Ljudevit Posavski on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Ljudevit () or Liudewit ( la, Liudewitus), often also , was the
 In January of 820, Borna made an alliance with the Frankish Emperor in
In January of 820, Borna made an alliance with the Frankish Emperor in
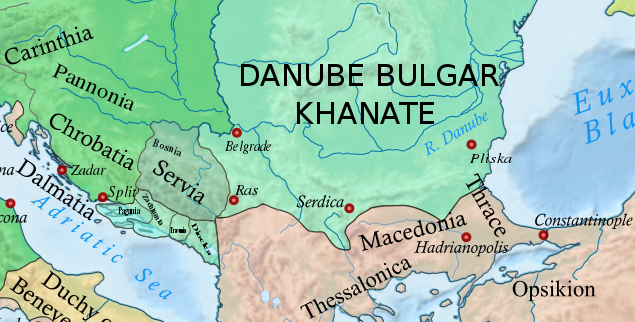 According to
According to
Duke
Duke is a male title either of a monarch ruling over a duchy, or of a member of royalty, or nobility. As rulers, dukes are ranked below emperors, kings, grand princes, grand dukes, and sovereign princes. As royalty or nobility, they are r ...
of the Slavs in Lower Pannonia
Early Slavs settled in the eastern and southern parts of the former Roman province of Pannonia. The term ''Lower Pannonia'' ( la, Pannonia inferior, hu, Alsó-pannoniai grófság, sh-Latn-Cyrl, Donja Panonija, Доња Панонија, sl, S ...
from 810 to 823. The capital of his realm was in Sisak
Sisak (; hu, Sziszek ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in central Croatia, spanning the confluence of the Kupa, Sava and Odra rivers, southeast of the Croatian capital Zagreb, and is usually considered to be where the Posavin ...
(today in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domovino"("Our Beautiful Homeland")
, image_map =
, map_caption =
, capi ...
). As the ruler of the Pannonian Slavs, he led a resistance to Frankish domination. Having lost the war against Franks, he fled to the south, presumably to Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
, first to an unknown Serb
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian ancestry, culture, history and language.
The majority of Serbs live in their na ...
župa (a topic of historical debates), and then to the Croat ruler Ljudemisl, who treacherously killed him.
Rebellions against the Franks
In 818 Ljudevit sent his emissaries toEmperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
Louis in Heristal. They described the horrors conducted by Margrave
Margrave was originally the medieval title for the military commander assigned to maintain the defence of one of the border provinces of the Holy Roman Empire or of a kingdom. That position became hereditary in certain feudal families in the ...
Cadolah of Friuli (800-819) and his men in Pannonia
Pannonia (, ) was a province of the Roman Empire bounded on the north and east by the Danube, coterminous westward with Noricum and upper Italy, and southward with Dalmatia and upper Moesia. Pannonia was located in the territory that is now west ...
, but the King of Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
refused to make peace. Ljudevit raised a rebellion against his Frankish rulers in 819 after he was seriously accused by the Frankish court. The Emperor
An emperor (from la, imperator, via fro, empereor) is a monarch, and usually the sovereign ruler of an empire or another type of imperial realm. Empress, the female equivalent, may indicate an emperor's wife ( empress consort), mother ( ...
Louis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
(814-840) sent Cadolah to quell the rebellion. The Frankish Frontier forces led by Cadolah have raided the land and tortured the population, most notably the children. As the Pannonian Slavs were amassing forces, so did the Franks
The Franks ( la, Franci or ) were a group of Germanic peoples whose name was first mentioned in 3rd-century Roman sources, and associated with tribes between the Lower Rhine and the Ems River, on the edge of the Roman Empire.H. Schutz: Tools ...
led by Cadolah return in 819. But the Frankish forces were soon defeated; and Cadolah himself had to retreat back to his home Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
, where soon he died of disease.
In July 819 on the Council in Ingelheim Ljudevit's emissaries offered truce conditions, but Emperor Louis refused; demanding more concessions to him. Ljudevit started to gather allies for his plight. His original ally was Duke Borna (Dux Dalmatiae et Liburniae) - the leader of the Guduscani (Gačani), but the Frankish ruler had promised Borna that he would make him ''Prince of Pannonia'' if he helped the Franks to crush Ljudevit's rebellion; so Borna accepted. Ljudevit found assistance among the Carantanian and Carniolan Slavs who, as neighbours of the margravate of Friuli
Friuli ( fur, Friûl, sl, Furlanija, german: Friaul) is an area of Northeast Italy with its own particular cultural and historical identity containing 1,000,000 Friulians. It comprises the major part of the autonomous region Friuli Venezia Giuli ...
, were jeopardized the same as the Pannonians. The Timočani
The Timočani (also Timochani, or Timochans; Serbian and Bulgarian: Тимочани) were a medieval South Slavic tribe that lived in the territory of present-day eastern Serbia, west of the Timok River, as well as in the regions of Banat, S ...
(living around the valley of Timok) also joined him, because they were jeopardized by the neighbouring Bulgars
The Bulgars (also Bulghars, Bulgari, Bolgars, Bolghars, Bolgari, Proto-Bulgarians) were Turkic semi-nomadic warrior tribes that flourished in the Pontic–Caspian steppe and the Volga region during the 7th century. They became known as noma ...
.
The Franks sent a large army led by the new Margrave of Friuli, duke Baldric of Friuli to meet Ljudevit in autumn, the same year while he was conscripting more Carantanian troops along the river. The Frankish forces had numerical advantage, so they pushed Ljudevit and his men from Carniola across the Drava. Ljudevit had to fall back to central parts of his realm. Baldric didn't chase Ljudevit, since he had to pacify the Carantanians. Borna moved with Ljudevit's father-in-law Dragomuž and their forces from the south-west. At the heat of the Battle of Kupa, his own Guduscani abandoned Borna and crossed to Ljudevit's side; while Dragomuž was killed. Borna escaped from the battlefield with the help of his bodyguards.
Ljudevit seized the opportunity and breached into and raided Dalmatia
Dalmatia (; hr, Dalmacija ; it, Dalmazia; see names in other languages) is one of the four historical regions of Croatia, alongside Croatia proper, Slavonia, and Istria. Dalmatia is a narrow belt of the east shore of the Adriatic Sea, str ...
in December. Borna was too weak, so the Dalmatians defended themselves through sneaky tactics and used attrition as their best ally to exhaust the Pannonian forces. Harsh winter came to the hill areas, forcing Ljudevit to retreat. According to Borna's reports to the Frankish Emperor, Ljudevit suffered heavy casualties: 3,000 soldiers, over 300 horses and much food.
War continues
 In January of 820, Borna made an alliance with the Frankish Emperor in
In January of 820, Borna made an alliance with the Frankish Emperor in Aachen
Aachen ( ; ; Aachen dialect: ''Oche'' ; French and traditional English: Aix-la-Chapelle; or ''Aquisgranum''; nl, Aken ; Polish: Akwizgran) is, with around 249,000 inhabitants, the 13th-largest city in North Rhine-Westphalia, and the 28th ...
. The plan was to crush Ljudevit's realm with a joint-attack from three sides. As soon as the winter retreated, massive Frankish armies were being amassed in Italia, East Francia
East Francia (Medieval Latin: ) or the Kingdom of the East Franks () was a successor state of Charlemagne's empire ruled by the Carolingian dynasty until 911. It was created through the Treaty of Verdun (843) which divided the former empire int ...
, Bavaria
Bavaria ( ; ), officially the Free State of Bavaria (german: Freistaat Bayern, link=no ), is a state in the south-east of Germany. With an area of , Bavaria is the largest German state by land area, comprising roughly a fifth of the total l ...
, Saxony
Saxony (german: Sachsen ; Upper Saxon German, Upper Saxon: ''Saggsn''; hsb, Sakska), officially the Free State of Saxony (german: Freistaat Sachsen, links=no ; Upper Saxon: ''Freischdaad Saggsn''; hsb, Swobodny stat Sakska, links=no), is a ...
and Alemannia that were going to simultaneously invade Ljudevit's lands in the spring. The northern Frankish group moved from Bavaria across Pannonia to make an invasion across the river of Drava. Ljudevit's forces successfully stopped this Army
An army (from Old French ''armee'', itself derived from the Latin verb ''armāre'', meaning "to arm", and related to the Latin noun ''arma'', meaning "arms" or "weapons"), ground force or land force is a fighting force that fights primarily on ...
at the river. The southern group moved across the Noric Alps Noric may refer to:
* Noricum, an ancient region
* Noric Alps
*Noric language
* Noric race
*Noric steel
Noric steel was a steel from Noricum, a Celtic kingdom located in modern Austria and Slovenia.
The proverbial hardness of Noric steel is expr ...
, using the road from Aquileia
Aquileia / / / / ;Bilingual name of ''Aquileja – Oglej'' in: vec, Aquiłeja / ; Slovenian: ''Oglej''), group=pron is an ancient Roman city in Italy, at the head of the Adriatic at the edge of the lagoons, about from the sea, on the river ...
to Emona. Ljudevit was successful again, as he stopped them before crossing the Alps. The central group moved from Tyrol
Tyrol (; historically the Tyrole; de-AT, Tirol ; it, Tirolo) is a historical region in the Alps - in Northern Italy and western Austria. The area was historically the core of the County of Tyrol, part of the Holy Roman Empire, Austrian Emp ...
to Carniola
Carniola ( sl, Kranjska; , german: Krain; it, Carniola; hu, Krajna) is a historical region that comprised parts of present-day Slovenia. Although as a whole it does not exist anymore, Slovenes living within the former borders of the region s ...
. Ljudevit attempted to halt its advance three times, but every single time would the Franks win, using numerical advantage. When this Army reached the , Ljudevit had to fall back to the heart of his realm.
The Franks have opened ways for the southern and northern Armies, so they launched a total invasion. Ljudevit concluded that all resistance would be futile, so he retreated to a stronghold that he built on top of hill that was heavily fortified; while his people took shelter in local forest
A forest is an area of land dominated by trees. Hundreds of definitions of forest are used throughout the world, incorporating factors such as tree density, tree height, land use, legal standing, and ecological function. The United Nations' ...
and swamps
A swamp is a forested wetland.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p. Swamps are considered to be transition zones because both land and water play a role in ...
. Ljudevit did not negotiate with the Franks. The Franks eventually retreated from his lands, with their ranks thinned by disease which the northern forces caught in the marshes
A marsh is a wetland that is dominated by herbaceous rather than woody plant species.Keddy, P.A. 2010. Wetland Ecology: Principles and Conservation (2nd edition). Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, UK. 497 p Marshes can often be found at ...
of . The Slavs
Slavs are the largest European ethnolinguistic group. They speak the various Slavic languages, belonging to the larger Balto-Slavic branch of the Indo-European languages. Slavs are geographically distributed throughout northern Eurasia, main ...
from Carantania
Carantania, also known as Carentania ( sl, Karantanija, german: Karantanien, in Old Slavic '), was a Slavic principality that emerged in the second half of the 7th century, in the territory of present-day southern Austria and north-eastern ...
lost their internal independence and were forced to recognize the Friulian margrave Balderic as their ruler, while some remained loyal to Ljudevit. Prince Borna died in 821, and was succeeded by Ljudevit's nephew, Vladislav. Emperor Louis recognized as ''Prince of Dalmatia and Liburnia'' in February 821 at the Council of Aachen A number of significant councils of the Latin Church were held at Aachen (also known in French as ''Aix-la-Chapelle'') in the early Middle Ages.
In the mixed council of 798, Charlemagne proclaimed a capitulary of eighty-one chapters, largely a repe ...
.
The Emperor discussed again about war plans against Ljudevit on that Council. The Franks decided to repeat the progress, and push towards Ljudevit from three sides again. Ljudevit saw that it was obvious that he couldn't fight the Franks on open field, so he began to construct massive fortifications
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''face ...
. He was helped by the Venetian Patriarch
The highest-ranking bishops in Eastern Orthodoxy, Oriental Orthodoxy, the Catholic Church (above major archbishop and primate), the Hussite Church, Church of the East, and some Independent Catholic Churches are termed patriarchs (and in c ...
Fortunat who sent him architects
An architect is a person who plans, designs and oversees the construction of buildings. To practice architecture means to provide services in connection with the design of buildings and the space within the site surrounding the buildings that h ...
and masons from Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...
.
During the last and final Frankish invasion of 822, the Patriarch from Grado, Fortunat, who was a supporter of Ljudevit, fled to Zadar
Zadar ( , ; historically known as Zara (from Venetian and Italian: ); see also other names), is the oldest continuously inhabited Croatian city. It is situated on the Adriatic Sea, at the northwestern part of Ravni Kotari region. Zadar ser ...
into exile with the Byzantines.
Flight to Serbs
 According to
According to Einhard
Einhard (also Eginhard or Einhart; la, E(g)inhardus; 775 – 14 March 840) was a Frankish scholar and courtier. Einhard was a dedicated servant of Charlemagne and his son Louis the Pious; his main work is a biography of Charlemagne, the ''Vita ...
, the writer of the '' Royal Frankish Annals'', following the final Frankish attack, Ljudevit fled from his seat in Sisak
Sisak (; hu, Sziszek ; also known by other alternative names) is a city in central Croatia, spanning the confluence of the Kupa, Sava and Odra rivers, southeast of the Croatian capital Zagreb, and is usually considered to be where the Posavin ...
to the Serbs
The Serbs ( sr-Cyr, Срби, Srbi, ) are the most numerous South Slavs, South Slavic ethnic group native to the Balkans in Southeastern Europe, who share a common Serbian Cultural heritage, ancestry, Culture of Serbia, culture, History of ...
in 822 (''Siscia civitate relicta, ad Sorabos, quae natio magnam Dalmatiae partem obtinere dicitur, fugiendo se contulit.''). Goldstein, 1985, p. 235. In the contemporary '' Vita Hludovici'' that description of the Serbs is omitted. Ljudevit later killed the local Serbian župan who took him in and temporarily took over the rule in his župa.
The location and nature of these Serbs mentioned in the primary sources has been a topic of interest for historians since the 19th century. Tadija Smičiklas did not attempt to define the area where Ljudevit fled, while Vjekoslav Klaić
Vjekoslav Klaić (21 June 1849 – 1 July 1928) was a Croatian historian and writer, most famous for his monumental work ''History of the Croats''.
Klaić was born in Garčin near Slavonski Brod as the son of a teacher. He was raised in Germa ...
wrote it was beyond Sava
The Sava (; , ; sr-cyr, Сава, hu, Száva) is a river in Central and Southeast Europe, a right-bank and the longest tributary of the Danube. It flows through Slovenia, Croatia and along its border with Bosnia and Herzegovina, and finally t ...
and Bosna. Ferdo Šišić put the ''ad Sorabos'' to the southeast of Sava and Vrbas, near the Dalmatian Croats. Vladimir Ćorović mentioned the flight to the Serbs, but didn't expound on it. The 1953 "History of the peoples of Yugoslavia" published by ''Školska knjiga
Školska knjiga (lit. ''Schoolbook'', ) is one of the largest publishing companies in Croatia
, image_flag = Flag of Croatia.svg
, image_coat = Coat of arms of Croatia.svg
, anthem = " Lijepa naša domo ...
'' added apparently fictitious details to the original story. Anto Babić discussed the original text and whether it was a reference to a single fort or a territory. Goldstein, 1985, p. 236. Svetislav M. Prvanović tried to connect Ljudevit and the Guduscani with the Roman city of Guduscum in eastern Serbia, but using only the interpretation of a single comma in Franjo Rački's text and conjecture. Sima Ćirković thought there was a consensus that the place was somewhere in Bosnia
Bosnia and Herzegovina ( sh, / , ), abbreviated BiH () or B&H, sometimes called Bosnia–Herzegovina and Pars pro toto#Geography, often known informally as Bosnia, is a country at the crossroads of Southern Europe, south and southeast Euro ...
, but called the claims of exact locations speculation. Nada Klaić
Nada Klaić (21 July 1920 – 2 August 1988) was a Croatian historian. She was a Croatian medievalist of the 20th century. A substantial part of the work was devoted to criticism of medieval sources.
Academic career
Nada Klaić was born in Zagre ...
thought that the place Ljudevit fled to was actually the medieval county of Srb
SRB or Srb may refer to:
Places
* Serbia (ISO 3166-1 alpha-3 country code SRB), a country in Central/Southeastern Europe
* Srb, a village in Croatia
Organizations
* State Research Bureau (organisation), former Ugandan intelligence agency
* Sin ...
by the river Una. Goldstein, 1985, p. 237. Relja Novaković analyzed Einhard and concluded that the area could be somewhere near Kozara, Grmeč, Una and Kupa
The Kupa () or Kolpa ( or ; from la, Colapis in Roman times; hu, Kulpa) river, a right tributary of the Sava, forms a natural border between north-west Croatia and southeast Slovenia. It is long, with its border part having a length of and ...
. Goldstein, 1985, p. 238. Ivo Goldstein acknowledged and accepted the theory that it was located in Srb, but advocated against misinterpreting the scarce historical records. Goldstein, 1985, p. 243–244. Radoslav Katičić argued against the theory, and Tibor Živković concurred with him. According to Mladen Ančić, the mentioning of "Dalmatia" in 822 and 833 as an old geographical term by the authors of Frankish Annals was '' Pars pro toto'' with a vague perception of what this geographical term actually referred to.
According to John Van Antwerp Fine Jr., it was hard to find Serbs in this area since the Byzantine sources were limited to the southern coast, but it is possible that among other tribes existed a tribe or group of small tribes of Serbs.John V. A. (Jr.) Fine; (2010) ''When Ethnicity Did Not Matter in the Balkans'' p. 35; University of Michigan Press, Živković's 2011 interpretation of the Latin text says the second-hand accounts given to the Franks by their agents in Siscia and Croatia establish the existence of some sort of a Serbian claim over parts of (Roman) Dalmatia, similar to the analogous Frankish claim, but not necessarily settlement outside of places already known from other sources. According to Neven Budak, it's difficult to pinpoint a place within the former province of Dalmatia, but most probably was in central or eastern Bosnia.
Death
Soon after the incident with the Serbs, Ljudevit sent an envoy to the Frankish court, claiming that he is ready to recognize the Frankish Emperor Louis the Pious as his supreme ruler. However, he again fled, now to Ljudemisl, Borna's uncle in Dalmatia which was the time ruled by new duke Vladislav. In the end Ljudemisl treacherously killed him.Annotations
References
Sources
* Royal Frankish Annales Annales Regni Francorum ed. G. H. Pertz. Monumenta Germanicae Historica, Scriptores rerum Germanicarum 6, (Hannover 1895) for the years 819-822. * * Life of the Emperor Louis ( Vita Hludowici), ed. E. Tremp. Monumenta Germaniae Historica: Scriptores rerum Germanicarum 64 (Hannover 1995) chapters 31-35. * * * * * {{Authority control 823 deaths Dukes of Croatia 9th century in Croatia 9th-century Slavs 9th-century rulers in Europe History of Slavonia Year of birth unknown Slavic warriors