List of communities in Saskatchewan on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]

 Communities in the Province of
Communities in the Province of
 Saskatchewan has 466 urban municipalities, which includes the sub-types of cities, towns, villages and resort villages.
Saskatchewan has 466 urban municipalities, which includes the sub-types of cities, towns, villages and resort villages.
 A rural municipality is created by the Minister of Municipal Affairs by ministerial order via section 49 of ''The Municipalities Act''. Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities, which are located in the central and southern portions of the province.
Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities.
A rural municipality is created by the Minister of Municipal Affairs by ministerial order via section 49 of ''The Municipalities Act''. Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities, which are located in the central and southern portions of the province.
Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities.
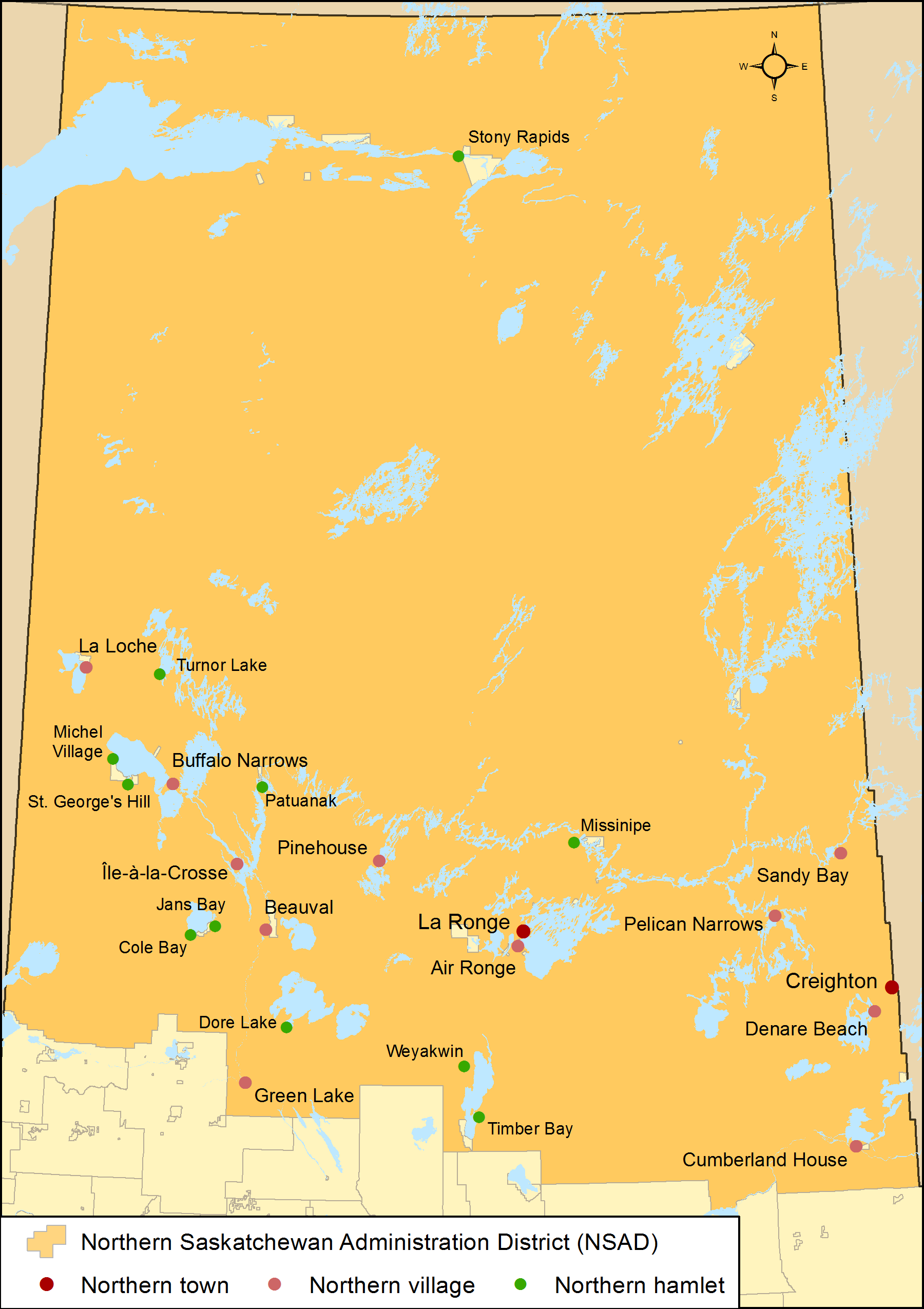 Saskatchewan has 24 northern municipalities, which includes the sub-types of northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets.
Saskatchewan has 24 northern municipalities, which includes the sub-types of northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets.
 Communities in the Province of
Communities in the Province of Saskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...
, Canada include incorporated municipalities
A municipal corporation is the legal term for a local governing body, including (but not necessarily limited to) cities, counties, towns, townships, charter townships, villages, and boroughs. The term can also be used to describe municipally own ...
, unincorporated communities and First Nations communities.
Types of incorporated municipalities include urban municipalities, rural municipalities
A rural municipality is a classification of municipality, a type of local government, found in several countries.
These include:
* Rural municipalities in Canada, a type of municipal status in the Canadian provinces of Manitoba, Saskatchewan, ...
and northern municipalities. Urban municipalities are further classified into four sub-types – cities, town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an o ...
s, village
A village is a clustered human settlement or community, larger than a hamlet but smaller than a town (although the word is often used to describe both hamlets and smaller towns), with a population typically ranging from a few hundred ...
s and resort villages. Northern municipalities, which are located in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District (NSAD), are further classified into three sub-types – northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets. Rural municipalities are not classified into sub-types.
Types of unincorporated communities include hamlets and organized hamlets within rural municipalities and northern settlements within the NSAD.
The administration of rural municipalities, towns, villages, resort villages, organized hamlets and hamlets is regulated by ''The Municipalities Act'', while the administration of cities is regulated by ''The Cities Act''. Administration of northern towns, northern villages, northern hamlets and northern settlements (those within the NSAD) is regulated by ''The Northern Municipalities Act''.
In the 2011 Census, Saskatchewan's communities combined for a total provincial population of 1,033,381.
Municipalities
Saskatchewan presently has 786 municipalities of various types (urban, rural and northern municipalities) and sub-types (cities, towns, villages, resort villages, northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets).Urban municipalities
 Saskatchewan has 466 urban municipalities, which includes the sub-types of cities, towns, villages and resort villages.
Saskatchewan has 466 urban municipalities, which includes the sub-types of cities, towns, villages and resort villages.
Cities
In Saskatchewan, towns must have a population above 5,000 in order to be granted city status. A city does not automatically revert to town status if the population drops below 5,000; this only occurs if the city council requests it, the majority of electors vote to revert to town status or the appropriate provincial minister is of the opinion that the reversion to town status is in the public interest. The city of Melville retains city status as of 2010 despite dropping below 5,000 population in the 1990s. Saskatchewan has 16 cities, including Lloydminster and not including Flin Flon.Towns
In Saskatchewan,town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an o ...
s are formed from villages or resort villages with a population of at least 500 people. The council of the village or resort village must request the change to town status. When a town's population exceeds 5,000 people, the council may request a change to city
A city is a human settlement of notable size.Goodall, B. (1987) ''The Penguin Dictionary of Human Geography''. London: Penguin.Kuper, A. and Kuper, J., eds (1996) ''The Social Science Encyclopedia''. 2nd edition. London: Routledge. It can be def ...
status, but the change in incorporation level is not mandatory. Towns with shrinking populations are allowed to retain town status even if the number of residents falls below the 500 limit. For example, the towns of Fleming, Francis, and Scott
Scott may refer to:
Places Canada
* Scott, Quebec, municipality in the Nouvelle-Beauce regional municipality in Quebec
* Scott, Saskatchewan, a town in the Rural Municipality of Tramping Lake No. 380
* Rural Municipality of Scott No. 98, Sask ...
have populations that have dropped under 500 people and are still qualified under town status. Towns with populations below the limit may, however, revert to village or resort village status if the town council requests it.
Saskatchewan has 146 towns.
Villages
The people of an organized hamlet may request that the hamlet be incorporated as a village or resort village. In order to qualify, the hamlet must have been an organized hamlet for at least 3 years, have a population of at least 100 in the most recent census, and contain at least 50 separate dwelling units or business premises. Saskatchewan has 260 villages.Resort villages
Saskatchewan has 40 resort villages.Rural municipalities
 A rural municipality is created by the Minister of Municipal Affairs by ministerial order via section 49 of ''The Municipalities Act''. Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities, which are located in the central and southern portions of the province.
Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities.
A rural municipality is created by the Minister of Municipal Affairs by ministerial order via section 49 of ''The Municipalities Act''. Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities, which are located in the central and southern portions of the province.
Saskatchewan has 296 rural municipalities.
Northern municipalities
 Saskatchewan has 24 northern municipalities, which includes the sub-types of northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets.
Saskatchewan has 24 northern municipalities, which includes the sub-types of northern towns, northern villages and northern hamlets.
Northern towns
A northern town is a town in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District. Its administration is regulated by ''The Northern Municipalities Act''. A northern village may apply for town status when the actual resident population is at least 500. Saskatchewan has two northern towns.Northern villages
A northern village is located in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District, and its administration is regulated by The Northern Municipalities Act. A northern hamlet may apply for northern village status when the population is at least 100 and the northern hamlet contains at least 50 separate dwelling units or business premises. Saskatchewan has 11 northern villages.Northern hamlets
A northern hamlet is located in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District, and its administration is regulated by The Northern Municipalities Act. A northern settlement may apply for northern hamlet status when the population is at least 50 and the northern settlement contains at least 25 separate dwelling units or business premises. Unlike hamlets and northern settlements, northern hamlets are municipal corporations. Saskatchewan has 11 northern hamlets.Unincorporated hamlets
In Saskatchewan, ahamlet
''The Tragedy of Hamlet, Prince of Denmark'', often shortened to ''Hamlet'' (), is a tragedy written by William Shakespeare sometime between 1599 and 1601. It is Shakespeare's longest play, with 29,551 words. Set in Denmark, the play depicts ...
is an unincorporated community that is under the jurisdiction of a rural municipality. It has at least five occupied dwellings situated on separate lots and at least 10 separate lots, the majority of which are an average size of less than one acre.
The Government of Saskatchewan recognizes three different types of hamlets – generic "hamlets", "special service areas" and "organized hamlets". Some organized hamlets in Saskatchewan are recognized as designated place
A designated place (DPL) is a type of community or settlement identified by Statistics Canada that does not meet the criteria used to define municipalities or population centres. DPLs are delineated every 5 years for the Canadian census as the ...
s by Statistics Canada
Statistics Canada (StatCan; french: Statistique Canada), formed in 1971, is the agency of the Government of Canada commissioned with producing statistics to help better understand Canada, its population, resources, economy, society, and cultu ...
, while unorganized hamlets are not.
Hamlets
Generic hamlets in Saskatchewan are under the jurisdiction of a rural municipality and do not have any decision-making powers or independent authorities. The following are hamlets that are neither special service areas nor organized hamlets.Special service areas
Like a generic hamlet, a special service area is under the jurisdiction of a rural municipality and does not have any decision-making powers or independent authorities. Unlike a generic hamlet, a special service area may form its own electoral division within the rural municipality and may have a different tax regime within the rural municipality compared to a generic hamlet.Organized hamlets
Saskatchewan has 151 organized hamlets that are established via ministerial order and under the jurisdiction of rural municipalities within southern and central Saskatchewan. The people in a hamlet may apply for organized hamlet status within the rural municipality in which the hamlet is located. The minimum requirements for organize status include a permanent population of at least 80 residents, 40 separate dwelling units or places of business, a taxable assessment of at least $4 million, and any other factor the minister may consider appropriate.Northern settlements
A northern settlement is an unincorporated community in the Northern Saskatchewan Administration District, and its administration is regulated by The Northern Municipalities Act. Saskatchewan has 11 northern settlements.Ghost towns
Aghost town
Ghost Town(s) or Ghosttown may refer to:
* Ghost town, a town that has been abandoned
Film and television
* ''Ghost Town'' (1936 film), an American Western film by Harry L. Fraser
* ''Ghost Town'' (1956 film), an American Western film by All ...
is a town
A town is a human settlement. Towns are generally larger than villages and smaller than cities, though the criteria to distinguish between them vary considerably in different parts of the world.
Origin and use
The word "town" shares an o ...
that once had a considerable population, that has since dwindled in numbers causing some or all of its businesses and services to close, either due to the rerouting of a highway
A highway is any public or private road or other public way on land. It is used for major roads, but also includes other public roads and public tracks. In some areas of the United States, it is used as an equivalent term to controlled-access ...
, railway
Rail transport (also known as train transport) is a means of transport that transfers passengers and goods on wheeled vehicles running on rails, which are incorporated in tracks. In contrast to road transport, where the vehicles run on a p ...
tracks being pulled, or exhaustion of some natural resource
Natural resources are resources that are drawn from nature and used with few modifications. This includes the sources of valued characteristics such as commercial and industrial use, aesthetic value, scientific interest and cultural value. ...
.
First Nations communities
Indian reserves
Metis settlements
See also
* List of cities in Canada *List of designated places in Saskatchewan
A designated place is a type of geographic unit used by Statistics Canada to disseminate census data. It is usually "a small community that does not meet the criteria used to define incorporated municipalities or Statistics Canada population c ...
Notes
References
Other sources
* {{DEFAULTSORT:Communities In SaskatchewanSaskatchewan
Saskatchewan ( ; ) is a Provinces and territories of Canada, province in Western Canada, western Canada, bordered on the west by Alberta, on the north by the Northwest Territories, on the east by Manitoba, to the northeast by Nunavut, and on t ...