List of Japanese cash coins by inscription on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 Cash coins were introduced to
Cash coins were introduced to
/ref> It was first minted in 708 CE on order of
 Cash coins were introduced to
Cash coins were introduced to Japan
Japan ( ja, 日本, or , and formally , ''Nihonkoku'') is an island country in East Asia. It is situated in the northwest Pacific Ocean, and is bordered on the west by the Sea of Japan, while extending from the Sea of Okhotsk in the n ...
in the century inspired by the Chinese Kaigen Tsūhō (開元通寳) cash coins from the Tang dynasty
The Tang dynasty (, ; zh, t= ), or Tang Empire, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China that ruled from 618 to 907 AD, with an Zhou dynasty (690–705), interregnum between 690 and 705. It was preceded by the Sui dyn ...
. Chinese cash coins also circulated in other countries and inspired similar currencies such as the Korean mun
The ''mun'' (Hanja: ) was introduced as the main currency of Korea in 1625 and stayed in use until 1892. Prior to the ''mun'', cash coins with the inscriptions ''tongbo'' (通寶) and ''jungbo'' (重寶) and silver vases called ''ŭnbyŏng'' ...
, Ryukyuan mon, Vietnamese văn, while they also circulated as far south as Indonesia. Because these currencies were so similar cash coins around the Far East
The ''Far East'' was a European term to refer to the geographical regions that includes East and Southeast Asia as well as the Russian Far East to a lesser extent. South Asia is sometimes also included for economic and cultural reasons.
The t ...
were interchangeable and Japanese cash coins circulated in other countries while foreign cash coins also circulated in Japan.
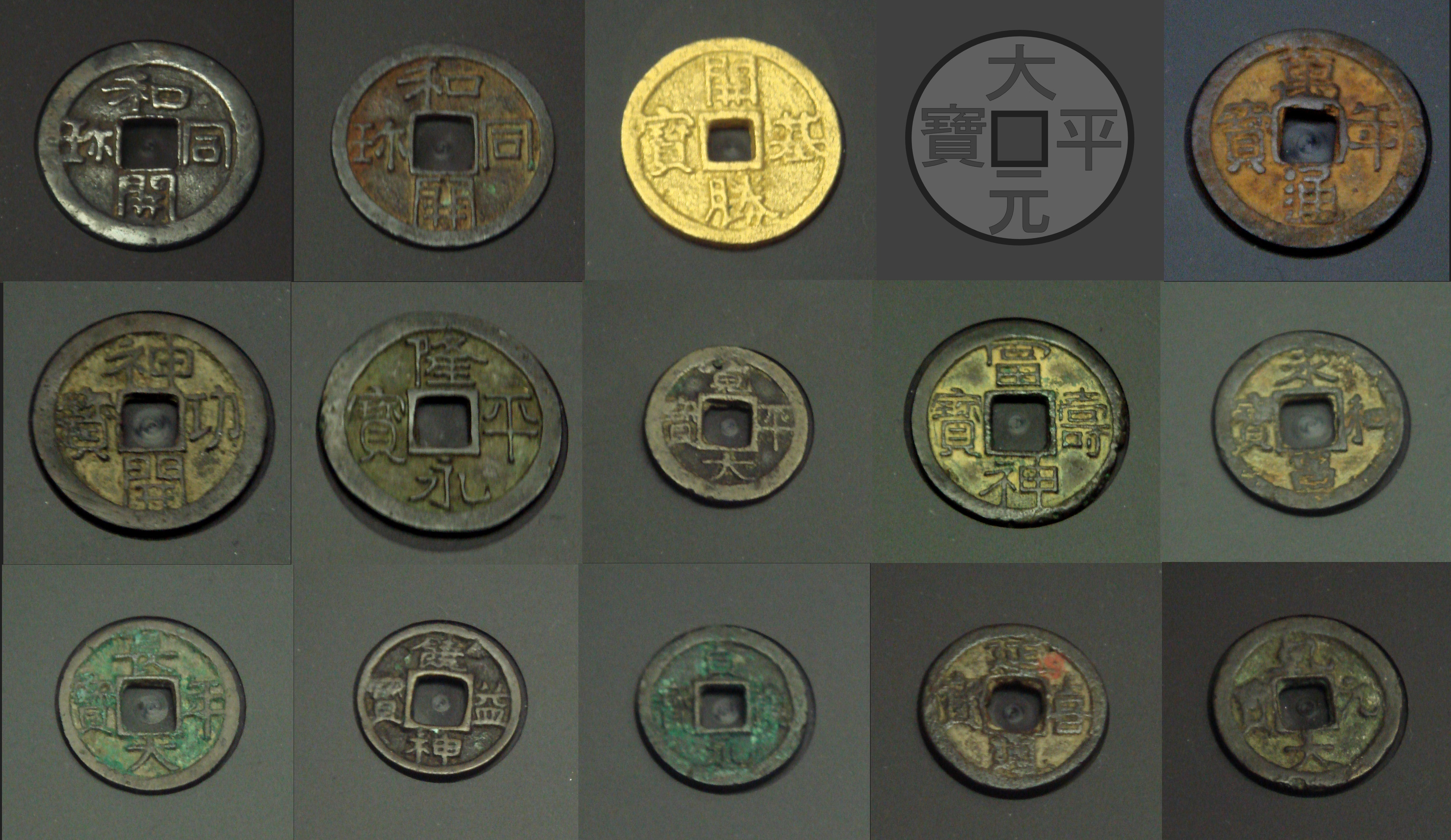
The first Japanese cash coins were the Wadōkaichin (和同開珎) which were produced from 29 August 708. In 760 Japanese currency was reformed and gold and silver cash coins were introduced, however by the end of the 10th century the value of Japanese coinage had severely fallen combined with a weak central government led the Japanese to return to barter
In trade, barter (derived from ''baretor'') is a system of exchange in which participants in a transaction directly exchange goods or services for other goods or services without using a medium of exchange, such as money. Economists disti ...
. From the 12th century onwards the Japanese started importing Chinese currency again even while the Southern Song dynasty
The Song dynasty (; ; 960–1279) was an imperial dynasty of China that began in 960 and lasted until 1279. The dynasty was founded by Emperor Taizu of Song following his usurpation of the throne of the Later Zhou. The Song conquered the res ...
banned the export of its coinage, while the import of Chinese cash coins surged again during the Ming dynasty
The Ming dynasty (), officially the Great Ming, was an Dynasties in Chinese history, imperial dynasty of China, ruling from 1368 to 1644 following the collapse of the Mongol Empire, Mongol-led Yuan dynasty. The Ming dynasty was the last ort ...
era when large amounts of Ming Chinese cash coins were imported.
The Japanese started locally imitating Chinese cash coins, which were known as ''Shichūsen'' (私鋳銭). But the quality of these cash coins varied severely depending on the mint. As many cash coins circulated in the market for a long time their quality diminished over time becoming known as ''Bitasen'' (鐚銭, "bad metal money"). After the Tokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
banned ''Bitasen'' in 1608 they started producing their own coinage and after 1859 provincial authorities were allowed to mint their own coinages. Japanese cash coins were officially demonetised
Legal tender is a form of money that courts of law are required to recognize as satisfactory payment for any monetary debt. Each jurisdiction determines what is legal tender, but essentially it is anything which when offered ("tendered") in pa ...
in 1891 after officially circulating as a division of the Japanese yen
The is the official currency of Japan. It is the third-most traded currency in the foreign exchange market, after the United States dollar (US$) and the euro. It is also widely used as a third reserve currency after the US dollar and the ...
with an exchange rate of 10.000 mon
Mon, MON or Mon. may refer to:
Places
* Mon State, a subdivision of Myanmar
* Mon, India, a town in Nagaland
* Mon district, Nagaland
* Mon, Raebareli, a village in Uttar Pradesh, India
* Mon, Switzerland, a village in the Canton of Grisons
* A ...
for 1 yen.
''Fuhonsen''
The first Japanese embassy to China is recorded to have been sent in 630, following with Japan, who adopted numerous Chinese cultural practices.Japan Currency Museum
__NOTOC__
The , formally known as the is a museum about Japanese currency located in front of the Bank of Japan building in Chūō, Tokyo.
The museum opened in November 1985.Edan CorkillBank of Japan Currency Museum invests in exhibition on wa ...
(日本貨幣博物館) permanent exhibit The importance of metallic currency appeared to Japanese nobles, probably leading to some coin minting at the end of the 7th century, such as the ' coinage (富本銭), discovered in 1998 through archaeological research in the area of Nara
The National Archives and Records Administration (NARA) is an " independent federal agency of the United States government within the executive branch", charged with the preservation and documentation of government and historical records. It ...
. An entry of the Nihon Shoki dated April 15, 683 mentions: "From now on, copper coins should be used, but silver coins should not be used", which is thought to order the adoption of the ''Fuhonsen'' copper coins. The first ''official'' cash coinage was struck in 708.
''Kōchōsen''
Early ''Kōchōsen''
Japan's first formal currency system was the ''Kōchōsen'' (Japanese: 皇朝銭, "Imperial currency"). It was exemplified by the adoption of Japan's first official coin type, the '' Wadōkaichin''.''The Cambridge history of Japan: Heian Japan'' John Whitney Hall, Donald H. (Donald Howard) Shively, William H. McCullough p.434/ref> It was first minted in 708 CE on order of
Empress Genmei
, also known as Empress Genmyō, was the 43rd monarch of Japan, Imperial Household Agency (''Kunaichō'') 元明天皇 (43) retrieved August 22, 2013. according to the traditional order of succession. Genmei's reign spanned the years 707 throu ...
, Japan's 43rd Imperial ruler. ''"Wadōkaichin"'' is the reading of the four characters printed on the coin, and is thought to be composed of the era name Wadō (和銅, "Japanese copper"), which could alternatively mean "happiness", and "Kaichin", thought to be related to "Currency".
Last ''Kōchōsen''
The ''Kōchōsen'' Japanese system of coinage became strongly debased, with its metallic content and value decreasing. By the middle of the 9th century, the value of a coin in rice had fallen to 1/150th of its value of the early 8th century. By the end of the 10th century, compounded with weaknesses in the political system, this led to the abandonment of the national currency, with the return torice
Rice is the seed of the grass species '' Oryza sativa'' (Asian rice) or less commonly ''Oryza glaberrima'' (African rice). The name wild rice is usually used for species of the genera '' Zizania'' and '' Porteresia'', both wild and domesticat ...
as a currency medium. The last official Japanese coin emission occurred in 958, with very low quality coins called ''Kengen Taihō'' (乾元大宝), which soon fell into disuse.
The last ''Kōchōsen'' coins produced after the Wadōkaichin was debased include:
''Toraisen, Shichūsen, and Bitasen''
List of ''Toraisen, Shichūsen, and Bitasen'' cash coins:Edo period
List of cash coins issued by the Tokugawa shogunate
During the history of the Japanese mon under theTokugawa shogunate
The Tokugawa shogunate (, Japanese 徳川幕府 ''Tokugawa bakufu''), also known as the , was the military government of Japan during the Edo period from 1603 to 1868. Nussbaum, Louis-Frédéric. (2005)"''Tokugawa-jidai''"in ''Japan Encyclopedia ...
, many different cash coins with different obverse inscriptions were cast, the main cash coins cast by the central government were:
List of Nagasaki trade coins
The following coins were minted in the city of Nagasaki for export to other countries:瀧澤武雄,西脇康 『日本史小百科「貨幣」』 東京堂出版、1999年 (inJapanese
Japanese may refer to:
* Something from or related to Japan, an island country in East Asia
* Japanese language, spoken mainly in Japan
* Japanese people, the ethnic group that identifies with Japan through ancestry or culture
** Japanese diaspor ...
).
Nagasaki trade coins notably bear the inscription of many Song dynasty coins because those coins were already widespread in circulation on the Southeast Asian market making the Nagasaki trade coins more familiar for its target demographic.
List of local cash coins cast during the Bakumatsu
Many Japanese domains produced their own currency which happened chaotically, so that the nation’s money supply expanded by 2.5 times between 1859 and 1869, leading to crumbling money values and soaring prices.Japan Currency Museum
__NOTOC__
The , formally known as the is a museum about Japanese currency located in front of the Bank of Japan building in Chūō, Tokyo.
The museum opened in November 1985.Edan CorkillBank of Japan Currency Museum invests in exhibition on wa ...
(日本貨幣博物館) permanent exhibit
These coins were often produced with the name of the domain or province
A province is almost always an administrative division within a country or state. The term derives from the ancient Roman ''provincia'', which was the major territorial and administrative unit of the Roman Empire's territorial possessions out ...
on them, the mon coins produced by domains are:
See also
*List of Chinese cash coins by inscription
Chinese cash coins were first produced during the Warring States period, and they became standardised as the Ban Liang (半兩) coinage during the Qin dynasty which followed. Over the years, cash coins have had many different inscriptions, and t ...
Notes
References
Sources
* ''Early Japanese Coins''. David Hartill. , Published: October 6, 2011. {{Japanese currency and coinage Coins of Japan Cash coins by inscription