Long Island, New York on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the
Accessed November 16, 2016. including research institute, research facilities at


 By the year 1643, there were 14 indigenous tribes living on Long Island: Canarsee, Rockaway,
By the year 1643, there were 14 indigenous tribes living on Long Island: Canarsee, Rockaway,




 The westernmost end of Long Island contains the New York City
The westernmost end of Long Island contains the New York City 


 Under the
Under the  Precipitation is distributed uniformly throughout the year, with approximately on average during each month. Average yearly snowfall totals range from approximately , with the north shore and western parts averaging more than the immediate south shore (South of Sunrise Hwy) and the east end. In any given winter, however, some parts of the island can see up to of snow or more. There are also milder winters, in which much of the island see less than of snow.
On August 13, 2014,
Precipitation is distributed uniformly throughout the year, with approximately on average during each month. Average yearly snowfall totals range from approximately , with the north shore and western parts averaging more than the immediate south shore (South of Sunrise Hwy) and the east end. In any given winter, however, some parts of the island can see up to of snow or more. There are also milder winters, in which much of the island see less than of snow.
On August 13, 2014,
 Several smaller islands, though geographically distinct, are in proximity to Long Island and are often grouped with it. These islands include
Several smaller islands, though geographically distinct, are in proximity to Long Island and are often grouped with it. These islands include
 According to a 2000 report on religion, which asked congregations to respond,
According to a 2000 report on religion, which asked congregations to respond,
Accessed September 3, 2017. Rapidly expanding Chinatowns in New York, Chinatowns have developed in Brooklyn (布魯克林) and
 Long Island has played a prominent role in
Long Island has played a prominent role in
 Nassau County and Suffolk County each have their own governments, with a
Nassau County and Suffolk County each have their own governments, with a
 Many public and private high schools on Long Island are ranked among the best in the United States. Nassau and Suffolk counties are the home of 125 public school districts containing 656 public schools. It also hosts
Many public and private high schools on Long Island are ranked among the best in the United States. Nassau and Suffolk counties are the home of 125 public school districts containing 656 public schools. It also hosts
 Long Island is home to a range of higher-education institutions, both public and private. Brooklyn and Queens contain five of eleven senior colleges within
Long Island is home to a range of higher-education institutions, both public and private. Brooklyn and Queens contain five of eleven senior colleges within  Several colleges and universities within the
Several colleges and universities within the
 Music on Long Island (Nassau and Suffolk) is strongly influenced by the proximity to New York City and by the
Music on Long Island (Nassau and Suffolk) is strongly influenced by the proximity to New York City and by the
 Long Island has historically been a center for fishing and
Long Island has historically been a center for fishing and  Of land-based produce, Long Island
Of land-based produce, Long Island
 The
The

 The
The
 Long Island has a wide variety of
Long Island has a wide variety of
 Many major forms of transportation serve Long Island, including aviation via
Many major forms of transportation serve Long Island, including aviation via
 The MTA implements mass transportation for the
The MTA implements mass transportation for the
 The
The
 Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE) provides bus service in Nassau County, while
Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE) provides bus service in Nassau County, while
 The
The
New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18th-most populous in the world. The island begins at New York Harbor approximately east of Manhattan Island and extends eastward about into the Atlantic Ocean
The Atlantic Ocean is the second-largest of the world's five oceans, with an area of about . It covers approximately 20% of Earth's surface and about 29% of its water surface area. It is known to separate the " Old World" of Africa, Europe ...
and 23 miles wide at its most distant points. The island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An isla ...
comprises four counties: Kings and Queens counties (the New York City
New York, often called New York City or NYC, is the List of United States cities by population, most populous city in the United States. With a 2020 population of 8,804,190 distributed over , New York City is also the L ...
boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
of Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, respectively) and Nassau County share the western third of the island, while Suffolk County occupies the eastern two thirds of the island. More than half of New York City's residents (58.4%) lived on Long Island as of 2020, in Brooklyn and in Queens. Culturally, many people in the New York metropolitan area colloquially use the term "Long Island" (or "the Island") to refer exclusively to Nassau and Suffolk counties, and conversely, employ the term "the City" to mean Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
alone. The Nassau-and-Suffolk-only definition of Long Island is recognized as a "region" by the state of New York. Although geographically an island, the Supreme Court of the United States
The Supreme Court of the United States (SCOTUS) is the highest court in the federal judiciary of the United States. It has ultimate appellate jurisdiction over all U.S. Federal tribunals in the United States, federal court cases, and over Stat ...
has held that given the island's extensive ties to the mainland, it should be treated like a peninsula, allowing the state to have jurisdiction within its maritime boundaries.
Long Island may refer both to the main island and the surrounding outer barrier islands
The Outer Barrier, also known as the Long Island and New York City barrier islands, refers to the string of barrier islands that divide the lagoons south of Long Island, New York from the Atlantic Ocean. These islands include Long Beach Barrier ...
. To its west, Long Island is separated from Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
and the Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New ...
by the East River
The East River is a saltwater tidal estuary in New York City. The waterway, which is actually not a river despite its name, connects Upper New York Bay on its south end to Long Island Sound on its north end. It separates the borough of Quee ...
tidal estuary. North of the island is Long Island Sound, across which lie Westchester County, New York, and the state of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the ...
. Across the Block Island Sound
Block Island Sound is a strait in the open Atlantic Ocean, approximately wide, separating Block Island from the coast of mainland Rhode Island. On the west, it extends to Montauk Point on the eastern tip of Long Island, as well as Plum Isl ...
to the northeast is the state of Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
. Block Island—which is part of Rhode Island—and numerous smaller islands extend further into the Atlantic. To the extreme southwest, Long Island, at Brooklyn, is separated from Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
and the state of New Jersey
New Jersey is a state in the Mid-Atlantic and Northeastern regions of the United States. It is bordered on the north and east by the state of New York; on the east, southeast, and south by the Atlantic Ocean; on the west by the Delawa ...
by Upper New York Bay, the Narrows, and Lower New York Bay
Lower New York Bay is a section of New York Bay south of the Narrows (the strait between Staten Island and Brooklyn). The eastern end of the Bay is marked by two spits of land, Sandy Hook, New Jersey, and Rockaway, Queens. The waterway ...
.
The longest and the largest island in the contiguous United States, Long Island extends eastward from New York Harbor to Montauk Point
Montauk ( ) is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Town of East Hampton in Suffolk County, New York, on the eastern end of the South Shore of Long Island. As of the 2020 United States census, the CDP's population was 4,318.
The ...
, with a maximum north-to-south distance of between Long Island Sound and the Atlantic coast. With a land area of , Long Island is the 11th-largest island in the United States and the 149th-largest island in the world—larger than the of the smallest U.S. state, Rhode Island.
With an enumerated population of 8,063,232 residents as of the 2020 U.S. Census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to off ...
, constituting 40% of the State of New York's population, Long Island is the most populated island in any U.S. state or territory, the third-most populous island in the Americas (after only Hispaniola and Cuba
Cuba ( , ), officially the Republic of Cuba ( es, República de Cuba, links=no ), is an island country comprising the island of Cuba, as well as Isla de la Juventud and several minor archipelagos. Cuba is located where the northern Caribb ...
), and the 18th-most populous island in the world (ahead of Ireland
Ireland ( ; ga, Éire ; Ulster-Scots: ) is an island in the North Atlantic Ocean, in north-western Europe. It is separated from Great Britain to its east by the North Channel, the Irish Sea, and St George's Channel. Ireland is the s ...
, Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
, and Hokkaidō
is Japan, Japan's Japanese archipelago, second largest island and comprises the largest and northernmost Prefectures of Japan, prefecture, making up its own List of regions of Japan, region. The Tsugaru Strait separates Hokkaidō from Honshu; th ...
). Its population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
is . If Long Island geographically constituted an independent metropolitan statistical area
In the United States, a metropolitan statistical area (MSA) is a geographical region with a relatively high population density at its core and close economic ties throughout the area. Such regions are neither legally incorporated as a city or tow ...
, it would rank fourth most populous in the United States; while if it were a U.S. state, Long Island would rank thirteenth in population and first in population density. Long Island is culturally and ethnically diverse, featuring some of the wealthiest and most expensive neighborhoods in the world near the shorelines, as well as working-class areas in all four counties.
As of 2019, Long Island had a gross domestic product
Gross domestic product (GDP) is a monetary measure of the market value of all the final goods and services produced and sold (not resold) in a specific time period by countries. Due to its complex and subjective nature this measure is of ...
of $197 billion. Between 2014 and 2019, Long Island experienced 4.3% growth in jobs. Median income on the island is $112,000 and the median home price is $450,000. Among those over the age of 25, 42.6% hold a college degree or higher educationally.
As a hub of commercial aviation
Commercial aviation is the part of civil aviation that involves operating aircraft for remuneration or hire, as opposed to private aviation.
Definition
Commercial aviation is not a rigorously defined category. All commercial air transport and ...
, Long Island is home to two of the nation's and New York City metropolitan area's three busiest airports, JFK International Airport and LaGuardia Airport, in addition to Long Island MacArthur Airport; as well as two major air traffic control
Air traffic control (ATC) is a service provided by ground-based air traffic controllers who direct aircraft on the ground and through a given section of controlled airspace, and can provide advisory services to aircraft in non-controlled airsp ...
radar facilities, the New York TRACON
The New York Terminal Radar Approach Control (TRACON) is located in Westbury, Long Island. New York TRACON, also known as N90, is a type of Federal Aviation Administration air traffic control facility known as a consolidated TRACON, meaning that ...
and the New York ARTCC. Nine bridges and thirteen navigable tunnels (road and railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
tunnels but not metropolitan water tunnels) connect Brooklyn and Queens to the three other boroughs of New York City. Ferries connect Suffolk County northward across Long Island Sound to the state of Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the ...
. The Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
is the busiest commuter railroad in North America and operates continually. Nassau County high school students often feature prominently as winners of the International Science and Engineering Fair and similar STEM
Stem or STEM may refer to:
Plant structures
* Plant stem, a plant's aboveground axis, made of vascular tissue, off which leaves and flowers hang
* Stipe (botany), a stalk to support some other structure
* Stipe (mycology), the stem of a mushro ...
-based academic awards. Biotechnology companies
Biotechnology is the integration of natural sciences and engineering sciences in order to achieve the application of organisms, cells, parts thereof and molecular analogues for products and services. The term ''biotechnology'' was first used by ...
and scientific research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific m ...
play a significant role in Long Island's economy,Accessed November 16, 2016. including research institute, research facilities at
Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment c ...
, Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
, New York Institute of Technology
The New York Institute of Technology (NYIT or New York Tech) is a private research university founded in 1955. It has two main campuses in New York—one in Old Westbury, on Long Island, and one in Manhattan. Additionally, it has a cyberse ...
, Plum Island Animal Disease Center
Plum Island Animal Disease Center (PIADC) is a United States federal research facility dedicated to the study of foreign animal diseases of livestock. It is part of the Department of Homeland Security Directorate for Science and Technology, an ...
, the New York University Tandon School of Engineering
The New York University Tandon School of Engineering (commonly referred to as Tandon) is the engineering and applied sciences school of New York University. Tandon is the second oldest private engineering and technology school in the United Sta ...
, the Hofstra Northwell School of Medicine, and the Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research
The Feinstein Institutes for Medical Research in Manhasset, Nassau County, New York, United States, on Long Island, constitute the research arm of Northwell Health. Feinstein is home to 50 research labs, 2,500 clinical research studies, and 5,00 ...
.
History
Early history


 By the year 1643, there were 14 indigenous tribes living on Long Island: Canarsee, Rockaway,
By the year 1643, there were 14 indigenous tribes living on Long Island: Canarsee, Rockaway, Metoac
Metoac is an erroneous term used by some to group together the Munsee-speaking Lenape (west), Quiripi-speaking Unquachog (center) and Pequot-speaking Montaukett (east) American Indians on what is now Long Island in New York state. The term wa ...
, Merrick, Massapequa, Nissequoge, Secatoag, Seatauket, Patchoag, Unquechogue, has Corchaug, Shinnecock, Manhasset and Montaukett
= Montauketts =
An indigenous Native American People.
Name and Identifications
The Montaukett (" Metoac" or Matouwac), currently more commonly known as Montauk. The meaning of the name ''Montauk'' is unknown.
Native Americans living on Long ...
.
The tribes used canoe
A canoe is a lightweight narrow water vessel, typically pointed at both ends and open on top, propelled by one or more seated or kneeling paddlers facing the direction of travel and using a single-bladed paddle.
In British English, the ter ...
s as a source of transportation, and since they lived by the shores, they went fishing. The fishermen used bows, arrows, and hooks to catch seafood such as crabs, scallops, and lobster. The farmers used fish for fertilizer and planted vegetables such as corn, beans, and squash, which were popular among the indigenous people. They were exceptional farmers; they had a great understanding of how the weather and soil affected the crops. Many of them hunted animals, such as deer, raccoon, and turkey in the forest.
The government that they set up was a participatory democracy and there was an alliance between the tribe
The term tribe is used in many different contexts to refer to a category of human social group. The predominant worldwide usage of the term in English is in the discipline of anthropology. This definition is contested, in part due to confl ...
s. Each tribe had their own territory and chief that was respected by other tribes. Prior to European contact, the Lenape
The Lenape (, , or Lenape , del, Lënapeyok) also called the Leni Lenape, Lenni Lenape and Delaware people, are an indigenous peoples of the Northeastern Woodlands, who live in the United States and Canada. Their historical territory inclu ...
people (named the ''Delaware'' by Europeans) inhabited the western end of Long Island, and spoke the Munsee
The Munsee (or Minsi or Muncee) or mə́n'si·w ( del, Monsiyok)Online Lenape Talking Dictionary, "Munsee Indians"Link/ref> are a subtribe of the Lenape, originally constituting one of the three great divisions of that nation and dwelling along ...
dialect of Lenape, part of the Algonquian language family. The Lenape (who were part of the Shinnecock Tribe) practiced record keeping and used wooden tablets, trees, and stones to keep record. They also used wampum
Wampum is a traditional shell bead of the Eastern Woodlands tribes of Native Americans. It includes white shell beads hand-fashioned from the North Atlantic channeled whelk shell and white and purple beads made from the quahog or Western Nor ...
belts to write down important messages. They also used their wampum to trade with the Europeans. The Lenape people, in specific, were seen as peacemakers by other indigenous tribes, although they would defend themselves if necessary. The Europeans admired their friendliness and their skills in mediation. ref
Giovanni da Verrazzano
Giovanni da Verrazzano ( , , often misspelled Verrazano in English; 1485–1528) was an Italian ( Florentine) explorer of North America, in the service of King Francis I of France.
He is renowned as the first European to explore the Atlanti ...
was the first European to record an encounter with the Lenapes, after entering what is now New York Bay
New York Bay is the large tidal body of water in the New York–New Jersey Harbor Estuary where the Hudson River, Raritan River, and Arthur Kill empty into the Atlantic Ocean between Sandy Hook and Rockaway Point.
Geography
New York Bay is usu ...
in 1524. The island's eastern portion was inhabited by speakers of the Mohegan-Pequot language
Mohegan-Pequot (also known as Mohegan-Pequot-Montauk, Secatogue, and Shinnecock-Poosepatuck; dialects in New England included Mohegan, Pequot, and Niantic; and on Long Island, Montaukett and Shinnecock) is an Algonquian language formerly sp ...
group of Algonquian language
Language is a structured system of communication. The structure of a language is its grammar and the free components are its vocabulary. Languages are the primary means by which humans communicate, and may be conveyed through a variety of ...
s; they were part of the Pequot and Narragansett people
The Narragansett people are an Algonquian American Indian tribe from Rhode Island. Today, Narragansett people are enrolled in the federally recognized Narragansett Indian Tribe. They gained federal recognition in 1983.
The tribe was nearly la ...
s inhabiting the area that now includes Connecticut
Connecticut () is the southernmost state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is bordered by Rhode Island to the east, Massachusetts to the north, New York (state), New York to the west, and Long Island Sound to the ...
and Rhode Island
Rhode Island (, like ''road'') is a U.S. state, state in the New England region of the Northeastern United States. It is the List of U.S. states by area, smallest U.S. state by area and the List of states and territories of the United States ...
.
In 1609, the English
English usually refers to:
* English language
* English people
English may also refer to:
Peoples, culture, and language
* ''English'', an adjective for something of, from, or related to England
** English national ...
navigator Henry Hudson
Henry Hudson ( 1565 – disappeared 23 June 1611) was an English sea explorer and navigator during the early 17th century, best known for his explorations of present-day Canada and parts of the northeastern United States.
In 1607 and 16 ...
explored the harbor and purportedly landed at Coney Island
Coney Island is a peninsular neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach and Manhattan Beach, Brooklyn, Manhattan Beach to its east, L ...
. Dutch explorer Adriaen Block
Adriaen (Arjan) Block (c. 1567 – buried April 27, 1627) was a Dutch private trader, privateer, and ship's captain who is best known for exploring the coastal and river valley areas between present-day New Jersey and Massachusetts during four v ...
followed in 1615, and is credited as the first European to determine that both Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
and Long Island are islands.
In 1636, Charles I of England
Charles I (19 November 1600 – 30 January 1649) was King of England, Scotland, and Ireland from 27 March 1625 until his execution in 1649. He was born into the House of Stuart as the second son of King James VI of Scotland, but after ...
, a Stuart, rewarded Scottish courtier
A courtier () is a person who attends the royal court of a monarch or other royalty. The earliest historical examples of courtiers were part of the retinues of rulers. Historically the court was the centre of government as well as the official ...
, diplomat, and colonial governor William Alexander's service to the Crown by creating him Lord Alexander of Tullibody
Tullibody ( gd, Tulach Bòide), is a town set in the Central Lowlands of Scotland. It lies north of the River Forth near to the foot of the Ochil Hills within the Forth Valley. The town is south-west of Alva, north-west of Alloa and east-n ...
and Viscount of Stirling
A viscount ( , for male) or viscountess (, for female) is a title used in certain European countries for a noble of varying status.
In many countries a viscount, and its historical equivalents, was a non-hereditary, administrative or judici ...
. On April 22 of that year Charles told the Plymouth Colony
Plymouth Colony (sometimes Plimouth) was, from 1620 to 1691, the first permanent English colony in New England and the second permanent English colony in North America, after the Jamestown Colony. It was first settled by the passengers on the ...
, which had laid claim to Long Island but had not settled it, to cede it to Alexander. When his agent James Farret arrived in New Amsterdam
New Amsterdam ( nl, Nieuw Amsterdam, or ) was a 17th-century Dutch settlement established at the southern tip of Manhattan Island that served as the seat of the colonial government in New Netherland. The initial trading ''factory'' gave rise ...
in 1637 to present his claim of English sovereignty he was arrested and sent to prison in Holland (but escaped).
In 1639, Lion Gardiner
Lion Gardiner (1599–1663) was an English engineer and colonist who founded the first English settlement in New York, acquiring land on eastern Long Island. He had been working in the Netherlands and was hired to construct fortifications on th ...
purchased an islet off of today's East Hampton, Gardiners Island
Gardiner's Island is a small island in the Town of East Hampton, New York, in Eastern Suffolk County. It is located in Gardiner's Bay between the two peninsulas at the east end of Long Island. It is long, wide and has of coastline.
The isl ...
, from the Montaukett, received Farret's approval of the transaction on behalf of Alexander (by then the 1st Earl of Stirling and Viscount Canada), and subsequently received a royal patent establishing him as Lord of the Manor
Lord of the Manor is a title that, in Anglo-Saxon England, referred to the landholder of a rural estate. The lord enjoyed manorial rights (the rights to establish and occupy a residence, known as the manor house and demesne) as well as seig ...
over it.
In 1640, English colonists attempted to settle at Cow Bay at what today is Port Washington. After an alert by Native leader Penhawitz, the colonists were arrested by the Dutch but released after saying they were mistaken about the title.
Through Farret (who personally received Shelter Island and Robins Island), Alexander in turn sold most of the eastern island to the New Haven Colony
The New Haven Colony was a small English colony in North America from 1638 to 1664 primarily in parts of what is now the state of Connecticut, but also with outposts in modern-day New York, New Jersey, Pennsylvania, and Delaware.
The history of ...
and Connecticut Colony
The ''Connecticut Colony'' or ''Colony of Connecticut'', originally known as the Connecticut River Colony or simply the River Colony, was an English colony in New England which later became Connecticut. It was organized on March 3, 1636 as a settl ...
.
In spite of these shifting claims to title and absentee land sales, European settlers continued to purchase land directly from the Indigenous people. In 1655 they split the acquired land amongst themselves and continued to search the island for more land for settlement. Other parts of indigenous land were bought, areas that are now known as Brookhaven, Bellport, and South haven. These purchases occurred on June 10, 1664, the exchange was four coats and what is now $16.25.
The white settlers and the indigenous people lived amicably together for a while. During King Philip's War
King Philip's War (sometimes called the First Indian War, Metacom's War, Metacomet's War, Pometacomet's Rebellion, or Metacom's Rebellion) was an armed conflict in 1675–1676 between indigenous inhabitants of New England and New England coloni ...
in 1675, the English governor of New York ordered all canoes that were east of Hell Gate to be confiscated. This was done to prevent the Indigenous people from helping their native allies on the mainland, who were attacking settlers there.
After the Dutch began to move into Manhattan many of the indigenous people moved to Pennsylvania
Pennsylvania (; ( Pennsylvania Dutch: )), officially the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, is a state spanning the Mid-Atlantic, Northeastern, Appalachian, and Great Lakes regions of the United States. It borders Delaware to its southeast, ...
and Delaware
Delaware ( ) is a state in the Mid-Atlantic region of the United States, bordering Maryland to its south and west; Pennsylvania to its north; and New Jersey and the Atlantic Ocean to its east. The state takes its name from the adjacent ...
. Many of them who stayed behind died from smallpox as North Americans had never been exposed to the disease before, resulting in large scale deaths due to lack of antibodies and natural resistance which Eurasian peoples gained.
Native American land deed
In common law, a deed is any legal instrument in writing which passes, affirms or confirms an interest, right, or property and that is signed, attested, delivered, and in some jurisdictions, sealed. It is commonly associated with transferrin ...
s recorded by the Dutch from 1636 state that the Indians referred to Long Island as ' (' and ' were other spellings in the transliteration of Lenape). ' was one of the terms for wampum
Wampum is a traditional shell bead of the Eastern Woodlands tribes of Native Americans. It includes white shell beads hand-fashioned from the North Atlantic channeled whelk shell and white and purple beads made from the quahog or Western Nor ...
(commemorative stringed shell beads, for a while also used as currency by colonists in trades with the Lenape), and is also translated as "loose" or "scattered", which may refer either to the wampum or to Long Island. The name "'t Lange Eylandt alias Matouwacs" appears in Dutch maps from the 1650s. Later, the English referred to the land as "Nassau Island", after the Dutch Prince William of Nassau, Prince of Orange (who later also ruled as King William III of England
England is a country that is part of the United Kingdom. It shares land borders with Wales to its west and Scotland to its north. The Irish Sea lies northwest and the Celtic Sea to the southwest. It is separated from continental Europe ...
). It is unclear when the name "Nassau Island" was discontinued. Another indigenous name from colonial time, Paumanok
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state of New York, part of the New York metropolitan area. With over 8 million people, Long Island is the most populous island in the United States and the 18th- ...
, comes from the Native American name for Long Island and means "the island that pays tribute."
The very first European settlements on Long Island were by settlers from England and its colonies in present-day New England
New England is a region comprising six states in the Northeastern United States: Connecticut, Maine, Massachusetts, New Hampshire, Rhode Island, and Vermont. It is bordered by the state of New York to the west and by the Canadian provinces ...
. Lion Gardiner settled nearby Gardiners Island. The first settlement on the geographic Long Island itself was on October 21, 1640, when Southold was established by the Rev. John Youngs and settlers from New Haven
New Haven is a city in the U.S. state of Connecticut. It is located on New Haven Harbor on the northern shore of Long Island Sound in New Haven County, Connecticut and is part of the New York City metropolitan area. With a population of 134,023 ...
, Connecticut. Peter Hallock, one of the settlers, drew the long straw and was granted the honor to step ashore first. He is considered the first New World settler on Long Island. Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
was settled in the same year. Hempstead followed in 1644, East Hampton in 1648, Huntington in 1653, Brookhaven in 1655, and Smithtown in 1665.
While the eastern region of Long Island was first settled by the English, the western portion of Long Island was settled by the Dutch; until 1664, the jurisdiction of Long Island was split between the Dutch and English, roughly at the present border between Nassau County and Suffolk County. The Dutch founded six towns in present-day Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
beginning in 1645. These included: Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, Gravesend
Gravesend is a town in northwest Kent, England, situated 21 miles (35 km) east-southeast of Charing Cross (central London) on the south bank of the River Thames and opposite Tilbury in Essex. Located in the diocese of Rochester, it is ...
, Flatlands, Flatbush, New Utrecht, and Bushwick
Bushwick is a neighborhood in the northern part of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. It is bounded by the neighborhood of Ridgewood, Queens, to the northeast; Williamsburg to the northwest; East New York and the cemeteries of Highland Pa ...
. The Dutch had granted an English settlement in Hempstead, New York
The Town of Hempstead (also known historically as South Hempstead) is the largest of the three towns in Nassau County (alongside North Hempstead and Oyster Bay) in the U.S. state of New York. It occupies the southwestern part of the county, o ...
(now in Nassau County) in 1644, but after a boundary dispute they drove out English settlers from the Oyster Bay area. However, in 1664, the English returned to take over the Dutch colony of New Netherland
New Netherland ( nl, Nieuw Nederland; la, Novum Belgium or ) was a 17th-century colonial province of the Dutch Republic that was located on the east coast of what is now the United States. The claimed territories extended from the Delmarva ...
, including Long Island.
The 1664 land patent granted to the Duke of York
Duke of York is a title of nobility in the Peerage of the United Kingdom. Since the 15th century, it has, when granted, usually been given to the second son of English (later British) monarchs. The equivalent title in the Scottish peerage was ...
included all islands in Long Island Sound. The Duke of York held a grudge against Connecticut, as New Haven had hidden three of the judges (John Dixwell
John Dixwell (1607 – 18 March 1689) was an English man who sat in Parliament, fought for the Parliamentary cause in the English Civil War, and was one of the Commissioners who sat in judgement on King Charles I and condemned him to death. At ...
, Edward Whalley
Edward Whalley (c. 1607 – c. 1675) was an English military leader during the English Civil War and was one of the regicides who signed the death warrant of King Charles I of England.
Early career
The exact dates of his birth and death are u ...
and William Goffe) who sentenced the Duke's father, King Charles I, to death in 1649. Settlers throughout Suffolk County pressed to stay part of Connecticut, but Governor Sir Edmund Andros
Sir Edmund Andros (6 December 1637 – 24 February 1714) was an English colonial administrator in British America. He was the governor of the Dominion of New England during most of its three-year existence. At other times, Andros served ...
threatened to eliminate the settlers' rights to land if they did not yield, which they did by 1676.
All of Long Island (as well as the islands between it and Connecticut) became part of the Province of New York
The Province of New York (1664–1776) was a British proprietary colony and later royal colony on the northeast coast of North America. As one of the Middle Colonies, New York achieved independence and worked with the others to found the U ...
within the Shire of York. Present-day Suffolk County was designated as the ''East Riding'' (of Yorkshire), present-day Brooklyn was part of the ''West Riding'', and present-day Queens and Nassau were part of the larger ''North Riding''. In 1683, Yorkshire was dissolved and the three original counties on Long Island were established: Kings, Queens, and Suffolk.
18th and 19th centuries


William Floyd
William Floyd (December 17, 1734 – August 4, 1821) was an American Founding Father, wealthy farmer, and political leader from New York. Floyd served as a delegate to the Continental Congress and was a signer of the Continental Association and ...
was born on Long Island on December 17, 1734. His family had emigrated to America in 1654 and by the time of his birth were well established and wealthy. He was a member of the Suffolk County Militia in the early conflict with Britain, attaining the rank of Major General. In 1774 he was chosen as a representative from New York to the First Continental Congress
The First Continental Congress was a meeting of delegates from 12 of the 13 British colonies that became the United States. It met from September 5 to October 26, 1774, at Carpenters' Hall in Philadelphia, Pennsylvania, after the British Nav ...
. His property was destroyed by the British and Tory sympathizers. In 1789 he was elected to the United States House of Representatives
The United States House of Representatives, often referred to as the House of Representatives, the U.S. House, or simply the House, is the lower chamber of the United States Congress, with the Senate being the upper chamber. Together they ...
, serving until 1791. Francis Lewis
Francis Lewis (March 21, 1713 – December 31, 1802) was an American merchant and a Founding Father of the United States. He was a signatory of the United States Declaration of Independence and Articles of Confederation as a representative of Ne ...
from Brookhaven on Long Island was another signer of the Declaration that also had his home destroyed by the British, who then imprisoned his wife. George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
managed her release by having the wives of two wealthy Philadelphia Tories arrested, then exchanging them for Mrs. Lewis.
Marinus Willett
Colonel Marinus Willett (July 31, 1740 – August 22, 1830) was an American military officer, politician and merchant who served as the mayor of New York City from 1807 to 1808. Willett is best known for his actions during the American Revolu ...
of Jamaica, Queens
Jamaica is a neighborhood in the New York City borough of Queens. It is mainly composed of a large commercial and retail area, though part of the neighborhood is also residential. Jamaica is bordered by Hollis to the east; St. Albans, Springf ...
enlisted in the colonial militia
Colonial troops or colonial army refers to various military units recruited from, or used as garrison troops in, colonial territories.
Colonial background
Such colonies may lie overseas or in areas dominated by neighbouring land powers such ...
after the French and Indian War
The French and Indian War (1754–1763) was a theater of the Seven Years' War, which pitted the North American colonies of the British Empire against those of the French, each side being supported by various Native American tribes. At the st ...
broke out in 1754. He participated in the Ticonderoga campaign and the capture of Fort Frontenac in 1758. Joining the revolutionary Sons of Liberty
The Sons of Liberty was a loosely organized, clandestine, sometimes violent, political organization active in the Thirteen American Colonies founded to advance the rights of the colonists and to fight taxation by the British government. It pl ...
in the 1770s, Willett shortly thereafter enlisted in the Continental Army
The Continental Army was the army of the United Colonies (the Thirteen Colonies) in the Revolutionary-era United States. It was formed by the Second Continental Congress after the outbreak of the American Revolutionary War, and was establis ...
in 1775. Serving in the 1st New York, he took part in the Invasion of Quebec before transferring to the 3rd New York in 1776. Seeing action at Monmouth, Willett then participated in the 1778 Sullivan Campaign
The 1779 Sullivan Expedition (also known as the Sullivan-Clinton Expedition, the Sullivan Campaign, and the Sullivan-Clinton Genocide) was a United States military campaign during the American Revolutionary War, lasting from June to October 177 ...
. He was made the colonel
Colonel (abbreviated as Col., Col or COL) is a senior military officer rank used in many countries. It is also used in some police forces and paramilitary organizations.
In the 17th, 18th and 19th centuries, a colonel was typically in charge ...
of the 5th New York in 1780 and the Tryon County militia in 1781, where he fought at Johnstown. On August 22, 1830, Willett died and was buried in the graveyard of Trinity Church. The Willets Point
Willets Point, also known locally as the Iron Triangle, is an industrial neighborhood within Corona, in the New York City borough of Queens. Located east of Citi Field near the Flushing River, it is known for its automobile shops and junkyard ...
and the accompanying Mets-Willets Point station is named in his honor.
Early in the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, the island was captured by the British from General George Washington
George Washington (February 22, 1732, 1799) was an American military officer, statesman, and Founding Father who served as the first president of the United States from 1789 to 1797. Appointed by the Continental Congress as commander of ...
in the Battle of Long Island
The Battle of Long Island, also known as the Battle of Brooklyn and the Battle of Brooklyn Heights, was an action of the American Revolutionary War fought on August 27, 1776, at the western edge of Long Island in present-day Brooklyn, New Yor ...
, a decisive battle after which Washington narrowly evacuated his troops from Brooklyn Heights
Brooklyn Heights is a residential neighborhood within the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Old Fulton Street near the Brooklyn Bridge on the north, Cadman Plaza West on the east, Atlantic Avenue on the south, ...
under a dense fog. After the British victory on Long Island, many Patriots withdrew, leaving mostly Loyalists
Loyalism, in the United Kingdom, its overseas territories and its former colonies, refers to the allegiance to the British crown or the United Kingdom. In North America, the most common usage of the term refers to loyalty to the British Cro ...
behind. The island was a British stronghold until the end of the war in 1783.
General Washington based his espionage
Espionage, spying, or intelligence gathering is the act of obtaining secret or confidential information ( intelligence) from non-disclosed sources or divulging of the same without the permission of the holder of the information for a tang ...
activities on Long Island, due to the western part of the island's proximity to the British military
The British Armed Forces, also known as His Majesty's Armed Forces, are the military forces responsible for the defence of the United Kingdom, its Overseas Territories and the Crown Dependencies. They also promote the UK's wider interests, su ...
headquarters in New York City. The Culper Spy Ring included agents operating between Setauket and Manhattan. This ring alerted Washington to valuable British secrets, including the treason of Benedict Arnold
Benedict Arnold ( Brandt (1994), p. 4June 14, 1801) was an American military officer who served during the Revolutionary War. He fought with distinction for the American Continental Army and rose to the rank of major general before defect ...
and a plan to use counterfeiting to induce economic sabotage.
Long Island's colonists served both Loyalist and Patriot causes, with many prominent families divided among both sides. During the occupation British troops used a number of civilian structures for defense and demanded to be quartered in the homes of civilians. A number of structures from this era remain. Among these are Raynham Hall
Raynham Hall is a country house in Norfolk, England. For nearly 400 years it has been the seat of the Townshend family. The hall gave its name to the five estate villages, known as The Raynhams, and is reported to be haunted, providing the sce ...
, the Oyster Bay home of patriot spy Robert Townsend, and the Caroline Church in Setauket, which contains bullet holes from a skirmish known as the Battle of Setauket. Also in existence is a reconstruction of Brooklyn's Old Stone House, on the site of the Maryland 400
The Maryland 400 were members of the 1st Maryland Regiment who repeatedly charged a numerically superior British force during the Battle of Long Island during the American Revolutionary War, Revolutionary War, sustaining heavy casualties, but al ...
's celebrated last stand during the Battle of Long Island
The Battle of Long Island, also known as the Battle of Brooklyn and the Battle of Brooklyn Heights, was an action of the American Revolutionary War fought on August 27, 1776, at the western edge of Long Island in present-day Brooklyn, New Yor ...
.
In the 19th century, Long Island was still mainly rural
In general, a rural area or a countryside is a geographic area that is located outside towns and cities. Typical rural areas have a low population density and small settlements. Agricultural areas and areas with forestry typically are de ...
and devoted to agriculture
Agriculture or farming is the practice of cultivating plants and livestock. Agriculture was the key development in the rise of sedentary human civilization, whereby farming of domesticated species created food surpluses that enabled people ...
. The predecessor to the Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
(LIRR) began service in 1836 from the South Ferry in Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, through the remainder of Brooklyn, to Jamaica
Jamaica (; ) is an island country situated in the Caribbean Sea. Spanning in area, it is the third-largest island of the Greater Antilles and the Caribbean (after Cuba and Hispaniola). Jamaica lies about south of Cuba, and west of Hispa ...
in Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
. The line was completed to the east end of Long Island in 1844 (as part of a plan for transportation to Boston). Competing railroads (soon absorbed by the LIRR) were built along the south shore to accommodate travellers from those more populated areas. For the century from 1830 until 1930, total population roughly doubled every twenty years, with more dense development in areas near Manhattan. Several cities were incorporated, such as the "City of Brooklyn" in Kings County, and Long Island City
Long Island City (LIC) is a residential and commercial neighborhood on the extreme western tip of Queens, a borough in New York City. It is bordered by Astoria to the north; the East River to the west; New Calvary Cemetery in Sunnyside to the ...
in Queens.
Until the 1883 completion of the Brooklyn Bridge
The Brooklyn Bridge is a hybrid cable-stayed/ suspension bridge in New York City, spanning the East River between the boroughs of Manhattan and Brooklyn. Opened on May 24, 1883, the Brooklyn Bridge was the first fixed crossing of the East Rive ...
, the only means of travel between Long Island and the rest of the United States was by boat or ship. As other bridges and tunnels were constructed, areas of the island began to be developed as residential suburbs, first around the railroads that offered commuting into the city. On January 1, 1898, Kings County and portions of Queens County were consolidated into the "City of Greater New York
The City of Greater New York was the term used by many politicians and scholars for the expanded City of New York created on January 1, 1898, by consolidating the existing City of New York with Brooklyn, western Queens County, and Staten Is ...
", abolishing all cities and towns within them. The easternmost of Queens County, which were not part of the consolidation plan,
separated from Queens in 1899 to form Nassau County.
At the close of the 19th century, wealthy industrialist
A business magnate, also known as a tycoon, is a person who has achieved immense wealth through the ownership of multiple lines of enterprise. The term characteristically refers to a powerful entrepreneur or investor who controls, through per ...
s who made vast fortunes during the Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Wes ...
began to construct large "baronial" country estates in Nassau County communities along the North Shore of Long Island, favoring the many properties
Property is the ownership of land, resources, improvements or other tangible objects, or intellectual property.
Property may also refer to:
Mathematics
* Property (mathematics)
Philosophy and science
* Property (philosophy), in philosophy an ...
with water views. Proximity to Manhattan attracted such men as J. P. Morgan
John Pierpont Morgan Sr. (April 17, 1837 – March 31, 1913) was an American financier and investment banker who dominated corporate finance on Wall Street throughout the Gilded Age. As the head of the banking firm that ultimately became known ...
, William K. Vanderbilt
William Kissam "Willie" Vanderbilt I (December 12, 1849 – July 22, 1920) was an American heir, businessman, philanthropist and horsebreeder. Born into the Vanderbilt family, he managed his family's railroad investments.
Early life
William Kiss ...
, and Charles Pratt
Charles Pratt (October 2, 1830 – May 4, 1891) was an American businessman. Pratt was a pioneer of the U.S. petroleum industry, and he established his kerosene refinery Astral Oil Works in Brooklyn, New York. He then lived with his growing fam ...
, whose estates led to this area being nicknamed the Gold Coast. This period and the area was immortalized in fiction, such as F. Scott Fitzgerald's ''The Great Gatsby
''The Great Gatsby'' is a 1925 novel by American writer F. Scott Fitzgerald. Set in the Jazz Age on Long Island, near New York City, the novel depicts first-person narrator Nick Carraway's interactions with mysterious millionaire Jay Gatsby ...
'', which has also been adapted in films
A film also called a movie, motion picture, moving picture, picture, photoplay or (slang) flick is a work of visual art that simulates experiences and otherwise communicates ideas, stories, perceptions, feelings, beauty, or atmospher ...
.
20th century
Charles Lindbergh
Charles Augustus Lindbergh (February 4, 1902 – August 26, 1974) was an American aviator, military officer, author, inventor, and activist. On May 20–21, 1927, Lindbergh made the first nonstop flight from New York City to Paris, a distance o ...
lifted off from Roosevelt Field
Roosevelt Field is a former airport, located east-southeast of Mineola, Long Island, New York. Originally called the Hempstead Plains Aerodrome, or sometimes Hempstead Plains field or the Garden City Aerodrome, it was a training field (Hazel ...
with his ''Spirit of Saint Louis
The ''Spirit of St. Louis'' (formally the Ryan NYP, registration: N-X-211) is the custom-built, single-engine, single-seat, high-wing monoplane that was flown by Charles Lindbergh on May 20–21, 1927, on the first solo nonstop transatlanti ...
'' for his historic 1927 solo flight to Europe, one of the events that helped to establish Long Island as an early center of aviation
Aviation includes the activities surrounding mechanical flight and the aircraft industry. ''Aircraft'' includes airplane, fixed-wing and helicopter, rotary-wing types, morphable wings, wing-less lifting bodies, as well as aerostat, lighter- ...
during the 20th century. Other famous aviators such as Wiley Post
Wiley Hardeman Post (November 22, 1898 – August 15, 1935) was a famed American aviator during the interwar period and the first pilot to fly solo around the world. Also known for his work in high-altitude flying, Post helped develop o ...
originated notable flights from Floyd Bennett Field
Floyd Bennett Field is an airfield in the Marine Park neighborhood of southeast Brooklyn in New York City, along the shore of Jamaica Bay. The airport originally hosted commercial and general aviation traffic before being used as a naval air ...
in Brooklyn, which became the first major airport serving New York City before it was superseded by the opening of La Guardia Airport in 1939. Long Island was also the site of Mitchel Air Force Base and was a major center of military aircraft production by companies such as Grumman
The Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, later Grumman Aerospace Corporation, was a 20th century American producer of military and civilian aircraft. Founded on December 6, 1929, by Leroy Grumman and his business partners, it merged in 1994 ...
and Fairchild Aircraft
Fairchild was an American aircraft and aerospace manufacturing company based at various times in Farmingdale, New York; Hagerstown, Maryland; and San Antonio, Texas.
History
Early aircraft
The company was founded by Sherman Fairchild in ...
during World War II and for some decades afterward. Aircraft production on Long Island extended all the way into the Space Age – Grumman was one of the major contractors that helped to build the early lunar flight and space shuttle vehicles. Although the aircraft companies eventually ended their Long Island operations and the early airports were all later closed – Roosevelt Field, for instance, became the site of a major shopping mall – the Cradle of Aviation Museum
The Cradle of Aviation Museum is an aerospace museum located in Garden City, New York on Long Island, established to commemorate Long Island's part in the history of aviation. It is located on land once part of Mitchel Air Force Base which, to ...
on the site of the former Mitchel Field documents the Island's key role in the history of aviation.
From the 1920s to the 1940s, Long Island began the transformation from backwoods and farms as developers created numerous suburbs. Numerous branches of the LIRR already enabled commuting from the suburbs to Manhattan. Robert Moses
Robert Moses (December 18, 1888 – July 29, 1981) was an American urban planner and public official who worked in the New York metropolitan area during the early to mid 20th century. Despite never being elected to any office, Moses is regarded ...
engineered various automobile parkway
A parkway is a landscaped thoroughfare.''"parkway."''Webster's Third New International Dictionary, Unabridged. Merriam-Webster, 2002. http://unabridged.merriam-webster.com (14 Apr. 2007). The term is particularly used for a roadway in a park or ...
projects to span the island, and developed beaches and state parks for the enjoyment of residents and visitors from the city. Gradually, development also followed these parkways, with various communities springing up along the more traveled routes.
After World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
, suburban development increased with incentives under the G.I. Bill, and Long Island's population skyrocketed, mostly in Nassau County and western Suffolk County. Second and third-generation children of immigrants moved out to eastern Long Island to settle in new housing developments built during the post-war boom. Levittown became noted as a suburb, where housing construction was simplified to be produced on a large scale. These provided opportunities for white World War II military veterans returning home to buy houses and start a family. In his 1966 book, ''My Private America'' (''Moja prywatna Ameryka''), Kazimierz Wierzyński
Kazimierz Wierzyński (Drohobycz, Kingdom of Galicia and Lodomeria, 27 August 1894 – 13 February 1969, London) was a Polish poet and journalist; an elected member of the prestigious Polish Academy of Literature in the Second Polish Repu ...
, a Polish poet who could not go back to Poland after World War II, describes Polish farmers living there, as "walking novels".
21st century
By the start of the 21st century, a number of Long Island communities had converted their assets from industrial uses topost-industrial
In sociology, the post-industrial society is the stage of society's development when the service sector generates more wealth than the manufacturing sector of the economy.
The term was originated by Alain Touraine and is closely related to s ...
roles. Brooklyn reversed decades of population decline and factory closings to resurface as a globally renowned cultural and intellectual hotbed. Gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
has affected much of Brooklyn and a portion of Queens, relocating a sizeable swath of New York City's population. On eastern Long Island, such villages as Port Jefferson, Patchogue
Patchogue (, ) is a village in Suffolk County, New York. The population was 11,798 at the time of the 2010 census. Patchogue is part of the town of Brookhaven, on the south shore of Long Island, adjoining Great South Bay. It is officially kno ...
, and Riverhead have been changed from inactive shipbuilding
Shipbuilding is the construction of ships and other floating vessels. It normally takes place in a specialized facility known as a shipyard. Shipbuilders, also called shipwrights, follow a specialized occupation that traces its roots to bef ...
and mill towns into tourist-centric commercial centers with cultural attractions.
The descendants of late 19th and early 20th-century immigrants from southern
Southern may refer to:
Businesses
* China Southern Airlines, airline based in Guangzhou, China
* Southern Airways, defunct US airline
* Southern Air, air cargo transportation company based in Norwalk, Connecticut, US
* Southern Airways Express, M ...
and eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
, and black migrants from the South, have been followed by more recent immigrants from Asia
Asia (, ) is one of the world's most notable geographical regions, which is either considered a continent in its own right or a subcontinent of Eurasia, which shares the continental landmass of Afro-Eurasia with Africa. Asia covers an are ...
and Latin America
Latin America or
* french: Amérique Latine, link=no
* ht, Amerik Latin, link=no
* pt, América Latina, link=no, name=a, sometimes referred to as LatAm is a large cultural region in the Americas where Romance languages — languages derived ...
. Long Island has many ethnic Irish, Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
, and Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
, as well as an increasing numbers of Asians
Asian people (or Asians, sometimes referred to as Asiatic people)United States National Library of Medicine. Medical Subject Headings. 2004. November 17, 200Nlm.nih.gov: ''Asian Continental Ancestry Group'' is also used for categorical purpos ...
and Hispanics
The term ''Hispanic'' ( es, hispano) refers to people, cultures, or countries related to Spain, the Spanish language, or Hispanidad.
The term commonly applies to countries with a cultural and historical link to Spain and to viceroyalties for ...
, reflecting later migrations.
Geography


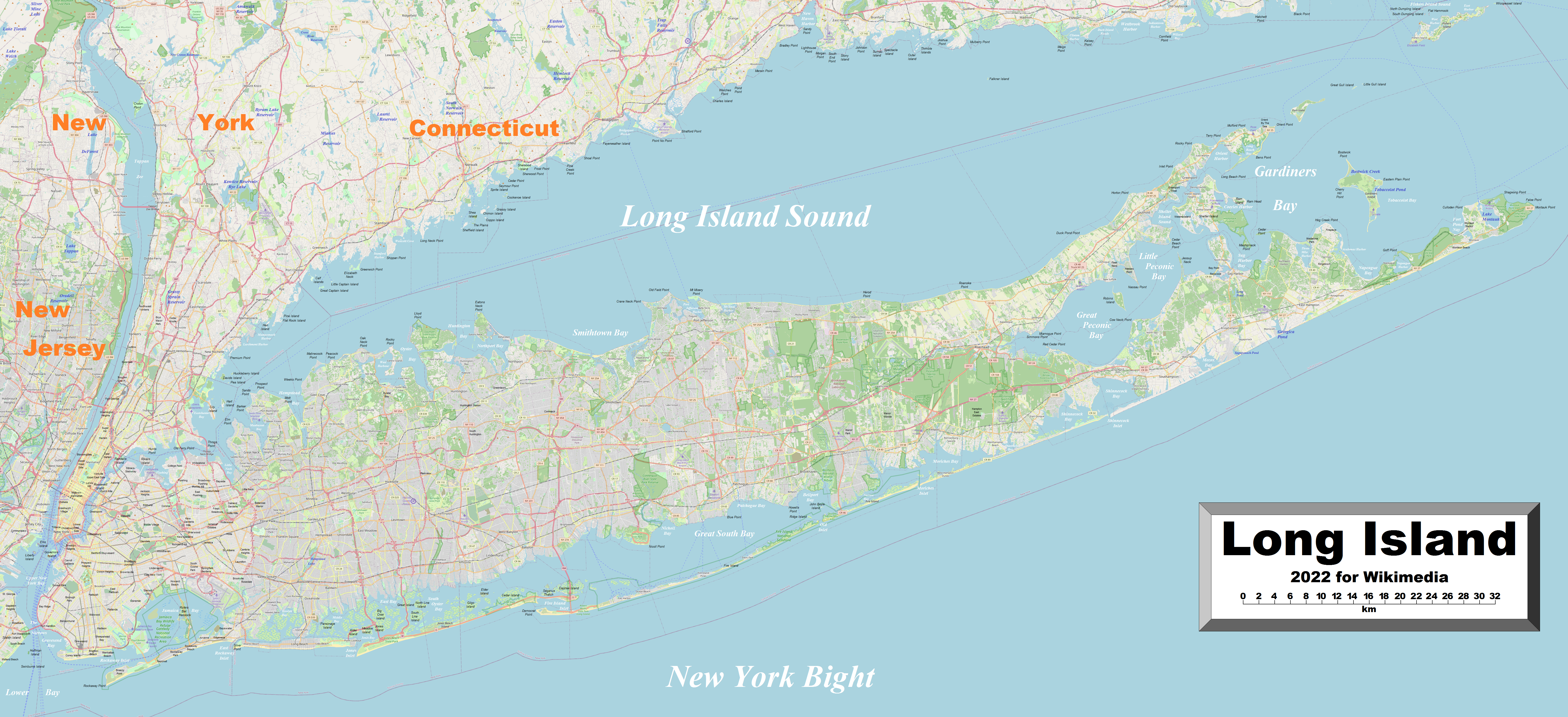
 The westernmost end of Long Island contains the New York City
The westernmost end of Long Island contains the New York City boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
of Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
(Kings County) and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
(Queens County). The central and eastern portions contain the suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separ ...
an Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
and Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
counties. However, colloquial usage of the term "Long Island" usually refers only to Nassau and Suffolk counties. For example, the Federal Reserve Bank of New York
The Federal Reserve Bank of New York is one of the 12 Federal Reserve Banks of the United States. It is responsible for the Second District of the Federal Reserve System, which encompasses the State of New York, the 12 northern counties of Ne ...
has a district named "Long Island (Nassau-Suffolk Metro Division)." At least as late as 1911, locations in Queens were still commonly referred to as being on Long Island. Some institutions in the New York City section of the island use the island's names, like Long Island University
Long Island University (LIU) is a private university with two main campuses, LIU Post and LIU Brooklyn, in the U.S. state of New York. It offers more than 500 academic programs at its main campuses, online, and at multiple non-residential. LIU ...
and Long Island Jewish Medical Center.
In 1985, the U.S. Supreme Court ruled in '' United States v. Maine'' that Long Island is integrally related to the mainland enough that Long Island Sound and the western part of Block Island Sound
Block Island Sound is a strait in the open Atlantic Ocean, approximately wide, separating Block Island from the coast of mainland Rhode Island. On the west, it extends to Montauk Point on the eastern tip of Long Island, as well as Plum Isl ...
constitute a "juridical bay" for the purpose of determining maritime state boundaries. In the popular media this has been often misinterpreted as a ruling that Long Island is legally not an island. The United States Board on Geographic Names
The United States Board on Geographic Names (BGN) is a federal body operating under the United States Secretary of the Interior. The purpose of the board is to establish and maintain uniform usage of geographic names throughout the federal govern ...
still considers Long Island an island, because it is surrounded by water.
There are few tall buildings on Long Island. Nassau County is more densely developed than Suffolk County. While affluent overall, Nassau County has pockets of more pronounced wealth with estates covering greater acreage within the Gold Coast of the North Shore and the Five Towns area on the South Shore. South Shore communities are built along protected wetland
A wetland is a distinct ecosystem that is flooded or saturated by water, either permanently (for years or decades) or seasonally (for weeks or months). Flooding results in oxygen-free (Anoxic waters, anoxic) processes prevailing, especially in t ...
s of the island and contain white sandy beaches of Outer Barrier Islands
The Outer Barrier, also known as the Long Island and New York City barrier islands, refers to the string of barrier islands that divide the lagoons south of Long Island, New York from the Atlantic Ocean. These islands include Long Beach Barrier ...
fronting on the Atlantic Ocean. Dutch and English settlers from the time before the American Revolutionary War
The American Revolutionary War (April 19, 1775 – September 3, 1783), also known as the Revolutionary War or American War of Independence, was a major war of the American Revolution. Widely considered as the war that secured the independence of t ...
, as well as communities of Native Americans, populated the island. The 19th century saw the infusion of the wealthiest Americans in the so-called Gold Coast of the North Shore, where wealthy Americans and Europeans in the Gilded Age
In United States history, the Gilded Age was an era extending roughly from 1877 to 1900, which was sandwiched between the Reconstruction era and the Progressive Era. It was a time of rapid economic growth, especially in the Northern and Wes ...
built lavish country homes.
In its easternmost sections, Suffolk County remains semi-rural, as in Greenport on the North Fork and some of the periphery of the area prominently known as The Hamptons
The Hamptons, part of the East End of Long Island, consist of the towns of Southampton and East Hampton, which together comprise the South Fork of Long Island, in Suffolk County, New York. The Hamptons are a popular seaside resort and one o ...
, although summer tourism swells the population in those areas. The North Fork peninsula of Suffolk County's East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
has developed a burgeoning wine region
This list of wine-producing regions catalogues significant growing regions where vineyards are planted. Wine grapes mostly grow between the 30th and the 50th degree of latitude, in both the Northern and Southern hemispheres. Grapes will sometimes ...
. In addition, the South Fork peninsula is known for beach communities, including the Hamptons, and for the Montauk Point Light
The Montauk Point Light, or Montauk Point Lighthouse, is a lighthouse located adjacent to Montauk Point State Park, at the easternmost point of Long Island, in the hamlet of Montauk in the Town of East Hampton in Suffolk County, New York. T ...
house at the eastern tip of the island. The Pine Barrens is a preserved pine
A pine is any conifer tree or shrub in the genus ''Pinus'' () of the family (biology), family Pinaceae. ''Pinus'' is the sole genus in the subfamily Pinoideae. The World Flora Online created by the Royal Botanic Gardens, Kew and Missouri Botanic ...
forest encompassing much of eastern Suffolk County.


Geology
A detailedgeomorphological
Geomorphology (from Ancient Greek: , ', "earth"; , ', "form"; and , ', "study") is the scientific study of the origin and evolution of topographic and bathymetric features created by physical, chemical or biological processes operating at or ...
study of Long Island provides evidence of glacial history of the kame
A kame, or ''knob'', is a glacial landform, an irregularly shaped hill or mound composed of sand, gravel and till that accumulates in a depression on a retreating glacier, and is then deposited on the land surface with further melting of the ...
and terminal moraines of the island which were formed by the advance and retreat of two ice sheet
In glaciology, an ice sheet, also known as a continental glacier, is a mass of glacial ice that covers surrounding terrain and is greater than . The only current ice sheets are in Antarctica and Greenland; during the Last Glacial Period at La ...
s. Long Island, as part of the Outer Lands
The Outer Lands is the prominent terminal moraine archipelagic region off the southern coast of New England in the United States. This eight-county region of Massachusetts, Rhode Island, and New York, comprises the peninsula of Cape Cod and th ...
region, is formed largely of two spines of glacial moraine, with a large, sandy outwash plain beyond. These moraines consist of gravel and loose rock left behind during the two most recent pulses of Wisconsin glaciation
The Wisconsin Glacial Episode, also called the Wisconsin glaciation, was the most recent glacial period of the North American ice sheet complex. This advance included the Cordilleran Ice Sheet, which nucleated in the northern North American Cord ...
during the ice ages some 21,000 years ago (19,000 BC). The northern moraine, which directly abuts the North Shore of Long Island
The North Shore of Long Island is the area along the northern coast of New York's Long Island bordering Long Island Sound. Known for its extreme wealth and lavish estates, the North Shore exploded into affluence at the turn of the 20th century, ...
at points, is known as the Harbor Hill moraine. The more southerly moraine, known as the Ronkonkoma moraine
The Ronkonkoma Moraine, in the geography of Long Island, forms the southern of two ridges along Long Island's "backbone."
Description
The Ronkonkoma Moraine, a terminal moraine, predates the Harbor Hill Moraine (which reached Long Island during ...
, forms the "backbone" of Long Island; it runs primarily through the very center of Long Island, roughly coinciding with the length of the Long Island Expressway
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music me ...
.
The land to the south of this moraine to the South Shore is the outwash plain of the last glacier. One part of the outwash plain was known as the Hempstead Plains, and this land contained one of the few natural prairies to exist east of the Appalachian Mountains. The glacier
A glacier (; ) is a persistent body of dense ice that is constantly moving under its own weight. A glacier forms where the accumulation of snow exceeds its ablation over many years, often centuries. It acquires distinguishing features, such a ...
s melted and receded to the north, resulting in the difference between the topography
Topography is the study of the forms and features of land surfaces. The topography of an area may refer to the land forms and features themselves, or a description or depiction in maps.
Topography is a field of geoscience and planetary sc ...
of the North Shore beaches and the South Shore beaches. The North Shore beaches are rocky from the remaining glacial debris, while the South Shore's are crisp, clear, outwash sand. Jayne's Hill
Jayne's Hill (also known as High Hill, West Hills, Oakley's Hill, and Janes Hill) is the highest point on Long Island, New York, with an elevation of between and above sea level. It is situated on the Harbor Hill moraine, a terminal moraine tha ...
, at , within Suffolk County near its border with Nassau County, is the highest hill along either moraine; another well-known summit is Bald Hill in Brookhaven Town, not far from its geographical center at Middle Island. The glaciers also formed Lake Ronkonkoma
Lake Ronkonkoma is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, on Long Island, in New York, United States. The population was 20,155 at the 2010 census.
Lake Ronkonkoma is mainly located in the Town of Brookhaven, but has s ...
in Suffolk County and Lake Success in Nassau County, each a deep kettle lake
A kettle (also known as a kettle lake, kettle hole, or pothole) is a depression/hole in an outwash plain formed by retreating glaciers or draining floodwaters. The kettles are formed as a result of blocks of dead ice left behind by retreating g ...
.
Countyscapes
Climate
 Under the
Under the Köppen climate classification
The Köppen climate classification is one of the most widely used climate classification systems. It was first published by German-Russian climatologist Wladimir Köppen (1846–1940) in 1884, with several later modifications by Köppen, nota ...
, Long Island lies in a transition zone between a humid subtropical climate
A humid subtropical climate is a zone of climate characterized by hot and humid summers, and cool to mild winters. These climates normally lie on the southeast side of all continents (except Antarctica), generally between latitudes 25° and 40° ...
(Cfa) and a hot-summer humid continental climate
A humid continental climate is a climatic region defined by Russo-German climatologist Wladimir Köppen in 1900, typified by four distinct seasons and large seasonal temperature differences, with warm to hot (and often humid) summers and freez ...
(Dfa). The climate features hot, usually humid summers with occasional thunderstorms, mild spring and fall weather, and cold winters with a mix of snow and rain and stormier conditions. Spring can be cool due to the relatively cooler temperatures of the Atlantic Ocean and occasional blocking. Thunderstorms rarely form directly over Long Island, but can form over inland areas and then move eastward. Some storms may weaken as they approach Long Island due to the moderating effects of the Atlantic Ocean. The ocean also brings afternoon sea breezes to the immediate South Shore areas (within ) that temper the heat in the warmer months. The temperatures south of Sunrise Highway ( NY Route 27) tend to be significantly cooler than the rest of Long Island in the spring and summer months because of the relatively cooler temperatures of the Atlantic Ocean. Long Island has a moderately sunny climate, averaging 2,400 to 2,800 hours of sunshine annually.
Due to its coastal location, Long Island winter temperatures are milder than most of the state. The coldest month is January, when average temperatures range from , and the warmest month is July, when average temperatures range from . Temperatures seldom fall below or rise above . Coldest temp ever recorded on Long Island was on January 22, 1961. Long Island temperatures vary from west to east, with the western part (Nassau County, Queens, and Brooklyn) generally 2 to 3 degrees F (1 to 2 degrees C) warmer than the east (Suffolk County). This is due to several factors: the western part is closer to the mainland and more densely developed, causing the "urban heat island
An urban heat island (UHI) is an urban or metropolitan area that is significantly warmer than its surrounding rural areas due to human activities. The temperature difference is usually larger at night than during the day, and is most apparent ...
" effect, and Long Island's land mass veers northward as one travels east. Also, daytime high temperatures on the eastern part of Long Island are cooler on most occasions, due to the moderating effect of the Atlantic Ocean and Long Island Sound. On dry nights with no clouds or wind, the Central Part of Suffolk County and Pine Barrens forest of eastern Suffolk County can be almost 5 to 10 F (3 to 5 C) cooler than the rest of the island, due to radiational cooling
In the study of heat transfer, radiative cooling is the process by which a body loses heat by thermal radiation. As Planck's law describes, every physical body spontaneously and continuously emits electromagnetic radiation.
Radiative cooling has ...
. Average dew point
The dew point is the temperature to which air must be cooled to become saturated with water vapor, assuming constant air pressure and water content. When cooled below the dew point, moisture capacity is reduced and airborne water vapor will ...
s, a measure of atmospheric moisture, typically lie in the range during July and August.
 Precipitation is distributed uniformly throughout the year, with approximately on average during each month. Average yearly snowfall totals range from approximately , with the north shore and western parts averaging more than the immediate south shore (South of Sunrise Hwy) and the east end. In any given winter, however, some parts of the island can see up to of snow or more. There are also milder winters, in which much of the island see less than of snow.
On August 13, 2014,
Precipitation is distributed uniformly throughout the year, with approximately on average during each month. Average yearly snowfall totals range from approximately , with the north shore and western parts averaging more than the immediate south shore (South of Sunrise Hwy) and the east end. In any given winter, however, some parts of the island can see up to of snow or more. There are also milder winters, in which much of the island see less than of snow.
On August 13, 2014, flash flood
A flash flood is a rapid flooding of low-lying areas: washes, rivers, dry lakes and depressions. It may be caused by heavy rain associated with a severe thunderstorm, hurricane, or tropical storm, or by meltwater from ice or snow flowing ...
ing occurred in western-central Suffolk County after a record-setting rainfall deposited more than three months' worth of precipitation on the area within a few hours.
Long Island is somewhat vulnerable to tropical cyclones
A tropical cyclone is a rapidly rotating storm system characterized by a low-pressure center, a closed low-level atmospheric circulation, strong winds, and a spiral arrangement of thunderstorms that produce heavy rain and squalls. Dependi ...
. While it lies north of where most tropical cyclones turn eastward and out to sea (most landfalls on the East Coast of the U.S. occur from North Carolina
North Carolina () is a U.S. state, state in the Southeastern United States, Southeastern region of the United States. The state is the List of U.S. states and territories by area, 28th largest and List of states and territories of the United ...
southward), several tropical cyclones have struck Long Island, including a devastating Category 3, the 1938 New England hurricane
The 1938 New England Hurricane (also referred to as the Great New England Hurricane and the Long Island Express Hurricane) was one of the deadliest and most destructive tropical cyclones to strike Long Island, New York, and New England. The storm ...
(also known as the "Long Island Express"), and another Category 3, Hurricane Carol in 1954. Other 20th-century storms that made landfall on Long Island at hurricane intensity include the 1944 Great Atlantic hurricane, Hurricane Donna
Hurricane Donna, known in Puerto Rico as Hurricane San Lorenzo, was the strongest hurricane of the 1960 Atlantic hurricane season, and caused severe damage to the Lesser Antilles, the Greater Antilles, and the East Coast of the United States, e ...
in 1960, Hurricane Belle
Hurricane Belle was a strong tropical cyclone that caused moderate damage across the East Coast of the United States in August 1976. In late July, a tropical wave emerged off the west coast of Africa. Traversing the Atlantic Ocean for more ...
in 1976, and Hurricane Gloria
Hurricane Gloria was a powerful hurricane that caused significant damage along the east coast of the United States and in Atlantic Canada during the 1985 Atlantic hurricane season. It was the first significant tropical cyclone to strike the nor ...
in 1985. Also, the eyewall of Hurricane Bob in 1991 brushed the eastern tip. In August 2011, portions of Long Island were evacuated in preparation for Hurricane Irene, a Category 1 hurricane which weakened to a tropical storm before it reached Long Island.
On October 29, 2012, Hurricane Sandy
Hurricane Sandy (unofficially referred to as ''Superstorm Sandy'') was an extremely destructive and strong Atlantic hurricane, as well as the largest Atlantic hurricane on record as measured by diameter, with tropical-storm-force winds spann ...
caused extensive damage to low-lying coastal areas of Nassau and Suffolk counties, Brooklyn, and Queens, destroying or severely damaging thousands of area homes and other structures by ocean and bay storm surges. Hundreds of thousands of residents were left without electric power for periods of time ranging up to several weeks while the damage was being repaired. The slow-moving "Superstorm Sandy" (so-nicknamed because it merged with a nor'easter
A nor'easter (also northeaster; see below), or an East Coast low is a synoptic-scale extratropical cyclone in the western North Atlantic Ocean. The name derives from the direction of the winds that blow from the northeast. The original use o ...
before it made landfall) caused 90% of Long Island households to lose power and an estimated $18 billion in damages in Nassau and Suffolk counties alone. The storm also had a devastating impact on coastal communities in the Brooklyn and Queens portions of the island, including Coney Island
Coney Island is a peninsular neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach and Manhattan Beach, Brooklyn, Manhattan Beach to its east, L ...
in Brooklyn and the Rockaway Peninsula in Queens, although estimates of monetary damages there are usually calculated as part of the overall losses suffered in New York City as a whole. When allowance is made for inflation
In economics, inflation is an increase in the general price level of goods and services in an economy. When the general price level rises, each unit of currency buys fewer goods and services; consequently, inflation corresponds to a reduct ...
, the extent of Sandy's damages is second only to that of those caused by the 1938 Long Island Express
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mensu ...
. Although a lower central pressure was recorded in Sandy, the National Hurricane Center estimates that the 1938 hurricane had a lower pressure at landfall. Hurricane Sandy and its profound impacts have prompted the discussion of constructing seawall
A seawall (or sea wall) is a form of coastal defense constructed where the sea, and associated coastal processes, impact directly upon the landforms of the coast. The purpose of a seawall is to protect areas of human habitation, conservation ...
s and other coastal barriers around the shorelines of Long Island and New York City to minimize the risk of destructive consequences from another such event in the future.
Additional islands
 Several smaller islands, though geographically distinct, are in proximity to Long Island and are often grouped with it. These islands include
Several smaller islands, though geographically distinct, are in proximity to Long Island and are often grouped with it. These islands include Fire Island
Fire Island is the large center island of the outer barrier islands parallel to the South Shore of Long Island, in the U.S. state of New York.
Occasionally, the name is used to refer collectively to not only the central island, but also Lon ...
, the largest of the outer barrier islands that parallels the southern shore of Long Island for approximately ; Plum Island, which was home to the Plum Island Animal Disease Center
Plum Island Animal Disease Center (PIADC) is a United States federal research facility dedicated to the study of foreign animal diseases of livestock. It is part of the Department of Homeland Security Directorate for Science and Technology, an ...
, a biological weapons
A biological agent (also called bio-agent, biological threat agent, biological warfare agent, biological weapon, or bioweapon) is a bacterium, virus, protozoan, parasite, fungus, or toxin that can be used purposefully as a weapon in bioterrorism ...
research facility
A research institute, research centre, research center or research organization, is an establishment founded for doing research. Research institutes may specialize in basic research or may be oriented to applied research. Although the term often i ...
; Fishers Island
Fishers Island (Pequot: ''Munnawtawkit'') is an island that is part of Southold, New York, United States at the eastern end of Long Island Sound, off the southeastern coast of Connecticut across Fishers Island Sound. About long and wide, it ...
and smaller islands Wicopesset Island, North Dumpling Island, South Dumpling Island, and Flat Hammock; as well as Robins Island, Gardiners Island
Gardiner's Island is a small island in the Town of East Hampton, New York, in Eastern Suffolk County. It is located in Gardiner's Bay between the two peninsulas at the east end of Long Island. It is long, wide and has of coastline.
The isl ...
, Long Beach Barrier Island
Long Beach is one of the outer barrier islands off the south coast of Long Island, New York, United States.
Long Beach is the westernmost of these barrier islands, fronting on Reynolds Channel to the north and the Atlantic Ocean to the south.
...
, Jones Beach Island, Great Gull Island, Little Gull Island
Little Gull Island Light is a lighthouse on Little Gull Island, a small island in Long Island Sound, located approximately northeast of Great Gull Island. Both islands are located in the Town of Southold, in Suffolk County, New York, and lie r ...
, and Shelter Island.
Demographics
Long Island is the most populous island and one of the most densely populated regions in the United States. At the2020 U.S. census
The United States census of 2020 was the twenty-fourth decennial United States census. Census Day, the reference day used for the census, was April 1, 2020. Other than a pilot study during the 2000 census, this was the first U.S. census to off ...
, the total population of all four counties of Long Island was 8,063,232, comprising 40% of the population of the State of New York. As of 2020, the proportion of New York City residents (total 8,804,190) living on Long Island had risen to 58.4%, given the 5,141,538 residents living in Brooklyn and Queens. Furthermore, the proportion of New York State's population residing on Long Island has also been increasing, with Long Island's Census-estimated population increasing 6.5% since 2010, to 8,063,232 in 2020, representing 40% of New York State's Census 2020-enumerated population of 20,215,751 and with a population density
Population density (in agriculture: standing stock or plant density) is a measurement of population per unit land area. It is mostly applied to humans, but sometimes to other living organisms too. It is a key geographical term.Matt RosenberPopu ...
of on Long Island; the island is more populous than 37 of the 50 U.S. states.
At the 2020 census, the combined population of Nassau and Suffolk counties was 2,921,694 people, Suffolk County's share being 1,525,920 and Nassau County's 1,395,774. Nassau County had a larger population for decades, but Suffolk County surpassed it in the 1990 census as growth and development continued to spread eastward. As Suffolk County has more than three times the land area of Nassau County, the latter still has a much higher population density, given its proximity to New York City. According to the U.S. Census Bureau
The United States Census Bureau (USCB), officially the Bureau of the Census, is a principal agency of the U.S. Federal Statistical System, responsible for producing data about the American people and economy. The Census Bureau is part of the ...
's 2008 American Community Survey
The American Community Survey (ACS) is a demographics survey program conducted by the U.S. Census Bureau. It regularly gathers information previously contained only in the long form of the decennial census, such as ancestry, citizenship, educati ...
, Nassau and Suffolk counties had the 10th and 26th highest median household income
The median income is the income amount that divides a population into two equal groups, half having an income above that amount, and half having an income below that amount. It may differ from the mean (or average) income. Both of these are ways ...
s in the nation, respectively.
Population figures from the U.S. Census Bureau ''Census 2010'' show that whites are the largest racial group in all four counties, and are in the majority in Nassau and Suffolk counties. In 2002, ''The New York Times
''The New York Times'' (''the Times'', ''NYT'', or the Gray Lady) is a daily newspaper based in New York City with a worldwide readership reported in 2020 to comprise a declining 840,000 paid print subscribers, and a growing 6 million paid ...
'' cited a study by the non-profit group ERASE Racism, which determined that Nassau and Suffolk counties constitute the most racially segregated suburbs in the United States.
In contrast, Queens is the most ethnically diverse county in the United States and the most diverse urban area in the world.
 According to a 2000 report on religion, which asked congregations to respond,
According to a 2000 report on religion, which asked congregations to respond, Catholics
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
are the largest religious group on Long Island, with non-affiliated in second place. Catholics make up 52% of the population of Nassau and Suffolk, versus 22% for the country as a whole, with Jews
Jews ( he, יְהוּדִים, , ) or Jewish people are an ethnoreligious group and nation originating from the Israelites Israelite origins and kingdom: "The first act in the long drama of Jewish history is the age of the Israelites""The ...
at 16% and 7%, respectively, versus 1.7% nationwide. Churches were asked for their membership numbers. ARDA estimates that most of the churches not reporting were black Protestant congregations. Only a small percentage of Protestants
Protestantism is a Christian denomination, branch of Christianity that follows the theological tenets of the Reformation, Protestant Reformation, a movement that began seeking to reform the Catholic Church from within in the 16th century agai ...
responded, 7% and 8% respectively, for Nassau and Suffolk counties. This is in contrast with 23% for the entire country on the same survey, and 50% on self-identification surveys.
A growing population of nearly half a million Chinese Americans
Chinese Americans are Americans of Han Chinese ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of East Asian Americans which also constitute a subgroup of Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans along with their ancestors trace lineage from ...
now live on Long Island.Accessed September 3, 2017. Rapidly expanding Chinatowns in New York, Chinatowns have developed in Brooklyn (布魯克林) and
Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, with Chinese immigrants also moving into Nassau County, as did earlier European immigrants, such as the Irish and Italians
, flag =
, flag_caption = The national flag of Italy
, population =
, regions = Italy 55,551,000
, region1 = Brazil
, pop1 = 25–33 million
, ref1 =
, region2 ...
. The busy intersection of Main Street, Kissena Boulevard
Kissena Boulevard is a thoroughfare spanning the Flushing and Pomonok neighborhoods of the borough of Queens in New York City, extending from Main Street in the Flushing Chinatown to Parsons Boulevard in Kew Gardens Hills. The road's nam ...
, and 41st Avenue defines the center of Downtown Flushing
There are multiple Chinatowns in the borough of Queens in New York City. The original Queens Chinatown emerged in Flushing, initially as a satellite of the original Manhattan Chinatown, before evolving its own identity, surpassing in scale th ...
and the Flushing Chinatown
There are multiple Chinatowns in the borough of Queens in New York City. The original Queens Chinatown emerged in Flushing, initially as a satellite of the original Manhattan Chinatown, before evolving its own identity, surpassing in scale the ...
, known as the "Chinese Times Square
Times Square is a major commercial intersection, tourist destination, entertainment hub, and neighborhood in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. It is formed by the junction of Broadway, Seventh Avenue, and 42nd Street. Together with adjacent ...
" or the "Chinese Manhattan
Manhattan (), known regionally as the City, is the most densely populated and geographically smallest of the five boroughs of New York City. The borough is also coextensive with New York County, one of the original counties of the U.S. state ...
". The segment of Main Street between Kissena Boulevard and Roosevelt Avenue, punctuated by the Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
trestle
ATLAS-I (Air Force Weapons Lab Transmission-Line Aircraft Simulator), better known as Trestle, was a unique electromagnetic pulse (EMP) generation and testing apparatus built between 1972 and 1980 during the Cold War at Sandia National Laborato ...
overpass, represents the cultural heart of the Flushing Chinatown. Housing over 30,000 individuals born in China alone, the largest by this metric outside Asia, Flushing has become home to the largest and one of the fastest-growing Chinatowns in the world as the heart of over 250,000 ethnic Chinese in Queens, representing the largest Chinese population of any U.S. municipality other than New York City in total. Conversely, the Flushing Chinatown has also become the epicenter of organized prostitution in the United States, importing women from China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
, Korea
Korea ( ko, 한국, or , ) is a peninsular region in East Asia. Since 1945, it has been divided at or near the 38th parallel, with North Korea (Democratic People's Republic of Korea) comprising its northern half and South Korea (Republic ...
, Thailand
Thailand ( ), historically known as Siam () and officially the Kingdom of Thailand, is a country in Southeast Asia, located at the centre of the Indochinese Peninsula, spanning , with a population of almost 70 million. The country is b ...
, and Eastern Europe
Eastern Europe is a subregion of the European continent. As a largely ambiguous term, it has a wide range of geopolitical, geographical, ethnic, cultural, and socio-economic connotations. The vast majority of the region is covered by Russia, whi ...
to sustain the underground North American sex trade. Flushing is undergoing rapid gentrification
Gentrification is the process of changing the character of a neighborhood through the influx of more affluent residents and businesses. It is a common and controversial topic in urban politics and planning. Gentrification often increases the ...
with investment by Chinese transnational entities,
More recently, a Little India community has emerged in Hicksville, Nassau County, spreading eastward from the more established Little India enclaves in Queens. Rapidly growing Chinatowns in New York, Chinatowns have developed in Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, as did earlier European immigrants, such as the Irish and Italians. As of 2019, the Asian population in Nassau County had grown by 39% since 2010 to an estimated 145,191 individuals, including approximately 50,000 Indian Americans
Indian Americans or Indo-Americans are citizens of the United States with ancestry from India. The United States Census Bureau uses the term Asian Indian to avoid confusion with Native Americans, who have also historically been referred to ...
and 40,000 Chinese Americans
Chinese Americans are Americans of Han Chinese ancestry. Chinese Americans constitute a subgroup of East Asian Americans which also constitute a subgroup of Asian Americans. Many Chinese Americans along with their ancestors trace lineage from ...
, as Nassau County has become the leading suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separ ...
an destination in the U.S. for Chinese immigrants
Overseas Chinese () refers to people of Chinese birth or ethnicity who reside outside Mainland China, Hong Kong, Macau, and Taiwan. As of 2011, there were over 40.3 million overseas Chinese.
Terminology
() or ''Hoan-kheh'' () in Hokkien, ...
. Likewise, the Long Island Koreatown originated in Flushing, Queens, and is expanding eastward along Northern Boulevard and into Nassau County.
Long Island is home to two Native American reservations, Poospatuck Reservation, and Shinnecock Reservation, both in Suffolk County. Numerous island place names are Native American in origin.
A 2010 article in ''The New York Times'' stated that the expansion of the immigrant workforce on Long Island has not displaced any jobs from other Long Island residents. Half of the immigrants on Long Island hold white-collar positions.
The counties of Nassau and Suffolk have been long renowned for their affluence. Long Island is home to some of the wealthiest communities in the United States, including The Hamptons
The Hamptons, part of the East End of Long Island, consist of the towns of Southampton and East Hampton, which together comprise the South Fork of Long Island, in Suffolk County, New York. The Hamptons are a popular seaside resort and one o ...
, on the East End
The East End of London, often referred to within the London area simply as the East End, is the historic core of wider East London, east of the Roman and medieval walls of the City of London and north of the River Thames. It does not have uni ...
of the South Shore of Suffolk County; the Gold Coast, in the vicinity of the island's North Shore, along Long Island Sound; and increasingly, the western shoreline of Brooklyn, facing Manhattan. In 2016, according to ''Business Insider
''Insider'', previously named ''Business Insider'' (''BI''), is an American financial and business news website founded in 2007. Since 2015, a majority stake in ''Business Insider''s parent company Insider Inc. has been owned by the German publ ...
'', the 11962 zip code encompassing Sagaponack
Sagaponack is a village in the Town of Southampton in Suffolk County, on the East End of Long Island, in New York, United States. The population of the village was 313 at the 2010 census.
Sagaponack is also the name of a popular seafood re ...
, within Southampton
Southampton () is a port city in the ceremonial county of Hampshire in southern England. It is located approximately south-west of London and west of Portsmouth. The city forms part of the South Hampshire built-up area, which also covers Po ...
, was listed as the most expensive in the U.S., with a median home sale price of $8.5 million.
Economy
 Long Island has played a prominent role in
Long Island has played a prominent role in scientific research
The scientific method is an empirical method for acquiring knowledge that has characterized the development of science since at least the 17th century (with notable practitioners in previous centuries; see the article history of scientific m ...
and in engineering
Engineering is the use of scientific principles to design and build machines, structures, and other items, including bridges, tunnels, roads, vehicles, and buildings. The discipline of engineering encompasses a broad range of more speciali ...
. It is the home of the Brookhaven National Laboratory
Brookhaven National Laboratory (BNL) is a United States Department of Energy national laboratory located in Upton, Long Island, and was formally established in 1947 at the site of Camp Upton, a former U.S. Army base and Japanese internment c ...
in nuclear physics
Nuclear physics is the field of physics that studies atomic nuclei and their constituents and interactions, in addition to the study of other forms of nuclear matter.
Nuclear physics should not be confused with atomic physics, which studies t ...
and Department of Energy research. Long Island is also home to the Cold Spring Harbor Laboratory, which was directed for 35 years by James D. Watson (who, along with Francis Crick
Francis Harry Compton Crick (8 June 1916 – 28 July 2004) was an English molecular biologist, biophysicist, and neuroscientist. He, James Watson, Rosalind Franklin, and Maurice Wilkins played crucial roles in deciphering the helical stru ...
and Rosalind Franklin
Rosalind Elsie Franklin (25 July 192016 April 1958) was a British chemist and X-ray crystallographer whose work was central to the understanding of the molecular structures of DNA (deoxyribonucleic acid), RNA (ribonucleic acid), viruses, ...
, discovered the double helix
A double is a look-alike or doppelgänger; one person or being that resembles another.
Double, The Double or Dubble may also refer to:
Film and television
* Double (filmmaking), someone who substitutes for the credited actor of a character
* ...
structure of DNA). Companies such as Sperry Corporation
Sperry Corporation was a major American equipment and electronics company whose existence spanned more than seven decades of the 20th century. Sperry ceased to exist in 1986 following a prolonged hostile takeover bid engineered by Burroug ...
, Computer Associates (headquartered in Islandia), Zebra Technologies
Zebra Technologies Corporation is an American mobile computing company specializing in technology used to sense, analyze, and act in real time. The company manufactures and sells marking, tracking, and computer printing technologies. Its product ...
(now occupying the former headquarters of Symbol Technologies, and a former Grumman
The Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, later Grumman Aerospace Corporation, was a 20th century American producer of military and civilian aircraft. Founded on December 6, 1929, by Leroy Grumman and his business partners, it merged in 1994 ...
plant in Holtsville), have made Long Island a center for the computer industry
A computer is a machine that can be programmed to carry out sequences of arithmetic or logical operations ( computation) automatically. Modern digital electronic computers can perform generic sets of operations known as programs. These progr ...
. Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
and New York Institute of Technology
The New York Institute of Technology (NYIT or New York Tech) is a private research university founded in 1955. It has two main campuses in New York—one in Old Westbury, on Long Island, and one in Manhattan. Additionally, it has a cyberse ...
conduct advanced medical and technological research.
Long Island is home to the East Coast's largest industrial park
An industrial park (also known as industrial estate, trading estate) is an area zoned and planned for the purpose of industrial development. An industrial park can be thought of as a more "heavyweight" version of a business park or office park ...
, the Hauppauge Industrial Park, hosting over 1,300 companies which employ more than 71,000 individuals. Companies in the park and abroad are represented by the Hauppauge Industrial Association
The Hauppauge Industrial Association (HIA), which has a membership of approximately 1,000 companies throughout Long Island, is a grass-roots, pro-active business organization The HIA had its start in 1978 due to the constant power outages by the Lo ...
. As many as 20% of Long Islanders commute to jobs in Manhattan. The island's eastern end is still partly agricultural. Development of vineyard
A vineyard (; also ) is a plantation of grape-bearing vines, grown mainly for winemaking, but also raisins, table grapes and non-alcoholic grape juice. The science, practice and study of vineyard production is known as viticulture. Vineyard ...
s on the North Fork has spawned a major viticultural industry, replacing potato fields. Pumpkin
A pumpkin is a vernacular term for mature winter squash of species and varieties in the genus ''Cucurbita'' that has culinary and cultural significance but no agreed upon botanical or scientific meaning. The term ''pumpkin'' is sometimes use ...
farms have been added to traditional truck farming. Farms allow fresh fruit
In botany, a fruit is the seed-bearing structure in flowering plants that is formed from the ovary after flowering.
Fruits are the means by which flowering plants (also known as angiosperms) disseminate their seeds. Edible fruits in partic ...
picking by Long Islanders for much of the year. Fishing
Fishing is the activity of trying to catch fish. Fish are often caught as wildlife from the natural environment, but may also be caught from fish stocking, stocked bodies of water such as fish pond, ponds, canals, park wetlands and reservoirs. ...
continues to be an important industry, especially at Huntington, Northport, Montauk, and other coastal communities of the East End and South Shore.
From about 1930 to about 1990, Long Island was considered one of the aerospace manufacturing centers of the United States, with companies such as Grumman
The Grumman Aircraft Engineering Corporation, later Grumman Aerospace Corporation, was a 20th century American producer of military and civilian aircraft. Founded on December 6, 1929, by Leroy Grumman and his business partners, it merged in 1994 ...
, Republic
A republic () is a " state in which power rests with the people or their representatives; specifically a state without a monarchy" and also a "government, or system of government, of such a state." Previously, especially in the 17th and 18th ...
, Fairchild, and Curtiss
Curtiss Aeroplane and Motor Company (1909 – 1929) was an American aircraft manufacturer originally founded by Glenn Hammond Curtiss and Augustus Moore Herring in Hammondsport, New York. After significant commercial success in its first decad ...
having their headquarters and factories on Long Island. These operations have largely been phased out or significantly diminished.
Government and politics
 Nassau County and Suffolk County each have their own governments, with a
Nassau County and Suffolk County each have their own governments, with a County Executive
A county executive, county manager or county mayor is the head of the executive branch of government in a United States county.
The executive may be an elected or an appointed position. When elected, the executive typically functions either as a ...
leading each. Each has a county legislature and countywide-elected officials, including district attorney
In the United States, a district attorney (DA), county attorney, state's attorney, prosecuting attorney, commonwealth's attorney, or state attorney is the chief prosecutor and/or chief law enforcement officer representing a U.S. state in a ...
, county clerk, and county comptroller
A comptroller (pronounced either the same as ''controller'' or as ) is a management-level position responsible for supervising the quality of accounting and financial reporting of an organization. A financial comptroller is a senior-level execut ...
. The towns
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an or ...
in both counties have their own governments as well, with town supervisors and a town council
A town council, city council or municipal council is a form of local government for small municipalities.
Usage of the term varies under different jurisdictions.
Republic of Ireland
Town Councils in the Republic of Ireland were the second ti ...
. Nassau County is divided into three towns
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an or ...
and two small incorporated cities ( Glen Cove and Long Beach
Long Beach is a city in Los Angeles County, California. It is the 42nd-most populous city in the United States, with a population of 466,742 as of 2020. A charter city, Long Beach is the seventh-most populous city in California.
Incorporat ...
). Suffolk County is divided into ten towns.
Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
and Queens
Queens is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Queens County, in the U.S. state of New York. Located on Long Island, it is the largest New York City borough by area. It is bordered by the borough of Brooklyn at the western tip of Long ...
, on the other hand, do not have county governments. As boroughs
A borough is an administrative division in various English-speaking countries. In principle, the term ''borough'' designates a self-governing walled town, although in practice, official use of the term varies widely.
History
In the Middle A ...
of New York City, both have borough presidents, which have been largely ceremonial offices since the shutdown of the New York City Board of Estimate. The respective Borough Presidents are responsible for appointing individuals to the Brooklyn Community Boards and Queens Community Boards, each of which serves an advisory function on local issues. Brooklyn's sixteen members and Queens' fourteen members represent the first and second largest borough contingents of the New York City Council
The New York City Council is the lawmaking body of New York City. It has 51 members from 51 council districts throughout the five boroughs.
The council serves as a check against the mayor in a mayor-council government model, the performance of ...
.
Law enforcement
Queens and Brooklyn are patrolled by theNew York City Police Department
The New York City Police Department (NYPD), officially the City of New York Police Department, established on May 23, 1845, is the primary municipal law enforcement
Law enforcement is the activity of some members of government who act i ...
. Nassau and Suffolk counties are served by the Nassau County Police Department
The Nassau County Police Department is the law enforcement agency of Nassau County, New York.
History
In 1925, concerned about rising crime rates, the County Board of Supervisors voted to create the Nassau County Police Department, replaci ...
and Suffolk County Police Department, respectively, although several dozen villages and the two cities in Nassau County have their own police departments. The Nassau County Sheriff's Department and Suffolk County Sheriff's Office
Suffolk County () is the easternmost county in the U.S. state of New York. It is mainly located on the eastern end of Long Island, but also includes several smaller islands. According to the 2020 United States census, the county's population ...
handle civil procedure
Civil procedure is the body of law that sets out the rules and standards that courts follow when adjudicating civil lawsuits (as opposed to procedures in criminal law matters). These rules govern how a lawsuit or case may be commenced; what kin ...
, evictions, warrant service and enforcement, prisoner transport and detention, and operation of the county jails. The Suffolk County Sheriff also has a patrol division, and in 2008, had patrol duties along the Long Island Expressway, when the County Executive briefly disbanded the Suffolk County Police Highway Patrol Division. The Suffolk County Sheriff's Office is the oldest law enforcement agency in the State of New York, founded in the year 1683. New York State Police patrol state parks and parkways
A parkway is a landscaped thoroughfare.''"parkway."''Webster's Third New International Dictionary, Unabridged. Merriam-Webster, 2002. http://unabridged.merriam-webster.com (14 Apr. 2007). The term is particularly used for a roadway in a park or ...
. The several SUNY colleges and universities are patrolled by the New York State University Police
The New York State University Police (NYSUP) is the law enforcement agency of the State University of New York (SUNY) system. Approximately 600 uniformed officers and investigators, as well as sixty-four chiefs, serve the 29 state college and u ...
.
Statehood proposals
The secession of Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island from New York State was proposed as early as 1896, but talk was revived towards the latter part of the twentieth century. On March 28, 2008, Suffolk CountyComptroller
A comptroller (pronounced either the same as ''controller'' or as ) is a management-level position responsible for supervising the quality of accounting and financial reporting of an organization. A financial comptroller is a senior-level execut ...
Joseph Sawicki proposed a plan that would make Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Island the 51st state
51st state in American political discourse refers to areas considered candidates for U.S. statehood, joining the 50 states that have constituted the United States since 1959. The phrase has been applied to external territories as well as parts ...
of the United States of America. Sawicki claimed all of Nassau and Suffolk taxpayers' money would remain locally, rather than the funds being dispersed all over the entire state of New York, with these counties sending to Albany over three billion dollars more than they receive. The state of Long Island would have included nearly 3 million people (a larger population than that of fifteen other states). Nassau County executive Ed Mangano
Edward P. Mangano (born March 24, 1962) is an American politician from the state of New York. A Republican, he was the Nassau County Executive from January 2010 to December 2017, and a former legislator in Nassau County, New York. He was elect ...
came out in support of such a proposal in April 2010 and commissioned a study on it.
Education
Primary and secondary education
 Many public and private high schools on Long Island are ranked among the best in the United States. Nassau and Suffolk counties are the home of 125 public school districts containing 656 public schools. It also hosts
Many public and private high schools on Long Island are ranked among the best in the United States. Nassau and Suffolk counties are the home of 125 public school districts containing 656 public schools. It also hosts private school
Private or privates may refer to:
Music
* " In Private", by Dusty Springfield from the 1990 album ''Reputation''
* Private (band), a Denmark-based band
* "Private" (Ryōko Hirosue song), from the 1999 album ''Private'', written and also recorde ...
s such as Friends Academy
Friends Academy is a Quaker, coeducational, independent, college preparatory school serving students from nursery school through the twelfth grade, located in Locust Valley, New York, United States. The school was founded in 1876 by 78-year-old Gi ...
, Chaminade High School
Chaminade High School is a Roman Catholic Marianist college preparatory high school for boys in Mineola, New York, United States. Chaminade’s main campus is also home to Saragossa Retreat Center, one of their three retreat houses.
Athletics ...
, Kellenberg Memorial High School, St. Anthony's High School, and North Shore Hebrew Academy
North Shore Hebrew Academy (NSHA or NSHAHS) is a Modern Orthodox yeshiva located in Great Neck, New York. The Academy has four divisions: Pre-K, Elementary (Grades K-5), Middle School (Grades 6-8) and High School (Grades 9-12).
The founding princ ...
, as well as parochial school
A parochial school is a private primary or secondary school affiliated with a religious organization, and whose curriculum includes general religious education in addition to secular subjects, such as science, mathematics and language arts. The wo ...
s, many of which are operated by the Catholic Diocese of Rockville Centre
The Roman Catholic Diocese of Rockville Centre ( la, Dioecesis Petropolitana in Insula Longa) is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church that comprises the territory of Nassau and Suffolk counties on Long Islan ...
.
In contrast, all of Brooklyn and Queens are served by the New York City Department of Education, the largest school district in the United States. Three of the nine specialized high schools in New York City are in the two Long Island boroughs, those being Brooklyn Latin School
The Brooklyn Latin School is a public specialized high school in New York City. It opened in September 2006. The ideals governing Brooklyn Latin are borrowed largely from the Boston Latin School, and popular society's ideals. The school’s found ...
, Brooklyn Technical High School
Brooklyn Technical High School, commonly called Brooklyn Tech and administratively designated High School 430, is an elite public high school in New York City that specializes in science, technology, engineering, and mathematics. It is one of ...
(one of the original three specialized schools), and Queens High School for the Sciences
Queens High School for the Sciences at York College (commonly called QHSSYC or QHSS) is a New York City public specialized high school operated by the New York City Department of Education specializing in mathematics and science. It admits st ...
. Like Nassau and Suffolk counties, they are home to private schools such as Poly Prep Country Day School
Poly Prep Country Day School (commonly known as Poly Prep) is an independent, co-educational day school with two campuses in Brooklyn, New York, United States. The Middle School (5th to 8th grades) and Upper School (9th to 12th grades) are loc ...
, Packer Collegiate Institute, and Saint Ann's School, and Berkeley Carroll School
The Berkeley Carroll School is a coed independent college prep school in New York City. Located in Park Slope, Brooklyn, it has a Lower School (preK – grade 4), Middle School (grades 5–8) and Upper School (grades 9–12).
History
The ...
, and parochial schools operated by the Catholic Diocese of Brooklyn
The Diocese of Brooklyn is a Latin Church ecclesiastical territory or diocese of the Catholic Church in the U.S. state of New York. It is headquartered in Brooklyn and its territory encompasses the New York City boroughs of Brooklyn and Queens. ...
.
Colleges and universities
 Long Island is home to a range of higher-education institutions, both public and private. Brooklyn and Queens contain five of eleven senior colleges within
Long Island is home to a range of higher-education institutions, both public and private. Brooklyn and Queens contain five of eleven senior colleges within CUNY
The City University of New York ( CUNY; , ) is the public university system of New York City. It is the largest urban university system in the United States, comprising 25 campuses: eleven senior colleges, seven community colleges and seven prof ...
, the public university system of New York City and one of the largest in the country. Among these are the notable institutions of Brooklyn College
, mottoeng = Nothing without great effort
, established =
, parent = CUNY
, type = Public university
, endowment = $98.0 million (2019)
, budget = $123.96 m ...
and Queens College
Queens College (QC) is a public college in the Queens borough of New York City. It is part of the City University of New York system. Its 80-acre campus is primarily located in Flushing, Queens. It has a student body representing more than 170 ...
. Brooklyn also contains private colleges such as Pratt Institute
Pratt Institute is a private university with its main campus in Brooklyn, New York. It has a satellite campus in Manhattan and an extension campus in Utica, New York at the Munson-Williams-Proctor Arts Institute. The school was founded in 1887 ...
and the New York University Polytechnic School of Engineering, an engineering college that merged with New York University
New York University (NYU) is a private research university in New York City. Chartered in 1831 by the New York State Legislature, NYU was founded by a group of New Yorkers led by then- Secretary of the Treasury Albert Gallatin.
In 1832, th ...
in 2014.
 Several colleges and universities within the
Several colleges and universities within the State University of New York
The State University of New York (SUNY, , ) is a system of public colleges and universities in the State of New York. It is one of the largest comprehensive system of universities, colleges, and community colleges in the United States. Led by ...
system are on Long Island, including Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
(which noted its health sciences research and medical center), as well as Nassau Community College
Nassau Community College (NCC) is a public community college in Uniondale, New York, using the Garden City, New York ZIP Code. It was founded in 1959 and is part of the State University of New York.
History
Nassau Community College was crea ...
and Suffolk County Community College
Suffolk County Community College (SCCC) is a public community college in Selden, New York. It is part of the State University of New York (SUNY) system and is funded in part by Suffolk County, New York. Suffolk County Community College wa ...
that serve their respective counties. Private institutions include Molloy College in Rockville Centre, the New York Institute of Technology
The New York Institute of Technology (NYIT or New York Tech) is a private research university founded in 1955. It has two main campuses in New York—one in Old Westbury, on Long Island, and one in Manhattan. Additionally, it has a cyberse ...
, Hofstra University
Hofstra University is a private university in Hempstead, New York. It is Long Island's largest private university. Hofstra originated in 1935 as an extension of New York University (NYU) under the name Nassau College – Hofstra Memorial of New ...
and Adelphi University
Adelphi University is a private university in Garden City, New York. Adelphi also has centers in Manhattan, Hudson Valley, and Suffolk County. There is also a virtual, online campus for remote students. It is the oldest institution of higher edu ...
(both in the Town of Hempstead), as well as Long Island University
Long Island University (LIU) is a private university with two main campuses, LIU Post and LIU Brooklyn, in the U.S. state of New York. It offers more than 500 academic programs at its main campuses, online, and at multiple non-residential. LIU ...
(with its C.W. Post campus, on a former Gold Coast estate in Brookville, and a satellite campus
A satellite campus or branch campus or regional campus is a campus of a university or college that is physically at a distance from the original university or college area. This branch campus may be located in a different city, state, or coun ...
in downtown Brooklyn). Long Island also contains the Webb Institute
Webb Institute is a private college focused on engineering and located in Glen Cove, New York. Each graduate of Webb Institute earns a Bachelor of Science degree in naval architecture and marine engineering. Successful candidates for admission ...
, a small naval architecture college in Glen Cove. The island is also home to the United States Merchant Marine Academy
The United States Merchant Marine Academy (USMMA or Kings Point) is a United States service academy in Kings Point, New York. It trains its midshipmen (as students at the academy are called) to serve as officers in the United States Merchant ...
, a Federal Service Academy in Kings Point, on the North Shore.
Culture
Music
 Music on Long Island (Nassau and Suffolk) is strongly influenced by the proximity to New York City and by the
Music on Long Island (Nassau and Suffolk) is strongly influenced by the proximity to New York City and by the youth culture Youth culture refers to the societal norms of children, adolescents, and young adults. Specifically, it comprises the processes and symbolic systems that are shared by the youth and are distinct from those of adults in the community.
An emphasi ...
of the suburb
A suburb (more broadly suburban area) is an area within a metropolitan area, which may include commercial and mixed-use, that is primarily a residential area. A suburb can exist either as part of a larger city/urban area or as a separ ...
s.
Psychedelic rock
Psychedelic rock is a rock music genre that is inspired, influenced, or representative of psychedelic culture, which is centered on perception-altering hallucinogenic drugs. The music incorporated new electronic sound effects and recording te ...
was widely popular in the 1960s as flocks of disaffected youth travelled to NYC to participate in protest and the culture of the time. R & B
Rhythm and blues, frequently abbreviated as R&B or R'n'B, is a genre of popular music that originated in African-American communities in the 1940s. The term was originally used by record companies to describe recordings marketed predominantly ...
also has a history on Long Island, most notably Huntington-born Mariah Carey
Mariah Carey (; born March 27, 1969) is an American singer, songwriter, actress, and record producer. Referred to as the " Songbird Supreme", she is noted for her five-octave vocal range, melismatic singing style and signature use of the w ...
, one of the top-selling musicians of all time. In the late 1970s through the 1980s, the influence of radio station WLIR made Long Island one of the first places in the U.S. to hear and embrace European New Wave bands such as Depeche Mode
Depeche Mode are an English electronic music band formed in Basildon, Essex, in 1980. The band currently consists of Dave Gahan (lead vocals and co-songwriting) and Martin Gore (keyboards, guitar, co-lead vocals and main songwriting).
Depech ...
, the Pet Shop Boys
The Pet Shop Boys are an English synth-pop duo formed in London in 1981. Consisting of primary vocalist Neil Tennant and keyboardist Chris Lowe, they have sold more than 50 million records worldwide, and were listed as the most successful duo ...
, and Culture Club
Culture Club are an English pop band formed in London in 1981. The band comprises Boy George (lead vocals), Roy Hay (guitar and keyboards), Mikey Craig (bass guitar) and formerly included Jon Moss (drums and percussion). Emerging in the New ...
. In the 1990s, hip-hop became popular with rap pioneers Rakim
William Michael Griffin Jr. (born January 28, 1968), better known by his stage name Rakim Allah or simply Rakim (), is an American rapper and record producer. One half of golden age hip hop duo Eric B. & Rakim, he is widely regarded as one of t ...
, EPMD
EPMD is an American hip hop duo from Brentwood, New York. The duo's name is a concatenation of the members' names "E" and "PMD" or an acronym for "Erick and Parrish Making Dollars", referring to its members: emcees Erick Sermon ("E" a.k.a. ...
, MF Doom
Daniel Dumile ( ; July 13, 1971October 31, 2020), best known by his stage name MF Doom or simply Doom (both stylized in all caps), was a British-American rapper and record producer. Noted for his intricate wordplay, signature metal mask, and ...
, and Public Enemy
"Public enemy" is a term which was first widely used in the United States in the 1930s to describe individuals whose activities were seen as criminal and extremely damaging to society, though the phrase had been used for centuries to describe ...
growing up on Long Island. Long Island was the home of a bustling emo
Emo is a rock music genre characterized by emotional, often confessional lyrics. It emerged as a style of and hardcore punk from the Washington D.C. hardcore punk scene, where it was known as emotional hardcore or emocore and pioneered b ...
scene in the 2000s, with bands such as Brand New, Taking Back Sunday
Taking Back Sunday is an American rock band from Long Island, New York. The band was formed by guitarist Eddie Reyes and bassist Jesse Lacey in 1999. The band's members currently are Adam Lazzara (lead vocals), John Nolan (lead guitar, keybo ...
, Straylight Run
Straylight Run is an emo band based in Baldwin, Nassau County, New York. The band released two albums, '' Straylight Run'' and ''The Needles the Space'', as well as three EPs, ''Prepare to Be Wrong'', ''About Time'', and ''Un Mas Dos''. In 2010 ...
, From Autumn to Ashes and As Tall as Lions. More recently, newer acts from Long Island, including Austin Schoeffel, Jon Bellion, and Envy on the Coast, have made a name for themselves.
Famous rock bands from Long Island include The Rascals, The Ramones
The Ramones were an American punk rock band that formed in the New York City neighborhood of Forest Hills, Queens, in 1974. They are often cited as the first true punk rock group. Despite achieving a limited commercial appeal in the United St ...
(from Queens), Dream Theater
Dream Theater is an American progressive metal band formed in 1985 under the name Majesty by John Petrucci, John Myung and Mike Portnoy while they attended Berklee College of Music in Boston, Massachusetts. They subsequently dropped out o ...
, Blue Öyster Cult, Twisted Sister
Twisted Sister was an American heavy metal band originally from Ho-Ho-Kus, New Jersey, and later based on Long Island, New York. Their best-known songs include " We're Not Gonna Take It" and " I Wanna Rock", both of which were associated with ...
, and guitar virtuosos Donald (Buck Dharma) Roeser, John Petrucci
John Peter Petrucci (born July 12, 1967) is an American guitarist, best known as a founding member of the progressive metal band Dream Theater. He produced or co-produced (often with former member Mike Portnoy before he departed the band in 201 ...
, Steve Vai
Steven Siro Vai (; born June 6, 1960) is an American guitarist, composer, songwriter, and producer. A three-time Grammy Award winner and fifteen-time nominee, Vai started his music career in 1978 at the age of eighteen as a transcriptionist f ...
, and Joe Satriani
Joseph Satriani (born July 15, 1956)Prato, Greg"Joe Satriani – Music Biography, Credits and Discography". '' AllMusic''. Rovi Corporation. Retrieved May 28, 2014. is an American guitarist, composer, songwriter, and guitar teacher. Early in his ...
, and drummer Mike Portnoy
Michael Stephen Portnoy (born April 20, 1967) is an American musician who is primarily known as the former drummer, backing vocalist, and co-founder of the progressive metal band Dream Theater. In September 2010, Portnoy announced his departure ...
. Rock and pop singer Billy Joel
William Martin Joel (born May 9, 1949) is an American singer, pianist and songwriter. Commonly nicknamed the "Piano Man" after his album and signature song of the same name, he has led a commercially successful career as a solo artist since th ...
grew up in Hicksville, and his music often reflects Long Island and his youth.
Nassau Coliseum
Nassau Veterans Memorial Coliseum (or simply the Nassau Coliseum) is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Uniondale, New York, east of New York City. The Long Island venue is approximately east of the eastern limits of the New York City Borough of ...
and Northwell Health at Jones Beach Theater are venues used by national touring acts as performance spaces for concerts. Northwell Health at Jones Beach Theater is an outdoor amphitheatre
An amphitheatre (British English) or amphitheater (American English; both ) is an open-air venue used for entertainment, performances, and sports. The term derives from the ancient Greek ('), from ('), meaning "on both sides" or "around" and ...
at Jones Beach State Park
Jones Beach State Park (colloquially "Jones Beach") is a state park in the U.S. state of New York. It is located in southern Nassau County on Jones Beach Island, a barrier island linked to Long Island by the Meadowbrook State Parkway, Wanta ...
. It is a popular place to view summer concerts that feature new and classic artists. It hosts a large Fourth of July
Independence Day (colloquially the Fourth of July) is a federal holiday in the United States commemorating the Declaration of Independence, which was ratified by the Second Continental Congress on July 4, 1776, establishing the United States ...
fireworks show every year which fills the stands.
Long Island is also known for its school music programs. Many schools in Suffolk County have distinguished music programs, with high numbers of students who are accepted into the statewide All-State music groups, or even the National All-Eastern Coast music groups. Both the Suffolk County and Nassau County Music Educator's Associations are recognized by The National Association for Music Education
''The'' () is a grammatical article in English, denoting persons or things already mentioned, under discussion, implied or otherwise presumed familiar to listeners, readers, or speakers. It is the definite article in English. ''The'' is the ...
(NAfME),
and host numerous events, competitions, and other music-related activities.
Cuisine
 Long Island has historically been a center for fishing and
Long Island has historically been a center for fishing and seafood
Seafood is any form of sea life regarded as food by humans, prominently including fish and shellfish. Shellfish include various species of molluscs (e.g. bivalve molluscs such as clams, oysters and mussels, and cephalopods such as octopus an ...
. This legacy continues in the Blue Point oyster
Oyster is the common name for a number of different families of salt-water bivalve molluscs that live in marine or brackish habitats. In some species, the valves are highly calcified, and many are somewhat irregular in shape. Many, but not ...
, a now ubiquitous variety originally harvested on the Great South Bay
The Great South Bay is a lagoon situated between Long Island and Fire Island, in the State of New York. It is about long and has an average depth of 4 feet 3 inches and is 20 feet at its deepest. It is protected from the Atlantic Ocean by Fire ...
that was the favorite oyster of Queen Victoria
Victoria (Alexandrina Victoria; 24 May 1819 – 22 January 1901) was Queen of the United Kingdom of Great Britain and Ireland from 20 June 1837 until her death in 1901. Her reign of 63 years and 216 days was longer than that of any previ ...
. Clams are also a popular food and clam digging
Clam digging is a North American term for a common way to harvest clams (edible infaunal bivalve mollusks) from below the surface of the tidal sand flats or mud flats where they live. It is done both recreationally (for enjoyment or as a so ...
a popular recreational pursuit, with Manhattan clam chowder
Clam chowder is any of several chowder soups in American cuisine containing clams. In addition to clams, common ingredients include diced potatoes, salt pork, and onions. Other vegetables are not typically used. It is believed that clams were us ...
reputed to have Long Island origins.
 Of land-based produce, Long Island
Of land-based produce, Long Island duck
Duck is the common name for numerous species of waterfowl in the family Anatidae. Ducks are generally smaller and shorter-necked than swans and geese, which are members of the same family. Divided among several subfamilies, they are a form ...
has a history of national recognition since the 19th century, with four duck farms continuing to produce 2 million ducks a year . Two symbols of Long Island's duck farming heritage are the Long Island Ducks
The Long Island Ducks are an American professional minor-league baseball team based on Long Island in Central Islip, New York. The Ducks compete in the North Division of the Atlantic League of Professional Baseball (ALPB), an independent "part ...
minor-league baseball team and the Big Duck
The Big Duck is a ferrocement building in the shape of a duck located in Flanders, New York, on Long Island. It was originally built in 1931 by duck farmer Martin Maurer in nearby Riverhead, and used as a shop to sell ducks and duck eggs. I ...
, a 1931 duck-shaped building that is a historic landmark and tourist attraction. In addition to Long Island's duck industry, Riverhead contains one of the largest buffalo farms on the East coast.
Long Island is well known for its production of alcoholic beverages. Eastern Long Island is a significant producer of wine
Wine is an alcoholic drink typically made from Fermentation in winemaking, fermented grapes. Yeast in winemaking, Yeast consumes the sugar in the grapes and converts it to ethanol and carbon dioxide, releasing heat in the process. Different ...
. Vineyards are most heavily concentrated on Long Island's North Fork, which contains 38 wineries. Most of these contain tasting rooms, which are popular attractions for visitors from across the New York metropolitan area. Long Island has also become a producer of diverse craft beer
Craft beer is a beer that has been made by craft breweries. They produce smaller amounts of beer, typically less than large breweries, and are often independently owned. Such breweries are generally perceived and marketed as having an emphasis o ...
s, with 15 microbreweries
Craft beer is a beer that has been made by craft breweries. They produce smaller amounts of beer, typically less than large breweries, and are often independently owned. Such breweries are generally perceived and marketed as having an emphasis o ...
across Nassau and Suffolk counties . The largest of these is Blue Point Brewing Company
Blue Point Brewing Company is a brewery that is a subsidiary of Anheuser-Busch InBev located on Long Island, in Patchogue, New York. The brewery offers a variety of year-round beers, and several seasonal brews, as well as a 'tasting room' which is ...
, best known for its ''toasted lager''. Long Island is also globally known for its signature cocktail, the Long Island Iced Tea, which was purportedly invented at the popular Babylon, Oak Beach Inn nightclub in the 1970s.
Long Island's eateries are largely a product of the region's local ethnic populations. Asian cuisine
Asian cuisine includes several major regional cuisines: Central Asian, East Asian, North Asian, South Asian, Southeast Asian, and West Asian. A cuisine is a characteristic style of cooking practices and traditions, usually associated with ...
s, Italian cuisine
Italian cuisine (, ) is a Mediterranean cuisine#CITEREFDavid1988, David 1988, Introduction, pp.101–103 consisting of the ingredients, recipes and List of cooking techniques, cooking techniques developed across the Italian Peninsula and late ...
, Jewish cuisine
Jewish cuisine refers to the worldwide cooking traditions of the Jewish people. During its evolution over the course of many centuries, it has been shaped by Jewish dietary laws (''kashrut''), Jewish festivals and holidays, and traditions ce ...
, and Latin American cuisine
Latin American cuisine is the typical foods, beverages, and cooking styles common to many of the countries and cultures in Latin America. Latin America is a highly diverse area of land whose nations have varying cuisines. Some items typical o ...
s were the most popular ethnic cuisines on Long Island as of the second decade of the 2000s. Asian cuisines are predominantly represented by East Asian
East Asia is the eastern region of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The modern states of East Asia include China, Japan, Mongolia, North Korea, South Korea, and Taiwan. China, North Korea, South Korea ...
, South Asian
South Asia is the southern subregion of Asia, which is defined in both geographical and ethno-cultural terms. The region consists of the countries of Afghanistan, Bangladesh, Bhutan, India, Maldives, Nepal, Pakistan, and Sri Lanka.;;;;;;;; ...
, and Middle Eastern
The Middle East ( ar, الشرق الأوسط, ISO 233: ) is a geopolitical region commonly encompassing Arabia (including the Arabian Peninsula and Bahrain), Asia Minor (Asian part of Turkey except Hatay Province), East Thrace (Europea ...
cuisines. Italian cuisine is found in ubiquitous pizzeria
A pizzeria is a restaurant focusing on pizza. As well as pizza, dishes at pizzerias can include kebab, salads and pasta.
Many pizzerias offer take-away, where the customer orders their food either in advance or at the restaurant and then take ...
s throughout the island, with the region hosting an annual competition, the Long Island Pizza Festival & Bake-Off. Jewish cuisine is likewise represented by delicatessen
Traditionally, a delicatessen or deli is a retail establishment that sells a selection of fine, exotic, or foreign prepared foods. Delicatessen originated in Germany (original: ) during the 18th century and spread to the United States in the m ...
s and bagel
A bagel ( yi, בײגל, translit=beygl; pl, bajgiel; also spelled beigel) is a bread roll originating in the Jewish communities of Poland. It is traditionally shaped by hand into a roughly hand-sized ring from yeasted wheat dough that is fi ...
stores. Latin American cuisines span their geographical origins, from Brazilian rodizios to Mexican
Mexican may refer to:
Mexico and its culture
*Being related to, from, or connected to the country of Mexico, in North America
** People
*** Mexicans, inhabitants of the country Mexico and their descendants
*** Mexica, ancient indigenous people ...
taquerias.
Sports
Major league sports
TheNew York Mets
The New York Mets are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of Queens. The Mets compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. They are one of two major lea ...
baseball team plays at Citi Field
Citi Field is a baseball stadium located in Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in New York City, United States. It opened in 2009 and is the home field of Major League Baseball's New York Mets. The stadium was built as a replacement for the adjacent ...
in Flushing Meadows-Corona Park
Flushing may refer to:
Places
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in the United Kingdom
* Flushing, Queens, New York City
** Flushing Bay, a bay off the north shore of Queens
** Flushing Chinatown (法拉盛華埠), a community in Queens
** Flushi ...
, Queens. Their former stadium, Shea Stadium
Shea Stadium (), formally known as William A. Shea Municipal Stadium, was a multi-purpose stadium in Flushing Meadows–Corona Park, Queens, New York City.
was also home for the New York Jets
The New York Jets are a professional American football team based in the New York metropolitan area. The Jets compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's American Football Conference (AFC) East division. The ...
football team from 1964 until 1983. The new stadium has an exterior façade and main entry rotunda inspired by Brooklyn's famous Ebbets Field
Ebbets Field was a Major League Baseball stadium in the Flatbush section of Brooklyn, New York. It is mainly known for having been the home of the Brooklyn Dodgers baseball team of the National League (1913–1957). It was also home to five pr ...
(see below). The New York Mets
The New York Mets are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of Queens. The Mets compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. They are one of two major lea ...
planned to move their Double-A farm team to Long Island, as part of the ambitious but now-defunct plan for Nassau County called The Lighthouse Project
The Lighthouse Project, officially named The Lighthouse at Long Island, was a proposed transformation of the Nassau Veterans Memorial Coliseum and the area surrounding it into a modern suburban area. The project was first introduced by New York ...
. The Brooklyn Cyclones
The Brooklyn Cyclones are a Minor League Baseball team of the South Atlantic League and the High-A affiliate of the New York Mets. They are based in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, and play at Maimonides Park, just off the Coney Islan ...
are a minor league baseball team, affiliated with the New York Mets. The Cyclones play at MCU Park just off the boardwalk on Coney Island
Coney Island is a peninsular neighborhood and entertainment area in the southwestern section of the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The neighborhood is bounded by Brighton Beach and Manhattan Beach, Brooklyn, Manhattan Beach to its east, L ...
in Brooklyn. An artificial turf
Artificial turf is a surface of synthetic fibers made to look like natural grass. It is most often used in arenas for sports that were originally or are normally played on grass. However, it is now being used on residential lawns and commerc ...
baseball complex named Baseball Heaven
Baseball Heaven (BBH) is a 27-acre baseball complex in Yaphank, New York
Yaphank () is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in Suffolk County, New York, United States. The population was 5,945 at the time of the 2010 census.
Yaphank is ...
is in Yaphank.
 The
The Barclays Center
Barclays Center is a multi-purpose list of indoor arenas, indoor arena in the New York City Boroughs of New York City, borough of Brooklyn. The arena is home to the Brooklyn Nets of the National Basketball Association and the New York Liberty o ...
, a sports arena
An arena is a large enclosed platform, often circular or oval-shaped, designed to showcase theatre, musical performances, or sporting events. It is composed of a large open space surrounded on most or all sides by tiered seating for spectator ...
, business, and residential complex built partly on a platform over the Atlantic Yards
Pacific Park is a mixed-use commercial and residential development project by Forest City Ratner that will consist of 17 high-rise buildings, under construction in Prospect Heights, adjacent to Downtown Brooklyn, Park Slope, and Fort Greene in ...
at Atlantic Avenue in Brooklyn, is the home of the Brooklyn Nets
The Brooklyn Nets are an American professional basketball team based in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The Nets compete in the National Basketball Association (NBA) as a member of the Atlantic Division of the Eastern Conference. The ...
basketball team. The move from New Jersey in the summer of 2012 marked the return to Long Island for the Nets franchise, which played at Nassau Veterans Memorial Coliseum in Uniondale from 1972 to 1977. The Islanders played at Nassau Coliseum from their 1972 inception through 2015, and then splitting time between Nassau Coliseum and Barclays Center from 2017 to 2021, playing their last full season at the Nassau Coliseum during the 2020-2021 NHL Season. The Islanders moved full-time to UBS Arena at Belmont Park, in Elmont, New York
Elmont is an unincorporated hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) located in northwestern Hempstead in Nassau County, New York, United States, along its border with the borough of Queens in New York City. The population was 35,265 at the 2 ...
, in November 2021.
Ebbets Field, which stood in Brooklyn from 1913 until its demolition in 1960, was the home of the Brooklyn Dodgers
The Brooklyn Dodgers were a Major League Baseball team founded in 1884 as a member of the American Association before joining the National League in 1890. They remained in Brooklyn until 1957, after which the club moved to Los Angeles, Californi ...
baseball team, who moved to California
California is a state in the Western United States, located along the Pacific Coast. With nearly 39.2million residents across a total area of approximately , it is the most populous U.S. state and the 3rd largest by area. It is also the m ...
after the 1957 Major League Baseball season to become the Los Angeles Dodgers
The Los Angeles Dodgers are an American professional baseball team based in Los Angeles. The Dodgers compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the National League (NL) National League West, West division. Established in 1883 i ...
. The Dodgers won several National League
The National League of Professional Baseball Clubs, known simply as the National League (NL), is the older of two leagues constituting Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, and the world's oldest extant professional team s ...
pennants in the 1940s and 1950s, losing several times in the World Series
The World Series is the annual championship series of Major League Baseball (MLB) in the United States and Canada, contested since 1903 between the champion teams of the American League (AL) and the National League (NL). The winner of the Worl ...
—often called '' Subway Series''—to their Bronx
The Bronx () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Bronx County, in the state of New York. It is south of Westchester County; north and east of the New York City borough of Manhattan, across the Harlem River; and north of the New Y ...
rivals, the New York Yankees
The New York Yankees are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of the Bronx. The Yankees compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member club of the American League (AL) East division. They are one ...
. The Dodgers won their lone championship in Brooklyn in the 1955 World Series versus the Yankees.
Despite this success during the latter part of the team's stay in Brooklyn, they were a second-division team with an unspectacular winning record for much of their history there – but nonetheless became legendary for the almost-fanatical devotion of the Brooklynites who packed the relatively small ballpark to vigorously root for the team they affectionately called, "Dem Bums". Loss of the Dodgers to California was locally considered a civic tragedy that negatively affected the community far more than the similar moves of other established teams to new cities in the 1950s, including the Dodgers' long-time arch-rival New York Giants
The New York Giants are a professional American football team based in the New York metropolitan area. The Giants compete in the National Football League (NFL) as a member club of the league's National Football Conference (NFC) East divisio ...
, who also left for California after 1957.
Minor league and college sports

 The
The Stony Brook Seawolves
The Stony Brook Seawolves are the athletic teams of Stony Brook University in Stony Brook, New York, United States. The school competes at the Division I level of the National Collegiate Athletic Association and joined the all-sports Colonial ...
represent Stony Brook University
Stony Brook University (SBU), officially the State University of New York at Stony Brook, is a public research university in Stony Brook, New York. Along with the University at Buffalo, it is one of the State University of New York system' ...
, and have had a bevy of athletic accomplishments such as reaching the 2012 College World Series as an underdog after defeating the LSU Tigers
The LSU Tigers and Lady Tigers are the athletic teams representing Louisiana State University (LSU), a state university located in Baton Rouge, Louisiana. LSU competes in NCAA Division I, Division I of the National Collegiate Athletic Associat ...
in a best-of-3 series.
Long Island is also home to the Long Island Ducks
The Long Island Ducks are an American professional minor-league baseball team based on Long Island in Central Islip, New York. The Ducks compete in the North Division of the Atlantic League of Professional Baseball (ALPB), an independent "part ...
minor league baseball team of the Atlantic League. Their stadium, Bethpage Ballpark
Fairfield Properties Ballpark is a 6,002-seat baseball park in Central Islip, New York that serves as the home of the Long Island Ducks, an independent professional baseball team that is a member of the Atlantic League of Professional Baseball. I ...
, is in Central Islip. The Brooklyn Cyclones
The Brooklyn Cyclones are a Minor League Baseball team of the South Atlantic League and the High-A affiliate of the New York Mets. They are based in the New York City borough of Brooklyn, and play at Maimonides Park, just off the Coney Islan ...
minor league baseball team, affiliated with the New York Mets
The New York Mets are an American professional baseball team based in the New York City borough of Queens. The Mets compete in Major League Baseball (MLB) as a member of the National League (NL) East division. They are one of two major lea ...
, plays in the High-A
High-A (officially Class High-A, formerly known as Class A-Advanced, and sometimes abbreviated "A+" in writing) is the third-highest level of play in Minor League Baseball in the United States and Canada, below Triple-A and Double-A, and abov ...
classification South Atlantic League
The South Atlantic League, often informally called the Sally League, is a Minor League Baseball league with teams predominantly in states along the Atlantic coast of the United States from New York to Georgia. A Class A league for most of its ...
. The Cyclones play at MCU Park just off the Coney Island Boardwalk in the New York City borough of Brooklyn. The New York Dragons of the Arena Football League
The Arena Football League (AFL) was a professional arena football league in the United States. It was founded in 1986, but played its first official games in the 1987 season, making it the third longest-running professional football league in ...
played their home games at Nassau Coliseum
Nassau Veterans Memorial Coliseum (or simply the Nassau Coliseum) is a multi-purpose indoor arena in Uniondale, New York, east of New York City. The Long Island venue is approximately east of the eastern limits of the New York City Borough of ...
. The two main rugby union
Rugby union, commonly known simply as rugby, is a close-contact team sport that originated at Rugby School in the first half of the 19th century. One of the two codes of rugby football, it is based on running with the ball in hand. In it ...
teams are the Long Island RFC
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music mensu ...
in East Meadow
East Meadow is a hamlet and census-designated place (CDP) in the Town of Hempstead in Nassau County, on Long Island, in New York. The population was 38,132 at the 2010 census.
Many residents commute to Manhattan, which is away.
History
In 16 ...
and the Suffolk Bull Moose in Stony Brook.
The New York Sharks is a women's American football team that is a member of the Women's Football Alliance
The Women's Football Alliance (WFA) is a professional full-contact Women's American football tackle minor league that began play in 2009. It is the largest 11-on-11 football league for women in the world, and the longest running active women's ...
. The New York Sharks home field is at Aviator Sports Complex in Brooklyn.
Long Island's professional soccer club, the New York Cosmos New York Cosmos may refer to
* New York Cosmos (1970–1985), a team in the North American Soccer League (then the top-tier soccer league in the United States and Canada)
* New York Cosmos (2010), a team playing since 2020 in the National Independ ...
, play in the Division 2 North American Soccer League The North American Soccer League may refer to:
*North American Soccer League (1968–1984), a former Division I league
*North American Soccer League (2011–2017)
The North American Soccer League (NASL) was a professional men's soccer league ba ...
at James M. Shuart Stadium
The James M. Shuart Stadium is an 11,929-seat multi-purpose stadium and sports facility, the facility serves as the home to Hofstra's lacrosse teams on the campus of Hofstra University in Hempstead, New York. First opened in 1963, and remodeled in ...
in Hempstead.
Long Island has historically been a hotbed of lacrosse
Lacrosse is a team sport played with a lacrosse stick and a lacrosse ball. It is the oldest organized sport in North America, with its origins with the indigenous people of North America as early as the 12th century. The game was extensiv ...
at the youth and college
A college (Latin: ''collegium'') is an educational institution or a constituent part of one. A college may be a degree-awarding tertiary educational institution, a part of a collegiate or federal university, an institution offerin ...
level, which made way for a Major League Lacrosse
Major League Lacrosse (MLL) was a men's field lacrosse league in the United States. The league's inaugural season was in 2001. Teams played anywhere from ten to 16 games in a summertime regular season. This was followed by a four-team playoff ...
team in 2001, the Long Island Lizards
The New York Lizards, originally the Long Island Lizards, were a Major League Lacrosse (MLL) team based in Hempstead, New York, located on Long Island. They are original members of the MLL. They lost the league's inaugural game on June 7, 2001 to ...
. The Lizards play at Mitchel Athletic Complex
The Mitchel Athletic Complex is part of the Mitchel Field complex, located in Uniondale, New York, on the site of the decommissioned Mitchel Air Force Base. The facility is owned by Nassau County. It is used mostly for football and soccer and a ...
in Uniondale.
Other sports
 Long Island has a wide variety of
Long Island has a wide variety of golf course
A golf course is the grounds on which the sport of golf is played. It consists of a series of holes, each consisting of a tee box, a fairway, the rough and other hazards, and a green with a cylindrical hole in the ground, known as a "cup". ...
s found all over the island. Two of the most well-known are the Shinnecock Hills Golf Club
Shinnecock Hills Golf Club is a links-style golf club located in an unincorporated area of the Town of Southampton on Long Island, New York, situated between the Peconic Bay and the Atlantic Ocean.
Shinnecock Hills is believed to be the oldes ...
and the public Bethpage Black Course that has hosted multiple U.S. Open tournaments as well as several other top level international championships. Queens also hosts one of the four tennis
Tennis is a racket sport that is played either individually against a single opponent (singles) or between two teams of two players each (doubles). Each player uses a tennis racket that is strung with cord to strike a hollow rubber ball cov ...
grand slams, the US Open. Every August (September, in Olympic years) the best tennis players in the world travel to Long Island to play the championships held in the USTA National Tennis Center
The USTA Billie Jean King National Tennis Center is a stadium complex within Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in Queens, New York City, United States. It has been the home of the US Open Grand Slam tennis tournament, played every year in Aug ...
, adjacent to Citi Field
Citi Field is a baseball stadium located in Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in New York City, United States. It opened in 2009 and is the home field of Major League Baseball's New York Mets. The stadium was built as a replacement for the adjacent ...
in Flushing Meadows Park
Flushing may refer to:
Places
* Flushing, Cornwall, a village in the United Kingdom
* Flushing, Queens, New York City
** Flushing Bay, a bay off the north shore of Queens
** Flushing Chinatown (法拉盛華埠), a community in Queens
** Flushi ...
. The complex also contains the biggest tennis stadium in the world, the Arthur Ashe Stadium
Arthur Ashe Stadium is a tennis stadium at Flushing Meadows–Corona Park in Queens, New York City. Part of the USTA Billie Jean King National Tennis Center, it is the main stadium of the US Open tennis tournament and has a capacity of 23,771, ...
.
Long Island also has two horse racing
Horse racing is an equestrian performance sport, typically involving two or more horses ridden by jockeys (or sometimes driven without riders) over a set distance for competition. It is one of the most ancient of all sports, as its basic pr ...
tracks, Aqueduct Racetrack
Aqueduct Racetrack is a Thoroughbred horse racing facility and casino in the South Ozone Park and Jamaica neighborhoods of Queens, New York City, United States. Aqueduct is the only racetrack located within New York City limits. Its racing m ...
in Ozone Park, Queens and Belmont Park
Belmont Park is a major thoroughbred horse racing facility in the northeastern United States, located in Elmont, New York, just east of the New York City limits. It was opened on May 4, 1905.
It is operated by the non-profit New York Racin ...
on the Queens/Nassau border in Elmont, home of the Belmont Stakes
The Belmont Stakes is an American Grade I stakes race for three-year-old Thoroughbreds run at Belmont Park in Elmont, New York. It is run over 1.5 miles (2,400 m). Colts and geldings carry a weight of ; fillies carry . The race, nickname ...
. The longest dirt thoroughbred racecourse in the world is also at Belmont Park. Another category of sporting events popular in this region involves firematic racing events, involving many local volunteer fire department
A volunteer fire department (VFD) is a fire department of volunteers who perform fire suppression and other related emergency services for a local jurisdiction. Volunteer and retained (on-call) firefighters are expected to be on call to respon ...
s.
Notable sportspeople and teams
Long Island is home to numerous famous athletes, includingHall of Fame
A hall, wall, or walk of fame is a list of individuals, achievements, or other entities, usually chosen by a group of electors, to mark their excellence or fame in their field. In some cases, these halls of fame consist of actual halls or muse ...
rs Jim Brown
James Nathaniel Brown (born February 17, 1936) is a former American football player, sports analyst and actor. He played as a fullback for the Cleveland Browns of the National Football League (NFL) from 1957 through 1965. Considered to be one ...
, Julius Erving, John Mackey, Whitey Ford
Edward Charles "Whitey" Ford (October 21, 1928 – October 8, 2020), nicknamed "the Chairman of the Board", was an American professional baseball pitcher who played his entire 16-year Major League Baseball (MLB) career with the New York Yankees ...
, Nick Drahos
Nick Drahos (December 6, 1918 – May 12, 2018) was an American football end. He played college football at Cornell University and was a member of the Sphinx Head Society. He was elected to the College Football Hall of Fame
The College Footb ...
, and Carl Yastrzemski
Carl Michael Yastrzemski ( ; nicknamed "Yaz"; born August 22, 1939) is an American former Major League Baseball player. He was elected to the Baseball Hall of Fame in 1989. Yastrzemski played his entire 23-year Major League career with the Bost ...
. Others include gold medalists Sue Bird
Suzanne Brigit Bird (born October 16, 1980) is an American former professional basketball player who played her entire career with the Seattle Storm of the Women's National Basketball Association ( WNBA) Bird was drafted by the Storm first over ...
, Sarah Hughes and Derrick Adkins
Derrick Ralph Adkins (born July 2, 1970) is a former American track and field athlete who specialized in the 400-meter hurdles. He was an Olympic gold medalist in that event at the 1996 Summer Olympics and World Champion at the 1995 World Cha ...
, USWNT World Cup champions Crystal Dunn and Alexandra Long
Alexandra Linsley Long (born August 13, 1987) is an American soccer player who plays as a midfielder for NJ/NY Gotham FC in the National Women's Soccer League and the United States national team. She made her debut for the national team on May ...
, D'Brickashaw Ferguson
D'Brickashaw Montgomery Ferguson (born December 10, 1983) is a former American football offensive tackle who played ten seasons for the New York Jets of the National Football League (NFL). He played college football for the University of Virgin ...
, Billy Donovan
William John Donovan Jr. (born May 30, 1965) is an American professional basketball coach and former player. He has served as head coach of the Chicago Bulls of the National Basketball Association (NBA) since September 2020 after previously coa ...
, Larry Brown, Rick Pitino, John McEnroe
John Patrick McEnroe Jr. (born February 16, 1959) is an American former professional tennis player. He was known for his shot-making and volleying skills, his rivalries with Björn Borg and Jimmy Connors, and his confrontational on-court beh ...
, Jumbo Elliott, Mick Foley
Michael Francis Foley (born June 7, 1965) is an American actor, author, retired professional wrestler, and color commentator. He is currently signed to WWE under the company's Legends program, acting as a company ambassador.
Foley worked for m ...
, Zack Ryder, Matt Serra
Matthew John Serra (born June 2, 1974) is an American former professional mixed martial artist and Brazilian Jiu-Jitsu practitioner who competed for the Ultimate Fighting Championship. He is the co-star of Dana White: Lookin' for a Fight and co ...
, Boomer Esiason, Vinny Testaverde
Vincent Frank Testaverde Sr. (; born November 13, 1963) is a former American football quarterback who played in the National Football League (NFL) for 21 seasons. He played college football at Miami, where he was an All-American and won the H ...
, Craig Biggio, Frank Catalanotto, Greg Sacks, Gilles Villemure
Joseph Hector Gilles Villemure (born May 30, 1940) is a Canadian former professional ice hockey goaltender. He played for the New York Rangers and Chicago Black Hawks in the 1960s and 1970s. Villemure was born in Trois-Rivières, Quebec.
Playing ...
, Rob Burnett, Steve Park, Frank Viola
Frank John Viola Jr. (born April 19, 1960) is an American former starting pitcher in Major League Baseball who played for the Minnesota Twins (1982–1989), New York Mets (1989–1991), Boston Red Sox (1992–1994), Cincinnati Reds (1995), and To ...
, Chris Weidman, Marques Colston
Marques E. Colston ( born June 5, 1983) is a former American football wide receiver. He played college football at Hofstra University, and was drafted by the New Orleans Saints in the seventh round of the 2006 NFL Draft. He helped the Saints ac ...
and Speedy Claxton.
Several NHL players were born and/or raised on Long Island, such as Vancouver Canucks Christopher Higgins and Matt Gilroy
Matthew J. Gilroy (born July 20, 1984) is an American former professional ice hockey defenseman who last played for the SC Rapperswil-Jona Lakers of the National League (NL). Gilroy played in National Hockey League (NHL) with the New York Range ...
, Nashville Predators Eric Nystrom, Toronto Maple Leaf Mike Komisarek, Pittsburgh Penguin Rob Scuderi
Robert John Scuderi (born December 30, 1978) is an American former professional ice hockey defenseman, currently serving as an assistant coach for the National Hockey League's Nashville Predators.
Known as a stay-at-home defenseman, he played i ...
, and New York Ranger Keith Kinkaid. Both Komisarek and Higgins played on the same Suffolk County Hockey League team at an early age, and later played on the Montreal Canadiens
The Montreal CanadiensEven in English, the French spelling is always used instead of ''Canadians''. The French spelling of ''Montréal'' is also sometimes used in the English media. (french: link=no, Les Canadiens de Montréal), officially ...
together. Nick Drahos was an All Scholastic and All Long Island honoree at Lawrence High School, Nassau Co. in 1936 and 1937, and a two-time Unanimous National College All-American in 1939 and 1940 at Cornell University.
Transportation
 Many major forms of transportation serve Long Island, including aviation via
Many major forms of transportation serve Long Island, including aviation via John F. Kennedy International Airport
John F. Kennedy International Airport (colloquially referred to as JFK Airport, Kennedy Airport, New York-JFK, or simply JFK) is the main international airport serving New York City. The airport is the busiest of the seven airports in the Avia ...
, LaGuardia Airport, and Long Island MacArthur Airport, and multiple smaller airports; rail transportation via the Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
and the New York City Subway
The New York City Subway is a rapid transit system owned by the government of New York City and leased to the New York City Transit Authority, an affiliate agency of the state-run Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA). Opened on October ...
; bus routes via MTA Regional Bus Operations, Nassau Inter-County Express, and Suffolk County Transit
Suffolk County Transit is the provider of bus services in Suffolk County, New York on Long Island and is an agency of the Suffolk County government. It was founded in 1980 as a county-run oversight and funding agency for a group of private contr ...
; ferry service via NYC Ferry
NYC Ferry is a public network of ferry routes in New York City operated by Hornblower Cruises. , there are six routes, as well as one seasonal route, connecting 25 ferry piers across all five boroughs. NYC Ferry has the largest passenger fleet ...
and multiple smaller ferry companies; and several major highways. There are historic and modern bridges, and recreational and commuter trails, serving various parts of Long Island.
There are eleven road crossings out of Long Island, all but one providing Brooklyn-Manhattan, Queens-Manhattan, and Queens-Bronx connections across the East River, with the Triborough Bridge providing two connections from Queens, one each to Manhattan and the Bronx. The single non-East River crossing is the Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge
The Verrazzano-Narrows Bridge ( ) is a suspension bridge connecting the New York City boroughs of Staten Island and Brooklyn. It spans the Narrows, a body of water linking the relatively enclosed New York Harbor with Lower New York Bay and t ...
, connecting Brooklyn to Staten Island
Staten Island ( ) is a Boroughs of New York City, borough of New York City, coextensive with Richmond County, in the U.S. state of New York (state), New York. Located in the city's southwest portion, the borough is separated from New Jersey b ...
across The Narrows. Plans for a Long Island Sound link
The Long Island Sound link is a proposed bridge or tunnel that would link Long Island, New York, to Westchester County or Connecticut, across Long Island Sound east of the Throgs Neck Bridge. The project has been studied and debated since the ...
at locations in Nassau and Suffolk counties (a proposed bridge or tunnel that would link Long Island to the south with Westchester County, New York or Connecticut to the north across Long Island Sound) have been discussed for decades, but there are no plans to construct such a crossing.
Public transportation
 The MTA implements mass transportation for the
The MTA implements mass transportation for the New York metropolitan area
The New York metropolitan area, also commonly referred to as the Tri-State area, is the largest metropolitan area in the world by urban area, urban landmass, at , and one of the list of most populous metropolitan areas, most populous urban agg ...
including all five boroughs of New York City, the suburban counties of Dutchess, Nassau
Nassau may refer to:
Places Bahamas
*Nassau, Bahamas, capital city of the Bahamas, on the island of New Providence
Canada
*Nassau District, renamed Home District, regional division in Upper Canada from 1788 to 1792
*Nassau Street (Winnipeg), ...
, Orange, Putnam, Rockland, Suffolk
Suffolk () is a ceremonial county of England in East Anglia. It borders Norfolk to the north, Cambridgeshire to the west and Essex to the south; the North Sea lies to the east. The county town is Ipswich; other important towns include ...
, and Westchester, all of which together are the "Metropolitan Commuter Transportation District (MCTD)".
The MTA considers itself to be the largest regional public transportation provider in the Western Hemisphere. , MTA agencies move about 8.6 million customers per day (translating to 2.65 billion rail and bus customers a year). The MTA's systems carry over 11 million passengers on an average weekday systemwide, and over 850,000 vehicles on its seven toll bridges and two tunnels per weekday.
Rail
Long Island Rail Road
The Long Island Rail Road , often abbreviated as the LIRR, is a commuter rail system in the southeastern part of the U.S. state of New York, stretching from Manhattan to the eastern tip of Suffolk County on Long Island. With an average week ...
(LIRR) is North America's busiest commuter railroad system, carrying an average of 282,400 passengers each weekday on 728 daily trains. Chartered on April 24, 1834, and operating continuously since, it is also the oldest railroad
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a prep ...
in the U.S. that still operates under its original charter and name. The Metropolitan Transportation Authority
The Metropolitan Transportation Authority (MTA) is a public benefit corporation responsible for public transportation in the New York City metropolitan area of the U.S. state of New York. The MTA is the largest public transit authority in th ...
has operated the LIRR as one of its two commuter railroads since 1966, and the LIRR is one of the few railroads worldwide that provides service all the time, year round. In July 2017, a $2 billion plan to add a third railroad track to the LIRR Main Line between the Floral Park and Hicksville station
Hicksville is a station on the Main Line and Port Jefferson Branch of the Long Island Rail Road located in Hicksville, New York. It is the busiest station east of Jamaica and Penn Station by combined weekday/weekend ridership. As of May 2011, ...
s in Nassau County was approved. Other LIRR projects, such as the Ronkonkoma Branch
The Ronkonkoma Branch is a rail service operated by the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR) in the U.S. state of New York. On LIRR maps and printed schedules, the "Ronkonkoma Branch" includes trains running along the railroad's Main Line from Hicksv ...
Double Track Project, are also underway. Five "readiness projects" across the LIRR system, which will cost a combined $495 million, are also under construction in preparation for expanded peak-hour LIRR service after the completion of East Side Access
East Side Access (ESA) is a public works project in New York City that extended the Long Island Rail Road (LIRR) from its Main Line in Queens into a new station under Grand Central Terminal on Manhattan's East Side. A project of the Metropo ...
, which will bring LIRR trains to Grand Central Terminal
Grand Central Terminal (GCT; also referred to as Grand Central Station or simply as Grand Central) is a commuter rail terminal located at 42nd Street and Park Avenue in Midtown Manhattan, New York City. Grand Central is the southern terminus ...
.
Bus
 Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE) provides bus service in Nassau County, while
Nassau Inter-County Express (NICE) provides bus service in Nassau County, while Suffolk County Transit
Suffolk County Transit is the provider of bus services in Suffolk County, New York on Long Island and is an agency of the Suffolk County government. It was founded in 1980 as a county-run oversight and funding agency for a group of private contr ...
, an agency of the Suffolk County government, provides bus service in Suffolk County. In 2012, NICE replaced the former MTA Long Island Bus in transporting Long Islanders across Nassau County while allowing them to use MTA MetroCards as payment.
Roads
 The
The Long Island Expressway
Long may refer to:
Measurement
* Long, characteristic of something of great duration
* Long, characteristic of something of great length
* Longitude (abbreviation: long.), a geographic coordinate
* Longa (music), note value in early music me ...
, Northern State Parkway, and Southern State Parkway
The Southern State Parkway (also known as the Southern State or Southern Parkway; abbreviated as SO on signage) is a limited-access highway on Long Island, New York, in the United States. The parkway begins at an interchange with the Belt and ...
, all products of the automobile-centered planning of Robert Moses
Robert Moses (December 18, 1888 – July 29, 1981) was an American urban planner and public official who worked in the New York metropolitan area during the early to mid 20th century. Despite never being elected to any office, Moses is regarded ...
, are the island's primary east–west high-speed controlled-access highway
A controlled-access highway is a type of highway that has been designed for high-speed vehicular traffic, with all traffic flow—ingress and egress—regulated. Common English terms are freeway, motorway and expressway. Other similar terms i ...
s.
Ground transportation
Several hundred transportation companies service the Long Island/New York City area. Winston Airport Shuttle, the oldest of these companies in business since 1973, was the first to introduce door-to-door shared-ride service to and from the major airports, which almost all transportation companies now use.See also
* List of tallest buildings on Long Island * Geography of New York City *List of films shot on Long Island
The following is a list of films shot fully or partially on Long Island.
References
{{Reflist
*
Films shot on Long Island
Films shot on
Long Island
Long Island is a densely populated island in the southeastern region of the U.S. state ...
* List of Long Island recreational facilities
* List of Long Islanders
This is a list of notable people either born in, from or connected to Long Island. List
Born on Long Island
* 50 Cent (rapper, actor)
* Hoodie Allen (rapper)
* Donatella Arpaia (restaurateur and a television personality)
* Ashanti (Singer) (sing ...
, famous residents of Nassau and Suffolk
* List of people from New York City, including famous residents of Brooklyn and Queens
* Long Island (proposed state)
* Timeline of town creation in Downstate New York The towns and cities of Downstate New York were created by the U.S. state of New York as municipalities in order to give residents more direct say over local government. Present-day Westchester, Bronx, New York, Richmond, Kings, Queens, Nassau, an ...
* Coastal Connecticut
* Jersey Shore
The Jersey Shore (known by locals simply as the Shore) is the coastal region of the U.S. state of New Jersey. Geographically, the term encompasses about of oceanfront bordering the Atlantic Ocean, from Perth Amboy in the north to Cape May P ...
Notes
References
External links
* {{authority control Coastal islands of New York (state) Islands of New York City Islands of New York (state) Landforms of Long Island Moraines of the United States New York metropolitan area