List of battleships of Russia and the Soviet Union on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 This is a list of battleships of Russian Empire and the Soviet Union.
__TOC__
This is a list of battleships of Russian Empire and the Soviet Union.
__TOC__
 ''Rostislav'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Black Sea Fleet in the 1890s. She was conceived as a small, inexpensive
''Rostislav'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Black Sea Fleet in the 1890s. She was conceived as a small, inexpensive
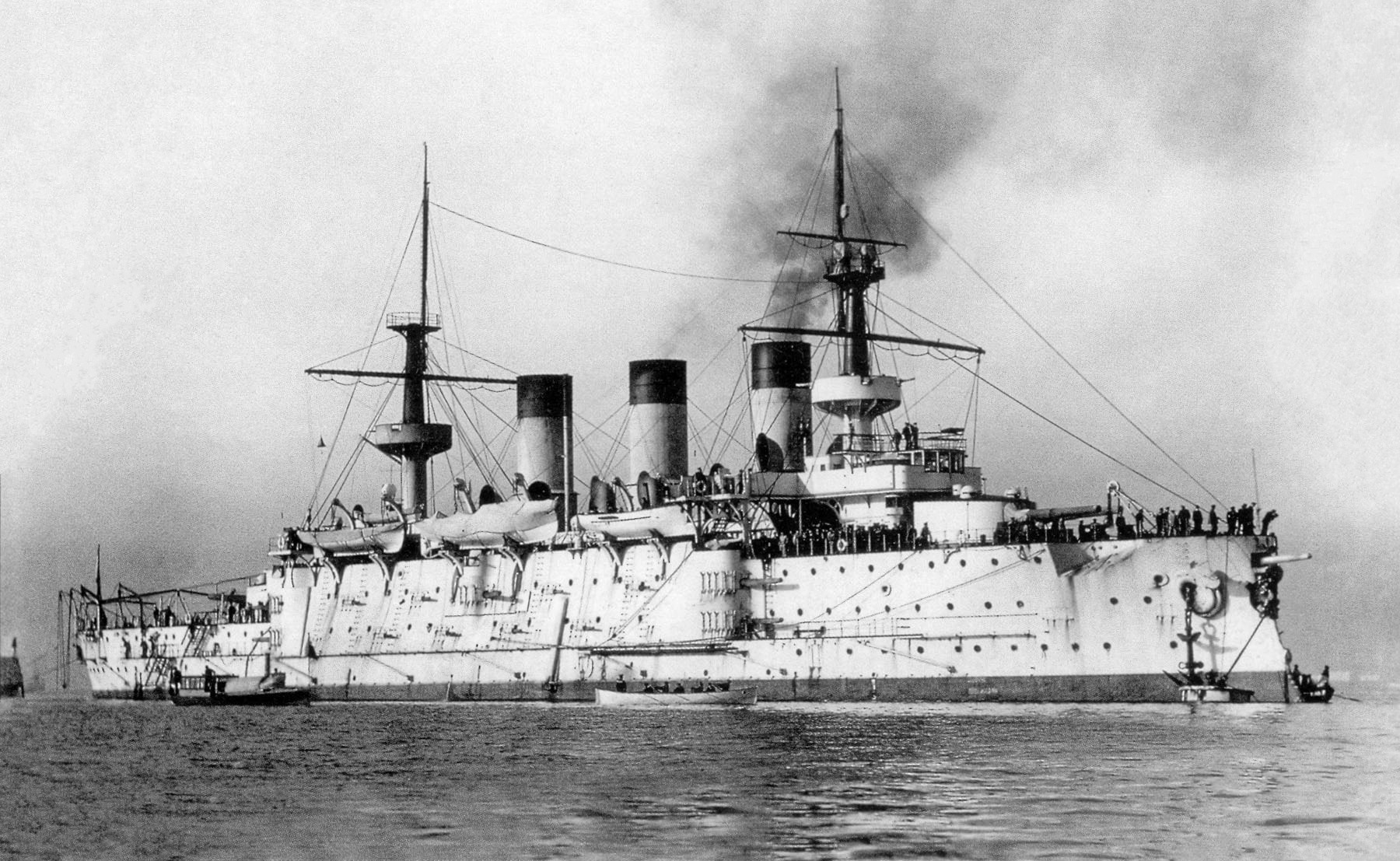 The ''Peresvet'' class was a
The ''Peresvet'' class was a
 The five ''Borodino''-class battleships (also known as the ''Suvorov'' class) were pre-dreadnoughts built between 1899 and 1905 for the Pacific Squadron. Three of the class were sunk and one captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Battle of Tsushima.
Historically, the ''Borodino''-class battleships established two records; under Russian Admiral
The five ''Borodino''-class battleships (also known as the ''Suvorov'' class) were pre-dreadnoughts built between 1899 and 1905 for the Pacific Squadron. Three of the class were sunk and one captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Battle of Tsushima.
Historically, the ''Borodino''-class battleships established two records; under Russian Admiral
 The ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class were the last predreadnought battleships built for the Baltic Fleet. They were conceived by the Naval Technical Committee in 1903 as an incremental development of the s with increased displacement and heavier
The ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class were the last predreadnought battleships built for the Baltic Fleet. They were conceived by the Naval Technical Committee in 1903 as an incremental development of the s with increased displacement and heavier
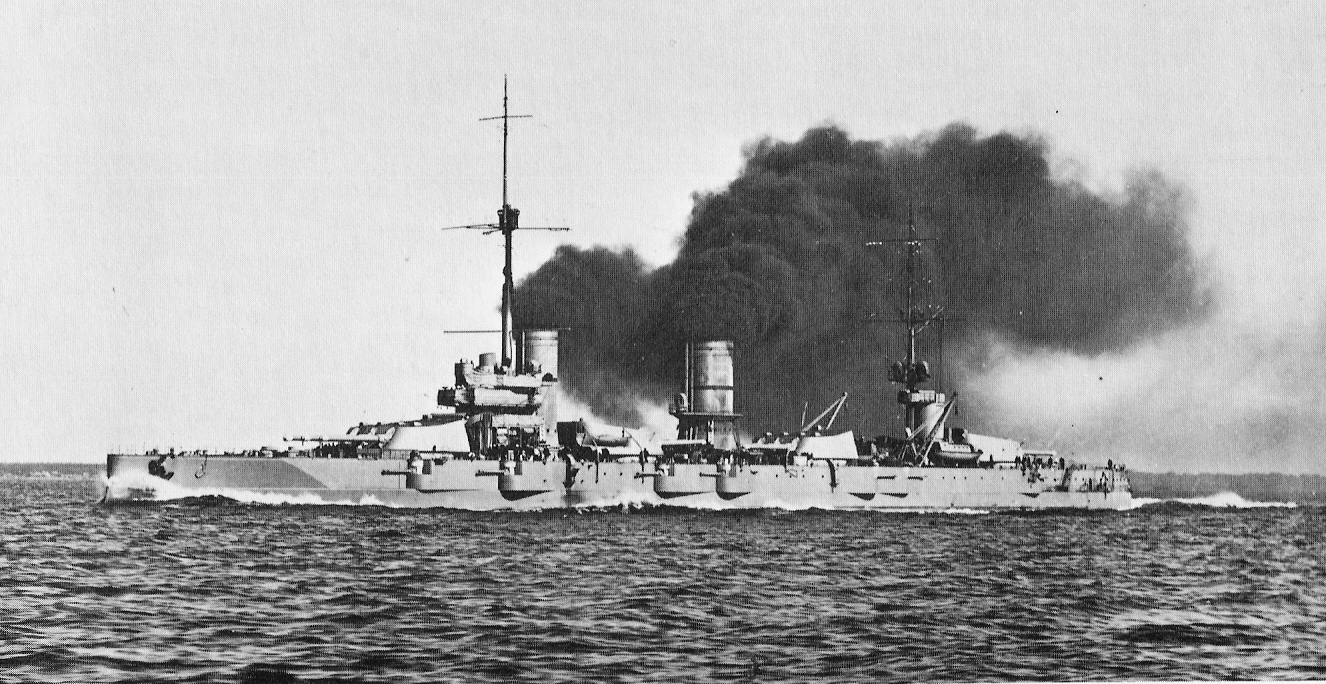 The ''Gangut''-class battleships were the first
The ''Gangut''-class battleships were the first
 was loaned by the
was loaned by the
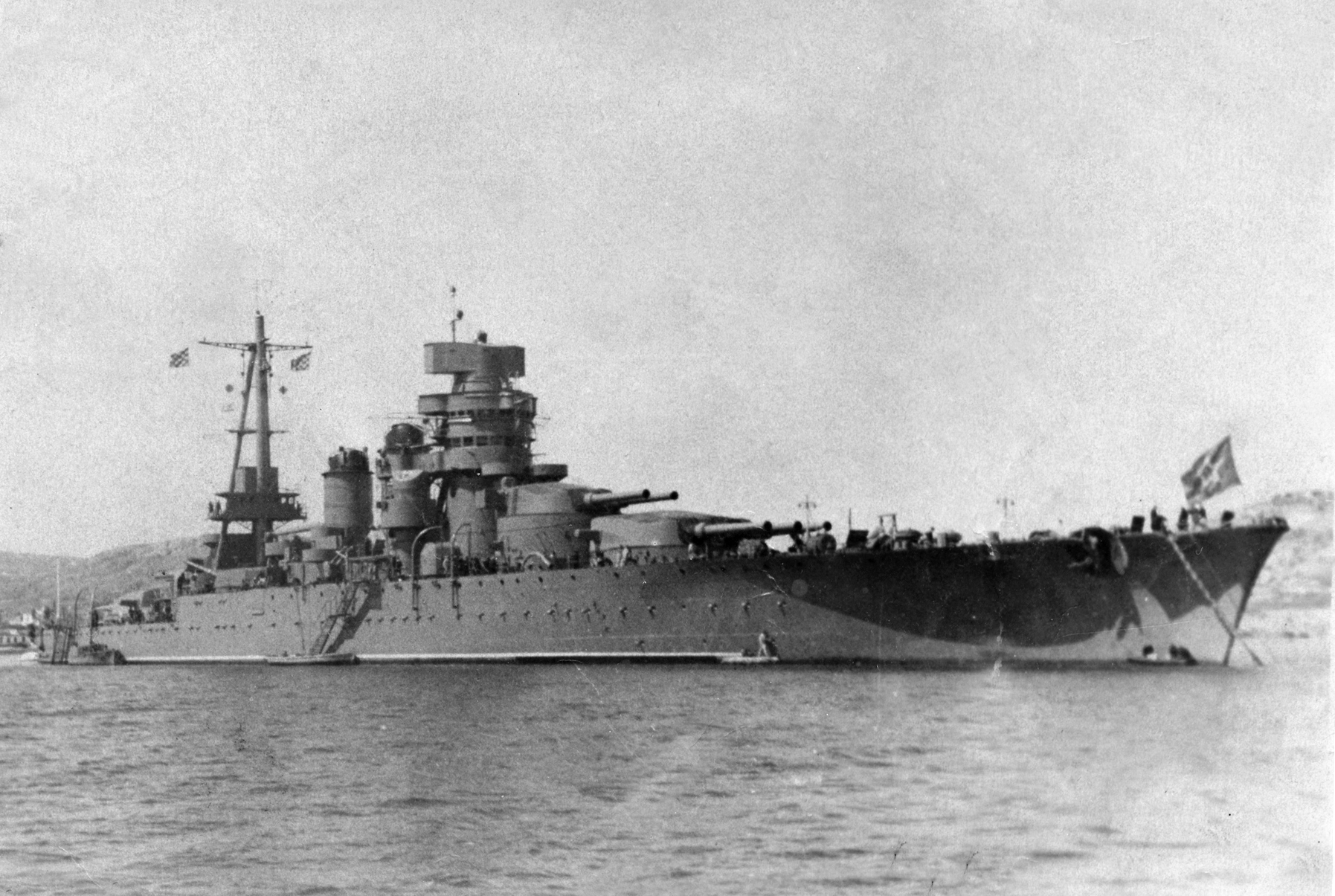 The Italian battleship ''Giulio Cesare'' was turned over to the Soviet Union by Italy in 1948 as
The Italian battleship ''Giulio Cesare'' was turned over to the Soviet Union by Italy in 1948 as
 This is a list of battleships of Russian Empire and the Soviet Union.
__TOC__
This is a list of battleships of Russian Empire and the Soviet Union.
__TOC__
Pre-Dreadnoughts
''Dvenadsat Apostolov''
''Dvenadsat Apostolov'' was apre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
built for the Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
. She joined the fleet in mid-1893, but was not fully ready for service until 1894. ''Dvenadsat Apostolov'' participated in the failed attempt to recapture the mutinous battleship in 1905. Decommissioned and disarmed in 1911, the ship became an immobile submarine depot ship
A submarine tender is a type of depot ship that supplies and supports submarines.
Development
Submarines are small compared to most oceangoing vessels, and generally do not have the ability to carry large amounts of food, fuel, torpedoes, a ...
the following year. ''Dvenadsat Apostolov'' was captured by the Germans in 1918 in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
and was handed over to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in December. Lying immobile in Sevastopol, she was captured by both sides in the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
before she was abandoned when the White Russians evacuated the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
in 1920. The ship was used as a stand-in for the title ship during the filming of ''The Battleship Potemkin
'' Battleship Potemkin'' (russian: Бронено́сец «Потёмкин», ''Bronenosets Potyomkin''), sometimes rendered as ''Battleship Potyomkin'', is a 1925 Soviet silent
drama film produced by Mosfilm. Directed and co-written by S ...
'' and was finally scrapped in 1931.
''Navarin''
''Navarin'' was apre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
built for the Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
in the late 1880s and early 1890s. The ship spent the early part of her career deployed in the Mediterranean and in the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
. She participated in the suppression of the Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an Xenophobia, anti-foreign, anti-colonialism, anti-colonial, and Persecution of Christians#China, anti-Christian uprising in China ...
in 1900 before returning to the Baltic Fleet in 1901. Several months after the beginning of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
in February 1904, she was assigned to the 2nd Pacific Squadron to relieve the Russian forces blockaded in Port Arthur. During the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:対馬沖海戦, Tsushimaoki''-Kaisen'', russian: Цусимское сражение, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known as the Battle of Tsushima Strait and the Naval Battle of Sea of Japan (Japanese: 日 ...
in May 1905, she was sunk by Japanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed ...
s which spread twenty-four linked mines across her path during the night. ''Navarin'' struck two of these mines and capsized with the loss of most of her crew.
''Tri Sviatitelia''
''Tri Sviatitelia'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Black Sea Fleet. She wasflagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
of the forces pursuing the mutinous battleship in June 1905. During World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
the ship encountered the German battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
(formally ''Yavuz Sultan Selim'') twice, but never hit the German ship, nor was she damaged by her. From 1915 onward she was relegated to the coast bombardment role as she was the oldest battleship in the Black Sea Fleet. ''Tri Sviatitelia'' was refitting in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
when the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
of 1917 began and she was never operational afterwards.
''Tri Sviatitelia'' was captured when the Germans took the city in May 1918 and was turned over to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
after the Armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
in November 1918. Her engines were destroyed in 1919 by the British when they withdrew from Sevastopol to prevent the advancing Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
from using her against the White Russians. She was abandoned when the Whites evacuated the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
in 1920 and was scrapped in 1923.
''Sissoi Veliky''
''Sissoi Veliky'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Baltic Fleet in the 1890s. The ship's construction was marred by organizational, logistical and engineering problems and dragged on for more than five years. She was commissioned in October 1896 with an appalling number of design and construction faults, and only a few of them were fixed during her lifetime. Immediately aftersea trial
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a " shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and ...
s, ''Sissoi Veliky'' sailed to the Mediterranean
The Mediterranean Sea is a sea connected to the Atlantic Ocean, surrounded by the Mediterranean Basin and almost completely enclosed by land: on the north by Western and Southern Europe and Anatolia, on the south by North Africa, and on ...
to enforce the naval blockade
A navy, naval force, or maritime force is the branch of a nation's armed forces principally designated for naval and amphibious warfare; namely, lake-borne, riverine, littoral, or ocean-borne combat operations and related functions. It include ...
of Crete
Crete ( el, Κρήτη, translit=, Modern: , Ancient: ) is the largest and most populous of the Greek islands, the 88th largest island in the world and the fifth largest island in the Mediterranean Sea, after Sicily, Sardinia, Cyprus, ...
during the Greco-Turkish War. In 1897 she suffered a devastating explosion of the aft gun turret
A gun turret (or simply turret) is a mounting platform from which weapons can be fired that affords protection, visibility and ability to turn and aim. A modern gun turret is generally a rotatable weapon mount that houses the crew or mechanis ...
that killed 21 men. After nine months in the docks of Toulon
Toulon (, , ; oc, label= Provençal, Tolon , , ) is a city on the French Riviera and a large port on the Mediterranean coast, with a major naval base. Located in the Provence-Alpes-Côte d'Azur region, and the Provence province, Toulon is th ...
for repairs, the ship sailed to the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
to reinforce the Russian presence there. In the summer of 1900, ''Sissoi Veliky'' supported the international campaign against the Boxer Rebellion
The Boxer Rebellion, also known as the Boxer Uprising, the Boxer Insurrection, or the Yihetuan Movement, was an Xenophobia, anti-foreign, anti-colonialism, anti-colonial, and Persecution of Christians#China, anti-Christian uprising in China ...
in China
China, officially the People's Republic of China (PRC), is a country in East Asia. It is the world's List of countries and dependencies by population, most populous country, with a Population of China, population exceeding 1.4 billion, slig ...
. Sailors from ''Sissoi Veliky'' and ''Navarin'' participated in the defence of the International Legations in Beijing
}
Beijing ( ; ; ), Chinese postal romanization, alternatively romanized as Peking ( ), is the Capital city, capital of the China, People's Republic of China. It is the center of power and development of the country. Beijing is the world's Li ...
for more than two months.
In 1902 the ship returned to Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
for repairs, but very little was achieved until the early losses of the Russo-Japanese War caused the formation of the Second Pacific Squadron to relieve the Russian forces blockaded in Port Arthur. ''Sissoi Veliky'' sailed for the Far East with the rest of the Baltic battleships and participated in the Battle of Tsushima
The Battle of Tsushima (Japanese:対馬沖海戦, Tsushimaoki''-Kaisen'', russian: Цусимское сражение, ''Tsusimskoye srazheniye''), also known as the Battle of Tsushima Strait and the Naval Battle of Sea of Japan (Japanese: 日 ...
on 27 May 1905. She survived the daytime artillery duel with Admiral Heihachirō Tōgō's ships, but was badly damaged and taking on water. During the night Japanese destroyer
In naval terminology, a destroyer is a fast, manoeuvrable, long-endurance warship intended to escort
larger vessels in a fleet, convoy or battle group and defend them against powerful short range attackers. They were originally developed ...
s scored a torpedo
A modern torpedo is an underwater ranged weapon launched above or below the water surface, self-propelled towards a target, and with an explosive warhead designed to detonate either on contact with or in proximity to the target. Historically, ...
hit on the ship that damaged her steering. The next morning the ship was unable to maintain speed because of flooding, and her crew surrendered to Japanese armed merchant cruisers. The ship capsized later that morning with the loss of 47 crewmen.
''Petropavlovsk'' class
The ''Petropavlovsk'' class, sometimes referred to as the ''Poltava'' class, was aclass
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differently ...
of three pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
s built for the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from ...
during the 1890s. They were transferred to the Pacific Squadron
The Pacific Squadron was part of the United States Navy squadron stationed in the Pacific Ocean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially with no United States ports in the Pacific, they operated out of storeships which provided naval s ...
upon completion and based at Port Arthur before the start of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905. All three ships participated in the Battle of Port Arthur
The of 8–9 February 1904 marked the commencement of the Russo-Japanese War. It began with a surprise night attack by a squadron of Japanese destroyers on the neutral Russian fleet anchored at Port Arthur, Manchuria, and continued with an ...
on the second day of the war. sank two months after the war began after striking one or more mines laid by the Japanese. The remaining two ships participated in the Battle of the Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea ( ja, 黄海海戦, Kōkai kaisen; russian: Бой в Жёлтом море) was a major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 A ...
in August 1904 and were sunk or scuttled
Scuttling is the deliberate sinking of a ship. Scuttling may be performed to dispose of an abandoned, old, or captured vessel; to prevent the vessel from becoming a navigation hazard; as an act of self-destruction to prevent the ship from being ...
during the final stages of the Siege of Port Arthur
The siege of Port Arthur ( ja, 旅順攻囲戦, ''Ryojun Kōisen''; russian: link=no, Оборона Порт-Артура, ''Oborona Port-Artura'', August 1, 1904 – January 2, 1905) was the longest and most violent land battle of the Russ ...
.
was salvaged after the Japanese captured Port Arthur and incorporated into the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
. The ship, renamed in Japanese service, participated in the Battle of Tsingtao
The siege of Tsingtao (or Tsingtau) was the attack on the German port of Tsingtao (now Qingdao) in China during World War I by Japan and the United Kingdom. The siege was waged against Imperial Germany between 27 August and 7 November 191 ...
in late 1914, during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. She was sold back to the Russians in 1916 and renamed as her original name was in use by another battleship. The ship became the flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
of the Russian Arctic Flotilla in 1917 and her crew supported the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s later that year. She was seized by the British in early 1918 when they intervened in the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, abandoned by them when they withdrew and scrapped
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
by the Soviets in 1924.
''Rostislav''
 ''Rostislav'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Black Sea Fleet in the 1890s. She was conceived as a small, inexpensive
''Rostislav'' was a pre-dreadnought battleship built for the Black Sea Fleet in the 1890s. She was conceived as a small, inexpensive coastal defence ship
Coastal defence ships (sometimes called coastal battleships or coast defence ships) were warships built for the purpose of coastal defence, mostly during the period from 1860 to 1920. They were small, often cruiser-sized warships that sacrifi ...
, but the Navy abandoned the concept in favor of a compact, seagoing battleship with a displacement of . Poor design and construction practices increased her actual displacement by more than . ''Rostislav'' became the world's first capital ship to burn fuel oil
Fuel oil is any of various fractions obtained from the distillation of petroleum (crude oil). Such oils include distillates (the lighter fractions) and residues (the heavier fractions). Fuel oils include heavy fuel oil, marine fuel oil (MFO), b ...
, rather than coal.Willmott, p. 57. Her combat ability was compromised by the use of main guns instead of the de facto
''De facto'' ( ; , "in fact") describes practices that exist in reality, whether or not they are officially recognized by laws or other formal norms. It is commonly used to refer to what happens in practice, in contrast with '' de jure'' ("by l ...
Russian standard of 12 inches.
Her hull was launched in September 1896, but non-delivery of the ship's main guns delayed her maiden voyage until 1899 and her completion until 1900. In May 1899 ''Rostislav'' became the first ship of the Imperial Navy to be commanded by a member of the House of Romanov
The House of Romanov (also transcribed Romanoff; rus, Романовы, Románovy, rɐˈmanəvɨ) was the reigning dynasty, imperial house of Russia from 1613 to 1917. They achieved prominence after the Tsarina, Anastacia of Russia, Anastasi ...
, Captain Alexander Mikhailovich. From 1903 to 1912 the ship was the flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
of the second-in-command
Second-in-command (2i/c or 2IC) is a title denoting that the holder of the title is the second-highest authority within a certain organisation.
Usage
In the British Army or Royal Marines, the second-in-command is the deputy commander of a unit, ...
of the Black Sea Fleet. During the 1905 Russian Revolution
The Russian Revolution of 1905,. also known as the First Russian Revolution,. occurred on 22 January 1905, and was a wave of mass political and social unrest that spread through vast areas of the Russian Empire. The mass unrest was directed again ...
her crew was on the verge of mutiny but remained loyal to the regime, and actively suppressed the mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among memb ...
of the cruiser .
''Rostislav'' was actively engaged in World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
until the collapse of the Black Sea Fleet in the beginning of 1918. She was the first Russian ship to fire upon enemy targets on land during World War I, the first Russian ship to be hit by a German airstrike
An airstrike, air strike or air raid is an offensive operation carried out by aircraft. Air strikes are delivered from aircraft such as blimps, balloons, fighters, heavy bombers, ground attack aircraft, attack helicopters and drones. The off ...
, and the first one to destroy a submarine, albeit a Russian one. In April 1918 the fleeing Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s abandoned ''Rostislav'' in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
. One year later the British occupation forces permanently disabled her engines. The White forces repurposed the ship as a towed floating battery, then scuttled her in the Strait of Kerch
The Kerch Strait, uk, Керченська протока, crh, Keriç boğazı, ady, Хы ТӀуалэ is a strait in Eastern Europe. It connects the Black Sea and the Sea of Azov, separating the Kerch Peninsula of Crimea in the west f ...
in November 1920.
''Peresvet'' class
 The ''Peresvet'' class was a
The ''Peresvet'' class was a class
Class or The Class may refer to:
Common uses not otherwise categorized
* Class (biology), a taxonomic rank
* Class (knowledge representation), a collection of individuals or objects
* Class (philosophy), an analytical concept used differently ...
of three pre-dreadnought battleship
Pre-dreadnought battleships were sea-going battleships built between the mid- to late- 1880s and 1905, before the launch of in 1906. The pre-dreadnought ships replaced the ironclad battleships of the 1870s and 1880s. Built from steel, protec ...
s built for the Imperial Russian Navy
The Imperial Russian Navy () operated as the navy of the Russian Tsardom and later the Russian Empire from 1696 to 1917. Formally established in 1696, it lasted until dissolved in the wake of the February Revolution of 1917. It developed from ...
around the end of the 19th century. and were transferred to the Pacific Squadron
The Pacific Squadron was part of the United States Navy squadron stationed in the Pacific Ocean in the 19th and early 20th centuries. Initially with no United States ports in the Pacific, they operated out of storeships which provided naval s ...
upon completion and based at Port Arthur from 1901 and 1903. All three ships were lost by the Russians in the Russo-Japanese War; ''Peresvet'' and ''Pobeda'' participated in the Battles of Port Arthur and the Yellow Sea
The Yellow Sea is a marginal sea of the Western Pacific Ocean located between mainland China and the Korean Peninsula, and can be considered the northwestern part of the East China Sea. It is one of four seas named after common colour ter ...
and were sunk during the Siege of Port Arthur
The siege of Port Arthur ( ja, 旅順攻囲戦, ''Ryojun Kōisen''; russian: link=no, Оборона Порт-Артура, ''Oborona Port-Artura'', August 1, 1904 – January 2, 1905) was the longest and most violent land battle of the Russ ...
. , the third ship, was sunk at the Battle of Tsushima with the loss of over half her crew. ''Peresvet'' and ''Pobeda'' were salvaged after the Japanese captured Port Arthur and incorporated into the Imperial Japanese Navy
The Imperial Japanese Navy (IJN; Kyūjitai: Shinjitai: ' 'Navy of the Greater Japanese Empire', or ''Nippon Kaigun'', 'Japanese Navy') was the navy of the Empire of Japan from 1868 to 1945, when it was dissolved following Japan's surrender ...
. ''Peresvet'' was sold back to the Russians during World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
and sank after hitting German mines in the Mediterranean in early 1917 while ''Pobeda'', renamed , participated in the Battle of Tsingtao
The siege of Tsingtao (or Tsingtau) was the attack on the German port of Tsingtao (now Qingdao) in China during World War I by Japan and the United Kingdom. The siege was waged against Imperial Germany between 27 August and 7 November 191 ...
in late 1914. She became a gunnery training ship in 1917 until she was disarmed and hulk
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of ''The Incredible Hulk (comic book), The Incredible Hulk' ...
ed in 1922–1923. The ship was scrapped
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
after the end of World War II
World War II or the Second World War, often abbreviated as WWII or WW2, was a world war that lasted from 1939 to 1945. It involved the World War II by country, vast majority of the world's countries—including all of the great power ...
.
''Potemkin''
(«Князь Потёмкин-Таврический», 1900 BSF) – Renamed («Пантелеймон») 1905, renamed («Потёмкин-Таврический) 1917, («Борец за Свободу») 1917, destroyed by British troops atSevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
1919
''Retvizan''
''Retvizan'' () was a pre-dreadnought battleship built before the Russo-Japanese War for the Imperial Russian Navy in theUnited States
The United States of America (U.S.A. or USA), commonly known as the United States (U.S. or US) or America, is a country Continental United States, primarily located in North America. It consists of 50 U.S. state, states, a Washington, D.C., ...
. She was built by the William Cramp & Sons
William Cramp & Sons Shipbuilding Company (also known as William Cramp & Sons Ship & Engine Building Company) of Philadelphia was founded in 1830 by William Cramp, and was the preeminent U.S. iron shipbuilder of the late 19th century.
Company hi ...
Ship & Engine Building Company of Philadelphia
Philadelphia, often called Philly, is the largest city in the Commonwealth of Pennsylvania, the sixth-largest city in the U.S., the second-largest city in both the Northeast megalopolis and Mid-Atlantic regions after New York City. Since ...
, although the armament was made at the Obukhov works in Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
and shipped to America for installation.
''Retvizan'' was torpedoed during the Japanese surprise attack on Port Arthur during the night of 8–9 February 1904 and grounded in the harbor entrance when she attempted to take refuge inside as her draft had significantly deepened from all of the water she had taken aboard after the torpedo hit. She was eventually refloated and repaired by mid-June. She joined the rest of the 1st Pacific Squadron when they attempted to reach Vladivostok
Vladivostok ( rus, Владивосто́к, a=Владивосток.ogg, p=vɫədʲɪvɐˈstok) is the largest city and the administrative center of Primorsky Krai, Russia. The city is located around the Golden Horn Bay on the Sea of Japan, ...
though the Japanese blockade on 10 August. The Japanese battle fleet engaged them in the Battle of the Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea ( ja, 黄海海戦, Kōkai kaisen; russian: Бой в Жёлтом море) was a major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 A ...
and forced most of the Russian ships to return to Port Arthur after killing the squadron commander and damaging his flagship
A flagship is a vessel used by the commanding officer of a group of naval ships, characteristically a flag officer entitled by custom to fly a distinguishing flag. Used more loosely, it is the lead ship in a fleet of vessels, typically the ...
. She was sunk by Japanese howitzer
A howitzer () is a long- ranged weapon, falling between a cannon (also known as an artillery gun in the United States), which fires shells at flat trajectories, and a mortar, which fires at high angles of ascent and descent. Howitzers, like ot ...
s in December after the Japanese had gained control of the heights around the harbor.
The Japanese raised her after the surrender of Port Arthur in January 1905 and repaired her. She was commissioned in the Imperial Japanese Navy as in 1908. In Sasebo when the Japanese declared war on Germany
Germany,, officially the Federal Republic of Germany, is a country in Central Europe. It is the second most populous country in Europe after Russia, and the most populous member state of the European Union. Germany is situated betwee ...
in 1914 she was sent to reinforce the weak British squadron in British Columbia
British Columbia (commonly abbreviated as BC) is the westernmost province of Canada, situated between the Pacific Ocean and the Rocky Mountains. It has a diverse geography, with rugged landscapes that include rocky coastlines, sandy beaches, for ...
, but was diverted to Hawaii
Hawaii ( ; haw, Hawaii or ) is a state in the Western United States, located in the Pacific Ocean about from the U.S. mainland. It is the only U.S. state outside North America, the only state that is an archipelago, and the only stat ...
when reports of the arrival of a German gunboat there were received. She was sent to search for other German ships after the Americans interned the German ship in November, but did not encounter any. After World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
she supported the Japanese intervention in the Russian Civil War
{{Infobox military conflict
, conflict = Russian Civil War
, partof = the Russian Revolution and the aftermath of World War I
, image =
, caption = Clockwise from top left:
{{flatlist,
*Soldiers ...
, but was disarmed in 1922 in accordance with the Washington Naval Treaty
The Washington Naval Treaty, also known as the Five-Power Treaty, was a treaty signed during 1922 among the major Allies of World War I, which agreed to prevent an arms race by limiting naval construction. It was negotiated at the Washington Nav ...
. She was sunk as a gunnery target in 1924.
''Tsesarevich''
''Tsesarevich'' () was a pre-dreadnought built inFrance
France (), officially the French Republic ( ), is a country primarily located in Western Europe. It also comprises of Overseas France, overseas regions and territories in the Americas and the Atlantic Ocean, Atlantic, Pacific Ocean, Pac ...
for the Pacific Squadron. She participated in the Russo-Japanese War, and was the flagship of Admiral
Admiral is one of the highest ranks in some navies. In the Commonwealth nations and the United States, a "full" admiral is equivalent to a "full" general in the army or the air force, and is above vice admiral and below admiral of the fleet ...
Wilgelm Vitgeft
Wilhelm Withöft (russian: Вильгельм Карлович Витгефт, tr. ; October 14, 1847 – August 10, 1904), more commonly known as Wilgelm Vitgeft, was a Russia-German admiral in the Imperial Russian Navy, noted for his servic ...
in the Battle of the Yellow Sea
The Battle of the Yellow Sea ( ja, 黄海海戦, Kōkai kaisen; russian: Бой в Жёлтом море) was a major naval battle of the Russo-Japanese War, fought on 10 August 1904. In the Russian Navy, it was referred to as the Battle of 10 A ...
. Her design was the basis of the s which were built in Russia.
''Borodino'' class
 The five ''Borodino''-class battleships (also known as the ''Suvorov'' class) were pre-dreadnoughts built between 1899 and 1905 for the Pacific Squadron. Three of the class were sunk and one captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Battle of Tsushima.
Historically, the ''Borodino''-class battleships established two records; under Russian Admiral
The five ''Borodino''-class battleships (also known as the ''Suvorov'' class) were pre-dreadnoughts built between 1899 and 1905 for the Pacific Squadron. Three of the class were sunk and one captured by the Imperial Japanese Navy during the Battle of Tsushima.
Historically, the ''Borodino''-class battleships established two records; under Russian Admiral Zinovy Rozhestvensky
Zinovy Petrovich Rozhestvensky (russian: Зиновий Петрович Рожественский, tr. ; – January 14, 1909) was an admiral of the Imperial Russian Navy. He was in command of the Second Pacific Squadron in the Battle of Tsu ...
riding in his flagship, , he led the Russian battleship fleet on the longest coal powered journey ever conducted by a steel battleship fleet during wartime, a voyage of over one way. Secondly, although sunk in battle, the ''Borodino''s participated in the only decisive battleship fleet action ever fought. Lastly, what may be the most distinctive item of interest for the future, is the fact that the ships were constructed with tumblehome
Tumblehome is a term describing a hull which grows narrower above the waterline than its beam. The opposite of tumblehome is flare.
A small amount of tumblehome is normal in many naval architecture designs in order to allow any small projecti ...
hulls, seemingly wider at the bottom then narrower towards the top. As a lesson from Tsushima, tumblehome construction was discarded in warship design, as they were regarded as unstable under combat conditions.
''Evstafi'' class
The ''Evstafi'' class were the last pre-dreadnought battleships built for the Black Sea Fleet. They were slightly enlarged versions of the , with increased armour and more guns. Numerous alterations were made as a result of experience in theRusso-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
of 1904–1905 that seriously delayed the completion of the two ships.
They were the most modern ships in the Black Sea Fleet when World War I began and formed the core of the fleet for the first year of the war, before the newer dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
s entered service. They forced the German battlecruiser
The battlecruiser (also written as battle cruiser or battle-cruiser) was a type of capital ship of the first half of the 20th century. These were similar in displacement, armament and cost to battleships, but differed in form and balance of attr ...
to disengage during the Battle of Cape Sarych shortly after Russia declared war on the Ottoman Empire in late 1914. Both ships covered several bombardments of the Bosporus
The Bosporus Strait (; grc, Βόσπορος ; tr, İstanbul Boğazı 'Istanbul strait', colloquially ''Boğaz'') or Bosphorus Strait is a natural strait and an internationally significant waterway located in Istanbul in northwestern Tu ...
fortifications in early 1915, including one where they were attacked by ''Goeben'', but they managed to drive her off. Later, and were relegated to secondary roles after the first dreadnought entered service in late 1915, and were subsequently put into reserve in 1918 in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
.
Both ships were captured when the Germans took the city in May 1918 and were turned over to the Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
after the Armistice
An armistice is a formal agreement of warring parties to stop fighting. It is not necessarily the end of a war, as it may constitute only a cessation of hostilities while an attempt is made to negotiate a lasting peace. It is derived from the ...
in November 1918. Their engines were destroyed in 1919 by the British when they withdrew from Sevastopol to prevent the advancing Bolsheviks
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
from using them against the White Russians. They were abandoned when the Whites evacuated the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
in 1920 and were scrapped in 1922–1923.
''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class
 The ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class were the last predreadnought battleships built for the Baltic Fleet. They were conceived by the Naval Technical Committee in 1903 as an incremental development of the s with increased displacement and heavier
The ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' class were the last predreadnought battleships built for the Baltic Fleet. They were conceived by the Naval Technical Committee in 1903 as an incremental development of the s with increased displacement and heavier secondary armament
Secondary armament is a term used to refer to smaller, faster-firing weapons that were typically effective at a shorter range than the main (heavy) weapons on military systems, including battleship- and cruiser-type warships, tanks/armored p ...
. Work on the lead ship
The lead ship, name ship, or class leader is the first of a series or class of ships all constructed according to the same general design. The term is applicable to naval ships and large civilian vessels.
Large ships are very complex and may ...
, (Saint Andrew
Andrew the Apostle ( grc-koi, Ἀνδρέᾱς, Andréās ; la, Andrēās ; , syc, ܐܰܢܕ݁ܪܶܐܘܳܣ, ʾAnd’reʾwās), also called Saint Andrew, was an apostle of Jesus according to the New Testament. He is the brother of Simon Pete ...
), commenced at the New Admiralty, Saint Petersburg
Saint Petersburg ( rus, links=no, Санкт-Петербург, a=Ru-Sankt Peterburg Leningrad Petrograd Piter.ogg, r=Sankt-Peterburg, p=ˈsankt pʲɪtʲɪrˈburk), formerly known as Petrograd (1914–1924) and later Leningrad (1924–1991), i ...
in March 1904; trailed by six months.
The disastrous experiences of the Russo-Japanese War
The Russo-Japanese War ( ja, 日露戦争, Nichiro sensō, Japanese-Russian War; russian: Ру́сско-япóнская войнá, Rússko-yapónskaya voyná) was fought between the Empire of Japan and the Russian Empire during 1904 and 1 ...
led to countless redesigns, change orders and delays in construction. After the completion of ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' its builders identified seventeen distinct stages of her design. ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' was launched in October 1906 but subsequent alterations delayed completion until 1911. Almost all of her hull was armored, albeit thinly; redesign and refinement of protective armor continued until 1912. The ship's armament mixed novel quick-firing, long-range, 8-inch guns with obsolescent 12-inch 40-caliber main guns. The ''Andrei Pervozvanny''-class battleships became the only battleships of the Old World
The "Old World" is a term for Afro-Eurasia that originated in Europe , after Europeans became aware of the existence of the Americas. It is used to contrast the continents of Africa, Europe, and Asia, which were previously thought of by thei ...
fitted with lattice mast
Lattice masts, or cage masts, or basket masts, are a type of observation mast common on United States Navy major warships in the early 20th century. They are a type of hyperboloid structure, whose weight-saving design was invented by the Russia ...
s, which were replaced with conventional masts at the beginning of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. The imposing ships, the largest in the Russian Navy until the completion of , were dated from the start: by the time of their sea trial
A sea trial is the testing phase of a watercraft (including boats, ships, and submarines). It is also referred to as a " shakedown cruise" by many naval personnel. It is usually the last phase of construction and takes place on open water, and ...
s the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
had already launched the super-dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
s.
In the first year of World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
, ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' and ''Imperator Pavel I'' comprised the battle core of the Baltic Fleet. For most of the war they remained moored in the safety of Sveaborg and Helsingfors
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the capital, primate, and most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of Uusimaa in southern Finland, and has a population of . The city' ...
. Idle, demoralized enlisted men subscribed to Bolshevik ideology and on took control of the ships in a violent mutiny. The battleships survived the Ice Cruise of 1918, and ''Andrei Pervozvanny'' later ruthlessly gunned down the Krasnaya Gorka fort
Krasnaya Gorka (Красная Горка meaning Red Hill) is a coastal artillery fortress in Lomonosovsky District, Leningrad Oblast, Russia. It is located on the southern shore of the Gulf of Finland, opposite Kotlin Island and the Baltic Flee ...
mutiny of 1919. After the Kronstadt rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion ( rus, Кронштадтское восстание, Kronshtadtskoye vosstaniye) was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors and civilians against the Bolshevik government in the Russian SFSR port city of Kronstadt. Loc ...
the Bolshevik government lost interest in maintaining the battleships, and they were laid up in November–December 1923.
Dreadnoughts
''Gangut'' class
 The ''Gangut''-class battleships were the first
The ''Gangut''-class battleships were the first dreadnought
The dreadnought (alternatively spelled dreadnaught) was the predominant type of battleship in the early 20th century. The first of the kind, the Royal Navy's , had such an impact when launched in 1906 that similar battleships built after her ...
s built for the Imperial Russian Navy, begun before World War I
World War I (28 July 1914 11 November 1918), often abbreviated as WWI, was List of wars and anthropogenic disasters by death toll, one of the deadliest global conflicts in history. Belligerents included much of Europe, the Russian Empire, ...
. Their role was to defend the mouth of the Gulf of Finland
The Gulf of Finland ( fi, Suomenlahti; et, Soome laht; rus, Фи́нский зали́в, r=Finskiy zaliv, p=ˈfʲinskʲɪj zɐˈlʲif; sv, Finska viken) is the easternmost arm of the Baltic Sea. It extends between Finland to the north and ...
against the Germans, who never tried to enter, so the ships spent their time training and providing cover for minelaying
A minelayer is any warship, submarine or military aircraft deploying explosive mines. Since World War I the term "minelayer" refers specifically to a naval ship used for deploying naval mines. "Mine planting" was the term for installing co ...
operations. Their crews participated in the general mutiny
Mutiny is a revolt among a group of people (typically of a military, of a crew or of a crew of pirates) to oppose, change, or overthrow an organization to which they were previously loyal. The term is commonly used for a rebellion among memb ...
of the Baltic Fleet
, image = Great emblem of the Baltic fleet.svg
, image_size = 150
, caption = Baltic Fleet Great ensign
, dates = 18 May 1703 – present
, country =
, allegiance = (1703–1721) (1721–1917) (1917–1922) (1922–1991)(1991–present)
...
after the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
in 1917, and joined the Bolshevik
The Bolsheviks (russian: Большевики́, from большинство́ ''bol'shinstvó'', 'majority'),; derived from ''bol'shinstvó'' (большинство́), "majority", literally meaning "one of the majority". also known in English ...
s the following year. The Russians were forced to evacuate their naval base at Helsinki
Helsinki ( or ; ; sv, Helsingfors, ) is the Capital city, capital, primate city, primate, and List of cities and towns in Finland, most populous city of Finland. Located on the shore of the Gulf of Finland, it is the seat of the region of U ...
after Finland
Finland ( fi, Suomi ; sv, Finland ), officially the Republic of Finland (; ), is a Nordic country in Northern Europe. It shares land borders with Sweden to the northwest, Norway to the north, and Russia to the east, with the Gulf of Bot ...
became independent in December 1917. The ''Gangut''-class ships led the first contingent of ships to Kronstadt
Kronstadt (russian: Кроншта́дт, Kronshtadt ), also spelled Kronshtadt, Cronstadt or Kronštádt (from german: link=no, Krone for " crown" and ''Stadt'' for "city") is a Russian port city in Kronshtadtsky District of the federal city ...
even though the Gulf of Finland was still frozen.
All of the dreadnoughts except for were laid up
A reserve fleet is a collection of naval vessels of all types that are fully equipped for service but are not currently needed; they are partially or fully decommissioned. A reserve fleet is informally said to be "in mothballs" or "mothballed"; a ...
in October–November 1918 for lack of manpower. was severely damaged by a fire while laid up in 1919. ''Petropavlovsk'' was retained in commission to defend Kronstadt and Leningrad against the British forces supporting the White Russians although she also helped to suppress a mutiny by the garrison of Fort Krasnaya Gorka in 1919. Her crew, and that of , joined the Kronstadt Rebellion
The Kronstadt rebellion ( rus, Кронштадтское восстание, Kronshtadtskoye vosstaniye) was a 1921 insurrection of Soviet sailors and civilians against the Bolshevik government in the Russian SFSR port city of Kronstadt. Loc ...
of March 1921. After it was bloodily crushed, those ships were given proper 'revolutionary' names. , the former ''Sevastopol'', was modified in 1928 to improve her sea-keeping abilities so that she could be transferred to the Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
which had nothing heavier than a light cruiser available. This proved to be the first of a series of modernizations where each ship of the class was progressively reconstructed and improved. A number of proposals were made in the 1930s to rebuild , ex-''Poltava'', to match her sisters
A sister is a woman or a girl who shares one or more parents with another individual; a female sibling. The male counterpart is a brother. Although the term typically refers to a familial relationship, it is sometimes used endearingly to refer to ...
or even as a battlecruiser by removing one turret, but these came to naught and she was hulk
The Hulk is a superhero appearing in American comic books published by Marvel Comics. Created by writer Stan Lee and artist Jack Kirby, the character first appeared in the debut issue of ''The Incredible Hulk (comic book), The Incredible Hulk' ...
ed preparatory to scrapping.
The two ships of the Baltic Fleet did not play a prominent role in the Winter War
The Winter War,, sv, Vinterkriget, rus, Зи́мняя война́, r=Zimnyaya voyna. The names Soviet–Finnish War 1939–1940 (russian: link=no, Сове́тско-финская война́ 1939–1940) and Soviet–Finland War 1 ...
, but did have their anti-aircraft
Anti-aircraft warfare, counter-air or air defence forces is the battlespace response to aerial warfare, defined by NATO as "all measures designed to nullify or reduce the effectiveness of hostile air action".AAP-6 It includes surface based ...
guns significantly increased before Operation Barbarossa
Operation Barbarossa (german: link=no, Unternehmen Barbarossa; ) was the invasion of the Soviet Union by Nazi Germany and many of its Axis allies, starting on Sunday, 22 June 1941, during the Second World War. The operation, code-named afte ...
in 1941. However this did not help either ship as they attempted to provide fire support for the defenders of Leningrad. had her bow blown off and was badly damaged by multiple bomb hits in September. The former was sunk, but later raised and became a floating battery for the duration of the Siege of Leningrad
The siege of Leningrad (russian: links=no, translit=Blokada Leningrada, Блокада Ленинграда; german: links=no, Leningrader Blockade; ) was a prolonged military blockade undertaken by the Axis powers against the Soviet city of ...
while the latter spent over a year under repair, although this was lengthened by subsequent bomb hits while in the hands of the shipyard. Both ships bombarded German and Finnish troops so long as they remained within reach, but ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' did not venture away from Kronstadt for the duration of the war. ''Parizhskaya Kommuna'' remained in Sevastopol until forced to evacuate by advancing German troops. She made one trip to besieged Sevastopol in December 1941 and made a number of bombardments in support of the Kerch Offensive during January–March 1942. She was withdrawn from combat in April as German aerial supremacy had made it too risky to risk such a large target.
''Sevastopol'' and ''Oktyabrskaya Revolyutsiya'' remained on the active list after the end of the war although little is known of their activities. Both were reclassified as 'school battleships' (''uchebnyi lineinyi korabl'') in 1954 and stricken in 1956 after which they were slowly scrapped
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
. There were several plans (Project 27) to reconstruct ''Petropavlovsk'' using the bow of ''Frunze'', but they were not accepted and were formally cancelled on 29 June 1948. She was renamed ''Volkhov'' in 1950 and served as a stationary training ship until stricken in 1953 and subsequently broken up. ''Frunze'' was finally scrapped beginning in 1949.
})
, align= center , 23 July 1911
, align= center , Stricken, 17 February 1956
''Imperatritsa Mariya'' class
The ''Imperatritsa Mariya''-class ships were the first dreadnoughts built for the Black Sea Fleet. All three ships were built in Nikolayev during World War I. Two ships were delivered in 1915 and saw some combat against ex-German warships that had been 'gifted' to theOttoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
, but the third was not completed until 1917 and saw no combat due to the disorder in the navy after the February Revolution
The February Revolution ( rus, Февра́льская револю́ция, r=Fevral'skaya revolyutsiya, p=fʲɪvˈralʲskəjə rʲɪvɐˈlʲutsɨjə), known in Soviet historiography as the February Bourgeois Democratic Revolution and some ...
earlier that year.
was sunk by a magazine
A magazine is a periodical publication, generally published on a regular schedule (often weekly or monthly), containing a variety of content. They are generally financed by advertising, purchase price, prepaid subscriptions, or by a combinatio ...
explosion in Sevastopol
Sevastopol (; uk, Севасто́поль, Sevastópolʹ, ; gkm, Σεβαστούπολις, Sevastoúpolis, ; crh, Акъя́р, Aqyár, ), sometimes written Sebastopol, is the largest city in Crimea, and a major port on the Black Sea ...
harbor in 1916. , having been renamed in 1917, was scuttled in Novorossiysk
Novorossiysk ( rus, Новоросси́йск, p=nəvərɐˈsʲijsk; ady, ЦIэмэз, translit=Chəməz, p=t͡sʼɜmɜz) is a city in Krasnodar Krai, Russia. It is one of the largest ports on the Black Sea. It is one of the few cities hono ...
harbor in 1918 to prevent her from being turned over to the Germans as required by the Treaty of Brest-Litovsk
The Treaty of Brest-Litovsk (also known as the Treaty of Brest in Russia) was a separate peace treaty signed on 3 March 1918 between Russia and the Central Powers ( Germany, Austria-Hungary, Bulgaria, and the Ottoman Empire), that ended Russi ...
. The crew of , as had been renamed in 1917, voted to turn her over to the Germans. They were only able to make one training cruise before they had to turn her over to the victorious Allies
An alliance is a relationship among people, groups, or states that have joined together for mutual benefit or to achieve some common purpose, whether or not explicit agreement has been worked out among them. Members of an alliance are called ...
in 1918 as part of the armistice terms. The British took control of her, but turned her over to the White Russians in 1920 who renamed her . She only had one operable gun turret by this time and she provided some fire support for the Whites, but it was not enough. They were forced to evacuate the Crimea
Crimea, crh, Къырым, Qırım, grc, Κιμμερία / Ταυρική, translit=Kimmería / Taurikḗ ( ) is a peninsula in Ukraine, on the northern coast of the Black Sea, that has been occupied by Russia since 2014. It has a p ...
later that year and sailed for Bizerte
Bizerte or Bizerta ( ar, بنزرت, translit=Binzart , it, Biserta, french: link=no, Bizérte) the classical Hippo, is a city of Bizerte Governorate in Tunisia. It is the northernmost city in Africa, located 65 km (40mil) north of the cap ...
where she was interned by the French. She was eventually scrapped there during the 1930s to pay her docking fees.
''Imperator Nikolai I''
''Imperator Nikolai I'' ( or Emperor Nikolai I) was built during World War I for service in theBlack Sea
The Black Sea is a marginal mediterranean sea of the Atlantic Ocean lying between Europe and Asia, east of the Balkans, south of the East European Plain, west of the Caucasus, and north of Anatolia. It is bounded by Bulgaria, Georgia, Rom ...
. She was designed to counter the multiple Ottoman orders for dreadnoughts which raised the possibility that the Russian dreadnoughts being built for the Black Sea Fleet
Chernomorskiy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Great emblem of the Black Sea fleet
, dates = May 13, ...
could be out-numbered. The ship used the same main armament as the preceding , but was larger and more heavily armored. ''Imperator Nikolai I'' was launched in 1916, but construction was suspended on 24 October 1917. The Soviets
Soviet people ( rus, сове́тский наро́д, r=sovyétsky naród), or citizens of the USSR ( rus, гра́ждане СССР, grázhdanye SSSR), was an umbrella demonym for the population of the Soviet Union.
Nationality policy in ...
considered completing her in 1923, but rejected the idea. She was towed to Sevastopol in 1927 and scrapped
Scrap consists of recyclable materials, usually metals, left over from product manufacturing and consumption, such as parts of vehicles, building supplies, and surplus materials. Unlike waste, scrap has monetary value, especially recovered me ...
.
''Sovetsky Soyuz'' class
The ''Sovetsky Soyuz''-class battleships (Project 23, ), also known as "Stalin's Republics", were a class of battleships begun by the Soviet Union in the late 1930s but never brought into service. They were designed in response to the battleships being built by Germany. Only four hulls of the sixteen originally planned had beenlaid down
Laying the keel or laying down is the formal recognition of the start of a ship's construction. It is often marked with a ceremony attended by dignitaries from the shipbuilding company and the ultimate owners of the ship.
Keel laying is one o ...
by 1940, when the decision was made to cut the program to only three ships to divert resources to an expanded army rearmament program.
These ships would have rivaled the Imperial Japanese in size if any had been completed, although with significantly weaker firepower: guns compared to the guns of the Japanese ships. The failure of the Soviet armor plate industry to build cemented armor plates thicker than would have negated any advantages from the ''Sovetsky Soyuz'' class's thicker armor in combat.
Construction of the first four ships was plagued with difficulties as the Soviet shipbuilding and related industries were not prepared to build such large ships. One battleship, ''Sovetskaya Belorussiya'', was cancelled on 19 October 1940 after serious construction flaws were found. Construction of the other three ships was suspended shortly after Nazi Germany invaded the Soviet Union in June 1941, and never resumed. All three of the surviving hulls were scrapped in the late 1940s.
Foreign-built ships
''Arkhangelsk''
 was loaned by the
was loaned by the Royal Navy
The Royal Navy (RN) is the United Kingdom's naval warfare force. Although warships were used by English and Scottish kings from the early medieval period, the first major maritime engagements were fought in the Hundred Years' War against Fr ...
in 1944 in lieu of reparations from Italy. She was assigned to the Northern Fleet
Severnyy flot
, image = Great emblem of the Northern Fleet.svg
, image_size = 150px
, caption = Northern Fleet's great emblem
, start_date = June 1, 1733; Sov ...
with the name of ''Arkhangelsk'' and used to escort convoys during the war. Returned to Britain in poor condition in 1949 when the USSR received the and sold for scrap.
''Novorossiysk''
 The Italian battleship ''Giulio Cesare'' was turned over to the Soviet Union by Italy in 1948 as
The Italian battleship ''Giulio Cesare'' was turned over to the Soviet Union by Italy in 1948 as war reparations
War reparations are compensation payments made after a war by one side to the other. They are intended to cover damage or injury inflicted during a war.
History
Making one party pay a war indemnity is a common practice with a long history.
...
. Renamed ''Novorossiysk'', she was assigned to the Black Sea Fleet. Sunk with 608 deaths following explosion in 1955; probably due to striking a leftover German mine.
See also
*List of battleships
The list of battleships includes all battleships built between 1859 and 1946, listed alphabetically.
The boundary between ironclads and the first battleships, the so-called 'pre-dreadnought battleship', is not obvious, as the characteristics of t ...
Notes
Footnotes
Citations
References
* * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * * {{BattleshipsBattleship
A battleship is a large armour, armored warship with a main artillery battery, battery consisting of large caliber guns. It dominated naval warfare in the late 19th and early 20th centuries.
The term ''battleship'' came into use in the late 1 ...
*
*
*
Russia
Russia (, , ), or the Russian Federation, is a transcontinental country spanning Eastern Europe and Northern Asia. It is the largest country in the world, with its internationally recognised territory covering , and encompassing one-ei ...