List of historic states of Italy on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Italy, up until the
 *
*
 *
*


* Agugliastra
*


 The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended the
The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended the
 Following the European wars of succession of the 18th century and the extinction of the
Following the European wars of succession of the 18th century and the extinction of the
 *
*
*
* Journal of the Private Life and Conversations of the Emperor, Vol. 3
Emmanuel-Auguste-Dieudonne comte de Las Cases. 1816. *
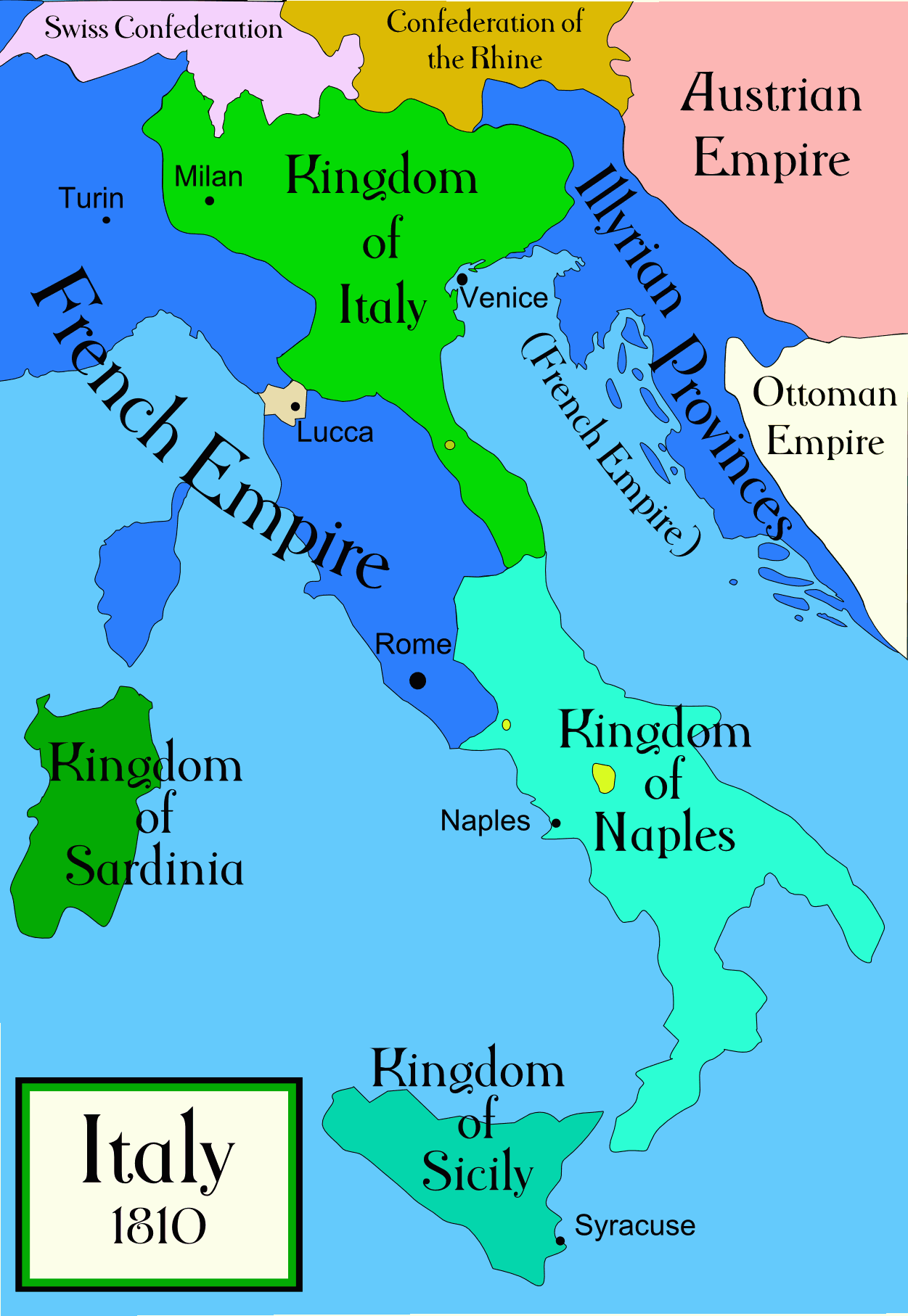
 Following the defeat of Napoleon's France, the
Following the defeat of Napoleon's France, the

 *
*
Italian unification
The unification of Italy ( it, Unità d'Italia ), also known as the ''Risorgimento'' (, ; ), was the 19th-century political and social movement that resulted in the consolidation of different states of the Italian Peninsula into a single ...
in 1861, was a conglomeration of city-states, republics, and other independent entities. The following is a list of the various Italian states during that period. Following the fall of the Western Roman Empire
The Western Roman Empire comprised the western provinces of the Roman Empire at any time during which they were administered by a separate independent Imperial court; in particular, this term is used in historiography to describe the period ...
and the arrival of the Middle Ages (in particular from the 11th century), the Italian peninsula was divided into numerous states. Many of these states consolidated into major political units that balanced the power on the Italian peninsula: the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
, the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
, the Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Fl ...
, the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
, the Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
and the Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
. Unlike all the other Italian states, the republics of Venice and Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
, thanks to their maritime powers, went beyond territorial conquests within the Italian peninsula, conquering various regions across the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
and Black Seas.
Archaic Italy
Italic peoples
The Italic peoples were an ethnolinguistic group identified by their use of Italic languages, a branch of the Indo-European language family.
The Italic peoples are descended from the Indo-European speaking peoples who inhabited Italy from at lea ...
:
** Latino-Faliscans:
*** Latins
The Latins were originally an Italic tribe in ancient central Italy from Latium. As Roman power and colonization spread Latin culture during the Roman Republic.
Latins culturally "Romanized" or "Latinized" the rest of Italy, and the word Latin ...
(Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom (also referred to as the Roman monarchy, or the regal period of ancient Rome) was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began wi ...
)
**** Romans
*** Falisci
** Osco-Umbrians, also called Sabellians:
*** Umbrians
**** Marsi
The Marsi were an Italic people of ancient Italy, whose chief centre was Marruvium, on the eastern shore of Lake Fucinus (which was drained for agricultural land in the late 19th century). The area in which they lived is now called Marsica. D ...
**** Umbri
The Umbri were an Italic people of ancient Italy. A region called Umbria still exists and is now occupied by Italian speakers. It is somewhat smaller than the ancient Umbria.
Most ancient Umbrian cities were settled in the 9th-4th centuries BC on ...
**** Volsci
The Volsci (, , ) were an Italic tribe, well known in the history of the first century of the Roman Republic. At the time they inhabited the partly hilly, partly marshy district of the south of Latium, bounded by the Aurunci and Samnites on the ...
*** Oscans
**** Marrucini
The Marrucini were an Italic tribe that occupied a small strip of territory around the ancient ''Teate'' (modern Chieti), on the east coast of Abruzzo, Italy, limited by the Aterno and Foro Rivers. Other Marrucinian centers included ''Ceio'' ( Sa ...
**** Osci
The Osci (also called Oscans, Opici, Opsci, Obsci, Opicans) were an Italic people of Campania and Latium adiectum before and during Roman times. They spoke the Oscan language, also spoken by the Samnites of Southern Italy. Although the languag ...
***** Aurunci
The Aurunci were an Italic tribe that lived in southern Italy from around the 1st millennium BC. They were eventually defeated by Rome and subsumed into the Roman Republic during the second half of the 4th century BC.
Identity
Aurunci is the n ...
***** Ausones
"Ausones" (; ), the original Greek form for the Latin "Aurunci", was a name applied by Greek writers to describe various Italic peoples inhabiting the southern and central regions of Italy. The term was used, specifically, to denote the partic ...
***** Campanians {{Short description, Ancient Italic tribe
The Campanians (also Campani) were an ancient Italic tribe, part of the Osci nation, speaking an Oscan language.
Descending from the Apennines, the proto-Osci settled in the areas of present-day Campani ...
**** Paeligni
**** Sabines
The Sabines (; lat, Sabini; it, Sabini, all exonyms) were an Italic people who lived in the central Apennine Mountains of the ancient Italian Peninsula, also inhabiting Latium north of the Anio before the founding of Rome.
The Sabines di ...
*** Samnitics
**** Bruttii The Bruttians (alternative spelling, Brettii) ( la, Bruttii) were an ancient Italic people. They inhabited the southern extremity of Italy, from the frontiers of Lucania to the Sicilian Straits and the promontory of Leucopetra. This roughly corr ...
**** Frentani
**** Lucani
**** Samnites
The Samnites () were an ancient Italic people who lived in Samnium, which is located in modern inland Abruzzo, Molise, and Campania in south-central Italy.
An Oscan-speaking people, who may have originated as an offshoot of the Sabines, they f ...
***** Pentri
***** Caraceni
***** Caudini The Caudini were a Samnite tribe that lived among the mountains ringing Campania and in the valleys of the Isclero and Volturnus rivers. Their capital was at Caudium, but it seems certain that the appellation was not confined to the citizens of Ca ...
***** Hirpini
The Hirpini ( Latin: ') were an ancient Samnite tribe of Southern Italy. While generally regarded as having been Samnites, sometimes they are treated as a distinct and independent nation. They inhabited the southern portion of Samnium, in the mo ...
*** Others
****Aequi
300px, Location of the Aequi (Equi) in central Italy, 5th century BC.
The Aequi ( grc, Αἴκουοι and Αἴκοι) were an Italic tribe on a stretch of the Apennine Mountains to the east of Latium in central Italy who appear in the early hist ...
**** Fidenates
**** Hernici
**** Picentes
**** Vestini
**** Sicels
The Sicels (; la, Siculi; grc, Σικελοί ''Sikeloi'') were an Italic tribe who inhabited eastern Sicily during the Iron Age. Their neighbours to the west were the Sicani. The Sicels gave Sicily the name it has held since antiquity, b ...
**** Venetics
**** Ligures
The Ligures (singular Ligur; Italian: liguri; English: Ligurians) were an ancient people after whom Liguria, a region of present-day north-western Italy, is named.
Ancient Liguria corresponded more or less to the current Italian regi ...
* Greek-speaking peoples of Southern Italy
*Etruscans
The Etruscan civilization () was developed by a people of Etruria in ancient Italy with a common language and culture who formed a federation of city-states. After conquering adjacent lands, its territory covered, at its greatest extent, roug ...
* Sardinians
Classical Italy
 *
* Roman Kingdom
The Roman Kingdom (also referred to as the Roman monarchy, or the regal period of ancient Rome) was the earliest period of Roman history when the city and its territory were ruled by kings. According to oral accounts, the Roman Kingdom began wi ...
* Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
* Roman Empire
The Roman Empire ( la, Imperium Romanum ; grc-gre, Βασιλεία τῶν Ῥωμαίων, Basileía tôn Rhōmaíōn) was the post-Roman Republic, Republican period of ancient Rome. As a polity, it included large territorial holdings aro ...
Early Middle Ages
*Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
* Ostrogothic Kingdom
The Ostrogothic Kingdom, officially the Kingdom of Italy (), existed under the control of the Germanic Ostrogoths in Italy and neighbouring areas from 493 to 553.
In Italy, the Ostrogoths led by Theodoric the Great killed and replaced Odoacer, ...
* Lombard Kingdom
The Kingdom of the Lombards ( la, Regnum Langobardorum; it, Regno dei Longobardi; lmo, Regn di Lombard) also known as the Lombard Kingdom; later the Kingdom of (all) Italy ( la, Regnum totius Italiae), was an early medieval state established ...
* Duchy of Rome
The Duchy of Rome ( la, Ducatus Romanus) was a state within the Byzantine Exarchate of Ravenna. Like other Byzantine states in Italy, it was ruled by an imperial functionary with the title ''dux''. The duchy often came into conflict with the Pap ...
(under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
)
* Exarchate of Ravenna
The Exarchate of Ravenna ( la, Exarchatus Ravennatis; el, Εξαρχάτο της Ραβέννας) or of Italy was a lordship of the Eastern Roman Empire (Byzantine Empire) in Italy, from 584 to 751, when the last exarch was put to death by the ...
(under the Byzantine Empire)
* Exarchate of Carthage (under the Byzantine Empire)
* Thema of Sicily (under the Byzantine Empire)
* Duchy of Benevento
* Duchy of Spoleto
The Duchy of Spoleto (, ) was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard '' dux'' Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.
Lombards
The Lombards had invaded Italy in 568 AD and conquered much of it, establishi ...
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
*Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples ( la, Ducatus Neapolitanus, it, Ducato di Napoli) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in ...
* Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
(under the Carolingian Empire
The Carolingian Empire (800–888) was a large Frankish-dominated empire in western and central Europe during the Early Middle Ages. It was ruled by the Carolingian dynasty, which had ruled as kings of the Franks since 751 and as kings of the L ...
)
* Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire)
High Middle Ages
States in Central and Northern Italy
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
* Republic of Pisa
The Republic of Pisa ( it, Repubblica di Pisa) was an independent state centered on the Tuscan city of Pisa, which existed from the 11th to the 15th century. It rose to become an economic powerhouse, a commercial center whose merchants dominated ...
* Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Fl ...
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Siena
* Republic of Ancona
* Republic of Noli
* Republic of Senarica
Senarica is a village in the Abruzzo region of central Italy. With a population of fewer than 300 people, Senarica was an independent republic for about four centuries until the end of the eighteenth century. It was the smallest state to maintain ...
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' ...
* Republic of San Marino
States in Southern Italy
* Principality of Benevento *Principality of Salerno
The Principality of Salerno ( la, Principatus Salerni) was a medieval Southern Italian state, formed in 851 out of the Principality of Benevento after a decade-long civil war. It was centred on the port city of Salerno. Although it owed al ...
* Catepanate of Italy (under the Byzantine Empire
The Byzantine Empire, also referred to as the Eastern Roman Empire or Byzantium, was the continuation of the Roman Empire primarily in its eastern provinces during Late Antiquity and the Middle Ages, when its capital city was Constantinopl ...
)
* Principality of Capua
The Principality of Capua ( la, italic=yes, Principatus Capuae or ''Capue'', it, italic=yes, Principato di Capua) was a Lombard state centred on Capua in Southern Italy, usually ''de facto'' independent, but under the varying suzerainty of ...
* Duchy of Gaeta
* Duchy of Naples
The Duchy of Naples ( la, Ducatus Neapolitanus, it, Ducato di Napoli) began as a Byzantine province that was constituted in the seventh century, in the reduced coastal lands that the Lombards had not conquered during their invasion of Italy in ...
* Duchy of Amalfi
The Duchy of Amalfi () or the Republic of Amalfi was a ''de facto'' independent state centered on the Southern Italian city of Amalfi during the 10th and 11th centuries. The city and its territory were originally part of the larger ''ducatus Nea ...
* Duchy of Sorrento
The Duchy of Sorrento was a small peninsular duchy of the Early Middle Ages centred on the Italian city of Sorrento.
Established in the 7th century as a fief of the Duchy of Naples, at the time still part of the Byzantine Empire.
Subsequently ...
* Emirate of Sicily
The Emirate of Sicily ( ar, إِمَارَة صِقِلِّيَة, ʾImārat Ṣiqilliya) was an Islamic kingdom that ruled the island of Sicily from 831 to 1091. Its capital was Palermo (Arabic: ''Balarm''), which during this period became ...
(under the Fatimid Caliphate
The Fatimid Caliphate was an Ismaili Shi'a caliphate extant from the tenth to the twelfth centuries AD. Spanning a large area of North Africa, it ranged from the Atlantic Ocean in the west to the Red Sea in the east. The Fatimids, a ...
)
* County of Sicily
* County of Apulia
The County of Apulia and Calabria (), later the Duchy of Apulia and Calabria (), was a Norman state founded by William of Hauteville in 1042 in the territories of Gargano, Capitanata, Apulia, Vulture, and most of Campania. It became a duchy when ...
* Duchy of Apulia
* Duchy of Calabria
* Duchy of Apulia and Calabria
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
States of the Holy Roman Empire
*Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
(also called Kingdom of Lombardy)
* Commune of Milan
* March of Tuscany
The March of Tuscany ( it, Marca di Tuscia; ) was a march of the Kingdom of Italy and the Holy Roman Empire during the Middle Ages. Located in northwestern central Italy, it bordered the Papal States to the south, the Ligurian Sea to the we ...
* March of Verona
The March of Verona and Aquileia was a vast Marches, march (frontier district) of the Holy Roman Empire in the northeastern Italian peninsula during the Middle Ages, centered on the cities of Verona and Aquileia. Seized by King Otto I, Holy Roman ...
* March of Treviso
The March of Treviso ( la, Marca trevisana, it, Marca trevigiana or ) was a medieval territory in Venetia, between the Garda and the Julian March. The territory corresponded roughly to the region around the city of Treviso, including Belluno, F ...
* March of Ivrea
* March of Turin
* March of Montferrat
* March of Genoa The March of Genoa or Eastern Liguria was created in 961 by the Emperor Otto I. It was originally called either the ''marca Obertenga'' after its first holder, Oberto I, or the ''marca Januensis'' after its original capital and chief city, Genoa. I ...
* Patriarchate of Aquileia (including March of Friuli
The March of Friuli was a Carolingian frontier march, established in 776 as the continuation of the Lombard Duchy of Friuli, established against the Slavs and Avars. It was ceded to the Duchy of Bavaria as the March of Verona in 952. Its territ ...
and March of Istria
The March of Istria (or Margraviate of Istria ) was originally a Carolingian frontier march covering the Istrian peninsula and surrounding territory conquered by Charlemagne's son Pepin of Italy in 789. After 1364, it was the name of the Istrian ...
)
* Duchy of Spoleto
The Duchy of Spoleto (, ) was a Lombard territory founded about 570 in central Italy by the Lombard '' dux'' Faroald. Its capital was the city of Spoleto.
Lombards
The Lombards had invaded Italy in 568 AD and conquered much of it, establishi ...
* Bishopric of Brixen
The Prince-Bishopric of Brixen (german: Hochstift Brixen, Fürstbistum Brixen, Bistum Brixen) was an ecclesiastical principality of the Holy Roman Empire in the present-day northern Italian province of South Tyrol. It should not be confused wi ...
* Bishopric of Trent
* County of Savoy
* County of Gorizia
The County of Gorizia ( it, Contea di Gorizia, german: Grafschaft Görz, sl, Goriška grofija, fur, Contee di Gurize), from 1365 Princely County of Gorizia, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. Originally mediate ''Vogts'' of the Patriarchs of ...
* Marquisate of Saluzzo
* Marquisate of Ceva
* Marquisate of Incisa
* Marquisate of FinaleArborea
Arborea is a town and '' comune'' in the province of Oristano, Sardinia, Italy, whose economy is largely based on agriculture and cattle breeding with production of vegetables, rice, fruit and milk (notably the local milk product Arborea).
Hi ...
* Cagliari
Cagliari (, also , , ; sc, Casteddu ; lat, Caralis) is an Italian municipality and the capital of the island of Sardinia, an autonomous region of Italy. Cagliari's Sardinian name ''Casteddu'' means ''castle''. It has about 155,000 inhabitant ...
* Gallura
Gallura ( sdn, Gaddura or ; sc, Caddura ) is a region in North-Eastern Sardinia, Italy.
The name ''Gallùra'' is allegedly supposed to mean "stony area".
Geography
Gallùra has a surface of and it is situated between 40°55'20"64 latitude ...
* Logudoro
Late Middle Ages


Major States
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
* Republic of Florence
The Republic of Florence, officially the Florentine Republic ( it, Repubblica Fiorentina, , or ), was a medieval and early modern state that was centered on the Italian city of Florence in Tuscany. The republic originated in 1115, when the Fl ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
Minor States
*Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
* Kingdom of Sardinia and Corsica
* Duchy of Ferrara
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Prince-Bishopric of Trent
* Marquisate of Saluzzo
* Marquisate of Montferrat
* Rebel city-states in Papal States
* Marquisate of Mantua
* Marquisate of Massa
* Marquisate of Finale
* Marquisate of Incisa
* Marquisate of Ceva
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Bastia
* County of Savoy (raised to Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
in 1416)
* County of Urbino (raised to Duchy of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino was an independent duchy in early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1625.
It was bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the east ...
in 1443)
* County of Mirandola
* Golden Ambrosian Republic
,
it, Aurea Repubblica Ambrosiana
, era = Late Middle Ages
, government_type = Directorial republic
, p1 = Duchy of Milan
, flag_p1 = Flag of the Duchy of Milan (1450).svg
, s1 ...
* County of Guastalla
The County of Guastalla was a feudal state in northern Italy, centered on Guastalla. The title of count was created in 1406 for Guido Torelli.
The Torelli family ruled Guastalla until 1539 when it was purchased by Ferrante Gonzaga. Another bran ...
* County of Nice
The County of Nice (french: Comté de Nice / Pays Niçois, it, Contea di Nizza/Paese Nizzardo, Niçard oc, Contèa de Niça/País Niçard) is a historical region of France located around the southeastern city of Nice and roughly equivalent t ...
(in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with Savoy)
* County of Gorizia
The County of Gorizia ( it, Contea di Gorizia, german: Grafschaft Görz, sl, Goriška grofija, fur, Contee di Gurize), from 1365 Princely County of Gorizia, was a State of the Holy Roman Empire. Originally mediate ''Vogts'' of the Patriarchs of ...
* County of Montechiarugolo
The County of Montechiarugolo was a small sovereign state of northern Italy which existed from 1456 to 1612. It included the other fief of Casei.
It was created from a splitting in the county of Guastalla between count Cristoforo Torelli and Pie ...
* County of Santa Fiora
The County of Santa Fiora ( it, Contea di Santa Fiora), also known as State of Santa Fiora ( it, Stato di Santa Fiora, links=no) was a small historical state of southern Tuscany, in central Italy. Together with the county of Sovana, it was one of ...
* County of Asti
Asti ( , , ; pms, Ast ) is a ''comune'' of 74,348 inhabitants (1-1-2021) located in the Piedmont region of northwestern Italy, about east of Turin in the plain of the Tanaro River. It is the capital of the province of Asti and it is deemed t ...
* County of Masserano
* County of Correggio
* County of Pitigliano
* County of Novellara
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
* County of Tende
* County of Sovana
* County of Scandiano
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Siena
* Republic of Ancona
* Republic of Noli
* Republic of Senarica
Senarica is a village in the Abruzzo region of central Italy. With a population of fewer than 300 people, Senarica was an independent republic for about four centuries until the end of the eighteenth century. It was the smallest state to maintain ...
* Republic of Cospaia
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' ...
* Republic of San Marino
After the Italian Wars
 The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended the
The Peace of Cateau Cambrésis ended the Italian Wars
The Italian Wars, also known as the Habsburg–Valois Wars, were a series of conflicts covering the period 1494 to 1559, fought mostly in the Italian peninsula, but later expanding into Flanders, the Rhineland and the Mediterranean Sea. The pr ...
in 1559. The kingdoms of Sicily
(man) it, Siciliana (woman)
, population_note =
, population_blank1_title =
, population_blank1 =
, demographics_type1 = Ethnicity
, demographics1_footnotes =
, demographi ...
, Sardinia
Sardinia ( ; it, Sardegna, label=Italian, Corsican and Tabarchino ; sc, Sardigna , sdc, Sardhigna; french: Sardaigne; sdn, Saldigna; ca, Sardenya, label= Algherese and Catalan) is the second-largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, aft ...
, Naples
Naples (; it, Napoli ; nap, Napule ), from grc, Νεάπολις, Neápolis, lit=new city. is the regional capital of Campania and the third-largest city of Italy, after Rome and Milan, with a population of 909,048 within the city's adm ...
(inclusive of the State of Presidi
The State of the ''Presidi'' ( it, Stato dei Presidi,. In french: État des Présides. Dhondt uses "Tuscan ''presidia''". meaning "state of the garrisons") was a small territory in Italy between 1557 and 1801. It consisted of the remnants of t ...
) and the Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
were left under the control of Spanish Habsburgs. France was in control of several fortresses and in particular of the Marquisate of Saluzzo. All the other Italian states remained independent, with the most powerful being the Venetian Republic
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
, the Medici's Duchy of Tuscany, the Savoyard state, the Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
, and the Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
. The Gonzaga in Mantua, the Este in Modena and Ferrara and the Farnese in Parma and Piacenza continued to be important dynasties. Parts of the north of Italy remained a part of the Holy Roman Empire
The Holy Roman Empire was a political entity in Western, Central, and Southern Europe that developed during the Early Middle Ages and continued until its dissolution in 1806 during the Napoleonic Wars.
From the accession of Otto I in 962 unt ...
.
Major States
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
* Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
Minor States
*Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
* Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. The following year, the Duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to ...
* Duchy of Parma and Piacenza
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna.
Originally a realm of the Farne ...
* Duchy of Ferrara
* Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
(under Spanish rule)
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio (In personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with Ferrara)
* Duchy of Urbino
The Duchy of Urbino was an independent duchy in early modern central Italy, corresponding to the northern half of the modern region of Marche. It was directly annexed by the Papal States in 1625.
It was bordered by the Adriatic Sea in the east ...
* Duchy of Castro (in personal union with Parma)
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Prince-Bishopric of Trent
* Principality of Piombino
The Lordship of Piombino (''Signoria di Piombino''), and after 1594 the Principality of Piombino (''Principato di Piombino''), was a small state on the Italian peninsula centred on the city of Piombino and including part of the island of Elba. I ...
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Monégasque dialect, Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riv ...
* Marquisate of Montferrat (raised to Duchy of Montferrat
The Duchy of Montferrat was a state located in Northern Italy. It was created out of what was left of the medieval March of Montferrat after the last Palaeologus heir had died (1533) and the margraviate had been briefly controlled by the Emperor ...
in 1574; in personal union with Mantua)
* Marquisate of Masserano (raised to Principality of Masserano in 1598)
* Marquisate of Sabbioneta
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman w ...
(raised to Duchy of Sabbioneta
A duchy, also called a dukedom, is a medieval country, territory, fief, or domain ruled by a duke or duchess, a ruler hierarchically second to the king or queen in Western European tradition.
There once existed an important difference be ...
in 1577)
* Marquisate of Finale
* Marquisate of Massa (raised to Principality of Massa in 1568)
* Marquisate of Carrara (in personal union with Massa)
* Marquisate of Castiglione
A marquess (; french: marquis ), es, marqués, pt, marquês. is a nobleman of high hereditary rank in various European peerages and in those of some of their former colonies. The German language equivalent is Markgraf (margrave). A woman ...
(raised to Principality of Castiglione
Castiglione della Pescaia (), regionally simply abbreviated as Castiglione, is an ancient seaside town in the province of Grosseto, in Tuscany, central Italy. The modern city grew around a medieval 12th century fortress ( it, castello) and a large ...
in 1609)
* Marquisate of Torriglia
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Bastia
* County of Guastalla
The County of Guastalla was a feudal state in northern Italy, centered on Guastalla. The title of count was created in 1406 for Guido Torelli.
The Torelli family ruled Guastalla until 1539 when it was purchased by Ferrante Gonzaga. Another bran ...
* County of Mirandola
* County of Montechiarugolo
The County of Montechiarugolo was a small sovereign state of northern Italy which existed from 1456 to 1612. It included the other fief of Casei.
It was created from a splitting in the county of Guastalla between count Cristoforo Torelli and Pie ...
* County of Correggio (raised to Principality of Correggio in 1616)
* County of Novellara
A county is a geographic region of a country used for administrative or other purposesChambers Dictionary, L. Brookes (ed.), 2005, Chambers Harrap Publishers Ltd, Edinburgh in certain modern nations. The term is derived from the Old French ...
* County of Pitigliano
* County of Tende
* County of Santa Fiora
The County of Santa Fiora ( it, Contea di Santa Fiora), also known as State of Santa Fiora ( it, Stato di Santa Fiora, links=no) was a small historical state of southern Tuscany, in central Italy. Together with the county of Sovana, it was one of ...
* Republic of Ancona
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' ...
* Republic of San Marino
* Republic of Noli
* Republic of Senarica
Senarica is a village in the Abruzzo region of central Italy. With a population of fewer than 300 people, Senarica was an independent republic for about four centuries until the end of the eighteenth century. It was the smallest state to maintain ...
* Republic of Cospaia
* Hospitaller Malta
Hospitaller Malta, officially the Monastic State of the Order of Malta, and known within Maltese history as the Knights' Period ( mt, Żmien il-Kavallieri, "Time of the Knights"), was a polity which existed between 1530 and 1798 when the Mediter ...
After the Wars of Succession of the 18th century
 Following the European wars of succession of the 18th century and the extinction of the
Following the European wars of succession of the 18th century and the extinction of the House of Medici
The House of Medici ( , ) was an Italian banking family and political dynasty that first began to gather prominence under Cosimo de' Medici, in the Republic of Florence during the first half of the 15th century. The family originated in the M ...
, the Grand Duchy of Tuscany was ruled by the Habsburg-Lorraine. Some minor states in Central and Northern Italy, such as Parma and Mantua, passed to the Austrian monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
. Southern Italy passed to a cadet branch of the House of Bourbon
The House of Bourbon (, also ; ) is a European dynasty of French origin, a branch of the Capetian dynasty, the royal House of France. Bourbon kings first ruled France and Navarre in the 16th century. By the 18th century, members of the Spani ...
, known as House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies. While other states such as Genoa, Savoy, Modena and Lucca remained with their governments unchanged.
Major States
*Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
* Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
(under the Austrian monarchy
The Habsburg monarchy (german: Habsburgermonarchie, ), also known as the Danubian monarchy (german: Donaumonarchie, ), or Habsburg Empire (german: Habsburgerreich, ), was the collection of empires, kingdoms, duchies, counties and other polities ...
from 1714 to 1734; in personal union with Sicily under the Bourbon-Two Sicilies
The House of Bourbon-Two Sicilies is a cadet branch of the Spanish royal family, Spanish Bourbons that ruled Southern Italy and Sicily for more than a century in the 18th and 19th centuries. It descends from the Capetian dynasty in legitimate ma ...
thereafter)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
(under Habsburg-Lorraine after 1737)
* Duchy of Savoy
The Duchy of Savoy ( it, Ducato di Savoia; french: Duché de Savoie) was a country in Western Europe that existed from 1416.
It was created when Sigismund, Holy Roman Emperor, raised the County of Savoy into a duchy for Amadeus VIII. The du ...
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
* Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
(under Habsburg Monarchy)
Minor states
*Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
(under Austrian monarchy from 1714 to 1720; in personal union with Savoy thereafter)
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
(under Savoy from 1714 to 1720; under Austrian monarchy from 1720 to 1734; in personal union
A personal union is the combination of two or more states that have the same monarch while their boundaries, laws, and interests remain distinct. A real union, by contrast, would involve the constituent states being to some extent interli ...
with Naples under the Bourbon-Two Sicilies thereafter)
* Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. The following year, the Duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to ...
(under Austrian Monarchy)
* Duchy of Parma and Piacenza
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna.
Originally a realm of the Farne ...
(under Habsburg Monarchy from 1734 to 1748)
* Duchy of Guastalla (in personal union with Parma from 1748)
* Duchy of Modena and ReggioDuchy of Massa and Carrara
The Duchy of Massa and Principality of Carrara ( it, Ducato di Massa e Principato di Carrara) was a small state that controlled the towns of Massa and Carrara from 1473 until 1829.
History
Although the city of Massa had already known its maxi ...
(in personal union with Modena from 1731)
* Duchy of Mirandola (in personal union with Modena from 1710)
* Prince-Bishopric of Brixen
* Prince-Bishopric of Trent
* Principality of Masserano
* Principality of Torriglia
A principality (or sometimes princedom) can either be a monarchical feudatory or a sovereign state, ruled or reigned over by a regnant-monarch with the title of prince and/or princess, or by a monarch with another title considered to fall und ...
* Principality of Piombino
The Lordship of Piombino (''Signoria di Piombino''), and after 1594 the Principality of Piombino (''Principato di Piombino''), was a small state on the Italian peninsula centred on the city of Piombino and including part of the island of Elba. I ...
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Monégasque dialect, Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riv ...
* Duchy of Montferrat
The Duchy of Montferrat was a state located in Northern Italy. It was created out of what was left of the medieval March of Montferrat after the last Palaeologus heir had died (1533) and the margraviate had been briefly controlled by the Emperor ...
* Marquisate of Fosdinovo
* Marquisate of Bastia
* Republic of Lucca
* Republic of San Marino
* Republic of Ragusa
The Republic of Ragusa ( dlm, Republica de Ragusa; la, Respublica Ragusina; it, Repubblica di Ragusa; hr, Dubrovačka Republika; vec, Repùblega de Raguxa) was an aristocratic maritime republic centered on the city of Dubrovnik (''Ragusa'' ...
* Republic of Noli
* Republic of Senarica
Senarica is a village in the Abruzzo region of central Italy. With a population of fewer than 300 people, Senarica was an independent republic for about four centuries until the end of the eighteenth century. It was the smallest state to maintain ...
* Republic of Cospaia
* City of Fiume and its District
Their populations and other vital statistics stood as follows in the late 18th century:Emmanuel-Auguste-Dieudonne comte de Las Cases. 1816. *
Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
(including Sicily): 6,000,000 (400,000 in Naples), army of 60,000 to 80,0000, 2 ships of the lines and some frigates
* Republic of Venice
The Republic of Venice ( vec, Repùblega de Venèsia) or Venetian Republic ( vec, Repùblega Vèneta, links=no), traditionally known as La Serenissima ( en, Most Serene Republic of Venice, italics=yes; vec, Serenìsima Repùblega de Venèsia ...
: 3,500,000 (140,000 in the city of Venice itself), standing army and navy of 30,000, 12-15 ships of at least 54 guns plus frigates and brigs
* Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
: 2,900,000 (2,400,000 on the mainland and 500,000 on the island), 12-15 fortified cities and towns (largest being Turin at 80,000), standing army of 25,000, which could be raised to 50,000 in a time of war and 100,000 with militia
* The Papal States: 2,400,000 (140,000 in the city of Rome), standing army of 6,000 to 7,000
* Austrian Lombardy (Duchy of Milan
The Duchy of Milan ( it, Ducato di Milano; lmo, Ducaa de Milan) was a state in northern Italy, created in 1395 by Gian Galeazzo Visconti, then the lord of Milan, and a member of the important Visconti family, which had been ruling the city sin ...
, Duchy of Mantua
The Duchy of Mantua was a duchy in Lombardy, northern Italy. Its first duke was Federico II Gonzaga, member of the House of Gonzaga that ruled Mantua since 1328. The following year, the Duchy also acquired the March of Montferrat, thanks to ...
, and minor territories): 1,100,000 (40,000 in the city of Milan itself)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
: 1,000,000 (80,000 in Florence), standing army of 6,000, navy of 3 frigates
* Republic of Genoa
The Republic of Genoa ( lij, Repúbrica de Zêna ; it, Repubblica di Genova; la, Res Publica Ianuensis) was a medieval and early modern maritime republic from the 11th century to 1797 in Liguria on the northwestern Italian coast. During the La ...
: 500,000 (100,000 in the city of Genoa itself)
* Duchy of Parma
The Duchy of Parma and Piacenza ( it, Ducato di Parma e Piacenza, la, Ducatus Parmae et Placentiae), was an Italian state created in 1545 and located in northern Italy, in the current region of Emilia-Romagna.
Originally a realm of the Farnese ...
: 500,000 (40,000 in the city of Parma itself), standing army of 2,500 to 3,000
* Duchy of Modena: 350,000 (20,000 in the city of Modena itself), standing army of 5,000 to 6,000
* Republic of Lucca: 100,000
Total: 18.3 million
During Napoleonic times (1792–1815)

Sister republics of Revolutionary France
* Republic of Alba *Anconine Republic
The Anconine Republic ( it, Repubblica Anconitana) was a revolutionary municipality formed on 19 November 1797. It came about after a French victory at Ancona in February 1797, and the consequent occupation of the city.Philip's Atlas of World H ...
* Astese Republic
* Republic of Bergamo
* Bolognese Republic
The Bolognese Republic was proclaimed in 1796 in the Central Italian city of Bologna.
History
It was a French client republic established when Papal authorities escaped from the city of Bologna in June 1796. It was annexed by the Cispadane Repub ...
* Republic of Brescia
The Republic of Brescia ( it, Repubblica bresciana) was a temporary French client republic in Italy. Established March 18, 1797, in the wake of the French occupation of Brescia and Bergamo, it became part of the Cisalpine Republic November 20, 1797 ...
* Cisalpine Republic
* Cispadane Republic
* Republic of Crema
* Italian Republic
* Ligurian Republic
* Jacobin State of Lucca
* Parthenopean Republic
* Republic of Pescara
Pescara (; nap, label= Abruzzese, Pescàrë; nap, label= Pescarese, Piscàrë) is the capital city of the Province of Pescara, in the Abruzzo region of Italy. It is the most populated city in Abruzzo, with 119,217 (2018) residents (and approxi ...
* Piedmontese Republic
* Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
* Subalpine Republic
The Subalpine Republic was a short-lived republic that existed between 1800 and 1802 on the territory of Piedmont during its military rule by Napoleonic France.
History
Piedmont was the main part of the Kingdom of Sardinia which, despite i ...
* Tiberina Republic
* Transpadane Republic
In personal union with France
*Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
Client states of the First French Empire
* Kingdom of Etruria *Kingdom of Naples
The Kingdom of Naples ( la, Regnum Neapolitanum; it, Regno di Napoli; nap, Regno 'e Napule), also known as the Kingdom of Sicily, was a state that ruled the part of the Italian Peninsula south of the Papal States between 1282 and 1816. It was ...
* Principality of Lucca and Piombino
*
* Principality of Pontecorvo
Other states
*Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
* Kingdom of Sicily
The Kingdom of Sicily ( la, Regnum Siciliae; it, Regno di Sicilia; scn, Regnu di Sicilia) was a state that existed in the south of the Italian Peninsula and for a time the region of Ifriqiya from its founding by Roger II of Sicily in 1130 un ...
* Principality of Elba (non-hereditary Monarchy under the exiled Emperor Napoleon)
* Republic of San Marino
* Republic of Cospaia
From the Restoration to the Unification
Congress of Vienna
The Congress of Vienna (, ) of 1814–1815 was a series of international diplomatic meetings to discuss and agree upon a possible new layout of the European political and constitutional order after the downfall of the French Emperor Napoleon ...
(1815) was convened to redraw the European continent. In Italy, the Congress restored the pre-Napoleonic patchwork of independent governments, either directly ruled or strongly influenced by the prevailing European powers, particularly Austria. The Congress also determined the end of two millenary republics: Genoa was annexed by the then Savoyard Kingdom of Sardinia, and Venice was incorporated with Milan into a new kingdom of the Austrian Empire.
At the time, the struggle for Italian unification was perceived to be waged primarily against the Habsburgs
The House of Habsburg (), alternatively spelled Hapsburg in Englishgerman: Haus Habsburg, ; es, Casa de Habsburgo; hu, Habsburg család, it, Casa di Asburgo, nl, Huis van Habsburg, pl, dom Habsburgów, pt, Casa de Habsburgo, la, Domus Hab ...
, since they directly controlled the predominantly Italian-speaking northeastern part of present-day Italy and were the most powerful force against the Italian unification. The Austrian Empire vigorously repressed nationalist sentiment growing in its domains on the Italian peninsula, as well as in the other parts of Habsburg domains.
* Papal States
The Papal States ( ; it, Stato Pontificio, ), officially the State of the Church ( it, Stato della Chiesa, ; la, Status Ecclesiasticus;), were a series of territories in the Italian Peninsula under the direct sovereign rule of the pope fro ...
* Kingdom of Sardinia
The Kingdom of Sardinia,The name of the state was originally Latin: , or when the kingdom was still considered to include Corsica. In Italian it is , in French , in Sardinian , and in Piedmontese . also referred to as the Kingdom of Savoy-S ...
* Kingdom of the Two Sicilies
The Kingdom of the Two Sicilies ( it, Regno delle Due Sicilie) was a kingdom in Southern Italy from 1816 to 1860. The kingdom was the largest sovereign state by population and size in Italy before Italian unification, comprising Sicily and al ...
* Kingdom of Lombardy–Venetia (under Austrian Empire
The Austrian Empire (german: link=no, Kaiserthum Oesterreich, modern spelling , ) was a Central- Eastern European multinational great power from 1804 to 1867, created by proclamation out of the realms of the Habsburgs. During its existence, ...
)
* Kingdom of Illyria
The Kingdom of Illyria was a crown land of the Austrian Empire from 1816 to 1849, the successor state of the Napoleonic Illyrian Provinces, which were reconquered by Austria in the War of the Sixth Coalition. It was established according to th ...
(under Austrian Empire)
* Grand Duchy of Tuscany
The Grand Duchy of Tuscany ( it, Granducato di Toscana; la, Magnus Ducatus Etruriae) was an Italian monarchy that existed, with interruptions, from 1569 to 1859, replacing the Republic of Florence. The grand duchy's capital was Florence. In th ...
* Duchy of Parma, Piacenza and Guastalla
* Duchy of Modena and Reggio
* Duchy of Massa and Carrara
The Duchy of Massa and Principality of Carrara ( it, Ducato di Massa e Principato di Carrara) was a small state that controlled the towns of Massa and Carrara from 1473 until 1829.
History
Although the city of Massa had already known its maxi ...
* Duchy of Lucca
The Duchy of Lucca was a small Italian state existing from 1815 to 1847. It was centered on the city of Lucca. By the Congress of Vienna of 1815 the Duchy was to revert to Tuscany on the end of its Bourbon-Parma line of rulers or when the line wou ...
* Principality of Monaco
Monaco (; ), officially the Principality of Monaco (french: Principauté de Monaco; Monégasque dialect, Ligurian: ; oc, Principat de Mónegue), is a Sovereign state, sovereign city-state and European microstates, microstate on the French Riv ...
* Republic of San Marino
* Republic of Cospaia
* Republic of San Marco
* Roman Republic
The Roman Republic ( la, Res publica Romana ) was a form of government of Rome and the era of the classical Roman civilization when it was run through public representation of the Roman people. Beginning with the overthrow of the Roman Ki ...
* United Provinces of Central Italy
Post-unification
Kingdom of Italy
The Kingdom of Italy ( it, Regno d'Italia) was a state that existed from 1861, when Victor Emmanuel II of Kingdom of Sardinia, Sardinia was proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, proclaimed King of Italy, until 1946, when civil discontent led to ...
* Italian Regency of Carnaro
* Free State of Fiume
The Free State of Fiume () was an independent free state that existed between 1920 and 1924. Its territory of comprised the city of Fiume (today Rijeka, Croatia) and rural areas to its north, with a corridor to its west connecting it to the ...
* Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
* Free Territory of Trieste
'' Micronation''
* Kingdom of Tavolara
* Republic of Rose Island
Italian Partisan Republics
The Italian Partisan Republics were the provisional state entities liberated byItalian partisans
The Italian resistance movement (the ''Resistenza italiana'' and ''la Resistenza'') is an umbrella term for the Italian resistance groups who fought the occupying forces of Nazi Germany and the fascist collaborationists of the Italian Socia ...
from the rule and occupation of Nazi Germany
Nazi Germany (lit. "National Socialist State"), ' (lit. "Nazi State") for short; also ' (lit. "National Socialist Germany") (officially known as the German Reich from 1933 until 1943, and the Greater German Reich from 1943 to 1945) was ...
and the Italian Social Republic
The Italian Social Republic ( it, Repubblica Sociale Italiana, ; RSI), known as the National Republican State of Italy ( it, Stato Nazionale Repubblicano d'Italia, SNRI) prior to December 1943 but more popularly known as the Republic of Salò ...
in 1944 during the Second World War
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great powers—forming two opposi ...
. They were universally short-lived, with most of them being reconquered by the Wehrmacht
The ''Wehrmacht'' (, ) were the unified armed forces of Nazi Germany from 1935 to 1945. It consisted of the ''Heer'' (army), the '' Kriegsmarine'' (navy) and the ''Luftwaffe'' (air force). The designation "''Wehrmacht''" replaced the previo ...
within weeks of their formal establishments and re-incorporated into the Italian Social Republic.
* Republic of Alba (10 October - 2 November)
* Republic of Alto Monferrato (September - 2 December)
* Republic of Alto Tortonese (September - December)
* Republic of Bobbio (7 July - 27 August)
* Republic of the Cansiglio (July - September)
* (26 September - 10 October)
* (2 February - March 1944)
* Republic of Oriental Friuli (30 June - September)
* Republic of Pigna (IM) (18 September 1944 - 8 October 1944)
* Republic of the Langhe (September - November)
* (17 June - 1º August)
* Republic of Ossola (10 September - 23 October)
* (26 June - 27 November)
* Republic of the Ceno Valley (10 June - 11 July)
* Republic of the Enza Valley and the Parma Valley (June - July)
* Republic of the Maira Valley and the Varaita Valley (June - 21 August)
* (15 June - 24 July)
* Republic of the Lanzo Valley (25 June - September)
* Republic of the Sesia Valley (11 June - 10 July)
* Republic of Varzi (19/24 September - 29 November)
See also
*Italian city-states
The Italian city-states were numerous political and independent territorial entities that existed in the Italian Peninsula from the beginning of the Middle Ages until the proclamation of the Kingdom of Italy, which took place in 1861.
After t ...
* Maritime republics
* Medieval commune
Medieval communes in the European Middle Ages had sworn allegiances of mutual defense (both physical defense and of traditional freedoms) among the citizens of a town or city. These took many forms and varied widely in organization and makeup.
C ...
* Signoria
References
Italy
Italy ( it, Italia ), officially the Italian Republic, ) or the Republic of Italy, is a country in Southern Europe. It is located in the middle of the Mediterranean Sea, and its territory largely coincides with the homonymous geographical ...