Life Studies on:
[Wikipedia]
[Google]
[Amazon]
''Life Studies'' is the fourth book of poems by Robert Lowell. Most critics (including Helen Vendler, Steven Gould Axelrod, Adam Kirsch, and others) consider it one of Lowell's most important books, and the Academy of American Poets named it one of their ''Groundbreaking Books.'' Helen Vendler called ''Life Studies'' Lowell's "most original book."
It won the National Book Award for Poetry in 1960."National Book Awards – 1960"
(With acceptance speech by Lowell and essay by Dilruba Ahmed from the Awards 60-year anniversary blog.)
 Part I of the book contains four poems that are similar in style and tone to the poems of Lowell's previous books, '' The Mills of the Kavanaughs'' and '' Lord Weary's Castle''. They are well-polished, formal in their use of meter and rhyme, and fairly impersonal. This first section can be interpreted as a transition section, signaling Lowell's move away from
Part I of the book contains four poems that are similar in style and tone to the poems of Lowell's previous books, '' The Mills of the Kavanaughs'' and '' Lord Weary's Castle''. They are well-polished, formal in their use of meter and rhyme, and fairly impersonal. This first section can be interpreted as a transition section, signaling Lowell's move away from  "91 Revere Street" also sets the stage for the portraits of his family members in the book's final section. According to Ian Hamilton, one of Lowell's unofficial biographers, this section was begun as a potentially therapeutic assignment suggested by Lowell's therapist. Lowell also stated that this prose exercise led him to the stylistic breakthrough of the poems in Part IV. The apartment at 91 Revere Street in Beacon Hill still exists and is noted by a Boston
"91 Revere Street" also sets the stage for the portraits of his family members in the book's final section. According to Ian Hamilton, one of Lowell's unofficial biographers, this section was begun as a potentially therapeutic assignment suggested by Lowell's therapist. Lowell also stated that this prose exercise led him to the stylistic breakthrough of the poems in Part IV. The apartment at 91 Revere Street in Beacon Hill still exists and is noted by a Boston
National Book Foundation
The National Book Foundation (NBF) is an American nonprofit organization established, "to raise the cultural appreciation of great writing in America". Established in 1989 by National Book Awards, Inc.,Edwin McDowell. "Book Notes: 'The Joy Luc ...
. Retrieved 2012-02-25.
(With acceptance speech by Lowell and essay by Dilruba Ahmed from the Awards 60-year anniversary blog.)
Publication
''Life Studies'' was first published in London byFaber & Faber
Faber and Faber Limited, usually abbreviated to Faber, is an independent publishing house in London. Published authors and poets include T. S. Eliot (an early Faber editor and director), W. H. Auden, Margaret Storey, William Golding, Samuel ...
. This was to allow for it to be entered for selection by the Poetry Book Society
The Poetry Book Society (PBS) was founded in 1953 by T. S. Eliot and friends, including Sir Basil Blackwell, "to propagate the art of poetry". Eric Walter White was secretary from December 1953 until 1971, and was subsequently the society's chai ...
, one condition being that the first edition must be British. Because of the rush to release the book in Britain, the British first edition does not include the "91 Revere Street" section. The first American edition was published in 1959
Events January
* January 1 - Cuba: Fulgencio Batista flees Havana when the forces of Fidel Castro advance.
* January 2 - Lunar probe Luna 1 was the first man-made object to attain escape velocity from Earth. It reached the vicinity of E ...
by Farrar, Straus and Cudahy
Farrar, Straus and Giroux (FSG) is an American book publishing company, founded in 1946 by Roger Williams Straus Jr. and John C. Farrar. FSG is known for publishing literary books, and its authors have won numerous awards, including Pulitzer ...
based in New York City.
Content
 Part I of the book contains four poems that are similar in style and tone to the poems of Lowell's previous books, '' The Mills of the Kavanaughs'' and '' Lord Weary's Castle''. They are well-polished, formal in their use of meter and rhyme, and fairly impersonal. This first section can be interpreted as a transition section, signaling Lowell's move away from
Part I of the book contains four poems that are similar in style and tone to the poems of Lowell's previous books, '' The Mills of the Kavanaughs'' and '' Lord Weary's Castle''. They are well-polished, formal in their use of meter and rhyme, and fairly impersonal. This first section can be interpreted as a transition section, signaling Lowell's move away from Catholicism
The Catholic Church, also known as the Roman Catholic Church, is the largest Christian church, with 1.3 billion baptized Catholics worldwide . It is among the world's oldest and largest international institutions, and has played a ...
, as evidenced by the book's first poem, " Beyond the Alps," as well as a move away from the traditional, dense, more impersonal style of poetry that characterized Lowell's writing while he was still a practicing Catholic and closely associated with New Critical poets like Allen Tate
John Orley Allen Tate (November 19, 1899 – February 9, 1979), known professionally as Allen Tate, was an American poet, essayist, social commentator, and poet laureate from 1943 to 1944.
Life
Early years
Tate was born near Winchester, ...
and John Crowe Ransom. Notably, at a 1963 poetry reading at the Guggenheim Museum
The Guggenheim Museums are a group of museums in different parts of the world established (or proposed to be established) by the Solomon R. Guggenheim Foundation.
Museums in this group include:
Locations
Americas
* The Solomon R. Guggenhei ...
, Lowell introduced his reading of "Beyond the Alps" by stating that, " he poem wasa declaration of my faith or lack of faith."
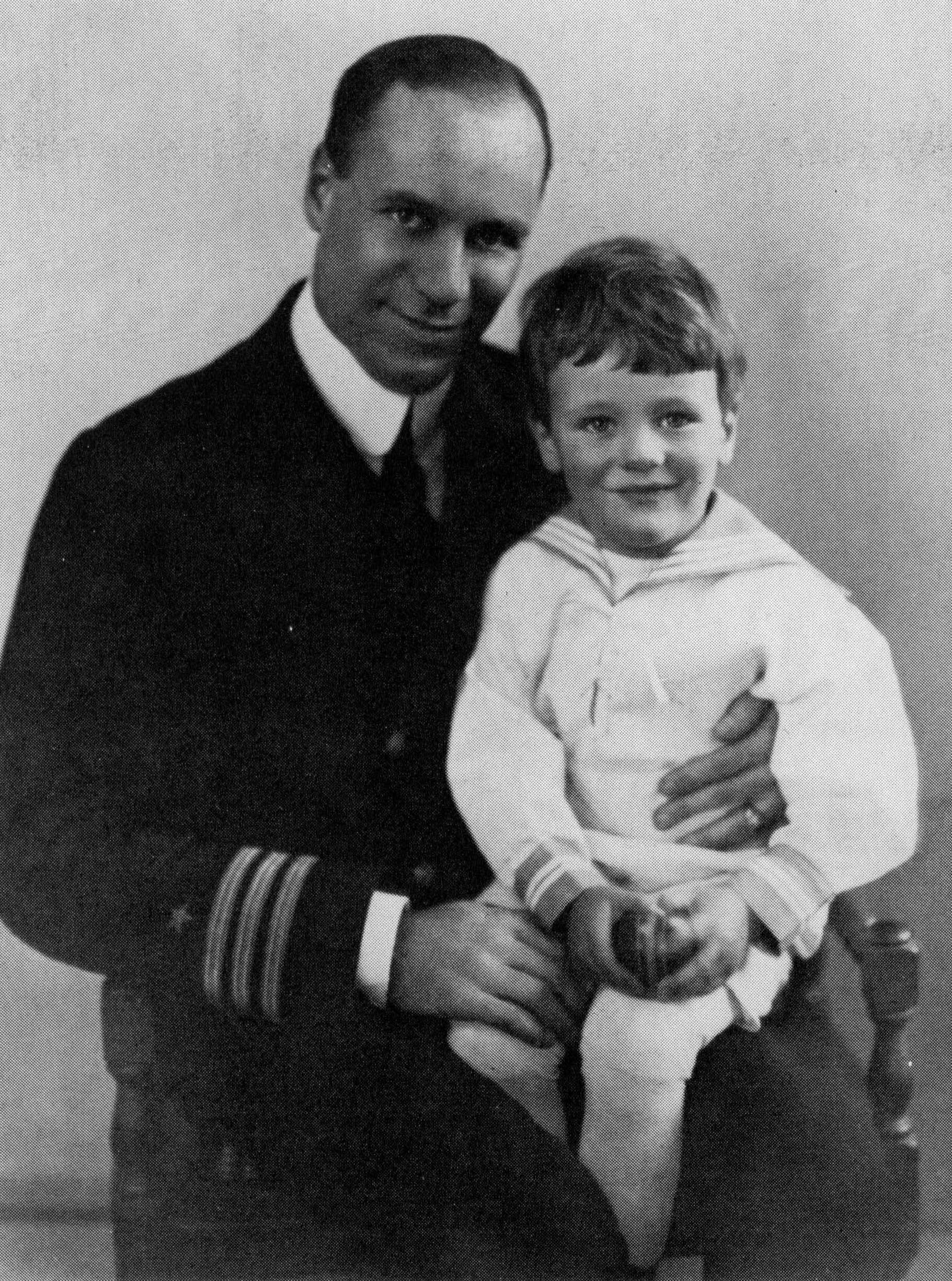
Part II contains only one piece which is titled "91 Revere Street" and is the first (and only) significant passage of prose to appear in one of Lowell's books of poems. It centers, with intricate detail, on Lowell's childhood when his family was living in Boston's Beacon Hill neighborhood at 91 Revere Street. The piece, which is the longest one in the book, also focuses on his parents' marriage as well as young Lowell's relationship with his parents, other relatives, and his childhood peers. Notable characters in the piece include Lowell's great-grandfather Mordecai Myers and his father's Navy buddy, Commander Billy Harkness.
 "91 Revere Street" also sets the stage for the portraits of his family members in the book's final section. According to Ian Hamilton, one of Lowell's unofficial biographers, this section was begun as a potentially therapeutic assignment suggested by Lowell's therapist. Lowell also stated that this prose exercise led him to the stylistic breakthrough of the poems in Part IV. The apartment at 91 Revere Street in Beacon Hill still exists and is noted by a Boston
"91 Revere Street" also sets the stage for the portraits of his family members in the book's final section. According to Ian Hamilton, one of Lowell's unofficial biographers, this section was begun as a potentially therapeutic assignment suggested by Lowell's therapist. Lowell also stated that this prose exercise led him to the stylistic breakthrough of the poems in Part IV. The apartment at 91 Revere Street in Beacon Hill still exists and is noted by a Boston historical marker
A commemorative plaque, or simply plaque, or in other places referred to as a historical marker, historic marker, or historic plaque, is a plate of metal, ceramic, stone, wood, or other material, typically attached to a wall, stone, or other ...
as Lowell's childhood home.
Part III contains odes to four writers: Hart Crane, Delmore Schwartz
Delmore Schwartz (December 8, 1913 – July 11, 1966) was an American poet and short story writer.
Early life
Schwartz was born in 1913 in Brooklyn, New York, where he also grew up. His parents, Harry and Rose, both Romanian Jews, separated when ...
, George Santayana
Jorge Agustín Nicolás Ruiz de Santayana y Borrás, known in English as George Santayana (; December 16, 1863 – September 26, 1952), was a Spanish and US-American philosopher, essayist, poet, and novelist. Born in Spain, Santayana was raised ...
, and Ford Madox Ford
Ford Madox Ford (né Joseph Leopold Ford Hermann Madox Hueffer ( ); 17 December 1873 – 26 June 1939) was an English novelist, poet, critic and editor whose journals '' The English Review'' and ''The Transatlantic Review'' were instrumental in ...
. At the time that Lowell published these poems, only Schwartz was still alive, and with the exception of Hart Crane, Lowell knew all of them personally and considered them to be mentors at different stages of his career.
Part IV contains the majority of the book's poems and is given the subheading of "Life Studies." These poems are the ones that critics refer to as "confessional." These "confessional" poems are the ones that document Lowell's struggle with mental illness and include pieces like " Skunk Hour", " Home After Three Months Away" and " Waking in the Blue." However, the majority of the poems in this section revolve around Lowell's family with a particular emphasis on the troubled marriage of his parents (as Lowell established in Part II). Lowell's maternal grandfather, Arthur Winslow, also receives significant attention in poems like "Dunbarton" and "Grandparents."
Critical response
M. L. Rosenthal wrote a review of ''Life Studies'', entitled " Poetry as Confession" which first applied the term "confessional" to Lowell's approach in ''Life Studies'', and led to the name of the school of Confessional poetry. For this reason, ''Life Studies'' is viewed as one of the first confessional books of poetry, although some poets and poetry critics such as Adam Kirsch andFrank Bidart
Frank Bidart (born May 27, 1939) is an American academic and poet, and a winner of the Pulitzer Prize for Poetry.
Biography
Bidart is a native of California and considered a career in acting or directing when he was young. In 1957, he began to s ...
question the accuracy of the confessional label. However, no one questions the book's lasting influence. The prominent poet Stanley Kunitz
Stanley Jasspon Kunitz (; July 29, 1905May 14, 2006) was an American poet. He was appointed Poet Laureate Consultant in Poetry to the Library of Congress twice, first in 1974 and then again in 2000.
Biography
Kunitz was born in Worcester, Massach ...
noted this tremendous influence when he wrote, in a 1985 essay, "''Life Studies''. . . asperhaps the most influential book of modern verse since T. S. Eliot's ''The Waste Land
''The Waste Land'' is a poem by T. S. Eliot, widely regarded as one of the most important poems of the 20th century and a central work of modernist poetry. Published in 1922, the 434-line poem first appeared in the United Kingdom in the Octob ...
.''"
In a 1962 interview with Peter Orr, Sylvia Plath
Sylvia Plath (; October 27, 1932 – February 11, 1963) was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer. She is credited with advancing the genre of confessional poetry and is best known for two of her published collections, '' Th ...
specifically cited Lowell's ''Life Studies'' as having had a profound influence over the poetry she was writing at that time (and which her husband would publish posthumously as ''Ariel
Ariel may refer to:
Film and television
*Ariel Award, a Mexican Academy of Film award
* ''Ariel'' (film), a 1988 Finnish film by Aki Kaurismäki
* ''ARIEL Visual'' and ''ARIEL Deluxe'', 1989 and 1991 anime video series based on the novel series ...
'' a few years later), stating, "I've been very excited by what I feel is the new breakthrough that came with, say, Robert Lowell's ''Life Studies'', this intense breakthrough into very serious, very personal, emotional experience which I feel has been partly taboo. Robert Lowell's poems about his experience in a mental hospital, for example, interested me very much."
The website for the Academy for American Poets states that, "Lowell's work in ''Life Studies'' had an especially profound impact that is discernible not only in the poetry of his direct contemporaries, such as Sylvia Plath
Sylvia Plath (; October 27, 1932 – February 11, 1963) was an American poet, novelist, and short story writer. She is credited with advancing the genre of confessional poetry and is best known for two of her published collections, '' Th ...
and Anne Sexton
Anne Sexton (born Anne Gray Harvey; November 9, 1928 – October 4, 1974) was an American poet known for her highly personal, confessional verse. She won the Pulitzer Prize for poetry in 1967 for her book '' Live or Die''. Her poetry details ...
, but also in the treatment of biographical detail by countless poets who followed." John Thompson in ''The Kenyon Review
''The Kenyon Review'' is a literary magazine based in Gambier, Ohio, US, home of Kenyon College. ''The Review'' was founded in 1939 by John Crowe Ransom, critic and professor of English at Kenyon College, who served as its editor until 1959. ' ...
'' supports this contention stating that, "For these poems, the question of propriety no longer exists. They have made a conquest: what they have won is a major expansion of the territory of poetry."Thompson, John, "Two Poets",Kenyon Review 21 (1959) pages 482 – 490.
Footnotes
{{Robert Lowell Works by Robert Lowell American poetry collections National Book Award for Poetry winning works