List of sieges on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
A chronological list of sieges follows.
File:Assyrian siege-engine attacking the city wall of Lachish, part of the ascending assaulting wave. Detail of a wall relief dating back to the reign of Sennacherib, 700-692 BCE. From Nineveh, Iraq, currently housed in the British Museum.jpg, Depiction of the
 (1895)
*
(1895)
* 
 * Siege of Singara (344) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (347) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (350) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
*
* Siege of Singara (344) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (347) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (350) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
*



 * Siege of Bergamo (701)
* Siege of Taranton (702) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
*
* Siege of Bergamo (701)
* Siege of Taranton (702) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
*  *
*
 *
*





 *
*  * Siege of Trapessac (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Baghras (1188) – Crusades
*
* Siege of Trapessac (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Baghras (1188) – Crusades
*
 *
*  * Siege of Lincoln Castle (1217) – First Barons' War
*
* Siege of Lincoln Castle (1217) – First Barons' War
*  *
*  * Siege(s) of
* Siege(s) of  *
*  *
*
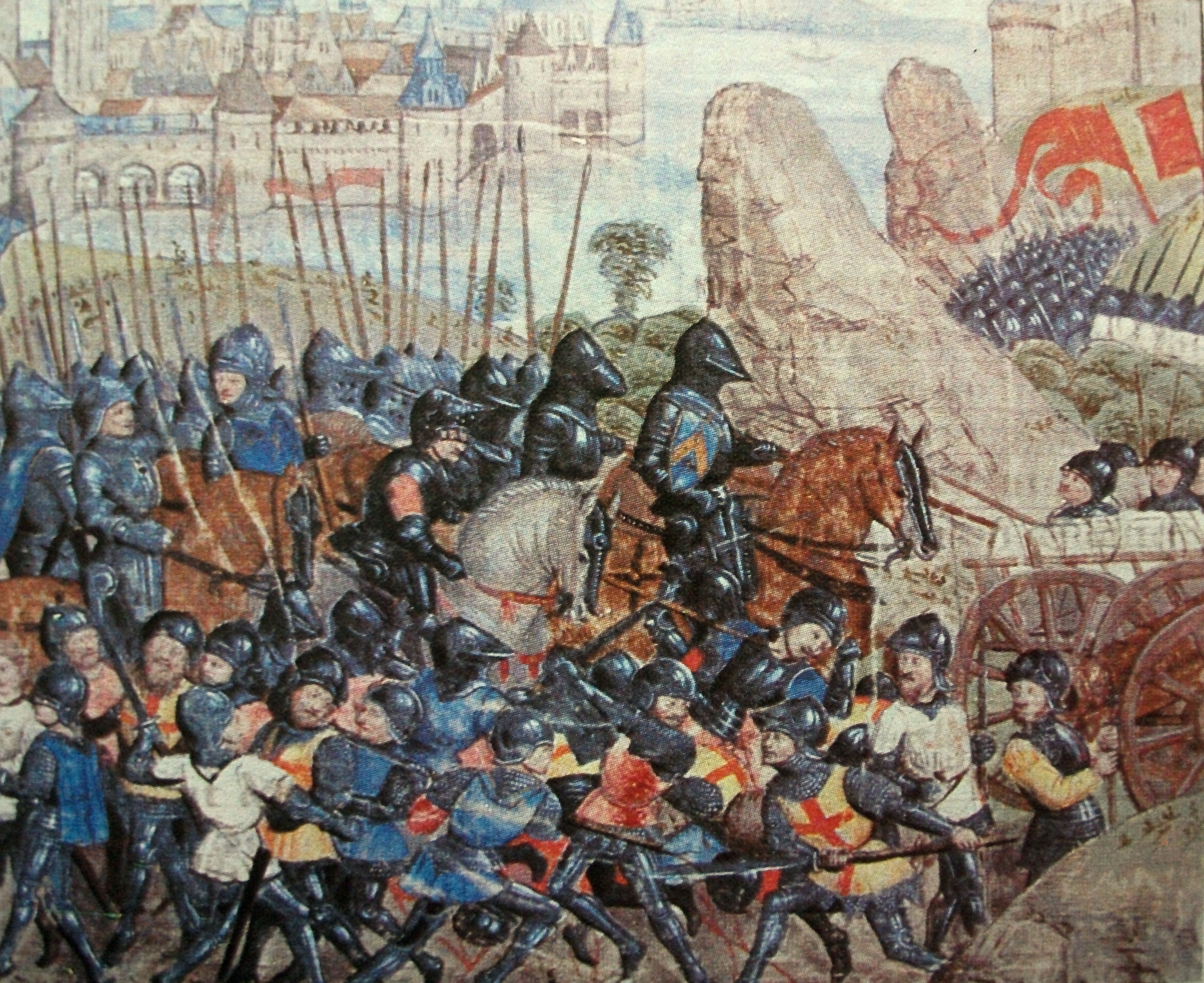 * Siege of Vannes (1342) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Hennebont (1342) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Algeciras (1342–1344) – Reconquista
* Siege of Caffa (1346)
*
* Siege of Vannes (1342) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Hennebont (1342) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Algeciras (1342–1344) – Reconquista
* Siege of Caffa (1346)
*
 *
*  *
*
 * Siege of Jajce (1463)
*
* Siege of Jajce (1463)
*
Military sieges
A militarysiege
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
is a prolonged military assault and blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
on a city or fortress
A fortification is a military construction or building designed for the defense of territories in warfare, and is also used to establish rule in a region during peacetime. The term is derived from Latin ''fortis'' ("strong") and ''facere'' ...
with the intent of conquering by force or attrition.
Ancient
Before 1000 BC
* Siege of Aratta (c. 2600 BC) *Siege of Uruk
Gilgamesh and Aga, sometimes referred to as incipit The envoys of Aga ( Sumerian: ''lu2 kin-gi4-a aka'') is an Old Babylonian poem written in Sumerian. The only one of the five poems of Gilgamesh that has no mythological aspects, it has been th ...
(c. 2580 BC)
*Siege of Qabra
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
(1780 BC)
* Siege of Hiritum
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteri ...
(1764 BC)
* Siege of Larsa
Larsa ( Sumerian logogram: UD.UNUGKI, read ''Larsamki''), also referred to as Larancha/Laranchon (Gk. Λαραγχων) by Berossos and connected with the biblical Ellasar, was an important city-state of ancient Sumer, the center of the cult ...
(1763 BC)
* Siege of Avaris (c. 1550 BC)
* Siege of Sharuhen (c. 1530 BC)
* Siege of Megiddo (c. 1457 BC)
* Siege of Jericho (c. 1400 BC)
* Siege of Dapur (1269 BC)
* Siege of Troy
In Greek mythology, the Trojan War was waged against the city of Troy by the Achaeans (Greeks) after Paris of Troy took Helen from her husband Menelaus, king of Sparta. The war is one of the most important events in Greek mythology and has ...
(c. 1200 BC)
10th century BC
* Siege ofRabbah
Amman (; ar, عَمَّان, ' ; Ammonite: 𐤓𐤁𐤕 𐤏𐤌𐤍 ''Rabat ʻAmān'') is the capital and largest city of Jordan, and the country's economic, political, and cultural center. With a population of 4,061,150 as of 2021, Amman is ...
(10th century BC) (Bible Reference: II Samuel 11–12)
* Siege of Abel-beth-maachah (10th century BC) (Bible Reference: II Samuel 20:15–22)
* Siege of Gezer (10th century BC)
* Sack of Jerusalem (925 BC)
Shishak, Shishaq or Susac (, Tiberian: , ) was, according to the Hebrew Bible, an Egyptian pharaoh who sacked Jerusalem in the 10th century BCE. He is usually identified with the pharaoh Shoshenq I.Troy Leiland Sagrillo. 2015.Shoshenq I and ...
by Egyptian pharaoh Shoshenq I
Hedjkheperre Setepenre Shoshenq I ( Egyptian ''ššnq''; reigned c. 943–922 BC)—also known as Shashank or Sheshonk or Sheshonq Ifor discussion of the spelling, see Shoshenq—was a pharaoh of ancient Egypt and the founder of the Twenty-sec ...
9th century BC
* Siege ofGath (city)
Gath or Gat ( he, גַּת, translit=Gaṯ, lit= wine press; la, Geth, Philistine: 𐤂𐤕 *''Gīt''), often referred to as Gath of the Philistines, was a major Philistine city and one of the five Philistine city-states during the Iron Age. ...
(ca. 830 BC) (Bible Reference: II Kings 12:17/18)
* Siege of Samaria (ancient city)
Samaria ( he, שֹׁמְרוֹן, translit=Šōmrōn; grc, Σαμάρεια, ''Samareia''; ar, السامرة, ''as-Samira'') was a city in the historical region of Samaria that served as the capital of the northern Kingdom of Israel during t ...
(9th century BC) (Bible Reference: II Kings 6:24 – 7:7)
8th century BC
* Siege of Tyre (724–720 BC) by the Assyrians underShalmaneser V
Shalmaneser V ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "Salmānu is foremost"; Biblical Hebrew: ) was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Tiglath-Pileser III in 727 BC to his deposition and death in 722 BC. Though Shalman ...
and Sargon II
Sargon II ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning "the faithful king" or "the legitimate king") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 722 BC to his death in battle in 705. Probably the son of Tiglath-Pileser III (745–727), Sargon is gener ...
* Siege of Gezer (c. 733 BC)
* Siege of Hermopolis
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
(701 BC)
* Siege of Azekah
The siege of Azekah was a battle between the Neo-Assyrian Empire and the Kingdom of Judah. It preceded the Siege of Lachish, making it the first known clash between the two kingdoms during Sennacherib's campaign in Judah. The most important so ...
(701 BC)
* Siege of Lachish
The siege of Lachish was the Neo-Assyrian Empire's siege and conquest of the town of Lachish in 701 BCE. The siege is documented in several sources including the Hebrew Bible, Assyrian documents and in the Lachish relief, a well-preserved serie ...
(701 BC)
* Siege of Jerusalem (701 BC) by the Assyrians under Sennacherib
Sennacherib ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: or , meaning " Sîn has replaced the brothers") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of his father Sargon II in 705BC to his own death in 681BC. The second king of the Sargonid dynas ...
* Siege of Tyre (701 BC) by the Assyrians under Sennacherib
7th century BC
*Siege of Babylon
The siege of Babylon in 689 BC took place after King of Assyria, Assyrian king Sennacherib's victory over the Elamites at the Battle of River Diyala. Although the Assyrians had suffered heavy casualties at the river, they had beaten the Elamites s ...
(689 BC)
* Siege of Tyre (671 BC) Siege of Tyre may refer to:
* Siege of Tyre (724–720 BC), a List of sieges, siege by the Assyrians under Shalmaneser V and Sargon II
* Siege of Tyre (701 BC), a siege by the Neo-Assyrian Empire, Assyrians under Sennacherib
* Siege of Tyre (671 BC) ...
by the Assyrians under Esarhaddon
Esarhaddon, also spelled Essarhaddon, Assarhaddon and Ashurhaddon ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , also , meaning " Ashur has given me a brother"; Biblical Hebrew: ''ʾĒsar-Ḥaddōn'') was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from the death of hi ...
* Siege of Tyre (663 BC) Siege of Tyre may refer to:
* Siege of Tyre (724–720 BC), a siege by the Assyrians under Shalmaneser V and Sargon II
* Siege of Tyre (701 BC), a siege by the Assyrians under Sennacherib
* Siege of Tyre (671 BC), a siege by the Assyrians und ...
by the Assyrians under Ashurbanipal
Ashurbanipal ( Neo-Assyrian cuneiform: , meaning " Ashur is the creator of the heir") was the king of the Neo-Assyrian Empire from 669 BCE to his death in 631. He is generally remembered as the last great king of Assyria. Inheriting the throne a ...
* Fall of Ashdod (635 BC)
* Fall of Assur
The Fall of Assur occurred when the first city and old capital of the Neo-Assyrian Empire fell to Median, Babylonian and other rebellion led forces. The sack of the city that followed destroyed the city to some degree; however it recovered during ...
(614 BC)
* Battle of Nineveh (612 BC)
The Battle of Nineveh is conventionally dated between 613 and 611 BC, with 612 BC being the most supported date. Rebelling against the Assyrians, an allied army which combined the forces of Medes and the Babylonians, besieged Nineveh and sacked ...
* Fall of Harran (610 BC)
* Siege of Harran (609 BC)
6th century BC
*Siege of Jerusalem (597 BC)
The siege of Jerusalem (597 BC) was a military campaign carried out by Nebuchadnezzar II, king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, in which he besieged Jerusalem, then capital of the Kingdom of Judah. The city surrendered, with king Jeconiah of Juda ...
by Nebuchadnezzar II
Nebuchadnezzar II (Babylonian cuneiform: ''Nabû-kudurri-uṣur'', meaning "Nabu, watch over my heir"; Biblical Hebrew: ''Nəḇūḵaḏneʾṣṣar''), also spelled Nebuchadrezzar II, was the second king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, ruling ...
* Siege of Jerusalem (587 BC)
The siege of Jerusalem (circa 589–587 BCE) was the final event of the Judahite revolts against Babylon, in which Nebuchadnezzar II, king of the Neo-Babylonian Empire, besieged Jerusalem, the capital city of the Kingdom of Judah. Jerusalem ...
by Nebuchadnezzar II
* Siege of Tyre (586–573 BC)
The siege of Tyre was waged by Nebuchadnezzar II of Babylon for 13 years from 586 to 573 BC.Vogelstein 1950–51, p. 198Garstad 2016, p. 179Ephʿal 2003, p. 186 The siege of Tyre, in Phoenicia, has a significant connection to the Book of Ez ...
by Nebuchadnezzar II
* Siege of Sardis (547 BC)
The siege of Sardis (547/546 BC) was the last decisive conflict after the Battle of Thymbra, which was fought between the forces of Croesus of Lydia and Cyrus the Great, Cyrus followed Croesus to his city, laid siege to it for 14 days and capture ...
* Siege of Gaza
The siege of Gaza took place in 332 BC, and was part of the Egyptian campaign of Alexander the Great, the ancient Greek king of Macedonia. It ended the Thirty-first Dynasty of Egypt, which functioned as a satrapy of the Achaemenid Persia ...
(525 BC)
* Siege of Memphis (525 BC)
siege of Lachish
The siege of Lachish was the Neo-Assyrian Empire's siege and conquest of the town of Lachish in 701 BCE. The siege is documented in several sources including the Hebrew Bible, Assyrian documents and in the Lachish relief, a well-preserved serie ...
from an Assyrian wall relief
File:Ramses II besieging the Cheta people in Dapur.jpg, A mural
A mural is any piece of graphic artwork that is painted or applied directly to a wall, ceiling or other permanent substrate. Mural techniques include fresco, mosaic, graffiti and marouflage.
Word mural in art
The word ''mural'' is a Spanis ...
from the tomb of Ramesses II
Ramesses II ( egy, rꜥ-ms-sw ''Rīʿa-məsī-sū'', , meaning "Ra is the one who bore him"; ), commonly known as Ramesses the Great, was the third pharaoh of the Nineteenth Dynasty of Egypt. Along with Thutmose III he is often regarded a ...
in Thebes depicting the siege of Dapur
File:Nebuchadnezzar camp outside Jerusalem. Famine in the city.jpg, A Medieval depiction of the siege of Jerusalem in 587 BC.
5th century BC
4th century BC
3rd century BC
* Siege of Messene (295 BC) – Wars of the Diadochi *Siege of Thebes (292–291 BC)
The siege of Thebes lasted from 292 until 291 BC. The city was put under siege by King Demetrius I of Macedon after it had revolted against Macedonian rule. History
In 293, the Boeotians had revolted against Demetrius' rule but the revolt was ...
* Siege of Athens (287 BC)
* Siege of Syracuse (278 BC) – Part of the Pyrrhic War
The Pyrrhic War (280–275 BC) was largely fought between the Roman Republic and Pyrrhus, the king of Epirus, who had been asked by the people of the Greek city of Tarentum in southern Italy to help them in their war against the Romans.
A sk ...
* Siege of Lilybaeum (278 BC) – Part of the Pyrrhic War
* Siege of Sparta
The siege of Sparta took place in 272 BC and was a battle fought between Epirus, led by King Pyrrhus, ( 297–272 BC) and an alliance consisting of Sparta, under the command of King Areus I ( 309–265 BC) and his heir Acrotatus, and Macedon ...
(272 BC) – Pyrrhus' invasion of the Peloponnese
Pyrrhus' invasion of the Peloponnese in 272 BC was an invasion of south Greece by Pyrrhus, King of Epirus. He was opposed by Macedon and a coalition of Greek city-states (''poleis''), most notably Sparta. The war ended in a joint victory by Ma ...
* Siege of Agrigentum (261 BC) – Part of the First Punic War
The First Punic War (264–241 BC) was the first of Punic Wars, three wars fought between Roman Republic, Rome and Ancient Carthage, Carthage, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the early 3rd century BC. For 23 years ...
* Siege of Aspis
The siege of Aspis or Clupea was fought in 255BC between Carthage and the Roman Republic. It was the first fighting on African land during the First Punic War.
Background
After defeating the Carthaginian navy sent to stop them from reaching Afric ...
(255 BC) – Part of the First Punic War
* Siege of Lilybaeum (250 BC) – Part of the First Punic War
* Siege of Drepana
The siege of Drepana took place from about 249 to 241 BC during the First Punic War.
Background
Drepana (today's Trapani) and Lilybaeum (today's Marsala) were two Carthaginian naval strongholds at the western end of Sicily that came under p ...
(249–241 BC) – Part of the First Punic War
* Battle of "The Saw" (238 BC) – Part of the Mercenary War
The Mercenary War, also known as the Truceless War, was a mutiny by troops that were employed by Carthage at the end of the First Punic War (264241 BC), supported by uprisings of African settlements revolting against Carthaginian contro ...
* Siege of Tunis (238 BC) – Part of the Mercenary War
* Siege of Medion (231 BC) – First Illyrian War
The Illyro-Roman Wars were a series of wars fought between the Roman Republic and the Ardiaei kingdom. In the ''First Illyrian War'', which lasted from 229 BC to 228 BC, Rome's concern was that the trade across the Adriatic Sea increased after the ...
* Siege of Issa
The siege of Issa took place from 230 BC to 229 BC between the forces of the Ancient Greek colony of Issa, aided by the Roman Republic, and the Ardiaean Kingdom of Illyria.
Prelude
Earlier in 230 BC, Illyrian forces under Queen Teuta and Sc ...
(230–229 BC) – First Illyrian War
* Siege of Epidamnus (229 BC) – First Illyrian War
 (1895)
*
(1895)
* Siege of Saguntum
The siege of Saguntum was a battle which took place in 219 BC between the Carthaginians and the Saguntines at the town of Saguntum, near the modern town of Sagunto in the province of Valencia, Spain. The battle is mainly remembered today because i ...
(219 BC) – ''casus belli'' for the Second Punic War
The Second Punic War (218 to 201 BC) was the second of three wars fought between Carthage and Rome, the two main powers of the western Mediterranean in the 3rd century BC. For 17 years the two states struggled for supremacy, primarily in Ital ...
* Siege of Casilinum (216–215 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Petelia (215 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Arpi (213 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Syracuse (213–212 BC) – the Roman siege
* Siege of Capua
The siege of Capua was a military operation involving the states of medieval southern Italy, beginning in May 1098 and lasting forty days. It was an interesting siege historically for the assemblage of great persons it saw and militarily for t ...
(211 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Agrigentum (210 BC) – Second Punic War
* Battle of Cartagena (209 BC)
The Battle of Cartagena in 209 BC was a successful Roman assault on the Carthaginian stronghold New Carthage ( Cartagena) in Iberia that took place in late January to early February of 209 BC.
Geography
New Carthage was a town situated on a pe ...
– Second Punic War
* Siege of Manduria (209 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Caulonia (209 BC) – Second Punic War
* Siege of Bactra
The siege of Bactra was a siege of the Hellenistic period that lasted from 208 to 206 BC. It was a siege of the city of Bactra by the Seleucid Empire after they defeated the Greco-Bactrians at the Battle of the Arius.
The Seleucids besieged the ...
(208–206 BC)
* Siege of Utica (204 BC)
The siege of Utica was a siege during the Second Punic War between the Roman Republic and Carthage in 204 BC. Roman general Scipio Africanus besieged Utica, intending to use it as a supply base for his campaign against Carthage in North Africa. ...
– Second Punic War
* Siege of Abydos (200 BC) – Cretan War (205–200 BC)
The Cretan War (205–200 BC) was fought by King Philip V of Macedon, the Aetolian League, many Cretan cities (of which Olous and Hierapytna were the most important) and Spartan pirates against the forces of Rhodes and later Attalus I of Perga ...

2nd century BC
*Siege of Gythium
The siege of Gythium was fought in 195 BC between Sparta and the coalition of Rome, Rhodes, the Achaean League, and Pergamum. As the port of Gythium was an important Spartan base, the allies decided to capture it before they advanced inland to ...
(195 BC) – War against Nabis
The Laconian War of 195 BC was fought between the Greek city-state of Sparta and a coalition composed of Rome, the Achaean League, Pergamum, Rhodes, and Macedon.
During the Second Macedonian War (200–196 BC), Macedon had given Sparta contr ...
* Siege of Eucratideia (169 BC)
* Siege of Carthage (149–146 BC) by Scipio Aemilianus Africanus
Publius Cornelius Scipio Africanus Aemilianus (185–129 BC), known as Scipio Aemilianus or Scipio Africanus the Younger, was a Roman general and statesman noted for his military exploits in the Third Punic War against Carthage and during the ...
* Siege of Numantia
The Celtiberian oppidum of Numantia was attacked more than once by Roman forces, but the Siege of Numantia refers to the culminating and pacifying action of the long-running Numantine War between the forces of the Roman Republic and those of th ...
(134–133 BC) by Scipio Aemilianus Africanus
* Siege of Cirta
The siege of Cirta was fought between the rival Numidian kings Adherbal and Jugurtha in 113BC. They were contesting the throne of Numidia after the death of King Micipsa. Jugurtha invaded Adherbal's territory, defeated him and besieged him in ...
(113 BC) – Jugurthine War
The Jugurthine War ( la, Bellum Iugurthinum; 112–106 BC) was an armed conflict between the Roman Republic and king Jugurtha of Numidia, a kingdom on the north African coast approximating to modern Algeria. Jugurtha was the nephew and adopte ...
1st century BC
*Siege of Athens and Piraeus (87–86 BC)
The siege of Athens and Piraeus was a siege of the First Mithridatic War that took place from Autumn of 87 BC to the Spring and Summer of 86 BC. The battle was fought between the forces of the Roman Republic, commanded by Lucius Cornelius Su ...
– First Mithridatic War
The First Mithridatic War (89–85 BC) was a war challenging the Roman Republic's expanding empire and rule over the Greek world. In this conflict, the Kingdom of Pontus and many Greek cities rebelling against Roman rule were led by Mithridat ...
* Siege of Mytilene (81 BC)
The siege of Mytilene was a military investment of the city of Mytilene on the island of Lesbos in 81 BC.
Mytilene, the capital city of the island of Lesbos in the Aegean Sea, revolted against Rome and was suspected of actively or tacitly aidin ...
* Siege of Cyzicus
The siege of Cyzicus took place in 73 BC between the armies of Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman-allied citizens of Cyzicus in Mysia and Roman Republican forces under Lucius Licinius Lucullus. It was in fact a siege and a counter-siege ...
(73 BC) – Third Mithridatic War
The Third Mithridatic War (73–63 BC), the last and longest of the three Mithridatic Wars, was fought between Mithridates VI of Pontus and the Roman Republic. Both sides were joined by a great number of allies dragging the entire east of th ...
* Siege of Jerusalem (63 BC) by Pompey the Great
* Siege of the Atuatuci
The siege of the Atuatuci in September 57 BC was the final battle in the second year of Julius Caesar's campaign that ultimately resulted in the Gallic Wars, conquest of Gaul. In this siege, Julius Caesar Investment (military), circumvallated the ...
(57 BC) – Gallic Wars
The Gallic Wars were waged between 58 and 50 BC by the Roman general Julius Caesar against the peoples of Gaul (present-day France, Belgium, Germany and Switzerland). Gallic, Germanic, and British tribes fought to defend their homel ...
* Siege of Avaricum (52 BC) – Gallic Wars
* Siege of Alesia
The Battle of Alesia or Siege of Alesia (September 52 BC) was a military engagement in the Gallic Wars around the Gallic ''oppidum'' (fortified settlement) of Alesia in modern France, a major centre of the Mandubii tribe. It was fought by ...
(52 BC) – Gallic Wars
* Siege of Uxellodunum (51 BC) – Gallic Wars
* Siege of Massilia (49 BC) – Caesar's Civil War
Caesar's civil war (49–45 BC) was one of the last politico-military conflicts of the Roman Republic before its reorganization into the Roman Empire. It began as a series of political and military confrontations between Gaius Julius Caesar an ...
* Siege of Utica (49 BC) – Caesar's Civil War
* Siege of Dyrrhachium (48 BC) – Caesar's Civil War
* Siege of Alexandria (48–47 BC) – Caesar's Civil War
* Siege of Jerusalem (37 BC) by Herod the Great
Herod I (; ; grc-gre, ; c. 72 – 4 or 1 BCE), also known as Herod the Great, was a Roman Jewish client king of Judea, referred to as the Herodian kingdom. He is known for his colossal building projects throughout Judea, including his renova ...
* Siege of Aracillum
The siege of Aracillum was a siege of the Cantabrian Wars that occurred in 25 BC. The battle took place between the forces of the Roman Empire, which consisted of five Roman legions commanded by Gaius Antistius Vetus and the forces of the Cantab ...
(25 BC) – Cantabrian Wars
The Cantabrian Wars (29–19 BC) (''Bellum Cantabricum''), sometimes also referred to as the Cantabrian and Asturian Wars (''Bellum Cantabricum et Asturicum''), were the final stage of the two-century long Roman conquest of Hispania, in what tod ...
After A. D. until 6th century
1st century
* Siege of Uspe (49) * Siege of Camulodunum (60–61) *Siege of Yodfat
The siege of Yodfat ( he, יוֹדְפַת, also Jotapata, Iotapata, Yodefat) was a 47-day siege by Roman forces of the Jewish town of Yodfat which took place in 67 CE, during the Great Revolt. Led by Roman General Vespasian and his son Titus, ...
(67) – First Jewish–Roman War
The First Jewish–Roman War (66–73 CE), sometimes called the Great Jewish Revolt ( he, המרד הגדול '), or The Jewish War, was the first of three major rebellions by the Jews against the Roman Empire, fought in Roman-controlled ...
* Siege of Gush Halav
The siege of Gush Halav refers to the Roman siege and sack of the fortified Galilean town of Gush Halav (Gischala, modern Jish), during the First Jewish–Roman War. Following the flight of the main Zealot fighting force from the town, the Romans ...
(67) – First Jewish–Roman War
* Zealot Temple Siege
The Zealot Temple Siege (68 AD) was a short siege of the Temple in Jerusalem fought between Jewish factions during the First Jewish–Roman War (66–70 AD). According to the historian Josephus, the forces of Ananus ben Ananus, one of the heads ...
(68) – First Jewish–Roman War
* Siege of Jerusalem (70) – the Roman siege by Titus
Titus Caesar Vespasianus ( ; 30 December 39 – 13 September 81 AD) was Roman emperor from 79 to 81. A member of the Flavian dynasty, Titus succeeded his father Vespasian upon his death.
Before becoming emperor, Titus gained renown as a mili ...
* Siege of Masada
The siege of Masada was one of the final events in the First Jewish–Roman War, occurring from 73 to 74 CE on and around a hilltop in present-day Israel.
The siege is known to history via a single source, Flavius Josephus, a Jewish rebel leade ...
(72–73 or 73–74) – First Jewish–Roman War
2nd century
*Battle of Sarmisegetusa
The Battle of Sarmizegetusa (also spelled ''Sarmizegethuza'') was a siege of Sarmizegetusa, the capital of Dacia, fought in 106 between the army of the Roman Emperor Trajan, and the Dacians led by King Decebalus.
Background
Because of the thr ...
(106) – Trajan's Dacian Wars
The Dacian Wars (101–102, 105–106) were two military campaigns fought between the Roman Empire and Dacia during Emperor Trajan's rule. The conflicts were triggered by the constant Dacian threat on the Danubian province of Moesia and also b ...
* Siege of Hatra (117)
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteri ...
– Trajan's Parthian campaign
Trajan's Parthian campaign was engaged by Roman Emperor Trajan in 115 against the Parthian Empire in Mesopotamia. The war was initially successful for the Romans, but a series of setbacks, including wide-scale rebellions in the Eastern Medit ...
* Siege of Hatra (193) – by Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
during Roman–Parthian Wars
The Roman–Parthian Wars (54 BC – 217 AD) were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.
Battles ...
* Siege of Byzantium (194–196) by forces of Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
.
* Siege of Hatra (197) – by Septimius Severus
Lucius Septimius Severus (; 11 April 145 – 4 February 211) was Roman emperor from 193 to 211. He was born in Leptis Magna (present-day Al-Khums, Libya) in the Roman province of Africa. As a young man he advanced through the customary suc ...
during Roman–Parthian Wars
The Roman–Parthian Wars (54 BC – 217 AD) were a series of conflicts between the Parthian Empire and the Roman Republic and Roman Empire. It was the first series of conflicts in what would be 682 years of Roman–Persian Wars.
Battles ...
3rd century
*Siege of Jicheng
The siege of Jicheng was a part of the campaign Ma Chao initiated in an attempt to retake Liang Province after the coalition of Guanxi (west of Hangu Pass) was defeated at the Battle of Tong Pass in the winter of 211 in the late Eastern Han dy ...
(213)
* Siege of Hatra
Hatra ( ar, الحضر; syr, ܚܛܪܐ) was an ancient city in Upper Mesopotamia located in present-day eastern Nineveh Governorate in northern Iraq. The city lies northwest of Baghdad and southwest of Mosul.
Hatra was a strongly fortifi ...
(220s) by Sasanians under Ardashir I
* Siege of Chencang (229) – Zhuge Liang's Northern Expeditions
Zhuge Liang's Northern Expeditions were a series of five military campaigns launched by the state of Shu Han against the rival state of Cao Wei from 228 to 234 during the Three Kingdoms period in China. All five expeditions were led by Zhuge ...
* Siege of Aquileia (238) – Year of the Six Emperors
* Siege of Hatra (240-241) by Sasanians under Shapur I
* Siege of Philippopolis (250)
The siege of Philippopolis was fought in about 250 between Rome and the Goths during the invasions of 249–253 at the Thracian city of Philippopolis, modern Plovdiv, Bulgaria. It was part of the long-running series of Gothic Wars.
The Goths w ...
* Siege of Thessalonica (254)
The siege of Thessalonica in 254 was the successful defense of the city of Thessalonica by local Roman militia during an invasion of the Balkans by the Goths.
Background
In 254 the Goths invaded and plundered Thrace and Macedonia. In 1979, He ...
* Siege of Dura-Europos (256)
* Siege of Tyana (272)
The Siege of Tyana occurred in 272 CE. The forces of the Roman Emperor Aurelian were seeking to conquer the Palmyrene Empire.
Background
In 269, while Claudius Gothicus (Gallienus' successor) was defending the borders of Italy and the Balk ...
* Siege of Palmyra (272)
4th century
* Siege of Byzantium (324) –Civil wars of the Tetrarchy
The Civil Wars of the Tetrarchy were a series of conflicts between the Tetrarchy, co-emperors of the Roman Empire, starting in 306 AD with the usurpation of Maxentius and the defeat of Flavius Valerius Severus, Severus and ending with the def ...
* Siege of Nisibis (337) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
 * Siege of Singara (344) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (347) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (350) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
*
* Siege of Singara (344) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (347) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Nisibis (350) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Autun
The siege of Autun was a conflict fought between the Roman Empire and the invading barbarian Alemanni tribe, who were ravaging Gaul, in 356 AD. The Romans successfully defended the city, and the barbarians retreated on the approach of reinforce ...
(356)
* Siege of Senonae
In 356, after leaving Cologne, Roman Emperor Julian the Apostate wintered in Senonae (possibly modern Sens) in Gaul. Following desertions from his German federated troops, hostile Germanic warbands learned that his force was under-strength and m ...
(356)
* Siege of Amida (359) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Singara (360) – Perso-Roman wars of 337–361
* Siege of Aquileia (361)
* Siege of Pirisabora
The siege of Pirisabora took place when the Roman Emperor Julian besieged the fortified city of Pirisabora under Mamersides in April 363.
After two days of fierce fighting, the Sasanians and the citizens abandoned the circuit walls and took up a ...
(363) – Julian's Persian War
Julian's Persian expedition was the last military undertaking of the Roman emperor Julian which began in March 363. It was a war against the Sasanian Empire which was ruled by Shapur II.
Aiming for the Sasanian winter capital Ctesiphon, Julia ...
* Siege of Maiozamalcha (363) – Julian's Persian War
* Siege of Adrianople (378)
The siege of Adrianople took place in 378 following the Gothic victory at the Battle of Adrianople. Gothic forces were unable to breach the city walls and retreated. It was followed by an unsuccessful Gothic attempt to breach the walls of Consta ...
– Gothic War (376–382)
Between 376 and 382 the Gothic War against the Eastern Roman Empire, and in particular the Battle of Adrianople, is commonly seen as a major turning point in the history of the Roman Empire, the first of a series of events over the next century ...
5th century
*Siege of Asti (402)
The siege of Asti was a siege in 402 CE, laid by the Visigoths under their king Alaric I after the Visigothic invasion of Northern Italy.
Emperor Honorius fled the Imperial capital in Mediolanum upon the rapid advance of the Goths through no ...
* Siege of Florence (405)
The siege of Florence was a battle that occurred in either 405 or 406 AD, between the Goths and the Roman Empire at Florence.
Background
In 402 the Geougen, a nomadic Tartar people of northern Asia, who during the fourth century had gradu ...
* Siege of Rome (408–410)
* Siege of Arles (411)
* Siege of Valence (411)
* Sack of Trier (413)
* Siege of Massilia (413)
The siege of Massilia was made by the Visigoths against the Roman city of Massilia, Gallia Narbonensis in 413. Campaigning in southern Gaul, the Visigothic king Ataulf had taken Toulouse and Narbonne and laid siege of Massilia. The city was defe ...
* Siege of Theodosiopolis (421) – Roman–Sasanian War (421–422)
* Siege of Arles (425)
* Siege of Hippo Regius
The siege of Hippo Regius was a siege from June 430 to August 431, carried out by the Vandals under their king Genseric against Roman defenders under Boniface, Count of Africa.
Having command of the sea, Boniface was able to keep the city well ...
(430–431)
* Siege of Narbonne (436–437)
* Siege of Noviodunum (437)
* Siege of Viminacium (441) by Attila
Attila (, ; ), frequently called Attila the Hun, was the ruler of the Huns from 434 until his death in March 453. He was also the leader of a tribal empire consisting of Huns, Ostrogoths, Alans, and Bulgars, among others, in Central and E ...
* Siege of Naissus (442) by Attila
* Siege of Sirmium (442) by Attila
* Siege of Ratiaria (447) by Attila
* Siege of Metz (451) by Attila
* Siege of Aurelianum (451) by Attila
* Siege of Aquileia (452) by Attila
* Siege of Castrum Cainonense (463)
* Siege of Singidunum (472)
* Siege of Taragona (472)
* Siege of Rome (472)
The siege of Rome was fought between supporters of the Suebian warrior Ricimer and the Western Roman emperor Anthemius. Ricimer had previously established Anthemius as emperor, but later fell out with his nominee and attacked Rome. With the h ...
by Ricimer
Flavius Ricimer ( , ; – 18/19 August 472) was a Romanized Germanic general who effectively ruled the remaining territory of the Western Roman Empire from 461 until his death in 472, with a brief interlude in which he contested power with An ...
* Siege of Papyrius (484–488)
* Siege of Ravenna (490–493) – Ostrogothic conquest of Italy
* Siege of Nisibis (498)
Medieval
6th century


7th century

8th century
 * Siege of Bergamo (701)
* Siege of Taranton (702) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
*
* Siege of Bergamo (701)
* Siege of Taranton (702) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Tyana (707–708)
The siege of Tyana was carried out by the Umayyad Caliphate in 707–708 or 708–709 in retaliation for a heavy defeat of an Umayyad army under Maimun the Mardaite by the Byzantine Empire in c. 706. The Arab army invaded Byzantine territory an ...
by the Umayyads
* Siege of Anchialus (708) – Byzantine-Bulgarian Wars
* Siege of Turanda (712) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Constantinople (717–718) by the Umayyads
* Siege of Toulouse (721) – Umayyad invasion of Gaul
The Umayyad invasion of Gaul occurred in two phases in 719 and 732. Although the Umayyads secured control of Septimania, their incursions beyond this into the Loire and Rhône valleys failed. By 759 they had lost Septimania to the Christian ...
* Siege of Angers (722)
* Siege of Nicaea (727)
The siege of Nicaea of 727 was an unsuccessful attempt by the Umayyad Caliphate to capture the Byzantine city of Nicaea, the capital of the Opsician Theme. Ever since its failure to capture the Byzantine Empire's capital, Constantinople, in 71 ...
by the Umayyads
* Siege of Kamarja (729) by the Turgesh
* Siege of Bordeaux (732) – Umayyad invasion of Gaul
* Siege of Avignon (737)
The siege of Avignon, in which Frankish forces led by Charles Martel beat the Umayyad garrison of Avignon and destroyed the stronghold, was contested in 737.
Contemporary view
Arabs had occupied the city of Avignon in 734, after it had been sur ...
– Umayyad invasion of Gaul
* Siege of Narbonne (737)
The siege of Narbonne was fought in 737 between the forces of Yusuf ibn 'Abd al-Rahman al-Fihri, Umayyad governor of Narbonne, and a Frankish army led by Charles Martel.
The city of Narbonne was captured by Al-Samh ibn Malik al-Khawlani, governor ...
– Umayyad invasion of Gaul
* Siege of Nîmes
The siege of Nîmes took place shortly after the capture and destruction of Avignon in 736. Charles Martel failed to capture the Umayyad city of Narbonne but devastated most of the other principal settlements of Septimania, including Nîmes, ...
(737) – Umayyad invasion of Gaul
* Siege of Synnada (740) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Laon (741)
* Siege of Loches (742)
* Siege of Emesa (745) – Third Fitna
The Third Fitna ( ar, الفتنة الثاﻟﺜـة, al-Fitna al-thālitha), was a series of civil wars and uprisings against the Umayyad Caliphate beginning with the overthrow of Caliph al-Walid II in 744 and ending with the victory of Marwan ...
* Siege of Wasit The siege of Wasit involved the army of the Abbasid Revolution under al-Hasan ibn Qahtaba and the future Caliph al-Mansur, and the Umayyad garrison of Wasit under the last Umayyad governor of Iraq, Yazid ibn Umar ibn Hubayra. Yazid had been forced t ...
(749–750) – Abbasid Revolution
The Abbasid Revolution, also called the Movement of the Men of the Black Raiment, was the overthrow of the Umayyad Caliphate (661–750 CE), the second of the four major Caliphates in early Islamic history, by the third, the Abbasid Calipha ...
* Siege of Melitene (750)
* Siege of Narbonne (752–59) Battle of Narbonne may refer to:
*Battle of Narbonne (436), between Rome and the Visigoths.
* Siege of Narbonne (737), between the forces of the Umayyad governor of Narbonne, and a Frankish army led by Charles Martel.
* Siege of Narbonne (752–59), ...
– Umayyad invasion of Gaul
* Siege of Pavia (755)
* Siege of Rome (756)
* Siege of Pavia (756)
* Siege of Suiyang
The siege of Suiyang () during the An Lushan Rebellion was a campaign for the city of Suiyang by the rebel Yan army against the loyalist forces of the Tang army. Although the battle was ultimately won by the Yan army, it suffered a major los ...
(757) - known because of acts of cannibalism
Cannibalism is the act of consuming another individual of the same species as food. Cannibalism is a common ecological interaction in the animal kingdom and has been recorded in more than 1,500 species. Human cannibalism is well documented, b ...
.
* Siege of Sythen (758)
* Siege of Bourbon (761)
The siege of Bourbon was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortress of Bourbon in 761 during the Aquitanian War. The Frankish army under King Pepin the Short invested, stormed and burned the fortress, taking the garrison prisoner.
Prelude
In ...
– Aquitanian War
* Siege of Clermont (761)
The siege of Clermont was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortress of Clermont in 761 during the Aquitanian War. The Frankish army under King Pepin the Short burned the fortress, with a large number of men, women and children dying in the ...
– Aquitanian War
* Siege of Chantelle (761)
The siege of Chantelle was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortress of Chantelle in 761 during the Aquitanian War. The Frankish army under King Pepin the Short took the fortress in battle. Pepin's army went on to Limoges, laying waste to th ...
– Aquitanian War
* Siege of Bourges (762) – Aquitanian War
* Siege of Thouars (762) – Aquitanian War
* Siege of Kamacha (766)
The siege of Kamacha by the Abbasid Caliphate took place in autumn 766, and involved the siege of the strategically important Byzantine fortress of Kamacha on the eastern bank of the Euphrates River, as well as a large-scale raid across eastern ...
– Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Toulouse (767)
The siege of Toulouse was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortified town of Toulouse in the winter of 767 during the Aquitanian War. The Frankish army under King Pepin the Short conquered the town and accepted the surrender of nearby Albi and ...
– Aquitanian War
* Siege of Syke (771) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
 *
* Siege of Pavia (773–774)
The siege or battle of Pavia was fought in 773–774 in northern Italy, near Ticinum (modern Pavia), and resulted in the victory of the Franks under Charlemagne against the Lombards under King Desiderius.
Background
Charlemagne, ''rex Fra ...
– Lombard kingdom
The Kingdom of the Lombards ( la, Regnum Langobardorum; it, Regno dei Longobardi; lmo, Regn di Lombard) also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy ( la, Regnum totius Italiae), was an early medieval state established ...
conquered by Charlemagne
Charlemagne ( , ) or Charles the Great ( la, Carolus Magnus; german: Karl der Große; 2 April 747 – 28 January 814), a member of the Carolingian dynasty, was King of the Franks from 768, King of the Lombards from 774, and the first E ...
* Siege of Syburg (775) – Saxon Wars
The Saxon Wars were the campaigns and insurrections of the thirty-three years from 772, when Charlemagne first entered Saxony with the intent to conquer, to 804, when the last rebellion of tribesmen was defeated. In all, 18 campaigns were fought ...
* Siege of Syburg (776) – Saxon Wars
* Siege of Barbād (776)
* Siege of Zaragoza (778) by Charlemagne
* Siege of Germanikeia (778) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Semaluos (780) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Nakoleia (782) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Huesca (797)
* Siege of Trsat (799)
9th century
* Siege of Barcelona (800–801) byLouis the Pious
Louis the Pious (german: Ludwig der Fromme; french: Louis le Pieux; 16 April 778 – 20 June 840), also called the Fair, and the Debonaire, was King of the Franks and co-emperor with his father, Charlemagne, from 813. He was also King of Aqu ...
* Siege of Lucera (802)
* Siege of Canburg (805)
* Siege of Patras (805 or 807) by the Slavs of the Peloponnese
* Siege of Melitene (805) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Heraclea (806) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Tortosa (809) by Louis the Pious
* Siege of Serdica (809)
The siege of Serdica ( bg, Обсадата на Сердика) took place in the spring of 809 at modern Sofia, Bulgaria. As a result, the city was annexed to the Bulgarian State and remained so until the fall of the First Bulgarian Empire.
H ...
– Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
The Byzantine–Bulgarian wars were a series of conflicts fought between the Byzantines and Bulgarians which began when the Bulgars first settled in the Balkan peninsula in the 5th century, and intensified with the expansion of the Bulgarian Em ...
* Siege of Venice (810)
* Siege of Debeltos (812) – Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
* Siege of Baghdad (812–813)
The siege of Baghdad was a part of a civil war between al-Amin and al-Ma'mun for the Abbasid Caliphate of Baghdad. The siege lasted from August 812 until September 813. The siege is described in great detail by Muhammad ibn Jarir al-Tabari in his ...
– Fourth Fitna
* Siege of Mesembria (812) – Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
* Siege of Adrianople (813)
The siege of Adrianople ( bg, Обсада на Одрин) in 813 was a part of the wars of the Byzantine Empire with the Bulgarian khan Krum ( Byzantine-Bulgarian Wars). It began soon after the Byzantine field army was defeated in the battle ...
– Byzantine–Bulgarian wars
* Siege of Constantinople (821–822)
* Siege of Arkadiopolis (823)
* Siege of Kaysum (824) – Fourth Fitna
* Siege of Syracuse (827–828) – Muslim conquest of Sicily
The Muslim conquest of Sicily began in June 827 and lasted until 902, when the last major Byzantine stronghold on the island, Taormina, fell. Isolated fortresses remained in Byzantine hands until 965, but the island was henceforth under Musli ...
* Siege and sack of Amorium (838) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Paris (845) – Viking expansion
Viking expansion was the historical movement which led Norse explorers, traders and warriors, the latter known in modern scholarship as Vikings, to sail most of the North Atlantic, reaching south as far as North Africa and east as far as Russi ...
* Siege of Rome (846)
* Siege of Marand (848)
* Capture of Faruriyyah
The Capture of Faruriyyah in 862 was a military campaign conducted by the Abbasid Caliphate against the Byzantine (Eastern Roman) Empire. Planned during the short caliphate of al-Muntasir (r. 861–862), it was commanded by the Turkish general ...
(862) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Dowina (864)
* Siege of Baghdad (865) – Abbasid civil war (865–866)
* Siege of Ragusa (866–868)
The siege of Ragusa (modern Dubrovnik in Croatia) by the Aghlabids of Ifriqiya lasted for fifteen months, beginning in 866 until the lifting of the siege at the approach of a Byzantine fleet in 868. The failure of the siege and the re-appearance ...
– Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Syracuse (868) – Muslim conquest of Sicily
* Siege of Dumbarton
The siege of Dumbarton was a successful four-month siege of the Brittonic fortress at Dumbarton Rock in 870, initiated by the Viking leaders Amlaíb, King of Dublin, and Ímar. Dumbarton was capital of the Kingdom of Alt Clut, the only survivi ...
(870) – Viking expansion
 *
* Siege of Melite (870)
The siege of Melite was the capture of the Byzantine city of Melite (modern Mdina, Malta) by an invading Aghlabid army in 870 AD. The siege was initially led by Halaf al-Hādim, a renowned engineer, but he was killed and replaced by Sawāda Ibn ...
– Muslim conquest of Sicily
* Siege of Bari (870–871)
The siege of Bari took place 1068–71, during the Middle Ages, when Norman forces, under the command of Robert Guiscard, laid siege to the city of Bari, a major stronghold of the Byzantines in Italy and the capital of the Catepanate of I ...
– Frankish conquest of the Emirate of Bari
* Siege of Salerno (871–872)
* Siege of Syracuse (877–878)
The siege of Syracuse from 877 to 878 led to the fall of the city of Syracuse, the Roman capital of Sicily, to the Aghlabids. The siege lasted from August 877 to 21 May 878 when the city, effectively left without assistance by the central Byzant ...
– Muslim conquest of Sicily
* Siege of al-Mukhtarah (881) – Zanj Rebellion
The Zanj Rebellion ( ar, ثورة الزنج ) was a major revolt against the Abbasid Caliphate, which took place from 869 until 883. Begun near the city of Basra in present-day southern Iraq and led by one Ali ibn Muhammad, the insurrection invol ...
* Siege of Asselt
The siege of Asselt was a Frankish siege of the Viking camp at Ascloha () in the Meuse valley in the year 882. Though the Vikings were not forced by arms to abandon their camp, they were compelled to come to terms whereby their leader, Godfrid, ...
(882) – Viking expansion
* Siege of Euripos
The siege of Euripos (modern Chalcis) occurred in the mid-880s, when an Abbasid fleet, led by the emir of Tarsos, Yazaman al-Khadim, laid siege to the city. The local Byzantine commander, Oiniates, successfully defended the city and destroyed a ...
(883) – Arab–Byzantine Wars
* Siege of Rochester (885)
* Siege of Paris (885–886)
The siege of Paris of 885–886 was part of a Viking raid on the Seine, in the Kingdom of the West Franks. The siege was the most important event of the reign of Charles the Fat, and a turning point in the fortunes of the Carolingian dynasty ...
– Viking expansion
* Siege of Buttington (893) – Viking expansion
* Siege of Bergamo (894)
* Siege of Rome (896)
* Siege of Spoleto (896)
* Siege of Amida (899)
10th century


11th century




12th century
* Siege of Haifa (1100) – Crusades * Siege of Le Mans (1100) * Second siege of Arsuf (1101) – Crusades * Siege of Caesarea (1101) – Crusades * Siege of Latakia (1101–1103) * Siege of Acre (1102) – Crusades * Siege of Arundel (1102) * Siege of Bridgnorth (1102) * Siege of Jaffa (1102) – Crusades *Siege of Tripoli
The siege of Tripoli lasted from 1102 until July 12, 1109. It took place on the site of the present day Lebanese city of Tripoli, in the aftermath of the First Crusade. It led to the establishment of the fourth crusader state, the County of Tri ...
(1102–1109) – Crusades
* Siege of Acre (1103) – Crusades
* Siege of Al-Rahba (1103)
* Siege of Acre (1104)
The siege of Acre took place in May 1104. It was of great importance for the consolidation of the Kingdom of Jerusalem, which had been founded only a few years earlier. With the help of a Republic of Genoa, Genoese fleet, King Baldwin I of Jerus ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Takrit
Tikrit ( ar, تِكْرِيت ''Tikrīt'' , Syriac: ܬܲܓܪܝܼܬܼ ''Tagrīṯ'') is a city in Iraq, located northwest of Baghdad and southeast of Mosul on the Tigris River. It is the administrative center of the Saladin Governorate. , it had ...
(sometime between 1105 and 1107) – Nizari–Seljuk conflicts
By the late 11th century, the Shi'a sub-sect of Isma'ilism, Ismailism (later Nizari Ismailism) had found many adherents in Iran, Persia, although the region was occupied by the Sunni Seljuk Empire. The hostile tendencies of the Sunni Revival, Abba ...
* Siege of Alamut
Alamut ( fa, الموت) is a region in Iran including western and eastern parts in the western edge of the Alborz (Elburz) range, between the dry and barren plain of Qazvin in the south and the densely forested slopes of the Mazandaran provin ...
(sometime between 1106 and 1109) – Nizari–Seljuk conflicts
* Siege of Shahdez (1107) – Nizari–Seljuk conflicts
* Siege of Nuremberg (1105)
* Siege of Cologne (1106)
* Siege of Apamea (1106) – Crusades - conflicts with the Assassins
* Siege of Apamea (September 1106) – Crusades - conflicts with the Assassins
* Siege of Malatya (1106)
* Siege of Castellum Arnaldi (1106) – Crusades
* Siege of Al-Rahba (1107)
* Siege of Hebron (1107) – Crusades
* Siege of Douai (1107)
* Siege of Dyrrhachium (1107–1108)
The siege of Dyrrhachium took place from November 1107 until September 1108, as the Italo-Normans under Bohemond I of Antioch besieged the Adriatic port city of Dyrrhachium. Dyrrhachium was held for the Byzantine Empire by its '' doux'' Alexio ...
– Byzantine–Norman wars
* Siege of Uclés (1108) – Reconquista
* Siege of Bratislava (1108)
* Siege of Sidon (1108) – Crusades
* Siege of Jableh (1109) – Crusades
* Siege of Nakło (1109)
* Siege of Głogów
The siege of Głogów or Defense of Głogów (german: Schlacht bei Glogau, pl, Obrona Głogowa) was fought on 24 August 1109 at the Silesian town of Głogów, between the Kingdom of Poland and the Holy Roman Empire. Recorded by the medieval c ...
(1109)
* Siege of Baalbek (1110)
* Siege of Beirut
The siege of Beirut took place in summer 1982, as part of the 1982 Lebanon War, which resulted from the breakdown of the ceasefire effected by the United Nations. The siege ended with the Palestinian Liberation Organization being forced out of Bei ...
(1110) – Crusades
* Siege of Novara (1110)
* Siege of Sidon
The siege of Sidon was an event in the aftermath of the First Crusade. The coastal city of Sidon was captured by the forces of Baldwin I of Jerusalem and Sigurd I of Norway, with assistance from the Ordelafo Faliero, Doge of Venice.
Backgrou ...
(1110) – Norwegian Crusade
The Norwegian Crusade, led by Norwegian King Sigurd I, was a crusade or a pilgrimage (sources differ) that lasted from 1107 to 1111, in the aftermath of the First Crusade. The Norwegian Crusade marks the first time a European king personally ...
* Siege of Atarib (1110) – Crusades
* Siege of Le Puiset (1111)
* Siege of Vetula (1111) – Crusades
* Siege of Tyre (1111–1112) Siege of Tyre may refer to:
* Siege of Tyre (724–720 BC), a siege by the Assyrians under Shalmaneser V and Sargon II
* Siege of Tyre (701 BC), a siege by the Assyrians under Sennacherib
* Siege of Tyre (671 BC), a siege by the Assyrians under ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Nicaea (1113)
The siege of Nicaea of 1113 occurred in the course of the Byzantine-Seljuk wars.
Following the success of the First Crusade and the failure of the Crusade of 1101, the Seljuq Turks resumed their offensive operations against the Byzantines. Emp ...
– Byzantine–Seljuq wars
* Siege of Hornburg Castle (1113)
* Siege of Mousson (1113)
* Siege of Bar (1113)
* Siege of Cologne (1114)
* Siege of Kafartab (1115) – Crusades
* Siege of Jaffa (1115) – Crusades
* Siege of Marqab (1116) – Crusades
* Siege of Alamut
Alamut ( fa, الموت) is a region in Iran including western and eastern parts in the western edge of the Alborz (Elburz) range, between the dry and barren plain of Qazvin in the south and the densely forested slopes of the Mazandaran provin ...
(1117–1118) – Nizari–Seljuk conflicts
* Siege of Lambsar (1117–1118) – Nizari–Seljuk conflicts
* Siege of Laodicea (1119)
The siege of Laodicea resulted in the Byzantine capture of the Seljuq Turkish city of Laodicea in 1119.
Background
Upon ascending the throne in 1118, the Byzantine emperor John II Komnenos was faced with the continued presence of Turks in Phry ...
– Byzantine–Seljuq wars
* Siege of Sozopolis (1120) – Byzantine–Seljuq wars
* Siege of Jerash (1121) – Crusades
* Siege of Mainz (1121)
* Siege of Tbilisi (1121–1122) – Georgian–Seljuk wars
* Siege of Aschaffenburg Castle (1122)
* Siege of Faulquemont Castle (1122)
* Siege of Zardana (1122) – Crusades
* Siege of Balis (1122) – Crusades
* Siege of Kharput (1123) – Crusades
* Siege of Jaffa (1123) – Crusades
* Siege of Schulenburg Castle (1123)
* Siege of Manbij (1124)
* Siege of Azaz (1124) – Crusades
* Siege of Tyre (1124) – Crusades
* Siege of Aleppo (1124–1125) – Crusades
* Siege of Raffaniya (1126) – Crusades
* Siege of Al-Rahba (1127)
* Siege of Bayonne (1130–1131)
* Siege of De'an
The siege of De'an (德安之戰) was fought as part of the Jin-Song Wars of China in 1132, during the Jin invasion of Hubei and Shaanxi. The battle between the besiegers, a group of rebels led by Li Heng and the Song Chinese defenders is impo ...
(1132) – Jin–Song Wars
The Jin–Song Wars were a series of conflicts between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty (1115–1234) and the Han-led Song dynasty (960–1279). In 1115, Jurchen tribes rebelled against their overlords, the Khitan-led Liao dynasty (916–1125), ...
* Siege of Kastamone (1132)
* Siege of Kastamone (1133)
* Siege of Savur (1134) – Crusades
* Siege of Gangra (1135)
* Siege of Montferrand (1137) – Crusades
* Siege of Anazarbos (1137) – Crusades
* Siege of Vahka (1137) – Crusades
* Siege of Antioch (1137) – Crusades
* Siege of Kafartab (1138) – Crusades
* Siege of Aleppo (1138) – Crusades
* Siege of Shaizar (1138) – Crusades
* Siege of Buza'a (1138) – Crusades
* Siege of Coria (1138)
The siege of Coria in July 1138 was the first and shorter of two attempts by Alfonso VII of León to take the city of Coria in Muslim Spain. Coria had previously been reconquered in 1079 by Alfonso VI, but was lost to the Almoravids not long a ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Baalbek (1139)
* Siege of Oreja
The siege of Oreja was a siege by the forces of Alfonso VII, Emperor of Spain, on the Spanish town Colmenar de Oreja that lasted from April until October 1139 when the Almoravid garrison surrendered. It was the first major victory of the renewed ' ...
(1139) – Reconquista
* Siege of Neocaesarea (1139–1140)
* Siege of Weinsberg
The siege of Weinsberg took place in Weinsberg, in the modern state of Baden-Württemberg, Germany, which was then part of the Holy Roman Empire. The siege was a decisive battle between two dynasties, the Welfs and the Hohenstaufen. The Welfs for ...
(1140)
* Siege of Banias (1140) – Crusades
* Siege of Coria (1142) – Reconquista
* Siege of Lisbon (1142)
In or about 1142 according to a brief reference in the Anglo-Norman text known as '' De expugnatione Lyxbonensi'' and the Portuguese text known as the '' Chronica Gothorum'', a group of Anglo-Norman crusaders on their way to Jerusalem were inv ...
- Reconquista
* Siege of Li Vaux Moise (1144) – Crusades
 *
* Siege of Edessa (1144)
The siege of Edessa (Arabic, ''fatḥ al-Ruhāʾ'', ) took place from November 28 to December 24, 1144, resulting in the fall of the capital of the crusader County of Edessa to Zengi, the atabeg of Mosul and Aleppo. This event was the cata ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Al-Bira (1144) – Crusades
* Siege of Edessa (1146) – Crusades
* Siege of Almería (1147)
The siege of Almería by the Kingdom of León and Castile and its allies lasted from July until October 1147. The siege was successful and the Almoravid garrison surrendered. The besieging force was under the overall command of King Alfonso VII. H ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Lisbon (1147) – Reconquista
* Siege of Tortosa (1148)
The siege of Tortosa (1 July – 30 December 1148) was a military action of the Second Crusade (1147–49) in Spain. A multinational force under the command of Count Raymond Berengar IV of Barcelona besieged the city of Tortosa (Arabic ''Ṭur� ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Damascus (1148)
The siege of Damascus took place between 24 and 28 July 1148, during the Second Crusade. It ended in a crusader defeat and led to the disintegration of the crusade. The two main Christian forces that marched to the Holy Land in response to Pop ...
– Second Crusade
The Second Crusade (1145–1149) was the second major crusade launched from Europe. The Second Crusade was started in response to the fall of the County of Edessa in 1144 to the forces of Zengi. The county had been founded during the First Cru ...
* Siege of Turbessel (1150) – Crusades
* Siege of Jerusalem (1152) – Crusades
* Siege of Ascalon
The siege of Ascalon took place in 1153, resulting in the capture of that Egyptian fortress by the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
Background
Ascalon was Fatimid Egypt's greatest and most important frontier fortress. The Battle of Ascalon was fought out ...
(1153) – Crusades
* Siege of Braničevo (1154)
* Siege of Tortona
The siege of Tortona in 1155 was the first major military engagement resulting from Holy Roman Emperor Frederick Barbarossa's ambition to enforce Imperial hegemony in Italy.
Background
Frederick began his first Italian campaign in October 115 ...
(1155)
* Siege of Brindisi (1155–1156)
* Siege of Shirakawa-den
The siege of the Shirakawa-den (白河殿夜討) was the central event of the Hōgen Rebellion, a succession dispute which broke out after the death of the cloistered Emperor Toba. The conflict grew to involve the Fujiwara, Minamoto, and Taira cla ...
(1156)
* Siege of Baghdad (1157)
The siege of Baghdad in 1157 was the last Seljuq attempt to capture Baghdad from the Abbasids. Caliph al-Muqtafi successfully defended his capital against the coalition armies of Seljuq Sultan Muhammad of Hamadan and Qutb ad-Din of Mosul.
B ...
* Siege of Banias (1157) – Crusades
* Siege of Shaizar (1157) – Crusades
* Siege of Casalia (1157–1158) – Crusades
* Siege of Harim (1158) – Crusades
* Siege of Milan (1158)
The Siege and capture of Milan was one of the episodes of the Hun wars fought in Italy. It was carried out by Attila and his Huns in 452, it resulted in the victory of the barbarians and the destruction of Milan. Milan, then called '' Mediolan ...
– Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor
The Holy Roman Emperor, originally and officially the Emperor of the Romans ( la, Imperator Romanorum, german: Kaiser der Römer) during the Middle Ages, and also known as the Roman-German Emperor since the early modern period ( la, Imperat ...
Frederick I Frederick I may refer to:
* Frederick of Utrecht or Frederick I (815/16–834/38), Bishop of Utrecht.
* Frederick I, Duke of Upper Lorraine (942–978)
* Frederick I, Duke of Swabia (1050–1105)
* Frederick I, Count of Zoll ...
and the Northern Italy
Northern Italy ( it, Italia settentrionale, it, Nord Italia, label=none, it, Alta Italia, label=none or just it, Nord, label=none) is a geographical and cultural region in the northern part of Italy. It consists of eight administrative region ...
cities
* Siege of Crema
The siege of Crema was a siege of the town of Crema, Lombardy by the Holy Roman Empire from 2 July 1159 to 25 January 1160. The Cremaschi attempted to defend their city from the Germans, but were eventually defeated by Frederick Barbarossa's men ...
(1159–1160) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I and the Northern Italy cities
* Siege of Sanjō Palace
The siege of the Sanjō Palace was the primary battle of the Heiji Rebellion (平治の乱, ''Heiji no ran'', January 19 – February 5, 1160) during the late Heian period of Japan . The conflict arose from feud between court advisors Fujiwara no ...
(1160) – the main action of the Heiji Rebellion took place in Kyoto
Kyoto (; Japanese: , ''Kyōto'' ), officially , is the capital city of Kyoto Prefecture in Japan. Located in the Kansai region on the island of Honshu, Kyoto forms a part of the Keihanshin metropolitan area along with Osaka and Kobe. , the c ...
* Siege of Ani (1161)
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteri ...
– Georgian–Seljuk wars
* Siege of Milan (1161–62) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I and the Northern Italy cities
* Siege of Harim (1164)
* Siege of Banias (1164)
* Siege of Alexandria (1167) – Crusader invasions of Egypt
The Crusader invasions of Egypt (1163–1169) were a series of campaigns undertaken by the Kingdom of Jerusalem to strengthen its position in the Levant by taking advantage of the weakness of Fatimid Egypt.
The war began as part of a successi ...
* Siege of Wexford (1169)
The siege of Wexford took place in early May 1169 and was the first major clash of the Norman invasion of Ireland. The town was besieged by a combined force of Normans under Robert Fitz-Stephen and soldiers loyal to Diarmait mac Murchadha. Af ...
– the first major clash of the Norman invasion of Ireland
The Anglo-Norman invasion of Ireland took place during the late 12th century, when Anglo-Normans gradually conquered and acquired large swathes of land from the Irish, over which the kings of England then claimed sovereignty, all allegedly san ...
* Siege of Damietta (1169) – Crusader invasions of Egypt
* Siege of Kerak (1170) – Crusades
* Siege of Sinjar (1170)
* Siege of Kerak (1173) – Crusades
* Siege of Derbent
Siege of Derbent in 1173 or 1174 was a successful siege of Derbent, by the Shirvanese and Georgian allies against Rus', Alan and Kipchak raiders.
History
Akhsitan I's reign saw raids of Rus' which sailed from Volga and threatening shores of ...
(1173) – Caspian expeditions of the Rus'
* Siege of Alexandria (1174)
* Siege of Alessandria (1174–1175) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick I and the Northern Italy cities
* Siege of Homs (1175)
* Siege of Montferrand (1175)
* Siege of Sinjar (1175)
* Siege of Azaz (1176)
* Siege of Masyaf (1176)
* Siege of Harim (1177) – Crusades
* Siege of Demmin (1177) – Brandenburg–Pomeranian conflict
Starting in the 12th century, the Margraviate, later Electorate, of Brandenburg was in conflict with the neighboring Duchy of Pomerania over frontier territories claimed by them both, and over the status of the Pomeranian duchy, which Brandenburg ...
* Siege of Claudiopolis
The siege of Claudiopolis was a Byzantine victory over a Seljuq Turk army in February–March 1179.
Background
After the Byzantine annihilation of a Seljuq Turkish army at the Battle of Hyelion and Leimocheir in 1177, the Byzantines laid wast ...
(1179) – Byzantine–Seljuq wars
* Siege of Jacob's Ford
The siege of Jacob's Ford was a victory of the Muslim sultan Saladin over the Christian King of Jerusalem, Baldwin IV. It occurred in August 1179, when Saladin conquered and destroyed Chastelet, a new border castle built by the Knights Templar ...
(1179) – Crusades
* Siege of Nara
Following the 1180 Battle of Uji, in which Minamoto no Yorimasa fought a small Taira army with the help of monks from the Mii-dera and other temples, the victorious Taira sought revenge. They burned the Miidera temple, before moving on to Nar ...
(1180) – Genpei War
The was a national civil war between the Taira and Minamoto clans during the late Heian period of Japan. It resulted in the downfall of the Taira and the establishment of the Kamakura shogunate under Minamoto no Yoritomo, who appointed himse ...
* Siege of Beirut (1182) – Crusades
* Siege of Mosul (1182
* Siege of Amida (1183)
* Siege of Hiuchi (1183) – Genpei War
* Siege of Fukuryūji (1183) – Genpei War
* Siege of Tell Khalid (1183)
* Siege of Kerak
The siege of Kerak of 1183 was an attack on the castle of Kerak by the forces of Saladin in the Crusader stronghold.
Prelude
Kerak was the stronghold of Raynald of Châtillon, Lord of Oultrejordain, 124 km south of Amman. The fortress w ...
(1183) – Crusades
* Siege of Hōjūjidono
The siege of Hōjūjidono (法住寺合戦, ''Hōjūji kassen'') was a siege that took place in Kyoto, Japan in 1184. It was part of the Genpei War and a key element of the conflict between Minamoto no Yoshinaka and his cousins Yoritomo and ...
(1184) – Genpei War
* Siege of Santarém (1184)
The siege of Santarém, lasted from June 1184 to July 1184. In the spring of 1184, Abu Yaqub Yusuf assembled an army, crossed the straits of Gibraltar and marched to Seville. From there he marched towards Badajoz and headed west to besiege Sant ...
* Siege of Kerak (1184) – Crusades
* Sack of Thessalonica (1185)
The sack of Thessalonica in 1185 by Normans of the Kingdom of Sicily was one of the worst disasters to befall the Byzantine Empire in the 12th century.
Siege
David Komnenos, the governor of the city, had neglected to make sufficient prepara ...
by the Normans
* Siege of Mayyafariqin (1185)
* Siege of Lovech
The siege of Lovech ( bg, Обсада на Ловеч, translit=Obsada na Lovech) took place in the spring of 1187 between the forces of Bulgaria and the Byzantine Empire. The three-month siege resulted in Bulgarian victory and Byzantine defeat ...
(1187)
* Siege of Kerak (1187) – Crusades
* Siege of Tiberias (1187) – Crusades
* Siege of Toron (1187) – Crusades
* Siege of Ascalon (1187) – Crusades
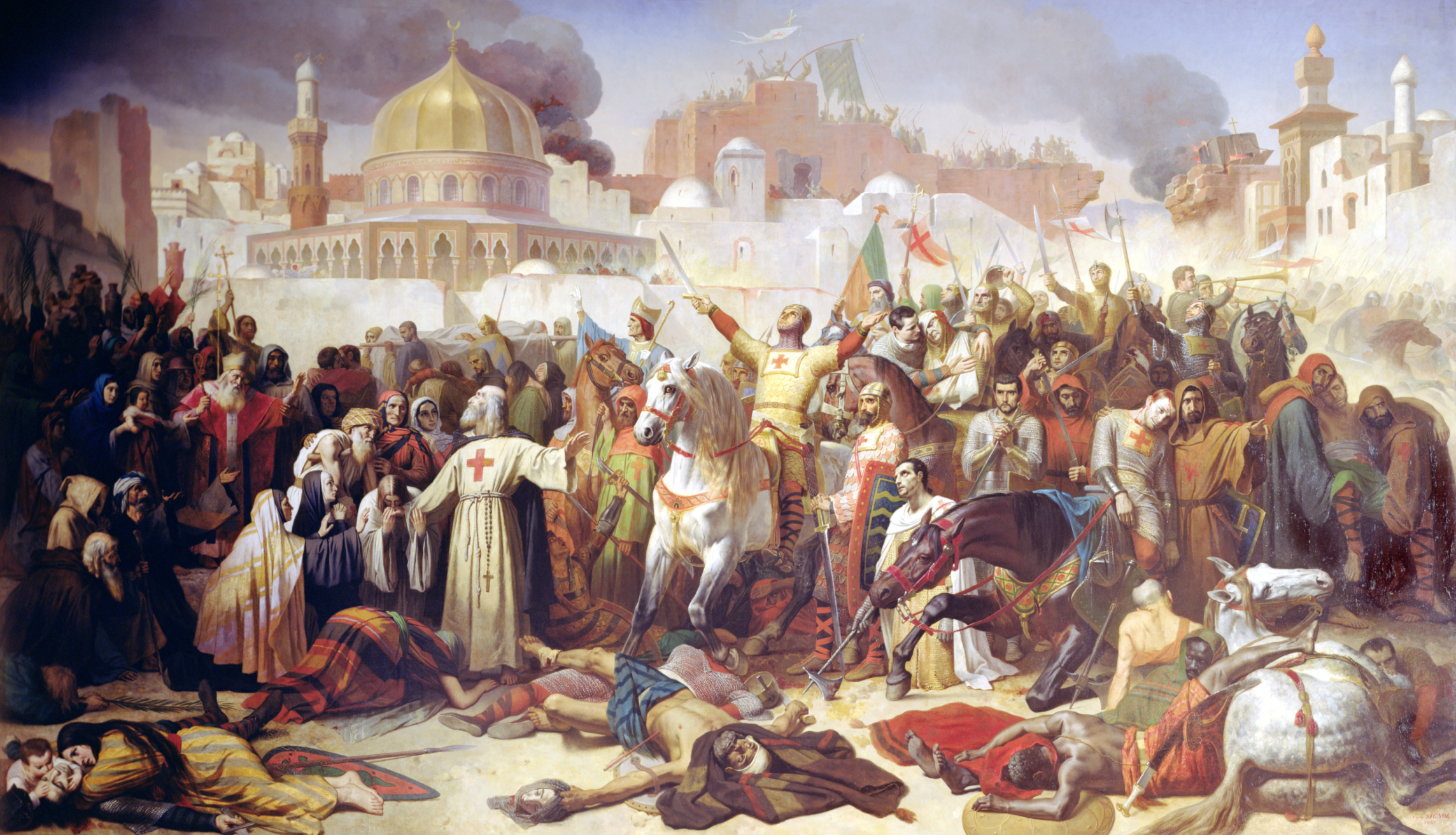
* Siege of Jerusalem (1187)
The siege of Jerusalem lasted from 20 September to 2 October 1187, when Balian of Ibelin surrendered the city to Saladin. Earlier that summer, Saladin had defeated the kingdom's army and conquered several cities. Balian was charged with or ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Tyre (1187)
The siege of Tyre took place from 12 November 1187 to 1 January 1188. An army commanded by Saladin made an amphibious assault on the city, defended by Conrad of Montferrat. After two months of continuous struggle, Saladin dismissed his army an ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Saone (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Shughr-Bakas (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Bourzey (1188) – Crusades
 * Siege of Trapessac (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Baghras (1188) – Crusades
*
* Siege of Trapessac (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Baghras (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Safed (1188)
The siege of Safed (November–December 1188) was part of Saladin's invasion of the Kingdom of Jerusalem.
The siege of the Templar-held castle began in early November 1188. Saladin was joined by his brother, Saphadin. Saladin employed a larg ...
– Crusades
* Siege of Belvoir (1188) – Crusades
* Siege of Acre (1189–1191)
The siege of Acre was the first significant counterattack by Guy of Lusignan, Guy of Jerusalem against Saladin, leader of the Muslims in Ayyubid dynasty, Syria and Egypt. This pivotal siege formed part of what later became known as the Third ...
– Third Crusade
The Third Crusade (1189–1192) was an attempt by three European monarchs of Western Christianity ( Philip II of France, Richard I of England and Frederick I, Holy Roman Emperor) to reconquer the Holy Land following the capture of Jerusalem by ...
* Siege of Naples (1191)
* Siege of Jaffa (1192) – Third Crusade
* Siege of Verneuil (1194)
* Siege of Loches (1195)
* Siege of Aumâle (1196)
* Siege of Jaffa (1197) – Crusades
* Siege of Toron (1197–1198) – Crusade of 1197
The Crusade of 1197, also known as the Crusade of Henry VI (german: Kreuzzug Heinrichs VI.) or the German Crusade (''Deutscher Kreuzzug''), was a crusade launched by the Hohenstaufen emperor Henry VI in response to the aborted attempt of his f ...
* Siege of Châlus (1199)
* Siege of Montferrand (1199)
13th century
 *
* Siege of Varna (1201)
The siege of Varna ( bg, Обсада на Варна) took place between 21 and 24 March 1201 at Varna, on the Bulgarian Black Sea coast between the Bulgarians and the Byzantines. The Bulgarians were victorious and captured the city.
Prelud ...
– Byzantine-Bulgarian Wars
* Siege of Zadar (1202) – Part of the Fourth Crusade
The Fourth Crusade (1202–1204) was a Latin Christian armed expedition called by Pope Innocent III. The stated intent of the expedition was to recapture the Muslim-controlled city of Jerusalem, by first defeating the powerful Egyptian Ayyubid S ...
* Siege of Constantinople (1203) – Part of the ''Fourth Crusade''
* Siege of Château Gaillard
The siege of Château Gaillard was a part of Philip II's campaign to conquer John, King of England's continental properties. The French king besieged Château Gaillard, a Norman fortress, for six months. The Anglo-Normans were beaten in the b ...
(1203–1204) – French invasion of Normandy (1202–1204)
The Normandy Campaigns were wars in Normandy from 1202 to 1204. The Kingdom of England fought the Kingdom of France as well as fighting off rebellions from nobles. Philip II of France conquered the Anglo-Angevin territories in Normandy, result ...
* Siege of Constantinople (1204)
The sack of Constantinople occurred in April 1204 and marked the culmination of the Fourth Crusade. Crusader armies captured, looted, and destroyed parts of Constantinople, then the capital of the Byzantine Empire. After the capture of the c ...
– Part of the ''Fourth Crusade''
* Siege of Trebizond (1205–1206) – Byzantine–Seljuk Wars
* Siege of Cologne (1205–1206) – German throne dispute
The German throne dispute or German throne controversy (german: Deutscher Thronstreit) was a political conflict in the Holy Roman Empire from 1198 to 1215. This dispute between the House of Hohenstaufen and House of Welf was over the successor to E ...
* Siege of Tripoli (1207) – Crusades
* Siege of Antalya (1207) – Byzantine–Seljuk Wars
* Siege of Beverin (1208) – Livonian Crusade
* Siege of Carcassonne (1209) – Albigensian Crusade
The Albigensian Crusade or the Cathar Crusade (; 1209–1229) was a military and ideological campaign initiated by Pope Innocent III to eliminate Catharism in Languedoc, southern France. The Crusade was prosecuted primarily by the French crow ...
* Siege of Bram (1210) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Al-Dāmūs
The siege of Al-Dāmūs was a battle of the Reconquista that occurred in the year 1210. The forces of the Kingdom of Aragon, together with auxiliary forces of the Knights Templar and Knights Hospitaller, were pitted against the defending forces ...
(1210) – Reconquista
* Siege of Cēsis (1210) – Livonian Crusade
* Siege of Minerve
The siege of Minerve was a military engagement which took place in June and July 1210 during the Albigensian Crusade in the town of Minerve in southern France. It was undertaken by the Catholic Crusaders against the Cathars in southern France ...
(1210) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Termes (1210) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Montferrand (1211) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Toulouse (1211) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Castelnaudary (1211) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Beverin (1211) – Livonian Crusade
* Siege of Viljandi (1211) – Livonian Crusade
* Siege of Weissensee (1212) – German throne dispute
* Siege of Ganja (1213)
* Siege of Sinope
The siege of Sinope in 1214 was a successful siege and capture of Sinope by the Sultanate of Rum under their Sultan, Kaykaus I (r. 1211–1220). Sinope was an important port city on the Black Sea coast of modern Turkey, at the time held by th ...
(1214) – Byzantine–Seljuk Wars
* Siege of Zhongdu (1215) – Genghis Khan
Genghis Khan (born Temüjin; ; xng, Temüjin, script=Latn; ., name=Temujin – August 25, 1227) was the founder and first Great Khan (Emperor) of the Mongol Empire, which became the List of largest empires, largest contiguous empire in history a ...
conquers Zhongdu, now Beijing
* Siege of Rochester castle (1215) – King John's Danish mercenaries attempt to take the castle of Rochester during the First Baron's war.
* Siege of Beaucaire (1216) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Dover Castle (1216) – First Barons' War
* Siege of Windsor Castle (1216) – First Barons' War
* Siege of Hertford (1216) – First Barons' War
 * Siege of Lincoln Castle (1217) – First Barons' War
*
* Siege of Lincoln Castle (1217) – First Barons' War
* Siege of Toulouse (1217–18) There have been several sieges known as the Siege of Toulouse, among them:
* Siege of Toulouse (721)
*Siege of Toulouse (767)
The siege of Toulouse was a Frankish siege of the Aquitanian fortified town of Toulouse in the winter of 767 during the ...
– Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Mount Tabor (1218) – Crusades
* Siege of Damietta (1218) Battle of Damietta, Sack of Damietta or Siege of Damietta may refer to:
*Sack of Damietta (853), a part of the Arab–Byzantine wars
* Siege of Damietta (1169), a part of the Crusader invasions of Egypt
*Siege of Damietta (1218–1219), a part of th ...
– Fifth Crusade
The Fifth Crusade (1217–1221) was a campaign in a series of Crusades by Western Europeans to reacquire Jerusalem and the rest of the Holy Land by first conquering Egypt, ruled by the powerful Ayyubid sultanate, led by Al-Adil I, al-Adil, brothe ...
* Siege of Marmande (1219) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Toulouse (1219) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Caesarea (1220) – Crusades
* Siege of Castelnaudary (1220–1221) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Bamyan (1221)
The Mongol conquest of Khorasan took place in 1220-21, during the Mongol conquest of the Khwarazmian Empire. As the Khwarazmian Empire disintegrated after the capture of the large cities of Samarkand and Bukhara by the Mongol Empire, Shah Muham ...
– Mongol conquest of Khwarezmia
The Mongol invasion of Khwarezmia ( fa, حمله مغول به خوارزمشاهیان) took place between 1219 and 1221, as troops of the Mongol Empire under Genghis Khan invaded the lands of the Khwarazmian Empire in Central Asia. The campa ...
* Siege of Nishapur (1221) – Mongol conquest of Khwarezmia
* Siege of Reval (1221) – Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was cond ...
* Siege of Trebizond (1222–1223)
The siege of Trebizond in 1222–1223 was an unsuccessful siege of Trebizond, the capital of the namesake empire, by the Sultanate of Rum under a certain Melik. According to the late 14th-century '' Synopsis of Saint Eugenios'' of John Lazaro ...
– Byzantine–Seljuk Wars
* Siege of Reval (1223) – Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was cond ...
* Siege of Fellin (1223) – Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was cond ...
* Siege of Reval (1223) – Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was cond ...
* Siege of Lohu (1223–1224) – Livonian Crusade
The Livonian crusade refers to the various military Christianisation campaigns in medieval Livonia – in what is now Latvia and Estonia – during the Papal -sanctioned Northern Crusades in the 12–13th century. The Livonian crusade was cond ...
* Siege of La Rochelle (1224)
The siege of La Rochelle of 1224 was the decisive engagement in the campaign between the Capetians and the Plantagenets for control of Poitou. French royal forces commanded by Capetian king Louis VIII laid siege to the strategic port of La Roch ...
* Siege of Tartu (1224)
The siege of Tartu took place in 1224 and resulted in the fall of the last major center of Estonian resistance in the mainland provinces to the Christian conquest of Estonia.
Background
In 1208, the Livonian Brothers of the Sword launched a c ...
– Livonian Crusade
* Siege of Jaén (1225)
The siege of Jaén was one of many sieges on the city during the long Spanish Reconquista. The siege, which was carried out by the combined allied forces of the Kingdom of Castile and the Taifa of Baeza, commanded by Ferdinand III of Castil ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Avignon (1226)
The siege of Avignon was the principal military action of the Albigensian Crusade of 1226. King Louis VIII of France besieged the town of Avignon, which lay within the Holy Roman Empire, from 10 June until 9 September, when it surrendered on terms ...
– Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Toulouse (1226) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Akhlat (1229)
* Siege of Jaén (1230)
The siege of Jaén was one of many sieges on that city during the Spanish Reconquista. The siege was carried out from 24 June through September, 1230 by forces of the Kingdom of Castile commanded by Ferdinand III of Castile against the defe ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Beirut (1231–1232)
* Siege of Amida (1232)
* Siege of Kaifeng (1232–1233) – Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty
The Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty, also known as the Mongol–Jin War, was fought between the Mongol Empire and the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty in Manchuria and North China. The war, which started in 1211, lasted over 23 years and ended wi ...
* Siege of Burriana
The siege of Burriana was one of the battles that occurred during the Conquest of Valencia by James I of Aragon. Burriana was an important Muslim city, being the capital of La Plana, Valencia. It was known as the "Green City". The city was bes ...
(1233) – Reconquista
* Siege of Caizhou
The siege of Caizhou between 1233 and 1234 was fought between the Jurchen-led Jin dynasty and the allied forces of the Mongol Empire and Southern Song dynasty. It was the last major battle in the Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty.
Backgrou ...
(1233–1234) – Mongol conquest of the Jin dynasty
 *
* Siege of Constantinople (1235)
The Siege of Constantinople (1235) was a joint Bulgarian-Nicaean siege on the capital of the Latin Empire. Latin emperor John of Brienne was besieged by the Nicaean emperor John III Doukas Vatatzes and Tsar Ivan Asen II of Bulgaria.
Prelude ...
– a joint Bulgarian-Nicaean siege on the capital of the Latin Empire.
* Siege of Bilär
The siege of Bilär was a battle for the capital city of the Volga Bulgaria between the Volga Bulgars and the Mongols. It took place in autumn 1236 and lasted for 45 days. It ended with the total destruction of Bilär and the massacre of its po ...
(1236) – Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria
The Mongol invasion of Volga Bulgaria lasted from 1223 to 1236. The Bulgar state, centered in lower Volga and Kama, was the center of the fur trade in Eurasia throughout most of its history. Before the Mongol conquest, Russians of Novgoro ...
* Siege of Córdoba (1236)
During the reconquista, the siege of Córdoba (1236) was a successful investment by the forces of Ferdinand III, king of Castile and León, marking the end of the Islamic rule over the city that had begun in 711.
In capturing the city, Ferdin ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Ryazan
Ryazan, capital of the Principality of Ryazan, was the first Russian city to be besieged by the Mongol invaders under Batu Khan.
Prelude
In the autumn of 1237 the Mongol Horde led by Batu Khan invaded the Rus' principality of Ryazan. The Pr ...
(1237) – Mongol invasion of Rus'
The Mongol Empire invaded and conquered Kievan Rus' in the 13th century, destroying numerous southern cities, including the largest cities, Kiev (50,000 inhabitants) and Chernihiv (30,000 inhabitants), with the only major cities escaping de ...
* Siege of Kolomna
Following the Battle of Voronezh River in December 1237, Yuri II of Vladimir sent both of his sons with "all his men" and Voivode Yeremey to defend the fortress of Kolomna, which was on the border to the Wild Fields.
Battle
In Kolomna, the ...
(1237–1238) – Mongol invasion of Rus'
* Siege of Moscow (1238)
The siege of Moscow was part of Mongol invasion of Rus.
Prelude
After the destruction of Ryazan on December 21, 1237, Grand Prince Yuri II sent his sons Vsevolod and Vladimir with most of Vladimir-Suzdal army to stop Mongol invaders at Kolom ...
– Mongol invasion of Rus'
* Siege of Vladimir (1238) – Mongol invasion of Rus'
* Siege of Kozelsk (1238) – Mongol invasion of Rus'
* Siege of Brescia
The siege of Brescia occurred in 1238. After his victory the previous year at the battle of Cortenuova, Emperor Frederick sought to bring about the unconditional surrender of the city of Milan and its allies. Assembling his army in Verona in ...
(1238) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Lombard League
*Siege of Mt. Tebulosmta (1238-1250) - Mongol invasions of Durdzuketia
During the 13th century, the Mongols launched long, massive invasions on the territory of modern Chechnya and Ingushetia, which also included the lands of Alania in the West. They caused massive destruction and human death for the Durdzuks, bu ...
* Siege of Faenza (1239) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Lombard League
* Siege of Jerusalem (1239) – Crusades
* Siege of Kiev (1240)
The siege of Kiev by the Mongols took place between November 28 and December 6, 1240, and resulted in a Mongol victory. It was a heavy morale and military blow to Halych-Volhynia and allowed Batu Khan to proceed westward into Europe.
Backgroun ...
– Mongol invasion of Rus'
* Siege of Esztergom (1242) – First Mongol invasion of Hungary
The first Mongol invasion of Hungary ( hu, tatárjárás) started in March 1241, and the Mongols started to withdraw in late March 1242.
Background Mongol invasion of Europe
The Hungarians had first learned about the Mongol threat in 1229, when ...
, Citadel of Esztergom,Turoc, Nyitra, Győr, Pannonhalma, Székesfehérvár, Segesd, Varasd, Kemlék, Csázma, Zágráb, Trogir, Veszprém, Tihany, Moson, Sopron, Vasvár, Zala, Léka, Pozsony, Komárom, Fülek and Abaújvár besieged but successfully resisted
* Siege of Viterbo (1243) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Lombard League
* Siege of Montségur
The siege of Montségur was a nine-month siege of the Cathar-held Château de Montségur by French royal forces starting in May 1243. After the castle surrendered, about 210 and unrepentant were burned in a bonfire on 16 March 1244.
Backgrou ...
(1243–1244) – Albigensian Crusade
* Siege of Jerusalem (1244)
The 1244 siege of Jerusalem took place after the Sixth Crusade, when a Khwarazmian army conquered the city on July 15, 1244.
Prelude
Emperor Frederick II of the Holy Roman Empire led the Sixth Crusade from 1228 to 1229 and claimed the t ...
by the Khwarezmians
* Siege of Damascus (1245)
* Siege of Jaén (1245–46) Siege of Jaén may refer to:
* Siege of Jaén (1225)
* Siege of Jaén (1230)
The siege of Jaén was one of many sieges on that city during the Spanish Reconquista. The siege was carried out from 24 June through September, 1230 by forces of ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Ascalon (1247) – Crusades
* Siege of Parma
The Battle of Parma was fought on 18 February 1248 between the forces of Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Lombard League. The Guelphs attacked the Imperial camp when Frederick II was away. The Imperial forces were defeated''The New Ca ...
(1247–1248) – Part of the wars between Holy Roman Emperor Frederick II and the Lombard League
* Siege of Seville
The siege of Seville (July 1247 – November 1248) was a 16-month successful investment during the ''Reconquista'' of Seville by forces of Ferdinand III of Castile. Although perhaps eclipsed in geopolitical importance by the rapid capture of ...
(1247–1248) – Reconquista
* Siege of Aachen (1248)
* Siege of Homs (1248–1249)
* Siege of Damietta (1249) – Seventh Crusade
* Siege of Naples (1252)
* Siege of Cologne (1252)
 * Siege(s) of
* Siege(s) of Gerdkuh
Gerdkuh was a castle of the Nizari Isma'ili state located near Damghan in the region of Qumis (modern-day Semnan Province of Iran).
Gerdkuh is a "fortified mountain"—a high vertical rock of 300 m in height with buildings on its summit a ...
(1253–1270) - Mongol campaign against the Nizaris
The Mongol campaign against the Nizaris of the Alamut period (the Assassins) began in 1253 after the Mongol conquest of the Khwarazmian Empire of Iran by the Mongol Empire and a series of Nizari–Mongol conflicts. The campaign was ordered by the ...
* Siege of Mehrin (1253)
* Siege of Tun
TUN or tun may refer to:
Biology
* Tun shells, large sea snails of the family '' Tonnidae''
* Tun, a tardigrade in its cryptobiotic state
* Tun or Toon, common name for trees of the genus '' Toona''
Places
* Tun, Sweden, a locality in Västra ...
(1253)
* Siege of Tun (1256)
* Siege of Maymun-Diz (1256)
* Siege of Alamut
Alamut ( fa, الموت) is a region in Iran including western and eastern parts in the western edge of the Alborz (Elburz) range, between the dry and barren plain of Qazvin in the south and the densely forested slopes of the Mazandaran provin ...
(1256)
* Siege of Lambsar (1256–1257)
* Siege of Cologne (1257)
 *
* Siege of Baghdad (1258)
The siege of Baghdad was a siege that took place in Baghdad in 1258, lasting for 13 days from January 29, 1258 until February 10, 1258. The siege, laid by Ilkhanate Mongol forces and allied troops, involved the investment, capture, and sac ...
* Siege of Mayyafariqin (1258–1259)
* Siege of Diaoyu Castle
The siege of Diaoyucheng, alternatively the Siege of Diaoyu Castle, was a battle between the Southern Song dynasty and the Mongol Empire in 1259.History of Yuan vol.3 It occurred at the Diaoyu Fortress in modern-day Hechuan District, Chongqing, ...
(1259) – Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty
The Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty or the Mongol invasion of China beginning under Ögedei Khan (r. 1229 – 1241) and completed under Kublai Khan (r. 1260–1294) was the final step for the Mongols to rule the whole of continental East A ...
* Siege of Al-Bira (1259) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
Starting in the 1240s, the Mongols made repeated invasions of Syria or attempts thereof. Most failed, but they did have some success in 1260 and 1300, capturing Aleppo and Damascus and destroying the Ayyubid dynasty. The Mongols were forced to r ...
* Siege of Aleppo (1260)
The siege of Aleppo lasted from 18 January to 24 January 1260.
After receiving the submission of Harran and Edessa, Mongol leader Hulagu Khan crossed the Euphrates, sacked Manbij and placed Aleppo under siege. He was supported by forces of Bohe ...
* Siege of Constantinople (1260) – Nicaean–Latin wars
The Nicaean–Latin wars were a series of wars between the Latin Empire and the Empire of Nicaea, starting with the dissolution of the Byzantine Empire by the Fourth Crusade in 1204. The Latin Empire was aided by other Crusader states established ...
* Siege of Cologne (1262)
* Siege of Königsberg
The siege of Königsberg was a siege laid upon Königsberg Castle, one of the main strongholds of the Teutonic Knights, by Prussians during the great Prussian uprising from 1262 possibly though 1265.
History
Background
Pagan Prussians rose aga ...
(1262–1265) – Prussian uprisings
The Prussian uprisings were two major and three smaller uprisings by the Old Prussians, one of the Baltic tribes, against the Teutonic Knights that took place in the 13th century during the Prussian Crusade. The crusading military order, sup ...
* Siege of Bartenstein
Siege of Bartenstein was a medieval siege laid upon the castle of Bartenstein (now Bartoszyce in Poland) by the Prussians during the Great Prussian Uprising. Bartenstein and Rößel were the two major Teutonic strongholds in Barta, one of the P ...
(1264) – Prussian uprisings
* Siege of al-Bira (1264–1265) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
* Fall of Arsuf
In late March 1265 Sultan Baibars, Muslim ruler of the Mamluks, laid siege to Arsuf. It was defended by 270 Knights Hospitallers. At the end of April, after 40 days of siege, the town surrendered. However, the Knights remained in their formidab ...
(1265)
* Siege of Kenilworth (1266) – Second Barons' War
The Second Barons' War (1264–1267) was a civil war in England between the forces of a number of barons led by Simon de Montfort against the royalist forces of King Henry III, led initially by the king himself and later by his son, the fu ...
* Siege of Safed (1266)
The siege of Safed (13 June – 23 July 1266) was part of the campaign of the Mamlūk sultan Baybars I to reduce the Kingdom of Jerusalem. The castle of Safed belonged to the Knights Templar and put up strong resistance. Direct assault, mining an ...
* Siege of Xiangyang
The Battle of Xiangyang () was a protracted series of battles between the Yuan dynasty and the Southern Song dynasty from 1267 to 1273. The battle was a significant victory for the Yuan dynasty and ended a 30-year defensive campaign waged by th ...
(1267–1273) – Mongol conquest of the Song dynasty
* Siege of Antioch (1268)
The siege of Antioch occurred in 1268 when the Mamluk Sultanate under Baibars finally succeeded in capturing the city of Antioch. Prior to the siege, the Crusader Principality was oblivious to the loss of the city, as demonstrated when Baibar ...
 *
* Fall of Krak des Chevaliers
The Crusader fortress of Krak des Chevaliers fell to the Mamluk sultan Baibars in 1271.
Baibars went north to deal with Krak des Chevaliers after the death of Louis IX of France on 29 November 1270.
Siege and surrender
Before marching on t ...
(1271)
* Siege of Tripoli (1271)
The 1271 siege of Tripoli was initiated by the Mamluk ruler Baibars against the Frankish ruler of the Principality of Antioch and the County of Tripoli, Bohemond VI. It followed the dramatic fall of Antioch in 1268, and was an attempt by the ...
* Siege of Al-Bira (1272) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
* Siege of Al-Rahba (1272) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
* Siege of Al-Bira (1275) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
* Siege of Algeciras (1278–1279) – Reconquista
* Siege of Berat (1280–1281)
The siege of Berat in Albania by the forces of the Angevin Kingdom of Sicily against the Byzantine garrison of the city took place in 1280–1281. Berat was a strategically important fortress, whose possession would allow the Angevins access ...
* Siege of Trebizond (1282)
* Siege of Albarracín (1284)
The siege of Albarracín was a battle fought during the reign of Peter III of Aragon, King of Aragón from the months of April to September 1284. Albarracín, which had Sinyoría d'Albarrazín, for some time belonged to Juan Núñez I de Lara, t ...
* Siege of Acre (1291)
The siege of Acre (also called the fall of Acre) took place in 1291 and resulted in the Crusaders losing control of Acre to the Mamluks. It is considered one of the most important battles of the period. Although the crusading movement continu ...
* Capture of Berwick (1296)
The Sack of Berwick was the first significant battle of the First War of Scottish Independence in 1296.
Background
Upon the death of Margaret, Maid of Norway, in late September 1290, there arose a number of claimants to the throne of Scotland. ...
– First War of Scottish Independence
The First War of Scottish Independence was the first of a series of wars between English and Scottish forces. It lasted from the English invasion of Scotland in 1296 until the ''de jure'' restoration of Scottish independence with the Treaty ...
* Siege of Lille (1297) – Franco-Flemish War
The Franco-Flemish War (french: Guerre de Flandre; nl, Vlaamse opstand) was a conflict between the Kingdom of France and the County of Flanders between 1297 and 1305.
Causes
Philip IV of France became king in 1285, and was determined to stre ...
* Siege of Damascus (1299–1300) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
14th century
*Siege of Ruad
The fall of Ruad in 1302 was one of the culminating events of the Crusades in the Eastern Mediterranean. When the garrison on the tiny Isle of Ruad fell, it marked the loss of the last Crusader outpost on the coast of the Levant. In 1291, the C ...
(1302)
*Siege of Buda by Charles I. (1302)
* Siege of Stirling Castle (1304) – First War of Scottish Independence
The First War of Scottish Independence was the first of a series of wars between English and Scottish forces. It lasted from the English invasion of Scotland in 1296 until the ''de jure'' restoration of Scottish independence with the Treaty ...
* Siege of Rhodes (1306–1310)
*Siege of Buda by Charles I. (1307)
* Siege of Gibraltar (1309) – First siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by Juan Alfonso de Guzman ''el Bueno'' in the Reconquista
* Siege of Algeciras (1309–10) The Battle of Algeciras or Siege of Algeciras may refer to:
* Siege of Algeciras (1278)
* Battle of Algeciras (1278)
* Siege of Algeciras (1309)
* Siege of Algeciras (1342-1344)
* Siege of Algeciras (1369)
* Battle of Algeciras (1801) or the ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Almería (1309)
The siege of Almería was an unsuccessful attempt by Aragon to capture the city of Almería from the Emirate of Granada in 1309. Almería, a Mediterranean port in the southeast of the emirate, was the initial Aragonese target in a joint Aragon ...
– Reconquista
* Siege of Warangal (1310)
In late 1309, the Delhi Sultanate ruler Alauddin Khalji sent his general Malik Kafur on an expedition to the Kakatiya capital Warangal. Malik Kafur reached Warangal in January 1310, after conquering a fort on the Kakatiya frontier and ransac ...
* Siege of Florence (1312)
Henry VII (German: ''Heinrich''; c. 1273 – 24 August 1313),Kleinhenz, pg. 494 also known as Henry of Luxembourg, was Count of Luxembourg, King of Germany (or ''Rex Romanorum'') from 1308 and Holy Roman Emperor from 1312. He was the first empe ...
* Siege of Al-Rahba (1312–1313) – Mongol invasions of the Levant
* Siege of Roxburgh (1314) – First War of Scottish Independence
* Second siege of Gibraltar (1315) – Second siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by the Nasrid caid Yahya in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Carlisle (1315)
The siege of Carlisle took place from 22 July to 1 August 1315, during the First War of Scottish Independence, near the town of Carlisle, in Cumbria, England.
Following victory at Bannockburn in 1314, Robert the Bruce, King of Scotland, ...
– First War of Scottish Independence
* Siege of Christmemel
The siege of Christmemel was an unsuccessful siege of the Teutonic Knights' castle of Christmemel by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania in autumn 1315.
Christmemel was an ''Ordensburg'' fortress made of earth and timber built on the Neman River in 1 ...
(1315) – Lithuanian Crusade
The Lithuanian Crusade was a series of economic Christian colonization campaigns by the Teutonic Order and the Livonian Order under the pretext of forcibly Christianizing the pagan Grand Duchy of Lithuania. The Livonian Order occupied Riga in ...
* Siege of Warangal (1318)
In 1318, the Delhi Sultanate ruler Qutbuddin Mubarak Shah sent an army to subjugate the Kakatiya ruler Prataparudra who had stopped making tribute payments to Delhi. The invading army, led by Khusrau Khan and other generals, besieged the Kakatiy ...
* Siege of Berwick (1318)
The siege of Berwick was an event in the First War of Scottish Independence which took place in April 1318. Sir James Douglas, Lord of Douglas took the town and castle of Berwick-upon-Tweed from the English, who had controlled the town sinc ...
– First War of Scottish Independence
* Siege of Padua (1319–1320), by Cangrande I della Scala
Cangrande (christened Can Francesco) della Scala (9 March 1291 – 22 July 1329) was an Italian nobleman, belonging to the della Scala family which ruled Verona from 1308 until 1387. Now perhaps best known as the leading patron of the poet Dante ...
, lord of Verona
Verona ( , ; vec, Verona or ) is a city on the Adige River in Veneto, Italy, with 258,031 inhabitants. It is one of the seven provincial capitals of the region. It is the largest city municipality in the region and the second largest in nor ...
* Siege of Bursa
The siege of Bursa occurred from 1317 until the capture on 6 April 1326, when the Ottomans deployed a bold plan to seize Prusa (modern-day Bursa, Turkey). The Ottomans had not captured a city before; the lack of expertise and adequate siege equ ...
(1320–1326) – Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
* Siege of Warangal (1323)
In 1323, the Delhi Sultanate ruler Ghiyath al-Din Tughluq sent an army led by his son Ulugh Khan (later Muhammad bin Tughluq) to the Kakatiya capital Warangal, after the Kakatiya ruler Prataparudra refused to make tribute payments. Ulugh Khan' ...
* Siege of Villa di Chiesa (1323–1324)
* Siege of Bristol (1326) – Invasion of England (1326)
The invasion of England in 1326 by the country's queen, Isabella of France, and her lover, Roger Mortimer, led to the capture and executions of Hugh Despenser the Younger and Hugh Despenser the Elder and the abdication of Isabella's husband, ...
* Siege of Nicaea (1328–1331)
The siege of Nicaea by the forces of Orhan I from 1328 to 1331, resulted in the conquest of a key Byzantine Greek city by the Ottoman Turks. It played an important role in the expansion of the Ottoman Empire.
Background
Following the recaptur ...
– Byzantine-Ottoman wars
* Siege of Medvėgalis
The siege of Medvėgalis was a brief siege of Medvėgalis, a Lithuanian fortress in Samogitia, in February 1329 by the Teutonic Order reinforced by many guest crusaders, including King John of Bohemia. The 18,000-strong Teutonic army captured ...
(1329) – Lithuanian Crusade
* Siege of Kasagi
The 1331 siege of Kasagi was among the first battles of the Genkō War, which brought an end to Japan's Kamakura period. Emperor Go-Daigo, who had been plotting against the shogunate
, officially , was the title of the military dictators of ...
(1331) – Genkō War
The , also known as the , was a civil war fought in Japan between the Emperor Go-Daigo and the Kamakura Shogunate from 1331 to 1333. The Genkō War was named after Genkō, the Japanese era corresponding to the period of 1331 to 1334 when the wa ...
* Siege of Akasaka
The siege of Akasaka was one of the earlier battles of the Genkō War between the figurehead Emperor Godaigo and the largely Hōjō controlled Kamakura shogunate during the final years of the Kamakura period in Japan. The battle in question was ...
(1331) – Genkō War
* Third siege of Gibraltar – Third siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
(1333), by a Marinids
The Marinid Sultanate was a Berber Muslim empire from the mid-13th to the 15th century which controlled present-day Morocco and, intermittently, other parts of North Africa (Algeria and Tunisia) and of the southern Iberian Peninsula (Spain) ar ...
army, led by Abd al-Malik in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Chihaya
The 1333 siege of Chihaya took place during the final year of Japan's Kamakura period. It was one of several battles of the Genkō War, in which Emperor Go-Daigo sought to eliminate the power of the Hōjō clan regents. Chihaya-jō (千早城, C ...
(1333) – Genkō War
* Siege of Berwick (1333)
The siege of Berwick lasted four months in 1333 and resulted in the Scottish-held town of Berwick-upon-Tweed being captured by an English army commanded by King Edward III (). The year before, Edward Balliol had seized the Scottish Crown, su ...
* Fourth siege of Gibraltar
The fourth siege of Gibraltar, fought from June until August 1333, pitted a Christian army under King Alfonso XI of Castile against a large Moorish army led by Muhammed IV of Granada and Abd al-Malik Abd al-Wahid of Fes. It followed on immedia ...
– Rourth siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
(1333), by King Alfonso XI of Castile
Alfonso XI (13 August 131126 March 1350), called the Avenger (''el Justiciero''), was King of Castile and León. He was the son of Ferdinand IV of Castile and his wife Constance of Portugal. Upon his father's death in 1312, several disputes en ...
in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Kamakura (1333)
The 1333 siege of Kamakura was a battle of the Genkō War, and marked the end of the power of the Hōjō clan, which had dominated the regency of the Kamakura shogunate for over a century. Forces loyal to Emperor Go-Daigo and led by Nitta Yoshis ...
– End of Ashikaga shogunate
The , also known as the , was the feudal military government of Japan during the Muromachi period from 1336 to 1573.Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Muromachi-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia'', p. 669.
The Ashikaga shogunate was establi ...
.
* Siege of Nicomedia
From 1299, the newly founded state of the Ottomans had been slowly but surely capturing territory from the Byzantine Greeks. The loss of Nicaea was the beginning of a series of Ottoman expansions that led to the final dissolution of the Byzant ...
(1333–1337) – Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
* Siege of Kanegasaki (1337)
The 1337 was the final battle for the Nitta family in their support of the Southern Imperial Court against the Ashikaga Pretenders of the Northern Court.
Nitta Yoshisada's fortress at Kanegasaki was besieged for three months by forces in suppo ...
* Siege of Kuromaru (1339)
* Siege of Tournai (1340) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
The Hundred Years' War (; 1337–1453) was a series of armed conflicts between the kingdoms of England and France during the Late Middle Ages. It originated from disputed claims to the French throne between the English House of Plantagen ...
Siege of Aiguillon
The siege of Aiguillon, an episode in the Hundred Years' War, began on 1 April 1346 when a French army commanded by John, Duke of Normandy, laid siege to the Gascon town of Aiguillon. The town was defended by an Anglo-Gascon army under Ra ...
(1346) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Calais (1346–1347) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Calais (1349)
The Battle of Calais took place in 1350 when an English force defeated an unsuspecting French army which was attempting to take the city. Despite a truce being in effect the French commander Geoffrey de Charny had planned to take the city b ...
– Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Gibraltar (1349–1350) – fifth siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by ''Alfonso XI'' in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély (1351) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Rennes (1356–57) – War of the Breton Succession
The War of the Breton Succession (, ) was a conflict between the Counts of Blois and the Montforts of Brittany for control of the Sovereign Duchy of Brittany, then a fief of the Kingdom of France. It was fought between 1341 and 12 April 1 ...
* Siege of Chartres Siege of Chartres may refer to:
*Siege of Chartres (911)
* Siege of Chartres (1360)
*Siege of Chartres (1568)
The siege of Chartres (28 February – 15 March 1568) was a key event of the second French Wars of Religion. The siege saw the Huguenot ...
(1360) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Kaunas
The siege of Kaunas was laid by the Teutonic Order on the newly built Kaunas Castle in spring 1362. It was the first brick castle built by the Grand Duchy of Lithuania. After a month-long siege, the castle was captured and destroyed. Its comman ...
(1362) – Lithuanian Crusade
* Siege of León (1368)
The siege of León of 1368 was a successful siege of the city by the pretender Henry of Trastámara, in the course of the Castilian Civil War.
History
In 1367, Henry of Castile, resoundingly defeated in the Battle of Nájera, went back to the P ...
* Siege of Algeciras (1369) – Reconquista
* Siege of Limoges
The town of Limoges had been under English control but in August 1370 it surrendered to the French, opening its gates to the Duke of Berry. The siege of Limoges was laid by the English army led by Edward the Black Prince in the second week in S ...
(1370) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Gibraltar (1374) – sixth siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by the Nasrid
The Nasrid dynasty ( ar, بنو نصر ''banū Naṣr'' or ''banū al-Aḥmar''; Spanish: ''Nazarí'') was the last Muslim dynasty in the Iberian Peninsula, ruling the Emirate of Granada from 1230 until 1492. Its members claimed to be of Arab ...
in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Philadelphia (1378–1390) – Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
* Siege of Moscow (1382)
The siege of Moscow in 1382 was a battle between the Muscovite forces and Tokhtamysh, the khan of the Golden Horde supported by Timur.
Background
After the death of Berdibeg, the Blue Horde fell into anarchy, with local khans in various places ...
* Siege of Sofia
The siege of Sofia took place in 1382 or 1385Андреев, p. 283 during the course of the Bulgarian–Ottoman wars. Unable to defend his country from the Ottomans, in 1373 the Bulgarian emperor Ivan Shishman agreed to become an Ottoman vassal ...
(1382 or 1385)
* Siege of Ypres (1383)
The siege of Ypres occurred between 8 June and 8 August 1383 as part of Despenser's Crusade and the Revolt of Ghent (1379–1385). It was conducted by English forces and forces from the Flemish city of Ghent. The siege was a failure.
Prelude ...
– Despenser's Crusade
* Siege of Lisbon (1384)
The siege of Lisbon was a siege of the city of Lisbon from 29 May to 3 September 1384, between the Portuguese defenders of the city led by John I of Portugal and the Castillian army led by King John I of Castile. The siege ended in a disaster fo ...
– 1383–1385 Portuguese interregnum
* Siege of Tbilisi (1386) – Timur's invasions of Georgia
* Siege of Isfahan (1387)
The siege of Isfahan was a siege of the city of Isfahan by the army of Timur in 1387.
Background
To annex the Muzaffarid kingdom Timur would have to capture its two main cities: Isfahan and Shiraz. When in 1387, Timur arrived with his army to I ...
* Siege of Tarnovo (1393)
* Siege of Anjudan
Anjudan ( fa, انجدان, also Romanized as Anjedān; also known as Andījān, Anjidān, and Injadān) is a village in Amanabad Rural District, in the Central District of Arak County, Markazi Province, Iran. At the 2006 census, its populatio ...
(1393)
* Siege of Constantinople (1394–1402)
The siege of Constantinople in 1394–1402 was a long blockade of the capital of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottoman Sultan Bayezid I. Already in 1391, the rapid Ottoman conquests in the Balkans had cut off the city from its hinterland. After ...
– Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
15th century
* Siege of Sivas (1400) *Siege of Damascus (1400)
The siege of Damascus (also known as the Sack of Damascus and the Capture of Damascus) was a major event in 1400 during the war between the Timurid Empire and Mamluk Egypt.
Background
Timur was one of the most powerful Central Asian rulers sinc ...
* Siege of Smyrna (1402)
* Siege of Birtvisi (1403) – Timur's invasions of Georgia
* Siege of Mercq (1405) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Marienburg (1410)
The siege of Marienburg was an unsuccessful two-month siege of the castle in Marienburg (Malbork), the capital of the monastic state of the Teutonic Knights. The joint Polish and Lithuanian forces, under command of King Władysław II Jagieł� ...
– in the aftermath of the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
* Siege of Constantinople (1411)– Byzantine-Ottoman Wars, during the Ottoman Interregnum
The Ottoman Interregnum, or the Ottoman Civil War ( 20 July 1402 – 5 July 1413; tr, Fetret Devri, , Interregnum Period), was a civil war in the Ottoman Empire between the sons of Sultan Bayezid I following the defeat of their father at the ...
* Sixth Siege of Gibraltar (1411)
* Siege of Bourges (1412) – Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War
The Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War was a conflict between two cadet branches of the French royal family – the House of Orléans ( Armagnac faction) and the House of Burgundy ( Burgundian faction) from 1407 to 1435. It began during a lull in th ...
 *
* Siege of Harfleur
The siege of Harfleur (18 August – 22 September 1415) was conducted by the English army of King Henry V in Normandy, France, during the Hundred Years' War. The defenders of Harfleur surrendered to the English on terms and were treated as pr ...
(1415) – reopening of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Rouen (1418–1419) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Đông Quan
The siege of Đông Quan was a 15th-century siege of the Ming dynasty city of Đông Quan by Vietnamese rebels led by Lê Lợi. Đông Quan was besieged for every year that the war raged. Lê Lợi's first siege attempt came at the Battle of Tha ...
(1418–1428) – Lam Sơn uprising
The Lam Sơn uprising (; vi, Khởi nghĩa Lam Sơn; vi-hantu, 起義藍山) was a Vietnamese rebellion led by Lê Lợi in the province of Jiaozhi from 1418 to 1427 against the rule of Ming China. The success of the rebellion led to the est ...
* Siege of Ceuta (1419)
The siege of Ceuta of 1419 (sometimes reported as 1418) was fought between the besieging forces of the Marinid Sultanate of Morocco, led by Sultan Abu Said Uthman III, including allied forces from the Emirate of Granada, and the Portuguese garri ...
* Siege of Sarai
The siege of Sarai (July - August 1420) was a siege of Sarai, the nominal capital of the Golden Horde.
Background
After the death of Yeremferden both Dawlat Berdi and Olugh Mokhammad sought control of the Golden Horde. Berdi, who was Yeremfer ...
(1420)
* Siege of Meaux
The siege of Meaux was fought in 1421-1422 between the English and the French during the Hundred Years' War. The English were led by King Henry V. Henry became ill while fighting this long battle, which took place during the winter months. He di ...
(1421–1422) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Constantinople (1422)
The first full-scale Ottoman siege of Constantinople took place in 1422 as a result of the Byzantine Emperor Manuel II's attempts to interfere in the succession of Ottoman Sultans, after the death of Mehmed I in 1421. This policy of the Byzan ...
– Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
* Siege of Thessalonica (1422–1430)
The siege of Thessalonica between 1422 and 1430 saw the Ottoman Empire, under Sultan Murad II, capture the city of Thessalonica, which remained in Ottoman hands for the next five centuries, until it became part of the Kingdom of Greece in 1912 ...
– Byzantine-Ottoman and Ottoman-Venetian Wars
* Siege of Golubac
The siege of Golubac ( hu, Galambóc) was a military conflict between the Hungarian– Wallachian–Lithuanian alliance and the Ottoman Empire in May 1428. This siege was the first battle in Hungarian military history in which the Hungarian arm ...
(1428)
* Siege of Orléans
The siege of Orléans (12 October 1428 – 8 May 1429) was the watershed of the Hundred Years' War between France and England. The siege took place at the pinnacle of English power during the later stages of the war. The city held strategic an ...
(1428–1429) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Inverness (1429)
The siege of Inverness of 1429 was a conflict between Alexander of Islay, Earl of Ross (also 3rd Lord of the Isles and chief of Clan Donald) and the Scottish crown. Alexander of Islay besieged the royal Inverness Castle and burnt the town of ...
* Siege of Paris (1429)
The siege of Paris was an assault undertaken in September 1429 during the Hundred Years' War by the troops of the recently crowned King Charles VII of France, with the notable presence of Joan of Arc, to take the city held by the English Burgund ...
– Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Malta (1429)
* Siege of Saint-Pierre-le-Moûtier
The siege of Saint-Pierre-le-Moûtier was a venture of the so-called Lancastrian War. The small town was however heavily fortified and surrounded by a deep moat. According to Joan of Arc's bodyguard, Jean d'Aulon, the initial assault failed and ...
– Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War
The Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War was a conflict between two cadet branches of the French royal family – the House of Orléans ( Armagnac faction) and the House of Burgundy ( Burgundian faction) from 1407 to 1435. It began during a lull in th ...
* Siege of La Charité
The siege of La Charité was incited by the order of Charles VII to Joan of Arc after the warlord Perrinet Gressard seized the town in 1423.
La Charité was not only strongly fortified, but fully victualled for a prolonged siege. Joan's forc ...
(1429) – Armagnac–Burgundian Civil War
* Siege of Compiègne
The siege of Compiègne (1430) was conducted by Duke Philip III of Burgundy after the town of Compiègne had refused to transfer allegiance to him under the terms of a treaty with Charles VII. The siege is perhaps best known for Joan of Arc's ca ...
(1430) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Angkor
The Fall of Angkor, also known as the Sack of Angkor or Siege of Angkor was a seven-month siege by the Ayutthaya Kingdom on the Khmer capital of Angkor. After the Khmer refused to recognize Thai authority, the Thai besieged Angkor and sacked the ...
(1431)
* Siege of Pouancé (1432) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Pilsen (1433–34) – Hussite Wars
The Hussite Wars, also called the Bohemian Wars or the Hussite Revolution, were a series of civil wars fought between the Hussites and the combined Catholic forces of Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, Holy Roman Emperor Sigismund, the Papacy, Eur ...
* Siege of Gaeta (1435)
* Siege of Saint-Denis
The siege of Saint-Denis (Late August – 4 October 1435) was the last instance of cooperation between the English and their Burgundian allies in the Hundred Years' War. Saint-Denis, the traditional burial place of the kings of France, was ...
(1435) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Calais (1436)
The siege of Calais between June and July 1436 was a failed siege of English-held Calais by Philip the Good, Duke of Burgundy, and Flemish militia.
Prelude
England and Burgundy had been allies against France in the Hundred Years' War since 1 ...
– Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Seventh Siege of Gibraltar (1436) – seventh siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by the count of Niebla in the ''Reconquista''
* Siege of Tangiers (1437)
 *
* Siege of Belgrade (1440)
The siege of Belgrade was a siege of Belgrade, an important fortified town of the Serbian Despotate and the key fortress of the Hungarian defense line after the Ottoman subjugation of Serbia in 1439, by the forces of the Ottoman Empire, spann ...
* Siege of Tartas (1440–1442) – Part of the Hundred Years' War
* Siege of Novo Brdo (1440–41)
* Siege of Metz (1444)
* Siege of Rhodes (1444)
The siege of Rhodes was a military engagement involving the Knights Hospitaller and Mamluk Sultanate. The Mamluk fleet landed on the island of Rhodes on 10 August 1444, besieging its citadel. Clashes took place on the western walls of the city ...
* Siege of Balkh (1447)
After the Battle of Nishapur and the peace treaty which gave the Chechektu valley to Ala al-Dawla Mirza, he placed in that outpost a certain Mirza Saleh who was an enemy of Abdal-Latif Mirza. Furthermore, Ala-ud-Daulah Mirza kept hostages, certa ...
* Siege of Herat (1448)
Ulugh Beg and his son Abdal-Latif Mirza marched towards Herat in the spring of 1448 in order to take Khurasan from his nephew, Ala al-Dawla Mirza, who had escaped to Quchan after the defeat at the Battle of Tarnab. They easily took the city exce ...
* Siege of Svetigrad (1448)
The siege of Svetigrad or Sfetigrad began on 14 May 1448 when an Ottoman army, led by Sultan Murad II, besieged the fortress of Svetigrad (now Kodžadžik). After the many failed Ottoman expeditions into Albania against the League of Lezhë, a ...
* Fifth Siege of Gibraltar (1449–1450)
* Siege of Krujë (1450)
The first siege of Krujë occurred in 1450 when an Ottoman army of 100,000 men tried to siege Albanian town of Krujë. The League of Lezhë, led by Skanderbeg, experienced low morale after losing Svetigrad and Berat between 1448 and 1450. ...
* Siege of Constantinople
The following is a list of sieges of Constantinople, a historic city located in an area which is today part of Istanbul, Turkey. The city was built on the land that links Europe to Asia through Bosporus and connects the Sea of Marmara and the ...
(1453) – Byzantine-Ottoman Wars
Early modern
15th century
* Siege of Marienburg (1454) –Thirteen Years' War (1454–66) Thirteen Years' War may refer to:
*the Thirteen Years' War (1454–1466) between the Prussian Confederation and Poland versus the Teutonic Order state
*the Long Turkish War (1593–1606) between the Habsburg Monarchy and the Ottoman Empire
*the Ru ...
* Siege of Berat (1455)
The siege of Berat took place in July 1455 when the Albanian army of Skanderbeg besieged the fortress in the Albanian city of Berat, which was held by Ottoman forces.
Background
When Skanderbeg began his rebellion, Berat belonged to the Alban ...
* Siege of Belgrade (1456)
The siege of Belgrade, Battle of Belgrade or siege of Nándorfehérvár ( hu, Nándorfehérvár ostroma or , "Triumph of Nándorfehérvár"; sr-Cyr, Опсада Београда, Opsada Beograda) was a military blockade of Belgrade that o ...
– Part of Ottoman wars in Europe
A series of military conflicts between the Ottoman Empire and various European states took place from the Late Middle Ages up through the early 20th century. The earliest conflicts began during the Byzantine–Ottoman wars, waged in Anatolia in ...
* Siege of Deventer (1456)
The siege of Deventer was a siege of Deventer (then a major Hanseatic city) in 1456 during a struggle between Duke Philip the Good of Burgundy and the church, the nobility, and cities of the Oversticht (Overijssel).
The Siege
Over the 15th cent ...
* Siege of Marienburg (1457–1460) – Thirteen Years' War (1454–66)
* Siege of Roxburgh (1460)
* Siege of Trebizond (1460–1461)
* Siege of Harlech Castle
Harlech Castle ( cy, Castell Harlech; ) in Harlech, Gwynedd, Wales, is a Grade I listed medieval fortification built onto a rocky knoll close to the Irish Sea. It was built by Edward I during his invasion of Wales between 1282 and 1289 ...
(1461–68) – Part of Wars of the Roses
The Wars of the Roses (1455–1487), known at the time and for more than a century after as the Civil Wars, were a series of civil wars fought over control of the throne of England, English throne in the mid-to-late fifteenth century. These w ...
. Longest siege in British history.
* Siege of Shahrukhiya (1461–63)
* Siege of Hostalric
The siege of Hostalric was the first major action of the War Against John II. It took place on 23 May 1462.
Background
In 1460, after John II imprisoned Charles of Viana, the Catalans at the Corts de Lleida formed the Council of the Principality ...
(1462) – Catalan Civil War
The Catalan Civil War, also called the Catalonian Civil War or the War against John II, was a civil war in the Principality of Catalonia, then part of the Crown of Aragon, between 1462 and 1472. The two factions, the royalists who supported John ...
* Eighth Siege of Gibraltar (1462), by a Castilian army in the ''Reconquista
The ' ( Spanish, Portuguese and Galician for "reconquest") is a historiographical construction describing the 781-year period in the history of the Iberian Peninsula between the Umayyad conquest of Hispania in 711 and the fall of the N ...
''
* Siege of Mytilene (1462)
* Siege of Barcelona (1462) – Catalan Civil War
 * Siege of Jajce (1463)
*
* Siege of Jajce (1463)
* Siege of Jajce (1464)
The siege of Jajce took place between 10 July and 24 August 1464, during the Ottoman conquest of Bosnia and Herzegovina, when an Ottoman army under Sultan Mehmed II made a new attempt to retrieve Bosnia and conquer the strategic fortress of Ja ...
* Siege of Barcelona (1465) Siege of Barcelona may refer to:
* Siege of Barcelona (801), during the Reconquista
* Siege of Barcelona (1462), during the Catalan Civil War
* Siege of Barcelona (1472), during the Catalan Civil War
* Siege of Barcelona (1651), during the Catalan ...
– Catalan Civil War
* Ninth Siege of Gibraltar (1466–1467), by the Duke of Medina Sidonia
Duke of Medina Sidonia ( es, Duque de Medina Sidonia) is a peerage grandee title of Spain in Medina-Sidonia, holding the oldest extant dukedom in the kingdom, first awarded by King John II of Castile in 1380.Siege of Krujë (1466–67)
* Siege of Krujë (1467)
*  *
*
 * Siege of Opochka (1517) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
*
* Siege of Opochka (1517) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
*  * Siege of Pavia (1524–25) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Sambhal (1526)
*
* Siege of Pavia (1524–25) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Sambhal (1526)
*  * Siege of Maribor (1532)
*
* Siege of Maribor (1532)
*  *
*  *
*  * Siege of Kiso Fukushima (1554)
*
* Siege of Kiso Fukushima (1554)
*  * Sieges of Oran and Mers El Kébir (1563)
* Capture of Älvsborg – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Concepción (1564)
* Siege of Chauragarh (1564)
* Siege of Kuragano (1565)
* Great Siege of Malta (1565)
* Siege of Minowa (1566)
* Siege of Szigetvár (1566) – Ottoman Empire, Ottoman siege during which Suleiman the Magnificent died
* Siege of Valenciennes (1567), Siege of Valenciennes (1566–67) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Inabayama Castle (1567)
* Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–1568), Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–68)
* Siege of Ranthambore (1568)
* Siege of Chartres (1568)
* Siege of Malacca (1568)
* Siege of Hachigata (1568)
* Siege of Odawara (1569)
* Siege of Kanbara (1569)
* Siege of Kakegawa (1569)
* Siege of Tachibana (1569)
* Siege of Varberg (1569) – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ogucji Castle (1569)
* Siege of Hanazawa (1570)
* Siege of Chōkō-ji (1570)
* Siege of Kanegasaki (1570)
* Siege of Nicosia, Cyprus (1570) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Famagusta, Cyprus (1570–71) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Reval (1570–71) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1570–71) - Livonian War
* Siege of Ishiyama Honganji (1570–1580) – longest siege in Japanese history
*Siege of Chale (1571) - War of the League of the Indies, War of the league of Indies
* Siege of Fukazawa (1571)
* Siege of Moscow (1571) – Part of Russo-Crimean Wars
* Sieges of Nagashima (1571, 1573, 1574)
* Siege of Mount Hiei (1571)
* Siege of Futamata (1572)
* Siege of Iwamura Castle (1572)
* Siege of Mons (1572) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Middelburg (1572–74) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle during the French Wars of Religion.
* Siege of Sancerre (1572–1573) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Haarlem (1572–1573) – conducted by the Spanish against the Dutch during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1572–73) - Livonian War
* Siege of Noda Castle (1573)
* Siege of Odani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Hikida Castle (1573)
* Siege of Ichijōdani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Alkmaar (1573) – turning point in the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leiden (1573–1574) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Wesenberg (1574) – Livonian War
* Siege of Itami (1574)
* Siege of Takatenjin (1574)
* Conquest of Tunis (1574), Siege of Tunis (1574)
* Lim Hong (pirate), Siege of Limahong (1574)
* Siege of Yoshida Castle (1575)
* Siege of Nagashino (1575)
* Siege of Schoonhoven (1575) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zierikzee (1575–1576)) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mitsuji (1576)
* Siege of Takabaru (1576)
* Sack of Antwerp, Siege of Antwerp (1576) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nanao (1577)
* Siege of Shigisan (1577)
* Siege of Reval (1577) – Livonian War
* Sieges of Oran and Mers El Kébir (1563)
* Capture of Älvsborg – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Concepción (1564)
* Siege of Chauragarh (1564)
* Siege of Kuragano (1565)
* Great Siege of Malta (1565)
* Siege of Minowa (1566)
* Siege of Szigetvár (1566) – Ottoman Empire, Ottoman siege during which Suleiman the Magnificent died
* Siege of Valenciennes (1567), Siege of Valenciennes (1566–67) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Inabayama Castle (1567)
* Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–1568), Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–68)
* Siege of Ranthambore (1568)
* Siege of Chartres (1568)
* Siege of Malacca (1568)
* Siege of Hachigata (1568)
* Siege of Odawara (1569)
* Siege of Kanbara (1569)
* Siege of Kakegawa (1569)
* Siege of Tachibana (1569)
* Siege of Varberg (1569) – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ogucji Castle (1569)
* Siege of Hanazawa (1570)
* Siege of Chōkō-ji (1570)
* Siege of Kanegasaki (1570)
* Siege of Nicosia, Cyprus (1570) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Famagusta, Cyprus (1570–71) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Reval (1570–71) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1570–71) - Livonian War
* Siege of Ishiyama Honganji (1570–1580) – longest siege in Japanese history
*Siege of Chale (1571) - War of the League of the Indies, War of the league of Indies
* Siege of Fukazawa (1571)
* Siege of Moscow (1571) – Part of Russo-Crimean Wars
* Sieges of Nagashima (1571, 1573, 1574)
* Siege of Mount Hiei (1571)
* Siege of Futamata (1572)
* Siege of Iwamura Castle (1572)
* Siege of Mons (1572) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Middelburg (1572–74) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle during the French Wars of Religion.
* Siege of Sancerre (1572–1573) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Haarlem (1572–1573) – conducted by the Spanish against the Dutch during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1572–73) - Livonian War
* Siege of Noda Castle (1573)
* Siege of Odani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Hikida Castle (1573)
* Siege of Ichijōdani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Alkmaar (1573) – turning point in the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leiden (1573–1574) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Wesenberg (1574) – Livonian War
* Siege of Itami (1574)
* Siege of Takatenjin (1574)
* Conquest of Tunis (1574), Siege of Tunis (1574)
* Lim Hong (pirate), Siege of Limahong (1574)
* Siege of Yoshida Castle (1575)
* Siege of Nagashino (1575)
* Siege of Schoonhoven (1575) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zierikzee (1575–1576)) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mitsuji (1576)
* Siege of Takabaru (1576)
* Sack of Antwerp, Siege of Antwerp (1576) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nanao (1577)
* Siege of Shigisan (1577)
* Siege of Reval (1577) – Livonian War
 * Siege of Danzig (1577) – Danzig rebellion
* Siege of Gvozdansko (1577–1578)
* Siege of Kōzuki Castle (1578)
* Siege of Otate (1578)
* Siege of Deventer (1578) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Miki (1578–1580)
* Siege of Itami (1579)
* Siege of Maastricht (1579) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Polotsk (1579) – Livonian War
* Siege of Velikiye Luki – Livonian War
* Siege of Carrigafoyle Castle (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Steenwijk (1580–1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Smerwick (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Takatenjin (1581), Siege of Takatenjin (1580–1581)
* Siege of Hijiyama (1581)
* Siege of Tottori (1581)
* Siege of Minamata Castle (1581)
* Siege of Narva (1581) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1581) - Livonian War
* Siege of Pskov (1581–1582) – Livonian War
* Siege of Niezijl (1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Danzig (1577) – Danzig rebellion
* Siege of Gvozdansko (1577–1578)
* Siege of Kōzuki Castle (1578)
* Siege of Otate (1578)
* Siege of Deventer (1578) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Miki (1578–1580)
* Siege of Itami (1579)
* Siege of Maastricht (1579) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Polotsk (1579) – Livonian War
* Siege of Velikiye Luki – Livonian War
* Siege of Carrigafoyle Castle (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Steenwijk (1580–1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Smerwick (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Takatenjin (1581), Siege of Takatenjin (1580–1581)
* Siege of Hijiyama (1581)
* Siege of Tottori (1581)
* Siege of Minamata Castle (1581)
* Siege of Narva (1581) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1581) - Livonian War
* Siege of Pskov (1581–1582) – Livonian War
* Siege of Niezijl (1581) – Eighty Years' War
 * Siege of Takamatsu (1582)
* Siege of Takatō (1582)
* Siege of Uozu (1582)
* Siege of Lochem (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lier (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eindhoven (1583) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Godesberg (1583)
* Siege of Kaganoi (1584)
* Siege of Takehana (1584)
* Siege of Kanie (1584)
* Siege of Suemori (1584)
* Siege of Ypres (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ghent (1583–1584), Siege of Ghent (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bruges (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Brussels (1584–85) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Toyama (1585)
* Siege of Negoro-ji (1585)
* Siege of Ōta Castle (1585)
* Siege of IJsseloord (1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Iwaya Castle (1586)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias (1586), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1586) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Grave (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Venlo (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Axel, Siege of Axel (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Destruction of Neuss, Second siege of Neuss (July 1586)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1586–1590) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ganjaku (1587)
* Siege of Akizuki (1587)
* Siege of Kagoshima (1587)
* Siege of Sluis (1587) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Johor (1587)
* Siege of Kraków (1587) – War of the Polish Succession (1587–88)
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1588) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kurokawa Castle (1589)
* Siege of Hachigata (1590)
* Siege of Paris (1590) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Odawara (1590), Siege of Odawara Castle (1590)
* Siege of Shimoda (1590)
* Siege of Oshi (1590)
* Siege of Zutphen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Deventer (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Knodsenburg (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Hulst (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nijmegen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Rouen (1591), Siege of Rouen (1591–1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Caudebec (1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Busanjin (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Dongrae (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Steenwijk (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bihać (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Pyongyang (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Jinju (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Pyongyang (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Haengju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Geertruidenberg (1593) – Eighty Years' War
* Battle of Sisak, Siege of Sisak (1593) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Jinju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1593), Siege of Coevorden (1593–1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groningen (1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Enniskillen (1594) – Tyrone's Rebellion
* Siege of Morlaix (1594) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Fort Crozon (1594) – Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
* Siege of Huy (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Preston Somers Expedition, Siege of Caracas (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Takamatsu (1582)
* Siege of Takatō (1582)
* Siege of Uozu (1582)
* Siege of Lochem (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lier (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eindhoven (1583) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Godesberg (1583)
* Siege of Kaganoi (1584)
* Siege of Takehana (1584)
* Siege of Kanie (1584)
* Siege of Suemori (1584)
* Siege of Ypres (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ghent (1583–1584), Siege of Ghent (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bruges (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Brussels (1584–85) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Toyama (1585)
* Siege of Negoro-ji (1585)
* Siege of Ōta Castle (1585)
* Siege of IJsseloord (1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Iwaya Castle (1586)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias (1586), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1586) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Grave (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Venlo (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Axel, Siege of Axel (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Destruction of Neuss, Second siege of Neuss (July 1586)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1586–1590) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ganjaku (1587)
* Siege of Akizuki (1587)
* Siege of Kagoshima (1587)
* Siege of Sluis (1587) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Johor (1587)
* Siege of Kraków (1587) – War of the Polish Succession (1587–88)
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1588) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kurokawa Castle (1589)
* Siege of Hachigata (1590)
* Siege of Paris (1590) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Odawara (1590), Siege of Odawara Castle (1590)
* Siege of Shimoda (1590)
* Siege of Oshi (1590)
* Siege of Zutphen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Deventer (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Knodsenburg (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Hulst (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nijmegen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Rouen (1591), Siege of Rouen (1591–1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Caudebec (1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Busanjin (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Dongrae (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Steenwijk (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bihać (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Pyongyang (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Jinju (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Pyongyang (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Haengju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Geertruidenberg (1593) – Eighty Years' War
* Battle of Sisak, Siege of Sisak (1593) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Jinju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1593), Siege of Coevorden (1593–1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groningen (1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Enniskillen (1594) – Tyrone's Rebellion
* Siege of Morlaix (1594) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Fort Crozon (1594) – Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
* Siege of Huy (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Preston Somers Expedition, Siege of Caracas (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
 * Siege of Le Catelet (1595) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Groenlo (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Doullens – French Wars of Religion
* Battle of San Juan (1595), Siege of San Juan (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Calais (1596) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Hulst (1596) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eger (1596) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Amiens (1597) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Rheinberg (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Meurs (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1597) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Namwon (1597) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Bredevoort (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Le Catelet (1595) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Groenlo (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Doullens – French Wars of Religion
* Battle of San Juan (1595), Siege of San Juan (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Calais (1596) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Hulst (1596) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eger (1596) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Amiens (1597) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Rheinberg (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Meurs (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1597) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Namwon (1597) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Bredevoort (1597) – Eighty Years' War
 * Capture of Enschede (1597), Siege of Enschede (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Ootmarsum, Siege of Ootmarsum (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lingen (1597) – Eighty Years' War
*:hu:Buda ostroma (1598), Siege of Buda (1598)
* Siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Second siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Suncheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Battle of Sacheon (1598), Siege of Sacheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Schenckenschans (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zaltbommel (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Cahir Castle (1599) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Rees (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Enschede (1597), Siege of Enschede (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Ootmarsum, Siege of Ootmarsum (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lingen (1597) – Eighty Years' War
*:hu:Buda ostroma (1598), Siege of Buda (1598)
* Siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Second siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Suncheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Battle of Sacheon (1598), Siege of Sacheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Schenckenschans (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zaltbommel (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Cahir Castle (1599) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Rees (1599) – Eighty Years' War
 * Siege of Tanabe (1600)
* Siege of Udo (1600)
* Siege of Yanagawa (1600)
* Siege of Pernau (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dorpat (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ostend (1601–04) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nagykanizsa (1601) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Donegal (1601) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Kinsale (1601–02) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Wolmar (1601) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Fellin (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dunboy (1602) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Grave (1602) – Eighty Years' War
* :hu:Buda ostroma (1602), Siege of Buda (1602–1603) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Sluis (1604) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1604) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Kromy (1605) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18)
* Siege of Lingen (1605) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kandahar (1605–06)
* Siege of Tanabe (1600)
* Siege of Udo (1600)
* Siege of Yanagawa (1600)
* Siege of Pernau (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dorpat (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ostend (1601–04) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nagykanizsa (1601) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Donegal (1601) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Kinsale (1601–02) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Wolmar (1601) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Fellin (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dunboy (1602) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Grave (1602) – Eighty Years' War
* :hu:Buda ostroma (1602), Siege of Buda (1602–1603) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Sluis (1604) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1604) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Kromy (1605) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18)
* Siege of Lingen (1605) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kandahar (1605–06)
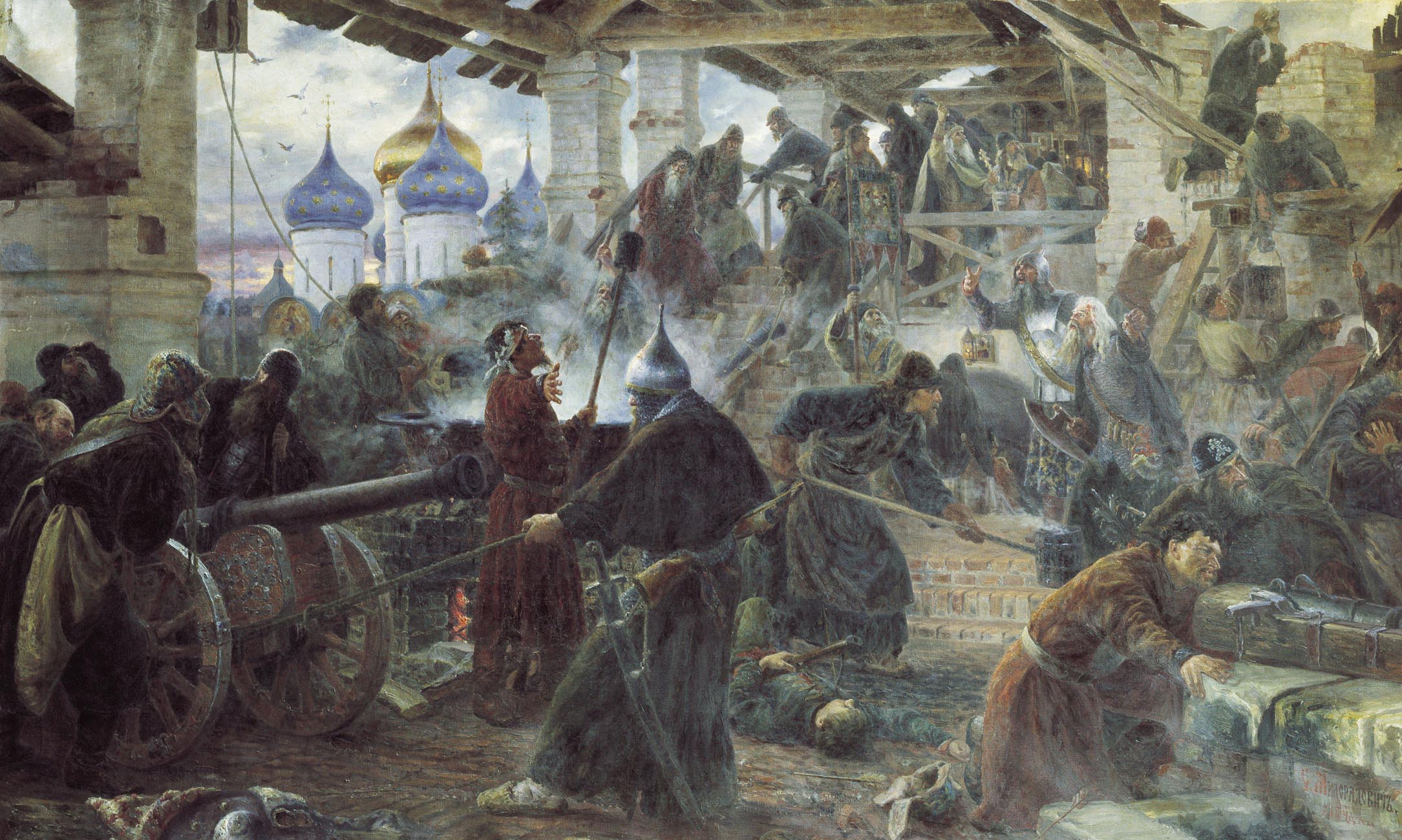 * Siege of Malacca (1606) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Ganja (1606) – Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–18)
* Siege of Groenlo (1606) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Tory Island (1608) – O'Doherty's rebellion
* Siege of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra (1608–10) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1608) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Pärnu (1609) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Smolensk (1609–11) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Kalmar (1611) – Kalmar War
* Storming of Kristianopel (1611) – Kalmar War
* Battle of Moscow (1612), Siege of Moscow (1612) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Smolensk (1613–17) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Malacca (1606) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Ganja (1606) – Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–18)
* Siege of Groenlo (1606) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Tory Island (1608) – O'Doherty's rebellion
* Siege of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra (1608–10) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1608) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Pärnu (1609) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Smolensk (1609–11) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Kalmar (1611) – Kalmar War
* Storming of Kristianopel (1611) – Kalmar War
* Battle of Moscow (1612), Siege of Moscow (1612) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Smolensk (1613–17) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
 * Siege of Tikhvin (1613) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Gdov (1614) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Aachen (1614) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Osaka (1614–15)
* Siege of Pskov (1615) – Ingrian War
* Uskok War#First Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1616) – Uskok War
* Uskok War#Second Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1617) – Uskok War
* Siege of Pilsen (1618) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Moscow (1618) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Budweis (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Kassa (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Battle of Humenné#Prelude, Siege of Vienna (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Bad Kreuznach (1620) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Neuhäusel (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Blockade of La Rochelle (1621–22) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Montauban (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Pressburg (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#First phase (1621–22), Siege of Riga (1621) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Siege of Jülich (1621–22) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Frankenthal (1621–1623) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Ormuz (1622), Siege of Ormuz (1622)
* Siege of Royan (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Nègrepelisse (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Tikhvin (1613) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Gdov (1614) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Aachen (1614) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Osaka (1614–15)
* Siege of Pskov (1615) – Ingrian War
* Uskok War#First Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1616) – Uskok War
* Uskok War#Second Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1617) – Uskok War
* Siege of Pilsen (1618) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Moscow (1618) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Budweis (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Kassa (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Battle of Humenné#Prelude, Siege of Vienna (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Bad Kreuznach (1620) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Neuhäusel (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Blockade of La Rochelle (1621–22) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Montauban (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Pressburg (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#First phase (1621–22), Siege of Riga (1621) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Siege of Jülich (1621–22) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Frankenthal (1621–1623) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Ormuz (1622), Siege of Ormuz (1622)
* Siege of Royan (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Nègrepelisse (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
 * Siege of Montpellier (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Bergen-op-Zoom (1622) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1622) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Mannheim (1622) – Thirty Years' War
*:es:Castillo de Araya, Siege of Araya Castle (1622–1623) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1624), Siege of Breda (1624–1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Gavi (1625)
* Relief of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1625)
* Recapture of Bahia (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Verrua (1625)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Koknese (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Dorpat (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Battle of San Juan (1625), Siege of San Juan (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1625)
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1626) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Montpellier (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Bergen-op-Zoom (1622) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1622) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Mannheim (1622) – Thirty Years' War
*:es:Castillo de Araya, Siege of Araya Castle (1622–1623) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1624), Siege of Breda (1624–1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Gavi (1625)
* Relief of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1625)
* Recapture of Bahia (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Verrua (1625)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Koknese (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Dorpat (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Battle of San Juan (1625), Siege of San Juan (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1625)
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1626) – Eighty Years' War
 * Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627) – Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nienburg (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1627) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Stralsund (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Glückstadt (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Batavia (1628–29)
* Siege of Mantua (1629–30)
* Siege of Casale Monferrato (1629–31)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1629) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Privas (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Alès (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Sack of Magdeburg (1631) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Maastricht, Siege of Maastricht (1632) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nuremberg (1632) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627) – Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nienburg (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1627) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Stralsund (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Glückstadt (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Batavia (1628–29)
* Siege of Mantua (1629–30)
* Siege of Casale Monferrato (1629–31)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1629) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Privas (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Alès (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Sack of Magdeburg (1631) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Maastricht, Siege of Maastricht (1632) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nuremberg (1632) – Thirty Years' War
 * Siege of Dorogobuzh (1632) – Smolensk War
* Siege of Smolensk (1632–33) – Smolensk War
* Battle of Oldendorf#Prelude, Siege of Hameln (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hagenau (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Konstanz (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Rheinfelden (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Belaya (1634)
* Siege of Überlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lüshun (1634)
* Siege of Hildesheim (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nördlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Minden (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leuven (1635) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Schenkenschans (1635–1636) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mainz (1635) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dôle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of La Capelle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Le Câtelet (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1636) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Corbie (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Leipzig (1637) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Landrecies (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Venlo (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leucate (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hara Castle (1637–1638)
* Siege of Azov (1637–1642) – Part of Russo-Turkish Wars
* Siege of Saint-Omer (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Fuenterrabía (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Battle of Breisach (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lemgo (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Baghdad (1638), Siege of Baghdad (1638) by Ottomans
* Siege of Hesdin (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Relief of Thionville (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Salses (1639–1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Casale (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Galle (1640) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Turin (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Arras (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Neunburg (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of São Filipe (1641–1642) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Siege of Dorsten (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Göttingen (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Perpignan (1642), Siege of Perpignan (1641–1642) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Olmütz (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Brieg (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leipzig (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hull (1642) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Portsmouth (1642) – First English Civil War
* Second siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Sieges of Bradford (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Reading (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Chichester (1642) – First English Civil War
* Battle of Rocroi#Prelude, Siege of Rocroi (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Thionville (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Worcester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lichfield (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Gloucester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sierck (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hull (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Newcastle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lathom House (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Überlingen (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lyme Regis (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of York (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lincoln (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lleida (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
*Siege of Gravelines (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Oxford (1644–1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sas van Gent (1644) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Relief of Montgomery Castle, Siege of Montgomery Castle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Sieges of Taunton (1644–1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Duncannon (1645) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Chester (1645) – First English Civil War
* Great Siege of Scarborough Castle (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Carlisle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Brünn (1645) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Mardyck (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Bristol (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Béthune (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Lillers (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Saint-Venant (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hulst (1645) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Worcester (1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Mardyck (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dunkirk (1646) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Augsburg (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lindau (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Armentières (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Landrecies (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Ypres (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Memmingen (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Candia (Crete) (1648–69) – claimed as the second-longest siege in history
* Siege of Pembroke (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Siege of Colchester (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Battle of Prague (1648), Siege of Prague (1648) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Inverness (1649)
* Siege of Zbarazh (1649) – Khmelnytsky uprising
* Siege of Dublin (1649)
* Siege of Drogheda (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Wexford (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Waterford (1649–1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Inverness (1650)
* Siege of Kilkenny (1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Clonmel (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Charlemont (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Limerick (1650–51), Cromwell's Siege of Limerick City, Ireland (1651) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Barcelona (1651), Siege of Barcelona (1651–1652), during the Reapers' War, Catalan Revolt
* Siege of Galway (1651–1652) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Battle of Arras (1654), Siege of Arras (1654) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Smolensk (1654) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Landrecies (1655) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1655) – Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60)
* Siege of Kraków (1655) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Danzig (1655–60) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Jasna Góra (1655) – during Deluge (history), The Deluge
* Battle of Valenciennes (1656), Siege of Valenciennes (1656) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Zamość (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Warsaw (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Nöteborg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Nyenschantz (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dyneburg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Riga (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorpat (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorogobuzh (1632) – Smolensk War
* Siege of Smolensk (1632–33) – Smolensk War
* Battle of Oldendorf#Prelude, Siege of Hameln (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hagenau (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Konstanz (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Rheinfelden (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Belaya (1634)
* Siege of Überlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lüshun (1634)
* Siege of Hildesheim (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nördlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Minden (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leuven (1635) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Schenkenschans (1635–1636) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mainz (1635) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dôle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of La Capelle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Le Câtelet (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1636) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Corbie (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Leipzig (1637) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Landrecies (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Venlo (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leucate (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hara Castle (1637–1638)
* Siege of Azov (1637–1642) – Part of Russo-Turkish Wars
* Siege of Saint-Omer (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Fuenterrabía (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Battle of Breisach (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lemgo (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Baghdad (1638), Siege of Baghdad (1638) by Ottomans
* Siege of Hesdin (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Relief of Thionville (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Salses (1639–1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Casale (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Galle (1640) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Turin (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Arras (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Neunburg (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of São Filipe (1641–1642) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Siege of Dorsten (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Göttingen (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Perpignan (1642), Siege of Perpignan (1641–1642) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Olmütz (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Brieg (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leipzig (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hull (1642) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Portsmouth (1642) – First English Civil War
* Second siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Sieges of Bradford (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Reading (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Chichester (1642) – First English Civil War
* Battle of Rocroi#Prelude, Siege of Rocroi (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Thionville (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Worcester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lichfield (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Gloucester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sierck (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hull (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Newcastle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lathom House (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Überlingen (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lyme Regis (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of York (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lincoln (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lleida (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
*Siege of Gravelines (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Oxford (1644–1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sas van Gent (1644) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Relief of Montgomery Castle, Siege of Montgomery Castle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Sieges of Taunton (1644–1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Duncannon (1645) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Chester (1645) – First English Civil War
* Great Siege of Scarborough Castle (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Carlisle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Brünn (1645) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Mardyck (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Bristol (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Béthune (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Lillers (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Saint-Venant (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hulst (1645) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Worcester (1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Mardyck (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dunkirk (1646) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Augsburg (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lindau (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Armentières (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Landrecies (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Ypres (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Memmingen (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Candia (Crete) (1648–69) – claimed as the second-longest siege in history
* Siege of Pembroke (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Siege of Colchester (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Battle of Prague (1648), Siege of Prague (1648) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Inverness (1649)
* Siege of Zbarazh (1649) – Khmelnytsky uprising
* Siege of Dublin (1649)
* Siege of Drogheda (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Wexford (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Waterford (1649–1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Inverness (1650)
* Siege of Kilkenny (1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Clonmel (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Charlemont (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Limerick (1650–51), Cromwell's Siege of Limerick City, Ireland (1651) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Barcelona (1651), Siege of Barcelona (1651–1652), during the Reapers' War, Catalan Revolt
* Siege of Galway (1651–1652) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Battle of Arras (1654), Siege of Arras (1654) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Smolensk (1654) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Landrecies (1655) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1655) – Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60)
* Siege of Kraków (1655) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Danzig (1655–60) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Jasna Góra (1655) – during Deluge (history), The Deluge
* Battle of Valenciennes (1656), Siege of Valenciennes (1656) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Zamość (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Warsaw (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Nöteborg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Nyenschantz (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dyneburg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Riga (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorpat (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
 * Siege of Bidar (1657)
* Siege of Kraków (1657) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1657) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dunkirk (1658) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Toruń (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Badajoz (1658) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Assault on Copenhagen (1659), Siege of Copenhagen (1658–1659) Second Northern War, Swedes defeated by Danish and Dutch defenders
* Siege of Kolding (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Lyakhavichy (1660) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Fort Zeelandia (1661–1662) – Sino-Dutch conflicts
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1663) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Hlukhiv (1664) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Valência de Alcântara (1664)
* Siege of Novi Zrin (1664), Siege of Novi Zrin Castle (1664) in northern Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia – Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
* Siege of Léva (1664) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Purandhar (1665)
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Charleroi (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Tournai (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Douai (1667) – War of Devolution
* Siege of Lille (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Franche-Comté, Siege of Dole (1668) – War of Devolution
* Solovetsky Monastery uprising, Siege of Solovetsky Monastery (1668–76) – eight years
* Siege of Groenlo (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Groningen (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Kamenets (1672) – Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76)
* Siege of Bidar (1657)
* Siege of Kraków (1657) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1657) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dunkirk (1658) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Toruń (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Badajoz (1658) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Assault on Copenhagen (1659), Siege of Copenhagen (1658–1659) Second Northern War, Swedes defeated by Danish and Dutch defenders
* Siege of Kolding (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Lyakhavichy (1660) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Fort Zeelandia (1661–1662) – Sino-Dutch conflicts
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1663) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Hlukhiv (1664) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Valência de Alcântara (1664)
* Siege of Novi Zrin (1664), Siege of Novi Zrin Castle (1664) in northern Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia – Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
* Siege of Léva (1664) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Purandhar (1665)
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Charleroi (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Tournai (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Douai (1667) – War of Devolution
* Siege of Lille (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Franche-Comté, Siege of Dole (1668) – War of Devolution
* Solovetsky Monastery uprising, Siege of Solovetsky Monastery (1668–76) – eight years
* Siege of Groenlo (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Groningen (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Kamenets (1672) – Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76)
 * Siege of Maastricht (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Bonn (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Besançon (1674) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ponda (1675)
* Siege of Maastricht (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Valenciennes (1676–77) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Freiburg (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Cambrai (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Malmö (1677) – Scanian War
* Siege of Ghent (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ypres (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Puigcerdà (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Stralsund (1678) – Scanian War
* Battle of Vienna, Siege of Vienna (1683) – siege of Vienna during the Great Turkish War
* Siege of Luxembourg (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Bombardment of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Siege of Buda (1684), Austrian army tried to take Buda from Ottoman Turkey
* Siege of Santa Maura (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Bijapur (1685–86)
* Morean War#Coron and Mani (1685), Siege of Cojor (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Maastricht (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Bonn (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Besançon (1674) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ponda (1675)
* Siege of Maastricht (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Valenciennes (1676–77) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Freiburg (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Cambrai (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Malmö (1677) – Scanian War
* Siege of Ghent (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ypres (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Puigcerdà (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Stralsund (1678) – Scanian War
* Battle of Vienna, Siege of Vienna (1683) – siege of Vienna during the Great Turkish War
* Siege of Luxembourg (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Bombardment of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Siege of Buda (1684), Austrian army tried to take Buda from Ottoman Turkey
* Siege of Santa Maura (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Bijapur (1685–86)
* Morean War#Coron and Mani (1685), Siege of Cojor (1685) – Morean War
 * Siege of Érsekújvár (1685) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Kelefa (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Navarino (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Buda (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Modon (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Nauplia (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Pécs (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Golconda (1687)
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Castelnuovo (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1685) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Kelefa (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Navarino (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Buda (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Modon (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Nauplia (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Pécs (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Golconda (1687)
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Castelnuovo (1687) – Morean War
 * Morean War#Patras and the completion of the conquest (1687), Siege of Monemvasia (1687–1690) – Morean War
* Morean War#Occupation of Athens (1687–88), Siege of the Acropolis (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Bangkok (1688) – Siamese revolution of 1688
* Siege of Negroponte (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Belgrade (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Knin (1688) – Morean War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mannheim (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Frankenthal (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Derry (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Kaiserswerth (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mainz (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Larache (1689)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Carrickfergus (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Bonn (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Gingee (1689–1698)
* First siege of Athlone (1690), Williamite War in Ireland
* Morean War#Capture of Valona and Kanina (1690), Siege of Kanina (1690) – Morean War
* Siege of Belgrade (1690), Siege of Niš (1690) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Patras and the completion of the conquest (1687), Siege of Monemvasia (1687–1690) – Morean War
* Morean War#Occupation of Athens (1687–88), Siege of the Acropolis (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Bangkok (1688) – Siamese revolution of 1688
* Siege of Negroponte (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Belgrade (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Knin (1688) – Morean War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mannheim (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Frankenthal (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Derry (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Kaiserswerth (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mainz (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Larache (1689)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Carrickfergus (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Bonn (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Gingee (1689–1698)
* First siege of Athlone (1690), Williamite War in Ireland
* Morean War#Capture of Valona and Kanina (1690), Siege of Kanina (1690) – Morean War
* Siege of Belgrade (1690), Siege of Niš (1690) – Great Turkish War
 * Siege of Cork (1690) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Belgrade (1690) – Great Turkish War
* Battle of Quebec (1690), Siege of Québec City (1690) – First siege of Québec City
* Siege of Jinji (1690–1698)
* Siege of Limerick (1691), Williamite War in Ireland
* Second siege of Athlone (1691), Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Mons (1691) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cuneo (1691) – Nine Years' War
* Morean War#Attack on Candia (1692), Siege of Candia (1692) – Morean War
* Siege of Namur (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Embrun (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Ebernburg (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Belgrade (1693) – Great Turkish War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Huy (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Charleroi (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Pinerolo (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Morean War#Final years of the war, Siege of Chios (1694) – Morean War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Palamos (1694) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Gerona (1694) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Huy (1694) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cork (1690) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Belgrade (1690) – Great Turkish War
* Battle of Quebec (1690), Siege of Québec City (1690) – First siege of Québec City
* Siege of Jinji (1690–1698)
* Siege of Limerick (1691), Williamite War in Ireland
* Second siege of Athlone (1691), Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Mons (1691) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cuneo (1691) – Nine Years' War
* Morean War#Attack on Candia (1692), Siege of Candia (1692) – Morean War
* Siege of Namur (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Embrun (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Ebernburg (1692) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Belgrade (1693) – Great Turkish War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Huy (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Charleroi (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Heavy fighting: 1692–93, Siege of Pinerolo (1693) – Nine Years' War
* Morean War#Final years of the war, Siege of Chios (1694) – Morean War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Palamos (1694) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Gerona (1694) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Huy (1694) – Nine Years' War
 * Siege of Ceuta (1694–1727) – claimed as the longest siege in history
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Casale (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Capitulation of Diksmuide (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Jesus (1696–1698)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Nashwaak (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Ath (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Barcelona (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Road to Ryswick: 1696–97, Siege of Ebernburg (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1697)
* Siege of Ceuta (1694–1727) – claimed as the longest siege in history
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Casale (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Capitulation of Diksmuide (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Jesus (1696–1698)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Nashwaak (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Ath (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Barcelona (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Road to Ryswick: 1696–97, Siege of Ebernburg (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1697)
 * Siege of Tönning (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Riga (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Narva (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Kaiserswerth (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Donas (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castiglione (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Borgoforte (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guastalla (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venlo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stevensweert (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Roermond (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Nöteborg (1702) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Liége (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Rheinberg (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of St. Augustine (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Andernach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Governolo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Riga (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Narva (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Kaiserswerth (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Donas (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castiglione (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Borgoforte (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guastalla (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venlo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stevensweert (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Roermond (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Nöteborg (1702) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Liége (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Rheinberg (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of St. Augustine (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Andernach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Governolo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Siege of Neubourg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kehl (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bonn (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Thorn (1703) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Nago (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Arco (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Breisach (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Huy (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Limburg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Augsburg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guadeloupe (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castello de Vide (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Wagingera (1704)
* Landing at Barcelona (1704), Siege of Barcelona (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Portalegre (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Vercelli (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Neubourg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kehl (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bonn (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Thorn (1703) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Nago (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Arco (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Breisach (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Huy (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Limburg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Augsburg (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guadeloupe (1703) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castello de Vide (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Wagingera (1704)
* Landing at Barcelona (1704), Siege of Barcelona (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Portalegre (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Vercelli (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Siege of Rain (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Narva (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Villingen (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fort Isabella (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Capture of Gibraltar, Siege of Gibraltar (1704) – eleventh siege of
* Siege of Rain (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Narva (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Villingen (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fort Isabella (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Capture of Gibraltar, Siege of Gibraltar (1704) – eleventh siege of  * Siege of San Mateo (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alcantara (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hagenau (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Turin (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oostende (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Menin (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Dendermonde (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ath (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pavia (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cuenca (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pizzigetone (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Elche (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cartagena (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Casale (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Milan (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Villena (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Xàtiva (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Toulon (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pensacola (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of San Mateo (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alcantara (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hagenau (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Turin (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oostende (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Menin (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Dendermonde (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ath (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pavia (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cuenca (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pizzigetone (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Elche (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cartagena (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Casale (1706) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Milan (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Villena (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Xàtiva (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Toulon (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Pensacola (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Siege of Susa (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lérida (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Morella (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oran (1707–1708) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Tortosa (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Exilles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lille (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fenestrelles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of San Felipe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Leffinghe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Denia (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Ghislain (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Brussels (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1708–09) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ghent (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Veprik (1709) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Tournai (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Mons (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Viborg (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Reval (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Douai (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Béthune (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Aire (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Venant (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1710–1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kassa (1711) – Rákóczi's War of Independence
* Siege of Aren fort (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venasque (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stralsund (1711–15) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Castel-Leon (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cardona (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landrecies (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Marchiennes (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Douai (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lérida (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Morella (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oran (1707–1708) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Tortosa (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Exilles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lille (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fenestrelles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of San Felipe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Leffinghe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Denia (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Ghislain (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Brussels (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1708–09) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ghent (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Veprik (1709) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Tournai (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Mons (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Viborg (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Reval (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Douai (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Béthune (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Aire (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Venant (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1710–1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kassa (1711) – Rákóczi's War of Independence
* Siege of Aren fort (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venasque (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stralsund (1711–15) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Castel-Leon (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cardona (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landrecies (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Marchiennes (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Douai (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Second siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1712–1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning#1713–1714, Siege of Tönning (1713–1714) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Landau (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1713–14), Siege of Barcelona (1713–14) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gurdaspur (1715)
* Siege of Brahan (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Siege of Inverness (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Second siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1712–1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning#1713–1714, Siege of Tönning (1713–1714) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Landau (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1713–14), Siege of Barcelona (1713–14) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gurdaspur (1715)
* Siege of Brahan (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Siege of Inverness (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
 * Siege of Temeşvar (1716) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Belgrade (1717) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Fredriksten (1718) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Isfahan (1722)
* Thirteenth Siege of Gibraltar (1727) – by a Spanish army
* Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), Siege of Oran (1732) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Kehl (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Pizzighettone (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Danzig (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Capua (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Philippsburg (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Messina (1734–1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Ganja (1734), Siege of Ganja (1734–1735) – Ottoman–Persian War (1730–35)
* Siege of Syracuse (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trapani (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Perekop (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Azov (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Banja Luka (1737) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Ochakov (1737) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Kandahar (1737–1738)
* Siege of Mehadia (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Orsova (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Temeşvar (1716) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Belgrade (1717) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Fredriksten (1718) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Isfahan (1722)
* Thirteenth Siege of Gibraltar (1727) – by a Spanish army
* Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), Siege of Oran (1732) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Kehl (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Pizzighettone (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Danzig (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Capua (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Philippsburg (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Messina (1734–1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Ganja (1734), Siege of Ganja (1734–1735) – Ottoman–Persian War (1730–35)
* Siege of Syracuse (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trapani (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Perekop (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Azov (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Banja Luka (1737) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Ochakov (1737) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Kandahar (1737–1738)
* Siege of Mehadia (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Orsova (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
 * Capture of Belgrade (1739), Siege of Belgrade (1739) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Battle of Portobello, Siege of Portobello (1739) – victory of British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of St. Augustine (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Fort Mose (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1741)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1741) – failed British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Brieg (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Invasion of Cuba (1741), Siege of Santiago (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Neisse (1741)
* Siege of Glatz (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mirandola (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Modena (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Prague (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of La Guaira, Siege of La Guaira (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Puerto Cabello, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Blockade of Straubing (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1743)
* Siege of Ingolstadt (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mosul (1743) – Ottoman–Persian War (1743–46)
* Siege of Menin (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ypres (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Furnes (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Prague (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuneo (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tabor (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tournai (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Louisbourg (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Port Toulouse (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Fall of Ghent (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Oudenarde (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ostend (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tortona (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Kosel (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Culloden House (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (November 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Stirling Castle (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Brussels (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Inverness (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (March 1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Blair Castle (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort William (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Genoa (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mons (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Capture of Belgrade (1739), Siege of Belgrade (1739) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Battle of Portobello, Siege of Portobello (1739) – victory of British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of St. Augustine (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Fort Mose (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1741)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1741) – failed British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Brieg (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Invasion of Cuba (1741), Siege of Santiago (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Neisse (1741)
* Siege of Glatz (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mirandola (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Modena (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Prague (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of La Guaira, Siege of La Guaira (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Puerto Cabello, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Blockade of Straubing (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1743)
* Siege of Ingolstadt (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mosul (1743) – Ottoman–Persian War (1743–46)
* Siege of Menin (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ypres (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Furnes (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Prague (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuneo (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tabor (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tournai (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Louisbourg (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Port Toulouse (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Fall of Ghent (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Oudenarde (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ostend (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tortona (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Kosel (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Culloden House (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (November 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Stirling Castle (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Brussels (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Inverness (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (March 1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Blair Castle (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort William (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Genoa (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mons (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
 * Siege of Namur (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Madras, Siege of Madras (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Genoa (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Maastricht (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuddalore (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Pondicherry (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Arcot (1751) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1751–52) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Fort St Philip (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pirna (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Prague (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort William Henry (1757) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Madras, Siege of Madras (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Genoa (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Maastricht (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuddalore (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Pondicherry (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Arcot (1751) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1751–52) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Fort St Philip (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pirna (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Prague (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort William Henry (1757) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1757) – Seven Years' War
 * Blockade of Liegnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Blockade of Stralsund (1757–1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Küstrin (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Louisbourg (1758) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Olomouc, Siege of Olmütz (1758) – by the Prussian army of Frederick the Great during the Seven Years' War
* Siege of Neisse (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Madras (1758–1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Masulipatam (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Battle of the Plains of Abraham, Siege of Québec (1759) – Second siege of Québec City, Québec, during the Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Second siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort Loudoun (1760) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Glatz (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Dresden (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Wittenberg (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1760), Siege of Pondicherry (1760–1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Kolberg (Seven Years' War), Sieges of Kolberg (1759, 1760, and 1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Havana (1762) – Seven Years' War. British fleet headed by George Keppel, 3rd Earl of Albemarle lays siege to Spanish controlled Havana for a month.
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Almeida (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ambur (1767) – First Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Khotyn (1769) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Bender (1770) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Giurgevo (1771) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Silistria (1773) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Melilla (1774), during Hispano-Moroccan wars
* Siege of Boston (1775–1776) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort St. Jean (1775) – American Revolutionary War
* Blockade of Liegnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Blockade of Stralsund (1757–1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Küstrin (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Louisbourg (1758) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Olomouc, Siege of Olmütz (1758) – by the Prussian army of Frederick the Great during the Seven Years' War
* Siege of Neisse (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Madras (1758–1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Masulipatam (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Battle of the Plains of Abraham, Siege of Québec (1759) – Second siege of Québec City, Québec, during the Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Second siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort Loudoun (1760) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Glatz (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Dresden (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Wittenberg (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1760), Siege of Pondicherry (1760–1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Kolberg (Seven Years' War), Sieges of Kolberg (1759, 1760, and 1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Havana (1762) – Seven Years' War. British fleet headed by George Keppel, 3rd Earl of Albemarle lays siege to Spanish controlled Havana for a month.
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Almeida (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ambur (1767) – First Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Khotyn (1769) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Bender (1770) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Giurgevo (1771) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Silistria (1773) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Melilla (1774), during Hispano-Moroccan wars
* Siege of Boston (1775–1776) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort St. Jean (1775) – American Revolutionary War
 * Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Stanwix (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Henry (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Mifflin (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1778) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Vincennes (1779) – American Revolutionary War
* Great Siege of Gibraltar (1779–83) – fourteenth siege of
* Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Stanwix (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Henry (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Mifflin (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1778) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Vincennes (1779) – American Revolutionary War
* Great Siege of Gibraltar (1779–83) – fourteenth siege of  * Siege of Pensacola (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Watson (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Motte (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Augusta (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Ninety-Six (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Yorktown (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Negapatam (1781) – Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
* Siege of Brimstone Hill (1782) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Henry (1782) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Cuddalore (1783) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mangalore (1783–1784) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Nargund (1785) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Badami (1786) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Bahadur Benda (1787) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Ochakov (1788) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Khotin (1788) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Pensacola (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Watson (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Motte (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Augusta (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Ninety-Six (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Yorktown (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Negapatam (1781) – Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
* Siege of Brimstone Hill (1782) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Henry (1782) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Cuddalore (1783) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mangalore (1783–1784) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Nargund (1785) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Badami (1786) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Bahadur Benda (1787) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Ochakov (1788) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Khotin (1788) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
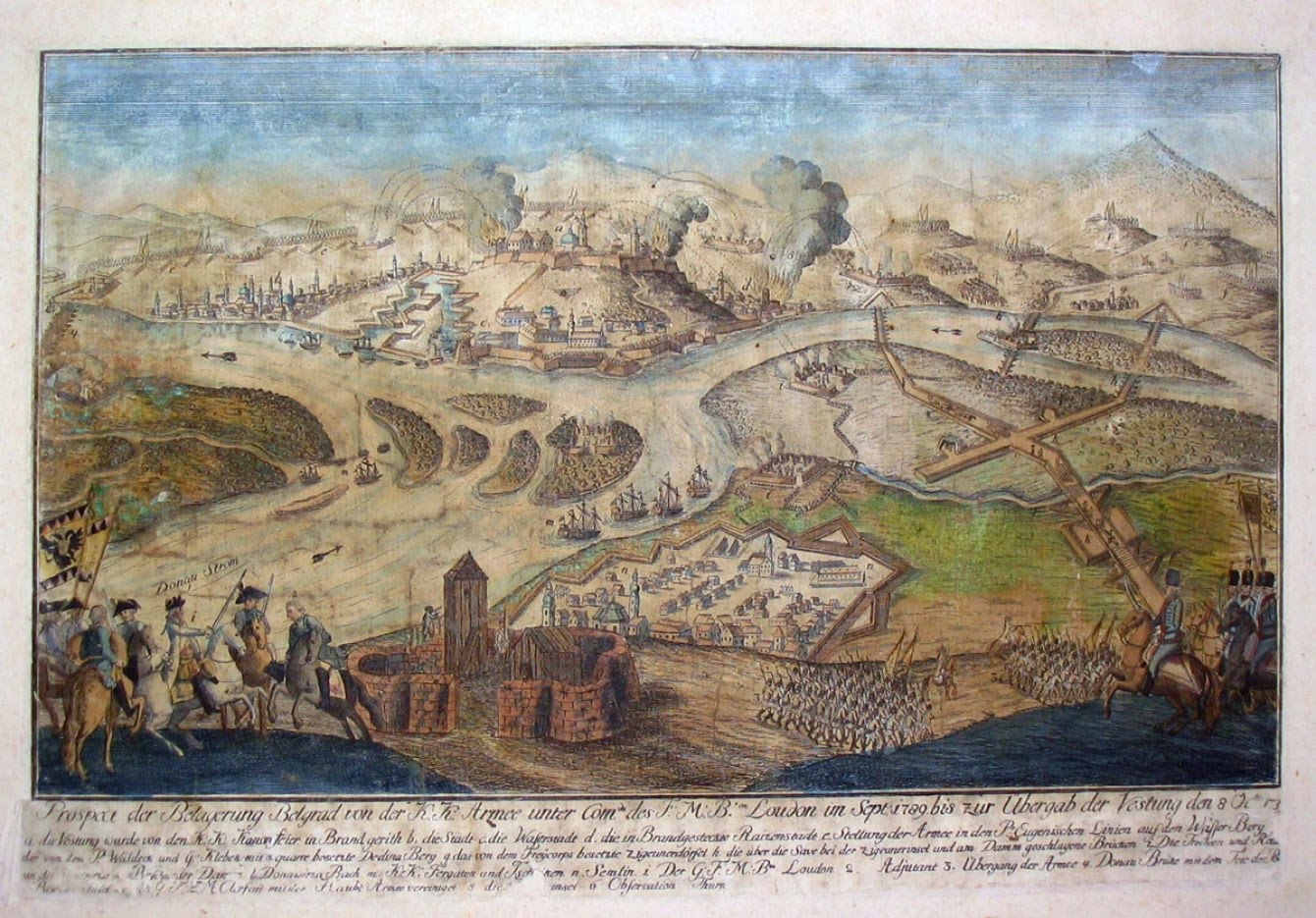 * Siege of Belgrade (1789) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Izmail (1789–1790) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Oran (1790–1792) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Darwar (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Koppal (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Bangalore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Coimbatore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Goorumconda (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Belgrade (1789) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Izmail (1789–1790) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Oran (1790–1792) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Darwar (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Koppal (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Bangalore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Coimbatore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Goorumconda (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
 * Siege of Nundydroog (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Savendroog (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Seringapatam (1792) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Thionville (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Battle of Verdun (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Lille (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Battle of Limburg (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Maastricht (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Condé (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Bellegarde (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Valenciennes (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Pondicherry (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Lyon (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Landau (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Dunkirk (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Toulon (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Maubeuge (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Fort-Louis (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Angers (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of San Fiorenzo (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Bastia (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Landrecies (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Collioure (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Ypres (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Calvi (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Luxembourg (1794–95) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Roses (1794–95) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Nundydroog (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Savendroog (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Seringapatam (1792) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Thionville (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Battle of Verdun (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Lille (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Battle of Limburg (1792) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Maastricht (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Condé (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Bellegarde (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Valenciennes (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Pondicherry (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Lyon (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Landau (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Dunkirk (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Toulon (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Maubeuge (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Fort-Louis (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Angers (1793) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of San Fiorenzo (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Bastia (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Landrecies (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Collioure (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Ypres (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Calvi (1794) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Luxembourg (1794–95) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Roses (1794–95) – War of the First Coalition
 * Siege of Mannheim (1795) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mantua (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition, French besieging
* Siege of Kehl (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Hüningen (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Invasion of Trinidad (1797), Siege of Port of Spain (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Battle of San Juan (1797), Siege of San Juan de Puerto Rico (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Siege of Malta (1798–1800), Siege of Malta (1798–1800), during the French Revolutionary Wars
* Siege of Corfu (1798–99) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of El Arish (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Jaffa (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Acre (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Mantua (1799) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of Seringapatam (1799) – Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mannheim (1795) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mantua (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition, French besieging
* Siege of Kehl (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Hüningen (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Invasion of Trinidad (1797), Siege of Port of Spain (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Battle of San Juan (1797), Siege of San Juan de Puerto Rico (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Siege of Malta (1798–1800), Siege of Malta (1798–1800), during the French Revolutionary Wars
* Siege of Corfu (1798–99) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of El Arish (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Jaffa (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Acre (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Mantua (1799) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of Seringapatam (1799) – Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
 * Siege of Bharatpur (1805) – Second Anglo-Maratha War
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1805)
* Siege of Gaeta (1806) – Invasion of Naples (1806)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1806) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Belgrade (1806) – First Serbian uprising
* Siege of Hameln (1806) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Stralsund (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Montevideo (1807) – during the British invasions of the River Plate
* Siege of Kolberg (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Danzig (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition, French siege of Prussians and Russians
* British invasions of the River Plate#2nd Battle of Buenos Aires, Siege of Buenos Aires (1807) – during the British invasions of the River Plate
* Battle of Copenhagen (1807) – Bombarded by British fleet and by ground forces commanded by Arthur Wellesley
* Siege of Bharatpur (1805) – Second Anglo-Maratha War
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1805)
* Siege of Gaeta (1806) – Invasion of Naples (1806)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1806) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Belgrade (1806) – First Serbian uprising
* Siege of Hameln (1806) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Stralsund (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Montevideo (1807) – during the British invasions of the River Plate
* Siege of Kolberg (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition
* Siege of Danzig (1807) – War of the Fourth Coalition, French siege of Prussians and Russians
* British invasions of the River Plate#2nd Battle of Buenos Aires, Siege of Buenos Aires (1807) – during the British invasions of the River Plate
* Battle of Copenhagen (1807) – Bombarded by British fleet and by ground forces commanded by Arthur Wellesley
 * Siege of Sveaborg (1808) – Finnish War
* Siege of Erivan (1808) – Russo-Persian War (1804–13)
* First siege of Zaragoza (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Barcelona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Battle of Valencia (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Gerona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Roses (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Zaragoza (1808–1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chaves (1809) – Peninsular War
* Third siege of Girona (1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Cádiz (1810–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Santa Maura (1810) – Adriatic campaign
* Siege of Astorga (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Lérida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810), First siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810) – Peninsular War by the French Marshal Michel Ney
* Siege of Mequinenza (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Almeida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tortosa (1810–11) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Olivenza (1811) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Figueras (1811) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tarragona (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Campaña de Valencia, es) (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Montevideo (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tarifa (1812), Siege of Tarifa (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (1812), Siege of Valencia (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Montevideo (1812–14) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812), Second siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812) – Peninsular War by Arthur Wellesley
* Siege of Cuautla (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Badajoz (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Huajuapan de León (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of the Salamanca Forts (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Astorga (1812) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1812), es) (1812) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Sveaborg (1808) – Finnish War
* Siege of Erivan (1808) – Russo-Persian War (1804–13)
* First siege of Zaragoza (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Barcelona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Battle of Valencia (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Gerona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Roses (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Zaragoza (1808–1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chaves (1809) – Peninsular War
* Third siege of Girona (1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Cádiz (1810–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Santa Maura (1810) – Adriatic campaign
* Siege of Astorga (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Lérida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810), First siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810) – Peninsular War by the French Marshal Michel Ney
* Siege of Mequinenza (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Almeida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tortosa (1810–11) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Olivenza (1811) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Figueras (1811) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tarragona (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Campaña de Valencia, es) (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Montevideo (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tarifa (1812), Siege of Tarifa (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (1812), Siege of Valencia (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Montevideo (1812–14) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812), Second siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812) – Peninsular War by Arthur Wellesley
* Siege of Cuautla (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Badajoz (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Huajuapan de León (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of the Salamanca Forts (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Astorga (1812) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1812), es) (1812) – Spanish American wars of independence
 * Siege of Riga (1812) – French invasion of Russia
* Siege of Fort Mackinac (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Detroit (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Harrison (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Wayne (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Burgos (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Danzig (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Acapulco (1813) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Fort Meigs (1813) – failed British siege of American garrison during the War of 1812
* Siege of Tarragona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Pamplona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of San Sebastián (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chillán (1813) – Chilean War of Independence
* Second siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1813), es) (1813) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cattaro (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1814), Siege of Mainz (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Zara (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Maturin (:es:Batalla de Maturin, es) (1813–1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Hamburg (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Metz (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Third siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1814), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Ragusa (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* First siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Segundo Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Prairie du Chien (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Erie (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Aragua de Barcelona (:es: Batalla de Aragua de Barcelona, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Santa Fe de Bogotá (:es:Asedio de Santafé de Bogotá, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Fort St. Philip (1815) – War of 1812
* Siege of Ancona (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Gaeta (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1815), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias, es) (1815) – List of wars 1800–99, Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Angostura (:es:Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Angostura (:es:Segunda Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1820-21), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias (1820–1821), es) (1820–21) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of El Callao (:es:Primer sitio del Callao, es) (1821) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tripolitsa (1821) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1821–22) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Fourth siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1822), es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pasto (:es: Batalla de Bombona, es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* San Felipe Castle, Fifth Siege of Puerto Cabello (1823) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pamplona (1823) – Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, 1823 French invasion of Spain
* Siege of Messolonghi (1825), First, second, and third sieges of Missolonghi (1822, 1823, 1825–1826)
* Second siege of El Callao (:es:Segundo sitio del Callao, es) (1824–1826) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1826–27) – by the Ottomans against the Greeks, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1832) – conducted by French forces against a Dutch garrison after the Ten Days' Campaign.
* Siege of Jerusalem (1834) Peasants' Revolt of 1834 (Palestine)
* Siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1835), es) (1835) – Reforms Revolution (Venezuela)
* Battle of the Alamo, Siege of the Alamo (1836) – Texas Revolution
* Siege of Herat (1838), Siege of Herat (1837–38)
* Third siege of El Callao (:es:Tercer sitio del Callao, es) (1838)
* Siege of Akhoulgo (1839)
* Great Siege of Montevideo (1843–1851)
* Siege of Fort Texas (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Riga (1812) – French invasion of Russia
* Siege of Fort Mackinac (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Detroit (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Harrison (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Wayne (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Burgos (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Danzig (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Acapulco (1813) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Fort Meigs (1813) – failed British siege of American garrison during the War of 1812
* Siege of Tarragona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Pamplona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of San Sebastián (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chillán (1813) – Chilean War of Independence
* Second siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1813), es) (1813) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cattaro (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1814), Siege of Mainz (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Zara (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Maturin (:es:Batalla de Maturin, es) (1813–1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Hamburg (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Metz (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Third siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1814), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Ragusa (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* First siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Segundo Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Prairie du Chien (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Erie (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Aragua de Barcelona (:es: Batalla de Aragua de Barcelona, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Santa Fe de Bogotá (:es:Asedio de Santafé de Bogotá, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Fort St. Philip (1815) – War of 1812
* Siege of Ancona (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Gaeta (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1815), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias, es) (1815) – List of wars 1800–99, Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Angostura (:es:Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Angostura (:es:Segunda Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1820-21), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias (1820–1821), es) (1820–21) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of El Callao (:es:Primer sitio del Callao, es) (1821) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tripolitsa (1821) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1821–22) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Fourth siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1822), es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pasto (:es: Batalla de Bombona, es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* San Felipe Castle, Fifth Siege of Puerto Cabello (1823) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pamplona (1823) – Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, 1823 French invasion of Spain
* Siege of Messolonghi (1825), First, second, and third sieges of Missolonghi (1822, 1823, 1825–1826)
* Second siege of El Callao (:es:Segundo sitio del Callao, es) (1824–1826) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1826–27) – by the Ottomans against the Greeks, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1832) – conducted by French forces against a Dutch garrison after the Ten Days' Campaign.
* Siege of Jerusalem (1834) Peasants' Revolt of 1834 (Palestine)
* Siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1835), es) (1835) – Reforms Revolution (Venezuela)
* Battle of the Alamo, Siege of the Alamo (1836) – Texas Revolution
* Siege of Herat (1838), Siege of Herat (1837–38)
* Third siege of El Callao (:es:Tercer sitio del Callao, es) (1838)
* Siege of Akhoulgo (1839)
* Great Siege of Montevideo (1843–1851)
* Siege of Fort Texas (1846) – Mexican–American War
 * Siege of Los Angeles (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Pueblo de Taos (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Puebla (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Veracruz (1847) – Mexican–American War. First U.S. amphibious warfare, amphibious landing
* Siege of San José del Cabo (1848) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Peschiera del Garda (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Osoppo (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Venice (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Rome (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Buda (1849), Siege of Buda (1849) – during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848–49
* Siege of La Serena (1851) – 1851 Chilean Revolution
* Siege of Calafat (1854) – Crimean War
* Siege of Los Angeles (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Pueblo de Taos (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Puebla (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Veracruz (1847) – Mexican–American War. First U.S. amphibious warfare, amphibious landing
* Siege of San José del Cabo (1848) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Peschiera del Garda (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Osoppo (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Venice (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Rome (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Buda (1849), Siege of Buda (1849) – during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848–49
* Siege of La Serena (1851) – 1851 Chilean Revolution
* Siege of Calafat (1854) – Crimean War
 * Siege of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (1854)
* Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55) – Crimean War
* Siege of Taganrog (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Kars (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Medina Fort (1857) – Toucouleur Empire, Toucouleurs besiege French Army, French for 97 days
* Siege of Delhi (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Cawnpore (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Lucknow (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Arrah (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Central India Campaign (1858), Siege of Jhansi (1858) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
*Siege of Đà Nẵng (1858–1860)
* Siege of Tourane (1858–1860)
* Siege of Saigon (1859)
* Siege of Ancona (1860) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Messina (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Civitella del Tronto (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Gaeta (1860–1861) – Italian Risorgimento
*Battle of Fort Sumter, Siege of Fort Sumter (1861) – Union soldiers in Fort Sumter surrendered after a few days of bombardment by Confederate forces starting the American Civil War.
* Siege of Tubac (1861) – Apache Wars
* Capture of New Orleans, Siege of New Orleans (1862) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War
* Siege of Vicksburg (1863) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War.
* Siege of Port Hudson (1863) – Union Army surrounded Confederate river stronghold for 48 days.
* Siege of Puebla (1863) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Petersburg (1864–1865) – American Civil War
* Siege of Fort Ampola (1866) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Callao, Fourth siege of El Callao (1866) – naval battle between Spain and Peru (and her allies)
* Siege of Querétaro (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Mexico City (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Battle of Hakodate, Siege of Hakodate (1869)
* Siege of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (1854)
* Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55) – Crimean War
* Siege of Taganrog (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Kars (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Medina Fort (1857) – Toucouleur Empire, Toucouleurs besiege French Army, French for 97 days
* Siege of Delhi (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Cawnpore (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Lucknow (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Arrah (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Central India Campaign (1858), Siege of Jhansi (1858) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
*Siege of Đà Nẵng (1858–1860)
* Siege of Tourane (1858–1860)
* Siege of Saigon (1859)
* Siege of Ancona (1860) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Messina (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Civitella del Tronto (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Gaeta (1860–1861) – Italian Risorgimento
*Battle of Fort Sumter, Siege of Fort Sumter (1861) – Union soldiers in Fort Sumter surrendered after a few days of bombardment by Confederate forces starting the American Civil War.
* Siege of Tubac (1861) – Apache Wars
* Capture of New Orleans, Siege of New Orleans (1862) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War
* Siege of Vicksburg (1863) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War.
* Siege of Port Hudson (1863) – Union Army surrounded Confederate river stronghold for 48 days.
* Siege of Puebla (1863) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Petersburg (1864–1865) – American Civil War
* Siege of Fort Ampola (1866) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Callao, Fourth siege of El Callao (1866) – naval battle between Spain and Peru (and her allies)
* Siege of Querétaro (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Mexico City (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Battle of Hakodate, Siege of Hakodate (1869)
 * Capture of Rome (1870) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Strasbourg (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Toul (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Metz (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris and the Paris Commune (1870–71)
* Siege of Belfort (1870–71) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena (1873–1874)
* Siege of Pamplona (1874) – First Spanish Republic
* Siege of Plevna (1877–1878) – Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
* Battle of Bear Paw, Siege of the Bears Paw (1877) – final engagement of the Nez Perce War.
* Siege of Eshowe (1879) – Anglo–Zulu War
* Bombardment of Callao, Fifth siege of El Callao (1880) – Chilean naval
* Capture of Rome (1870) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Strasbourg (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Toul (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Metz (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris and the Paris Commune (1870–71)
* Siege of Belfort (1870–71) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena (1873–1874)
* Siege of Pamplona (1874) – First Spanish Republic
* Siege of Plevna (1877–1878) – Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
* Battle of Bear Paw, Siege of the Bears Paw (1877) – final engagement of the Nez Perce War.
* Siege of Eshowe (1879) – Anglo–Zulu War
* Bombardment of Callao, Fifth siege of El Callao (1880) – Chilean naval  * Siege of Zamboanga (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
* Battle of Bucaramanga (1899), Siege of Bucaramanga (1899) – Thousand Days' War (Colombia)
* Siege of Mafeking (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Kimberley (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Ladysmith (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Zamboanga (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
* Battle of Bucaramanga (1899), Siege of Bucaramanga (1899) – Thousand Days' War (Colombia)
* Siege of Mafeking (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Kimberley (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Ladysmith (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
 * Siege of Vidin (1913) – Second Balkan War
* United States occupation of Veracruz, Siege of Veracruz (1914)
* Battle of Liège (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Namur (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Maubeuge (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Toma (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Przemyśl (1914–15) – World War I
* Siege of Antwerp (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Tsingtao (1914) – World War I
* Defense of Van (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Novogeorgievsk (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Kut (1915–16) – World War I
* Siege of Medina (1916–19) – World War I
* Battle of Jerusalem (1917) – World War I
* Siege of Najaf (1918) – World War I
* Siege of Aintab (1920–1921) – Franco-Turkish War
* Siege of Perekop (1920) – Russian Civil War
* Siege of Naco (1929) – Escobar Rebellion
* Siege of Cuartel de la Montaña (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Cuartel de Loyola (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gijón (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Oviedo (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of the Alcázar (1936) – Second Spanish Republic militias besieged the Alcázar of Toledo in the Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Santuario de Nuestra Señora de la Cabeza (1936–1937) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Madrid (1936–1939) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gandesa (1938) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Warsaw (1939) – World War II
* Battle of Hegra Fortress, Siege of Hegra Fortress (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Calais (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Lille (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Malta (World War II), Siege of Malta (1940–1943)– World War II
* Siege of Vidin (1913) – Second Balkan War
* United States occupation of Veracruz, Siege of Veracruz (1914)
* Battle of Liège (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Namur (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Maubeuge (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Toma (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Przemyśl (1914–15) – World War I
* Siege of Antwerp (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Tsingtao (1914) – World War I
* Defense of Van (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Novogeorgievsk (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Kut (1915–16) – World War I
* Siege of Medina (1916–19) – World War I
* Battle of Jerusalem (1917) – World War I
* Siege of Najaf (1918) – World War I
* Siege of Aintab (1920–1921) – Franco-Turkish War
* Siege of Perekop (1920) – Russian Civil War
* Siege of Naco (1929) – Escobar Rebellion
* Siege of Cuartel de la Montaña (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Cuartel de Loyola (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gijón (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Oviedo (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of the Alcázar (1936) – Second Spanish Republic militias besieged the Alcázar of Toledo in the Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Santuario de Nuestra Señora de la Cabeza (1936–1937) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Madrid (1936–1939) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gandesa (1938) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Warsaw (1939) – World War II
* Battle of Hegra Fortress, Siege of Hegra Fortress (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Calais (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Lille (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Malta (World War II), Siege of Malta (1940–1943)– World War II
 * Siege of Giarabub (1940–1941) – World War II
* Siege of Saïo (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Tobruk (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Mogilev (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Odessa (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Leningrad (1941–1944) – also known as the 900-Day Siege, probably the most gruesome in history, World War II.
* Siege of Rogatica (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942) – World War II
* Battle of Yenangyaung, Siege of Yenangyaung (1942) – World War II
* Battle of Stalingrad, Siege of Stalingrad (1942–1943) – World War II
* Siege of Turjak (1943) – World War II
* Battle of Imphal, Siege of Imphal (1944) – World War II
* Battle of Kohima, Siege of Kohima (1944) – World War II
* Siege of Myitkyina (1944) – World War II
* Battle of Mount Song, Siege of Mount Song (1944) – World War II
* Defense of Hengyang, Siege of Hengyang (1944) – World War II
* Allied siege of La Rochelle, Siege of La Rochelle (1944–1945) – World War II
* Siege of Dunkirk (1944–45), Siege of Dunkirk (1944–1945) – World War II
* Siege of Bastogne (1944) – World War II
* Siege of Budapest (1944–1945)– World War II
* Siege of Breslau (1945) – World War II
* Battle of Berlin, Siege of Berlin (1945) – World War II
* Siege of Jerusalem (1948), Siege of Jerusalem (1947–1948) – 1948 Arab–Israeli War – Palestinian Arabs laid siege to the Jewish quarters of Jerusalem, but were driven back. Siege was resumed in May by regular Jordanian and Egyptian forces. Ended in armistice.
* Siege of Changchun (1948) – Chinese Civil War
* Berlin Blockade (1948–49) – No military action, but the tactic to starve a city by cutting her supply lines is a feature of a siege. The famous Berlin Air Lift supplied the city with food, coal, medical supplies and other goods for nearly a year.
* Blockade of Wonsan (1951–53) – Korean War
* Siege of Dien Bien Phu (1954) – Vietnamese Viet Minh forces besieged French forces, effecting a final defeat on France's colonial occupation.
* Ifni War#Siege of Sidi Ifni, Siege of Sidi Ifni (1957–58) – Ifni War
* Siege of Jadotville (1961) – Congo Crisis
* El Porteñazo, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1962) – Venezuelan political crisis
* Siege of Erenköy (1964) – Turkish Cypriots holding out against attacking Greek and Greek Cypriot forces. Turkish invasion of Cyprus
* Encirclement of Jerusalem (1967) – Six-Day War
* Siege of Sana'a (1967), Siege of Sana'a (1967–68) – North Yemen Civil War
* Battle of Khe Sanh, Siege of Khe Sanh (1968) – Vietnam War
* Battle of Huế, Siege of Huế (1968) – Vietnam War
* Hue-Da Nang Campaign, Siege of Da Nang (1968) – Vietnam War
* Fall of Saigon, Siege of Saigon (1975) – Vietnam War
* Siege of Tel al-Zaatar (1976) – Lebanese Civil War
* Grand Mosque seizure (1979)
* Siege of Khost (1980–91) – Soviet–Afghan War
* Siege of Aleppo (1980) – Islamist uprising in Syria
* Siege of Abadan (1980–81) – Iran–Iraq War
* Siege of Beirut (1982) – 1982 Lebanon War
* Siege of Urgun (1983–84) – Soviet–Afghan War
* Badaber uprising (1985) – Soviet–Afghan War
* War of the Camps (1985–88) – Lebanese Civil War
* Siege of Basra (1987) – Iran–Iraq War
* Operation Pawan, Siege of Jeffna (1987) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Battle of Kokavil (1990) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* First Battle of Elephant Pass (1991) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Siege of Kijevo (1991) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Vukovar (1991) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Dubrovnik (1991–92) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Stepanakert (1991–92) – First Nagorno-Karabakh War
* Siege of Sarajevo (1992–96) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Mostar (1992–93,1993–94) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Doboj (1992) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Bihać (1992–95) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Tkvarcheli (1992–93) – War in Abkhazia (1992–93)
* Siege of Goražde (1992–95) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Srebrenica (1993–1995) – Bosnian War
* Battle of Jaffna (1995) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Battle of Junik, Siege of Junik (1998) – Kosovo War
* Battle of Grozny (1999–2000), Battle of Grozny (1999–2000) – Second Chechen War
* Siege of Giarabub (1940–1941) – World War II
* Siege of Saïo (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Tobruk (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Mogilev (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Odessa (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Leningrad (1941–1944) – also known as the 900-Day Siege, probably the most gruesome in history, World War II.
* Siege of Rogatica (1941) – World War II
* Siege of Sevastopol (1941–1942) – World War II
* Battle of Yenangyaung, Siege of Yenangyaung (1942) – World War II
* Battle of Stalingrad, Siege of Stalingrad (1942–1943) – World War II
* Siege of Turjak (1943) – World War II
* Battle of Imphal, Siege of Imphal (1944) – World War II
* Battle of Kohima, Siege of Kohima (1944) – World War II
* Siege of Myitkyina (1944) – World War II
* Battle of Mount Song, Siege of Mount Song (1944) – World War II
* Defense of Hengyang, Siege of Hengyang (1944) – World War II
* Allied siege of La Rochelle, Siege of La Rochelle (1944–1945) – World War II
* Siege of Dunkirk (1944–45), Siege of Dunkirk (1944–1945) – World War II
* Siege of Bastogne (1944) – World War II
* Siege of Budapest (1944–1945)– World War II
* Siege of Breslau (1945) – World War II
* Battle of Berlin, Siege of Berlin (1945) – World War II
* Siege of Jerusalem (1948), Siege of Jerusalem (1947–1948) – 1948 Arab–Israeli War – Palestinian Arabs laid siege to the Jewish quarters of Jerusalem, but were driven back. Siege was resumed in May by regular Jordanian and Egyptian forces. Ended in armistice.
* Siege of Changchun (1948) – Chinese Civil War
* Berlin Blockade (1948–49) – No military action, but the tactic to starve a city by cutting her supply lines is a feature of a siege. The famous Berlin Air Lift supplied the city with food, coal, medical supplies and other goods for nearly a year.
* Blockade of Wonsan (1951–53) – Korean War
* Siege of Dien Bien Phu (1954) – Vietnamese Viet Minh forces besieged French forces, effecting a final defeat on France's colonial occupation.
* Ifni War#Siege of Sidi Ifni, Siege of Sidi Ifni (1957–58) – Ifni War
* Siege of Jadotville (1961) – Congo Crisis
* El Porteñazo, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1962) – Venezuelan political crisis
* Siege of Erenköy (1964) – Turkish Cypriots holding out against attacking Greek and Greek Cypriot forces. Turkish invasion of Cyprus
* Encirclement of Jerusalem (1967) – Six-Day War
* Siege of Sana'a (1967), Siege of Sana'a (1967–68) – North Yemen Civil War
* Battle of Khe Sanh, Siege of Khe Sanh (1968) – Vietnam War
* Battle of Huế, Siege of Huế (1968) – Vietnam War
* Hue-Da Nang Campaign, Siege of Da Nang (1968) – Vietnam War
* Fall of Saigon, Siege of Saigon (1975) – Vietnam War
* Siege of Tel al-Zaatar (1976) – Lebanese Civil War
* Grand Mosque seizure (1979)
* Siege of Khost (1980–91) – Soviet–Afghan War
* Siege of Aleppo (1980) – Islamist uprising in Syria
* Siege of Abadan (1980–81) – Iran–Iraq War
* Siege of Beirut (1982) – 1982 Lebanon War
* Siege of Urgun (1983–84) – Soviet–Afghan War
* Badaber uprising (1985) – Soviet–Afghan War
* War of the Camps (1985–88) – Lebanese Civil War
* Siege of Basra (1987) – Iran–Iraq War
* Operation Pawan, Siege of Jeffna (1987) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Battle of Kokavil (1990) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* First Battle of Elephant Pass (1991) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Siege of Kijevo (1991) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Vukovar (1991) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Dubrovnik (1991–92) – Croatian War of Independence
* Siege of Stepanakert (1991–92) – First Nagorno-Karabakh War
* Siege of Sarajevo (1992–96) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Mostar (1992–93,1993–94) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Doboj (1992) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Bihać (1992–95) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Tkvarcheli (1992–93) – War in Abkhazia (1992–93)
* Siege of Goražde (1992–95) – Bosnian War
* Siege of Srebrenica (1993–1995) – Bosnian War
* Battle of Jaffna (1995) – Sri Lankan Civil War
* Battle of Junik, Siege of Junik (1998) – Kosovo War
* Battle of Grozny (1999–2000), Battle of Grozny (1999–2000) – Second Chechen War
 * First siege of Wadi Deif (2012–2013) – Syrian Civil War
* Zamboanga City crisis (2013) – Moro conflict
* Ghouta, Siege of Eastern Ghouta (2013–2018) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of PK5 district (2013-2020) – Central African Republic Civil War (2012-present)
* Siege of Wadi Barada (2013–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Second siege of Wadi Deif (2014) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Sloviansk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of the Luhansk Border Base (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Amirli (2014) – Iraqi civil war (2014–present), Iraqi Civil War
* Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–17), Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Battle of Ilovaisk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Kobanî (2014–2015) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015), Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Cizre operation (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Silvan (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Sur (2016), Siege of Sur (2015–2016) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* December 2015–February 2016 Cizre curfew, Siege of Cizre (2015–2016) Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Fallujah (2016) – Iraqi Civil War
* First siege of Wadi Deif (2012–2013) – Syrian Civil War
* Zamboanga City crisis (2013) – Moro conflict
* Ghouta, Siege of Eastern Ghouta (2013–2018) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of PK5 district (2013-2020) – Central African Republic Civil War (2012-present)
* Siege of Wadi Barada (2013–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Second siege of Wadi Deif (2014) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Sloviansk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of the Luhansk Border Base (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Amirli (2014) – Iraqi civil war (2014–present), Iraqi Civil War
* Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–17), Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Battle of Ilovaisk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Kobanî (2014–2015) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015), Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Cizre operation (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Silvan (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Sur (2016), Siege of Sur (2015–2016) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* December 2015–February 2016 Cizre curfew, Siege of Cizre (2015–2016) Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Fallujah (2016) – Iraqi Civil War
 * Siege of Derna (2016–2018) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Mosul (2016–17), Siege of Mosul (2016–2017) – Iraqi Civil War
* Battle of Tabqa (2017), Siege of Tabqa (2017) – Syrian Civil War
* 2014–17 Venezuelan protests, Siege of Miraflores (2017) – Venezuelan political and civil Crisis
* Marawi crisis (2017) – Philippine war against insurgency
* Battle of Benghazi (2014–2017)#Sidi Akribesh siege, Siege of Sidi Akribesh (2017) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Baghuz Fawqani, Siege of Baghuz Fawqani – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Battle of the Jabara Valley, Siege of the Jabara Valley (2019) – Yemeni Civil War (2015–present), Yemeni Civil War
* Battle of Ras al-Ayn (2019), Siege of Ras al-Ayn – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Qamishli and Al-Hasakah (2021) – Syrian Civil War
* Panjshir conflict, Siege of Panjshir (2021) – Aftermath of the War in Afghanistan (2001-2021)
* Siege of Chernihiv (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Mariupol (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Derna (2016–2018) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Mosul (2016–17), Siege of Mosul (2016–2017) – Iraqi Civil War
* Battle of Tabqa (2017), Siege of Tabqa (2017) – Syrian Civil War
* 2014–17 Venezuelan protests, Siege of Miraflores (2017) – Venezuelan political and civil Crisis
* Marawi crisis (2017) – Philippine war against insurgency
* Battle of Benghazi (2014–2017)#Sidi Akribesh siege, Siege of Sidi Akribesh (2017) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Baghuz Fawqani, Siege of Baghuz Fawqani – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Battle of the Jabara Valley, Siege of the Jabara Valley (2019) – Yemeni Civil War (2015–present), Yemeni Civil War
* Battle of Ras al-Ayn (2019), Siege of Ras al-Ayn – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Qamishli and Al-Hasakah (2021) – Syrian Civil War
* Panjshir conflict, Siege of Panjshir (2021) – Aftermath of the War in Afghanistan (2001-2021)
* Siege of Chernihiv (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Mariupol (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
Siege of Negroponte (1470)
The siege of Negroponte was fought between the forces of the Ottoman Empire, led by Sultan Mehmed II in person, and the garrison of the Venetian colony of Negroponte ( Chalcis), the capital of the Venetian possession of Euboea in Central Greece ...
– Ottoman–Venetian War (1463–1479)
The First Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Republic of Venice and her allies and the Ottoman Empire from 1463 to 1479. Fought shortly after the capture of Constantinople and the remnants of the Byzantine Empire by the Ottomans, it ...
* Siege of Barcelona (1472), during the Catalan Civil War
The Catalan Civil War, also called the Catalonian Civil War or the War against John II, was a civil war in the Principality of Catalonia, then part of the Crown of Aragon, between 1462 and 1472. The two factions, the royalists who supported John ...
* Siege of Shkodra (1474)
The siege of Shkodra of 1474 was an Ottoman attack upon Venetian-controlled Shkodra (Scutari in Italian) in Albania Veneta during the First Ottoman-Venetian War (1463–79). It is not to be confused with the siege of Shkodra of 1478–79.
...
* Siege of Neuss (1474–1475) – Burgundian Wars
The Burgundian Wars (1474–1477) were a conflict between the Burgundian State and the Old Swiss Confederacy and its allies. Open war broke out in 1474, and the Duke of Burgundy, Charles the Bold, was defeated three times on the battlefield in th ...
* Siege of Burgos
At the siege of Burgos, from 19 September to 21 October 1812, the Anglo-Portuguese Army led by General Arthur Wellesley, Marquess of Wellington tried to capture the castle of Burgos from its French garrison under the command of General o ...
(1475–1476) – War of the Castilian Succession
The War of the Castilian Succession was the military conflict contested from 1475 to 1479 for the succession of the Crown of Castile fought between the supporters of Joanna 'la Beltraneja', reputed daughter of the late monarch Henry IV of Castile ...
* Siege of Neamț Citadel
The siege of Neamț Citadel in 1476 was an important event in the history of Moldavia.
Neamț Citadel was a fortress rumored to have been built in the thirteenth century by the Teutonic Knights, in defence against Tatar incursions.
In 1476, after ...
(1476)
* Siege of Krujë (1477–1478)
* Siege of Shkodra
The fourth siege of Shkodra of 1478–79 was a confrontation between the Ottoman Empire and the Venetians together with the League of Lezhe and other Albanians at Shkodra (Scutari in Italian) and its Rozafa Castle during the First Ottoman-V ...
(1478–1479)
* Siege of Gdov (1580) – Russian-Livonian War (1480–81)
* Siege of Izborsk (1580) – Russian-Livonian War (1480–81)
* Siege of Fellin (1580) – Russian-Livonian War (1480–81)
* Siege of Izborsk (1580) – Russian-Livonian War (1480–81)
* Siege of Pskov (1580) – Russian-Livonian War (1480–81)
* Siege of Rhodes (1480)
In 1480 the small Knights Hospitaller garrison of Rhodes withstood an attack of the Ottoman Empire.
Attack
On 23 May 1480 an Ottoman fleet of 160 ships appeared before Rhodes, at the gulf of Trianda, along with an army of 70,000 men under the c ...
– First siege of Rhodes
* Sieges of Otranto (1480–1481)
 *
* Siege of Hainburg
The siege of Hainburg were two sieges of Hainburg conducted by Matthias Corvinus, Matthias I, King of Hungary, during the Austro-Hungarian War (1477–88). The first siege was broken in July 1482 by the Imperial Army of the Holy Roman Empire. Corv ...
(1482) – Austrian-Hungarian War (1477–1488)
Austria-Hungary, often referred to as the Austro-Hungarian Empire,, the Dual Monarchy, or Austria, was a constitutional monarchy and great power in Central Europe between 1867 and 1918. It was formed with the Austro-Hungarian Compromise of ...
* Siege of Utrecht (1483)
The siege of Utrecht took place between June 23 and August 31, 1483 as part of the Hook and Cod wars and the Second Utrecht Civil War.
Prelude
The Burgundians had tried to control the Bishopric of Utrecht since 1456, when David of Burgundy had b ...
– Second Utrecht Civil War
The second (symbol: s) is the unit of time in the International System of Units (SI), historically defined as of a day – this factor derived from the division of the day first into 24 hours, then to 60 minutes and finally to 60 seconds each ...
* Siege of Vienna (1485)
The siege of Vienna was a decisive siege in 1485 of the Austrian–Hungarian War. It was a consequence of the ongoing conflict between Frederick III and Matthias Corvinus. After the fall of Vienna it was merged with Hungary from 1485 to 1490. ...
– Austrian-Hungarian War (1477–1488)
* Siege of Retz
The siege of Retz was a conflict between the Holy Roman Empire and the Kingdom of Hungary in 1486. It was part of the Austro-Hungarian War. The Hungarian capture of the town eventually led to the prosperity of its wine industry.
The siege
After ...
(1486) – Austrian-Hungarian War (1477–1488)
* Siege of Wiener Neustadt
The siege of Wiener Neustad, part of the Austrian–Hungarian War (1477–1488), Austrian-Hungarian War, was an assault from January 1486 to August 1487 on the Austrian town of Wiener Neustadt. Launched by Matthias Corvinus, King of Kingdom of Hu ...
(1487) – Austrian-Hungarian War (1477–1488)
* Siege of Málaga (1487)
The siege of Málaga (1487) was an action during the Reconquest of Spain in which the Catholic Monarchs of Spain conquered the city of Mālaqa from the Emirate of Granada. The siege lasted about four months.
It was the first conflict in which ...
– Granada War
The Granada War ( es, Guerra de Granada) was a series of military campaigns between 1482 and 1491 during the reign of the Catholic Monarchs, Isabella I of Castile and Ferdinand II of Aragon, against the Nasrid dynasty's Emirate of Granada. It e ...
* Siege of Granada (1491–1492)
* Siege of Boulogne (1492)
The siege of Boulogne took place during the autumn of 1492. Henry VII of England had led an expeditionary force of 12,000 troops across the Channel to Calais and began to besiege the French port of Boulogne on 18 October. After several weeks the ...
* Siege of Samarkand (1494)
* Siege of Samarkand (1497)
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Siege of Samarkand
, partof = Timurid-Uzbek Wars Timurid Civil Wars
, image =
, image_size =
, caption =
, date = May 1497
, place ...
16th century
* Siege of the Castle of Saint George (1500) –Ottoman–Venetian War (1499–1503)
The Second Ottoman–Venetian War was fought between the Islamic Ottoman Empire and the Republic of Venice for control of the lands that were contested between the two parties in the Aegean Sea, Ionian Sea, and the Adriatic Sea. The war lasted f ...
* Siege of Tabriz (1501)
The Siege of Tabriz (Persian: محاصره تبریز) took place in 1501 just after the Safavids had defeated the Aq Qoyunlu in the Battle of Sharur. In the preceding battle the Safavids were able to defeat the Aq Qoyunlus that had an army wh ...
* Siege of Samarkand (1501)
* Siege of Smolensk (1502)
The siege of Smolensk was an unsuccessful attempt to capture Smolensk by the forces of the Grand Duchy of Moscow in summer 1502. It was the last major military engagement during the Muscovite–Lithuanian War (1500–1503).
Smolensk, a stron ...
– Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
The Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars (also known as Russo-Lithuanian Wars, or just either Muscovite Wars or Lithuanian Wars)The conflicts are referred to as 'Muscovite wars' ( pl, wojny moskiewskie) in Polish historiography and as 'Lithuanian wars' in ...
* Siege of Kabul (1504)
In 1504, Babur besieged Kabul and took the city from the Arghuns under Mukim Beg Arghun, to become the new king of Kabul and Ghazni regions. The territory gave him respite from his Uzbek troubles in Central Asia and allowed him to build his ...
* Tenth Siege of Gibraltar (1506) – by the Duke of Medina Sidonia
* Siege of Anjadiva (1506)
* Siege of Cannanore (1507)
The siege of Cannanore was a four-month siege, from April to August 1507, when troops of the local ruler (the Kōlattiri Raja of Cannanore), supported by the Zamorin of Calicut and Arabs, besieged the Portuguese garrison at St. Angelo Fort in C ...
* Spanish conquest of Oran (1509)
* Siege of Padua
The siege of Padua was a major engagement early in the War of the League of Cambrai.
Imperial forces had captured the Venetian city of Padua in June 1509. On 17 July, Venetian forces commanded by Andrea Gritti marched quickly from Treviso wit ...
(1509) – War of the League of Cambrai
* Siege of Gongenyama (1510)
* Spanish conquest of Tripoli (1510)
* Portuguese conquest of Goa
The Portuguese conquest of Goa occurred when the governor Afonso de Albuquerque captured the city in 1510 from the Adil Shahis. Goa became the capital of the Portuguese State of India which included possessions such as Fort Manuel, the territ ...
(1510)
* Siege of Mirandola (1511)
The siege of Mirandola occurred in January 1511 as a part of Pope Julius II's campaign to keep France from dominating northern Italy during the War of the League of Cambrai. At that time Mirandola was the capital of the Duchy of Mirandola ...
– War of the League of Cambrai
* Capture of Malacca (1511)
The Capture of Malacca in 1511 occurred when the governor of Portuguese India Afonso de Albuquerque conquered the city of Malacca in 1511.
The port city of Malacca controlled the narrow, strategic Strait of Malacca, through which all seagoing ...
* Siege of Aden (1513)
* Siege of Dijon
The siege of Dijon between 8 and 13 September 1513 was a successful campaign of the Swiss army against the French city of Dijon during the War of the League of Cambrai.
After the French had lost the Battle of Novara, several contingents of ...
(1513) – War of the League of Cambrai
* Siege of Smolensk (1514) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
* Siege of Arai (1516)
* Siege of Cairo
The siege of Cairo, also known as the Cairo campaign, was a siege that took place during the French Revolutionary Wars, between French and British with Ottoman forces and was the penultimate action of the Egyptian Campaign. British commander ...
(1517)
 * Siege of Opochka (1517) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
*
* Siege of Opochka (1517) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
* Siege of Polotsk
The siege of Polotsk was laid in 1518 by forces of the Grand Duchy of Moscow on Polotsk during the Fourth Muscovite–Lithuanian War (1512–1522). The Lithuanians defended the city. According to a legend, Prince Casimir Jagiellon appeared b ...
(1518) – Muscovite–Lithuanian Wars
* Siege of Allenstein (1521) – Polish–Teutonic War (1519–21)
Polish–Teutonic War may refer to:
* Teutonic takeover of Danzig (Gdańsk) (1308–1309)
* Polish–Teutonic War (1326–1332) over Pomerelia, concluded by the Treaty of Kalisz (1343)
*the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War or ''Great War'' (14 ...
* Siege of Pampeluna (1521) – Italian War of 1521–26
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional It ...
* Siege of Tenochtitlan (1521) – fall of the Aztec
The Aztecs () were a Mesoamerican culture that flourished in central Mexico in the post-classic period from 1300 to 1521. The Aztec people included different ethnic groups of central Mexico, particularly those groups who spoke the Nahuatl ...
Empire.
* Siege of Mézières (1521) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Tournai (1521) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Belgrade (1521)
The siege of Belgrade in 1521 is an event that followed as a result of the third major Ottoman attack on this Hungarian stronghold in the Ottoman–Hungarian wars at the time of the greatest expansion of the Ottoman Empire to the west. Ottom ...
* Siege of Knin
The siege of Knin ( hr, Opsada Knina) was a siege of the city of Knin, the capital of the Kingdom of Croatia, by the Ottoman Empire in 1522. After two failed attempts in 1513 and 1514, Ottoman forces led by Ghazi Husrev Bey, sanjak-bey (gove ...
(1522)
* Siege of Genoa (1522) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Rhodes (1522)
The siege of Rhodes of 1522 was the second and ultimately successful attempt by the Ottoman Empire to expel the Knights of Rhodes from their island stronghold and thereby secure Ottoman control of the Eastern Mediterranean. The first siege i ...
– Second siege of Rhodes
* Siege of Marseille (1522–1524) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Conquest of Kalmar
The Conquest of Kalmar ( sv, Erövringen av Kalmar) took place on 27 May 1523, during the Swedish War of Liberation (1521-1523). In the beginning of 1523, Kalmar and Stockholm remained as the only real Danish strongholds in Sweden. The situat ...
(1523)
* Conquest of Stockholm
The Conquest of Stockholm ( sv, Erövringen av Stockholm) was a battle in the Swedish War of Liberation that took place in Stockholm, Sweden on 17 June 1523. The Swedish forces had for a long time laid siege to Stockholm, which was the last Dani ...
(1523)
* Siege of Fuenterrabía (1523–1524)
The siege of the fortress of Fuenterrabía took place when the Franco-Navarrese army had taken it in a new incursion, after the failure of the third attempt to reconquer the Kingdom of Navarre, which had been invaded in 1512 by troops from the ...
– Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Edo (1524)
 * Siege of Pavia (1524–25) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Sambhal (1526)
*
* Siege of Pavia (1524–25) – Italian War of 1521–26
* Siege of Sambhal (1526)
* Siege of Calicut (1526)
The siege of Calicut occurred in 1526, when the Zamorin, the local Indian ruler, captured the fort of Calicut from the Portuguese.
The Portuguese had plans for establishing a fort at Calicut since 1500, when Pedro Álvares Cabral received thi ...
* Siege of Kamakura (1526)
In the 1526 siege of Kamakura (大永鎌倉合戦; "Daiei (era) Battle of Kamakura"), Satomi Sanetaka led forces of the Uesugi clan against the Hōjō, who had taken Edo from the Uesugi two years earlier. The city was defended by a number of r ...
* Sack of Rome (1527)
The Sack of Rome, then part of the Papal States, followed the capture of the city on 6 May 1527 by the mutinous troops of Charles V, Holy Roman Emperor during the War of the League of Cognac. Despite not being ordered to storm the city, wit ...
– War of the League of Cognac
* Siege of Naples (1528)
The siege of Naples was a siege of the Italian city of Naples in 1528 during the War of the League of Cognac.
Course
In April 1528 the French commander Odet de Foix laid siege to the city while Andrea Doria's nephew Filippino organised a nav ...
– War of the League of Cognac
* Capture of Peñón of Algiers (1529)
The capture of ''Peñón of Algiers'' was accomplished when the beylerbey of Algiers Hayreddin Barbarossa took a fortress (called Peñón of Algiers) in a small islet facing the Algerian city of Algiers from the Habsburg Spaniards. Backgrou ...
* Siege of Vienna (1529) – First siege of Vienna
* Siege of Florence (1529–1530) – War of the League of Cognac
* Siege of Buda (1530) by Wilhelm von Roggendorf and Bálint Török
* Siege of Diu (1531)
The siege of Diu occurred when a combined Ottoman- Gujarati force defeated a Portuguese attempt to capture the city of Diu in 1531. The victory was partly the result of Ottoman firepower over the Portuguese besiegers deployed by Mustafa B ...
* Siege of Güns
The siege of Kőszeg ( hu, Kőszeg ostroma) or siege of Güns ( tr, Güns Kuşatması), also known as German Campaign ( tr, Alman Seferi) was a siege of Kőszeg (german: Güns)During the Ottoman–Habsburg wars, the small border fort was called G ...
(1532)
 * Siege of Maribor (1532)
*
* Siege of Maribor (1532)
* Siege of Coron
The siege of Coron in 1532–1534 involved the siege and capture of the Ottoman-held fortress of Koroni (Coron) in Messenia, Greece, by the forces of the Habsburg Empire, and its subsequent recapture by the Ottomans.
Coron had been a posse ...
(1532–1534)
* Siege of Baghdad (1534) – by Ottomans
* Siege of Tunis (1534)
* Conquest of Tunis (1535)
The Habsburg Empire of Charles V and its allies conquered Tunis in 1535, wresting the city away from the control of the Ottoman Empire.
Background
In 1533, Suleiman the Magnificent ordered Hayreddin Barbarossa, whom he had summoned from Alg ...
* Siege of Chittorgarh (1535)
The siege of Chittorgarh took place in 1535, when Sultan Bahadur Shah of Gujarat attacked Chittor Fort, after the death of Rana Sanga, with the aim of expanding his kingdom. The forts defense was led by the Widows of Sanga.
Background
Rana Vikr ...
* Siege of Cusco (1536–1537)
* Siege of Klis
The siege of Klis or Battle of Klis ( hr, Opsada Klisa, Bitka kod Klisa, tr, Klise Kuşatması) was a siege of Klis Fortress in the Kingdom of Croatia within Habsburg monarchy. The siege of the fortress, which lasted for more than two decad ...
(1536–1537)
* Siege of Musashi-Matsuyama (1537)
The 1537 siege of Musashi-Matsuyama was the first of several sieges of Matsuyama castle in Japan's Musashi province over the course of the Sengoku period (1467-1603). The Uesugi clan controlled the castle in 1537, but lost it to the Hōjō clan ...
* Siege of Corfu (1537) – Ottoman–Venetian War (1537–1540)
The Third Ottoman Venetian War (1537–1540) was one of the Ottoman–Venetian wars which took place during the 16th century. The war arose out of the Franco-Ottoman alliance between Francis I of France and Süleyman I of the Ottoman Empire ...
* Siege of Diu
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteriz ...
(1538)
* Siege of Castelnuovo
The siege of Castelnuovo was an engagement during the Ottoman-Habsburg struggle for control of the Mediterranean, which took place in July 1539 at the walled town of Castelnuovo, present-day Herceg Novi, Montenegro. Castelnuovo had been conquer ...
(1539) – Ottoman–Venetian War (1537–1540)
* Siege of Koriyama
took place from September, 1540 until January, 1541 in Yoshida, Aki Province, Japan during the Sengoku period. Amago Haruhisa, with 30,000 men, attacked Kōriyama Castle, which belonged to Mōri Motonari and was defended by 8,000 men. When the ...
(1540–1541)
* Siege of Buda (1540) by Leonhard von Fels and Niklas Salm
* Fall of Agadir
The Fall of Agadir refers to the conquest of the city in Morocco by the Saadians against the Portuguese in 1541.
Background Establishment and trade role
Agadir had been a Portuguese base since 1505. Before that, a few unsuccessful attempts to c ...
(1541)
* Siege of Buda (1541)
The siege of Buda (4 May – 21 August 1541) ended with the capture of the city of Buda, Hungary by the Ottoman Empire, leading to 150 years of Ottoman control of Hungary. The siege, part of the Little War in Hungary, was one of the most import ...
– capture of the city of Buda by the Turkish Ottoman Emperor Suleiman the Magnificent, as he invaded central Hungary
* Algiers expedition (1541)
The 1541 Algiers expedition occurred when Charles V of the Holy Roman Empire and king of Spain attempted to lead an amphibious attack against regency of Algiers, in modern Algeria. Inadequate planning, particularly against unfavourable weather ...
* Siege of Uehara
The siege of Uehara was the first of many steps taken by Takeda Shingen in his bid to seize control of Shinano Province. Uehara Castle had been controlled by Suwa Yorishige (1516–1544) was a Japanese samurai and head of the Suwa clan. He was d ...
(1541)
* Siege of Fukuyo
The siege of Fukuyo was one of many steps taken by Takeda Shingen in his bid to seize control of Shinano Province. The fortress at Fukuyo lay in the Ina valley, south of Lake Suwa
is a lake in the Kiso Mountains, in the central region of Na ...
(1542)
* Siege of Kuwabara
The siege of Kuwabara took place the day after the siege of Uehara; Takeda Shingen continued to gain power in Shinano Province by seizing Kuwabara castle from Suwa Yorishige. Suwa was escorted back to the provincial capital of Kōfu
is the c ...
(1542)
* Siege of Pest (1542) – an attempt to recapture Buda from the Turks
 *
* Siege of Perpignan (1542)
The siege of Perpignan took place in 1542, at Perpignan, between a larger French army commanded by Henry, Dauphin of France and the Spanish garrison at Perpignan. The Spaniards resisted until the arrival of the Spanish army under Don Fernando ...
– Italian War of 1542–1546
The Italian War of 1542–1546 was a conflict late in the Italian Wars, pitting Francis I of France and Suleiman I of the Ottoman Empire against the Holy Roman Emperor Charles V and Henry VIII of England. The course of the war saw extensive ...
* Siege of Toda Castle
The was a battle during the Sengoku period (16th century) of Japan.
The siege of the castle was personally led by Ōuchi Yoshitaka against Gassantoda Castle located within Izumo Province, under the control of Amago Haruhisa.
In this battle Mo ...
(1542–1543)
* Siege of Nagakubo (1543)
* Siege of Landrecies (1543) – Italian War of 1542–1546
* Siege of Esztergom (1543)
The siege of Esztergom occurred between 25 July and 10 August 1543, when the Ottoman army, led by Sultan Suleiman the Magnificent, besieged the city of Esztergom in modern Hungary. The city was captured by the Ottomans after two weeks.
Backgrou ...
* Siege of Nice (1543) – Italian War of 1542–1546
* Siege of Kojinyama
In the 1544 siege of Kojinyama, Takeda Shingen continued his invasion of Shinano Province
or is an old province of Japan that is now Nagano Prefecture.
Shinano bordered on Echigo, Etchū, Hida, Kai, Kōzuke, Mikawa, Mino, Musashi, S ...
(1544)
* Siege of Kōriyama Castle (1544)
* Siege of St. Dizier (1544) – Italian War of 1542–46
* Sieges of Boulogne (1544–46) Siege of Boulogne may refer to:
*Siege of Boulogne (1492)
The siege of Boulogne took place during the autumn of 1492. Henry VII of England had led an expeditionary force of 12,000 troops across the Channel to Calais and began to besiege the Fren ...
– Italian War of 1542–46
* Siege of Ryūgasaki
The 1545 siege of Ryūgasaki was one of many battles fought by Takeda Shingen in his bid to control Shinano Province during Japan's Sengoku period. The fortress was a satellite castle
A castle is a type of fortified structure built duri ...
(1545)
* Siege of Takatō (1545)
* Siege of Kawagoe Castle (1545–1546)
* Second siege of Diu
The Third Siege of Diu was a siege of the Portuguese Indian city of Diu by the Gujarat Sultanate in 1546. It ended with a major Portuguese victory.
Background
At the beginning of the 16th century, the Muslim Sultanate of Gujarat was the pr ...
(1546)
* Siege of Uchiyama (1546)
* Siege of Shika Castle
The siege of Shika castle, which took place in September 1547, was one of many battles fought in Takeda Shingen's bid to seize control of Shinano Province.
Background
The battle took place during the 16th-century Sengoku period, also known as ...
(1546–1547)
* Siege of Van (1548)
The siege of Van occurred in 1548 when Suleiman the Magnificent attacked Persia in his second campaign of the Ottoman-Safavid War (1532–1555).
The city of Van, which has long been strategic in Eastern Anatolia, was surrounded, put under sie ...
– Ottoman–Safavid War (1532–55)
* Siege of Aden (1548)
* Siege of Kajiki
The siege of Kajiki was fought in 1549 the Shimazu clan besieged the castle of Kajiki in what is now Kagoshima prefecture, Japan. The siege succeeded and the castle was taken. The siege is notable for the first time "Portuguese derived" arquebuse ...
(1549)
* Siege of Fukashi
The 1550 siege of Fukashi was one of a series of battles waged by Takeda Shingen in his long campaign to conquer Shinano province, which was ruled by a number of minor ''daimyō'', notably the Suwa, Ogasawara, and Takato.
Shingen mounted hi ...
(1549)
 *
* Siege of Beijing
Altan Khan of the Tümed (1507–1582; mn, ᠠᠯᠲᠠᠨ ᠬᠠᠨ, Алтан хан; Chinese: 阿勒坦汗), whose given name was Anda ( Mongolian: ; Chinese: 俺答), was the leader of the Tümed Mongols and de facto ruler of the Right Win ...
(1550)
* Capture of Mahdia (1550)
The capture of Mahdia was an amphibious military operation that took place from June to September, 1550, during the struggle between the Ottoman Empire and the Spanish Habsburgs for the control of the Mediterranean. A Spanish naval expedition ...
* Sieges of Toishi
The took place during Takeda Shingen's campaign to take over Shinano Province. His army, led by Sanada Yukitaka, began besieging the castle in 1550. The defending lord, Murakami Yoshikiyo
Murakami Yoshikiyo (村上 義清, 1501–1573) was a ...
(1550–51)
* Siege of Gozo (1551)
* Siege of Mirandola (1551–1552) – Italian War of 1551–1559
Italian(s) may refer to:
* Anything of, from, or related to the people of Italy over the centuries
** Italians, an ethnic group or simply a citizen of the Italian Republic or Italian Kingdom
** Italian language, a Romance language
*** Regional ...
* Siege of Tripoli (1551)
The siege of Tripoli occurred in 1551 when the Ottoman Turks and Barbary pirates besieged and vanquished the Knights of Malta in the Red Castle of Tripoli, modern Libya. The Spanish had established an outpost in Tripoli in 1510, and Charle ...
* Siege of Eger (1552)
The siege of Eger ( hu, Eger ostroma) occurred during the 16th century Ottoman Wars in Europe. In 1552 the forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Kara Ahmed Pasha laid siege to the Castle of Eger, located in the northern part of the Kingdom ...
* Siege of Temesvár (1552)
The siege of Temesvár was a military conflict between the Habsburg monarchy and the Ottoman Empire in 1552. The siege resulted with a decisive Ottoman victory and Temesvár came under Ottoman control for 164 years.
Background
After the Battl ...
* Siege of Muscat (1552)
* Siege of Metz (1552–53) – Italian War of 1551–1559
* Siege of Kazan
The siege of Kazan in 1552 was the final battle of the Russo-Kazan Wars and led to the fall of the Khanate of Kazan. Conflict continued after the fall of Kazan, however, as rebel governments formed in Çalım and Mişätamaq, and a new kha ...
(1552) – Part of the Russo-Kazan wars
The Russo-Kazan Wars was a series of wars fought between the Grand Duchy of Moscow and the Khanate of Kazan from 1439, until Kazan was finally conquered by the Tsardom of Russia under Ivan the Terrible in 1552.
General
Before it separated fr ...
* Siege of Hormuz (1552–54)
* Siege of Eger (1552)
The siege of Eger ( hu, Eger ostroma) occurred during the 16th century Ottoman Wars in Europe. In 1552 the forces of the Ottoman Empire led by Kara Ahmed Pasha laid siege to the Castle of Eger, located in the northern part of the Kingdom ...
– Part of Ottoman–Habsburg wars
The Ottoman–Habsburg wars were fought from the 16th through the 18th centuries between the Ottoman Empire and the Habsburg monarchy, which was at times supported by the Kingdom of Hungary, Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, and Habsburg Spai ...
* Siege of Katsurao
The 1553 siege of Katsurao was one of many sieges undertaken by the warlord Takeda Shingen in his long campaign to gain control of Japan's Shinano province, which was ruled by a hodgepodge of minor ''daimyō'', notably the Suwa, Ogasawara, and ...
(1553)
* Siege of Iwatsurugi Castle (1554)
 * Siege of Kiso Fukushima (1554)
*
* Siege of Kiso Fukushima (1554)
* Siege of Kannomine
The 1554 siege of Kannomine was one of many battles fought in Takeda Shingen's campaign to seize control of Shinano Province. This took place during Japan's Sengoku period; Shingen was one of many feudal lords (''daimyō
were powerful Japa ...
(1554)
* Siege of Matsuo
The 1554 siege of Matsuo was one of many sieges undertaken by the ''daimyō'' Takeda Shingen in his campaign to conquer Japan's Shinano Province. This took place during Japan's Sengoku period, in which feudal lords (''daimyō
were powerful ...
(1554)
* Siege of Siena (1554–55) – Italian War of 1551–1559
* Siege of Oran (1556)
* Siege of Katsurayama (1557)
* Siege of Kotte (1557–58)
A siege is a military blockade of a city, or fortress, with the intent of conquering by attrition, or a well-prepared assault. This derives from la, sedere, lit=to sit. Siege warfare is a form of constant, low-intensity conflict characteri ...
– Sinhalese–Portuguese War
* Siege of Calais (1558)
The French siege of Calais in early 1558 was part of the Italian War of 1551–1559 between France and England and their respective allies. It resulted in the seizure of the town by France.
The Pale of Calais had been ruled by England since ...
– Italian War of 1551–1559
* Siege of Narva (1558)
The siege of Narva ( et, Narva piiramine; russian: Осада Нарвы) was a Russian siege of the Livonian city of Narva (in modern-day eastern Estonia) from April through May 1558, during the Livonian War. After capturing the city in July ...
– Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) was the Russian invasion of Old Livonia, and the prolonged series of military conflicts that followed, in which Tsar Ivan the Terrible of Russia (Muscovy) unsuccessfully fought for control of the region (pr ...
* Siege of Thionville (1558) – Italian War of 1551–1559
* Siege of Bahrain (1559)
* Siege of Dorpat (1558) – Livonian War
The Livonian War (1558–1583) was the Russian invasion of Old Livonia, and the prolonged series of military conflicts that followed, in which Tsar Ivan the Terrible of Russia (Muscovy) unsuccessfully fought for control of the region (pr ...
* Siege of Weissenstein (1558) - Livonian War
* Siege of Dorpat (1559) - Livonian War
* Siege of Lais (1559) - Livonian War
* Siege of Fellin (1560) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1560) – Livonian War
* Siege of Leith (1560)
* Siege of Marune (1560)
* Siege of Moji (1561)
* Siege of Odawara (1561)
* Siege of Kaminogō Castle (1562)
* Siege of Inverness (1562)
* Siege of Rouen (1562) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Weissenstein (1562) - Livonian War
* Siege of Musashi-Matsuyama (1563)
* Siege of Orleans (1563) – French Wars of Religion
 * Sieges of Oran and Mers El Kébir (1563)
* Capture of Älvsborg – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Concepción (1564)
* Siege of Chauragarh (1564)
* Siege of Kuragano (1565)
* Great Siege of Malta (1565)
* Siege of Minowa (1566)
* Siege of Szigetvár (1566) – Ottoman Empire, Ottoman siege during which Suleiman the Magnificent died
* Siege of Valenciennes (1567), Siege of Valenciennes (1566–67) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Inabayama Castle (1567)
* Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–1568), Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–68)
* Siege of Ranthambore (1568)
* Siege of Chartres (1568)
* Siege of Malacca (1568)
* Siege of Hachigata (1568)
* Siege of Odawara (1569)
* Siege of Kanbara (1569)
* Siege of Kakegawa (1569)
* Siege of Tachibana (1569)
* Siege of Varberg (1569) – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ogucji Castle (1569)
* Siege of Hanazawa (1570)
* Siege of Chōkō-ji (1570)
* Siege of Kanegasaki (1570)
* Siege of Nicosia, Cyprus (1570) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Famagusta, Cyprus (1570–71) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Reval (1570–71) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1570–71) - Livonian War
* Siege of Ishiyama Honganji (1570–1580) – longest siege in Japanese history
*Siege of Chale (1571) - War of the League of the Indies, War of the league of Indies
* Siege of Fukazawa (1571)
* Siege of Moscow (1571) – Part of Russo-Crimean Wars
* Sieges of Nagashima (1571, 1573, 1574)
* Siege of Mount Hiei (1571)
* Siege of Futamata (1572)
* Siege of Iwamura Castle (1572)
* Siege of Mons (1572) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Middelburg (1572–74) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle during the French Wars of Religion.
* Siege of Sancerre (1572–1573) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Haarlem (1572–1573) – conducted by the Spanish against the Dutch during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1572–73) - Livonian War
* Siege of Noda Castle (1573)
* Siege of Odani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Hikida Castle (1573)
* Siege of Ichijōdani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Alkmaar (1573) – turning point in the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leiden (1573–1574) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Wesenberg (1574) – Livonian War
* Siege of Itami (1574)
* Siege of Takatenjin (1574)
* Conquest of Tunis (1574), Siege of Tunis (1574)
* Lim Hong (pirate), Siege of Limahong (1574)
* Siege of Yoshida Castle (1575)
* Siege of Nagashino (1575)
* Siege of Schoonhoven (1575) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zierikzee (1575–1576)) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mitsuji (1576)
* Siege of Takabaru (1576)
* Sack of Antwerp, Siege of Antwerp (1576) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nanao (1577)
* Siege of Shigisan (1577)
* Siege of Reval (1577) – Livonian War
* Sieges of Oran and Mers El Kébir (1563)
* Capture of Älvsborg – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Concepción (1564)
* Siege of Chauragarh (1564)
* Siege of Kuragano (1565)
* Great Siege of Malta (1565)
* Siege of Minowa (1566)
* Siege of Szigetvár (1566) – Ottoman Empire, Ottoman siege during which Suleiman the Magnificent died
* Siege of Valenciennes (1567), Siege of Valenciennes (1566–67) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Inabayama Castle (1567)
* Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–1568), Siege of Chittorgarh (1567–68)
* Siege of Ranthambore (1568)
* Siege of Chartres (1568)
* Siege of Malacca (1568)
* Siege of Hachigata (1568)
* Siege of Odawara (1569)
* Siege of Kanbara (1569)
* Siege of Kakegawa (1569)
* Siege of Tachibana (1569)
* Siege of Varberg (1569) – Northern Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ogucji Castle (1569)
* Siege of Hanazawa (1570)
* Siege of Chōkō-ji (1570)
* Siege of Kanegasaki (1570)
* Siege of Nicosia, Cyprus (1570) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Famagusta, Cyprus (1570–71) – Fourth Ottoman–Venetian War
* Siege of Reval (1570–71) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1570–71) - Livonian War
* Siege of Ishiyama Honganji (1570–1580) – longest siege in Japanese history
*Siege of Chale (1571) - War of the League of the Indies, War of the league of Indies
* Siege of Fukazawa (1571)
* Siege of Moscow (1571) – Part of Russo-Crimean Wars
* Sieges of Nagashima (1571, 1573, 1574)
* Siege of Mount Hiei (1571)
* Siege of Futamata (1572)
* Siege of Iwamura Castle (1572)
* Siege of Mons (1572) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Middelburg (1572–74) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), Siege of La Rochelle (1572–1573), assault on the Huguenot city of La Rochelle during the French Wars of Religion.
* Siege of Sancerre (1572–1573) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Haarlem (1572–1573) – conducted by the Spanish against the Dutch during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1572–73) - Livonian War
* Siege of Noda Castle (1573)
* Siege of Odani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Hikida Castle (1573)
* Siege of Ichijōdani Castle (1573)
* Siege of Alkmaar (1573) – turning point in the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leiden (1573–1574) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Wesenberg (1574) – Livonian War
* Siege of Itami (1574)
* Siege of Takatenjin (1574)
* Conquest of Tunis (1574), Siege of Tunis (1574)
* Lim Hong (pirate), Siege of Limahong (1574)
* Siege of Yoshida Castle (1575)
* Siege of Nagashino (1575)
* Siege of Schoonhoven (1575) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zierikzee (1575–1576)) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mitsuji (1576)
* Siege of Takabaru (1576)
* Sack of Antwerp, Siege of Antwerp (1576) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nanao (1577)
* Siege of Shigisan (1577)
* Siege of Reval (1577) – Livonian War
 * Siege of Danzig (1577) – Danzig rebellion
* Siege of Gvozdansko (1577–1578)
* Siege of Kōzuki Castle (1578)
* Siege of Otate (1578)
* Siege of Deventer (1578) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Miki (1578–1580)
* Siege of Itami (1579)
* Siege of Maastricht (1579) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Polotsk (1579) – Livonian War
* Siege of Velikiye Luki – Livonian War
* Siege of Carrigafoyle Castle (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Steenwijk (1580–1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Smerwick (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Takatenjin (1581), Siege of Takatenjin (1580–1581)
* Siege of Hijiyama (1581)
* Siege of Tottori (1581)
* Siege of Minamata Castle (1581)
* Siege of Narva (1581) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1581) - Livonian War
* Siege of Pskov (1581–1582) – Livonian War
* Siege of Niezijl (1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Danzig (1577) – Danzig rebellion
* Siege of Gvozdansko (1577–1578)
* Siege of Kōzuki Castle (1578)
* Siege of Otate (1578)
* Siege of Deventer (1578) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Miki (1578–1580)
* Siege of Itami (1579)
* Siege of Maastricht (1579) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Polotsk (1579) – Livonian War
* Siege of Velikiye Luki – Livonian War
* Siege of Carrigafoyle Castle (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Steenwijk (1580–1581) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Smerwick (1580) – Second Desmond Rebellion
* Siege of Takatenjin (1581), Siege of Takatenjin (1580–1581)
* Siege of Hijiyama (1581)
* Siege of Tottori (1581)
* Siege of Minamata Castle (1581)
* Siege of Narva (1581) – Livonian War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1581) - Livonian War
* Siege of Pskov (1581–1582) – Livonian War
* Siege of Niezijl (1581) – Eighty Years' War
 * Siege of Takamatsu (1582)
* Siege of Takatō (1582)
* Siege of Uozu (1582)
* Siege of Lochem (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lier (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eindhoven (1583) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Godesberg (1583)
* Siege of Kaganoi (1584)
* Siege of Takehana (1584)
* Siege of Kanie (1584)
* Siege of Suemori (1584)
* Siege of Ypres (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ghent (1583–1584), Siege of Ghent (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bruges (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Brussels (1584–85) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Toyama (1585)
* Siege of Negoro-ji (1585)
* Siege of Ōta Castle (1585)
* Siege of IJsseloord (1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Iwaya Castle (1586)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias (1586), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1586) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Grave (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Venlo (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Axel, Siege of Axel (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Destruction of Neuss, Second siege of Neuss (July 1586)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1586–1590) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ganjaku (1587)
* Siege of Akizuki (1587)
* Siege of Kagoshima (1587)
* Siege of Sluis (1587) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Johor (1587)
* Siege of Kraków (1587) – War of the Polish Succession (1587–88)
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1588) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kurokawa Castle (1589)
* Siege of Hachigata (1590)
* Siege of Paris (1590) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Odawara (1590), Siege of Odawara Castle (1590)
* Siege of Shimoda (1590)
* Siege of Oshi (1590)
* Siege of Zutphen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Deventer (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Knodsenburg (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Hulst (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nijmegen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Rouen (1591), Siege of Rouen (1591–1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Caudebec (1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Busanjin (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Dongrae (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Steenwijk (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bihać (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Pyongyang (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Jinju (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Pyongyang (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Haengju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Geertruidenberg (1593) – Eighty Years' War
* Battle of Sisak, Siege of Sisak (1593) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Jinju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1593), Siege of Coevorden (1593–1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groningen (1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Enniskillen (1594) – Tyrone's Rebellion
* Siege of Morlaix (1594) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Fort Crozon (1594) – Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
* Siege of Huy (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Preston Somers Expedition, Siege of Caracas (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Takamatsu (1582)
* Siege of Takatō (1582)
* Siege of Uozu (1582)
* Siege of Lochem (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lier (1582) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eindhoven (1583) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Godesberg (1583)
* Siege of Kaganoi (1584)
* Siege of Takehana (1584)
* Siege of Kanie (1584)
* Siege of Suemori (1584)
* Siege of Ypres (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ghent (1583–1584), Siege of Ghent (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Antwerp (1584–1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bruges (1584) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Brussels (1584–85) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Toyama (1585)
* Siege of Negoro-ji (1585)
* Siege of Ōta Castle (1585)
* Siege of IJsseloord (1585) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Iwaya Castle (1586)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias (1586), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1586) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Grave (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Venlo (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Axel, Siege of Axel (1586) – Eighty Years' War
* Destruction of Neuss, Second siege of Neuss (July 1586)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1586–1590) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ganjaku (1587)
* Siege of Akizuki (1587)
* Siege of Kagoshima (1587)
* Siege of Sluis (1587) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Johor (1587)
* Siege of Kraków (1587) – War of the Polish Succession (1587–88)
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1588) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kurokawa Castle (1589)
* Siege of Hachigata (1590)
* Siege of Paris (1590) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Odawara (1590), Siege of Odawara Castle (1590)
* Siege of Shimoda (1590)
* Siege of Oshi (1590)
* Siege of Zutphen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Deventer (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Knodsenburg (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Hulst (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nijmegen (1591) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Rouen (1591), Siege of Rouen (1591–1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Caudebec (1592) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Busanjin (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Dongrae (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Steenwijk (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Bihać (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Pyongyang (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1592) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Jinju (1592) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Pyongyang (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Haengju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Geertruidenberg (1593) – Eighty Years' War
* Battle of Sisak, Siege of Sisak (1593) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Jinju (1593) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Coevorden (1593), Siege of Coevorden (1593–1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groningen (1594) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Enniskillen (1594) – Tyrone's Rebellion
* Siege of Morlaix (1594) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Fort Crozon (1594) – Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604)
* Siege of Huy (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Preston Somers Expedition, Siege of Caracas (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
 * Siege of Le Catelet (1595) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Groenlo (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Doullens – French Wars of Religion
* Battle of San Juan (1595), Siege of San Juan (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Calais (1596) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Hulst (1596) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eger (1596) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Amiens (1597) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Rheinberg (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Meurs (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1597) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Namwon (1597) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Bredevoort (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Le Catelet (1595) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Groenlo (1595) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Doullens – French Wars of Religion
* Battle of San Juan (1595), Siege of San Juan (1595) during the Anglo-Spanish War (1585–1604), Anglo–Spanish War
* Siege of Calais (1596) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Hulst (1596) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Eger (1596) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Amiens (1597) – French Wars of Religion
* Siege of Rheinberg (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Meurs (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1597) – during the Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Namwon (1597) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Bredevoort (1597) – Eighty Years' War
 * Capture of Enschede (1597), Siege of Enschede (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Ootmarsum, Siege of Ootmarsum (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lingen (1597) – Eighty Years' War
*:hu:Buda ostroma (1598), Siege of Buda (1598)
* Siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Second siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Suncheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Battle of Sacheon (1598), Siege of Sacheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Schenckenschans (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zaltbommel (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Cahir Castle (1599) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Rees (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Enschede (1597), Siege of Enschede (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Capture of Ootmarsum, Siege of Ootmarsum (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1597) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Lingen (1597) – Eighty Years' War
*:hu:Buda ostroma (1598), Siege of Buda (1598)
* Siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Second siege of Ulsan (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Suncheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Battle of Sacheon (1598), Siege of Sacheon (1598) – Japanese invasions of Korea (1592–98)
* Siege of Schenckenschans (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Zaltbommel (1599) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Cahir Castle (1599) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Rees (1599) – Eighty Years' War
17th century
* Siege of San Andreas (1600) – Eighty Years' War * Siege of Ueda (1600) * Siege of Fushimi (1600) * Siege of Ōtsu (1600) * Siege of Shiroishi (1600) * Siege of Hataya (1600) * Siege of Kaminoyama (1600) * Siege of Hasedō (1600) * Siege of Tanabe (1600)
* Siege of Udo (1600)
* Siege of Yanagawa (1600)
* Siege of Pernau (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dorpat (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ostend (1601–04) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nagykanizsa (1601) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Donegal (1601) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Kinsale (1601–02) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Wolmar (1601) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Fellin (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dunboy (1602) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Grave (1602) – Eighty Years' War
* :hu:Buda ostroma (1602), Siege of Buda (1602–1603) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Sluis (1604) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1604) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Kromy (1605) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18)
* Siege of Lingen (1605) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kandahar (1605–06)
* Siege of Tanabe (1600)
* Siege of Udo (1600)
* Siege of Yanagawa (1600)
* Siege of Pernau (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dorpat (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Rheinberg (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Ostend (1601–04) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nagykanizsa (1601) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Donegal (1601) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Kinsale (1601–02) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Wolmar (1601) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1601) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Fellin (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1602) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Dunboy (1602) – Nine Years' War (Ireland)
* Siege of Grave (1602) – Eighty Years' War
* :hu:Buda ostroma (1602), Siege of Buda (1602–1603) – Long Turkish War
* Siege of Sluis (1604) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Weissenstein (1604) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Kromy (1605) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–18)
* Siege of Lingen (1605) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Kandahar (1605–06)
 * Siege of Malacca (1606) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Ganja (1606) – Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–18)
* Siege of Groenlo (1606) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Tory Island (1608) – O'Doherty's rebellion
* Siege of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra (1608–10) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1608) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Pärnu (1609) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Smolensk (1609–11) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Kalmar (1611) – Kalmar War
* Storming of Kristianopel (1611) – Kalmar War
* Battle of Moscow (1612), Siege of Moscow (1612) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Smolensk (1613–17) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Malacca (1606) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Ganja (1606) – Ottoman–Safavid War (1603–18)
* Siege of Groenlo (1606) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Tory Island (1608) – O'Doherty's rebellion
* Siege of Troitse-Sergiyeva Lavra (1608–10) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Fellin (1600) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Weissenstein (1608) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Pärnu (1609) – Polish–Swedish War (1600–11)
* Siege of Smolensk (1609–11) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Kalmar (1611) – Kalmar War
* Storming of Kristianopel (1611) – Kalmar War
* Battle of Moscow (1612), Siege of Moscow (1612) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Smolensk (1613–17) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
 * Siege of Tikhvin (1613) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Gdov (1614) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Aachen (1614) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Osaka (1614–15)
* Siege of Pskov (1615) – Ingrian War
* Uskok War#First Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1616) – Uskok War
* Uskok War#Second Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1617) – Uskok War
* Siege of Pilsen (1618) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Moscow (1618) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Budweis (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Kassa (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Battle of Humenné#Prelude, Siege of Vienna (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Bad Kreuznach (1620) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Neuhäusel (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Blockade of La Rochelle (1621–22) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Montauban (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Pressburg (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#First phase (1621–22), Siege of Riga (1621) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Siege of Jülich (1621–22) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Frankenthal (1621–1623) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Ormuz (1622), Siege of Ormuz (1622)
* Siege of Royan (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Nègrepelisse (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Tikhvin (1613) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Gdov (1614) – Ingrian War
* Siege of Aachen (1614) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Osaka (1614–15)
* Siege of Pskov (1615) – Ingrian War
* Uskok War#First Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1616) – Uskok War
* Uskok War#Second Siege of Gradisca, Siege of Gradisca (1617) – Uskok War
* Siege of Pilsen (1618) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Moscow (1618) – Polish–Muscovite War (1605–1618)
* Siege of Budweis (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Kassa (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Battle of Humenné#Prelude, Siege of Vienna (1619) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Bad Kreuznach (1620) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Neuhäusel (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Jean-d'Angély (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Blockade of La Rochelle (1621–22) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Montauban (1621) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Pressburg (1621) – Thirty Years' War
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#First phase (1621–22), Siege of Riga (1621) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Siege of Jülich (1621–22) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Frankenthal (1621–1623) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Ormuz (1622), Siege of Ormuz (1622)
* Siege of Royan (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Nègrepelisse (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
 * Siege of Montpellier (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Bergen-op-Zoom (1622) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1622) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Mannheim (1622) – Thirty Years' War
*:es:Castillo de Araya, Siege of Araya Castle (1622–1623) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1624), Siege of Breda (1624–1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Gavi (1625)
* Relief of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1625)
* Recapture of Bahia (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Verrua (1625)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Koknese (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Dorpat (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Battle of San Juan (1625), Siege of San Juan (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1625)
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1626) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Montpellier (1622) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Bergen-op-Zoom (1622) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1622) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Mannheim (1622) – Thirty Years' War
*:es:Castillo de Araya, Siege of Araya Castle (1622–1623) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1624), Siege of Breda (1624–1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Gavi (1625)
* Relief of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1625)
* Recapture of Bahia (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Relief of Genoa#Piedmontese theatre, Siege of Verrua (1625)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Koknese (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)#Second phase (1625–26), Siege of Dorpat (1625) – Polish–Swedish War (1621–25)
* Battle of San Juan (1625), Siege of San Juan (1625) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1625)
* Siege of Oldenzaal (1626) – Eighty Years' War
 * Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627) – Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nienburg (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1627) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Stralsund (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Glückstadt (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Batavia (1628–29)
* Siege of Mantua (1629–30)
* Siege of Casale Monferrato (1629–31)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1629) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Privas (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Alès (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Sack of Magdeburg (1631) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Maastricht, Siege of Maastricht (1632) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nuremberg (1632) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Saint-Martin-de-Ré (1627) – Anglo-French War (1627–1629)
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nienburg (1627) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Groenlo (1627) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of La Rochelle (1627–1628) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Stralsund (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Glückstadt (1628) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Batavia (1628–29)
* Siege of Mantua (1629–30)
* Siege of Casale Monferrato (1629–31)
* Siege of 's-Hertogenbosch (1629) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Privas (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Siege of Alès (1629) – Huguenot rebellions
* Sack of Magdeburg (1631) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Maastricht, Siege of Maastricht (1632) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Nuremberg (1632) – Thirty Years' War
 * Siege of Dorogobuzh (1632) – Smolensk War
* Siege of Smolensk (1632–33) – Smolensk War
* Battle of Oldendorf#Prelude, Siege of Hameln (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hagenau (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Konstanz (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Rheinfelden (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Belaya (1634)
* Siege of Überlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lüshun (1634)
* Siege of Hildesheim (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nördlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Minden (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leuven (1635) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Schenkenschans (1635–1636) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mainz (1635) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dôle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of La Capelle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Le Câtelet (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1636) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Corbie (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Leipzig (1637) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Landrecies (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Venlo (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leucate (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hara Castle (1637–1638)
* Siege of Azov (1637–1642) – Part of Russo-Turkish Wars
* Siege of Saint-Omer (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Fuenterrabía (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Battle of Breisach (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lemgo (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Baghdad (1638), Siege of Baghdad (1638) by Ottomans
* Siege of Hesdin (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Relief of Thionville (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Salses (1639–1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Casale (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Galle (1640) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Turin (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Arras (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Neunburg (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of São Filipe (1641–1642) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Siege of Dorsten (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Göttingen (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Perpignan (1642), Siege of Perpignan (1641–1642) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Olmütz (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Brieg (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leipzig (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hull (1642) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Portsmouth (1642) – First English Civil War
* Second siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Sieges of Bradford (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Reading (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Chichester (1642) – First English Civil War
* Battle of Rocroi#Prelude, Siege of Rocroi (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Thionville (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Worcester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lichfield (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Gloucester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sierck (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hull (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Newcastle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lathom House (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Überlingen (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lyme Regis (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of York (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lincoln (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lleida (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
*Siege of Gravelines (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Oxford (1644–1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sas van Gent (1644) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Relief of Montgomery Castle, Siege of Montgomery Castle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Sieges of Taunton (1644–1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Duncannon (1645) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Chester (1645) – First English Civil War
* Great Siege of Scarborough Castle (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Carlisle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Brünn (1645) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Mardyck (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Bristol (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Béthune (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Lillers (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Saint-Venant (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hulst (1645) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Worcester (1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Mardyck (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dunkirk (1646) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Augsburg (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lindau (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Armentières (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Landrecies (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Ypres (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Memmingen (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Candia (Crete) (1648–69) – claimed as the second-longest siege in history
* Siege of Pembroke (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Siege of Colchester (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Battle of Prague (1648), Siege of Prague (1648) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Inverness (1649)
* Siege of Zbarazh (1649) – Khmelnytsky uprising
* Siege of Dublin (1649)
* Siege of Drogheda (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Wexford (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Waterford (1649–1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Inverness (1650)
* Siege of Kilkenny (1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Clonmel (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Charlemont (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Limerick (1650–51), Cromwell's Siege of Limerick City, Ireland (1651) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Barcelona (1651), Siege of Barcelona (1651–1652), during the Reapers' War, Catalan Revolt
* Siege of Galway (1651–1652) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Battle of Arras (1654), Siege of Arras (1654) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Smolensk (1654) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Landrecies (1655) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1655) – Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60)
* Siege of Kraków (1655) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Danzig (1655–60) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Jasna Góra (1655) – during Deluge (history), The Deluge
* Battle of Valenciennes (1656), Siege of Valenciennes (1656) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Zamość (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Warsaw (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Nöteborg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Nyenschantz (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dyneburg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Riga (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorpat (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorogobuzh (1632) – Smolensk War
* Siege of Smolensk (1632–33) – Smolensk War
* Battle of Oldendorf#Prelude, Siege of Hameln (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hagenau (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Konstanz (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Rheinfelden (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1633) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Belaya (1634)
* Siege of Überlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Regensburg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lüshun (1634)
* Siege of Hildesheim (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Nördlingen (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Minden (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Heidelberg (1634) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leuven (1635) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Schenkenschans (1635–1636) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Mainz (1635) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dôle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of La Capelle (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Le Câtelet (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Magdeburg (1636) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Corbie (1636) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Leipzig (1637) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Breda (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Landrecies (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Venlo (1637) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Leucate (1637) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hara Castle (1637–1638)
* Siege of Azov (1637–1642) – Part of Russo-Turkish Wars
* Siege of Saint-Omer (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Fuenterrabía (1638) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Battle of Breisach (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lemgo (1638) – Thirty Years' War
* Capture of Baghdad (1638), Siege of Baghdad (1638) by Ottomans
* Siege of Hesdin (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Relief of Thionville (1639) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Salses (1639–1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Casale (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Galle (1640) – Dutch-Portuguese War
* Siege of Turin (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Arras (1640) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Neunburg (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Wolfenbüttel (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of São Filipe (1641–1642) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Siege of Dorsten (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Göttingen (1641) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Perpignan (1642), Siege of Perpignan (1641–1642) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Olmütz (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Brieg (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Leipzig (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Hull (1642) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Portsmouth (1642) – First English Civil War
* Second siege of Glogau (1642) – Thirty Years' War
* Sieges of Bradford (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Reading (1642–1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Chichester (1642) – First English Civil War
* Battle of Rocroi#Prelude, Siege of Rocroi (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Thionville (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Worcester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lichfield (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Gloucester (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sierck (1643) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hull (1643) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Newcastle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lathom House (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Überlingen (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lyme Regis (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of York (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lincoln (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Lleida (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
*Siege of Gravelines (1644) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Oxford (1644–1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Sas van Gent (1644) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1644) – Thirty Years' War
* Relief of Montgomery Castle, Siege of Montgomery Castle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Sieges of Taunton (1644–1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Duncannon (1645) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Chester (1645) – First English Civil War
* Great Siege of Scarborough Castle (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Carlisle (1644) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Brünn (1645) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Mardyck (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Bristol (1645) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Béthune (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Lillers (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Saint-Venant (1645) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Hulst (1645) – Eighty Years' War
* Siege of Worcester (1646) – First English Civil War
* Siege of Mardyck (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Dunkirk (1646) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Augsburg (1646) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Lindau (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Armentières (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Landrecies (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Ypres (1647) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Memmingen (1647) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Candia (Crete) (1648–69) – claimed as the second-longest siege in history
* Siege of Pembroke (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Siege of Colchester (1648) – Second English Civil War
* Battle of Prague (1648), Siege of Prague (1648) – Thirty Years' War
* Siege of Inverness (1649)
* Siege of Zbarazh (1649) – Khmelnytsky uprising
* Siege of Dublin (1649)
* Siege of Drogheda (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Wexford (1649) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Waterford (1649–1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Inverness (1650)
* Siege of Kilkenny (1650) – Cromwellian conquest of Ireland
* Siege of Clonmel (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Charlemont (1650) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Limerick (1650–51), Cromwell's Siege of Limerick City, Ireland (1651) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Siege of Barcelona (1651), Siege of Barcelona (1651–1652), during the Reapers' War, Catalan Revolt
* Siege of Galway (1651–1652) – Irish Confederate Wars
* Battle of Arras (1654), Siege of Arras (1654) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Smolensk (1654) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Landrecies (1655) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Santo Domingo (1655) – Anglo-Spanish War (1654–60)
* Siege of Kraków (1655) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Danzig (1655–60) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Jasna Góra (1655) – during Deluge (history), The Deluge
* Battle of Valenciennes (1656), Siege of Valenciennes (1656) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Zamość (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Warsaw (1656) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Nöteborg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Nyenschantz (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dyneburg (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Riga (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dorpat (1656) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
 * Siege of Bidar (1657)
* Siege of Kraków (1657) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1657) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dunkirk (1658) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Toruń (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Badajoz (1658) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Assault on Copenhagen (1659), Siege of Copenhagen (1658–1659) Second Northern War, Swedes defeated by Danish and Dutch defenders
* Siege of Kolding (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Lyakhavichy (1660) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Fort Zeelandia (1661–1662) – Sino-Dutch conflicts
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1663) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Hlukhiv (1664) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Valência de Alcântara (1664)
* Siege of Novi Zrin (1664), Siege of Novi Zrin Castle (1664) in northern Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia – Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
* Siege of Léva (1664) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Purandhar (1665)
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Charleroi (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Tournai (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Douai (1667) – War of Devolution
* Siege of Lille (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Franche-Comté, Siege of Dole (1668) – War of Devolution
* Solovetsky Monastery uprising, Siege of Solovetsky Monastery (1668–76) – eight years
* Siege of Groenlo (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Groningen (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Kamenets (1672) – Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76)
* Siege of Bidar (1657)
* Siege of Kraków (1657) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1657) – Russo-Swedish War (1656–58)
* Siege of Dunkirk (1658) – Franco-Spanish War (1635–59)
* Siege of Toruń (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Badajoz (1658) – Portuguese Restoration War
* Assault on Copenhagen (1659), Siege of Copenhagen (1658–1659) Second Northern War, Swedes defeated by Danish and Dutch defenders
* Siege of Kolding (1658) – Second Northern War
* Siege of Lyakhavichy (1660) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Fort Zeelandia (1661–1662) – Sino-Dutch conflicts
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1663) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Hlukhiv (1664) – Russo-Polish War (1654–67)
* Siege of Valência de Alcântara (1664)
* Siege of Novi Zrin (1664), Siege of Novi Zrin Castle (1664) in northern Kingdom of Croatia (Habsburg), Croatia – Austro-Turkish War (1663–64)
* Siege of Léva (1664) – Austro-Turkish War (1663–1664)
* Siege of Purandhar (1665)
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Charleroi (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Tournai (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Spanish Netherlands, Siege of Douai (1667) – War of Devolution
* Siege of Lille (1667) – War of Devolution
* War of Devolution#Campaign in the Franche-Comté, Siege of Dole (1668) – War of Devolution
* Solovetsky Monastery uprising, Siege of Solovetsky Monastery (1668–76) – eight years
* Siege of Groenlo (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Groningen (1672) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Kamenets (1672) – Polish–Ottoman War (1672–76)
 * Siege of Maastricht (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Bonn (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Besançon (1674) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ponda (1675)
* Siege of Maastricht (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Valenciennes (1676–77) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Freiburg (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Cambrai (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Malmö (1677) – Scanian War
* Siege of Ghent (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ypres (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Puigcerdà (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Stralsund (1678) – Scanian War
* Battle of Vienna, Siege of Vienna (1683) – siege of Vienna during the Great Turkish War
* Siege of Luxembourg (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Bombardment of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Siege of Buda (1684), Austrian army tried to take Buda from Ottoman Turkey
* Siege of Santa Maura (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Bijapur (1685–86)
* Morean War#Coron and Mani (1685), Siege of Cojor (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Maastricht (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Bonn (1673) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Besançon (1674) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ponda (1675)
* Siege of Maastricht (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1676) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Valenciennes (1676–77) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Freiburg (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Cambrai (1677) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Malmö (1677) – Scanian War
* Siege of Ghent (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Ypres (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Puigcerdà (1678) – Franco-Dutch War
* Siege of Stralsund (1678) – Scanian War
* Battle of Vienna, Siege of Vienna (1683) – siege of Vienna during the Great Turkish War
* Siege of Luxembourg (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Bombardment of Genoa, Siege of Genoa (1684) – War of the Reunions
* Siege of Buda (1684), Austrian army tried to take Buda from Ottoman Turkey
* Siege of Santa Maura (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1684) – Morean War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Sinj (1685) – Morean War
* Siege of Bijapur (1685–86)
* Morean War#Coron and Mani (1685), Siege of Cojor (1685) – Morean War
 * Siege of Érsekújvár (1685) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Kelefa (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Navarino (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Buda (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Modon (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Nauplia (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Pécs (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Golconda (1687)
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Castelnuovo (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Érsekújvár (1685) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Kelefa (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Navarino (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Buda (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Modon (1686) – Morean War
* Morean War#Navarino, Modon, and Nauplia (1686), Siege of Nauplia (1686) – Morean War
* Siege of Pécs (1686) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Golconda (1687)
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Castelnuovo (1687) – Morean War
 * Morean War#Patras and the completion of the conquest (1687), Siege of Monemvasia (1687–1690) – Morean War
* Morean War#Occupation of Athens (1687–88), Siege of the Acropolis (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Bangkok (1688) – Siamese revolution of 1688
* Siege of Negroponte (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Belgrade (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Knin (1688) – Morean War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mannheim (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Frankenthal (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Derry (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Kaiserswerth (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mainz (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Larache (1689)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Carrickfergus (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Bonn (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Gingee (1689–1698)
* First siege of Athlone (1690), Williamite War in Ireland
* Morean War#Capture of Valona and Kanina (1690), Siege of Kanina (1690) – Morean War
* Siege of Belgrade (1690), Siege of Niš (1690) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Patras and the completion of the conquest (1687), Siege of Monemvasia (1687–1690) – Morean War
* Morean War#Occupation of Athens (1687–88), Siege of the Acropolis (1687) – Morean War
* Siege of Bangkok (1688) – Siamese revolution of 1688
* Siege of Negroponte (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Siege of Belgrade (1688) – Great Turkish War
* Morean War#Battles in Dalmatia, Siege of Knin (1688) – Morean War
* Siege of Philippsburg (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mannheim (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Frankenthal (1688) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Derry (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Kaiserswerth (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Rhineland and the Empire, Siege of Mainz (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Larache (1689)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Carrickfergus (1689) – Williamite War in Ireland
* Siege of Bonn (1689) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Gingee (1689–1698)
* First siege of Athlone (1690), Williamite War in Ireland
* Morean War#Capture of Valona and Kanina (1690), Siege of Kanina (1690) – Morean War
* Siege of Belgrade (1690), Siege of Niš (1690) – Great Turkish War
 * Siege of Ceuta (1694–1727) – claimed as the longest siege in history
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Casale (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Capitulation of Diksmuide (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Jesus (1696–1698)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Nashwaak (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Ath (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Barcelona (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Road to Ryswick: 1696–97, Siege of Ebernburg (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1697)
* Siege of Ceuta (1694–1727) – claimed as the longest siege in history
* Nine Years' War#War and diplomacy: 1694–95, Siege of Casale (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Capitulation of Diksmuide (1695) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Jesus (1696–1698)
* Siege of Pemaquid (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Fort Nashwaak (1696) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Ath (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Barcelona (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Nine Years' War#Road to Ryswick: 1696–97, Siege of Ebernburg (1697) – Nine Years' War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1697)
18th century
* Siege of Riga (1700) – Great Northern War * Siege of Tönning (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Riga (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Narva (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Kaiserswerth (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Donas (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castiglione (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Borgoforte (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guastalla (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venlo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stevensweert (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Roermond (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Nöteborg (1702) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Liége (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Rheinberg (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of St. Augustine (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Andernach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Governolo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Riga (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Narva (1700) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Kaiserswerth (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Donas (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Castiglione (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Borgoforte (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Guastalla (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venlo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stevensweert (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Roermond (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Nöteborg (1702) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Liége (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Rheinberg (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of St. Augustine (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Andernach (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Governolo (1702) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Siege of Rain (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Narva (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Villingen (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fort Isabella (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Capture of Gibraltar, Siege of Gibraltar (1704) – eleventh siege of
* Siege of Rain (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Narva (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Dorpat (1704) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Villingen (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fort Isabella (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Capture of Gibraltar, Siege of Gibraltar (1704) – eleventh siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by Sir George Rooke's Anglo-Dutch fleet
* Siege of Ulm (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Twelfth Siege of Gibraltar (1704–05) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ivree (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landau (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Verrua (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1704) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Colonia del Sacramento (1704–1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of St. John's (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Valencia de Alcantara (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Albuquerque (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Huy (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Liège (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Second siege of Huy (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Chivasso (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Mirandola (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Nice (1705), Siege of Nice (1705–06) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Zoutleeuw (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Hagenau (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Badajoz (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Zandvliet (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Diest (1705) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Siege of Susa (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lérida (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Morella (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oran (1707–1708) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Tortosa (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Exilles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lille (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fenestrelles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of San Felipe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Leffinghe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Denia (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Ghislain (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Brussels (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1708–09) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ghent (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Veprik (1709) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Tournai (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Mons (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Viborg (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Reval (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Douai (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Béthune (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Aire (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Venant (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1710–1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kassa (1711) – Rákóczi's War of Independence
* Siege of Aren fort (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venasque (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stralsund (1711–15) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Castel-Leon (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cardona (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landrecies (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Marchiennes (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Douai (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Susa (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lérida (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Morella (1707) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Oran (1707–1708) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Tortosa (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Exilles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Lille (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Fenestrelles (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of San Felipe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Leffinghe (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Denia (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Ghislain (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Brussels (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Alicante (1708–09) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Ghent (1708) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Veprik (1709) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Tournai (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Mons (1709) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Viborg (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Reval (1710) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Douai (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Béthune (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Aire (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Saint Venant (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Port Royal (1710) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1710–1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Kassa (1711) – Rákóczi's War of Independence
* Siege of Aren fort (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Venasque (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Stralsund (1711–15) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Castel-Leon (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Cardona (1711) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Landrecies (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Marchiennes (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Douai (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
 * Second siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1712–1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning#1713–1714, Siege of Tönning (1713–1714) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Landau (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1713–14), Siege of Barcelona (1713–14) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gurdaspur (1715)
* Siege of Brahan (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Siege of Inverness (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Second siege of Le Quesnoy (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Bouchain (1712) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gerona (1712–1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Tönning#1713–1714, Siege of Tönning (1713–1714) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Landau (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Barcelona (1713–14), Siege of Barcelona (1713–14) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1713) – War of the Spanish Succession
* Siege of Gurdaspur (1715)
* Siege of Brahan (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
* Siege of Inverness (1715) – Jacobite rising of 1715
 * Siege of Temeşvar (1716) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Belgrade (1717) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Fredriksten (1718) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Isfahan (1722)
* Thirteenth Siege of Gibraltar (1727) – by a Spanish army
* Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), Siege of Oran (1732) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Kehl (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Pizzighettone (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Danzig (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Capua (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Philippsburg (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Messina (1734–1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Ganja (1734), Siege of Ganja (1734–1735) – Ottoman–Persian War (1730–35)
* Siege of Syracuse (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trapani (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Perekop (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Azov (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Banja Luka (1737) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Ochakov (1737) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Kandahar (1737–1738)
* Siege of Mehadia (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Orsova (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Temeşvar (1716) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Belgrade (1717) – Austro-Turkish War (1716–1718)
* Siege of Fredriksten (1718) – Great Northern War
* Siege of Isfahan (1722)
* Thirteenth Siege of Gibraltar (1727) – by a Spanish army
* Spanish conquest of Oran (1732), Siege of Oran (1732) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Kehl (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Pizzighettone (1733) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Danzig (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Gaeta (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trarbach (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Capua (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Philippsburg (1734) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Messina (1734–1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Ganja (1734), Siege of Ganja (1734–1735) – Ottoman–Persian War (1730–35)
* Siege of Syracuse (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Trapani (1735) – War of the Polish Succession
* Siege of Perekop (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Azov (1736) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Banja Luka (1737) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Ochakov (1737) – Russo-Turkish War (1735–1739)
* Siege of Kandahar (1737–1738)
* Siege of Mehadia (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Siege of Orsova (1738) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
 * Capture of Belgrade (1739), Siege of Belgrade (1739) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Battle of Portobello, Siege of Portobello (1739) – victory of British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of St. Augustine (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Fort Mose (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1741)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1741) – failed British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Brieg (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Invasion of Cuba (1741), Siege of Santiago (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Neisse (1741)
* Siege of Glatz (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mirandola (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Modena (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Prague (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of La Guaira, Siege of La Guaira (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Puerto Cabello, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Blockade of Straubing (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1743)
* Siege of Ingolstadt (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mosul (1743) – Ottoman–Persian War (1743–46)
* Siege of Menin (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ypres (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Furnes (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Prague (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuneo (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tabor (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tournai (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Louisbourg (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Port Toulouse (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Fall of Ghent (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Oudenarde (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ostend (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tortona (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Kosel (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Culloden House (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (November 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Stirling Castle (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Brussels (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Inverness (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (March 1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Blair Castle (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort William (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Genoa (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mons (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Capture of Belgrade (1739), Siege of Belgrade (1739) – Austro-Turkish War (1737–1739)
* Battle of Portobello, Siege of Portobello (1739) – victory of British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of St. Augustine (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Fort Mose (1740) – War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1741)
* Battle of Cartagena de Indias, Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1741) – failed British siege by Edward Vernon in the War of Jenkins' Ear
* Siege of Brieg (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Invasion of Cuba (1741), Siege of Santiago (1741) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Neisse (1741)
* Siege of Glatz (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mirandola (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Modena (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Prague (1742) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of La Guaira, Siege of La Guaira (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Eger (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Puerto Cabello, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Blockade of Straubing (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1743)
* Siege of Ingolstadt (1743) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mosul (1743) – Ottoman–Persian War (1743–46)
* Siege of Menin (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ypres (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Furnes (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Prague (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuneo (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Freiburg (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tabor (1744) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tournai (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Louisbourg (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Port Toulouse (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Siege of Annapolis Royal (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession (King George's War)
* Fall of Ghent (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Oudenarde (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ostend (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Tortona (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Kosel (1745) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Culloden House (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (November 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Carlisle (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (December 1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Stirling Castle (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Brussels (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Ruthven Barracks (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Inverness (1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort Augustus (March 1746) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Blair Castle (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Fort William (1745) – Jacobite rising of 1745
* Siege of Genoa (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Mons (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
 * Siege of Namur (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Madras, Siege of Madras (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Genoa (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Maastricht (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuddalore (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Pondicherry (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Arcot (1751) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1751–52) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Fort St Philip (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pirna (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Prague (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort William Henry (1757) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Namur (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Battle of Madras, Siege of Madras (1746) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Genoa (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Hulst (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1747) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Maastricht (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Cuddalore (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Pondicherry (1748) – War of the Austrian Succession
* Siege of Arcot (1751) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Trichinopoly (1751–52) – Second Carnatic War
* Siege of Fort St Philip (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pirna (1756) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Prague (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort William Henry (1757) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1757) – Seven Years' War
 * Blockade of Liegnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Blockade of Stralsund (1757–1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Küstrin (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Louisbourg (1758) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Olomouc, Siege of Olmütz (1758) – by the Prussian army of Frederick the Great during the Seven Years' War
* Siege of Neisse (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Madras (1758–1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Masulipatam (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Battle of the Plains of Abraham, Siege of Québec (1759) – Second siege of Québec City, Québec, during the Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Second siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort Loudoun (1760) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Glatz (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Dresden (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Wittenberg (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1760), Siege of Pondicherry (1760–1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Kolberg (Seven Years' War), Sieges of Kolberg (1759, 1760, and 1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Havana (1762) – Seven Years' War. British fleet headed by George Keppel, 3rd Earl of Albemarle lays siege to Spanish controlled Havana for a month.
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Almeida (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ambur (1767) – First Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Khotyn (1769) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Bender (1770) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Giurgevo (1771) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Silistria (1773) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Melilla (1774), during Hispano-Moroccan wars
* Siege of Boston (1775–1776) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort St. Jean (1775) – American Revolutionary War
* Blockade of Liegnitz (1757) – Seven Years' War
* Blockade of Stralsund (1757–1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Küstrin (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Louisbourg (1758) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Olomouc, Siege of Olmütz (1758) – by the Prussian army of Frederick the Great during the Seven Years' War
* Siege of Neisse (1758) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Madras (1758–1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Masulipatam (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Battle of the Plains of Abraham, Siege of Québec (1759) – Second siege of Québec City, Québec, during the Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Second siege of Münster (1759) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Fort Loudoun (1760) – Seven Years' War (French and Indian War)
* Siege of Glatz (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Dresden (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Breslau (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Wittenberg (1760) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1760), Siege of Pondicherry (1760–1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Kolberg (Seven Years' War), Sieges of Kolberg (1759, 1760, and 1761) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Havana (1762) – Seven Years' War. British fleet headed by George Keppel, 3rd Earl of Albemarle lays siege to Spanish controlled Havana for a month.
* Siege of Schweidnitz (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Almeida (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Cassel (1762) – Seven Years' War
* Siege of Ambur (1767) – First Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Khotyn (1769) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Bender (1770) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Giurgevo (1771) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Silistria (1773) – Russo-Turkish War (1768–1774)
* Siege of Melilla (1774), during Hispano-Moroccan wars
* Siege of Boston (1775–1776) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort St. Jean (1775) – American Revolutionary War
 * Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Stanwix (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Henry (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Mifflin (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1778) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Vincennes (1779) – American Revolutionary War
* Great Siege of Gibraltar (1779–83) – fourteenth siege of
* Siege of Fort Ticonderoga (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Stanwix (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Henry (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Mifflin (1777) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Pondicherry (1778) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Vincennes (1779) – American Revolutionary War
* Great Siege of Gibraltar (1779–83) – fourteenth siege of Gibraltar
)
, anthem = " God Save the King"
, song = "Gibraltar Anthem"
, image_map = Gibraltar location in Europe.svg
, map_alt = Location of Gibraltar in Europe
, map_caption = United Kingdom shown in pale green
, mapsize =
, image_map2 = Gibr ...
, by a Spanish-French army in the American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Savannah (1779) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Tellicherry (1779–82) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Charleston (1780) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Kastania (1780)
* Siege of Vellore (1780–82) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
 * Siege of Pensacola (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Watson (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Motte (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Augusta (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Ninety-Six (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Yorktown (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Negapatam (1781) – Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
* Siege of Brimstone Hill (1782) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Henry (1782) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Cuddalore (1783) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mangalore (1783–1784) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Nargund (1785) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Badami (1786) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Bahadur Benda (1787) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Ochakov (1788) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Khotin (1788) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Pensacola (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Watson (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Fort Motte (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Augusta (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Ninety-Six (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Yorktown (1781) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Negapatam (1781) – Fourth Anglo-Dutch War
* Siege of Brimstone Hill (1782) – Anglo-French War (1778–1783)
* Siege of Fort Henry (1782) – American Revolutionary War
* Siege of Cuddalore (1783) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mangalore (1783–1784) – Second Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Nargund (1785) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Badami (1786) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Bahadur Benda (1787) – Maratha–Mysore War
* Siege of Ochakov (1788) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Khotin (1788) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
 * Siege of Belgrade (1789) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Izmail (1789–1790) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Oran (1790–1792) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Darwar (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Koppal (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Bangalore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Coimbatore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Goorumconda (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Belgrade (1789) – Austro-Turkish War (1788–1791)
* Siege of Izmail (1789–1790) – Russo-Turkish War (1787–1792)
* Siege of Oran (1790–1792) – Conflicts between Spain and Algiers
* Siege of Darwar (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Koppal (1790–1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Bangalore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Coimbatore (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Goorumconda (1791) – Third Anglo-Mysore War
 * Siege of Mannheim (1795) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mantua (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition, French besieging
* Siege of Kehl (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Hüningen (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Invasion of Trinidad (1797), Siege of Port of Spain (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Battle of San Juan (1797), Siege of San Juan de Puerto Rico (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Siege of Malta (1798–1800), Siege of Malta (1798–1800), during the French Revolutionary Wars
* Siege of Corfu (1798–99) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of El Arish (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Jaffa (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Acre (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Mantua (1799) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of Seringapatam (1799) – Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
* Siege of Mannheim (1795) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Mantua (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition, French besieging
* Siege of Kehl (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Siege of Hüningen (1796–97) – War of the First Coalition
* Invasion of Trinidad (1797), Siege of Port of Spain (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Battle of San Juan (1797), Siege of San Juan de Puerto Rico (1797), during the Anglo-Spanish War (1796–1808), Anglo-Spanish War
* Siege of Malta (1798–1800), Siege of Malta (1798–1800), during the French Revolutionary Wars
* Siege of Corfu (1798–99) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of El Arish (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Jaffa (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Acre (1799) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria
* Siege of Mantua (1799) – War of the Second Coalition
* Siege of Seringapatam (1799) – Fourth Anglo-Mysore War
Modern military sieges
19th century
* Siege of Genoa (1800) – War of the Second Coalition * Siege of Fort Bard (1800) – War of the Second Coalition * Siege of Fort Julien (1801) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria * Siege of Porto Ferrajo (1801) – War of the Second Coalition * Siege of Alexandria (1801), Siege of Alexandria (1801) – French campaign in Egypt and Syria * Siege of Ahmednagar (1803) – Second Anglo-Maratha War * Siege of Aligarh (1803) – Second Anglo-Maratha War * Siege of Erivan (1804) – Russo-Persian War (1804–13) * Siege of Delhi (1804) – Second Anglo-Maratha War * Siege of Deeg (1804) – Second Anglo-Maratha War * Siege of Sveaborg (1808) – Finnish War
* Siege of Erivan (1808) – Russo-Persian War (1804–13)
* First siege of Zaragoza (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Barcelona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Battle of Valencia (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Gerona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Roses (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Zaragoza (1808–1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chaves (1809) – Peninsular War
* Third siege of Girona (1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Cádiz (1810–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Santa Maura (1810) – Adriatic campaign
* Siege of Astorga (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Lérida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810), First siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810) – Peninsular War by the French Marshal Michel Ney
* Siege of Mequinenza (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Almeida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tortosa (1810–11) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Olivenza (1811) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Figueras (1811) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tarragona (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Campaña de Valencia, es) (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Montevideo (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tarifa (1812), Siege of Tarifa (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (1812), Siege of Valencia (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Montevideo (1812–14) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812), Second siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812) – Peninsular War by Arthur Wellesley
* Siege of Cuautla (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Badajoz (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Huajuapan de León (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of the Salamanca Forts (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Astorga (1812) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1812), es) (1812) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Sveaborg (1808) – Finnish War
* Siege of Erivan (1808) – Russo-Persian War (1804–13)
* First siege of Zaragoza (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Barcelona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Battle of Valencia (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Gerona (1808) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Roses (1808) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Zaragoza (1808–1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chaves (1809) – Peninsular War
* Third siege of Girona (1809) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Cádiz (1810–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Santa Maura (1810) – Adriatic campaign
* Siege of Astorga (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Lérida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810), First siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1810) – Peninsular War by the French Marshal Michel Ney
* Siege of Mequinenza (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Almeida (1810) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tortosa (1810–11) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Olivenza (1811) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Figueras (1811) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Badajoz (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Tarragona (1811) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Campaña de Valencia, es) (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Montevideo (1811) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tarifa (1812), Siege of Tarifa (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Valencia (1812), Siege of Valencia (1811–1812) – Peninsular War
* Second siege of Montevideo (1812–14) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812), Second siege of Ciudad Rodrigo (1812) – Peninsular War by Arthur Wellesley
* Siege of Cuautla (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Badajoz (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Huajuapan de León (1812) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of the Salamanca Forts (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Astorga (1812) – Peninsular War
* First siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1812), es) (1812) – Spanish American wars of independence
 * Siege of Riga (1812) – French invasion of Russia
* Siege of Fort Mackinac (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Detroit (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Harrison (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Wayne (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Burgos (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Danzig (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Acapulco (1813) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Fort Meigs (1813) – failed British siege of American garrison during the War of 1812
* Siege of Tarragona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Pamplona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of San Sebastián (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chillán (1813) – Chilean War of Independence
* Second siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1813), es) (1813) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cattaro (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1814), Siege of Mainz (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Zara (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Maturin (:es:Batalla de Maturin, es) (1813–1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Hamburg (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Metz (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Third siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1814), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Ragusa (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* First siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Segundo Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Prairie du Chien (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Erie (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Aragua de Barcelona (:es: Batalla de Aragua de Barcelona, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Santa Fe de Bogotá (:es:Asedio de Santafé de Bogotá, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Fort St. Philip (1815) – War of 1812
* Siege of Ancona (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Gaeta (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1815), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias, es) (1815) – List of wars 1800–99, Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Angostura (:es:Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Angostura (:es:Segunda Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1820-21), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias (1820–1821), es) (1820–21) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of El Callao (:es:Primer sitio del Callao, es) (1821) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tripolitsa (1821) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1821–22) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Fourth siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1822), es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pasto (:es: Batalla de Bombona, es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* San Felipe Castle, Fifth Siege of Puerto Cabello (1823) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pamplona (1823) – Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, 1823 French invasion of Spain
* Siege of Messolonghi (1825), First, second, and third sieges of Missolonghi (1822, 1823, 1825–1826)
* Second siege of El Callao (:es:Segundo sitio del Callao, es) (1824–1826) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1826–27) – by the Ottomans against the Greeks, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1832) – conducted by French forces against a Dutch garrison after the Ten Days' Campaign.
* Siege of Jerusalem (1834) Peasants' Revolt of 1834 (Palestine)
* Siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1835), es) (1835) – Reforms Revolution (Venezuela)
* Battle of the Alamo, Siege of the Alamo (1836) – Texas Revolution
* Siege of Herat (1838), Siege of Herat (1837–38)
* Third siege of El Callao (:es:Tercer sitio del Callao, es) (1838)
* Siege of Akhoulgo (1839)
* Great Siege of Montevideo (1843–1851)
* Siege of Fort Texas (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Riga (1812) – French invasion of Russia
* Siege of Fort Mackinac (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Detroit (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Harrison (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Wayne (1812) – War of 1812
* Siege of Burgos (1812) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Danzig (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Acapulco (1813) – Mexican War of Independence
* Siege of Fort Meigs (1813) – failed British siege of American garrison during the War of 1812
* Siege of Tarragona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Pamplona (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of San Sebastián (1813) – Peninsular War
* Siege of Chillán (1813) – Chilean War of Independence
* Second siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1813), es) (1813) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cattaro (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Mainz (1814), Siege of Mainz (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Zara (1813) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Maturin (:es:Batalla de Maturin, es) (1813–1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Hamburg (1813–1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Metz (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Third siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1814), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Ragusa (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* Siege of Bergen op Zoom (1814) – War of the Sixth Coalition
* First siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Valencia (Venezuela) (:es:Segundo Asedio de Valencia (Venezuela), es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Prairie du Chien (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Fort Erie (1814) – War of 1812
* Siege of Aragua de Barcelona (:es: Batalla de Aragua de Barcelona, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Santa Fe de Bogotá (:es:Asedio de Santafé de Bogotá, es) (1814) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Fort St. Philip (1815) – War of 1812
* Siege of Ancona (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Gaeta (1815) – Neapolitan War
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1815), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias, es) (1815) – List of wars 1800–99, Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of Angostura (:es:Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Second siege of Angostura (:es:Segunda Batalla de Angostura, es) (1817) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Cartagena de Indias (1820-21), Siege of Cartagena de Indias (:es:Asedio de Cartagena de Indias (1820–1821), es) (1820–21) – Spanish American wars of independence
* First siege of El Callao (:es:Primer sitio del Callao, es) (1821) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Tripolitsa (1821) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1821–22) – by the Greeks against the Ottomans, during the Greek War of Independence
* Fourth siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1822), es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pasto (:es: Batalla de Bombona, es) (1822) – Spanish American wars of independence
* San Felipe Castle, Fifth Siege of Puerto Cabello (1823) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of Pamplona (1823) – Hundred Thousand Sons of Saint Louis, 1823 French invasion of Spain
* Siege of Messolonghi (1825), First, second, and third sieges of Missolonghi (1822, 1823, 1825–1826)
* Second siege of El Callao (:es:Segundo sitio del Callao, es) (1824–1826) – Spanish American wars of independence
* Siege of the Acropolis (1826–27) – by the Ottomans against the Greeks, during the Greek War of Independence
* Siege of Antwerp (1832) – conducted by French forces against a Dutch garrison after the Ten Days' Campaign.
* Siege of Jerusalem (1834) Peasants' Revolt of 1834 (Palestine)
* Siege of Puerto Cabello (:es:Asedio de Puerto Cabello (1835), es) (1835) – Reforms Revolution (Venezuela)
* Battle of the Alamo, Siege of the Alamo (1836) – Texas Revolution
* Siege of Herat (1838), Siege of Herat (1837–38)
* Third siege of El Callao (:es:Tercer sitio del Callao, es) (1838)
* Siege of Akhoulgo (1839)
* Great Siege of Montevideo (1843–1851)
* Siege of Fort Texas (1846) – Mexican–American War
 * Siege of Los Angeles (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Pueblo de Taos (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Puebla (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Veracruz (1847) – Mexican–American War. First U.S. amphibious warfare, amphibious landing
* Siege of San José del Cabo (1848) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Peschiera del Garda (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Osoppo (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Venice (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Rome (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Buda (1849), Siege of Buda (1849) – during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848–49
* Siege of La Serena (1851) – 1851 Chilean Revolution
* Siege of Calafat (1854) – Crimean War
* Siege of Los Angeles (1846) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Pueblo de Taos (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Puebla (1847) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Veracruz (1847) – Mexican–American War. First U.S. amphibious warfare, amphibious landing
* Siege of San José del Cabo (1848) – Mexican–American War
* Siege of Peschiera del Garda (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Osoppo (1848) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Venice (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Rome (1849) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Buda (1849), Siege of Buda (1849) – during the Hungarian Revolution of 1848–49
* Siege of La Serena (1851) – 1851 Chilean Revolution
* Siege of Calafat (1854) – Crimean War
 * Siege of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (1854)
* Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55) – Crimean War
* Siege of Taganrog (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Kars (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Medina Fort (1857) – Toucouleur Empire, Toucouleurs besiege French Army, French for 97 days
* Siege of Delhi (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Cawnpore (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Lucknow (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Arrah (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Central India Campaign (1858), Siege of Jhansi (1858) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
*Siege of Đà Nẵng (1858–1860)
* Siege of Tourane (1858–1860)
* Siege of Saigon (1859)
* Siege of Ancona (1860) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Messina (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Civitella del Tronto (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Gaeta (1860–1861) – Italian Risorgimento
*Battle of Fort Sumter, Siege of Fort Sumter (1861) – Union soldiers in Fort Sumter surrendered after a few days of bombardment by Confederate forces starting the American Civil War.
* Siege of Tubac (1861) – Apache Wars
* Capture of New Orleans, Siege of New Orleans (1862) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War
* Siege of Vicksburg (1863) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War.
* Siege of Port Hudson (1863) – Union Army surrounded Confederate river stronghold for 48 days.
* Siege of Puebla (1863) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Petersburg (1864–1865) – American Civil War
* Siege of Fort Ampola (1866) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Callao, Fourth siege of El Callao (1866) – naval battle between Spain and Peru (and her allies)
* Siege of Querétaro (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Mexico City (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Battle of Hakodate, Siege of Hakodate (1869)
* Siege of Petropavlovsk-Kamchatsky (1854)
* Siege of Sevastopol (1854–55) – Crimean War
* Siege of Taganrog (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Kars (1855) – Crimean War
* Siege of Medina Fort (1857) – Toucouleur Empire, Toucouleurs besiege French Army, French for 97 days
* Siege of Delhi (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Cawnpore (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Lucknow (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Siege of Arrah (1857) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
* Central India Campaign (1858), Siege of Jhansi (1858) – Indian Rebellion of 1857
*Siege of Đà Nẵng (1858–1860)
* Siege of Tourane (1858–1860)
* Siege of Saigon (1859)
* Siege of Ancona (1860) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Messina (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Civitella del Tronto (1860–61) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Gaeta (1860–1861) – Italian Risorgimento
*Battle of Fort Sumter, Siege of Fort Sumter (1861) – Union soldiers in Fort Sumter surrendered after a few days of bombardment by Confederate forces starting the American Civil War.
* Siege of Tubac (1861) – Apache Wars
* Capture of New Orleans, Siege of New Orleans (1862) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War
* Siege of Vicksburg (1863) – Union Army besieged a Confederate States of America, Confederate city in the American Civil War.
* Siege of Port Hudson (1863) – Union Army surrounded Confederate river stronghold for 48 days.
* Siege of Puebla (1863) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Petersburg (1864–1865) – American Civil War
* Siege of Fort Ampola (1866) – Italian Risorgimento
* Battle of Callao, Fourth siege of El Callao (1866) – naval battle between Spain and Peru (and her allies)
* Siege of Querétaro (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Siege of Mexico City (1867) – Second French intervention in Mexico
* Battle of Hakodate, Siege of Hakodate (1869)
 * Capture of Rome (1870) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Strasbourg (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Toul (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Metz (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris and the Paris Commune (1870–71)
* Siege of Belfort (1870–71) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena (1873–1874)
* Siege of Pamplona (1874) – First Spanish Republic
* Siege of Plevna (1877–1878) – Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
* Battle of Bear Paw, Siege of the Bears Paw (1877) – final engagement of the Nez Perce War.
* Siege of Eshowe (1879) – Anglo–Zulu War
* Bombardment of Callao, Fifth siege of El Callao (1880) – Chilean naval
* Capture of Rome (1870) – Italian Risorgimento
* Siege of Strasbourg (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Toul (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Metz (1870) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Paris (1870–71), Siege of Paris and the Paris Commune (1870–71)
* Siege of Belfort (1870–71) – Franco-Prussian War
* Siege of Cartagena, Spain, Cartagena (1873–1874)
* Siege of Pamplona (1874) – First Spanish Republic
* Siege of Plevna (1877–1878) – Russo-Turkish War (1877–78), Russo-Turkish War (1877–78)
* Battle of Bear Paw, Siege of the Bears Paw (1877) – final engagement of the Nez Perce War.
* Siege of Eshowe (1879) – Anglo–Zulu War
* Bombardment of Callao, Fifth siege of El Callao (1880) – Chilean naval blockade
A blockade is the act of actively preventing a country or region from receiving or sending out food, supplies, weapons, or communications, and sometimes people, by military force.
A blockade differs from an embargo or sanction, which are leg ...
and bombardment of El Callao (Peru), during the War of the Pacific
* Battle of Miraflores, Siege of Miraflores (1880) – Chilean siege of Lima (Peru), during the War of the Pacific
* Siege of Marabastad (1881) – First Boer War
* Siege of Khartoum (1884–85) – Mahdist War
* Siege of Tuyên Quang (1884–85) – Sino-French War
*Siege of Lapa (1893) – Federalist Revolution
* Battle of Mek'ele, Siege of Mek'elè (1896) – First Italo-Ethiopian War
* Siege of Santiago (1898) – Spanish–American War
*Bombardment of San Juan, First siege of San Juan (1898) – Spanish–American War
*Second Battle of San Juan (1898), Second siege of San Juan (1898) – Spanish–American War
*Spanish–American War, Siege of Manila (1898) – Spanish–American War
* Siege of Baler (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
* Siege of Masbate (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
 * Siege of Zamboanga (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
* Battle of Bucaramanga (1899), Siege of Bucaramanga (1899) – Thousand Days' War (Colombia)
* Siege of Mafeking (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Kimberley (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Ladysmith (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Zamboanga (1898–99) – Philippine Revolution
* Battle of Bucaramanga (1899), Siege of Bucaramanga (1899) – Thousand Days' War (Colombia)
* Siege of Mafeking (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Kimberley (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
* Siege of Ladysmith (1899–1900) – Second Boer War
20th century
* Siege of the International Legations (1900) – Boxer Rebellion * Battle of San Cristobal, Siege of San Cristobal (1901) – Thousand Days' War (Venezuela) * :es:Batalla de La Victoria (1902), Siege of La Victoria (1902)- Revolución Libertadora (Venezuela) * Venezuelan crisis of 1902–03, Siege of Puerto Cabello (1902–1903)- Naval blockade of Venezuela * Venezuelan crisis of 1902–03, Siege of La Guaira (1902–1903)- Naval blockade of Venezuela * Bombardment of Fort San Carlos, Siege of Castle San Carlos (1903)- Naval blockade of Venezuela * :es:Batalla de Ciudad Bolivar (1903), Siege of Ciudad Bolivar (1903)- Revolución Libertadora (Venezuela) * Siege of Port Arthur (1904–05) Russo-Japanese War * Siege of Scutari (1912–13) – First Balkan War * Siege of Adrianople (1912–13), Siege of Adrianople (1912–13) – First Balkan War * Siege of Vidin (1913) – Second Balkan War
* United States occupation of Veracruz, Siege of Veracruz (1914)
* Battle of Liège (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Namur (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Maubeuge (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Toma (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Przemyśl (1914–15) – World War I
* Siege of Antwerp (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Tsingtao (1914) – World War I
* Defense of Van (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Novogeorgievsk (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Kut (1915–16) – World War I
* Siege of Medina (1916–19) – World War I
* Battle of Jerusalem (1917) – World War I
* Siege of Najaf (1918) – World War I
* Siege of Aintab (1920–1921) – Franco-Turkish War
* Siege of Perekop (1920) – Russian Civil War
* Siege of Naco (1929) – Escobar Rebellion
* Siege of Cuartel de la Montaña (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Cuartel de Loyola (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gijón (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Oviedo (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of the Alcázar (1936) – Second Spanish Republic militias besieged the Alcázar of Toledo in the Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Santuario de Nuestra Señora de la Cabeza (1936–1937) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Madrid (1936–1939) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gandesa (1938) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Warsaw (1939) – World War II
* Battle of Hegra Fortress, Siege of Hegra Fortress (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Calais (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Lille (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Malta (World War II), Siege of Malta (1940–1943)– World War II
* Siege of Vidin (1913) – Second Balkan War
* United States occupation of Veracruz, Siege of Veracruz (1914)
* Battle of Liège (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Namur (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Maubeuge (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Toma (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Przemyśl (1914–15) – World War I
* Siege of Antwerp (1914) – World War I
* Siege of Tsingtao (1914) – World War I
* Defense of Van (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Novogeorgievsk (1915) – World War I
* Siege of Kut (1915–16) – World War I
* Siege of Medina (1916–19) – World War I
* Battle of Jerusalem (1917) – World War I
* Siege of Najaf (1918) – World War I
* Siege of Aintab (1920–1921) – Franco-Turkish War
* Siege of Perekop (1920) – Russian Civil War
* Siege of Naco (1929) – Escobar Rebellion
* Siege of Cuartel de la Montaña (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Cuartel de Loyola (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gijón (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Oviedo (1936) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of the Alcázar (1936) – Second Spanish Republic militias besieged the Alcázar of Toledo in the Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Santuario de Nuestra Señora de la Cabeza (1936–1937) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Madrid (1936–1939) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Gandesa (1938) – Spanish Civil War
* Siege of Warsaw (1939) – World War II
* Battle of Hegra Fortress, Siege of Hegra Fortress (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Calais (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Lille (1940) – World War II
* Siege of Malta (World War II), Siege of Malta (1940–1943)– World War II
21st century
* Siege of Kunduz (2001) – War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) * Siege of the Church of the Nativity in Bethlehem (2002) – Second Intifada * Siege of Monrovia (2003) – Second Liberian Civil War * Siege of Sadr City (2004–2008) – Iraq War * Siege of Sangin (2006–2007) – War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) * Siege of Musa Qala (2006) – War in Afghanistan (2001–2021) * CIMIC-House, Siege of Al Amarah (2006) – Iraq War * Siege of UK bases in Basra (2007) – Iraq War * Siege of Nahr el-Bared (2007) – Lebanon * Blockade of the Gaza Strip (2007–present) – Gaza Strip * Siege of Lal Masjid (2007) – War in North-West Pakistan * Siege of Misrata (2011) – 2011 Libyan Civil War, Libyan Civil War * Siege of Daraa (2011) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Homs (2011–2014) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Baniyas (2011) – Syrian Civil War * May 2011 Talkalakh siege, Siege of Talkalakh (2011) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Rastan and Talbiseh (2011) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Hama (2011) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Latakia (2011) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Dammaj (2011–12, 2013–14) – Yemeni Revolution / Houthi insurgency in Yemen * Battle of Aleppo (2012–2016), Siege of Aleppo (2012–2016) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Nubl and Al-Zahraa (2012–2016) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Menagh Air Base (2012–2013) – Syrian Civil War * Siege of Bani Walid (2012) – Factional violence in Libya (2011–14) * First siege of Wadi Deif (2012–2013) – Syrian Civil War
* Zamboanga City crisis (2013) – Moro conflict
* Ghouta, Siege of Eastern Ghouta (2013–2018) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of PK5 district (2013-2020) – Central African Republic Civil War (2012-present)
* Siege of Wadi Barada (2013–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Second siege of Wadi Deif (2014) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Sloviansk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of the Luhansk Border Base (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Amirli (2014) – Iraqi civil war (2014–present), Iraqi Civil War
* Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–17), Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Battle of Ilovaisk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Kobanî (2014–2015) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015), Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Cizre operation (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Silvan (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Sur (2016), Siege of Sur (2015–2016) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* December 2015–February 2016 Cizre curfew, Siege of Cizre (2015–2016) Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Fallujah (2016) – Iraqi Civil War
* First siege of Wadi Deif (2012–2013) – Syrian Civil War
* Zamboanga City crisis (2013) – Moro conflict
* Ghouta, Siege of Eastern Ghouta (2013–2018) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of PK5 district (2013-2020) – Central African Republic Civil War (2012-present)
* Siege of Wadi Barada (2013–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Second siege of Wadi Deif (2014) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Sloviansk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of the Luhansk Border Base (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Amirli (2014) – Iraqi civil war (2014–present), Iraqi Civil War
* Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–17), Siege of Deir ez-Zor (2014–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Battle of Ilovaisk (2014) – Russo-Ukrainian War
* Siege of Kobanî (2014–2015) – Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015), Siege of Al-Fu'ah-Kafriya (2015–2017) – Syrian Civil War
* Cizre operation (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Silvan (2015) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Sur (2016), Siege of Sur (2015–2016) – Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* December 2015–February 2016 Cizre curfew, Siege of Cizre (2015–2016) Kurdish–Turkish conflict (2015–present)
* Siege of Fallujah (2016) – Iraqi Civil War
 * Siege of Derna (2016–2018) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Mosul (2016–17), Siege of Mosul (2016–2017) – Iraqi Civil War
* Battle of Tabqa (2017), Siege of Tabqa (2017) – Syrian Civil War
* 2014–17 Venezuelan protests, Siege of Miraflores (2017) – Venezuelan political and civil Crisis
* Marawi crisis (2017) – Philippine war against insurgency
* Battle of Benghazi (2014–2017)#Sidi Akribesh siege, Siege of Sidi Akribesh (2017) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Baghuz Fawqani, Siege of Baghuz Fawqani – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Battle of the Jabara Valley, Siege of the Jabara Valley (2019) – Yemeni Civil War (2015–present), Yemeni Civil War
* Battle of Ras al-Ayn (2019), Siege of Ras al-Ayn – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Qamishli and Al-Hasakah (2021) – Syrian Civil War
* Panjshir conflict, Siege of Panjshir (2021) – Aftermath of the War in Afghanistan (2001-2021)
* Siege of Chernihiv (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Mariupol (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Derna (2016–2018) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Mosul (2016–17), Siege of Mosul (2016–2017) – Iraqi Civil War
* Battle of Tabqa (2017), Siege of Tabqa (2017) – Syrian Civil War
* 2014–17 Venezuelan protests, Siege of Miraflores (2017) – Venezuelan political and civil Crisis
* Marawi crisis (2017) – Philippine war against insurgency
* Battle of Benghazi (2014–2017)#Sidi Akribesh siege, Siege of Sidi Akribesh (2017) – Libyan Civil War (2014–present)
* Battle of Baghuz Fawqani, Siege of Baghuz Fawqani – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Battle of the Jabara Valley, Siege of the Jabara Valley (2019) – Yemeni Civil War (2015–present), Yemeni Civil War
* Battle of Ras al-Ayn (2019), Siege of Ras al-Ayn – (2019) Syrian Civil War
* Siege of Qamishli and Al-Hasakah (2021) – Syrian Civil War
* Panjshir conflict, Siege of Panjshir (2021) – Aftermath of the War in Afghanistan (2001-2021)
* Siege of Chernihiv (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
* Siege of Mariupol (2022) – Russo-Ukrainian War (2022)
Police sieges
A police siege is a standoff between law enforcement officers and armed criminals, suspects, or protesters. * Siege of Sidney Street (1911) England * Attica Prison riots, Attica Siege (1971) United States of America * Munich Olympic massacre (1972) Germany * Wounded Knee Incident (1973) United States of America * Norrmalmstorg robbery (1973) famous for the Stockholm syndrome Sweden * Huntsville Prison siege (1974) United States of America * Spaghetti House siege (1975) England * Balcombe Street Siege (1975) England * 1977 Washington, D.C. attack and hostage taking, Hanafi Siege (1977) United States of America * MOVE (Philadelphia organization), MOVE Siege (1978) United States of America * Iranian Embassy Siege (1980) England * Murder of Yvonne Fletcher#Siege: 18–27 April 1984, Siege of the Libyan Embassy in London (1984) United Kingdom * Palace of Justice siege (1985) Colombia * Oka Crisis (1990) Quebec, Canada * Ruby Ridge Siege (1992) United States of America * Waco Siege (1993) United States of America * Chiapas conflict (1994–present) Chiapas, Mexico * Gustafsen Lake Standoff (1995) British Columbia, Canada * Montana Freemen Siege (1996) United States of America * Japanese embassy hostage crisis (1996–1997) Peru * Republic of Texas (group), Republic of Texas Embassy Siege (1997) United States of America * Moscow theater hostage crisis (2002) Russia * Beslan hostage crisis (2004) Russia * Napier shootings (2009) New Zealand * Siege of Complexo do Alemão's slums, major urban conflict in Rio de Janeiro (2010) Brazil * 2011 Hectorville siege, Hectorville siege (2011) Australia * Wukan protests (2011) China * Siege of Eker (2012) Bahrain * 2014 Sydney hostage crisis, Sydney hostage crisis (2014) Australia * Hypercacher kosher supermarket siege (2015) France * 2016 Yerevan hostage crisis (2016) Armenia * 2017 Kidapawan jail siege, Kidapawan jail siege (2017) Philippines * 2017 Brighton siege, Brighton siege (2017) Australia * 2019 Chinese University of Hong Kong conflict, Siege of the Chinese University of Hong Kong (2019) * 2019 Hong Kong Polytechnic University conflict, Siege of the Hong Kong Polytechnic University (2019)Other
* Gwangju uprising (1980) South Korea * Storming of the Legislative Council Complex (2019) Hong KongReferences
{{Reflist Lists of battles, Sieges Sieges, *List