List of geological features on Titan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
This is a list of named geological features on Saturn's moon Titan. Official names for these features have only been announced very recently, as Titan's surface was virtually unknown before the arrival of the '' Cassini–Huygens'' probe. Some features were known by informal nicknames beforehand; these names are noted where appropriate. Note that some features with a physical size given by "diameter" may not be circular; then the number refers to the length.


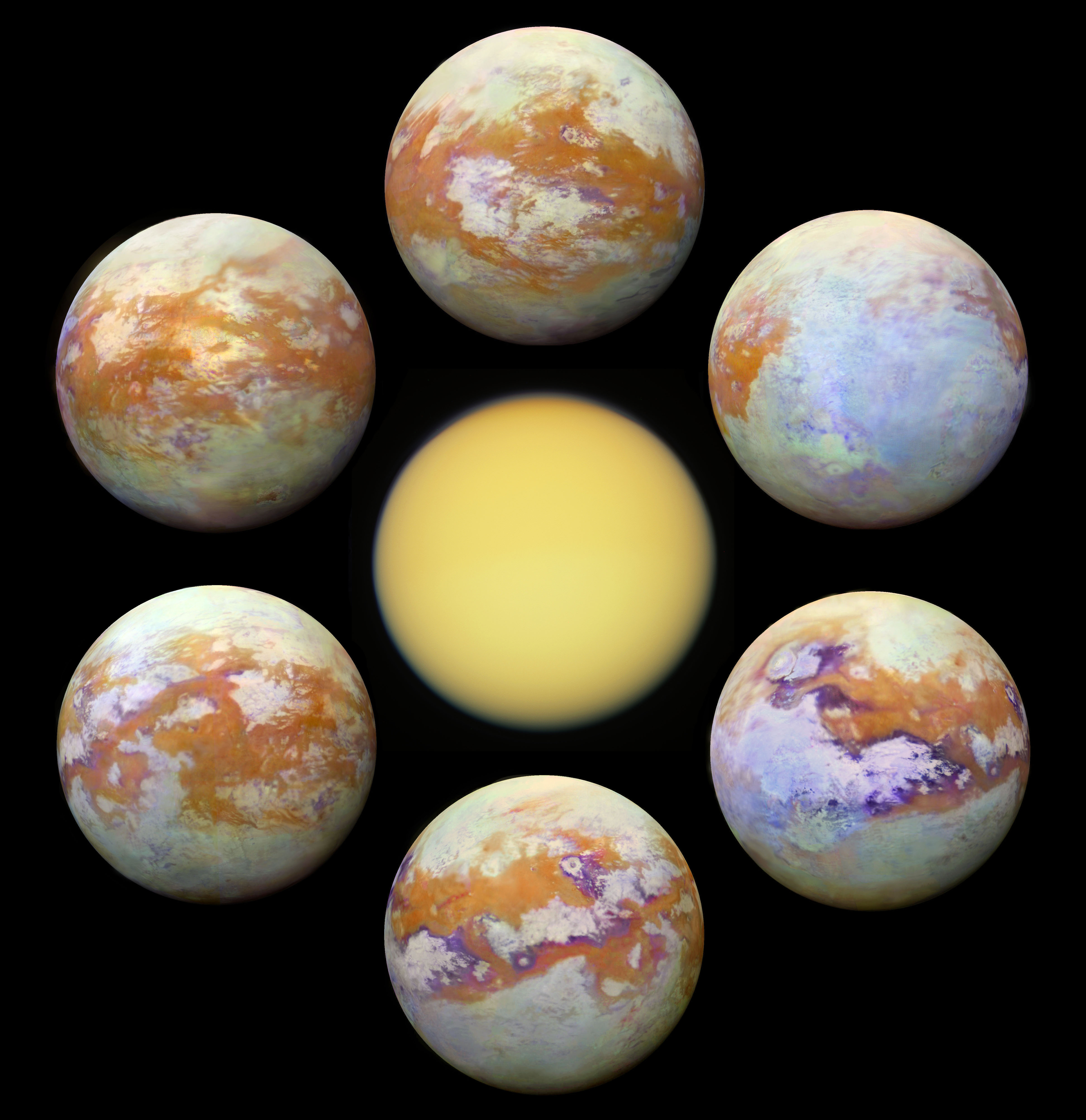 Albedo features on Titan are named after sacred or enchanted places in world mythologies and literature.
Albedo features on Titan are named after sacred or enchanted places in world mythologies and literature.
USGS: Titan nomenclatureUSGS links to PDF maps with nomenclature
{{Surface features of space objects * Titan Titan, geological features


Albedo features
 Albedo features on Titan are named after sacred or enchanted places in world mythologies and literature.
Albedo features on Titan are named after sacred or enchanted places in world mythologies and literature.
Bright albedo features
Dark albedo features
Arcūs
Titanean arcūs (arc-shaped features) are named after deities of happiness.Colles
Colles are small hills or knobs which are named after characters inJ. R. R. Tolkien
John Ronald Reuel Tolkien (, ; 3 January 1892 – 2 September 1973) was an English writer and philologist. He was the author of the high fantasy works ''The Hobbit'' and ''The Lord of the Rings''.
From 1925 to 1945, Tolkien was the Rawlins ...
's Middle-earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is ...
.
Craters
Craters on Titan are named after deities of wisdom.Faculae
Facula
A facula (plural: faculae ), Latin for "little torch", is literally a "bright spot". The term has several common technical uses. It is used in planetary nomenclature for naming certain surface features of planets and moons,. and is also a type of ...
e (bright spots) are named after island
An island (or isle) is an isolated piece of habitat that is surrounded by a dramatically different habitat, such as water. Very small islands such as emergent land features on atolls can be called islets, skerries, cays or keys. An island ...
s on Earth that are not politically independent. Groups of faculae are named after archipelago
An archipelago ( ), sometimes called an island group or island chain, is a chain, cluster, or collection of islands, or sometimes a sea containing a small number of scattered islands.
Examples of archipelagos include: the Indonesian Arc ...
s on Earth.
Fluctūs
The term " fluctus" refers to flow terrain. Fluctūs on Titan are named after mythological figures associated withbeauty
Beauty is commonly described as a feature of objects that makes these objects pleasurable to perceive. Such objects include landscapes, sunsets, humans and works of art. Beauty, together with art and taste, is the main subject of aesthetics, o ...
.
Flumina
A flumen is a feature that looks like a channel carved by liquid. Flumina refers to a network of rivers. Some flumina are not found near liquid bodies, which are labelled as "dry valley". They are named after mythical or imaginary rivers.Freta
A fretum (plural ''freta'') is a strait of liquid connecting two larger liquid bodies. They are named after characters from the Foundation series of science fiction novels by Isaac Asimov.Insulae
Insulae are islands within Titan's seas. They are named after legendary islands.Labyrinthi
Labyrinthi (complexes of intersecting valleys or ridges) on Titan are named after planets from the fictional ''Dune'' universe created by Frank Herbert.Lacunae
Lacunae are dark areas with the appearance of dry lake beds, which are named after intermittent lakes on Earth.Lacūs
Lacūs (plural form of lacus used in Titan geological nomenclature) are hydrocarbon lakes.Large ringed features
Large ring features are named after deities of wisdom in world mythology.Maculae
Titanean maculae (dark spots) are named after deities of happiness, peace, and harmony in world mythology.Maria
Maria (plural of mare) are hydrocarbon seas.Montes
Mountains are named after mountains from the fictionalMiddle-Earth
Middle-earth is the fictional setting of much of the English writer J. R. R. Tolkien's fantasy. The term is equivalent to the '' Miðgarðr'' of Norse mythology and ''Middangeard'' in Old English works, including ''Beowulf''. Middle-earth is ...
created by J.R.R. Tolkien.
Paterae
Paterae
In the material culture of classical antiquity, a ''phiale'' ( ) or ''patera'' () is a shallow ceramic or metal libation bowl. It often has a bulbous indentation (''omphalos'', "bellybutton") in the center underside to facilitate holding it, in ...
are caldera
A caldera ( ) is a large cauldron-like hollow that forms shortly after the emptying of a magma chamber in a volcano eruption. When large volumes of magma are erupted over a short time, structural support for the rock above the magma chamber is ...
or deep-wall craters with a possible volcanic origin. Sotra Patera was formerly named Sotra Facula, which followed the naming theme for Faculae
A facula (plural: faculae ), Latin for "little torch", is literally a "bright spot". The term has several common technical uses. It is used in planetary nomenclature for naming certain surface features of planets and moons,. and is also a type of ...
. No nomenclature
Nomenclature (, ) is a system of names or terms, or the rules for forming these terms in a particular field of arts or sciences. The principles of naming vary from the relatively informal conventions of everyday speech to the internationally ag ...
currently exists for this class of features on Titan.
Planitiae
Planitiae (low plains) on Titan are named after planets from the fictional ''Dune'' universe created by Frank Herbert.Regiones
Regiones (regions distinctly different from their surroundings) are named after deities of peace and happiness.Sinūs
Sinus (bays) within seas or lakes are named after terrestrial bays, coves, fjords or inlets.Terrae
Terrae are extensive landmasses. As with the albedo features, they are named after sacred and enchanted locations from cultures across the world.Undae
Undae are dune fields. On Titan they are named afterGreek deities
The following is a list of gods, goddesses, and many other divine and semi-divine figures from ancient Greek mythology and ancient Greek religion.
Immortals
The Greeks created images of their deities for many purposes. A temple would house the ...
of wind.
Virgae
Virgae (streaks of colour) are named after rain gods in world mythologies.Informal names for previously unnamed features
Because the exact nature of many surface features remain mysterious, a number of features took time to receive formal names and are known by nicknames. In most cases, indications of brightness and darkness refer not to visible light, but to theinfrared
Infrared (IR), sometimes called infrared light, is electromagnetic radiation (EMR) with wavelengths longer than those of visible light. It is therefore invisible to the human eye. IR is generally understood to encompass wavelengths from around ...
images used to look through Titan's obscuring haze.
*' The Sickle': a large, dark, sickle-shaped region identified by the Hubble Space Telescope.
*' Throat of Kraken': unofficial name for the strait that separates the north and south basins of Kraken Mare
Kraken Mare is the largest known body of liquid on the surface of Saturn's moon Titan. It was discovered by the space probe '' Cassini'' in 2006, and was named in 2008 after the Kraken, a legendary sea monster. It covers an area slightly bigger ...
, before officially being named Seldon Fretum. It was used in early publications that hypothesized about its role with tidal dissipation and surface currents between the two basins of Kraken Mare.
See also
*Lakes of Titan
Lakes of ethane and methane on Titan, Saturn's largest moon, have been detected by the ''Cassini–Huygens'' space probe, and had been suspected long before. The large ones are known as maria (seas) and the small ones as lacūs (lakes).
History
...
Notes
References
External links
USGS: Titan nomenclature
{{Surface features of space objects * Titan Titan, geological features