Saxe-Weimar
Saxe-Weimar (german: Sachsen-Weimar) was one of the Saxon duchies held by the Ernestine branch of the Wettin dynasty in present-day Thuringia. The chief town and capital was Weimar. The Weimar branch was the most genealogically senior extant ...
, where he associated with Johann Wolfgang von Goethe
Johann Wolfgang von Goethe (28 August 1749 – 22 March 1832) was a German poet, playwright, novelist, scientist, statesman, theatre director, and critic. His works include plays, poetry, literature, and aesthetic criticism, as well as t ...
. Even after the stay, Louis was in correspondence with the Weimar court and Goethe, and also with Friedrich von Schiller
Johann Christoph Friedrich von Schiller (, short: ; 10 November 17599 May 1805) was a German playwright, poet, and philosopher. During the last seventeen years of his life (1788–1805), Schiller developed a productive, if complicated, friendsh ...
. Louis married his cousin Princess Louise of Hesse-Darmstadt, daughter of his uncle Prince George William of Hesse-Darmstadt
Prince George William of Hesse-Darmstadt (11 July 1722 – 21 June 1782) was a Prince of Hesse-Darmstadt. He was born in Darmstadt.
He was the second son of Landgrave Louis VIII and Charlotte Christine Magdalene Johanna of Hanau-Lichtenberg ...
, on 19 February 1777 in Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest city in the state of Hesse ...
. The couple lived alternately in Darmstadt and in ''Fürstenlager Auerbach''. They had six children.
Landgrave of Hesse-Darmstadt
Louis succeeded as Landgrave of Hessen-Darmstadt on the death of his father in 1790. He presided over a significant increase in territory for Hesse-Darmstadt during the imperial reorganizations of 1801-1803, most notably theDuchy of Westphalia
The Duchy of Westphalia (german: Herzogtum Westfalen) was a historic territory in the Holy Roman Empire, which existed from 1102 to 1803. It was located in the greater region of Westphalia, originally one of the three main regions in the Germ ...
, hitherto subject to the Archbishop of Cologne
The Archbishop of Cologne is an archbishop governing the Archdiocese of Cologne of the Catholic Church in western North Rhine-Westphalia and is also a historical state in the Rhine holding the birthplace of Beethoven and northern Rhineland-Palat ...
.
Grand duke of Hesse
 Allied to
Allied to Napoleon I of France
Napoleon Bonaparte ; it, Napoleone Bonaparte, ; co, Napulione Buonaparte. (born Napoleone Buonaparte; 15 August 1769 – 5 May 1821), later known by his regnal name Napoleon I, was a French military commander and political leader wh ...
, Louis was elevated to the title of a ''Grand Duke of Hesse'' in 1806 and joined the Confederation of the Rhine
The Confederated States of the Rhine, simply known as the Confederation of the Rhine, also known as Napoleonic Germany, was a confederation of German client states established at the behest of Napoleon some months after he defeated Austria a ...
, leading to the dissolution of the Empire. At the Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
in 1814/15, Louis had to give up his Westphalia
Westphalia (; german: Westfalen ; nds, Westfalen ) is a region of northwestern Germany and one of the three historic parts of the state of North Rhine-Westphalia. It has an area of and 7.9 million inhabitants.
The territory of the regio ...
n territories, but was compensated with the district of Rheinhessen
Rhenish Hesse or Rhine HesseDickinson, Robert E (1964). ''Germany: A regional and economic geography'' (2nd ed.). London: Methuen, p. 542. . (german: Rheinhessen) is a region and a former government district () in the German state of Rhineland- ...
, with his capital Mainz
Mainz () is the capital and largest city of Rhineland-Palatinate, Germany.
Mainz is on the left bank of the Rhine, opposite to the place that the Main joins the Rhine. Downstream of the confluence, the Rhine flows to the north-west, with Ma ...
on the left bank of the Rhine. Because of this addition, he amended his title to ''Grand Duke of Hesse and by Rhine''.
 Grand Duke Louis I died at the age of 76 on 6 April 1830 in his capital Darmstadt. He was succeeded as Grand Duke by his eldest son Louis II.
In 1844, a 33-meter column called ''Langer Ludwig'' (meaning ''Long Louis''), was set up in his commemoration in the middle of the ''Luisenplatz'', the largest square of
Grand Duke Louis I died at the age of 76 on 6 April 1830 in his capital Darmstadt. He was succeeded as Grand Duke by his eldest son Louis II.
In 1844, a 33-meter column called ''Langer Ludwig'' (meaning ''Long Louis''), was set up in his commemoration in the middle of the ''Luisenplatz'', the largest square of Darmstadt
Darmstadt () is a city in the state of Hesse in Germany, located in the southern part of the Rhine-Main-Area (Frankfurt Metropolitan Region). Darmstadt has around 160,000 inhabitants, making it the fourth largest city in the state of Hesse ...
.
Marriage and family
On 19 February 1777, Louis married his first cousin, Princess Louise of Hesse-Darmstadt ( 15 February 1761 – 24 October 1829), a daughter ofPrince George William of Hesse-Darmstadt
Prince George William of Hesse-Darmstadt (11 July 1722 – 21 June 1782) was a Prince of Hesse-Darmstadt. He was born in Darmstadt.
He was the second son of Landgrave Louis VIII and Charlotte Christine Magdalene Johanna of Hanau-Lichtenberg ...
. Together, they had eight children:
* Louis, later Grand Duke Louis II of Hesse (26 December 1777 – 16 June 1848). Married his double first cousin Wilhelmine of Baden and had issue.
* Louise (16 January 1779 – 18 April 1811). Married Louis of Anhalt-Köthen and had issue.
* Ludwig ''Georg'' Karl Friedrich(31 August 1780 – 17 April 1856). Married, morganatically, Caroline Török de Szendrö and had issue.
* ''Friedrich'' August Karl (14 May 1788 – 16 March 1867)
* Stillborn twin daughters (11 May 1789).
* Emil
Emil or Emile may refer to:
Literature
*''Emile, or On Education'' (1762), a treatise on education by Jean-Jacques Rousseau
* ''Émile'' (novel) (1827), an autobiographical novel based on Émile de Girardin's early life
*''Emil and the Detective ...
(3 September 1790 – 30 April 1856)
* Ferdinand ''Gustav'' Wilhelm Friedrich (18 December 1791 – 30 January 1806)
Ancestry
References
Bibliography
* *External links
{{DEFAULTSORT:Louis I, Grand Duke Of Hesse 1753 births 1830 deaths People from Prenzlau House of Hesse-Darmstadt Grand Dukes of Hesse Landgraves of Hesse-Darmstadt Burials at the Mausoleum for the Grand Ducal House of Hesse, Rosenhöhe (Darmstadt)