List of castra in Dacia on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
Castra (
:
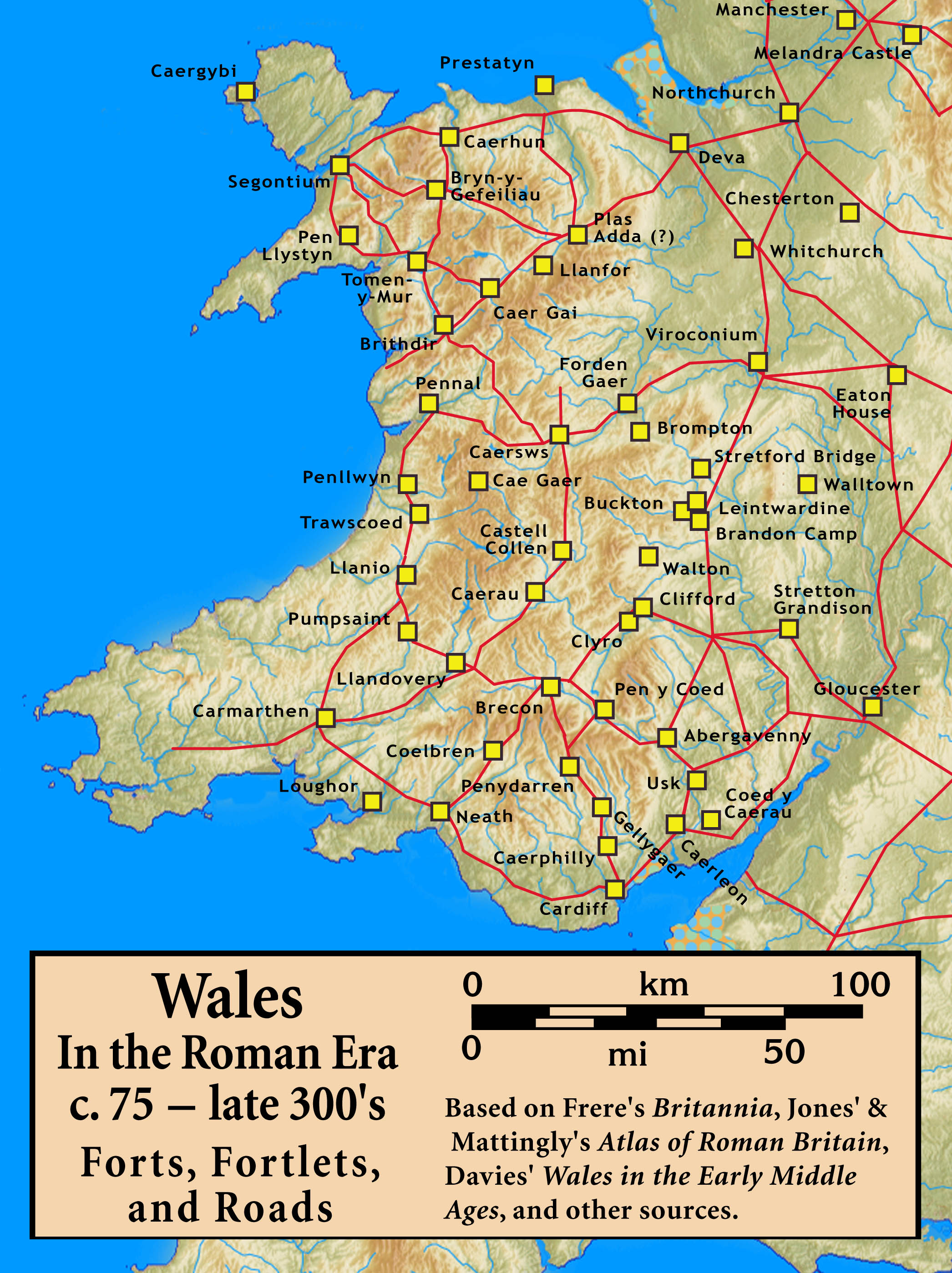 : Alauna,
: Alauna,
Latin
Latin (, or , ) is a classical language belonging to the Italic branch of the Indo-European languages. Latin was originally a dialect spoken in the lower Tiber area (then known as Latium) around present-day Rome, but through the power of the ...
, singular castrum) were military forts of various sizes used by the Roman army
The Roman army (Latin: ) was the armed forces deployed by the Romans throughout the duration of Ancient Rome, from the Roman Kingdom (c. 500 BC) to the Roman Republic (500–31 BC) and the Roman Empire (31 BC–395 AD), and its medieval contin ...
throughout the Empire
An empire is a "political unit" made up of several territories and peoples, "usually created by conquest, and divided between a dominant center and subordinate peripheries". The center of the empire (sometimes referred to as the metropole) ex ...
in various places of Europe, Asia and Africa.
The largest castra were permanent legionary fortresses.
Locations
The disposition of the castra reflects the most important zones of the empire from a military point of view. Many castra were disposed along frontiers particularly in Northern and Central Europe. Another focal point was the Eastern border, where the Roman Empire confronted one of its long-term enemies, the Persian Empire. Other castra were located in strategically important zones, as in Egypt, from which most of the wealth of the empire came. Finally, other castra were located in zones in which the Romans experienced local unrest, such as Northern Spain and Judea. Provinces where the Roman power was unchallenged, such as Italy, Gaul, Africa and Greece, were provided with few or no castra. In the long history of the Roman Empire, the character of the military policy of the Roman Empire changed, and consequently the location and dimension of the castra changed. Under EmperorsGallienus
Publius Licinius Egnatius Gallienus (; c. 218 – September 268) was Roman emperor with his father Valerian from 253 to 260 and alone from 260 to 268. He ruled during the Crisis of the Third Century that nearly caused the collapse of the empi ...
and Aurelian (and later Diocletian), the Roman army was organized into a high-mobility central army (the ''comitatus
''Comitatus'' was in ancient times the Latin term for an armed escort or retinue. The term is used especially in the context of Germanic warrior culture for a warband tied to a leader by an oath of fealty and describes the relations between a lo ...
'') and in local troops (the ''limitanei
The ''līmitāneī'' (Latin, also called ''rīpēnsēs''), meaning respectively "the soldiers in frontier districts" (from the Latin phrase līmēs, meaning a military district of a frontier province) or "the soldiers on the riverbank" (from the ...
''). Some castra lost importance, others were built in new zones, and in general they lost the role of permanent quarter for huge corps of troops.
Castra by Roman province
Alexandria
Alexandria ( or ; ar, ٱلْإِسْكَنْدَرِيَّةُ ; grc-gre, Αλεξάνδρεια, Alexándria) is the second largest city in Egypt, and the largest city on the Mediterranean coast. Founded in by Alexander the Great, Alexandri ...
, Babylon, Coptos
Qift ( arz, قفط ; cop, Ⲕⲉϥⲧ, link=no ''Keft'' or ''Kebto''; Egyptian Gebtu; grc, Κόπτος, link=no ''Coptos'' / ''Koptos''; Roman Justinianopolis) is a small town in the Qena Governorate of Egypt about north of Luxor, situated un ...
, Nicopolis (Egypt)
Africa
Africa is the world's second-largest and second-most populous continent, after Asia in both cases. At about 30.3 million km2 (11.7 million square miles) including adjacent islands, it covers 6% of Earth's total surface area ...
: Ammaedara, Lambaesis
Lambaesis (Lambæsis), Lambaisis or Lambaesa (''Lambèse'' in colonial French), is a Roman archaeological site in Algeria, southeast of Batna and west of Timgad, located next to the modern village of Tazoult. The former bishopric is also a Lat ...
, Thamugas, Theveste
Theveste was a Roman colony situated in the present Tébessa, Algeria.
History
In 146 BC, the Romans conquered the region, where existed an old city called " Tbessa". Theveste was founded by the Romans in 75 AD near an old Berber village locate ...
Arabia Petraea
Arabia Petraea or Petrea, also known as Rome's Arabian Province ( la, Provincia Arabia; ar, العربية البترائية; grc, Ἐπαρχία Πετραίας Ἀραβίας) or simply Arabia, was a frontier province of the Roman Emp ...
and its limes
:Betthorus
Betthorus was a Roman legionary fortress on the Limes Arabicus. It is located in today's (from ''Legio''), Karak Governorate, Jordan,Al Lajjun in Mapcarta north-east of Al Karak. The place is in proximity to the spring , in a wadi of the same nam ...
(modern el-Lejjun in Jordan), legionary fortress on the Limes Arabicus where the Legio IV Martia Legio IV (or IIII) Martia was a legion of the Roman Empire, part of the Late Roman army. Its genesis is uncertain, but it probably existed in the time of Diocletian, and certainly in the time of ''Notitia Dignitatum''. That document places the legi ...
was stationed in the 4th century.
Armenia
Armenia (), , group=pron officially the Republic of Armenia,, is a landlocked country in the Armenian Highlands of Western Asia.The UNbr>classification of world regions places Armenia in Western Asia; the CIA World Factbook , , and ' ...
:Satala
Located in Turkey, the settlement of Satala ( xcl, Սատաղ ''Satał'', grc, Σάταλα), according to the ancient geographers, was situated in a valley surrounded by mountains, a little north of the Euphrates, where the road from Trapez ...
Britannia
Britannia () is the national personification of Britain as a helmeted female warrior holding a trident and shield. An image first used in classical antiquity, the Latin ''Britannia'' was the name variously applied to the British Isles, Great ...
 : Alauna,
: Alauna, Arbeia
Arbeia was a large Roman fort in South Shields, Tyne & Wear, England, now ruined, and which has been partially reconstructed. It was first excavated in the 1870s and all modern buildings on the site were cleared in the 1970s. It is managed by Ty ...
, Banna, Branodunum, Bremenium, Burrium
Burrium was a legionary fortress in the Roman province of Britannia Superior or Roman Britain. Its remains today lie beneath the town of Usk in Monmouthshire, south east Wales.
The Romans founded the fortress around AD 55, probably for the Legio ...
, Camulodunum
Camulodunum (; la, ), the Ancient Roman name for what is now Colchester in Essex, was an important castrum and city in Roman Britain, and the first capital of the province. A temporary "strapline" in the 1960s identifying it as the "oldest re ...
, Derventio Coritanorum
Derventio was a small town in the Roman province of Britannia. Today the area is known as Little Chester, on the outskirts of Derby, located in the English county of Derbyshire.
Description
The first Roman fort in the area was built on the op ...
, Derventio ( Malton), Deva Victrix
Deva Victrix, or simply Deva, was a legionary fortress and town in the Roman province of Britannia on the site of the modern city of Chester. The fortress was built by the Legio II ''Adiutrix'' in the 70s AD as the Roman army advanced north ag ...
, Eboracum
Eboracum () was a fort and later a city in the Roman province of Britannia. In its prime it was the largest town in northern Britain and a provincial capital. The site remained occupied after the decline of the Western Roman Empire and ultimat ...
, Epiacum, Glevum
Glevum (or, more formally, Colonia Nervia Glevensium, or occasionally ''Glouvia'') was originally a Roman fort in Roman Britain that became a " colonia" of retired legionaries in AD 97. Today, it is known as Gloucester, in the English county o ...
, Isca Dumnoniorum
Isca Dumnoniorum, also known simply as Isca, was originally a Roman legionary fortress for the Second Augustan Legion (established ) in the Roman province of Britannia at the site of present-day Exeter in Devon.
The town grew up around this ...
, Isca Augusta
Isca, variously specified as Isca Augusta or Isca Silurum, was the site of a Roman legionary fortress and settlement or ''vicus'', the remains of which lie beneath parts of the present-day suburban village of Caerleon in the north of the city of ...
, Condercum
Condercum was a Roman fort on the site of the modern-day Condercum Estate in Benwell, a suburb of Newcastle upon Tyne, England. It was the third fort on Hadrian's Wall, after Segedunum (Wallsend) and Pons Aelius (Newcastle), and was situated ...
, Concangis
Concangis was an auxiliary castra in the Roman province of Lower Britain (''Britannia Inferior''). Its ruins are located in Chester-le-Street, Durham, in England, and are now known as Chester-le-Street Roman Fort. It is situated north of Dur ...
, Corinium
Corinium Dobunnorum was the Romano-British settlement at Cirencester in the present-day England, English counties of England, county of Gloucestershire. Its 2nd-century walls enclosed the second-largest area of a city in Ancient Romans, Roman Ro ...
, Galava, Glannoventa
Glannoventa is a Roman fort associated with the Roman naval base at Ravenglass in Cumbria, England. Its name is derived from the Latin place-name ''Clanoventa'' as recorded in the 2nd-century Antonine Itinerary, ''Glannibanta'' in the 4th-centu ...
, Leucarum
Leucarum was a coastal auxiliary fort in the Roman province of Britannia. Its remains are located beneath the town of Loughor in the Welsh city of Swansea.
The Romans built a rectangular or trapezoidal fort at the mouth of the River Loughor in ...
, Lindum
Lindum Colonia was the Latin name for the settlement which is now the City of Lincoln in Lincolnshire. It was founded as a Roman Legionary Fortress during the reign of the Emperor Nero (58–68 AD) or possibly later. Evidence from Roman tomb ...
, Mamucium
Mamucium, also known as Mancunium, is a former Roman fort in the Castlefield area of Manchester in North West England. The ''castrum'', which was founded c. AD 79 within the Roman province of Roman Britain, was garrisoned by a cohort ...
, Manduessedum
Manduessedum or Manduesedum was a Roman fort and later a civilian small town in the Roman Province of Britannia. It was located on and immediately to the east of the site of the modern village of Mancetter, located in the English county of Warwi ...
, Mediobogdum, Navio, Morbium, Olicana
Ilkley Roman Fort is a castra, Roman fort on the south bank of the River Wharfe, at the centre of the modern town of Ilkley, a Victorian spa town in West Yorkshire, England.
Identification
The traditional view is that ''Olicana'' is the fort at ...
, Pinnata Castra, Portus Adurni
Portus Adurni was a Roman fort in the Roman province of Britannia situated at the north end of Portsmouth Harbour. It was part of the Saxon Shore, and is the best-preserved Roman fort north of the Alps. Around an eighth of the fort has been exca ...
, Regulbium
Regulbium was the name of an ancient Roman fort of the Saxon Shore in the vicinity of the modern English resort of Reculver in Kent. Its name derives from the local Brythonic language, meaning "great headland" (*''Rogulbion'').
History
The f ...
, Segedunum
Segedunum was a Roman fort at modern-day Wallsend, North Tyneside in North East England. The fort lay at the eastern end of Hadrian's Wall (in Wallsend) near the banks of the River Tyne, forming the easternmost portion of the wall. It was in use ...
, Trimontium, Vindolanda
Vindolanda was a Roman auxiliary fort ('' castrum'') just south of Hadrian's Wall in northern England, which it originally pre-dated.British windo- 'fair, white, blessed', landa 'enclosure/meadow/prairie/grassy plain' (the modern Welsh word ...
, Vinovia
Vinovia or Vinovium was a Roman fort and settlement situated just over to the north of the town of Bishop Auckland on the banks of the River Wear in County Durham, England. The fort was the site of a hamlet until the late Middle Ages, but t ...
, Viroconium
Viroconium or Uriconium, formally Viroconium Cornoviorum, was a Roman city, one corner of which is now occupied by Wroxeter, a small village in Shropshire, England, about east-south-east of Shrewsbury. At its peak, Viroconium is estimated to ...
, Voreda
:Also castra of unknown name:
:Bar Hill
Bar Hill is a purpose-built village with a population of 4,000 about 4 miles (7 km) northwest of Cambridge, England on the A14 road, just east of the Prime Meridian.
History
Prior to the building of the Bar Hill settlement the area was ...
, Bearsden, Lunt Fort, Normandykes
Normandykes (Grid Reference: NO 830994) is the site of a Roman marching camp to the southwest of Peterculter, City of Aberdeen, Scotland. The near-rectangular site, measuring approximately , covers about of the summit and eastern slopes of a hil ...
, Raedykes
Raedykes is the site of a Roman marching camp located just over northwest of Stonehaven, Aberdeenshire, Scotland. National Grid Reference NO 842902. It is designated as a scheduled monument. A marching camp was a temporary camp used mainly for ...
, Templeborough
Templeborough (historically Templebrough) is a suburb of Rotherham, South Yorkshire, England. The suburb falls within the Brinsworth and Catcliffe ward of Rotherham Metropolitan Borough Council. The area takes its name from the remains of the ...
Cappadocia
Cappadocia or Capadocia (; tr, Kapadokya), is a historical region in Central Anatolia, Turkey. It largely is in the provinces Nevşehir, Kayseri, Aksaray, Kırşehir, Sivas and Niğde.
According to Herodotus, in the time of the Ionian Re ...
: Melitene
Commagene
Commagene ( grc-gre, Κομμαγηνή) was an ancient Greco-Iranian kingdom ruled by a Hellenized branch of the Iranian Orontid dynasty that had ruled over Armenia. The kingdom was located in and around the ancient city of Samosata, which s ...
:Samosata
Samsat ( ku, Samîsad), formerly Samosata ( grc, Σαμόσατα) is a small town in the Adıyaman Province of Turkey, situated on the upper Euphrates river. It is the seat of Samsat District.Zeugma
: Aleria, Aurelianus
Roman castra from Romania - Google Maps
Earth
{{Webarchive, url=https://archive.is/20121205025930/http://bbs.keyhole.com/ubb/showflat.php/Cat/0/Number/1274893/Main/1274893 , date=2012-12-05 Roman fortifications by province, de:Legionslager la:Castra ro:Castra
Dacia
Dacia (, ; ) was the land inhabited by the Dacians, its core in Transylvania, stretching to the Danube in the south, the Black Sea in the east, and the Tisza in the west. The Carpathian Mountains were located in the middle of Dacia. It ...
:Acidava
Acidava (''Acidaua'') was a Dacian and later Roman fortress on the Olt river near the lower Danube. The settlements remains are located in today's Enoşeşti, Olt County, Oltenia, Romania.
History
After the Roman conquest of Dacia by Roman ...
, Ad Mutrium, Ad Pannonios, Agnaviae, Aizis, Altenum, Angustia, Apulum, Arcidava, Arcobara, Arutela, Auraria Daciae, Bacaucis, Berzovia
Berzovia ( hu, Zsidovin) is a commune in Caraș-Severin County, Banat, Romania with a population of 4,165 people. It is composed of three villages: Berzovia, Fizeș (''Krassófűzes'') and Gherteniș (''Gertenyes'').
It is mentioned on the Tabula ...
, Buridava
Buridava (''Burridava'') was a Dacian town. situated in Dacia, later Dacia Apulensis, now Romania, on the banks of the river Aluta, now Olt.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
The name is Geto- ...
, Caput Bubali, Caput Stenarum, Castra Traiana, Castra Nova, Certinae, Cumidava, Dierna, Drobeta, Jidava, Largiana, Micia, Naissus, Napoca, Optatiana, Partiscum, Pelendava
Pelendava (''Pelendoua'', ''Potulatensioi'', ''Polonda'' ) was a Dacian town.
Ancient sources
Ptolemy's Geographia
Tabula Peutingeriana
Etymology
History
Dacian town
Roman times
Archaeology
See also
* Daci ...
, Pons Aluti, Pons Vetus, Porolissum
Porolissum was an ancient Roman city in Dacia. Established as a military camp in 106 during Trajan's Dacian Wars, the city quickly grew through trade with the native Dacians and became the capital of the province Dacia Porolissensis in 124. The si ...
, Potaissa, Praetoria Augusta, Praetorium (Copăceni), Praetorium (Mehadia), Resculum, Romula
Romula or Malva was an ancient city in Roman Dacia, later the village of Reşca, Dobrosloveni Commune, Olt County, Romania. It was the capital of Dacia Malvensis, one of the three subdivisions of the province of Dacia.
History
The Roman ...
, Rupes
Rupes (plural ) is the Latin word for 'cliff'. It is used in planetary geology to refer to escarpments on other worlds. , the IAU has named 62 such features in the Solar System, on Mercury (17), Venus (7), the Moon (8), Mars (23), the asteroids ...
, Rusidava
Rusidava (or Zusidava) was a Dacian town mentioned in Tabula Peutingeriana between Acidava and Pons Aluti, today's Drăgășani, Vâlcea County, Romania.
See also
* Dacian davae
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia
* Dacia
D ...
, Samum, Sucidava
Sucidava (Sykibid, Skedevà after Procopius,Olga Karagiorgou Σucidava after Vasile Pârvan, where Σ is pronounced "sh"Pârvan - știri din Dacia Malvensis http://www.cimec.ro/Arheologie/ParvanArticole/ParvanStiriNouaDinDaciaMalvensis.pdf)) ...
, Tibiscum, Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa
Colonia Ulpia Traiana Augusta Dacica Sarmizegetusa was the capital and the largest city of Roman Dacia, later named ''Ulpia Traiana Sarmizegetusa'' after the former Dacian capital, located some 40 km away. Built on the ground of a camp of t ...
:Also castra of unknown name:
: Albești, Bădeni, Băile Homorod, Boroșneu Mare
Boroșneu Mare ( ro, Boroşneu Mare; hu, Nagyborosnyó) is a commune in Covasna County, Transylvania, Romania composed of six villages: Boroșneu Mare, Boroșneu Mic (''Kisborosnyó''), Dobolii de Sus (''Feldoboly''), Leț (''Lécfalva''), Țufal ...
, Brusturi, Brâncovenești, Bucium, Buciumi, Bulci, Bumbești-Jiu - Gară, Bumbești-Jiu - Vârtop, Băneasa, Bănița, Chitid, Cigmău, Cincșor, Cioroiu Nou, Colțești, Constantin Daicoviciu, Cornuțel, Cristești, Crâmpoia, Călugăreni, Desa, Duleu - Cornet cetate, Duleu - Odăi, Federi, Feldioara
Feldioara (german: Marienburg, ; hu, Földvár or ''Barcaföldvár'') is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania, about 15 kilometres from the city of Brașov. It is composed of three villages: Colonia Reconstrucția (''Bohntelep''), ...
, Fizești, Fâlfani, Gherla
Gherla (; hu, Szamosújvár; german: Neuschloss) is a municipiu, municipality in Cluj County, Romania (in the historical region of Transylvania). It is located from Cluj-Napoca on the river Someșul Mic, and has a population of 20,203. Three vil ...
, Gilău, Gresia, Hinova, Hoghiz
Hoghiz (german: Warmwasser; hu, Hévíz or ''Olthévíz'') is a commune in Brașov County, Transylvania, Romania. It is composed of six villages: Bogata Olteană (''Oltbogát''), Cuciulata (''Katscheloden''; ''Kucsuláta''), Dopca (''Dopich''; '' ...
, Hunedoara
Hunedoara (; german: Eisenmarkt; hu, Vajdahunyad ) is a city in Hunedoara County, Transylvania, Romania. It is located in southwestern Transylvania near the Poiana Ruscă Mountains, and administers five villages: Boș (''Bós''), Groș (''Grós' ...
, Ighiu, Islaz
Islaz is a commune in southern Romania, located in the southwestern Teleorman County, west of Turnu Măgurele. It is part of the historical province Oltenia, and is composed of two villages, Islaz and Moldoveni.
The commune is situated in the s ...
, Izbășești, Izvoarele, Jac, Livezile, Luncani / Târsa, Moldova Nouă
Moldova Nouă (; ; ; or ''Bošňák''; sr, Нова Молдава) is a town in southwestern Romania in Caraș-Severin County (the historical region of Banat), in an area known as '' Clisura Dunării''. The town administers three villages: M ...
, Negreni, Ocna Sibiului
Ocna Sibiului (; ) is a town in the centre of Sibiu County, in southern Transylvania, central Romania, 10 km to the north-west of the county capital Sibiu. The town administers a single village, Topârcea (''Tschapertsch''; ''Toporcsa'').
A ...
, Olteni, Odorheiu Secuiesc
Odorheiu Secuiesc (; hu, Székelyudvarhely, ; german: Odorhellen) is the second largest municipality in Harghita County, Transylvania, Romania. In its short form, it is also known as ''Odorhei'' in Romanian and ''Udvarhely'' in Hungarian. The Hun ...
, Orheiu Bistriței, Pietroasele, Pietroșani, Ploiești
Ploiești ( , , ), formerly spelled Ploești, is a city and county seat in Prahova County, Romania. Part of the historical region of Muntenia, it is located north of Bucharest.
The area of Ploiești is around , and it borders the Blejoi commune ...
, Plosca, Poiana, Pojejena, Porceni, Purcăreni, Putineiu, Puținei, Roșiorii de Vede
Roșiorii de Vede (; sometimes Roșiori de Vede or, in old versions, Rușii de Vede) is a city in Teleorman County, Romania. Located in the Muntenia region, it is one of the oldest cities in the country. It was first mentioned in a document whic ...
, Râu Bărbat, Răcarii de Jos, Războieni-Cetate, Reci
Reci ( hu, Réty, Hungarian pronunciation: ) is a commune in Covasna County, Transylvania, Romania composed of four villages:
*Aninoasa / Egerpatak
*Bita / Bita
*Reci
*Saciova / Szacsva
It also included Comolău (''Komolló'') village until 196 ...
, Salcia, Sfârleanca, Castra of Sighișoara, Sighișoara, Castra of Slăveni, Slăveni, Castra of Stremț, Stremț, Castra of Surducu Mare, Surducu Mare, Castra of Sânpaul (Harghita), Sânpaul (Harghita), Castra of Sânpaul (Mureș), Sânpaul (Mureș), Castra of Săpata de Jos, Săpata de Jos, Castra of Sărățeni, Sărățeni, Sfârleanca, Castra of Tihău, Tihău, Castra of Titești, Titești, Castra of Târnăveni, Târnăveni, Castra of Urlueni, Urlueni, Castra of Voinești, Voinești, Castra of Voislova, Voislova, Castra of Șinca Veche, Șinca Veche, Castra of Zăvoi, Zăvoi
:Possible castra mentioned on Tabula Peutingeriana but not investigated:
:Ad Aquas/Aquae, Brucla, Gaganis, Masclianis, Petris, Salinae/Salinis
Dalmatia
:Delminium, Burnum, Dubrovnik, Ragusia or Laus, Tilurium, Split, Croatia, SplitGaul, Gallia
:Argentoratum, Harfleur, Castra Constantia, Lugdunum :Also castra of unknown name: :OudenburgGermania
:Abensberg, Abusina, Augsburg, Augusta Vindelicorum, Bonna, History of Cologne, Colonia Agrippinae, Velsen, Flevum, Mainz, Moguntiacum, Neuss, Novaesium, Nijmegen, Noviomagus, Traiectum (Utrecht), Traiectum, Xanten, Vetera :Also castra of unknown name: :SaalburgHispania
:Astorga, Spain, Asturica Augusta, Cáceres, Spain, Castra Servilia, León, Spain, Legio, Lugo, Lucus Augusti, Tarragona, TarracoItalia (Roman province), Italia
:Castra ad Fluvium Frigidum, Albano Laziale, Castra Albana, Castra Nova equitum singularium, Castra of ancient Rome, Castra Peregrina, Castra Praetoria, Cremona, Emona, Turin, Castra Taurinorum, Piacenza, PlacentiaJudaea Province, Judaea
See also Syria Palaestina. Included here are the Galilee and Perea. :Legio, Aelia Capitolina , RaphanaMesopotamia (Roman province), Mesopotamia
:Nisibis, Sinjar, Singara, ZiataMoesia
:Ad Stoma (castra), Ad Stoma, Arrubium (castra), Arrubium, Altinum, Argamum (castra), Argamum, Axiopolis (castra), Axiopolis, Frecăţei, Tulcea, Beroe, Callatis, Capidava (castra), Capidava, Carsium (castra), Carsium, Cius, Dinogetia (castra), Dinogetia, Castra of Drajna de Sus, Drajna de Sus, Histriopolis (castra), Histriopolis, Halmyris (castra), Halmyris, Libida, Novae (fortress), Novae, Noviodunum, Oescus, Ratiaria, Sacidava (castra), Sacidava, Salsovia, Skopje, Scupi, Singidunum, Stratonis (castra), Stratonis, Tomis (castra), Tomis, Troesmis (castra), Troesmis, Ulmetum (castra), Ulmetum, Viminacium :Also castra of unknown name: :Castra of Basarabi-Murfatlar, Basarabi-Murfatlar, Castra of Tirighina-Bărboși, Tirighina-Bărboși, Castra of Cernavodă, CernavodăNoricum
:Asturis (Zwentendorf), Cannabiaca (Zeiselmauer-Wolfpassing), Comagena, Lauriacum, LentiaOsrhoene
:CircesiumPannonia
:Aquincum, Szőny, Brigetio, Carnuntum, Osijek, Mursa, Ptuj, Poetovio, Sirmium, Taurunum, Vienna, VindobonaRaetia
:Bregenz, Brigantium, Castra Regina, Passau, Batavis, Meran, Castra MaienseMaxima Sequanorum
:Augusta Raurica, VindonissaSyria (Roman province), Syria
:Androna, Apamea (Syria), Apamea, Bosra, Bostra, Dura-Europos, Dura, Homs, EmesaSee also
* List of ancient cities in Thrace and Dacia * :ro:Listă de castre romane din România, List of castra in Romania (Romanian version)References
External links
Roman castra from Romania - Google Maps
Earth
{{Webarchive, url=https://archive.is/20121205025930/http://bbs.keyhole.com/ubb/showflat.php/Cat/0/Number/1274893/Main/1274893 , date=2012-12-05 Roman fortifications by province, de:Legionslager la:Castra ro:Castra