Limit cycle on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
 In
In
 Limit cycles are important in many scientific applications where systems with self-sustained oscillations are modelled. Some examples include:
* Aerodynamic limit-cycle oscillations
* The
Limit cycles are important in many scientific applications where systems with self-sustained oscillations are modelled. Some examples include:
* Aerodynamic limit-cycle oscillations
* The
mathematics
Mathematics is an area of knowledge that includes the topics of numbers, formulas and related structures, shapes and the spaces in which they are contained, and quantities and their changes. These topics are represented in modern mathematics ...
, in the study of dynamical systems
In mathematics, a dynamical system is a system in which a function describes the time dependence of a point in an ambient space. Examples include the mathematical models that describe the swinging of a clock pendulum, the flow of water in a p ...
with two-dimensional phase space, a limit cycle is a closed trajectory
A trajectory or flight path is the path that an object with mass in motion follows through space as a function of time. In classical mechanics, a trajectory is defined by Hamiltonian mechanics via canonical coordinates; hence, a complete tra ...
in phase space having the property that at least one other trajectory spirals into it either as time approaches infinity or as time approaches negative infinity. Such behavior is exhibited in some nonlinear systems
In mathematics and science, a nonlinear system is a system in which the change of the output is not proportional to the change of the input. Nonlinear problems are of interest to engineers, biologists, physicists, mathematicians, and many other ...
. Limit cycles have been used to model the behavior of a great many real-world oscillatory systems. The study of limit cycles was initiated by Henri Poincaré (1854–1912).
Definition
We consider a two-dimensional dynamical system of the form where is a smooth function. A ''trajectory'' of this system is some smooth function with values in which satisfies this differential equation. Such a trajectory is called ''closed'' (or ''periodic'') if it is not constant but returns to its starting point, i.e. if there exists some such that for all . Anorbit
In celestial mechanics, an orbit is the curved trajectory of an object such as the trajectory of a planet around a star, or of a natural satellite around a planet, or of an artificial satellite around an object or position in space such as a p ...
is the image
An image is a visual representation of something. It can be two-dimensional, three-dimensional, or somehow otherwise feed into the visual system to convey information. An image can be an artifact, such as a photograph or other two-dimensiona ...
of a trajectory, a subset of . A ''closed orbit'', or ''cycle'', is the image of a closed trajectory. A ''limit cycle'' is a cycle which is the limit set
In mathematics, especially in the study of dynamical systems, a limit set is the state a dynamical system reaches after an infinite amount of time has passed, by either going forward or backwards in time. Limit sets are important because they ca ...
of some other trajectory.
Properties
By theJordan curve theorem
In topology, the Jordan curve theorem asserts that every '' Jordan curve'' (a plane simple closed curve) divides the plane into an " interior" region bounded by the curve and an " exterior" region containing all of the nearby and far away exteri ...
, every closed trajectory divides the plane into two regions, the interior and the exterior of the curve.
Given a limit cycle and a trajectory in its interior that approaches the limit cycle for time approaching , then there is a neighborhood around the limit cycle such that ''all'' trajectories in the interior that start in the neighborhood approach the limit cycle for time approaching . The corresponding statement holds for a trajectory in the interior that approaches the limit cycle for time approaching , and also for trajectories in the exterior approaching the limit cycle.
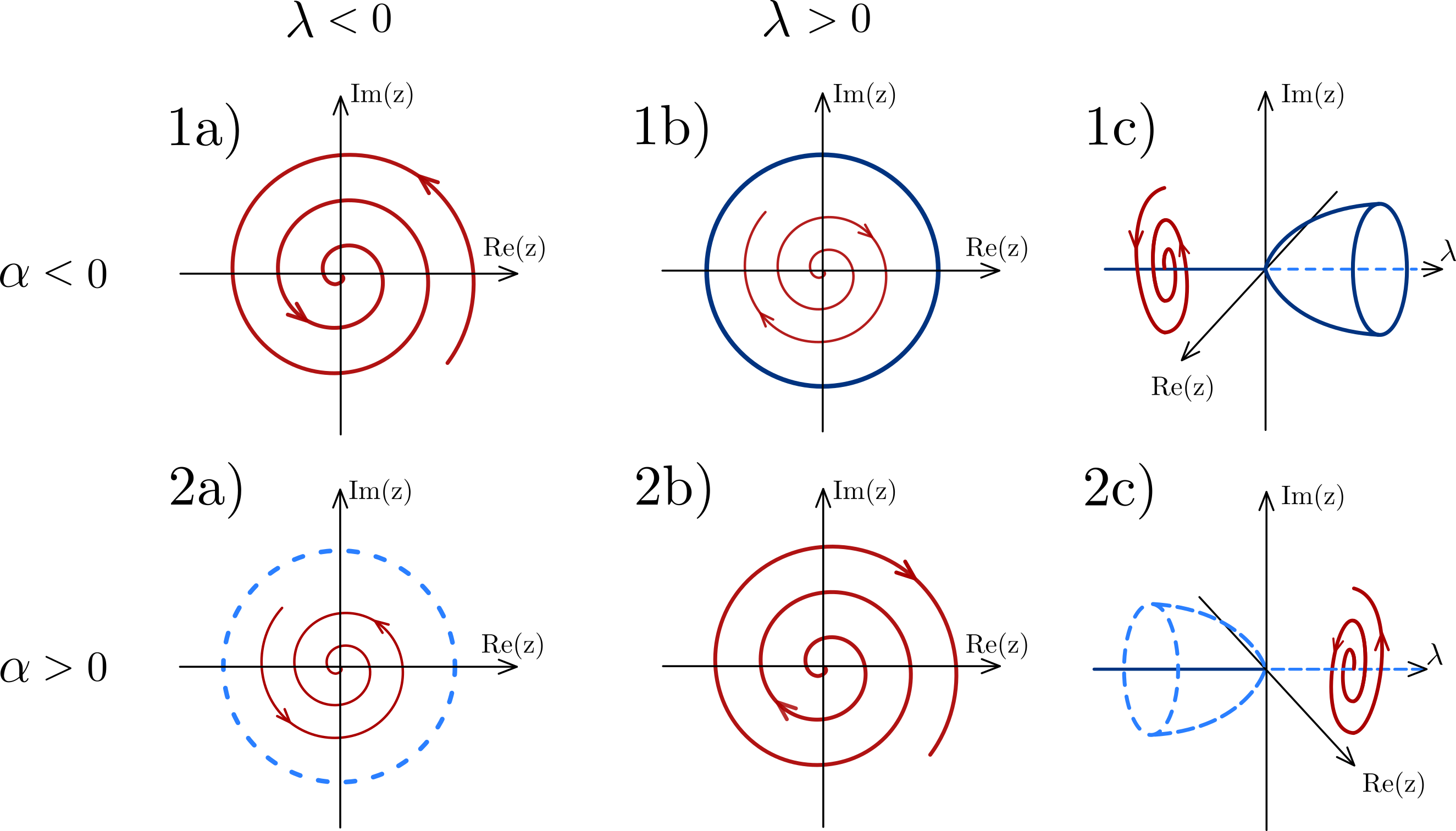
Stable, unstable and semi-stable limit cycles
In the case where all the neighboring trajectories approach the limit cycle as time approaches infinity, it is called a '' stable'' or ''attractive'' limit cycle (ω-limit cycle). If instead, all neighboring trajectories approach it as time approaches negative infinity, then it is an ''unstable'' limit cycle (α-limit cycle). If there is a neighboring trajectory which spirals into the limit cycle as time approaches infinity, and another one which spirals into it as time approaches negative infinity, then it is a ''semi-stable'' limit cycle. There are also limit cycles that are neither stable, unstable nor semi-stable: for instance, a neighboring trajectory may approach the limit cycle from the outside, but the inside of the limit cycle is approached by a family of other cycles (which wouldn't be limit cycles). Stable limit cycles are examples ofattractor
In the mathematical field of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of states toward which a system tends to evolve, for a wide variety of starting conditions of the system. System values that get close enough to the attractor values remain ...
s. They imply self-sustained oscillations
Oscillation is the repetitive or periodic variation, typically in time, of some measure about a central value (often a point of equilibrium) or between two or more different states. Familiar examples of oscillation include a swinging pendulum ...
: the closed trajectory describes the perfect periodic behavior of the system, and any small perturbation from this closed trajectory causes the system to return to it, making the system stick to the limit cycle.
Finding limit cycles
Every closed trajectory contains within its interior astationary point
In mathematics, particularly in calculus, a stationary point of a differentiable function of one variable is a point on the graph of the function where the function's derivative is zero. Informally, it is a point where the function "stops" in ...
of the system, i.e. a point where . The Bendixson–Dulac theorem In mathematics, the Bendixson–Dulac theorem on dynamical systems states that if there exists a C^1 function \varphi(x, y) (called the Dulac function) such that the expression
:\frac + \frac
has the same sign (\neq 0) almost everywhere in a ...
and the Poincaré–Bendixson theorem
In mathematics, the Poincaré–Bendixson theorem is a statement about the long-term behaviour of orbits of continuous dynamical systems on the plane, cylinder, or two-sphere.
Theorem
Given a differentiable real dynamical system defined on an op ...
predict the absence or existence, respectively, of limit cycles of two-dimensional nonlinear dynamical systems.
Open problems
Finding limit cycles, in general, is a very difficult problem. The number of limit cycles of a polynomial differential equation in the plane is the main object of the second part ofHilbert's sixteenth problem
Hilbert's 16th problem was posed by David Hilbert at the Paris conference of the International Congress of Mathematicians in 1900, as part of his list of 23 problems in mathematics.
The original problem was posed as the ''Problem of the topolo ...
. It is unknown, for instance, whether there is any system in the plane where both components of are quadratic polynomials of the two variables, such that the system has more than 4 limit cycles.
Applications
 Limit cycles are important in many scientific applications where systems with self-sustained oscillations are modelled. Some examples include:
* Aerodynamic limit-cycle oscillations
* The
Limit cycles are important in many scientific applications where systems with self-sustained oscillations are modelled. Some examples include:
* Aerodynamic limit-cycle oscillations
* The Hodgkin–Huxley model
The Hodgkin–Huxley model, or conductance-based model, is a mathematical model that describes how action potentials in neurons are initiated and propagated. It is a set of nonlinear differential equations that approximates the electrical charact ...
for action potential
An action potential occurs when the membrane potential of a specific cell location rapidly rises and falls. This depolarization then causes adjacent locations to similarly depolarize. Action potentials occur in several types of animal cells, ...
s in neuron
A neuron, neurone, or nerve cell is an electrically excitable cell that communicates with other cells via specialized connections called synapses. The neuron is the main component of nervous tissue in all animals except sponges and placozoa. N ...
s.
* The Sel'kov model of glycolysis.
* The daily oscillations in gene expression, hormone levels and body temperature of animals, which are part of the circadian rhythm
A circadian rhythm (), or circadian cycle, is a natural, internal process that regulates the sleep–wake cycle and repeats roughly every 24 hours. It can refer to any process that originates within an organism (i.e., Endogeny (biology), endogeno ...
, although this is contradicted by more recent evidence.
* The migration
Migration, migratory, or migrate may refer to: Human migration
* Human migration, physical movement by humans from one region to another
** International migration, when peoples cross state boundaries and stay in the host state for some minimum le ...
of cancer cell
Cancer cells are cells that divide continually, forming solid tumors or flooding the blood with abnormal cells. Cell division is a normal process used by the body for growth and repair. A parent cell divides to form two daughter cells, and these d ...
s in confining micro-environments follows limit cycle oscillations.
* Some non-linear electrical circuits
An electrical network is an interconnection of electrical components (e.g., batteries, resistors, inductors, capacitors, switches, transistors) or a model of such an interconnection, consisting of electrical elements (e.g., voltage sources, c ...
exhibit limit cycle oscillations, which inspired the original Van der Pol model.
*The control of respiration and hematopoiesis, as appearing in the Mackey-Glass equations.
See also
*Attractor
In the mathematical field of dynamical systems, an attractor is a set of states toward which a system tends to evolve, for a wide variety of starting conditions of the system. System values that get close enough to the attractor values remain ...
* Hyperbolic set In dynamical systems theory, a subset Λ of a smooth manifold ''M'' is said to have a hyperbolic structure with respect to a smooth map ''f'' if its tangent bundle may be split into two invariant subbundles, one of which is contracting and th ...
* Periodic point In mathematics, in the study of iterated functions and dynamical systems, a periodic point of a function is a point which the system returns to after a certain number of function iterations or a certain amount of time.
Iterated functions
Given a ...
* Self-oscillation
Self-oscillation is the generation and maintenance of a periodic motion by a source of power that lacks any corresponding periodicity. The oscillator itself controls the phase with which the external power acts on it. Self-oscillators are therefor ...
* Stable manifold
In mathematics, and in particular the study of dynamical systems, the idea of ''stable and unstable sets'' or stable and unstable manifolds give a formal mathematical definition to the general notions embodied in the idea of an attractor or repello ...
References
Further reading
* * * Philip Hartman, "Ordinary Differential Equation", Society for Industrial and Applied Mathematics, 2002. * Witold Hurewicz, "Lectures on Ordinary Differential Equations", Dover, 2002. * Solomon Lefschetz, "Differential Equations: Geometric Theory", Dover, 2005. * Lawrence Perko, "Differential Equations and Dynamical Systems", Springer-Verlag, 2006. * Arthur Mattuck, Limit Cycles: Existence and Non-existence Criteria, MIT Open Courseware http://videolectures.net/mit1803s06_mattuck_lec32/#External links
* {{cite web , url=https://planetmath.org/limitcycle , website=planetmath.org , title=limit cycle , access-date=2019-07-06 Limit sets Nonlinear systems Dynamical systems