Lipka Tatars on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
The Lipka Tatars (Lipka – refers to ''
Towards the end of the 14th century, another wave of Tatars – this time,
 The name Lipka is derived from the old Crimean Tatar name of Lithuania. The record of the name Lipka in Oriental sources permits us to infer an original Libķa/Lipķa, from which the Polish derivative Lipka was formed, with possible
The name Lipka is derived from the old Crimean Tatar name of Lithuania. The record of the name Lipka in Oriental sources permits us to infer an original Libķa/Lipķa, from which the Polish derivative Lipka was formed, with possible
 The migration of Tatars into the lands of Lithuania and Poland from
The migration of Tatars into the lands of Lithuania and Poland from


 * 1397: The Italian city state of
* 1397: The Italian city state of

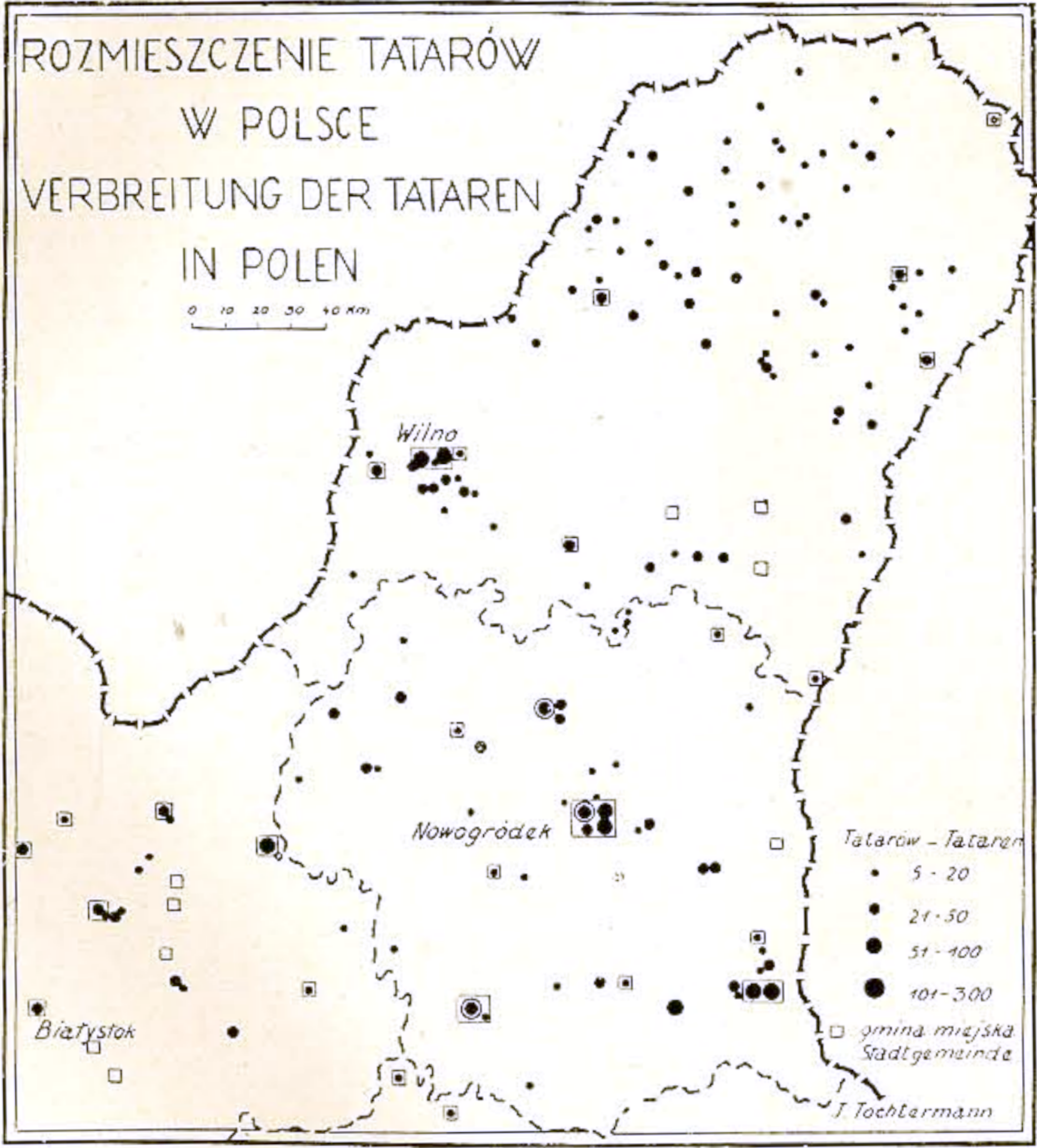
 Today there are about 10,000–15,000 Lipka Tatars in the former areas of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The majority of descendants of Tatar families in Poland can trace their descent from the nobles of the early Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lipka Tatars had settlements in north-east Poland, Belarus, Lithuania, south-east
Today there are about 10,000–15,000 Lipka Tatars in the former areas of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The majority of descendants of Tatar families in Poland can trace their descent from the nobles of the early Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. Lipka Tatars had settlements in north-east Poland, Belarus, Lithuania, south-east
File:Iǔje, miačet (8.08.2010).jpg, Tatar mosque in the town Iwye, Belarus
File:Navahrudak Mosque.JPG, Tatar mosque in the city
File:Muzułmański Cmentarz Tatarski w Warszawie 2017b.jpg,
File:Muzułmański Cmentarz Tatarski w Warszawie 2017a.jpg
File:Cmentarz tatarski 2014.10 02.jpg
A Short History of the Lipka Tatars of the White Horde
Jakub Mirza Lipka
Selim Mirza-Juszenski Chazbijewicz - translated into English by Paul de Nowina-Konopka
The Lithuanian Tatars
article in The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire {{European Muslims Social history of Belarus Ethnic groups in Belarus Ethnic groups in Lithuania Ethnic groups in Poland Social history of Lithuania Islam in Belarus Islam in Poland Muslim communities in Europe
Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
'', also known as Lithuanian Tatars; later also – Polish Tatars, Polish-Lithuanian Tatars, ''Lipkowie'', ''Lipcani'', ''Muślimi'', ''Lietuvos totoriai'') are a Turkic ethnic group
An ethnic group or an ethnicity is a grouping of people who identify with each other on the basis of shared attributes that distinguish them from other groups. Those attributes can include common sets of traditions, ancestry, language, history, ...
who originally settled in the Grand Duchy of Lithuania
The Grand Duchy of Lithuania was a European state that existed from the 13th century to 1795, when the territory was Partitions of Poland, partitioned among the Russian Empire, the Kingdom of Prussia, and the Habsburg Empire, Habsburg Empire of ...
at the beginning of the 14th century. The first Tatar settlers tried to preserve their shamanistic religion and sought asylum amongst the non-Christian Lithuanians.Lietuvos totoriai ir jų šventoji knyga - KoranasTowards the end of the 14th century, another wave of Tatars – this time,
Muslims
Muslims ( ar, المسلمون, , ) are people who adhere to Islam, a monotheistic religion belonging to the Abrahamic tradition. They consider the Quran, the foundational religious text of Islam, to be the verbatim word of the God of Abrah ...
, were invited into the Grand Duchy by Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
. These Tatars first settled in Lithuania proper around Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
, Trakai
Trakai (; see names section for alternative and historic names) is a historic town and lake resort in Lithuania. It lies west of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. Because of its proximity to Vilnius, Trakai is a popular tourist destination. ...
, Hrodna and Kaunas
Kaunas (; ; also see other names) is the second-largest city in Lithuania after Vilnius and an important centre of Lithuanian economic, academic, and cultural life. Kaunas was the largest city and the centre of a county in the Duchy of Traka ...
and later spread to other parts of the Grand Duchy that later became part of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
. These areas comprise parts of present-day Lithuania
Lithuania (; lt, Lietuva ), officially the Republic of Lithuania ( lt, Lietuvos Respublika, links=no ), is a country in the Baltic region of Europe. It is one of three Baltic states and lies on the eastern shore of the Baltic Sea. Lithuania ...
, Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
and Poland
Poland, officially the Republic of Poland, is a country in Central Europe. It is divided into 16 administrative provinces called voivodeships, covering an area of . Poland has a population of over 38 million and is the fifth-most populou ...
. From the very beginning of their settlement in Lithuania they were known as the Lipka Tatars. While maintaining their religion, they united their fate with that of the mainly Christian
Christians () are people who follow or adhere to Christianity, a monotheistic Abrahamic religion based on the life and teachings of Jesus Christ. The words ''Christ'' and ''Christian'' derive from the Koine Greek title ''Christós'' (Χρι� ...
Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. From the Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
onwards the Lipka Tatar light cavalry regiments participated in every significant military campaign of Lithuania and Poland.
The Lipka Tatar origins can be traced back to the descendant states of the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
, the Crimean Khanate and Kazan Khanate
The Khanate of Kazan ( tt, Казан ханлыгы, Kazan xanlıgı; russian: Казанское ханство, Kazanskoye khanstvo) was a medieval Tatar Turkic state that occupied the territory of former Volga Bulgaria between 1438 and 155 ...
. They initially served as a noble military caste but later they became urban-dwellers known for their crafts, horses and gardening skills. Throughout centuries they resisted assimilation and kept their traditional lifestyle. While they remained very attached to their religion, over time they lost their original Tatar language, from the Kipchak group of the Turkic languages
The Turkic languages are a language family of over 35 documented languages, spoken by the Turkic peoples of Eurasia from Eastern Europe and Southern Europe to Central Asia, East Asia, North Asia ( Siberia), and Western Asia. The Turki ...
and for the most part adopted Belarusian, Lithuanian and Polish.Harvard Encyclopedia of American Ethnic Groups, "Polish or Lithuanian Tartars", Harvard University Press, pg. 990 There are still small groups of Lipka Tatars living in today's Belarus, Lithuania and Poland, as well as their communities in the United States.
Name
 The name Lipka is derived from the old Crimean Tatar name of Lithuania. The record of the name Lipka in Oriental sources permits us to infer an original Libķa/Lipķa, from which the Polish derivative Lipka was formed, with possible
The name Lipka is derived from the old Crimean Tatar name of Lithuania. The record of the name Lipka in Oriental sources permits us to infer an original Libķa/Lipķa, from which the Polish derivative Lipka was formed, with possible contamination
Contamination is the presence of a constituent, impurity, or some other undesirable element that spoils, corrupts, infects, makes unfit, or makes inferior a material, physical body, natural environment, workplace, etc.
Types of contamination
...
from contact
Contact may refer to:
Interaction Physical interaction
* Contact (geology), a common geological feature
* Contact lens or contact, a lens placed on the eye
* Contact sport, a sport in which players make contact with other players or objects
* C ...
with the Polish ''lipka'' "small lime-tree"; this etymology was suggested by the Tatar author S. Tuhan-Baranowski. A less frequent Polish form, Łubka, is corroborated in Łubka/Łupka, the Crimean Tatar name of the Lipkas up to the end of the 19th century. The Crimean Tatar term ''Lipka Tatarłar'' meaning ''Lithuanian Tatars'', later started to be used by the Polish–Lithuanian Tatars to describe themselves.
In religion and culture the Lipka Tatars differed from most other Islamic communities in respect of the treatment of their women, who always enjoyed a large degree of freedom, even during the years when the Lipkas were in the service of the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
. Co-education of male and female children was the norm, and Lipka women did not wear the veil – except at the marriage ceremony. While traditionally Islamic, the customs and religious practices of the Lipka Tatars also accommodated many Christian elements adopted during their 600 years residence in Belarus, Poland, Ukraine and Lithuania while still maintaining the traditions and superstitions from their nomadic past.
Over time, the lower and middle Lipka Tatar nobles adopted the Ruthenian language
Ruthenian ( Belarusian: руская мова; Ukrainian: руська мова; Ruthenian: руска(ѧ) мова; also see other names) is an exonymic linguonym for a closely-related group of East Slavic linguistic varieties, particularl ...
then later the Belarusian language
Belarusian ( be, беларуская мова, biełaruskaja mova, link=no, ) is an East Slavic language. It is the native language of many Belarusians and one of the two official state languages in Belarus. Additionally, it is spoken in some ...
as their native language.Selim Mirza-Juszeński Chazbijewicz, "Szlachta tatarska w Rzeczypospolitej" (Tartar Nobility in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth), Verbum Nobile no 2 (1993), Sopot, Poland, However, they used the Arabic alphabet to write in Belarusian until the 1930s. The upper nobility of Lipka Tatars spoke Polish.
Diplomatic correspondence between the Crimean Khanate and Poland from the early 16th century refers to Poland and Lithuania as the "land of the Poles and the Lipkas". By the 17th century the term Lipka Tatar began to appear in the official documents of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
History
Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
began during the 14th century and lasted until the end of the 17th. There was a subsequent wave of Tatar immigrants from Russia after the October Revolution
The October Revolution,. officially known as the Great October Socialist Revolution. in the Soviet Union, also known as the Bolshevik Revolution, was a revolution in Russia led by the Bolshevik Party of Vladimir Lenin that was a key mom ...
of 1917, although these consisted mostly of political and national activists.
According to some estimates, by 1590–1591 there were about 200,000 Lipka Tatars living in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
and about 400 mosques serving them. According to the ''Risāle-yi Tatar-i Leh'' (trans: ''Message Concerning the Tatars of Poland'', an account of the Lipka Tatars written for Suleiman the Magnificent by an anonymous Polish Muslim during a stay in Constantinople
la, Constantinopolis ota, قسطنطينيه
, alternate_name = Byzantion (earlier Greek name), Nova Roma ("New Rome"), Miklagard/Miklagarth (Old Norse), Tsargrad ( Slavic), Qustantiniya (Arabic), Basileuousa ("Queen of Cities"), Megalopolis (" ...
in 1557–1558 on his way to Mecca
Mecca (; officially Makkah al-Mukarramah, commonly shortened to Makkah ()) is a city and administrative center of the Mecca Province of Saudi Arabia, and the holiest city in Islam. It is inland from Jeddah on the Red Sea, in a narrow v ...
) there were 100 Lipka Tatar settlements with mosques in Poland. The largest communities existed in the cities of Lida
Lida ( be, Лі́да ; russian: Ли́да ; lt, Lyda; lv, Ļida; pl, Lida ; yi, לידע, Lyde) is a city 168 km (104 mi) west of Minsk in western Belarus in Grodno Region.
Etymology
The name ''Lida'' arises from its Lithu ...
, Navahrudak
Novogrudok ( be, Навагрудак, Navahrudak; lt, Naugardukas; pl, Nowogródek; russian: Новогрудок, Novogrudok; yi, נאַוואַראַדאָק, Novhardok, Navaradok) is a town in the Grodno Region, Belarus.
In the Middle A ...
and Iwye. There was a Lipka Tatar settlement in Vilnius
Vilnius ( , ; see also other names) is the capital and largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the municipality of Vilnius). The population of Vilnius's functional urba ...
, known as Totorių Lukiškės, Tatar quarter in Trakai
Trakai (; see names section for alternative and historic names) is a historic town and lake resort in Lithuania. It lies west of Vilnius, the capital of Lithuania. Because of its proximity to Vilnius, Trakai is a popular tourist destination. ...
and in Minsk
Minsk ( be, Мінск ; russian: Минск) is the capital and the largest city of Belarus, located on the Svislach (Berezina), Svislach and the now subterranean Nyamiha, Niamiha rivers. As the capital, Minsk has a special administrative stat ...
, today's capital of Belarus, known as Tatarskaya Slabada.
In the year 1672, the Tatar subjects rose up in open rebellion against the Commonwealth. This was the widely remembered Lipka rebellion. Thanks to the efforts of King John III Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobi ...
, who was held in great esteem by the Tatar soldiers, many of the Lipkas seeking asylum and service in the Turkish army returned to his command and participated in the struggles with the Ottoman Empire up to the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
in 1699, including the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna; pl, odsiecz wiedeńska, lit=Relief of Vienna or ''bitwa pod Wiedniem''; ota, Beç Ḳalʿası Muḥāṣarası, lit=siege of Beç; tr, İkinci Viyana Kuşatması, lit=second siege of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mo ...
(1683) that was to turn the tide of Islamic expansion into Europe and mark the beginning of the end for the Ottoman Empire.
Beginning in the late 18th and throughout the 19th century the Lipkas became successively more and more polonized. The upper and middle classes in particular adopted Polish language and customs (although they kept Islam as their religion), while the lower ranks became Ruthenized. At the same time, the Tatars held the Lithuanian Grand Duke Vytautas
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
(Wattad in Tatar, or "defender of Muslims in non Muslim lands"), who encouraged and supported their settlement in the late 14th and early 15th century, in great esteem, including him in many legends, prayers and their folklore. Throughout the 20th and since the 21st centuries, most Tatars no longer view religious identity as being as important as it once was, and the religious and linguistic subgroups have intermingled considerably; for example, the Tatar women in Poland do not practice veiling (wearing headscarf/hijab) or view it as a mandatory religious obligation, but rather an influence of Arab culture on Islamic customs. Many Polish Tatars, especially and mainly the youth, also drink alcohol.
Timeline
* 1226: The Khanate of the White Horde was established as one of the successor states to the Mongol Empire of Genghis Khan. The first Khan, Orda was the second son of Jochi, the eldest son of Genghis Khan. The White Horde occupied the southern Siberiansteppe
In physical geography, a steppe () is an ecoregion characterized by grassland plains without trees apart from those near rivers and lakes.
Steppe biomes may include:
* the montane grasslands and shrublands biome
* the temperate gras ...
from the east of the Urals
The Ural Mountains ( ; rus, Ура́льские го́ры, r=Uralskiye gory, p=ʊˈralʲskʲɪjə ˈɡorɨ; ba, Урал тауҙары) or simply the Urals, are a mountain range that runs approximately from north to south through western ...
and the Caspian Sea
The Caspian Sea is the world's largest inland body of water, often described as the world's largest lake or a full-fledged sea. An endorheic basin, it lies between Europe and Asia; east of the Caucasus, west of the broad steppe of Central A ...
to Mongolia
Mongolia; Mongolian script: , , ; lit. "Mongol Nation" or "State of Mongolia" () is a landlocked country in East Asia, bordered by Russia to the north and China to the south. It covers an area of , with a population of just 3.3 million ...
.
* 1380: Khan Tokhtamysh, the hereditary ruler of the White Horde, crossed west over the Urals and merged the White Horde with the Golden Horde
The Golden Horde, self-designated as Ulug Ulus, 'Great State' in Turkic, was originally a Mongol and later Turkicized khanate established in the 13th century and originating as the northwestern sector of the Mongol Empire. With the fragmen ...
whose first khan was Batu, the eldest son of Jochi. In 1382 the White and Golden Hordes sacked and burned Moscow. Tokhtamysh, allied with the great central Asian Tatar conqueror Tamerlane, reasserted Mongol power in Russia.
* 1397: After a series of disastrous military campaigns against his former protector, the great Tatar warlord Tamerlane, Tokhtamysh and the remnants of his clan were granted asylum and given estates and noble status in Grand Duchy of Lithuania by Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
. The settlement of the Lipka Tatars in Lithuania in 1397 is recorded in the Chronicles of Jan Długosz.



 * 1397: The Italian city state of
* 1397: The Italian city state of Genoa
Genoa ( ; it, Genova ; lij, Zêna ). is the capital of the Italian region of Liguria and the sixth-largest city in Italy. In 2015, 594,733 people lived within the city's administrative limits. As of the 2011 Italian census, the Province of ...
funded a joint expedition by the forces of Khan Tokhtamysh and Grand Duke Vytautas against Tamerlane. This campaign was notable for the fact that the Lipka Tatars and Lithuanian armies were armed with handguns, but no major victories were achieved.
* 15 July 1410: The Battle of Grunwald
The Battle of Grunwald, Battle of Žalgiris or First Battle of Tannenberg was fought on 15 July 1410 during the Polish–Lithuanian–Teutonic War. The alliance of the Crown of the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, led respec ...
took place between the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania on one side (c. 39,000 troops), and the Teutonic Knights
The Order of Brothers of the German House of Saint Mary in Jerusalem, commonly known as the Teutonic Order, is a Catholic religious institution founded as a military society in Acre, Kingdom of Jerusalem. It was formed to aid Christians o ...
on the other (c. 27,000 troops). The Teutonic knights were defeated and never recovered their former influence. After the battle, rumours spread across Europe that the Germans had only been defeated thanks to the aid of tens of thousands of heathen Tatars, though it is likely there were no more than 1,000 Tatar horse archers at the battle, the core being the entourage of Jalal ad-Din, son of Khan Tokhtamysh. At the start of the battle, Jalal ad-Din led the Lipka Tatar and Lithuanian light cavalry on a suicide charge against the Teutonic Knights' artillery positions – the original "Charge of the Light Brigade
The Charge of the Light Brigade was a failed military action involving the British light cavalry led by Lord Cardigan against Russian forces during the Battle of Balaclava on 25 October 1854 in the Crimean War. Lord Raglan had intended to ...
". The Teutonic Knights' Grand Master Ulrich von Jungingen responded by ordering his own heavy cavalry to pursue the Lipkas away from the field of battle, trampling through their own infantry in the process. The resulting destruction of the Teutonic Knights' line of battle was a major factor in their subsequent defeat. This incident forms one of the highlights of Aleksander Ford
Aleksander Ford (born Mosze Lifszyc; 24 November 1908 in Kiev, Russian Empire – 4 April 1980 in Naples, Florida, U.S.) was a Polish film director; and head of the Polish People's Army Film Crew in the Soviet Union during World War II. Follo ...
's 1960 film ''Krzyżacy'' ('' Knights of the Teutonic Order''), based on the historical novel of the same name by Nobel laureate Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, espe ...
.
* 1528: The Polish ( szlachta) and Lithuanian nobility's legal right to retribution on the grounds of the wounding or killing of a nobleman or a member of his family is extended to the Lipka Tatars.
* 1569: The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth
The Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, formally known as the Kingdom of Poland and the Grand Duchy of Lithuania, and, after 1791, as the Commonwealth of Poland, was a bi-confederal state, sometimes called a federation, of Crown of the Kingdom of ...
is founded at the Union of Lublin
The Union of Lublin ( pl, Unia lubelska; lt, Liublino unija) was signed on 1 July 1569 in Lublin, Poland, and created a single state, the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth, one of the largest countries in Europe at the time. It replaced the per ...
. Companies of Lipka Tatar light cavalry for a long time constituted one of the foundations of the military power of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. The Lithuanian Tatars, from the very beginning of their residence in Lithuania were known as the Lipkas. They united their fate with that of Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth. From the Battle of Grunwald onwards they participated in every significant military campaign.
* 1591: The rule of the fervent Catholic Sigismund III (1587–1632) and the Counter-Reformation
The Counter-Reformation (), also called the Catholic Reformation () or the Catholic Revival, was the period of Catholic resurgence that was initiated in response to the Protestant Reformation. It began with the Council of Trent (1545–1563) a ...
movement brought a number of restrictions to the liberties granted to non-Catholics in Poland, the Lipkas amongst others. This led to a diplomatic intervention by Sultan Murad III
Murad III ( ota, مراد ثالث, Murād-i sālis; tr, III. Murad; 4 July 1546 – 16 January 1595) was Sultan of the Ottoman Empire from 1574 until his death in 1595. His rule saw battles with the Habsburgs and exhausting wars with the Sa ...
with the Polish king in 1591 on the question of freedom of religious observance for the Lipkas. This was undertaken at the request of Polish Muslims who had accompanied the Polish King's envoy to Istanbul
)
, postal_code_type = Postal code
, postal_code = 34000 to 34990
, area_code = +90 212 (European side) +90 216 (Asian side)
, registration_plate = 34
, blank_name_sec2 = GeoTLD
, blank_i ...
.
* 1672: The Lipka Rebellion. As a reaction to restrictions on their religious freedoms and the erosion of their ancient rights and privileges, the Lipka Tatar regiments stationed in the Podolia
Podolia or Podilia ( uk, Поділля, Podillia, ; russian: Подолье, Podolye; ro, Podolia; pl, Podole; german: Podolien; be, Падолле, Padollie; lt, Podolė), is a historic region in Eastern Europe, located in the west-centra ...
region of south-east Poland abandoned the Commonwealth at the start of the late 17th century Polish–Ottoman Wars
Polish–Ottoman Wars can refer to one of the several conflicts between the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth and the Ottoman Empire:
* Crusade of Varna (1443-1444)
* Polish–Ottoman War (1485–1503)
* Jan Olbracht's Moldavian expedition of 1 ...
that were to last until the end of the 17th century with the Treaty of Karlowitz
The Treaty of Karlowitz was signed in Karlowitz, Military Frontier of Archduchy of Austria (present-day Sremski Karlovci, Serbia), on 26 January 1699, concluding the Great Turkish War of 1683–1697 in which the Ottoman Empire was defeated by ...
in 1699. The Lipka Rebellion forms the background to the novel '' Pan Wolodyjowski'', the final volume of the historical '' Trylogia'' by Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, espe ...
, the Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
winning author (1905) who was himself descended from Christianised Lipka Tatars. The 1969 film ''Pan Wolodyjowski'', directed by Jerzy Hoffman and starring Daniel Olbrychski as Azja Tuhaj-bejowicz, still remains among the biggest box-office successes in the history of Polish cinema.
* 1674: After the famous Polish victory at Chocim, the Lipka Tatars who held the Podolia for Turkey from the stronghold of Bar were besieged by the armies of Jan Sobieski
John III Sobieski ( pl, Jan III Sobieski; lt, Jonas III Sobieskis; la, Ioannes III Sobiscius; 17 August 1629 – 17 June 1696) was King of Poland and Grand Duke of Lithuania from 1674 until his death in 1696.
Born into Polish nobility, Sobie ...
, and a deal was struck that the Lipkas would return to the Polish side subject to their ancient rights and privileges being restored.
* 1676: The Treaty of Zurawno that brought a temporary end to the Polish–Ottoman wars stipulated that the Lipka Tatars were to be given a free individual choice of whether they wanted to serve the Ottoman Empire
The Ottoman Empire, * ; is an archaic version. The definite article forms and were synonymous * and el, Оθωμανική Αυτοκρατορία, Othōmanikē Avtokratoria, label=none * info page on book at Martin Luther University ...
or the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth.
* 1677: The Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
in March 1677 confirmed all the ancient Tatar rights and privileges. The Lipka Tatars were permitted to rebuild all their old mosques, to settle Christian labour on their estates and to buy up noble estates that had not previously belonged to Tatars. The Lipka Tatars were also freed from all taxation.
* 1679: As a reward for their return to the Commonwealth the Lipka Tatars were settled by King Jan Sobieski on Crown Estates in the provinces of Brest, Kobryn and Hrodna. The Tatars received land that had been cleared of the previous occupants, from 0.5 to 7.5 square kilometres per head, according to rank and length of service.
* 1683: Many of the Lipka Tatar rebels who returned to the service of the Commonwealth in 1674 were later to take part in the Vienna campaign of 1683. This included the 60 Polish Tatars in the light cavalry company of Samuel Mirza Krzeczowski, who was later to save the life of King Jan III Sobieski during the disastrous first day of the Battle of Parkany, a few weeks after the great victory of the Battle of Vienna
The Battle of Vienna; pl, odsiecz wiedeńska, lit=Relief of Vienna or ''bitwa pod Wiedniem''; ota, Beç Ḳalʿası Muḥāṣarası, lit=siege of Beç; tr, İkinci Viyana Kuşatması, lit=second siege of Vienna took place at Kahlenberg Mo ...
that was to turn the tide of Islamic expansion into Europe and mark the beginning of the end for the Ottoman Empire. The Lipka Tatars who fought on the Polish side at the Battle of Vienna, on 12 September 1683, wore a sprig of straw in their helmets to distinguish themselves from the Tatars fighting under Kara Mustafa on the Turkish side. Lipkas visiting Vienna traditionally wear straw hats to commemorate their ancestors' participation in the breaking of the Siege of Vienna.
* 1699: Some of the Kamieniec-based Lipka Tatars who had remained loyal to the Turkish Sultan
Sultan (; ar, سلطان ', ) is a position with several historical meanings. Originally, it was an Arabic abstract noun meaning "strength", "authority", "rulership", derived from the verbal noun ', meaning "authority" or "power". Later, it c ...
were settled in Bessarabia
Bessarabia (; Gagauz: ''Besarabiya''; Romanian: ''Basarabia''; Ukrainian: ''Бессара́бія'') is a historical region in Eastern Europe, bounded by the Dniester river on the east and the Prut river on the west. About two thirds o ...
along the borderlands between the Ottoman Empire and the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth as well as in the environs of Chocim
Khotyn ( uk, Хотин, ; ro, Hotin, ; see other names) is a city in Dnistrovskyi Raion, Chernivtsi Oblast of western Ukraine and is located south-west of Kamianets-Podilskyi. It hosts the administration of Khotyn urban hromada, one of ...
and Kamieniec-Podolski and in the town known as Lipkany. A further large scale emigration of Lipkas to Ottoman controlled lands took place early in the 18th century, after the victory won by King Augustus II
Augustus II; german: August der Starke; lt, Augustas II; in Saxony also known as Frederick Augustus I – Friedrich August I (12 May 16701 February 1733), most commonly known as Augustus the Strong, was Elector of Saxony from 1694 as well as Ki ...
over the Polish-born King Stanisław Leszczyński, whom the Lipkas had supported in his war against the Saxon King.
* 1775: The Polish Lipkas came back into favour during the reign of the last King, Stanislas Augustus (1765–95). In 1775 the Sejm
The Sejm (English: , Polish: ), officially known as the Sejm of the Republic of Poland ( Polish: ''Sejm Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej''), is the lower house of the bicameral parliament of Poland.
The Sejm has been the highest governing body of ...
reaffirmed the noble status of the Polish Lithuanian Tatars. After the Partitions of Poland
The Partitions of Poland were three partitions of the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth that took place toward the end of the 18th century and ended the existence of the state, resulting in the elimination of sovereign Poland and Lithuania for 12 ...
, the Lipkas played their part in the various national uprisings, and also served alongside the Poles in the Napoleonic army.
* 1919: The Polish Lipkas joined the newly created Polish Army formations; Pułk Jazdy Tatarskiej and later, 13th Regiment of Wilno Uhlans.
* 1939: With the re-emergence of the Polish state after the First World War, a Polish Tatar regiment was re-established in the Polish Army which was distinguished by its own uniforms and banners. After the fall of Poland in 1939, the Polish Tatars in the Wilno
Vilnius ( , ; see also #Etymology and other names, other names) is the capital and List of cities in Lithuania#Cities, largest city of Lithuania, with a population of 592,389 (according to the state register) or 625,107 (according to the munic ...
(Vilnius) based 13th Cavalry Regiment were one of the last Polish Army units recorded carrying on the fight against the German aggressors while led by Major Aleksander Jeljaszewicz.
Present status

Latvia
Latvia ( or ; lv, Latvija ; ltg, Latveja; liv, Leţmō), officially the Republic of Latvia ( lv, Latvijas Republika, links=no, ltg, Latvejas Republika, links=no, liv, Leţmō Vabāmō, links=no), is a country in the Baltic region of ...
and Ukraine. Today most reside in Poland, Lithuania, and Belarus. Most of the Lipka Tatars (80%) assimilated into the ranks of the nobility in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth while some lower noble Tatars assimilated to the Belarusian, Polish, Ukrainian
Ukrainian may refer to:
* Something of, from, or related to Ukraine
* Something relating to Ukrainians, an East Slavic people from Eastern Europe
* Something relating to demographics of Ukraine in terms of demography and population of Ukraine
* So ...
and Lithuanian townsfolk and peasant populations.
A number of the Polish Tatars emigrated to the US at the beginning of the 20th century and settled mostly in the north eastern states, although there is also an enclave in Florida. A small but active community of Lipka Tatars exists in New York City. " The Islamic Center of Polish Tatars" was built in 1928 in Brooklyn
Brooklyn () is a borough of New York City, coextensive with Kings County, in the U.S. state of New York. Kings County is the most populous county in the State of New York, and the second-most densely populated county in the United States, be ...
, New York City, and functioned until recently.
After the annexation of eastern Poland into the Soviet Union in 1939 and then following World War II, Poland was left with only 2 Tatar villages, Bohoniki
Bohoniki ( Polish Arabic: بوـحـونيكي) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sokółka, within Sokółka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It lies approximately ...
and Kruszyniany. A significant number of the Tatars in the territories annexed by the USSR repatriated to Poland and clustered in cities such as Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
(Maciej Musa Konopacki - patriarch of the Polish Orient), Białystok
Białystok is the largest city in northeastern Poland and the capital of the Podlaskie Voivodeship. It is the tenth-largest city in Poland, second in terms of population density, and thirteenth in area.
Białystok is located in the Białystok U ...
, Warsaw
Warsaw ( pl, Warszawa, ), officially the Capital City of Warsaw,, abbreviation: ''m.st. Warszawa'' is the capital and largest city of Poland. The metropolis stands on the River Vistula in east-central Poland, and its population is officiall ...
and Gorzów Wielkopolski
Gorzów Wielkopolski (; german: Landsberg an der Warthe) often abbreviated to Gorzów Wlkp. or simply Gorzów, is a city in western Poland, on the Warta river. It is the second largest city in the Lubusz Voivodeship with 120,087 inhabitants (Decem ...
totaling some 3,000 people. One of the neighborhoods of Gorzów Wielkopolski
Gorzów Wielkopolski (; german: Landsberg an der Warthe) often abbreviated to Gorzów Wlkp. or simply Gorzów, is a city in western Poland, on the Warta river. It is the second largest city in the Lubusz Voivodeship with 120,087 inhabitants (Decem ...
where relocated Tatar families resettled has come to be referred to as "the Tatar Hills", or in Polish "Górki Tatarskie".
In 1925 the Muslim Religion Association ( pl, Muzułmański Związek Religijny) was formed in Białystok, Poland. In 1992, the Organization of Tatars of the Polish Republic ( pl, Związek Tatarów Rzeczypospolitej Polskiej) with autonomous branches in Białystok and Gdańsk, began operating.
In Poland, the 2011 census showed 1,916 people declaring Tatar ethnicity.
In November 2010, a monument to Poland's Tatar populace was unveiled in the port city of Gdańsk
Gdańsk ( , also ; ; csb, Gduńsk;Stefan Ramułt, ''Słownik języka pomorskiego, czyli kaszubskiego'', Kraków 1893, Gdańsk 2003, ISBN 83-87408-64-6. , Johann Georg Theodor Grässe, ''Orbis latinus oder Verzeichniss der lateinischen Benen ...
at a ceremony attended by President Bronislaw Komorowski, as well as Tatar
The Tatars ()Tatar
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
representatives from across Poland and abroad. The monument is a symbol of the important role of Tatars in Polish history. "Tatars shed their blood in all national independence uprisings. Their blood seeped into the foundations of the reborn Polish Republic," President Komorowski said at the unveiling. The monument is the first of its kind to be erected in Europe.
in the Collins English Dictionary is an umbrella term for different
Famous Lipka Tatar descendants
* Gasan (Hasan) Konopackiy – Russian,Belarus
Belarus,, , ; alternatively and formerly known as Byelorussia (from Russian ). officially the Republic of Belarus,; rus, Республика Беларусь, Respublika Belarus. is a landlocked country in Eastern Europe. It is bordered by ...
ian and Polish military and political leader
* Aleksander Jeljaszewicz – Major of the Polish Army; commander of the last Tatar/Islamic unit in the Polish military
* Ibrahim Kanapacki
Ibrahim Barysavič Kanapacki ( be, Ібрагім Барысавіч Канапацкі; tt-Cyrl, Ибраһим Борис улы Канапацкий, ''Ibrahim Boris uly Kanapatsky''; 28 February 1949 – 9 September 2005) was a Belarusian ...
– Belarusian socio-political, cultural and religious figure, historian
* Tomasz Miśkiewicz – Polish mufti
* Ferdynand Antoni Ossendowski
Ferdynand Antoni Ossendowski (27 May 1876 – 3 January 1945) was a Polish writer, explorer, university professor, and anticommunist political activist. He is known for his books about Lenin and the Russian Civil War in which he participated.
...
- Polish writer and political activist
* Aleksander Romanowicz – General of cavalry in Russian Imperial Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian A ...
and Polish Army
* Aleksander Sulkiewicz – Polish politician of, activist in socialist and independence movements and one of the co-founders of Polish Socialist Party
* Charles Bronson
Charles Bronson (born Charles Dennis Buchinsky; November 3, 1921 – August 30, 2003) was an American actor. Known for his "granite features and brawny physique," he gained international fame for his starring roles in action, Western, and wa ...
– American Hollywood actor (father Lipka Tatar)
* Elena Glinskaya – Russian regent
* Fatma Mukhtarova – Soviet opera singer (mother Lipka Tatar)
* Henryk Sienkiewicz
Henryk Adam Aleksander Pius Sienkiewicz ( , ; 5 May 1846 – 15 November 1916), also known by the pseudonym Litwos (), was a Polish writer, novelist, journalist and Nobel Prize laureate. He is best remembered for his historical novels, espe ...
– Polish Nobel Prize
The Nobel Prizes ( ; sv, Nobelpriset ; no, Nobelprisen ) are five separate prizes that, according to Alfred Nobel's will of 1895, are awarded to "those who, during the preceding year, have conferred the greatest benefit to humankind." Alfr ...
-winning novelist (paternally of distant Lipka Tatar ancestry)
* Kevin Simm
Kevin Ian Simm (born 5 September 1980) is an English pop singer. He won ''The Voice UK'' on 9 April 2016. Simm was in the group Liberty X from 2001 until their split in 2007, and is currently the lead singer of the group Wet Wet Wet.
Early li ...
– Russian singer
* Maciej Sulkiewicz – lieutenant general
Lieutenant general (Lt Gen, LTG and similar) is a three-star military rank (NATO code OF-8) used in many countries. The rank traces its origins to the Middle Ages, where the title of lieutenant general was held by the second-in-command on th ...
of the Russian Imperial Army
The Imperial Russian Army (russian: Ру́сская импера́торская а́рмия, tr. ) was the armed land force of the Russian Empire, active from around 1721 to the Russian Revolution of 1917. In the early 1850s, the Russian A ...
, Prime Minister
A prime minister, premier or chief of cabinet is the head of the cabinet and the leader of the ministers in the executive branch of government, often in a parliamentary or semi-presidential system. Under those systems, a prime minister is ...
of the Crimean Regional Government, and Chief of General Staff of Azerbaijani Armed Forces in 1918–1920
* Mikhail Tugan-Baranovsky – Ukrainian statesman, economical scientist of the Russian Empire
The Russian Empire was an empire and the final period of the Russian monarchy from 1721 to 1917, ruling across large parts of Eurasia. It succeeded the Tsardom of Russia following the Treaty of Nystad, which ended the Great Northern War ...
(paternally of partial Lipka Tatar ancestry)
* Osman Achmatowicz – chemist
* Mustafa Edige Kirimal – politician in Crimea
* Jakub Szynkiewicz – Polish mufti
*Halina Konopacka
Halina Konopacka (Leonarda Kazimiera Konopacka-Matuszewska-Szczerbińska) (26 February 1900 – 28 January 1989) was a Polish athlete. She won the discus throw event at the 1928 Summer Olympics, defeating American silver medal winner Lillian Cop ...
- Polish Olympian
Two distantly related members of the Abakanowicz family
* Bruno Abakanowicz – mathematician, inventor and electrical engineer (distant paternal Lipka Tatar ancestry)Por. S. Dziadulewicz, ''Herbarz rodzin tatarskich'', Wilno 1929, s. 365.
* Magdalena Abakanowicz – Polish artist whose family is of distant Tatar origin (distant paternal Lipka Tatar ancestry)
Lipka Tatar mosques
Navahrudak
Novogrudok ( be, Навагрудак, Navahrudak; lt, Naugardukas; pl, Nowogródek; russian: Новогрудок, Novogrudok; yi, נאַוואַראַדאָק, Novhardok, Navaradok) is a town in the Grodno Region, Belarus.
In the Middle A ...
, Belarus
File:Nemėžis, mečetė 1.JPG, Tatar mosque in Nemėžis, Lithuania
File:Keturiasdesimt Totoriu mecete.JPG, Mosque in Keturiasdešimt Totorių, Lithuania
File:2019. Mečetė, Kaunas.JPG, Mosque, built in Kaunas in 1930, quincentennial year of Vytautas the Great
Vytautas (c. 135027 October 1430), also known as Vytautas the Great ( Lithuanian: ', be, Вітаўт, ''Vitaŭt'', pl, Witold Kiejstutowicz, ''Witold Aleksander'' or ''Witold Wielki'' Ruthenian: ''Vitovt'', Latin: ''Alexander Vitoldus'', O ...
passing
File:Bohoniki - Mosque 05.jpg, Mosque in Bohoniki
Bohoniki ( Polish Arabic: بوـحـونيكي) is a village in the administrative district of Gmina Sokółka, within Sokółka County, Podlaskie Voivodeship, in north-eastern Poland, close to the border with Belarus. It lies approximately ...
, Poland
File:Meczet_w_Kruszynianach_front_side.jpg, Mosque in Kruszyniany, Poland
Tatar graves at Powązki cemetery in Warsaw
See also
* Lipka rebellion *Powers Street Mosque
The Powers Street Mosque in Brooklyn, New York City is one of the oldest mosques in the United States. It was founded by a small group of Lipka Tatars, originating from the Białystok region of Poland. This was the first Muslim organization in Ne ...
* Tatar invasions
* List of Polish wars
This is a chronological list of military conflicts in which Polish armed forces fought or took place on Polish territory from the reign of Mieszko I (960–992) to the ongoing military operations.
This list does not include peacekeeping operatio ...
* Uhlan
* Aleksander Sulkiewicz
* Kaliz
* Almış (Almas) iltäbär
* Aleksander Jeljaszewicz
* Belarusian Arabic alphabet
The Belarusian Arabic alphabet ( be, Беларускі арабскі алфавіт, ''Biełaruski arabski ałfavit'') or Arabitsa (, ''Arabica'') was based on the Arabic script and was developed in the 16th century (possibly 15th). It consisted ...
* Lithuanian Tartars of the Imperial Guard
* Islam in Belarus
A continuous presence of Islam in Belarus began in the 14th century. From this time it was primarily associated with the Lipka Tatars, many of whom settled in the Polish–Lithuanian Commonwealth while continuing their traditions and religiou ...
* Islam in Lithuania
* Islam in Poland
References
External links
A Short History of the Lipka Tatars of the White Horde
Jakub Mirza Lipka
Selim Mirza-Juszenski Chazbijewicz - translated into English by Paul de Nowina-Konopka
The Lithuanian Tatars
article in The Red Book of the Peoples of the Russian Empire {{European Muslims Social history of Belarus Ethnic groups in Belarus Ethnic groups in Lithuania Ethnic groups in Poland Social history of Lithuania Islam in Belarus Islam in Poland Muslim communities in Europe